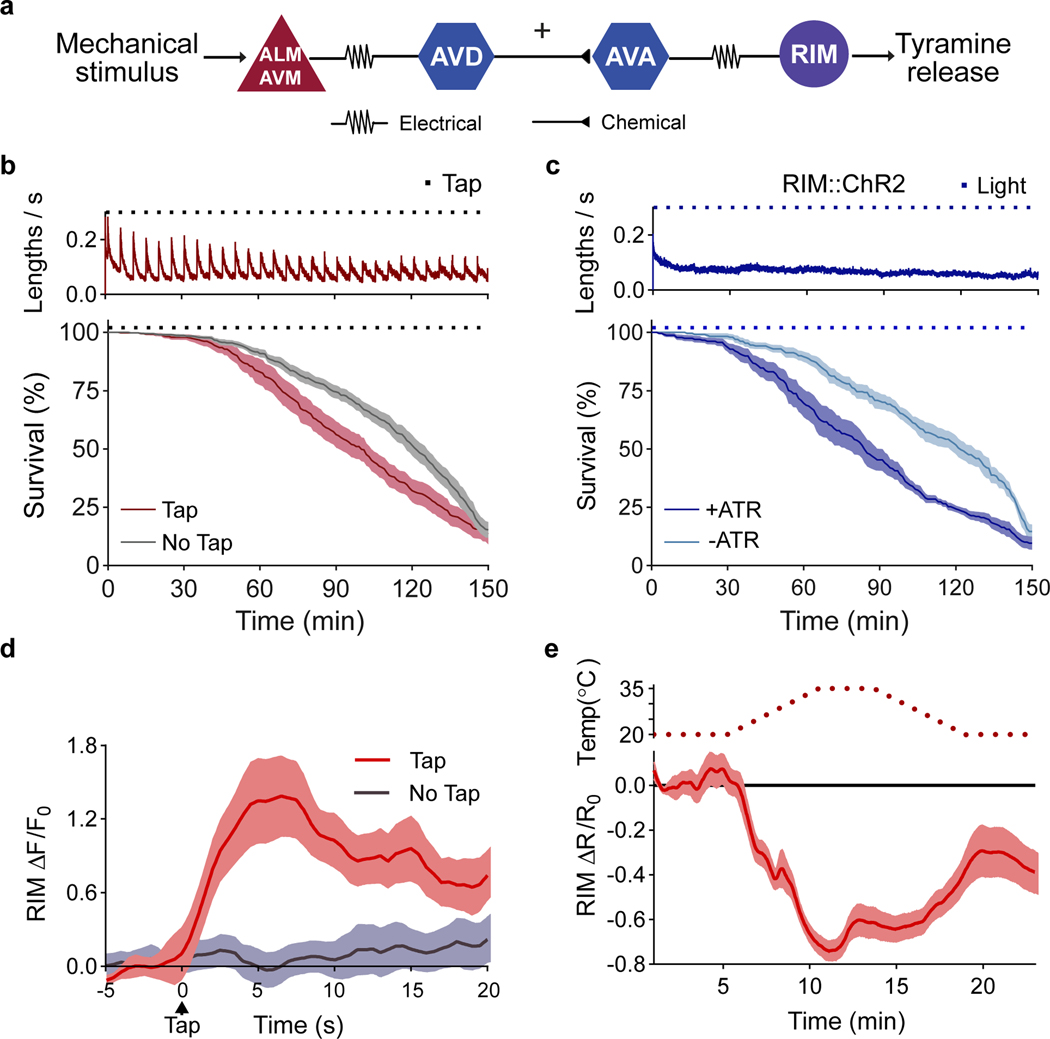
Figure 2. The RIM neuron exhibits opposing activity patterns during the flight response vs exposure to environmental stressors.
a, Circuit for C. elegans flight response triggered by mechanical stimulation. b, Velocity traces (top, n=10 independent experiments) and survival curves (bottom) during oxidative stress for wild-type animals in the absence (n=13 independent experiments) or presence (n=10 independent experiments) of a mechanical stimulus (black squares). c, Velocity (n=7 independent experiments) and survival curves of animals exposed to oxidative stress and RIM optogenetic activation with (+ ATR) or without all-trans retinal (- ATR) (n=6 independent experiments per condition). Blue squares indicate light stimulus. d, Ca2+ dynamics of RIM::GCaMP6 (ΔF/F0) upon a mechanical stimulus t=0, tap: n=13 animals (red), no tap: n=14 animals (grey). e, Ca2+ responses upon heat stress (n=29 animals). Central lines indicate mean; shaded regions indicate SEM.