Abstract
Background
Little is known about the complex interactions between the diet, the gut microbiota, and enteropathogens. Here, the impact of two specific diets on the composition of the mouse gut microbiota and on the transcriptional response of Salmonella Typhimurium (S. Typhimurium) was analyzed in an enteritis model.
Results
Mice were fed for two weeks a fibre-rich, plant-based diet (PD), or a Westernized diet (WD) rich in animal fat and proteins and in simple sugars, and then infected with an invasin-negative S. Typhimurium strain ST4/74 following streptomycin-treatment. Seventy-two hours post infection, fecal pathogen loads were equal in both diet groups, suggesting that neither of the diets had negatively influenced the ability of this ST4/74 strain to colonize and proliferate in the gut at this time point. To define its diet-dependent gene expression pattern, S. Typhimurium was immunomagnetically isolated from the gut content, and its transcriptome was analyzed. A total of 66 genes were more strongly expressed in mice fed the plant-based diet. The majority of these genes was involved in metabolic functions degrading substrates of fruits and plants. Four of them are part of the gat gene cluster responsible for the uptake and metabolism of galactitol and D-tagatose. In line with this finding, 16S rRNA gene amplicon analysis revealed higher relative abundance of bacterial families able to degrade fiber and nutritive carbohydrates in PD-fed mice in comparison with those nourished with a WD. Competitive mice infection experiments performed with strain ST4/74 and ST4/74 ΔSTM3254 lacking tagatose-1,6-biphosphate aldolase, which is essential for galactitol and tagatose utilization, did not reveal a growth advantage of strain ST4/74 in the gastrointestinal tract of mice fed plant-based diet as compared to the deletion mutant.
Conclusion
A Westernized diet and a plant-based diet evoke distinct transcriptional responses of S. Typhimurium during infection that allows the pathogen to adapt its metabolic activities to the diet-derived nutrients. This study therefore provides new insights into the dynamic interplay between nutrient availability, indigenous gut microbiota, and proliferation of S. Typhimurium.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s42523-021-00082-8.
Keywords: Transcriptome, Gut microbiota, Salmonella Typhimurium, Diet, Metabolism
Background
Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica (S. enterica) is one of the most important model organisms to investigate bacterial genetics and pathogenicity. Its serovar Typhimurium (S. Typhimurium) is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic microorganism that causes non-thypoidal gastroenteritis in humans and typhoid-like disease in mice [1]. It is a food-borne pathogen that invades its host by contaminated food or water, eventually leading to salmonellosis [2]. During infection, S. Typhimurium needs sufficient energy as well as carbon and nitrogen sources to proliferate, colonize the epithelial barrier, produce virulence factors and withstand the host immune responses. A broad metabolic capacity is therefore a prerequisite for salmonellae to successfully compete with and outgrow commensal microorganisms in the terminal ileum and the colon. However, the acquisition of nutrients is a major challenge for S. Typhimurium due to colonization resistance of the commensal microbiota. This complex bacterial community forms a highly competitive environment via for instance the production of antimicrobial peptides and growth-inhibiting metabolites, and by reducing the amount of substrates freely available in the gut [3]. Moreover, as growth on only one carbon source is probably the exception for most bacteria invading the gut, S. Typhimurium is urged to rapidly switch from one nutrient to another, and thus to adapt its metabolic profile according to the metabolic status of each microenvironment encountered during infection.
The intestine of mammals and humans is a nutrient-rich reactor that is continuously fueled with substrates from the diet or, indirectly, with metabolites derived from the food or released from the mucus by bacterial enzymes [4]. Some of the main substrates in the gut are poly- and monosaccharides, fibres, proteins, starch, pectin, triglycerides, lactose, raffinose, creatine, mannan, xylan and cellulose. The indigenous microbiota produces approximately 9000 glycoside-hydrolases and 200 polysaccharide lyases [5], thereby aiding the host to optimally exploit dietary nutrients. This broad enzymatic capacity of commensal microbes results in the delivery of numerous simple sugars (glucose, xylose, galactose, fructose, mannose, arabinose, ribose), and many other metabolites such as phospholipids, glycerol, ethanolamine, lactate succinate, cholines, phenols, inositols, polyamines, indoles, short-chain fatty acids and other metabolites. Enzymes particularly produced by members of the phylum Bacteroidetes are able to digest mucus-derived glycans, thus providing galactose, gluconate, arabinose, fucose, rhamnose, 1,2-propanediol, sialic acid, N-acetyl-glucosamine, xylose, mannose, branched-chain fatty acids, di- and oligopeptides, and amino acids [4, 6]. Although such a wide range of nutrients is available in the gut, it is assumed that most metabolic niches, however, are already occupied by commensal microbes [7]. To overcome this metabolic competition, the gut-invading pathogen S. Typhimurium acquired and evolved specific metabolic capacities that include the utilization of sialic acid, fucose, melibiose, rhamnose, glycerol, ethanolamine, propanediol or myo-inositol [4, 8–12]. In the case of ethanolamine and 1,2-propanediol, both intestinal inflammation and the respiration of a microbiota-derived fermentation product enable this metabolic activity [13].
Any kind of perturbations that trigger substantial alteration of the gut microbiota can influence the conditions underlying bacterial growth and infection. Beside diseases and inflammation, antibiotic treatment and dietary changes are known to significantly interfere with the metabolic balance between host, gut microbiota and pathogens. Antibiosis usually strongly reduces microbial diversity and may thereby supports the expansion of non-targeted members of the gut microbiota. Moreover, colonization resistance is weakened by antibiotic treatment, resulting in an increased susceptibility to infection [14]. Nutritional changes have also been shown to change the structure and functions of gut microbial populations [15–18].
The complex and multiple interdependencies between the gut microbiota and an invading enteropathogen under varying dietary conditions remain to be elucidated in more detail. In particular, we tested the role of the gut microbiota as a key player in providing varying luminal conditions driven by different feeding protocols. For this purpose, we analyzed gut microbiota shifts and the resulting in vivo transcription patterns of Salmonella during proliferation in the gut of mice. We provide evidence that the transcriptional response of S. Typhimurium is diet-adapted, and that the diet-specific microbiota contributes to this adaptation by providing corresponding substrates.
Results
Effects of two experimental diets on the fecal microbiota structure
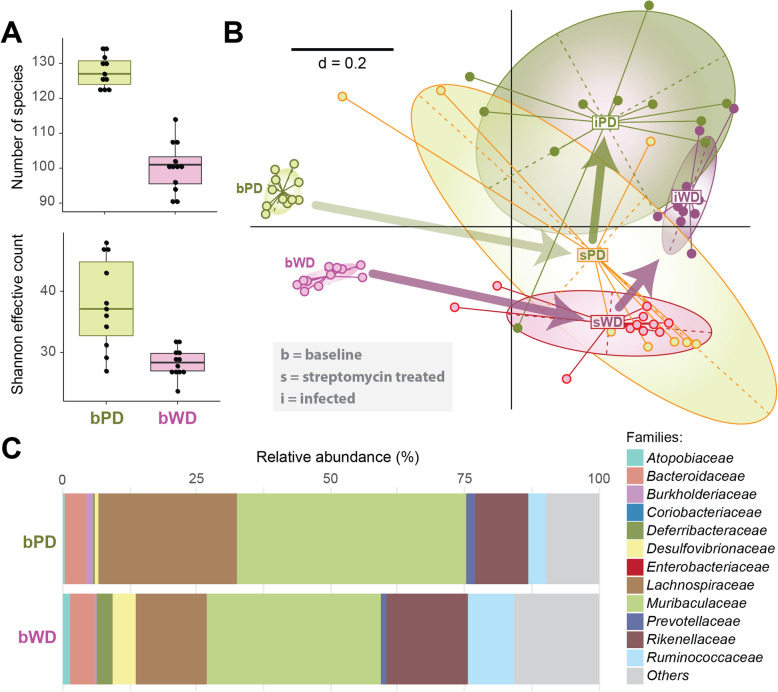
Twelve mice were fed either a Westernized diet (WD) or a plant-based diet (PD) for 13 days. Both diets had equal energy contents, and mice did not differ in terms of body weight at the time of feces collection (data not shown). The microbiota of PD fed mice were characterized by significantly higher species richness and higher Shannon effective counts compared with that of mice in the WD group (Fig. 1a). Non-metric multidimensional scatter (NMDS) plots of generalized UniFrac distances demonstrated clearly separated microbial phylogenetic makeup between the two dietary groups at baseline (Fig. 1b). In the fecal microbiota of untreated mice (baseline), eight different phyla were detected in both groups, of which Bacteroidetes (~ 61–64% relative abundance) and Firmicutes (~ 25–33%) were the most dominant. Family-level classification showed that members of the Atopobiaceae (phylum Actinobacteria) and Deferribacteraceae (represented by the species Mucispirillum schaedleri) were more abundant in WD mice (Fig. 1c, Additional files 1 and 2). The distribution of families within the phylum Bacteroidetes was also diet-dependent with a higher relative abundance of Rikenellaceae and Tannerellaceae in WD fed mice, whereas PD fed mice harbored predominantly the families Prevotellaceae and Muribaculaceae. The families Lachnospiraceae and Burkholderiaceae belonging to the phyla Firmicutes and Proteobacteria, respectively, exhibited higher proportions in the PD group, whereas Ruminococcaceae and Desulfovibrionaceae were more abundant in mice exposed to WD. The family Anaeroplasmataceae (phylum Tenericutes) occurred only in PD fed mice. Remarkably, the families Prevotellaceae, Muribaculaceae, and Lachnospiraceae are known to degrade carbohydrates such as fibers, hemicelluloses and starch, thus providing nutrients accessible for the host, other commensals and eventually invading pathogens.
Fig. 1.
Differences in the fecal microbiota diversity and composition in to dietary mice groups. a Changes in α-diversity are shown as boxplots. All differences between two samples are significant (p ≤ 0.05) according to the pairwise Wilcoxon Rank Sum Test (n of WD fed mice = 12, n of PD fed mice = 11). b β-diversity analysis displayed as a nonmetric multidimensional scaling plot (metaNMDS) computed from generalized UniFrac distances, which were calculated from normalized OTU tables and phylogenetic distance trees (n of WD fed, untreated mice = 12, n of WD fed, streptomycin-treated/infected mice = 11, n of PD fed, untreated/infected mice = 11, n of PD fed, streptomycin-treated mice = 8). c An overview of relative abundances of major bacterial families is given by stacked bar plots. Cumulative abundances were calculated from all single OTUs classified within one family as per the best possible taxonomy using both the RDP and Silva. N of WD fed mice = 12, n of PD fed mice = 11
These findings were confirmed and further differentiated by analyses at the level of OTUs (Additional files 2, 3, and 4). All differences in the microbiota composition described here and below were statistically evaluated as significant (p ≤ 0.05) according to the pairwise Wilcoxon Rank Sum Test and/or the Fisher’s Exact Test.
In vitro phenotype of strain ST4/74 ΔinvA
To analyse the transcriptome of strain ST4/74 during infection, but independently of the hostʼs immune response, we constructed mutant ST4/74 ΔinvA that is unable to invade epithelial cells, resulting in a retarded immune reaction [19–23]. To monitor effects of the two diets on growth of the mutant, diet pellets were mashed using sterile water and inoculated 1:100 with an overnight culture of ST4/74 ΔinvA in LB medium. During incubation at 37 °C, aliquots of the cultures were taken and plated on LB agar plates to determine colony forming units (CFU). Starting with 1.0 × 107 CFU/ml (PD) and 1.8 × 107 CFU/ml (WD) immediately after inoculation, the cultures reached counts of 2.0 × 109 CFU/ml (PD) and 8.4 × 108 CFU/ml after 24 h. Slightly different growth properties were observed, indicating nearly equal growth of mutant ST4/74 ΔinvA in the two diets (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
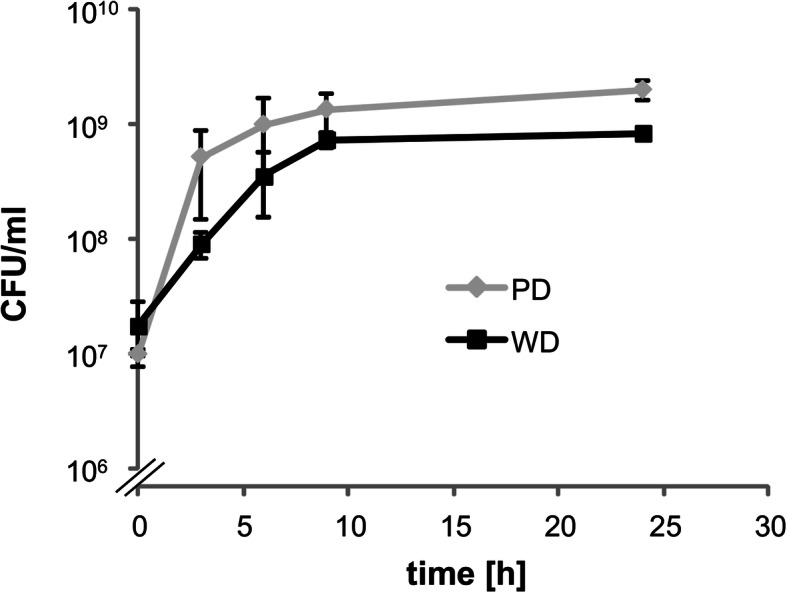
Growth phenotype of strain ST4/74 ΔinvA in medium with PD and WD pellets. The growth behaviour of strain ST4/74 ΔinvA was tested in medium with food pellets for PD (gray line) or WD (black line) dissolved in water. The CFU of three biological replicates were determined by plating three aliquots at each time point. Error bars show the standard deviation
Streptomycin treatment
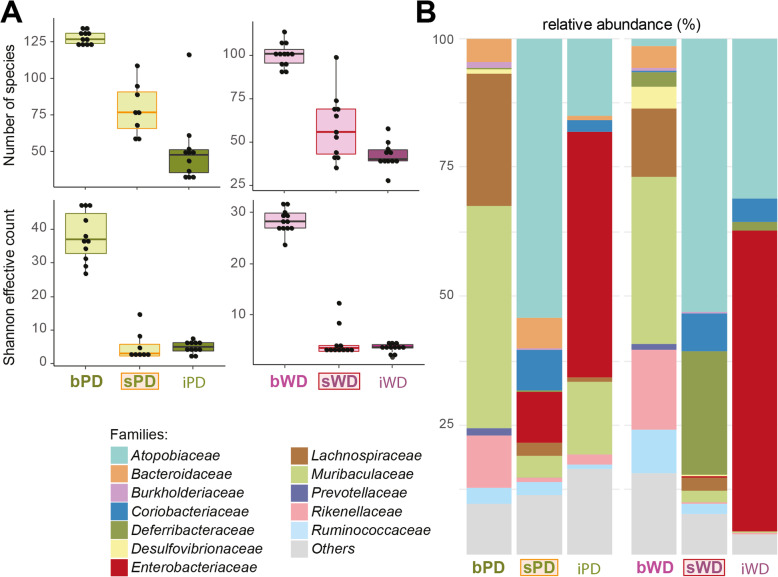
Mice were treated with 20 mg streptomycin 24 h before infection to evoke a gastroenteritis and a retarded systemic infection, resulting in a higher susceptibility for and proliferation of Salmonella [24, 25]. Such a pathogen expansion is a prerequisite for an in vivo transcriptome analysis that requires a high cell number to isolate sufficient amounts of RNA. The treatment with streptomycin decreased species richness and Shannon effective counts (Fig. 3a) in feces independent of the diet, and the differences between the two diets remained equally significant. β-diversity analysis showed drastic shifts in the phylogenetic makeup of the microbiota after antibiosis (Fig. 1b). At the level of families, the application of streptomycin to both PD and WD fed mice markedly increased the relative abundance of Atopobiaceae and Coriobacteriaceae, whereas Burkholderiaceae, Desulfovibrionaceae, Lachnospiraceae, Muribaculaceae, Prevotellaceae and Rikenellaceae were sensitive to the antibiotic or/and were outcompeted by the other commensals. In the case of PD in particular, marked inter-individual differences were observed, indicating very diverse trajectories of changes following treatment. Here, but not in WD fed mice, streptomycin increased the proportion of Anaeroplasmataceae and Bacteroidaceae, and reduced that of Erysipelotrichaceae. In the intestine of WD fed mice, streptomycin treatment increased proportions of the family Deferribacteraceae, and decreased that of the families Bacteroidaceae, Tannerellaceae and Ruminococcaceae as compared with the PD fed group (Fig. 3b) (Additional files 1 and 5).
Fig. 3.
Microbial shifts in mice following streptomycin treatment and infection. a α-diversity changes are shown as boxplots. N of WD fed, untreated mice = 12, n of WD fed, streptomycin-treated/infected mice = 11, n of PD fed, untreated/infected mice = 11, n of PD fed, streptomycin-treated mice = 8. b For both PD or WD fed mice after streptomycin application and infection with S. Typhimurium, an overview of cumulative relative abundances of all dominant families are displayed. See legend of Fig. 1c for statistical details
Infection with ST4/74 ΔinvA
Twenty-four h after the application of streptomycin, the mice were orally infected with 5 × 107 ST4/74 ΔinvA cells. After further 24 h, 109–1011 Salmonella cells were found in the mouse gut, without significant differences in cell numbers between the two dietary groups (Fig. 4). The infection with S. Typhimurium caused a further decrease in species richness and shift of β-diversity of the fecal microbiota in both dietary groups in comparison with streptomycin-treated samples before infection (Fig. 1b, Fig. 3b). In line with the high number of Salmonella cells introduced into and proliferating in the gut, a high relative abundance of Enterobacteriaceae, the bacterial family to which Salmonella belongs, represented by 47.5% (PD) and 58.1% (WD) of all reads (Additional file 6), was observed 24 h after infection. Accordingly, the proportions of most other families decreased in both dietary groups, with the exception of Coriobacteriaceae in mice fed WD (Fig. 3b, Additional file 1).
Fig. 4.
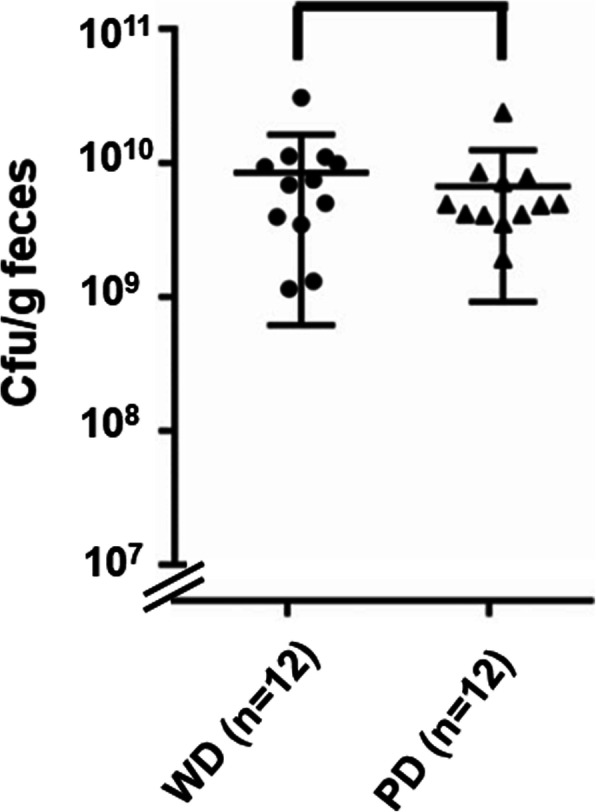
Diet-dependent load of S. Typhimurium 24 h post infection. Twelve mice per group were infected with 5 × 107 cells of strain ST4/74 ΔinvA. No significant difference between the averaged CFU were detected
Validation of immunomagnetic separation to isolate S. Typhimurium from the gut content
As a prerequisite to analyze the in vivo transcriptome of S. Typhimurium ST4/74 ΔinvA, we established a method to separate ST4/74 ΔinvA cells from the commensal gut microbiota of mice by immunomagnetic separation (IMS) [26, 27]. We first tested Salmonella-specific antibodies (BacTrace; ViroStat, Maryland, ME, USA) for their selectivity and their cross-reactivity with related Enterobacteriaceae. Salmonella cells were separated from a 1:1 mixture of Escherichia coli DH5α/pBR322 and S. Typhimurium ST4/74 ΔinvA by IMS, and the number of S. Typhimurium cells was determined before and after the separation by plating the suspensions on agar selective for S. Typhimurium ST4/74 ΔinvA (NalR) and E. coli DH5α/pBR322 (TetR). A reduction of E. coli by 99.5% was achieved using the BacTrace antibody, whereas no significant separation of both bacteria was obtained using the ViroStat antibody. Even when the Salmonella and the E. coli strain were mixed at a ratio of 1:10.000, ST4/74 ΔinvA cells were enriched to a final ratio of 11:1 following IMS with the BacTrace antibody, indicating its high binding specificity. Then, ST4/74 ΔinvA cells were mixed with cecum content isolated from mice to concentrations of 1.57 × 106 CFU/ml, 5.36 × 107 CFU/ml and 3.78 × 108 CFU/ml, with the highest concentration corresponding to that found in the caecum of mice 20 h after infection [28]. Applying IMS, approximately 21, 33 and 41%, respectively, of the Salmonella cells were retrieved. We also inoculated the caecum content with a 60:40 mixture of E. coli DH5α/pBR322 and S. Typhimurium ST4/4 and noted a reduction of E. coli to 10% after one IMS separation and to 3% of all bacterial cells after a second application of the antibodies. These data validated IMS for the separation of Salmonella cells from the gut of infected mice after infection.
In vivo transcriptome of S. Typhimurium
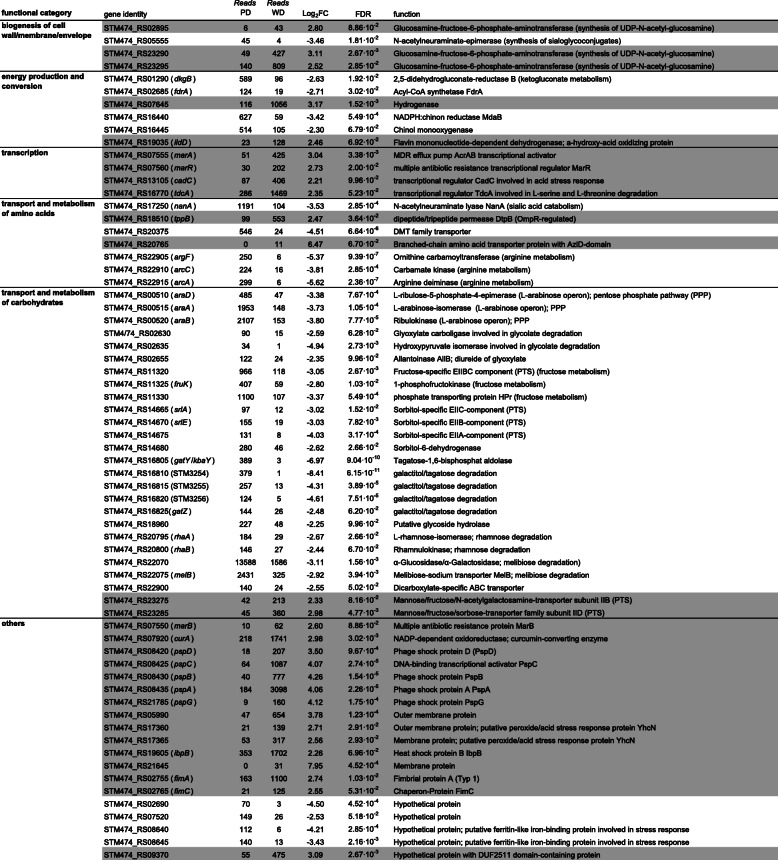
Cecum and ileum content of mice infected with strain ST4/74 ΔinvA were dissected together to isolate Salmonella cells via IMS 24 h after infection. The mice did not show signs of illness. The time point was chosen to reduce possible inflammation that might interfere with diet-dependent effects. After RNA isolation, a cDNA library was constructed and sequenced. We identified 66 Salmonella genes that were differentially regulated in mice fed with one of the two diets in comparison with the other one. Thirty-eight of these genes were found to be more strongly induced in ST4/74 ΔinvA infected mice fed PD than in those fed WD. Of those 38 genes, the remarkably high number of 29 belong to the categories transport and metabolism of carbohydrates. This includes genes responsible for the metabolism of arabinose and the uptake and/or utilization of glycolate, fructose, sorbitol, tagatose, galactitol, rhamnose and melibiose (Table 1). All these sugars and polyols are found in plants, and the upregulated genes directly reflect the higher amount of plant material in the PD. In addition, genes involved in arginine metabolism (arcA, arcC, argF) and in sialic acid catabolism (nanA), and four genes attributed to energy production and conversion revealed to be upregulated in mice fed predominantly with plant material.
Table 1.
Transcriptome analysis of strain ST4/74 isolated from mice fed WD or PD. FDR, false discovery rate. Positive log2 fold-changes (FC) (gray) indicate a higher gene expression in WD fed mice in comparison with the PD fed group, negative FC (white) vice versa
In contrast, 28 ST4/74 genes were upregulated following infection of mice fed WD as compared to the other dietary group. Many of these genes are involved in stress response and encode phage shock proteins PspA-D and PspG, the heat shock protein IbpB, the acid stress response regulator CadC, and two putative proteins responding to peroxide or acid stress (Table 1). Remarkably, the multiple antibiotic resistance (marRAB) operon, three genes homologous to glucosamine-fructose-6-phosphate-aminotransferase genes, two genes involved in mannose/sorbose transport, and two genes involved in the production of fimbriae were also found to be upregulated under this condition. Taken together, a PD results in a specific induction of metabolic genes in S. Typhimurium, whereas a WD predominantly activates stress genes.
The gat operon contributes to tagatose utilization
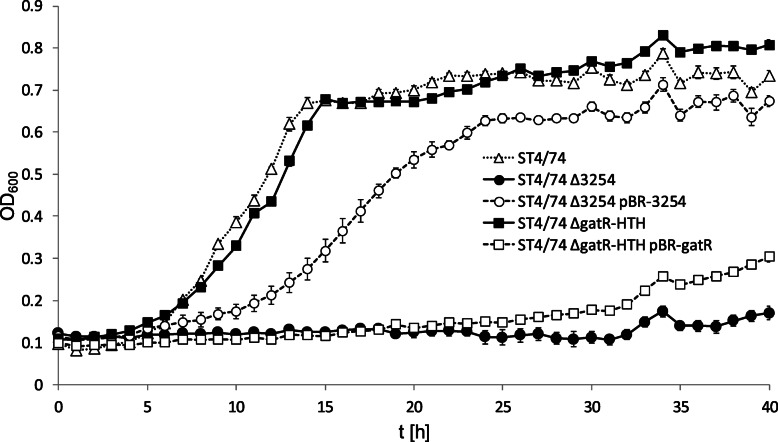
Five of the Salmonella genes upregulated in mice fed PD are part of the gat operon known to be responsible for galactitol utilization [29]. Three of the gene products of the gat operon are predicted to be involved in tagatose metabolism (Table 1). We deleted one of them, gene STM3254 encoding a hypothetical tagatose-1-phosphate kinase, which is essential for galactitol utilization, and tested its growth in MM with tagatose as sole carbon and energy source. Under this condition, mutant ST4/74 ΔSTM3254 exhibited a zero growth phenotype that could be complemented by providing the gene in trans using plasmid pBR-3254 (Fig. 5). When we tested another mutant, ST4/74 ΔgatR-HTH (Table 2), which is not able to repress the gat promoters due to a lack of the nucleotides of gatR encoding the DNA-binding site of the repressor GatR [29], a growth behavior with tagatose similar to that of parental strain ST4/74 was observed. This finding is in line with the assumption that the gat promoters are activated in the presence of galactitol and tagatose. Upon complementation of ST4/74 ΔgatR-HTH with plasmid pBR-gatR, growth was inhibited probably due to the high number of repressor molecules. Taken together, we could demonstrate that the gat operon of S. Typhimurium is responsible for D-tagatose utilization, and that mutant ST4/74 ΔSTM3254 is unable to degrade this sugar.
Fig. 5.
Tagatose-dependent growth phenotypes of S. Typhimurium. Growth curves of strains ST4/74, ST4/74 ΔSTM3254, ST4/74 ΔSTM3254/pBR-3254, ST4/74 ΔgatR-HTH, and ST4/74 ΔgatR-HTH/pBR-gatR in MM with 1% D-tagatose as sole carbon source. Standard deviations of three replicates are shown
Table 2.
Strains and plasmids used in this study
| Strains | Description and relevant features | references |
|---|---|---|
| S. Typhimurium ST4/74 | NalR | [30] |
| ST4/74 ΔinvA | Non-polar invA deletion mutant | This study |
| ST4/74 ΔSTM3254 | Non-polar STM3254 deletion mutant with zero growth phenotype in galactitol | [29] |
| ST4/74 ΔSTM3254::KanR | Mutant with allelic exchange of STM3254 against a kanamycin resistance gene | This study |
| ST4/74 ΔgatR-HTH | Partial non-polar deletion of gatR lacking the nucleotides encoding the helix-turn-helix motif (HTH) | This study |
| E. coli | ||
| DH5α | F– endA1 glnV44 thi-1 recA1 relA1 gyrA96 deoR nupG purB20 φ80ΔlacZΔM15 Δ(lacZYA-argF )U169, hsdR17 (rK–mK+), λ– | |
| Plasmids | ||
| pBR322 | AmpR, TetR | [31] |
| pBR-STM3254 | pBR322 with gene STM3254 | This study |
| pBR-gatR | pBR322 with repressor gene gatR | This study |
| pKD4 | KanR, pir-dependent, FRT sites | [32] |
| pKD46 | λ-Red helper plasmid, AmpR | [32] |
| pCP20 | FLP recombinase plasmid, CmR, AmpR | [32] |
Galactitol utilization does not provide a growth advantage of S. Typhimurium in C57/BL6J
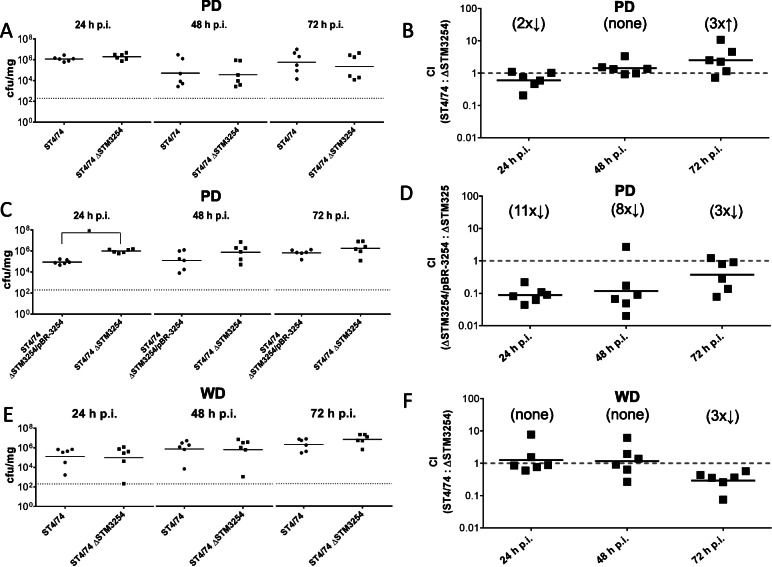
We hypothesized that the ability to metabolize galactitol and/or tagatose enhances the ability of S. Typhimurium strain ST4/74 to compete with gut microbiota and to persist in the intestinal lumen following oral transmission. To test this, female C57/BL6J mice were co-infected with a 1:1 ratio of ST4/74 and an isogenic mutant ST4/74 ΔSTM3254, or with a 1:1 ratio of ST4/74 ΔSTM3254 and ST4/74 ΔSTM3254/pBR-3254 (total of 5 × 107 CFU/mouse) that were differentially tagged with antibiotic resistances. Recombinant pBR322 retains its stability in S. Typhimurium in vivo [33]. Two groups were fed the PD, and one group was fed WD (n = 6 per group). Feces were collected daily for up to 3 days p.i., and the total number of strain per mg of feces and the competitive index (CI) was determined. In stool from PD-fed mice, about 106 CFU of S. Typhimurium were recovered after 24 h p.i. with the average number of ST4/74 ΔSTM3254 mutant bacteria being slightly higher than the wild type strain (Fig. 6a). At 48 h p.i., the CFU of both strains reached equal levels, and after 72 h numbers of ST4/74 surpassed the ST4/74 ΔSTM3254 mutant. This was also reflected by the calculated CI values, which increased over time (Fig. 6b). Surprisingly, the complementation strain ST4/74 ΔSTM3254/pBR-3254 was recovered in significantly (p < 0.0017) lesser numbers as compared to the ST4/74 ΔSTM3254 mutant at 24 h p.i. (Fig. 6c). This discrepancy in the CFU decreased from an 11-fold to a 3-fold difference over time as indicated by the increasing CI values (Fig. 6d). Looking at stool from WD-fed mice, the average CFU of ST4/74 ΔSTM3254 and the wild type strain were equal at 24 h and 48 h p.i., (Fig. 6e) as indicated by CI values of 1 (Fig. 6f). At 72 h p.i., the ST4/74 ΔSTM3254 mutant was recovered in 3-fold higher fecal numbers than ST4/74. The CFU for both strains steadily increased over time, in contrast to mice fed PD. Taken together, the absence of the genes encoding the galactitol utilization pathway did not cause a significant phenotype in the mouse gastrointestinal tract under plant-derived feed, although the gat operon is specifically upregulated in mice fed this diet. This finding suggests that other metabolic pathways compensate for the metabolic deficiency of the mutant strain.
Fig. 6.
Deletion of STM3254 leads to reduced infection numbers in C57/BL6J mice over time. Two groups of female C57/BL6J mice (n = 6 each group) were fed the PD or the WD and orally infected with a 1:1 ratio of ST4/74 and ST4/74 ΔSTM3254::KanR, and on group (n = 6) was fed the PD and infected with a 1:1 ration of ST4/74 ΔSTM3254::KanR and ST4/74 ΔSTM3254::KanR /pBR-3254. The total inoculum was 5 × 107 CFU/mouse. Stool samples were taken every 24 h up to 3 days (a, c, e). The CFU per mg feces of each strain are shown over time. The numbers of ST4/74 (circles) ST4/74 ΔSTM3254::KanR (squares) (or ST4/74 ΔSTM3254::KanR (circles) and ST4/74 ΔSTM3254::KanR /pBR-3254 (squares) recovered in each mouse after co-infection are depicted. Solid horizontal lines indicate mean values while dashed lines lines represent the detection limit for each sample. b, d, f) CIs depict the ratio of ST4/74 and ST4/74 ΔSTM3254::KanR, or ST4/74 ΔSTM3254::KanR and ST4/74 ΔSTM3254::KanR /pBR-3254). The geometric mean for each group was compared to the theoretical value of 1.0 and the fold-change difference is indicated in parentheses. Significant differences (p value ≤0.05) are indicated by asterisks
Discussion
Diet modifications, antibiotic therapy or chronic gut diseases can lead to a substantial change in microbial gut communities. This might enable non-native enteric pathogens to overcome barriers created by the communities of commensals and thus successfully persist and colonize the gut. Distinct differences in dietary formula have often been associated with alterations in the composition of gut microbial populations [34], particularly regarding WD versus Mediterranean, vegan or PD [35–39]. Here, we investigated the effect of two diets containing either monosaccharides as well as protein and fatty acids of animal origins (WD), or polysaccharides and plant-based proteins and fatty acids (PD), on the transcriptional response of S. Typhimurium, taking into account changes affecting the gut microbiota of mice.
Fecal microbiota analysis of feces revealed substantial differences of the two dietary groups at the level of major taxonomic groups. PD fed mice were characterized by high relative abundances of the family Muribaculaceae (43.01%), many members of which can degrade a variety of complex carbohydrates [40], and also of Prevotellaceae spp. able to hydrolyse hemicellulose. Another major group of commensal bacteria involved in fiber degradation, the Lachnospiraceae, was also more abundant in PD fed mice (25.61%) than in those exposed to WD (13.10%). Although Firmicutes are often associated with a high intake of animal-associated foods [36], their role in polysaccharide breakdown has been underestimated [41], an assumption that might explain their prevalence in mice fed PD. Vice versa, a higher proportion of Rikenellaceae which was observed to thrive on high-fat diets [17], was detected in the microbiota of mice fed WD. Taken together, the gut microbiota profiles were dependent on the composition of the two diets. We particularly hypothesize that the microbiota of PD fed mice provided plant-derived substrates that are accessible for S. Typhimurium and feed its metabolism during infection. Subsequent treatment with streptomycin lowered the colonization resistance due to partial depletion of commensal microbes, particularly of facultative anaerobes [14, 42], and allowed an expansion of S. Typhimurium for the benefit of the in vivo transcriptome. Although this experimental step possibly perturbed the digestion of the diet, the post-streptomycin analysis of the microbiota demonstrated that families involved in the degradation of carbohydrates were still present in the mouse gut (Additional file 5).
The main question in our study was whether or not the enteropathogen S. Typhimurium responds specifically to distinct diets. We separated the S. Typhimurium cells 24 h after infection from the commensal bacteria using immunomagnetic beads and analyzed their transcriptome. To exclude that the IMS procedure, which took approximately 30 min, impacts the results, the gut content was transferred into RNA later, and all IMS steps were performed at 4 °C if possible.
We hypothesized that at this early stage of infection by an invasion-negative strain, at least a part of the transcriptional response is associated with metabolic properties reflecting the pathogen’s efforts to adapt to the substrate availability in the mouse gut. Strikingly, the majority of the Salmonella genes upregulated in mice fed PD belongs to the categories transport and metabolism of carbohydrates and amino acids. According to their upregulation, plant-derived substrates like glycolate, fructose, sorbitol, tagatose, galactitol, rhamnose, and melibiose are used by the enteropathogen to fulfill its metabolic needs. Thus, the upregulation of the respective utilization pathways in mice fed PD, but not in rodents fed WD, points to a metabolic adaptation of S. Typhimurium to the plant-rich diet and the substrates derived thereof by the digestive activity of the host and its commensal microbiota. For example, melibiose is a disaccharide composed of glucose and galactose and, together with fructose, a cleavage product of another plant sugar, raffinose.
The utilization of mucosal carbohydrates by bacterial pathogens, especially after antibiotic treatment, has been described for Clostridium difficile, S. enterica, Listeria monocytogenes, and E. coli [13, 43–46]. Although we identified nanA involved in sialic acid catabolism, the large gene cluster responsible for the degradation of fucose [4] was missing in the list of differentially regulated Salmonella genes in our study. Possible reasons are the short infection time of one day and a depletion of commensal bacteria such as Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, which are specialized to cleave fucose from glycans of the gut mucus.
While S. Typhimurium ST4/74 specifically responded to PD by the upregulation of genes involved in carbohydrate utilization, no specific metabolic adaptation was observed to the high concentration of fat in WD fed mice. This suggests that sucrose (33.44% in the WD and 5% in the PD) is a readily usable energy source for S. Typhimurium that is preferred over metabolizable proteins or fat. In contrast to most of the above-mentioned plant-derived carbohydrates, the relevance of tagatose and galactitol for in vivo replication of S. Typhimurium had not been investigated so far. Galactitol is a reduction product of galactose, a common sugar in the gut lumen. Tagatose is obtainable by microbial oxidation of galactitol and a degradation product of galactosamine and N-acetylgalactosamine, both present in the intestinal mucin. Therefore, both substrates are considered to be part of the hostʼs galactose metabolism [47–49]. The gat operon was demonstrated by gene deletions to link galactitol degradation [29] with tagatose utilization (this study). Interestingly, transposon-directed knockout of three genes of the gat operon resulted in an attenuated colonization of chicken, calves and pigs by S. Typhimurium strain ST4/74, supporting the role of galactitol and tagatose utilization in vivo [50]. Furthermore, tagatose plays an anti-diabetic role by controlling the blood glucose level. Therefore, the upregulation of the genes responsible for tagatose utilization particularly in mice fed PD points to a microbiota composition in the animals of the respective dietary group that may help to decrease the risk of diabetes [49].
The total CFU of S. Typhimurium in the two dietary groups seventy-two hours p.i. did not differ significantly from each other, but an approximately 10-fold increase of CFU from 24 h to 72 h was observed in the group fed WD. An even 102–105 higher stool pathogen load reported recently for mice reared with a high-fat WD in comparison to the control group [51]. The competitive infection experiments performed in our study using mutants with a deletion of gene STM3254 and its complementation did not support the relevance of galactitol utilization for S. Typhimurium in vivo, although the gat operon was specifically upregulated in mice fed the PD. However, we had chosen to use a setting without streptomycin treatment, in which the microbiota is not reduced and confers colonization resistance. It can therefore not be excluded that galactitol degradation by S. Typhimurium provides a significant growth and colonization advantage in other infection models, or that other carbohydrates are utilized by S. Typhimurium to compensate for this deficiency.
The colitis model based on streptomycin treatment [25] was applied here to overcome colonization resistance conferred by the C57/BL6J microbiota to obtain high bacteria numbers for the RNA sequencing. Given that this treatment significantly alters the microbial composition as demonstrated here, we cannot exclude that the microbiota dysbiosis at least partially affected the diet-dependent transcriptional response of S. Typhimurium assessed here. It is also known that gastrointestinal colonization evokes a significant gastrointestinal inflammation starting eight hours post infection [28], resulting in gut oxygenation. To avoid or reduce inflammation that might distort the transcriptional response of S. Typhimurium to the diets, we used an invA deletion mutant with reduced capacity to invade epithelial cells, thus not resulting in tissue inflammation [20]. Although gut inflammation cannot be excluded to play a role in our experimental setting, we hypothesize here that the specific transcriptome of strain ST4/74 is indeed mainly triggered by the distinct metabolic properties of a diet-driven microbiota, which, however, exhibited a reduced species richness due to streptomycin treatment.
Conclusion
During infection, salmonellae encounter the colonization resistance of the gut that is, among others, based on the limitation of nutrients due to metabolic niche occupation by the commensal microbiota. S. enterica have acquired specific metabolic adaptations that help them to overcome this hurdle. However, the influence of the diet and the gut microbiota on the metabolic behaviour of this pathogen is largely unknown. This study therefore investigated the interaction between diet, gut microbiota composition, and the transcriptional response of Salmonella enterica during mice infection. To our best knowledge, this is the first study that describes the in vivo transcriptome of salmonellae separated from the gut microbiota. We show that a plant-based diet, in concert with the microbiota composition, specifically provokes the activation of metabolic pathways of Salmonella involved in the utilization of substrates that are derived from fruits and plants. This confirms the assumption that S. Typhimurium possesses a robust metabolism able to adapt to diverse metabolic niches and conditions, and that substrates beside galactitol are used by the pathogen in the gut lumen [52]. To conclude, the findings described here go a step forward in deciphering the metabolic adaptation of an enteropathogen to the specific nutrient conditions shaped by the complex interaction between diet and microbiota.
Methods
Growth of bacterial strains
The strains and plasmids used in this study are listed in Table 2. S. Typhimurium strain 4/74 (ST4/74) was grown in lysogenic broth (LB: 10 g/L tryptone, 5 g/L yeast extract, 5 g/L NaCl) or in minimal medium (MM) consisting of M9 medium supplemented with 2 mM MgSO4, 0.1 mM CaCl2 and 55.5 mM (1% w/v) tagatose. If appropriate, the media were supplemented with the following antibiotics: kanamycin, ampicillin (50 μg/ml each), nalidixic acid (20 µg/ml), or tetracycline (12 µg/ml). For solid media, 1.5% agar (w/v) was added. For all growth experiments, bacterial strains were grown in LB medium overnight at 37 °C and inoculated 1:100 in the desired liquid growth medium. Growth curves were obtained from bacterial cultures incubated at 37 °C without agitation in 15 ml falcon tubes with 10 ml medium. Colony-forming units (CFU) per ml were counted by plate streaking.
Standard molecular techniques
DNA manipulations and isolation of chromosomal and plasmid DNA were performed according to standard protocols [53], and following the manufacturersʼ instructions. GeneRuler™ DNA Ladder Mix (Fermentas, St. Leon-Rot, Germany) was used as a marker for DNA analysis. Plasmid DNA was transformed via electroporation using a Bio-Rad Gene pulser II as recommended by the manufacturer and as described previously [54]. Polymerase chain reactions (PCRs) were carried out with Taq polymerase (Fermentas). As template for PCR, chromosomal DNA, plasmid DNA, or an aliquot of a single colony resuspended in 100 μl H2O was used. Oligonucleotides used in this study are listed in Additional file 7. Genes invA, STM3254 and gatR-HTH were deleted using the λ-Red recombinase [32]. Briefly, PCR products containing the kanamycin resistance cassette of plasmid pKD4 and the flanking FRT sites were generated using primers of 70 nucleotides in length that included 20 nucleotides priming sequences for pKD4 as template DNA. The fragments were transformed into ST4/74 cells harboring plasmid pKD46, and the allelic replacement of the target genes was controlled by PCR. A nonpolar deletion mutant was obtained by transformation with pCP20 and validated by PCR analysis and DNA sequencing.
Mouse infection assays
Female C57/BL6J mice at the age of 6–10 weeks obtained from in-house breeding at the Kleintierforschungszentrum Weihenstephan (Freising, Germany) were transferred and maintained in a specific-pathogen-free facility with a 14-h light and 10-h dark cycle. After one week of acclimatization, mice (n = 12 per group) were fed either a Westernized diet or a plant-based diet (both from ssniff, Soest, Germany) (Table 3). After two weeks, mice were treated with 20 mg streptomycin by gavage 24 h before the infection. Mice were orally infected by gavage with 5–8 × 107 ST4/74 ΔinvA.
Table 3.
Diet composition
| TD88137 – Westernized diet (WD) | S5745-E750 – plant-based diet (PD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Casein | % | 19.5 | – |
| Cholesterol | % | 0.21 | – |
| Isolate of soy protein | % | – | 5 |
| Concentrate of soy protein | % | – | 20 |
| Sucrose | % | 33.44 | 5 |
| Maize starch | % | – | 41.79 |
| Cellulose | % | 5 | 7 |
| Lignocellulose | % | – | 3 |
| Fructooligosaccharide /Chicorée inulin | % | – | 2 |
| Appel marc | % | – | 4 |
| DL-Methionine | % | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| Mix of mineral and trace elements | % | 4.3 | 3.5 |
| Mix of vitamines | % | 1 | 1 |
| Calcium | % | 0.76 | – |
| Calciumcarbonate | % | – | 0.3 |
| Cholin Cl | % | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Ascorbic acid | % | 0.1 | – |
| Butylhydroxytoluol | % | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Butter fat | % | 21 | – |
| Soybean oil | % | – | 7 |
| Approximate composition of nutrients | |||
| Protein | % | 17.5 | 17.5 |
| Fat | % | 21.2 | 7.3 |
| Fibres | % | 5 | 12.7 |
| Mineral elements | % | 4.5 | 4.9 |
| Starch | % | 14.6 | 40.8 |
| Sugar | % | 33.2 | 7.2 |
| Calcium | % | 0.76 | 0.73 |
| Phosphor | % | 0.46 | 0.51 |
| Sodium | % | 0.37 | 0.25 |
| Magnesium | % | 0.1 | – |
| Potassium | % | 0.54 | – |
| Fatty acids | |||
| C 4:0 | % | 0.8 | – |
| C 6:0 | % | 0.53 | – |
| C 8:0 | % | 0.29 | – |
| C 10:0 | % | 0.63 | – |
| C 12:0 | % | 0.72 | – |
| C 14:0 | % | 2.21 | – |
| C 16:0 | % | 5.74 | 0.84 |
| C 17:0 | % | 0.13 | 0.01 |
| C 18:0 | % | 2.04 | 0.25 |
| C 20:0 | % | 0.04 | 0.03 |
| C 16:1 | % | 0.38 | 0.01 |
| C 18:1 | % | 4.63 | 1.8 |
| C 18:2 | % | 0.38 | 3.8 |
| C 18:3 | % | 0.11 | 0.42 |
| C 20:1 | % | 0.02 | – |
| Metabolizable energy | MJ/kg | 19.2 | 14.6 |
| Protein | kJ% | 15 | 20 |
| Fat | kJ% | 42 | 19 |
| Carbohydrates | kJ% | 43 | 61 |
To perform competitive infections, overnight cultures of ST4/74, ST4/74 ΔSTM3254::KanR and ST4/74 ΔSTM3254::KanR/pBR-3254 were adjusted to 5 × 108 CFU/ml, and 1:1 mixtures of two strains (ST4/74 and ST4/74 ΔSTM3254::KanR, or ST4/74 ΔSTM3254::KanR and ST4/74 ΔSTM3254::KanR/pBR-3254) with a total of 5 × 107 CFU/mouse were used for oral infection of female C57/BL6J mice by gavage. Two group of mice were fed the PD, and one group the WD (n = 6 per group). Sample collection and handling was performed as follows: One to three stool pellets were collected every 24 h, weighed and suspended in sterile PBS. Samples were homogenized in a FastPrep-24 benchtop homogenizer (MP Biomedicals, Eschwege, Germany) using 1 mm (Ø) silica beads (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). Serial dilutions were plated on Salmonella-Shigella-agar (Roth, Karlsruhe, Germany) containing the appropriate antibiotics and incubated for 24–48 h.
Isolation of S. Typhimurium cells from the gut of infected mice
Animals were sacrified 24 h after infection. Cecum and ileum content were transferred into Eppendorf tubes containing 1 ml RNAlater (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Langenselbold, Germany) and 0.1 mm (Ø) Zirkonia/Silica beads (BioSpec Products, Bartlesville, OK, USA) prior to storage at − 80 °C. After thawing, 100 μl TritonX-100 were added, and the gut preparations were homogenized with a ribolyser (MP Biomedicals, Eschwege, Germany). The gut content was passed through three filters with a pore size of 100 μm, 70 μm and 30 μm (Miltenyi Biotech GmbH, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany), respectively, and the bacteria were pelleted by centrifugation at 6500×g for 5 min. The pellet was resuspended in 1 ml buffer (1 × PBS, 0.5% biotin-free BSA) containing 10% (v/v) RNAlater. Ten μl of Salmonella-specific antibodies (BacTrace, KPL Inc., Maryland, USA) diluted 1:10 were added, and the mixture was incubated with shaking at 4 °C for 10 min. The sediment, obtained by centrifugation at 9600×g for 2 min, was washed with cold separation buffer (1 × PBS, 0.5% biotin-free BSA, 2 mM EDTA pH 7.4) containing 10% RNAlater, centrifuged, resuspended in the same buffer and incubated with 10 μl of streptavidin-coupled magnetic beads for 15 min. The washing and centrifugation steps from above were repeated, and the sediment was resuspended in 500 μl separation buffer containing 10% RNAlater. S. Typhimurium cells were separated using a MACS cell separation system with a LS coloumn (Miltenyi Biotech, Aubum, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
RNA isolation
RNA was extracted and purified from 1 ml of a Salmonella suspension isolated from cecum using a NucleoSpin® RNA kit (Macherey-Nagel GmbH & Co. KG, Düren, Deutschland) according to the manufacturerʼs instruction. Briefly, the bacterial pellet was solved in 100 μl TE buffer with 1 mg/ml lysozyme and incubated for 10 min at 37 °C. For further cell lysis, 350 μl RA1 buffer and 3.5 μl β-mercaptoethanol were added and vortexed vigorously. The lysate was filtrated for 1 min at 11,000 x g, and 350 μl of 70% ethanol were added. The RNA was bound to a column via centrifugation for 30 s at 11,000 x g, and 350 μl MDB was added to desalt the silica membrane, followed by centrifugation for 1 min at 11,000 x g. 95 μl of a reaction mixture containing 10 μl rDNase and 90 μl reaction buffer were applied onto the silica membrane of the column and incubated at room temperature for 15 min. The membrane was successively washed with 200 μl buffer RAW2 (30 s at 11,000 g), and with 600 μl and 250 μl buffer RA3 (30 s at 11,000 x g and 2 min at 11,000 x g, respectively). Finally, the RNA was eluted in 60 μl of RNase-free H2O. RNA quality was assessed using a 2100 Bioanalyser (Agilent, Waldbronn, Germany).
Transcriptome analysis
Whole-transcriptome RNA library preparation with isolated RNA was performed as described [55]. Briefly, ribosomal RNAs were depleted using the RiboMinus Transcriptome Isolation Kit (Invitrogen, Darmstadt, Germany), and RNA was fragmented via sonication using a Covaris sonicator. After dephosphorylation and rephosphorylation, the TruSeq Small RNA Sample Kit (Illumina, Munich, Germany) was used, and the resulting cDNAs were size-selected using polyamide-gel electrophoresis. Libraries were then diluted and sequenced on a MiSeq sequencer (Illumina, Munich, Germany) using a MiSeq Reagent Kit v2 (50 cycles), resulting in 50 bp single-end reads. Illumina FASTQ files were mapped to the reference genome of S. Typhimurium ST4/74 (GenBank: CP002487.1) using Bowtie2 for Illumina implemented in Galaxy [56, 57]. Artemis was used to visualize and calculate the number of reads mapping on each gene [58, 59]. Gene counts of each library were normalized to the smallest library in the comparison and reads per kilobase per million mapped reads (RPKM) values were calculated. Fold changes between the different conditions were calculated.
Sequencing of 16S rRNA gene amplicons
Mice feces were collected in 600 μl DNA stabilization solution (STRATEC biomedical) and frozen at − 20 °C. After thawing on ice, 400 μl phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1; Sigma-Aldrich) and about 500 mg 0.1 mm glass beads (Roth) were added. Microbial cells were lyzed using a FastPrep-24 (MP Biomedicals) fitted with a 24 × 2 ml cooling adaptor for 3 × 30 s at maximum speed. After a short heat treatment (95 °C, 5 min) and centrifugation (15,000×g, 5 min, 4 °C), supernatants were treated with RNase A (0.1 μg/μl, 30 min, 37 °C). Complete DNA was purified using gDNA columns (Macherey-Nagel) following the manufacturer’s instructions. DNA was controlled using a NanoDrop photometer and a Qubit fluorometer (Thermo Scientific). The V3-V4 region of 16S rRNA genes were amplified in a two-step PCR following [60], starting with 12 ng of metagenomic DNA. The primers 341F and 785R [61] fitted with overhangs were used in the first PCR for 15 cycles. The second PCR was conducted with barcoded primers for additional 15 cycles. Amplicons were purified using AMPure XP (Beckmann) and pooled. The pool was amended with 15% PhiX standard and sequenced (paired end, 2 × 300 cycles) using a MiSeq system (Illumina, Inc.) following the manufacturer’s instructions.
Sequencing data analysis
To analyse the 16S rRNA gene sequencing data, raw reads were processed with the Integrated Microbial Next Generation Sequencing (IMNGS) pipeline [62] based on UPARSE [63]. Sequences were demultiplexed, trimmed to the first base with a quality score < 3, and then paired. Assemblies with a size < 250 and > 600 nucleotides or an expected error > 3 were excluded. Remaining reads were trimmed by ten nucleotides at each end to prevent the analysis of regions with distorted base composition. The presence of chimeras was tested with UCHIME [64]. Operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were clustered at 97% sequence identity, and only those with a relative abundance ≥0.5% in at least one sample were kept. Taxonomies were assigned at 80% confidence level by taking into account results from both the RDP classifier [65] and SILVA using SINA (v1.2.11) [66]. All further analyses were performed in the R programming environment using Rhea [67], following scripts and instructions available online (https://lagkouvardos.github.io/Rhea/). A PERMANOVA test (vegan::adonis) is performed in each case to determine if the separation of sample groups is significant, as a whole and in pairs. Counts are, by standard, normalized via simple division to their sample size and then multiplication by the size of the smaller sample, thus avoiding to introduce random variance or loss of data. The filtered and normalized OTU table used as basis for all analyses is provided in the Supplemental Material (Additional file 3). β-diversity was computed based on generalized UniFrac distances [68]. α-diversity was assessed on the basis of species richness and Shannon effective diversity [69] as explained in detail in Rhea. P values were corrected for multiple comparisons according to the Benjamini-Hochberg method. Only taxa with a prevalence ≥30% (proportion of samples positive for the given taxa) in one given group were considered for statistical testing.
To analyse the transcriptome data, the fastq data files were uploaded on the Galaxy server (https://usegalaxy.org/) to map the sequencves via Bowtie2 on the genome of S. Typhimurium ST4/74 (accession numbers CP002487-CP002490). Read sorting by coordinates was done via the picard software (http://sourceforge.net/projects/picard/files/picard-tools). Statistical analysis of the data was performed within R.
Statistics and data evaluation
Statistical analyses for all experiments were performed using the Student’s t-Test with Welch’s correction, which is less influenced by unequal sample sizes, in Prism6 (GraphPad, La Jolla, CA, USA). P values ≤0.05 were considered as mentioned in the text.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1 Fig. S1. Overview of relative abundances of major bacterial genera shown as stacked bar plots. Cumulative abundances were calculated from all single OTUs classified within one genus as per the best possible taxonomy using both the RDP and Silva. N of WD fed, untreated mice = 12, n of WD fed, streptomycin-treated/infected mice = 11, n of PD fed, untreated/infected mice = 11, n of PD fed, streptomycin-treated mice = 8.
Additional file 2 Table S1. Significant influences of two diets on the microbiota composition.
Additional file 4 Table S3. OTU sequences.
Additional file 5 Table S4. Significant influences of streptomycin on the microbiota composition.
Additional file 6 Table S5. Significant influences of the S. Typhimurium infection on the microbiota composition.
Additional file 7 Table S6. Oligonucleotides used in this study.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dietmar Zehn for helpful discussion. Angela Felsl, Patrick Schiwek and Judit Desztics are acknowledged for excellent technical assistance. We thank Caroline Ziegler from the Core Facility Microbiome for outstanding technical help with sequencing.
Abbreviations
- PD
Plant-based diet
- CFU
Colony forming units
- WD
Westernized diet
- NMDS
Non-metric multidimensional scatter
- OTUs
Operational taxonomic units
Authors’ contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: N.N. and T.M.F. Performed the experiments: N.N. and J.S. Analysed the data: N.N., S.W., J.S., K.N., T.C., and T.M.F. Wrote the manuscript: S.W., K.N., T.C., and T.M.F. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from the ZIEL – Institute for Food & Health within the PhD graduate school “Microbe-host interactions”. Thomas Clavel reveived funding from the German Research Foundation (DFG) as part of the Collaborative Research Center 1382 “Gut-liver axis”.
Availability of data and materials
Raw sequence data are available at the European Nucleotide Archive (Microbiota data: SRA accession PRJNA560458, BioSample accessions SAMN12586589, SAMN12586590, SAMN12586591, SAMN12586592, SRR9983045; transcriptomic data: SRA accession: PRJNA560458, BioSample accessions SAMN12593626, SAMN12593627, SAMN12593628, SAMN12593629, SAMN12593630, SAMN12593631). All other data generated or analysed during the current study are included in the manuscript and its supplementary files.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All procedures were performed in accordance with international guidelines and regulations for the use of animals in research. The study protocol was approved by the Regierung von Oberbayern, München, Germany (approval number 55.2–1-54-2532-214-2014).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Tsolis RM, Adams LG, Ficht TA, Baumler AJ. Contribution of Salmonella typhimurium virulence factors to diarrheal disease in calves. Infect Immun. 1999;67:4879–4885. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.9.4879-4885.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Agbaje M, Begum RH, Oyekunle MA, Ojo OE, Adenubi OT. Evolution of Salmonella nomenclature: a critical note. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 2011;56:497–503. doi: 10.1007/s12223-011-0075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Stecher B, Hardt WD. Mechanisms controlling pathogen colonization of the gut. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2011;14:82–91. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2010.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Staib L, Fuchs TM. From food to cell: nutrient exploitation strategies of enteropathogens. Microbiol. 2014;160:1020–1039. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.078105-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.El Kaoutari A, Armougom F, Gordon JI, Raoult D, Henrissat B. The abundance and variety of carbohydrate-active enzymes in the human gut microbiota. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013;11:497–504. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hooper LV, Midtvedt T, Gordon JI. How host-microbial interactions shape the nutrient environment of the mammalian intestine. Annu Rev Nutr. 2002;22:283–307. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.22.011602.092259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Freter R, Brickner H, Botney M, Cleven D, Aranki A. Mechanisms that control bacterial populations in continuous-flow culture models of mouse large intestinal flora. Infect Immun. 1983;39:676–685. doi: 10.1128/IAI.39.2.676-685.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Winter SE, Thiennimitr P, Winter MG, Butler BP, Huseby DL, Crawford RW, Russell JM, Bevins CL, Adams LG, Tsolis RM, et al. Gut inflammation provides a respiratory electron acceptor for Salmonella. Nature. 2010;467:426–429. doi: 10.1038/nature09415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Thiennimitr P, Winter SE, Winter MG, Xavier MN, Tolstikov V, Huseby DL, Sterzenbach T, Tsolis RM, Roth JR, Bäumler AJ. Intestinal inflammation allows Salmonella to use ethanolamine to compete with the microbiota. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:17480–17485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1107857108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Srikumar S, Fuchs TM. Ethanolamine utilization contributes to proliferation of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in food and in nematodes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011;77:281–290. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01403-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kröger C, Fuchs TM. Characterization of the myo-inositol utilization island of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 2009;191:545–554. doi: 10.1128/JB.01253-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fuchs TM, Eisenreich W, Heesemann J, Goebel W. Metabolic adaptation of human pathogenic and related nonpathogenic bacteria to extra- and intracellular habitats. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2012;36:435–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Faber F, Thiennimitr P, Spiga L, Byndloss MX, Litvak Y, Lawhon S, Andrews-Polymenis HL, Winter SE, Baumler AJ. Respiration of microbiota-derived 1,2-propanediol drives Salmonella expansion during colitis. PLoS Pathog. 2017;13:e1006129. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Que JU, Hentges DJ. Effect of streptomycin administration on colonization resistance to Salmonella typhimurium in mice. Infect Immun. 1985;48:169–174. doi: 10.1128/IAI.48.1.169-174.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI. Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature. 2006;444:1022–1023. doi: 10.1038/4441022a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Duncan SH, Belenguer A, Holtrop G, Johnstone AM, Flint HJ, Lobley GE. Reduced dietary intake of carbohydrates by obese subjects results in decreased concentrations of butyrate and butyrate-producing bacteria in feces. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007;73:1073–1078. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02340-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Daniel H, Gholami AM, Berry D, Desmarchelier C, Hahne H, Loh G, Mondot S, Lepage P, Rothballer M, Walker A, et al. High-fat diet alters gut microbiota physiology in mice. ISME J. 2014;8:295–308. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2013.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sonnenburg ED, Smits SA, Tikhonov M, Higginbottom SK, Wingreen NS, Sonnenburg JL. Diet-induced extinctions in the gut microbiota compound over generations. Nature. 2016;529:212–215. doi: 10.1038/nature16504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Galan JE, Ginocchio C, Costeas P. Molecular and functional characterization of the Salmonella invasion gene invA: homology of InvA to members of a new protein family. J Bacteriol. 1992;174:4338–4349. doi: 10.1128/JB.174.13.4338-4349.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Everest P, Ketley J, Hardy S, Douce G, Khan S, Shea J, Holden D, Maskell D, Dougan G. Evaluation of Salmonella typhimurium mutants in a model of experimental gastroenteritis. Infect Immun. 1999;67:2815–2821. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.6.2815-2821.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Forbester JL, Goulding D, Vallier L, Hannan N, Hale C, Pickard D, Mukhopadhyay S, Dougan G. Interaction of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium with intestinal Organoids derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Infect Immun. 2015;83:2926–2934. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00161-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Galan JE, Curtiss R., 3rd Distribution of the invA, −B, −C, and -D genes of Salmonella typhimurium among other Salmonella serovars: invA mutants of Salmonella typhi are deficient for entry into mammalian cells. Infect Immun. 1991;59:2901–2908. doi: 10.1128/IAI.59.9.2901-2908.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hapfelmeier S, Stecher B, Barthel M, Kremer M, Muller AJ, Heikenwalder M, Stallmach T, Hensel M, Pfeffer K, Akira S, et al. The Salmonella pathogenicity island (SPI)-2 and SPI-1 type III secretion systems allow Salmonella serovar typhimurium to trigger colitis via MyD88-dependent and MyD88-independent mechanisms. J Immunol. 2005;174:1675–1685. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.3.1675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bohnhoff M, Miller CP, Martin WR. Resistance of the mouse's intestinal tract to experimental Salmonella infection. II. Factors responsible for its loss following streptomycin treatment. J Exp Med. 1964;120:817–828. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.5.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Barthel M, Hapfelmeier S, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Kremer M, Rohde M, Hogardt M, Pfeffer K, Russmann H, Hardt WD. Pretreatment of mice with streptomycin provides a Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium colitis model that allows analysis of both pathogen and host. Infect Immun. 2003;71:2839–2858. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.5.2839-2858.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dai D, Holder D, Raskin L, Xi C. Separation of the bacterial species, Escherichia coli, from mixed-species microbial communities for transcriptome analysis. BMC Microbiol. 2011;11:59. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kern T, Kutzner E, Eisenreich W, Fuchs TM. Pathogen-nematode interaction: nitrogen supply of Listeria monocytogenes during growth in Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ Microbiol Rep. 2016;8:20–29. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Stecher B, Macpherson AJ, Hapfelmeier S, Kremer M, Stallmach T, Hardt WD. Comparison of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium colitis in germfree mice and mice pretreated with streptomycin. Infect Immun. 2005;73:3228–3241. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.6.3228-3241.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Nolle N, Felsl A, Heermann R, Fuchs TM. Genetic characterization of the galactitol utilization pathway of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 2017;199:e00595-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 30.Richardson EJ, Limaye B, Inamdar H, Datta A, Manjari KS, Pullinger GD, Thomson NR, Joshi RR, Watson M, Stevens MP. Genome sequences of Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium, Choleraesuis, Dublin, and Gallinarum strains of well- defined virulence in food-producing animals. J Bacteriol. 2011;193:3162–3163. doi: 10.1128/JB.00394-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bolivar F, Rodriguez RL, Greene PJ, Betlach MC, Heyneker HL, Boyer HW, Crosa JH, Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2:95–113. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90000-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Datsenko KA, Wanner BL. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97:6640–6645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.120163297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Dunstan SJ, Simmons CP, Strugnell RA. In vitro and in vivo stability of recombinant plasmids in a vaccine strain of Salmonella enterica var. Typhimurium FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2003;37:111–119. doi: 10.1016/S0928-8244(03)00065-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Cotillard A, Kennedy SP, Kong LC, Prifti E, Pons N, Le Chatelier E, Almeida M, Quinquis B, Levenez F, Galleron N, et al. Dietary intervention impact on gut microbial gene richness. Nature. 2013;500:585–588. doi: 10.1038/nature12480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.De Filippo C, Cavalieri D, Di Paola M, Ramazzotti M, Poullet JB, Massart S, Collini S, Pieraccini G, Lionetti P. Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:14691–14696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1005963107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.De Filippis F, Pellegrini N, Vannini L, Jeffery IB, La Storia A, Laghi L, Serrazanetti DI, Di Cagno R, Ferrocino I, Lazzi C, et al. High-level adherence to a mediterranean diet beneficially impacts the gut microbiota and associated metabolome. Gut. 2016;65:1812–1821. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-309957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Albenberg LG, Wu GD. Diet and the intestinal microbiome: associations, functions, and implications for health and disease. Gastroenterol. 2014;146:1564–1572. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.01.058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Schnorr SL, Candela M, Rampelli S, Centanni M, Consolandi C, Basaglia G, Turroni S, Biagi E, Peano C, Severgnini M, et al. Gut microbiome of the Hadza hunter-gatherers. Nat Commun. 2014;5:3654. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wu GD, Chen J, Hoffmann C, Bittinger K, Chen YY, Keilbaugh SA, Bewtra M, Knights D, Walters WA, Knight R, et al. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science. 2011;334:105–108. doi: 10.1126/science.1208344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lagkouvardos I, Lesker TR, Hitch TCA, Galvez EJC, Smit N, Neuhaus K, Wang J, Baines JF, Abt B, Stecher B, et al. Sequence and cultivation study of Muribaculaceae reveals novel species, host preference, and functional potential of this yet undescribed family. Microbiome. 2019;7:28. doi: 10.1186/s40168-019-0637-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Flint HJ, Scott KP, Duncan SH, Louis P, Forano E. Microbial degradation of complex carbohydrates in the gut. Gut Microbes. 2012;3:289–306. doi: 10.4161/gmic.19897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Conway T, Krogfelt KA, Cohen PS. The life of commensal Escherichia coli in the mammalian intestine. EcoSal Plus. 2004;1. 10.1128/ecosalplus.8.3.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 43.Ng KM, Ferreyra JA, Higginbottom SK, Lynch JB, Kashyap PC, Gopinath S, Naidu N, Choudhury B, Weimer BC, Monack DM, et al. Microbiota-liberated host sugars facilitate post-antibiotic expansion of enteric pathogens. Nature. 2013;502:96–99. doi: 10.1038/nature12503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Staib L, Fuchs TM. Regulation of fucose and 1,2-propanediol utilization by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Front Microbiol. 2015;6:1116. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Schardt J, Jones G, Muller-Herbst S, Schauer K, D'Orazio SEF, Fuchs TM. Comparison between Listeria sensu stricto and Listeria sensu lato strains identifies novel determinants involved in infection. Sci Rep. 2017;7:17821. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17570-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Chang DE, Smalley DJ, Tucker DL, Leatham MP, Norris WE, Stevenson SJ, Anderson AB, Grissom JE, Laux DC, Cohen PS, et al. Carbon nutrition of Escherichia coli in the mouse intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:7427–7432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307888101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Barroso-Batista J, Sousa A, Lourenco M, Bergman ML, Sobral D, Demengeot J, Xavier KB, Gordo I. The first steps of adaptation of Escherichia coli to the gut are dominated by soft sweeps. PLoS Genet. 2014;10:e1004182. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Sousa A, Ramiro RS, Barroso-Batista J, Guleresi D, Lourenco M, Gordo I. Recurrent reverse evolution maintains polymorphism after strong bottlenecks in commensal gut bacteria. Mol Biol Evol. 2017;34:2879–2892. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msx221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zhu Y, Cong W, Shen L, Wei H, Wang Y, Wang L, Ruan K, Wu F, Feng Y. Fecal metabonomic study of a polysaccharide, MDG-1 from Ophiopogon japonicus on diabetic mice based on gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC TOF/MS) Mol BioSyst. 2014;10:304–312. doi: 10.1039/C3MB70392D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Chaudhuri RR, Morgan E, Peters SE, Pleasance SJ, Hudson DL, Davies HM, Wang J, van Diemen PM, Buckley AM, Bowen AJ, et al. Comprehensive assignment of roles for Salmonella typhimurium genes in intestinal colonization of food-producing animals. PLoS Genet. 2013;9:e1003456. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wotzka SY, Kreuzer M, Maier L, Arnoldini M, Nguyen BD, Brachmann AO, Berthold DL, Zund M, Hausmann A, Bakkeren E, et al. Escherichia coli limits Salmonella Typhimurium infections after diet shifts and fat-mediated microbiota perturbation in mice. Nature Microbiol. 2019;4:2164–2174. doi: 10.1038/s41564-019-0568-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Becker D, Selbach M, Rollenhagen C, Ballmaier M, Meyer TF, Mann M, Bumann D. Robust Salmonella metabolism limits possibilities for new antimicrobials. Nature. 2006;440:303–307. doi: 10.1038/nature04616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Sambrook J, Russell DW. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. 3. Cold Spring Harbor, N. Y: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Klumpp J, Fuchs TM. Identification of novel genes in genomic islands that contribute to Salmonella typhimurium replication in macrophages. Microbiol. 2007;153:1207–1220. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2006/004747-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Landstorfer R, Simon S, Schober S, Keim D, Scherer S, Neuhaus K. Comparison of strand-specific transcriptomes of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 EDL933 (EHEC) under eleven different environmental conditions including radish sprouts and cattle feces. BMC Genomics. 2014;15:353. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Blankenberg D, Von Kuster G, Coraor N, Ananda G, Lazarus R, Mangan M, Nekrutenko A, Taylor J. Galaxy: a web-based genome analysis tool for experimentalists. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2010;Chapter 19:Unit 19 10:11–21. doi: 10.1002/0471142727.mb1910s89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Goecks J, Nekrutenko A, Taylor J, Galaxy T. Galaxy: a comprehensive approach for supporting accessible, reproducible, and transparent computational research in the life sciences. Genome Biol. 2010;11:R86. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-8-r86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Rutherford K, Parkhill J, Crook J, Horsnell T, Rice P, Rajandream MA, Barrell B. Artemis: sequence visualization and annotation. Bioinformatics. 2000;16:944–945. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/16.10.944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Carver T, Bohme U, Otto TD, Parkhill J, Berriman M. BamView: viewing mapped read alignment data in the context of the reference sequence. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:676–677. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Berry D, Ben Mahfoudh K, Wagner M, Loy A. Barcoded primers used in multiplex amplicon pyrosequencing bias amplification. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011;77:7846–7849. doi: 10.1128/AEM.05220-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Klindworth A, Pruesse E, Schweer T, Peplies J, Quast C, Horn M, Glockner FO. Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:e1. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Lagkouvardos I, Joseph D, Kapfhammer M, Giritli S, Horn M, Haller D, Clavel T. IMNGS: a comprehensive open resource of processed 16S rRNA microbial profiles for ecology and diversity studies. Sci Rep. 2016;6:33721. doi: 10.1038/srep33721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Edgar RC. UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods. 2013;10:996–998. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics. 2011;27:2194–2200. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007;73:5261–5267. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00062-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Pruesse E, Peplies J, Glockner FO. SINA: accurate high-throughput multiple sequence alignment of ribosomal RNA genes. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:1823–1829. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Lagkouvardos I, Fischer S, Kumar N, Clavel T. Rhea: a transparent and modular R pipeline for microbial profiling based on 16S rRNA gene amplicons. PeerJ. 2017;5:e2836. doi: 10.7717/peerj.2836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Chen J, Bittinger K, Charlson ES, Hoffmann C, Lewis J, Wu GD, Collman RG, Bushman FD, Li H. Associating microbiome composition with environmental covariates using generalized UniFrac distances. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:2106–2113. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Jost L. Partitioning diversity into independent alpha and beta components. Ecology. 2007;88:2427–2439. doi: 10.1890/06-1736.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1 Fig. S1. Overview of relative abundances of major bacterial genera shown as stacked bar plots. Cumulative abundances were calculated from all single OTUs classified within one genus as per the best possible taxonomy using both the RDP and Silva. N of WD fed, untreated mice = 12, n of WD fed, streptomycin-treated/infected mice = 11, n of PD fed, untreated/infected mice = 11, n of PD fed, streptomycin-treated mice = 8.
Additional file 2 Table S1. Significant influences of two diets on the microbiota composition.
Additional file 4 Table S3. OTU sequences.
Additional file 5 Table S4. Significant influences of streptomycin on the microbiota composition.
Additional file 6 Table S5. Significant influences of the S. Typhimurium infection on the microbiota composition.
Additional file 7 Table S6. Oligonucleotides used in this study.
Data Availability Statement
Raw sequence data are available at the European Nucleotide Archive (Microbiota data: SRA accession PRJNA560458, BioSample accessions SAMN12586589, SAMN12586590, SAMN12586591, SAMN12586592, SRR9983045; transcriptomic data: SRA accession: PRJNA560458, BioSample accessions SAMN12593626, SAMN12593627, SAMN12593628, SAMN12593629, SAMN12593630, SAMN12593631). All other data generated or analysed during the current study are included in the manuscript and its supplementary files.