Abstract
Intradermal administration of low molecular weight hyaluronan (LMWH) in the hindpaw induced dose-dependent (0.1, 1, or 10 μg) mechanical hyperalgesia, of similar magnitude in male and female rats. However, the duration of LMWH hyperalgesia was greater in females. This sexual dimorphism was eliminated by bilateral ovariectomy, and by intrathecal administration of an oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN) antisense to the G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPR30) mRNA, in females, indicating estrogen dependence. To assess the receptors at which LMWH acts to induce hyperalgesia, LMWH was administered to groups of male and female rats that had been pretreated with ODN antisense (or mismatch) to the mRNA for one of three hyaluronan receptors, cluster of differentiation 44 (CD44), toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) or receptor for HA-mediated motility (RHAMM). While LMWH-induced hyperalgesia was attenuated in both male and female rats pretreated with ODN antisense for CD44 and TLR4 mRNA, RHAMM antisense pretreatment only attenuated LMWH-induced hyperalgesia in males. ODN antisense for RHAMM, however, attenuated LMWH-induced hyperalgesia in female rats treated with ODN antisense to GPR30, as well as in ovariectomized females. LMWH-induced hyperalgesia was significantly attenuated by pretreatment with high molecular weight hyaluronan (HMWH) in male, but not in female rats. Following gonadectomy or treatment with ODN antisense to GPR30 expression in females, HMWH produced similar attenuation of LMWH-induced hyperalgesia to that seen in males. These experiments identify nociceptors at which LMWH acts to produce mechanical hyperalgesia, establishes estrogen dependence in the role of RHAMM in female rats, and establishes estrogen-dependence in the inhibition of LMWH-induced hyperalgesia by HMWH.
INTRODUCTION
The extracellular matrix (ECM), a complex of glycoproteins and glycosaminoglycans, is an important constituent of the cellular microenvironment. Beyond providing structural support [85], ECM is involved in cell signaling [42], integrating mechanical and chemical signals [35,37], including in nociceptors [26,34] via its interaction with integrins, cluster of differentiation 44 (CD44), toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and cytoskeleton [22,46,49,61]. The glycosaminoglycan hyaluronan, a ubiquitous component of the ECM, is synthesized as a high molecular weight polymer (high molecular weight hyaluronan [HMWH]). However, under pathological conditions (e.g. inflammation, oxidative stress, and trauma) HMWH is degraded by hyaluronidases and reactive oxygen species, to low molecular weight hyaluronan (LMWH) fragments [58,75] as small as oligosaccharides [19]. Both HMWH and LMWH bind to and signal via multiple membrane receptors, including CD44, receptor for HA-mediated motility (RHAMM) and TLR4 [71,83,87]. Of note, LMWH and HMWH of the sizes used in this study have different interactions with CD44, with, for example, only HMWH able to induced CD44 clustering [13], while LMWH inhibits this clustering, leading to activation of different signaling pathways [51,89].
Pain mechanisms are sexually dimorphic. Women have a greater prevalence of chronic pain disorders [47,53,57] and experience more postoperative pain [21,55,78]. Sexual dimorphism in pain mechanisms, including in nociceptor function have been reported [20,47,52,57], some of which are sex hormone-dependent [11,40,88]. We have demonstrated sexual dimorphism in nociceptor function [6,8,23,24,41,45], with cutaneous and muscle mechanical nociceptive thresholds having a similar sexual dimorphism [33]. Both estrogen and inflammation increased excitability of temporomandibular joint neurons [27], and inflammation altered nociceptor activity [20] to a greater extent in female rats. Therefore, in the present experiments we have evaluated for sex differences in the nociceptive effects of hyaluronan.
We have previously shown that in male rats LMWH induces mechanical hyperalgesia that is attenuated by both a CD44 receptor antagonist [22] and intrathecal administration of an oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN) antisense to CD44 mRNA [25]. In the current study, we compared the nociceptive effects of LMWH and the contribution of CD44, TLR4 and RHAMM, in male and female rats.
METHODS
Animals
Experiments were performed on 220–400 g female and male Sprague Dawley rats (Charles River Laboratories, Hollister, CA, USA). Experimental animals were housed, same sex, 3 per cage, under a 12 h light/dark cycle, in a temperature- and humidity-controlled room in the animal care facility at the University of California, San Francisco. Food and water were available ad libitum. Experimental protocols, designed to minimize the number of animals used and their suffering, were approved by the UCSF Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, and adhered to the National Institutes of Health Guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals.
Nociceptive threshold testing
Mechanical nociceptive threshold was quantified using an Ugo Basile Analgesymeter (Stoelting, Wood Dale, IL, USA), to perform the Randall-Selitto paw-withdrawal test [66]. This analgesymeter applies a linearly increasing mechanical force to the dorsum of the rat’s hindpaw, as previously described [80,81]. Nociceptive threshold is defined as the force in grams at which the rat withdraws its paw. Baseline paw-pressure threshold was defined as the mean of three readings taken before a test agent was injected. Only one paw per rat was used for drug administration and nociceptive threshold testing. Each experiment was performed on a different group of rats by individuals blind to experimental treatments. Data are presented as mean (±SEM) change from baseline nociceptive threshold.
Drug administration
The following drugs were used in this study: HMWH (hyaluronan sodium salt from Streptococcus pyogenes), from Calbiochem (San Diego, CA, USA); LMWH (hyaluronic acid sodium salt from Streptococcus equi), 17β-estradiol and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) from Sigma-Aldrich (Millipore Sigma, Darmstadt, Germany). Drug doses were selected based on our previous studies [22,26,44] and pilot experiments. The PGE2 stock solution was made in absolute ethanol, at a concentration of 1 μg/μL, and further diluted with 0.9% NaCl (1:50, final concentration 0.2 μg/μL) immediately before experiments. The ethanol concentration of the final PGE2 solution was ~2%, a concentration that we have previously shown does not affect mechanical nociceptive threshold [24]. HMWH and LMWH were dissolved in distilled water to a concentration of 1 μg/μL and, at the time of the experiment, were further diluted in 0.9% NaCl to the desired concentration. All drugs were administered intradermally, in a volume of 5 μL, on the dorsum of the hindpaw, using a 30-gauge beveled hypodermic needle attached by a short length of polyethylene (PE-10) tubing to a 50-μL micro-syringe (Hamilton, Reno, NV, USA).
Gonadectomy
Gonadectomy was performed on male and female rats at 3 weeks of age (ie, prepubertal), and animals were used for behavioral experiments 3 weeks later (ie, as adults) [31]. For surgery, animals were anesthetized with isoflurane (3% in oxygen) and received preoperative meloxicam (~5 mg/kg, s.c.) and bupivacaine (~0.1 mg/kg s.c. was injected at the incision site) for pain control.
Ovariectomy.
Briefly, ovaries were accessed by means of bilateral cutaneous and peritoneal incisions. Once located, ovaries and their vascular bundles were ligatured with 4–0 silk suture (Perma-Hand Silk® Ethicon, Johnson & Johnson, Somerville, NJ). Ovaries were then excised, and the peritoneal and cutaneous incisions closed with 5–0 silk suture (Perma-Hand Silk® Ethicon, Johnson & Johnson, Somerville, NJ). In some rats, we implanted 10 mm long segments of Silastic tubing filled with crystalline 17β-estradiol, as previously described [32] to provide chronic administration of 17β-estradiol to gonadectomized female rats.
Orchiectomy.
A single cutaneous incision was made through the scrotal skin and underlying tunica to expose the testes. Their vascular bundles were tied off with 5–0 silk suture, and the testes removed. The cutaneous incision was closed with 5–0 silk suture.
Oligodeoxynucleotide antisense to G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPR30) mRNA
To investigate the role of nociceptor G-protein coupled estrogen receptor, GPR30, in sexual dimorphic effects of HMWH and LMWH, female rats were treated with an ODN antisense for GPR30 mRNA [4,50]. The sequence for GPR30 antisense ODN, 5′-ATG TTC AGA GAG GTC CCC AG-3′ (Invitrogen Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA), is directed against a unique region of the rat GPR30 mRNA sequence (GeneBank accession number NM_133573). A mismatch ODN sequence, 5′-AGG TCC AGA AAG ATG CCA AG-3′, for GPR30 mRNA was a scrambled version of the antisense sequence that has the same base pairs and GC ratio, in randomized order, with little or no homology to any mRNA sequences posted at GenBank.
To assess the role of CD44, TLR4 and RHAMM in the mechanical hyperalgesia induced by LMWH, male and female rats were treated with ODNs antisense to mRNA for each of these HA receptors. The antisense ODN sequence to CD44 mRNA, 5’-GAA AAG GGT CGC GGG GG-3’, synthesized by Invitrogen, was directed against a unique region of rat CD44 mRNA, previously shown [13] to decrease CD44 protein expression (GenBank accession number NM_012924). The mismatch ODN sequence 5’-CCC CCG CGA CCC TTT TC-3’, was used as the antisense ODN control. A search of the National Center for Biotechnology Information database for Rattus norvegicus identified no other homologous sequences. The antisense ODN sequence for TLR4, 5’-AGG AAG TGA GAG TGC CAA CC-3’, is directed against a unique region of rat TLR4 (UniProtKB database entry Q9QX05). The mismatch ODN sequence, 5′-ACG ATG CGA GAG AGT CAC CG-3′ corresponds to the antisense sequence with 7 mismatched bases (denoted by bold letters). The antisense ODN sequence for RHAMM, 5’-ACC TGG AGA TGG AGC ACA AC-3’, is directed against a unique region of rat RHAMM (UniProtKB database entry Q9WUF7); the mismatch ODN sequence, 5’-GCC TGA AGA TAG ACG ACA AT-3’ for RHAMM, corresponds to the antisense sequence with 7 bases mismatched. We have previously demonstrated that antisense ODN reduces the expression of CD44, TLR4 and RHAMM in rat dorsal root ganglia (DRG) [7,13].
Before use, ODNs were reconstituted in nuclease-free 0.9% NaCl and then administered intrathecally at a dose of 6 μg/μL in a volume of 20 μL, daily for 3 consecutive days. As described previously [3] rats were anesthetized with isoflurane (2.5% in O2) and 120 μg of ODN, in a volume of 20 μL injected using a 100 μL microsyringe (Hamilton, Reno NV, USA) attached to a 30-gauge needle that was inserted into the subarachnoid space, between the L4 and L5 vertebrae. The intrathecal site of injection was confirmed by a sudden flick of the rat’s tail, a reflex that is evoked by bolus injection into the subarachnoid space [54]. Animals regained consciousness approximately 1 min after intrathecal injections. The use of antisense ODNs, administered intrathecally to attenuate the expression of proteins, essential for their role in nociceptor sensitization, is well supported by previous studies, by others [64,77], as well as our group [5,9,12,24]. Of note, in experiments in which rats received antisense for both GPR30 and RHAMM, antisense for GPR30 was administered 6 h after antisense for RHAMM.
Statistical analysis.
In all behavioral experiments, the dependent variable is percentage change from baseline mechanical nociceptive paw withdrawal threshold. Prism 8.3 (GraphPad Software) was used for graphics and data was analyzed using repeated-measures two-way ANOVA, followed by Holm-Šídák multiple comparison test; P<0.05 is considered statistically significant. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.
RESULTS
1. LMWH-induces sexually dimorphic dose-dependent hyperalgesia
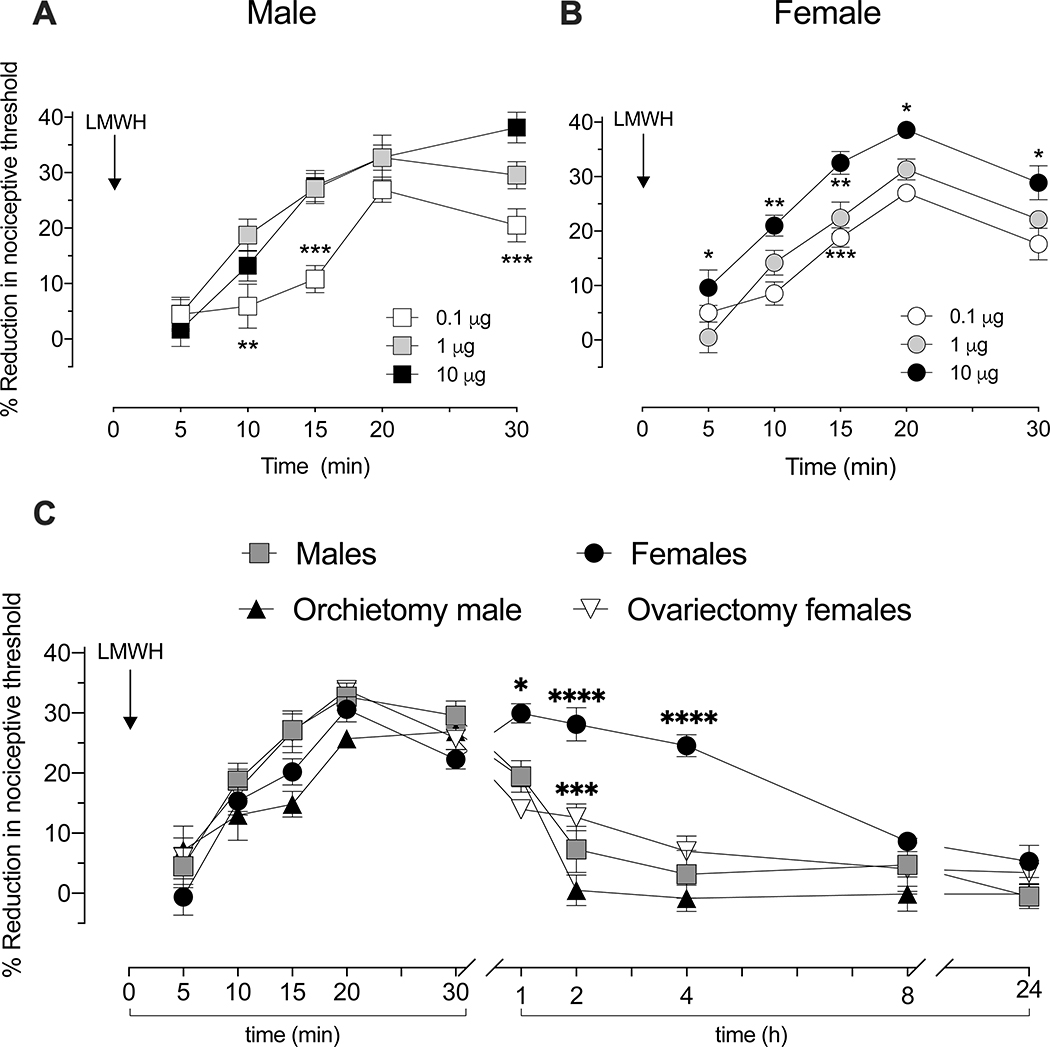
We compared the dose-dependence and time course of LMWH-induced mechanical hyperalgesia in male and female rats. LMWH (0.1, 1, or 10 μg) was administered intradermally on the dorsum of the hindpaw, in a volume of 5 μL, and mechanical nociceptive threshold evaluated 5, 10, 15, 20 and 30 min later. LMWH produced robust, dose-dependent, mechanical hyperalgesia in male (Fig 1A) and female rats (Fig 1B). Over the first 30 min there was no significant difference between males and females, in the magnitude of hyperalgesia, at any dose. However, when nociceptive threshold was evaluated over 24 h after administration, in separate groups of rats, the duration of hyperalgesia induced by LMWH (1 μg) was significantly longer in females (Fig 1C). To test if the prolonged hyperalgesia in females is sex hormone-dependent, LMWH was administered to castrated male and female rats. In ovariectomized female rats, when compared to intact females, hyperalgesia was now significantly attenuated (Fig 1C). LMWH-induced hyperalgesia was not different in orchiectomized compared to gonad intact male rats (Fig 1C).
Figure 1. Dose- and time-dependence of LMWH-induced hyperalgesia.
Different groups of male (A) and female (B) rats received an intradermal injection of one of three doses of LMWH (0.1, 1, 10 μg/5 μL), on the dorsum of the hind paw. Mechanical nociceptive threshold was then measured 5, 10, 15, 20 and 30 min after the injection of LMWH. Measurement of mechanical nociceptive threshold showed that LMWH produced robust mechanical hyperalgesia in male (A. Significant effect of Time F4,60=50.19, p<0.0001, Dose F2,15=12.28, p=0.0007 and their Interaction F8,60=2.908, p=0.0083. Two-way ANOVA followed Holm-Šídák multiple comparisons test showed significant differences at 10 mins for 0.1 vs. 1 μg **p=0.0081; at 15 mins for 0.1 vs. 1 μg ***p=0.0004; and 0.1 vs. 10 μg, ***p=0.0004; and at 30 mins for 0.1 vs. 10 μg ***p=0.0002), and female (B. Significant effect of Time F4,72=68.75, p<0.0001, Dose F2,18=25.94, p<0.0001, but not their Interaction F8,72=1.641, P=1.641. Two-way ANOVA followed Holm-Šídák multiple comparison test showed that significant differences at 5 min for 1 vs. 10 μg *p=0.0184; at 10 mins for 0.1 vs. 10 μg ***p=0.0007, at 15 mins for 0.1 vs. 10 μg ***p=0.0001 and 1 vs. 10 μg **p=0.0045; and at 20 and 30 mins for 0.1 vs. 10 μg **p=0.0016 and **p=0.0022, respectively) rats.
Sex differences. Repeated measures ANOVA showed that at a dose of 0.1 μg of LMWH while there was a significant effect of Time (F4,44=28.63, p<0.0001), there was no significant effect of Sex (F1,11=0.9382, p=0.3536) or Sex X Time Interaction (F4,44=1.441, p=0.2365); at 1 μg, there was a significant effect of Time (F4,44=46.26, p<0.0001), and Sex (F1,11=5.522 p=0.0385) but no significant Interaction (F4,44=0.4066, p=0.8029); and at 10 μg, there was a significant effect of Time (F4,32=32.38, p<0.0001), but no significant effect of Sex (F1,8=1.849, p=0.2017) or their Interaction (F4,32=5.515, p=0.0017). n=6 for each Male group, n=7 for each Female group. Over the first 30 min there was no significant difference between males and females, in the magnitude of hyperalgesia, at any dose.
C. Time course of LMWH-induced hyperalgesia. Different groups of male, female, orchiectomized male, and ovariectomized female rats received an intradermal injection of LMWH (1 μg/5 μL), on the dorsum of the hind paw. Mechanical nociceptive threshold was evaluated before and then 5, 10, 15, 20 and 30 min, and 1, 2, 4, 8 and 24 h after intradermal LMWH. While LMWH hyperalgesia was no longer present in males, 2 h after administration, it was still present in intact females 4h after administration (F(5,25)=19.38, *p<0.0250, when the female-group was compared with male-, ovariectomized female- and orchiectomized male- group respectively 1 h after intradermal LMWH; ****p<0.0001, when the female-group was compared with male- and orchiectomized male-group and ***p=0.0002, when the ovariectomized female-group was compared with orchiectomized male-group 2 h after intradermal LMWH; ****p<0.0001, when the female-group was compared with male-, ovariectomized female- and orchiectomized male-group and 4 h after intradermal LMWH; two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Holm-Šídák multiple comparison test) n=6 per group.
2. Receptors mediating LMWH-induced hyperalgesia
To evaluate the role of CD44, TLR4 and RHAMM in LMWH hyperalgesia, separate groups of female and male rats were treated with antisense or mismatch ODNs targeting mRNA for CD44 (Fig 2), TLR4 (Fig 3), or RHAMM (Fig 4), daily for 3 consecutive days. Approximately 24 h after the 3rd injection of ODNs, LMWH was injected intradermally, on the dorsum of the hind paw, and mechanical nociceptive threshold evaluated over the subsequent 24 h.
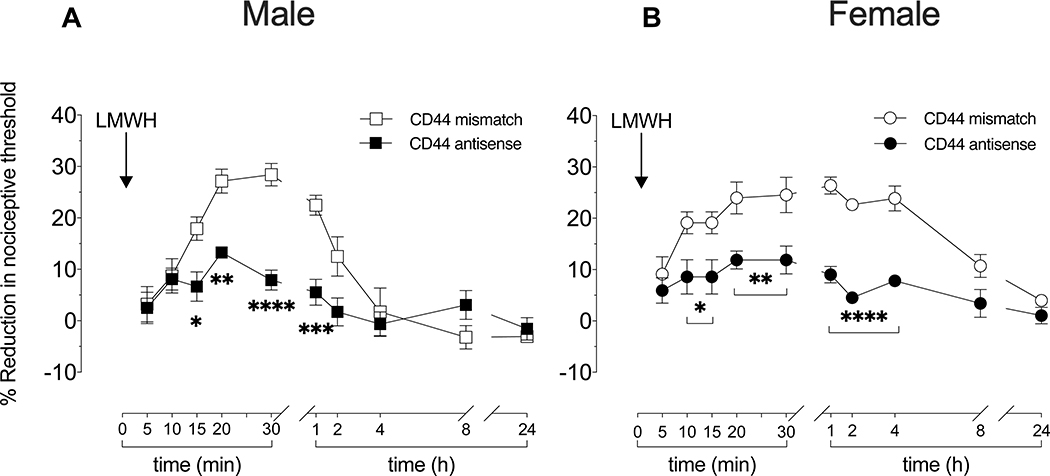
Figure 2. Role of CD44 in LMWH-induced hyperalgesia in male and female rats.
Male and female rats received intrathecal injections of antisense (120 μg/20 μL) or mismatch (120 μg/20 μL) ODN against CD44 mRNA, once a day for three consecutive days. On the fourth day, 24 h after the last intrathecal administration of ODNs, LMWH (1 μg/5 μL) was injected intradermally, on the dorsum of the hind paw, and mechanical nociceptive threshold evaluated 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 min later. An additional group of male and female rats received intrathecal ODN treatment against CD44 mRNA, LMWH injected intradermally, and mechanical nociceptive threshold evaluated 1, 2, 4, 8 and 24 h after LMWH.
A. Males: On the fourth day, at which time the mechanical nociceptive threshold was not significantly different from mismatch controls (t(5)=0.0000; p>0.9999; for antisense ODN male group and t(5)=1.000; p=0.3632 to mismatch ODN male group, when the mechanical nociceptive threshold is compared before the 1st and approximately 24 h after the 3rd intrathecal injection of ODNs; paired Student’s t test), LMWH-induced hyperalgesia was significantly attenuated 15, 20 and 30 min and 1 h after its injection, in the group of male rats treated with CD44 antisense ODN, compared to male rats treated with CD44 mismatch ODN (F(1,10)=20.31, *p=0.0373, **p=0.0042, ****p<0.0001 and ***p=0.0002; when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between CD44 antisense ODN- and mismatch ODN-treated groups 15, 20, 30 min and 1 h after intradermal LMWH, respectively; two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Holm-Šídák multiple comparison test). n=6 per group.
B. Females: In female rats, at a time at which the mechanical nociceptive threshold was not significantly different from mismatch controls (t(5)=2.236; p=0.0756; for antisense ODN female group and t(5)=0.0000; p>0.9999 to mismatch ODN female group; paired Student’s t test) rats treated with CD44 antisense ODN or mismatch ODN, LMWH-induced hyperalgesia was significantly attenuated, 10, 15, 20, 30 min and 1, 2 and 4 h later, in the CD44 antisense ODN treated group (F(1,10)=48.63, *p=0.0210, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between CD44 antisense ODN- and CD44 mismatch ODN treated groups 10 and 15 min after intradermal LMWH; **p=0.0047, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between CD44 antisense ODN- and CD44 mismatch ODN-treated groups 20 and 30 min after intradermal LMWH,****p<0.0001; when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between CD44 antisense ODN- and CD44 mismatch ODN-treated groups 1, 2 and 4 h after intradermal LMWH; two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Holm-Šídák multiple comparison test). n=6 per group.
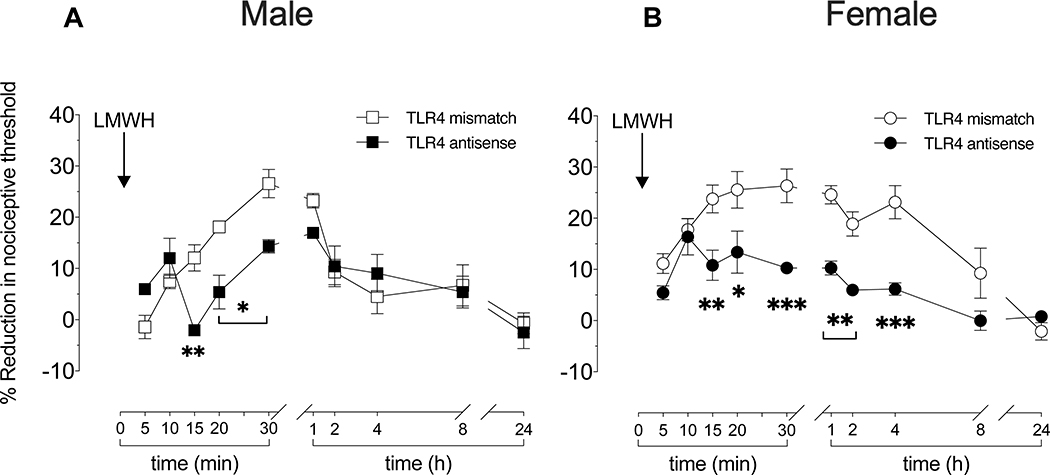
Figure 3. Role of TLR4 in LMWH-induced hyperalgesia.
Male and female rats received intrathecal injections of antisense (120 μg/20 μL) or mismatch (120 μg/20 μL) ODN for TLR4 mRNA, once a day for three consecutive days. On the fourth day, 24 h after the last intrathecal administration of ODN, LMWH (1 μg/5 μL) was injected intradermally, on the dorsum of the hind paw, and mechanical nociceptive threshold evaluated 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 min after injection of LMWH. An additional group of male and female rats received the same intrathecal ODN treatment against TLR4 mRNA and LMWH intradermally, and mechanical nociceptive threshold evaluated 1, 2, 4, 8 and 24 h after LMWH.
A. Males: In male rats treated with TLR4 ODN, pre-ODN baseline mechanical nociceptive threshold was not significantly different from threshold in mismatch controls (t(5)=1.865; p=0.1212; for antisense ODN male group and t(5)=1.000; p=0.3632 to mismatch ODN male group; paired Student’s t test), hyperalgesia induced by i.d. LMWH was significantly attenuated at the 15–30 min time points, in male rats treated with TLR4 antisense ODN (F(1,10)=2.103, **p=0.0030, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between TLR4 antisense ODN- and TLR4 mismatch ODN-treated groups 15 min after intradermal LMWH; *p=0.0154, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between TLR4 antisense ODN- and TLR4 mismatch ODN-treated groups 20 and 30 min after intradermal LMWH, respectively; two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Holm-Šídák multiple comparison test). n=6 per group.
B. Females: In female rats, treated with antisense ODN for TLR4 mRNA, pre-ODN baseline mechanical nociceptive threshold was not significantly different from the threshold in mismatch controls (t(5)=0.8771; p=0.4206; to antisense ODN female group and t(5)=1.234; p=0.2722 to mismatch ODN female group; paired Student’s t test). In the TLR4 antisense ODN-treated group, LMWH-induced hyperalgesia was also significantly attenuated 15–25 min later (F(1,10)=48.63, **p=0.0068, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between TLR4 antisense ODN- and TLR4 mismatch ODN-treated groups 15 min after intradermal LMWH; *p=0.0135, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between TLR4 antisense ODN- and TLR4 mismatch ODN-treated groups 20 after intradermal LMWH; ***p=0.0003, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between TLR4 antisense ODN- and TLR4 mismatch ODN-treated group 30 after intradermal LMWH; **p=0.0070; when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between TLR4 antisense ODN- and TLR4 mismatch ODN-treated groups 1 and 2 h after intradermal LMWH; ***p=0.0001; when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between TLR4 antisense ODN- and TLR4 mismatch ODN-treated groups 4 h after intradermal LMWH; two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Holm-Šídák multiple comparison test). n=6 per group.
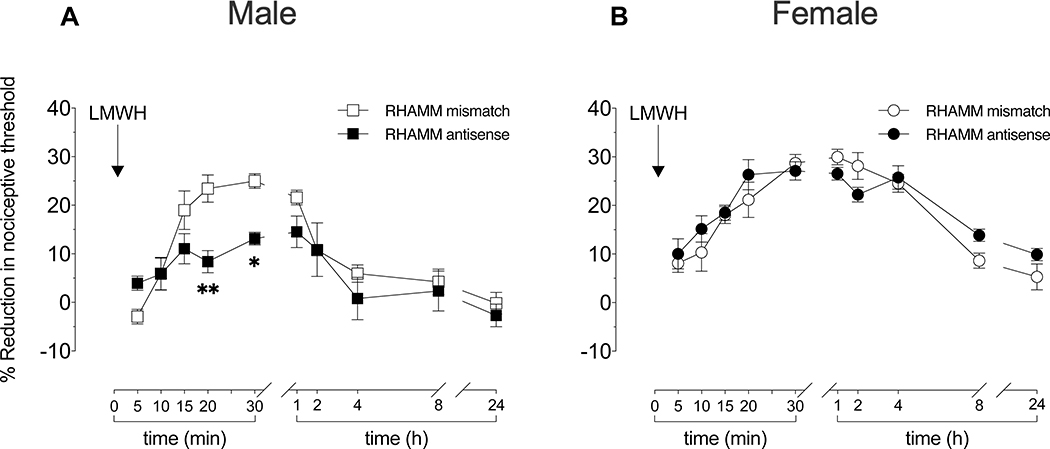
Figure 4. Role of RHAMM in LMWH-induced hyperalgesia.
Male and female rats received intrathecal injections of antisense (120 μg/20 μL) or mismatch (120 μg/20 μL) ODN against RHAMM mRNA, once a day for three consecutive days. On the fourth day, after the last intrathecal administration of ODN, LMWH (1 μg/5 μL) was injected intradermally, on the dorsum of the hind paw, and mechanical nociceptive threshold evaluated 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 min later. An additional group of male and female rats received the same intrathecal ODN treatment against RHAMM mRNA, LMWH injected intradermally, and mechanical nociceptive threshold evaluated 1, 2, 4, 8 and 24 h after LMWH.
A. Males: While pre-ODN baseline mechanical nociceptive threshold was not significantly different in male rats treated with antisense or mismatch ODN for RHAMM mRNA (t(5)=2.445; p=0.0583; for the antisense ODN male group and t(5)=1.732; p=0.1438 for the mismatch ODN male group; paired Student’s t test), in male rats treated with RHAMM antisense ODN, the hyperalgesia induced by intradermal LMWH was significantly attenuated when measured 20–25 min later (F(1,10)=4.270, **p=0.0042, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between RHAMM antisense ODN- and RHAMM mismatch ODN-treated groups 20 min after intradermal LMWH; *p=0.0488, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between RHAMM antisense ODN- and RHAMM mismatch ODN-treated groups 30 min after intradermal LMWH, respectively; two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Holm-Šídák multiple comparison test). n=6 per group.
B. Females: In female rats treated with antisense or mismatch ODN for RHAMM mRNA, pre-ODN baseline mechanical nociceptive thresholds were not significantly different (t(5)=1.291; p=0.2532; for the antisense ODN female group and t(5)=0.5222; p=0.6238 for the mismatch ODN female group; paired Student’s t test). In groups treated with RHAMM antisense or mismatch ODN, LMWH-induced hyperalgesia was present at all time points (F(1,10)=0.6706, p=0.4319; two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Holm-Šídák multiple comparison test). Our findings support the suggestion that in both male and female rats LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is dependent on CD44 and TLR4. However, the hyperalgesia induced by LMWH is dependent on RHAMM in male rats, but not females. n=6 paws per group.
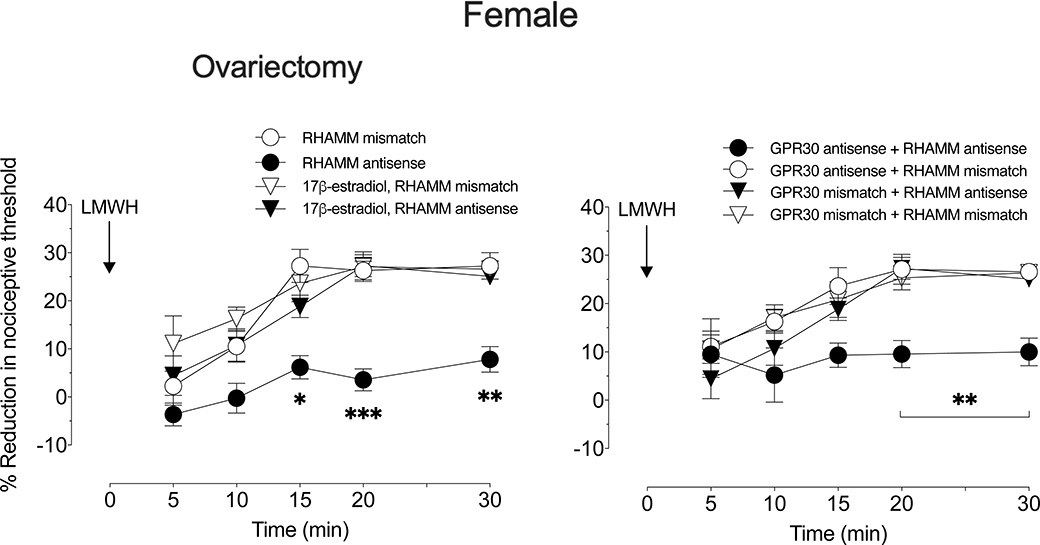
LMWH-induced hyperalgesia was attenuated in both male and female rats pretreated with antisense ODN for CD44 (Fig 2) or TLR4 (Fig 3), while treatment with antisense ODN for RHAMM attenuated LMWH-induced hyperalgesia in males (Fig 4A), but not females (Fig 4B). To test the hypothesis that the observed sexual dimorphism in the contribution of RHAMM is sex hormone-dependent, the experiment was repeated in additional groups of female rats: one group ovariectomized 2 weeks prior, one group ovariectomized 2 weeks prior with replacement of 17β-estradiol, and groups treated with antisense (or mismatch) to GPR30. In females that received GPR30 antisense ODN, as well as in ovariectomized females (Fig 5), LMWH-induced hyperalgesia was now significantly attenuated by RHAMM antisense ODN. Ovariectomized female rats received 17β-estradiol replacement show similar response to gonad intact females (Fig 5A).
Figure 5. Sex difference in LMWH-induced hyperalgesia.
A. Ovariectomy. Groups of female rats underwent ovariectomy, and one group of rats also received 17β-estradiol replacement, 14 days prior to intrathecal injection of antisense (120 μg/20 μL) or mismatch (120 μg/20 μL) ODN for RHAMM mRNA, once a day for three consecutive days. On the fourth day, after the last intrathecal administration of ODN, LMWH (1 μg/5 μL) was injected intradermally, on the dorsum of the hind paw, and mechanical nociceptive threshold evaluated 5, 10, 15, 20, and 30 min later. The magnitude of the mechanical hyperalgesia in ovariectomized female rats was attenuated in those treated with RHAMM antisense ODN, compared to those treated with its mismatch ODN, while ovariectomized females with 17β-estradiol replacement showed a similar response to the gonad intact female group. (F(3,20)=17.93, *p=0.0182, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between RHAMM antisense ODN- and RHAMM mismatch ODN-, 17β-estradiol plus RHAMM antisense ODN- and 17β-estradiol plus RHAMM mismatch ODN-treated groups 15 min after intradermal LMWH; ***p=0.0008, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between RHAMM antisense ODN- and RHAMM mismatch ODN-, 17β-estradiol plus RHAMM antisense ODN- and 17β-estradiol plus RHAMM mismatch ODN-treated groups 20 min after intradermal LMWH; **p=0.0024, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between RHAMM antisense ODN- and RHAMM mismatch ODN-, 17β-estradiol plus RHAMM antisense ODN- and 17β-estradiol plus RHAMM mismatch ODN-treated groups 30 min after intradermal LMWH; two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Holm-Šídák multiple comparison test). n=6 paws per group.
B. GPR30 ODN-treatment. Female rats were treated daily with spinal intrathecal injections of antisense or mismatch ODN (120 μg/20 μl) to GPR30 and RHAMM mRNA, for 3 consecutive days. On the fourth day, LMWH (1 μg/5 μL) was injected intradermally, on the dorsum of the hind paw, and the magnitude of mechanical nociceptive threshold, evaluated over 30 min. LMWH-induced hyperalgesia was significantly attenuated in rats that received antisense to both GPR30 and to RHAMM mRNA (F(3,20)=6.789, **p=0.0094, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between GPR30 antisense ODN + RHAMM antisense ODN- and others-treated groups 20 and 30 min after intradermal LMWH; two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Holm-Šídák multiple comparison test). Antisense ODN to GPR30 alone did not affect the magnitude of LMWH-induced hyperalgesia (data not shown). n=6 paws per group.
3. Sexual dimorphism in the attenuation of LMWH-induced hyperalgesia by HMWH
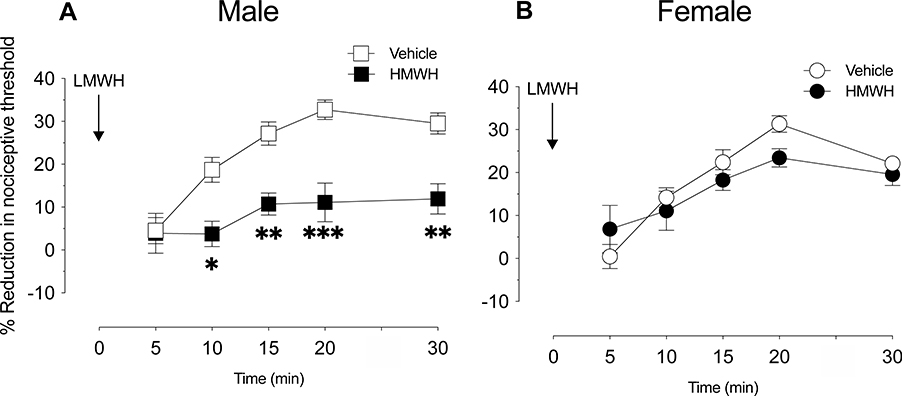
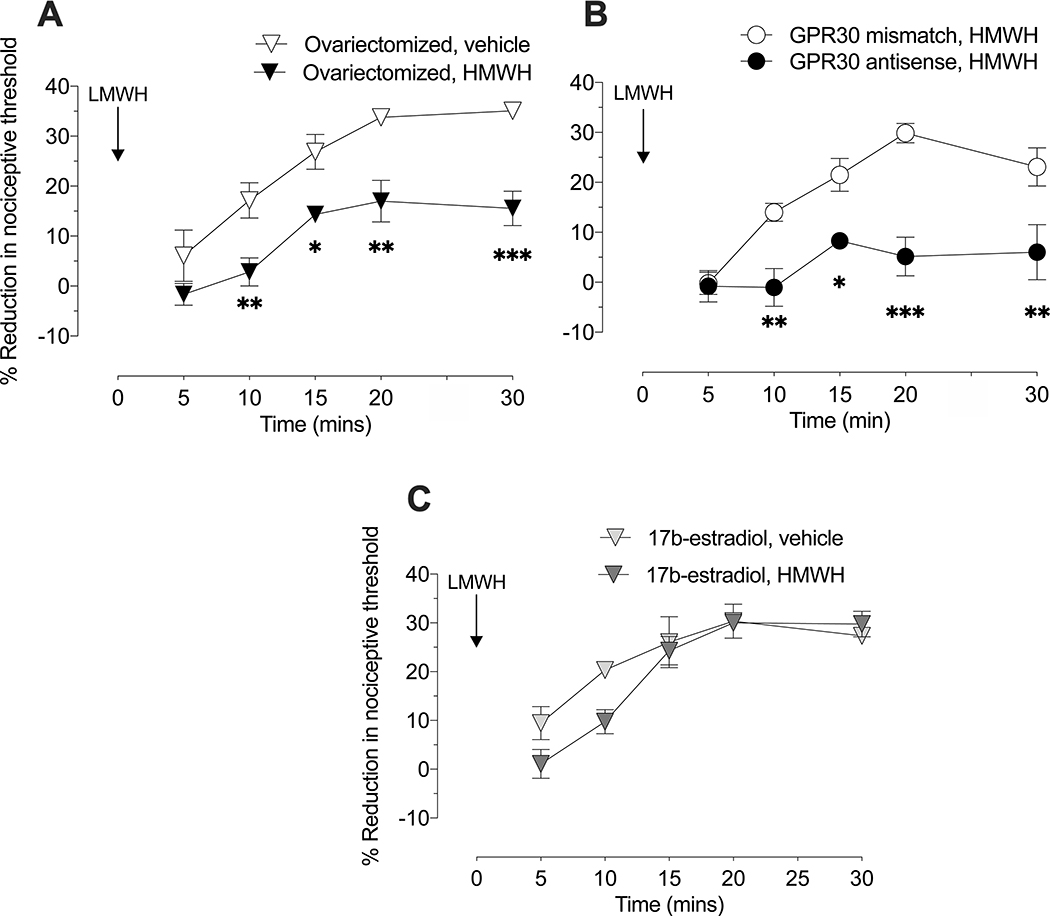
We have previously shown that intradermal HMWH (1 μg) is anti-hyperalgesic against by (and that of other pronociceptive mediators) LMWH-induced hyperalgesia, in male rats [13,25]. In the current study we compared the effect of HMWH anti-hyperalgesia against LMWH-induced hyperalgesia in female and male rats. When HMWH (1 μg) was administered 10 min before LMWH (1 μg), LMWH-induced hyperalgesia was significantly attenuated in male (Fig 6A), but not in female (Fig 6B) rats. To test the hypothesis that this sexual dimorphism is also dependent on female sex steroids, the experiment was repeated in female rats that had undergone ovariectomy 2 weeks prior. In contrast to gonad-intact females, LMWH-induced hyperalgesia was significantly attenuated by HMWH in ovariectomized females (Fig 7A). To test the hypothesis that this effect is dependent on the action of estradiol at GPR30, present on nociceptors, gonad-intact female rats were treated with antisense ODN targeting GPR30 mRNA to decrease expression of GPR30 in nociceptors, as previously described [4]. In antisense ODN-treated females, administration of HMWH now prevented LMWH-induced hyperalgesia (Fig 7B), to a degree similar to that seen in males.
Figure 6. Attenuation of LMWH hyperalgesia by HMWH.
Male and female rats received HMWH (1 μg/5 μL) or vehicle (5 μL) intradermally, on the dorsum of the hind paw, 10 min after LMWH (1 μg/5 μL) was injected in the same site. Mechanical nociceptive threshold was evaluated over the 30 min after LMWH administration.
A. Male: HMWH significantly attenuated LMWH-induced hyperalgesia in males (F(1,10)=33.54, *p=0.0103, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between HMWH- and vehicle-treated groups 10 min after intradermal LMWH; **p=0.0040, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between HMWH- and vehicle-treated groups 15 and 30 min after intradermal LMWH; ***p=0.0001, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between HMWH- and vehicle-treated groups 20 min after intradermal LMWH; two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Holm-Šídák multiple comparison test). n=6 paws per group.
B. Female: HMWH did not significantly attenuate LMWH-induced hyperalgesia in females (F(1,11)=0.6400, p=0.440, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between HMWH- and vehicle-treated groups after intradermal LMWH; two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Holm-Šídák multiple comparison test). n=6 paws per group.
Figure 7. HMWH attenuates LMWH hyperalgesia in ovariectomized female rats and in female rats treated with ODN antisense to GPR30 mRNA.
A. Ovariectomy. Female rats underwent ovariectomy 14 days prior to administration of HMWH (1 μg/5 μL) or vehicle (5 μL), injected intradermally on the dorsum of the hind paw, 10 min after LMWH (1 μg/5 μL) was injected in the same site. Magnitude of mechanical hyperalgesia, evaluated over 30 min after intradermal LMWH, in ovariectomized females was attenuated by HMWH (in contrast to intact females (see Figure 2)) (F(1,10)=33.37, **p=0.0073, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between HMWH- and vehicle-treated groups 10 min after intradermal LMWH; *p=0.0143, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between HMWH- and vehicle-treated groups 15 min after intradermal LMWH; **p=0.0018, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between HMWH- and vehicle-treated groups 20 min after intradermal LMWH; ***p=0.0003, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between HMWH- and vehicle-treated groups 30 min after intradermal LMWH; two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Holm-Šídák multiple comparison test). n=6 paws per group.
B. GPR30 ODN-treated. Female rats were treated daily with spinal intrathecal injections of antisense or mismatch ODN (120 μg/20 μL) to GPR30 mRNA, for 3 consecutive days. On the fourth day, HMWH (1 μg/5 μL) was injected intradermally, on the dorsum of the hind paw, and 10 min later, LMWH (1 μg/5 μL) was injected in the same site. The magnitude of mechanical hyperalgesia, evaluated over 30 min after intradermal LMWH, was significantly attenuated in rats treated with antisense, compared to mismatch, GPR30 ODN (F(1,10)=33.59, **p=0.0071, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between GPR30 antisense ODN- and GPR30 mismatch ODN treated groups 10 and 30 min after intradermal LMWH; *p=0.0142, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between GPR30 antisense ODN and GPR30 mismatch ODN treated groups 15 min after intradermal LMWH; ****p<0.0001, when the LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is compared between GPR30 antisense ODN- and GPR30 mismatch ODN-treated groups 20 min after intradermal LMWH; two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Holm-Šídák multiple comparison test). n=6 paws per group.
C. Ovariectomy plus 17β-estradiol. A group of female rats that underwent ovariectomy received 17β-estradiol replacement, 14 days prior to administration of HMWH (1 μg/5 μL) or vehicle (5 μL), injected intradermally on the dorsum of the hind paw, 10 min after LMWH (1 μg/5 μL) was injected in the same site. The magnitude of mechanical hyperalgesia was evaluated over 30 min after intradermal LMWH. Ovariectomized females with 17β-estradiol replacement show similar response to gonad intact female group, HMWH did not attenuate LMWH hyperalgesia (F(1,10)=1.471, p=0.2531; two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Holm-Šídák multiple comparison test). n=6 paws per group.
DISCUSSION
The ECM plays an important role in the pathophysiology of diverse clinical conditions [76,79,86], including those characterized by acute and chronic pain associated with tissue [59,82] or nerve [65] injury. Hyaluronan (HA), predominantly HMWH, is the main non-protein component of the ECM, in healthy tissue. High levels of LMWH, generated from HMWH in the setting of inflammatory diseases, such as arthritis [17,60,91], produces marked mechanical hyperalgesia and nociceptor sensitization that can be attenuated by HMWH [13,22,25]. Since several inflammatory diseases are more common in one sex (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis in females and ankylosing spondylitis in males [48]), and many of these conditions are frequently reported as being greater in females [1,30,43,] in the present study, we examined the hypothesis that the pronociceptive effect of LMWH, LMWH-induced hyperalgesia, and the anti-hyperalgesic effect of HMWH for LMWH-induced hyperalgesia are sexually dimorphic. While HMWH anti-hyperalgesia for LMWH-induced mechanical hyperalgesia, was sexually dimorphic, we previously observed that HMWH anti-hyperalgesia, for prostaglandin E2-induced mechanical hyperalgesia, is not sexually dimorphic [13]. Thus, the sexual dimorphism for both LMWH hyperalgesia and HMWH anti-hyperalgesia, is likely due to sexual dimorphism in hyaluronan receptors and downstream second messenger signaling pathways shared by both LWMH and HMWH. Our findings also support the suggestion that LMWH hyperalgesia and HMWH anti-hyperalgesia are female sex hormone-dependent, mediated by action of estradiol at GPR30 on nociceptors.
In the present experiments we demonstrated that LMWH induces dose- and time-dependent mechanical hyperalgesia in female and male rats, and that there is a marked sexual dimorphism in its duration. In female rats LMWH-induced hyperalgesia is still maximal 4 h after administration, while in males, nociceptive threshold returned to baseline 2 h after LMWH administration. Intrathecal antisense ODN treatment against CD44 mRNA markedly attenuated the magnitude of LMWH hyperalgesia in both male and female rats, and the duration of LMWH hyperalgesia in female rats. Antisense ODN knockdown of nociceptor TLR4 also attenuated LMWH hyperalgesia in both male and female rats. Unlike antisense knockdown of nociceptor CD44 and TLR4, we observed sexual dimorphism for antisense knockdown of RHAMM, where LMWH hyperalgesia was attenuated only in males. In addition, we observed sexual dimorphism for HMWH anti-LMWH hyperalgesia, with anti-hyperalgesia observed only in males. That these sex differences are dependent on female sex hormones, is supported by our observation that ovariectomy or antisense ODN knockdown of GPR30 expression, on nociceptors, both produced a switch in phenotype in females to one similar to that in males, for the duration of LMWH-induced hyperalgesia, the contribution of RHAMM to LMWH-induced hyperalgesia, and HMWH anti-hyperalgesia. The underlying mechanism of the sex hormone dependence in the contribution of RHAMM to the pharmacological effects of LMWH and HMWH remains to be elucidated.
We have suggested that LMWH and HMWH can act at nociceptor receptors to produce pro- and anti-hyperalgesic effects, respectively [13,25]. Mechanisms underlying the sexual dimorphism in LMWH-induced hyperalgesia, and HMWH anti-LMWH-induced hyperalgesia, are here demonstrated to be female sex hormone-dependent. While details of the mechanisms underlying these sex differences remain to be determined, they may be related to interactions of GPR30 with hyaluronan receptors. Of note, in this regard, knockdown of GPR30 in fibroblasts decreases CD44 expression [38], while GPR30 activation decreases TLR4 expression in macrophages [67]. Estradiol also alters the response of TLR4 to its ligands, in ectocervical epithelial cells [69]; and, dermal RHAMM expression is estradiol-dependent [68]. Degradation of HMWH to LMWH in the setting of pathophysiological processes, such as tissue injury [18,84], inflammation [10,17], and cancer [70,73], leads to generation of LMWH, which may contribute to pain associated with these clinical conditions. Further insight into the different effects of LMWH and HMWH has been provided by the observation that HMWH, but not LMWH, signaling is dependent on lipid rafts [13,89] leading to activation of different signaling pathways [51,89]. CD44 translocation into lipid rafts is required for HMWH signaling via CD44 [56,90], while disrupting lipid rafts [28,29,36] suppresses HMWH-induced CD44 clustering and the subsequent activation of downstream signaling pathways [14,15]. Our experiments confirm distinct functions of low and high molecular weight forms of hyaluronan in the nervous system, interacting with many receptors to produce different effects, as suggested by previous reports [13,16,25,62,63,72].
In addition to increased levels of LMWH in several pain conditions, a gene expression study in female mice showed a selective increase in expression of hyaluronan receptors in DRG: increased CD44, but not RHAMM, in the spared nerve injury neuropathic pain model, and a significant increased RHAMM, but not CD44, expression in the complete Freund’s adjuvant inflammatory pain model [59]. The regulation of hyaluronan receptors and their second messenger signaling pathways by inflammation and other pathological states remains to be elucidated. Since inflammation stimulates the secretion of hyaluronidase, expressed in the nervous system [2,74] and by resident cells [39], which degrades hyaluronan, generating products that can act at cell surface receptors known to be on DRG neurons [10,17,19,75,83] to produce a wide range of effects [39,63,72,89], the hyperalgesia resulting from LMWH, is most likely via a direct effect at the nociceptor.
The results of the present experiments support the suggestion that LMWH and HMWH play a role in diverse clinical pain states. Studies of the mechanisms responsible for the sexual dimorphism in the hyperalgesic effect of LMWH and anti-hyperalgesic effects of HMWH against LMWH-induced hyperalgesia could lead to the development of novel approaches for the treatment of inflammatory and neuropathic pain.
Acknowledgements:
The authors would like to thank Monica Lee and Samantha Stevens for technical assistance. This study was funded by National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant AR075334.
Footnotes
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- [1].Ageberg E, Forssblad M, Herbertsson P, Roos EM. Sex differences in patient-reported outcomes after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: data from the Swedish knee ligament register. Am J Sports Med 2010; 38: 1334–1342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [2].Al’Qteishat A, Gaffney J, Krupinski J, Rubio F, West D, Kumar S, Kumar P, Mitsios N, Slevin M. Changes in hyaluronan production and metabolism following ischaemic stroke in man. Brain 2006; 129: 2158–2176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [3].Alessandri-Haber N, Yeh JJ, Boyd AE, Parada CA, Chen X, Reichling DB, Levine JD. Hypotonicity induces TRPV4-mediated nociception in rat. Neuron 2003; 39: 497–511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [4].Alvarez P, Bogen O, Levine JD. Role of nociceptor estrogen receptor GPR30 in a rat model of endometriosis pain. Pain 2014; 155: 2680–2686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [5].Alvarez P, Green PG, Levine JD. Role for monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in the induction of chronic muscle pain in the rat. Pain 2014; 155: 1161–1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [6].Alvarez P, Green PG, Levine JD. Neonatal Handling Produces Sex Hormone-Dependent Resilience to Stress-Induced Muscle Hyperalgesia in Rats. Journal of Pain 2018; 19: 670–677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [7].Araldi D, Bogen O, Green PG, Levine JD. Role of Nociceptor Toll-like Receptor 4 (TLR4) in Opioid-Induced Hyperalgesia and Hyperalgesic Priming Title : Role of Nociceptor Toll-like Receptor 4 (TLR4) in Opioid-Induced Hyperalgesia and Hyperalgesic Priming Abbreviated title : Role of TLR4 in O. 2019; 4: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- [8].Araldi D, Ferrari LF, Green P, Levine JD. Marked sexual dimorphism in 5-HT1 receptors mediating pronociceptive effects of sumatriptan. Neuroscience 2017; 344: 394–405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [9].Araldi D, Ferrari LF, Levine JD. Repeated mu-opioid exposure induces a novel form of the hyperalgesic priming model for transition to chronic pain. Journal of Neuroscience 2015; 35: 12502–12517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [10].Avenoso A, Bruschetta G, D’Ascola A, Scuruchi M, Mandraffino G, Gullace R, Saitta A, Campo S, Campo GM. Hyaluronan fragments produced during tissue injury: A signal amplifying the inflammatory response. Arch Biochem Biophys 2019; 663: 228–238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [11].Bennett HL, Gustafsson JA, Keast JR. Estrogen receptor expression in lumbosacral dorsal root ganglion cells innervating the female rat urinary bladder. Auton Neurosci 2003; 105: 90–100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [12].Bogen O, Alessandri-Haber N, Chu C, Gear RW, Levine JD. Generation of a pain memory in the primary afferent nociceptor triggered by PKCε activation of CPEB. Journal of Neuroscience 2012; 32: 2018–2026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [13].Bonet IJM, Araldi D, Khomula EV, Bogen O, Green PG, Levine JD. Mechanisms Mediating High-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronan-Induced Antihyperalgesia. J Neurosci 2020; 40: 6477–6488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [14].Bourguignon LY, Singleton PA, Zhu H, Diedrich F. Hyaluronan-mediated CD44 interaction with RhoGEF and Rho kinase promotes Grb2-associated binder-1 phosphorylation and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling leading to cytokine (macrophage-colony stimulating factor) production and breast tumor progression. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 29420–29434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [15].Bourguignon LY, Zhu H, Shao L, Chen YW. CD44 interaction with tiam1 promotes Rac1 signaling and hyaluronic acid-mediated breast tumor cell migration. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 1829–1838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [16].Caires R, Luis E, Taberner FJ, Fernandez-Ballester G, Ferrer-Montiel A, Balazs EA, Gomis A, Belmonte C, de la Peña E. Hyaluronan modulates TRPV1 channel opening, reducing peripheral nociceptor activity and pain. Nat Commun 2015; 6: 8095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [17].Campo GM, Avenoso A, D’Ascola A, Scuruchi M, Prestipino V, Nastasi G, Calatroni A, Campo S. The inhibition of hyaluronan degradation reduced pro-inflammatory cytokines in mouse synovial fibroblasts subjected to collagen-induced arthritis. J Cell Biochem 2012; 113: 1852–1867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [18].Chajara A, Raoudi M, Delpech B, Leroy M, Basuyau JP, Levesque H. Increased hyaluronan and hyaluronidase production and hyaluronan degradation in injured aorta of insulin-resistant rats. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2000; 20: 1480–1487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [19].Cyphert JM, Trempus CS, Garantziotis S. Size Matters: Molecular Weight Specificity of Hyaluronan Effects in Cell Biology. Int J Cell Biol 2015; 2015: 563818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [20].Dickie AC, McCormick B, Lukito V, Wilson KL, Torsney C. Inflammatory Pain Reduces C Fiber Activity-Dependent Slowing in a Sex-Dependent Manner, Amplifying Nociceptive Input to the Spinal Cord. J Neurosci 2017; 37: 6488–6502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [21].Edgley C, Hogg M, De Silva A, Braat S, Bucknill A, Leslie K. Severe acute pain and persistent post-surgical pain in orthopaedic trauma patients: a cohort study. Br J Anaesth 2019; 123: 350–359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [22].Ferrari LF, Araldi D, Bogen O, Levine JD. Extracellular matrix hyaluronan signals via its CD44 receptor in the increased responsiveness to mechanical stimulation. Neuroscience 2016; 324: 390–398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [23].Ferrari LF, Araldi D, Green PG, Levine JD. Marked sexual dimorphism in neuroendocrine mechanisms for the exacerbation of paclitaxel-induced painful peripheral neuropathy by stress. Pain 2020; 161: 865–874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [24].Ferrari LF, Khomula EV, Araldi D, Levine JD . Marked Sexual Dimorphism in the Role of the Ryanodine Receptor in a Model of Pain Chronification in the Rat. Sci Rep 2016; 6: 31221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [25].Ferrari LF, Khomula EV, Araldi D, Levine JD. CD44 Signaling Mediates High Molecular Weight Hyaluronan-Induced Antihyperalgesia. J Neurosci 2018; 38: 308–321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [26].Ferrari LF, Levine JD. Plasma membrane mechanisms in a preclinical rat model of chronic pain. J Pain 2015; 16: 60–66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [27].Flake NM, Bonebreak DB, Gold MS. Estrogen and inflammation increase the excitability of rat temporomandibular joint afferent neurons. J Neurophysiol 2005; 93: 1585–1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [28].Föger N, Marhaba R, Zöller M. Involvement of CD44 in cytoskeleton rearrangement and raft reorganization in T cells. J Cell Sci 2001; 114: 1169–1178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [29].Ghatak S, Misra S, Toole BP. Hyaluronan constitutively regulates ErbB2 phosphorylation and signaling complex formation in carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 8875–8883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [30].Green CR, Hart-Johnson T, Loeffler DR. Cancer-related chronic pain: examining quality of life in diverse cancer survivors. Cancer 2011; 117: 1994–2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [31].Green PG, Dahlqvist SR, Isenberg WM, Miao FJ, Levine JD. Role of adrenal medulla in development of sexual dimorphism in inflammation. Eur J Neurosci 2001; 14: 1436–1444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [32].Green PG, Dahlqvist SR, Isenberg WM, Strausbaugh HJ, Miao FJ, Levine JD. Sex steroid regulation of the inflammatory response: sympathoadrenal dependence in the female rat. J Neurosci 1999; 19: 4082–4089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [33].Hendrich J, Alvarez P, Chen X, Levine JD. GDNF induces mechanical hyperalgesia in muscle by reducing IBK in isolectin B4-positive nociceptors. Neuroscience 2012; 219: 204–213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [34].Hucho T, Levine JD. Signaling Pathways in Sensitization: Toward a Nociceptor Cell Biology. Neuron 2007; 55: 365–376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [35].Humphrey JD, Dufresne ER, Schwartz MA. Mechanotransduction and extracellular matrix homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2014; 15: 802–812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [36].Ito T, Williams JD, Fraser DJ, Phillips AO. Hyaluronan regulates transforming growth factor-beta1 receptor compartmentalization. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 25326–25332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [37].Jansen KA, Atherton P, Ballestrem C. Mechanotransduction at the cell-matrix interface. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2017; 71: 75–83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [38].Jia B, Gao Y, Li M, Shi J, Peng Y, Du X, Klocker H, Sampson N, Shen Y, Liu M, Zhang J. GPR30 Promotes Prostate Stromal Cell Activation via Suppression of ERα Expression and Its Downstream Signaling Pathway. Endocrinology 2016; 157: 3023–3035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [39].Jiang D, Liang J, Noble PW. Hyaluronan as an immune regulator in human diseases. Physiol Rev 2011; 91: 221–264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [40].Joseph EK, Levine JD. Sexual dimorphism for protein kinase c epsilon signaling in a rat model of vincristine-induced painful peripheral neuropathy. Neuroscience 2003; 119: 831–838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [41].Joseph EK, Levine JD. Sexual dimorphism in endothelin-1 induced mechanical hyperalgesia in the rat. Exp Neurol 2012; 233: 505–512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [42].Juliano RL, Haskill S. Signal transduction from the extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol 1993; 120: 577–585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [43].Karshikoff B, Lekander M, Soop A, Lindstedt F, Ingvar M, Kosek E, Olgart Höglund C, Axelsson J. Modality and sex differences in pain sensitivity during human endotoxemia. Brain Behav Immun 2015; 46: 35–43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [44].Khasar SG, Isenberg WM, Miao FJ, Gear RW, Green PG, Levine JD. Gender and gonadal hormone effects on vagal modulation of tonic nociception. J Pain 2001; 2: 91–100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [45].Khomula EV, Ferrari LF, Araldi D, Levine JD. Sexual Dimorphism in a Reciprocal Interaction of Ryanodine and IP 3 Receptors in the Induction of Hyperalgesic Priming. The Journal of Neuroscience 2017; 37: 2032–2044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [46].Kim SH, Turnbull J, Guimond S. Extracellular matrix and cell signalling: the dynamic cooperation of integrin, proteoglycan and growth factor receptor. J Endocrinol 2011; 209: 139–151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [47].Korczeniewska OA, Khan J, Tao Y, Eliav E, Benoliel R. Effects of Sex and Stress on Trigeminal Neuropathic Pain-Like Behavior in Rats. J Oral Facial Pain Headache 2017; 31: 381–397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [48].Krasselt M, Baerwald C. Sex, Symptom Severity, and Quality of Life in Rheumatology. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 2019; 56: 346–361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [49].Li S, Li C, Zhang Y, He X, Chen X, Zeng X, Liu F, Chen Y, Chen J. Targeting Mechanics-Induced Fibroblast Activation through CD44-RhoA-YAP Pathway Ameliorates Crystalline Silica-Induced Silicosis. Theranostics 2019; 9: 4993–5008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [50].Liang SL, Pan JT. Pretreatment with antisense oligodeoxynucleotide against D(2) or D(3) receptor mRNA diminished dopamine’s inhibitory effect on dorsomedial arcuate neurons in brain slices of estrogen-treated ovariectomized rats. Brain Res 2002; 926: 156–164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [51].Litwiniuk M, Krejner A, Speyrer MS, Gauto AR, Grzela T. Hyaluronic Acid in Inflammation and Tissue Regeneration. Wounds 2016; 28: 78–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [52].Luo X, Huh Y, Bang S, He Q, Zhang L, Matsuda M, Ji RR. Macrophage Toll-like Receptor 9 Contributes to Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Male Mice. J Neurosci 2019; 39: 6848–6864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [53].Maurer AJ, Lissounov A, Knezevic I, Candido KD, Knezevic NN. Pain and sex hormones: a review of current understanding. Pain Manag 2016; 6: 285–296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [54].Mestre C, Pélissier T, Fialip J, Wilcox G, Eschalier A. A method to perform direct transcutaneous intrathecal injection in rats. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 1994; 32: 197–200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [55].Mobini A, Mehra P, Chigurupati R. Postoperative Pain and Opioid Analgesic Requirements After Orthognathic Surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2018; 76: 2285–2295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [56].Murai T Lipid raft-mediated regulation of hyaluronan-CD44 interactions in inflammation and cancer. Frontiers in Immunology 2015; 6: 1–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [57].Nicotra L, Tuke J, Grace PM, Rolan PE, Hutchinson MR. Sex differences in mechanical allodynia: how can it be preclinically quantified and analyzed. Front Behav Neurosci 2014; 8: 40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [58].Noble PW. Hyaluronan and its catabolic products in tissue injury and repair. Matrix Biol 2002; 21: 25–29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [59].Parisien M, Samoshkin A, Tansley SN, Piltonen MH, Martin LJ, El-Hachem N, Dagostino C, Allegri M, Mogil JS, Khoutorsky A, Diatchenko L. Genetic pathway analysis reveals a major role for extracellular matrix organization in inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Pain 2019; 160: 932–944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [60].Poole AR, Witter J, Roberts N, Piccolo F, Brandt R, Paquin J, Baron M. Inflammation and cartilage metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis. Studies of the blood markers hyaluronic acid, orosomucoid, and keratan sulfate. Arthritis Rheum 1990; 33: 790–799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [61].Prein C, Beier F. ECM signaling in cartilage development and endochondral ossification. Curr Top Dev Biol 2019; 133: 25–47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [62].Preston M, Gong X, Su W, Matsumoto SG, Banine F, Winkler C, Foster S, Xing R, Struve J, Dean J, Baggenstoss B, Weigel PH, Montine TJ, Back SA, Sherman LS. Digestion products of the PH20 hyaluronidase inhibit remyelination. Ann Neurol 2013; 73: 266–280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [63].Preston M, Sherman LS. Neural stem cell niches: roles for the hyaluronan-based extracellular matrix. Front Biosci (Schol Ed) 2011; 3: 1165–1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [64].Quanhong Z, Ying X, Moxi C, Tao X, Jing W, Xin Z, Li W, Derong C, Xiaoli Z, Wei J. Intrathecal PLC(β3) oligodeoxynucleotides antisense potentiates acute morphine efficacy and attenuates chronic morphine tolerance. Brain Res 2012; 1472: 38–44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [65].Radojčić MR, Thudium CS, Henriksen K, Tan K, Karlsten R, Dudley A, Chessell I, Karsdal MA, Bay-Jensen AC, Crema MD, Guermazi A. Biomarker of extracellular matrix remodelling C1M and proinflammatory cytokine interleukin 6 are related to synovitis and pain in end-stage knee osteoarthritis patients. Pain 2017; 158: 1254–1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [66].Randall LO, Selitto JJ. A method for measurement of analgesic activity on inflamed tissue. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 1957; 111: 409–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [67].Rettew JA, McCall SH, Marriott I. GPR30/GPER-1 mediates rapid decreases in TLR4 expression on murine macrophages. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2010; 328: 87–92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [68].Röck K, Meusch M, Fuchs N, Tigges J, Zipper P, Fritsche E, Krutmann J, Homey B, Reifenberger J, Fischer JW. Estradiol protects dermal hyaluronan/versican matrix during photoaging by release of epidermal growth factor from keratinocytes. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 20056–20069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [69].S Lashkari B, Anumba DO. Estradiol alters the immune-responsiveness of cervical epithelial cells stimulated with ligands of Toll-like receptors 2 and 4. PLoS One 2017; 12: e0173646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [70].Schmaus A, Klusmeier S, Rothley M, Dimmler A, Sipos B, Faller G, Thiele W, Allgayer H, Hohenberger P, Post S, Sleeman JP. Accumulation of small hyaluronan oligosaccharides in tumour interstitial fluid correlates with lymphatic invasion and lymph node metastasis. Br J Cancer 2014; 111: 559–567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [71].Scuruchi M, D’Ascola A, Avenoso A, Campana S, Abusamra YA, Spina E, Calatroni A, Campo GM, Campo S. 6-Mer Hyaluronan Oligosaccharides Modulate Neuroinflammation and α-Synuclein Expression in Neuron-Like SH-SY5Y Cells. J Cell Biochem 2016; 117: 2835–2843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [72].Sherman LS, Back SA. A ‘GAG’ reflex prevents repair of the damaged CNS. Trends Neurosci 2008; 31: 44–52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [73].Singleton PA. Hyaluronan regulation of endothelial barrier function in cancer. Adv Cancer Res 2014; 123: 191–209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [74].Sloane JA, Batt C, Ma Y, Harris ZM, Trapp B, Vartanian T. Hyaluronan blocks oligodendrocyte progenitor maturation and remyelination through TLR2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010; 107: 11555–11560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [75].Soltés L, Kogan G, Stankovska M, Mendichi R, Rychlý J, Schiller J, Gemeiner P. Degradation of high-molar-mass hyaluronan and characterization of fragments. Biomacromolecules 2007; 8: 2697–2705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [76].Sonbol HS. Extracellular Matrix Remodeling in Human Disease. J Microsc Ultrastruct 2018; 6: 123–128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [77].Song MJ, Wang YQ, Wu GC. Additive anti-hyperalgesia of electroacupuncture and intrathecal antisense oligodeoxynucleotide to interleukin-1 receptor type I on carrageenan-induced inflammatory pain in rats. Brain Res Bull 2009; 78: 335–341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [78].Storesund A, Krukhaug Y, Olsen MV, Rygh LJ, Nilsen RM, Norekvål TM. Females report higher postoperative pain scores than males after ankle surgery. Scand J Pain 2016; 12: 85–93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [79].Taha IN, Naba A. Exploring the extracellular matrix in health and disease using proteomics. Essays Biochem 2019; 63: 417–432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [80].Taiwo YO, Coderre TJ, Levine JD. The contribution of training to sensitivity in the nociceptive paw-withdrawal test. Brain Res 1989; 487: 148–151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [81].Taiwo YO, Levine JD. Prostaglandin effects after elimination of indirect hyperalgesic mechanisms in the skin of the rat. Brain Res 1989; 492: 397–399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [82].Tajerian M, Clark JD. The role of the extracellular matrix in chronic pain following injury. Pain 2015; 156: 366–370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [83].Tavianatou AG, Caon I, Franchi M, Piperigkou Z, Galesso D, Karamanos NK. Hyaluronan: molecular size-dependent signaling and biological functions in inflammation and cancer. The FEBS Journal 2019; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [84].Taylor KR, Trowbridge JM, Rudisill JA, Termeer CC, Simon JC, Gallo RL. Hyaluronan fragments stimulate endothelial recognition of injury through TLR4. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 17079–17084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [85].Theocharis AD, Skandalis SS, Gialeli C, Karamanos NK. Extracellular matrix structure. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2016; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [86].Theocharis AD, Manou D, Karamanos NK. The extracellular matrix as a multitasking player in disease. FEBS J 2019; 286: 2830–2869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [87].Vigetti D, Karousou E, Viola M, Deleonibus S, De Luca G, Passi A. Hyaluronan: biosynthesis and signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta 2014; 1840: 2452–2459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [88].Xu S, Cheng Y, Keast JR, Osborne PB. 17beta-estradiol activates estrogen receptor beta-signalling and inhibits transient receptor potential vanilloid receptor 1 activation by capsaicin in adult rat nociceptor neurons. Endocrinology 2008; 149: 5540–5548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [89].Yang C, Cao M, Liu H, He Y, Xu J, Du Y, Liu Y, Wang W, Cui L, Hu J, Gao F. The high and low molecular weight forms of hyaluronan have distinct effects on CD44 clustering. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 43094–43107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [90].Yang Z, Qin W, Chen Y, Yuan B, Song X, Wang B, Shen F, Fu J, Wang H. Cholesterol inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma invasion and metastasis by promoting CD44 localization in lipid rafts. Cancer Lett 2018; 429: 66–77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [91].Yoshida M, Sai S, Marumo K, Tanaka T, Itano N, Kimata K, Fujii K. Expression analysis of three isoforms of hyaluronan synthase and hyaluronidase in the synovium of knees in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis by quantitative real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. Arthritis Res Ther 2004; 6: R514–20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]