Abstract
The sinoatrial block is a new side effect of meglumine antimoniate. Prompt interruption of the drug results in the normalization of electrographic changes and prevents sudden cardiac arrest.
Keywords: cardiotoxicity, cutaneous leishmaniasis, meglumine antimoniate
The sinoatrial block is a new side effect of meglumine antimoniate. Prompt interruption of the drug results in the normalization of electrographic changes and prevents sudden cardiac arrest.
![]()
1. CASE HISTORY
Pentavalent antimonials are the treatment of choice for leishmaniasis. It may cause hazardous side effects such as cardiotoxicity. We report a case of sudden sinoatrial block (SAB) type 2 occurring in a young patient treated with systemic meglumine antimoniate (MAT) for cutaneous leishmaniasis, which regresses after stopping the drug.
A 23‐year‐old man was treated with intramuscularly MAT (20 mg/kg/d of antimony) for cutaneous leishmaniasis. Pretherapeutic investigations did not reveal any significant abnormalities (Figure 1). On the 10th day of treatment, electrocardiogram showed flattened T waves in V3‐V4‐V5‐V6, a corrected QT (QTc) prolongation, and a SAB type 2 (Figure 2). Four days after interrupting MAT, ECG returned to normal (Figure 3). Cutaneous lesions healed progressively.
FIGURE 1.
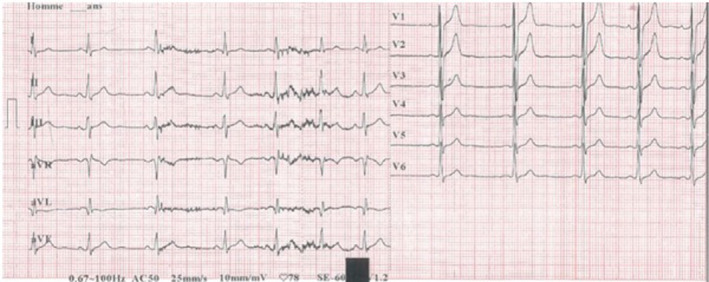
ECG before meglumine antimoniate: Positive T waves in V4‐V5‐V6, QTc = 410 ms, FC = 78 bpm
FIGURE 2.
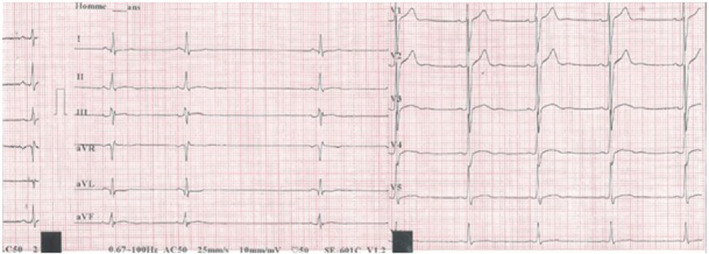
ECG after 10 days of meglumine antimoniate: Flattened T waves in V3‐V4‐V5‐V6, sinoauricular block type 2, QTc = 474 ms, FC = 50 bpm
FIGURE 3.
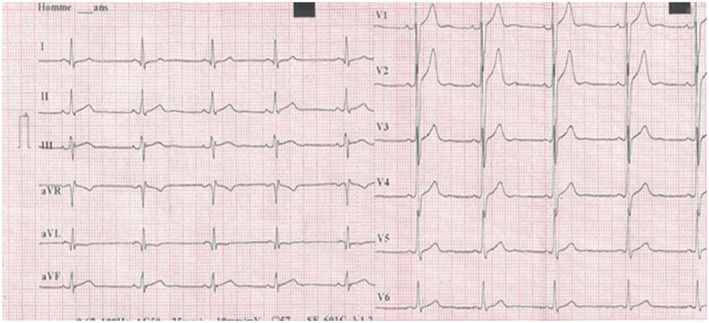
ECG 4 days after interrupting meglumine antimoniate: Positive T waves in V4‐V5‐V6, QTc = 428 ms, FC = 57 bpm
Cardiotoxicity is among the most serious adverse reactions of systemic administration of MAT. T wave changes are seen in about 50% of patients. 1 , 2 Serious ECG alterations as elevated or concave ST segment, prolonged QT interval, and ventricular fibrillation are uncommon, occurring in <10% of cases. 1 , 2 Pathophysiologically, it has been proved that antimonial compounds increase cardiac calcium currents leading to QT prolongation and other electrocardiographic changes. 3 In our patient, besides prolonged QTc interval and flattened T waves, ECG showed a SAB type 2. To our knowledge, SAB attributed to MAT cardiotoxicity had not been reported yet. ECG normalization is generally observed in a few days to 2 weeks after treatment interruption. 1 Thus, therapy should be discontinued if any sign of cardiotoxicity appears to prevent sudden cardiac arrest.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
No conflict of interest.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
DN: collected clinical data, managed the patient, helped in writing the manuscript, and did literature search. SY: managed the patient, conceptualized the article, and did final proofreading of the submission. AH: was consulted for the electrocardiogram changes and confirmed cardiac abnormalities. SH: helped in writing the manuscript and took clinical pictures. KJ: revised the manuscript. ND and MRD: revised and approved the final version of the manuscript. All authors have approved the final manuscript.
ETHICAL APPROVAL
Appropriate consent has been obtained, prior to submission, for the publication of images and data.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
None.
Daadaa N, Youssef S, Haggui A, et al. New onset of sinoatrial block in a young patient treated with systemic meglumine antimoniate. Clin Case Rep. 2021;9:1797–1798. 10.1002/ccr3.3768
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
REFERENCES
- 1. Matoussi N, Ameur HB, Amor SB, Fitouri Z, Becher SB. Toxicité cardiaque de l’antimoniate de meglumine (Glucantime) à propos d’une obsevation. Med Mal Infect. 2007;37:257‐259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Sundar S, Probhat R, Nutan KA, et al. A cluster of cases of severe cardio toxicity among Kala –Azar patients treated with a high osmolarity lot of sodium antimony gluconate. Am Trop Med Hyg. 1998;59:139‐143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Kuryshev YA, Wang L, Wible BA, Yuri A, Wan X, Ficker E. Antimony‐based anti leishmanial compounds prolong the cardiac action potential by an increase in cardia calcium currents. Mol Pharmacol. 2006;69:1216‐1225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.


