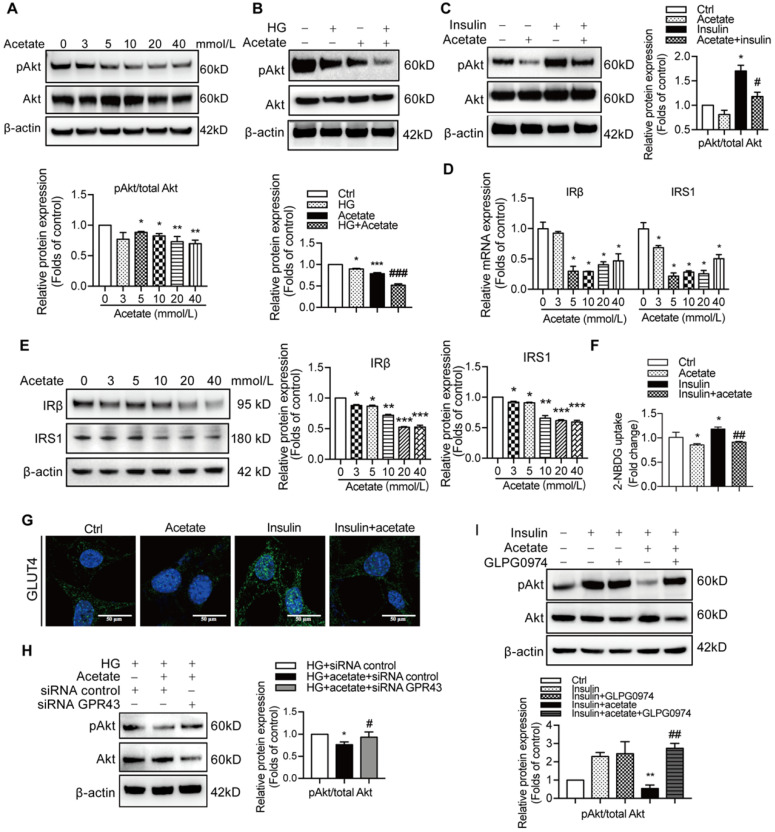
Figure 3.
The activation of GPR43 suppressed insulin signalling in podocytes. (A) Inhibitory effects of acetate (3, 5, 10, 20 and 40 mmol/L) on Akt phosphorylation in podocytes under the HG condition for 24h. (mean ± SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. Ctrl, n = 3). (B) Inhibitory effects of acetate (10 mmol/L) on Akt phosphorylation in podocytes (mean ± SD, *P < 0.05 vs. Ctrl, ***P < 0.001 vs. Ctrl, and ###P < 0.001 vs. HG, n = 3). (C) Inhibitory effects of acetate (10 mmol/L) on the suppression of insulin-induced Akt phosphorylation in podocytes (mean ± SD, *P < 0.05 vs. Ctrl, #P < 0.05 vs. Insulin, n = 3). (D) Inhibitory effects of acetate (3, 5, 10, 20 and 40 mmol/L) on the suppression of the IRβ and IRS1 mRNA expression in podocytes under the HG condition for 24h (mean ± SD,*P < 0.05 vs. Ctrl, n = 3). IRβ, insulin receptor β; IRS1, insulin receptor substrate 1. (E) Inhibitory effects of acetate (3, 5, 10, 20 and 40 mmol/L) on the suppression of IRβ and IRS1 protein expression in podocytes under the HG condition for 24h (mean ± SD,*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. Ctrl, n = 3). (F) Podocytes significantly increased 2-NBDG uptake in response to insulin, and acetate (10 mmol/L) selectively reduced 2-NBDG uptake (mean ± SD, *P < 0.05 vs. Ctrl, ##P < 0.01 vs. Insulin, n = 3). (G) Representative confocal immunofluorescent images illustrating the suppression of the insulin-induced translocation of GLUT4 protein to the cellular membrane of podocytes mediated by acetate (GLUT4, Green; DAPI, Blue; original magnification × 600, scale bars, 50 µm). (H) Effects of GPR43 knockdown by siRNA on restoration of insulin-induced Akt phosphorylation regulated by acetate (mean ± SD, *P < 0.05 vs. HG + siRNA control, #P < 0.05 vs. HG + acetate + siRNA control, n = 3). (I) Effects of GPR43 inhibition by GLPG0974 on restoration of insulin-induced Akt phosphorylation regulated by acetate (mean ± SD, **P < 0.01 vs. HG + siRNA control, ##P < 0.01 vs. HG + acetate + siRNA control, n = 3).