Abstract
The lower Cenomanian Kachin amber from Myanmar contains a species-rich assemblage with numerous plant and animal fossils. Terrestrial and, to a lesser degree, freshwater species predominate in this assemblage, while a few taxa with marine affinities were also discovered, e.g. isopods, ammonites, and piddocks. Here, we describe the Kachin amber piddock †Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov. It appears to be an ancestral stem lineage of the recent Lignopholas piddocks, which are estuarine to freshwater bivalves, boring into wood and mudstone rocks. Frequent occurrences and high abundance of †Palaeolignopholas borings and preserved shells in the Kachin amber could indicate that the resin-producing forest was partly situated near a downstream (estuarine to freshwater) section of a river. Multiple records of freshwater invertebrates (caddisflies, mayflies, stoneflies, odonates, and chironomids) in this amber could also manifest in favor of our paleo-environmental reconstruction, although a variety of local freshwater environments is known to occur in coastal settings.
Subject terms: Taxonomy, Zoology, Biogeography, Palaeoecology
Introduction
Piddocks (Bivalvia: Pholadidae) are a primarily marine family of bivalves1–4. These clams represent a group of ecosystem engineers driving macrobioerosion and sedimentation processes in marine environments, and increasing surface complexity of rocks, coral reefs, wood, and other hard substrates5–8. Several piddocks such as members of the recent genera Lignopholas Turner, 1955 and Martesia Sowerby 1824 can tolerate a wide range of salinity, being common inhabitants of estuarine environments9–12. Moreover, at least two primarily estuarine Lignopholas species can establish permanent populations in freshwater habitats, i.e. the wood-borer L. rivicola (Sowerby, 1849)11, and the rock-borer L. fluminalis (Blanford, 1867)13,14.
Club-shaped (clavate) borings produced by piddocks are common trace fossils occurring in a broad variety of substrates5, including amber from Columbia, Mexico, Myanmar, Lebanon, France, and Spain15. Bivalve shells and borings in Cretaceous amber from northern Myanmar were initially identified as plant antheridia or fungal sporangia, and the first careful reconstruction of this fossil, showing immature shell with interior and exterior futures was presented16. Later, the piddock trace fossils were described as sporocarps of the non-gilled hymenomycete Palaeoclavaria burmitis Poinar & Brown, 200317,18. Further researchers recorded fossil remains of piddock shells inside the borings and those “floating” in the amber15,19,20. Based on conchological characters, these shells were considered belonging to the subfamily Martesiinae19, and, more specifically, to the genus Martesia15.
This study aims to (1) describe a new genus and species of Mesozoic piddocks; (2) assess the taxonomic placement of this taxon and its relationships with other genera of the Martesiinae; and (3) discuss taphonomic issues regarding aquatic environments near the early Cenomanian amber-producing forest in northern Myanmar.
Results
Altogether nine polished pieces of the lower Cenomanian Kachin amber from northern Myanmar (Figs. 1A–D, 2A–E) were examined in this study (depository: Russian Museum of Biodiversity Hotspots, N. Laverov Federal Center for Integrated Arctic Research of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Arkhangelsk, Russia). A brief description of each amber piece is given below.
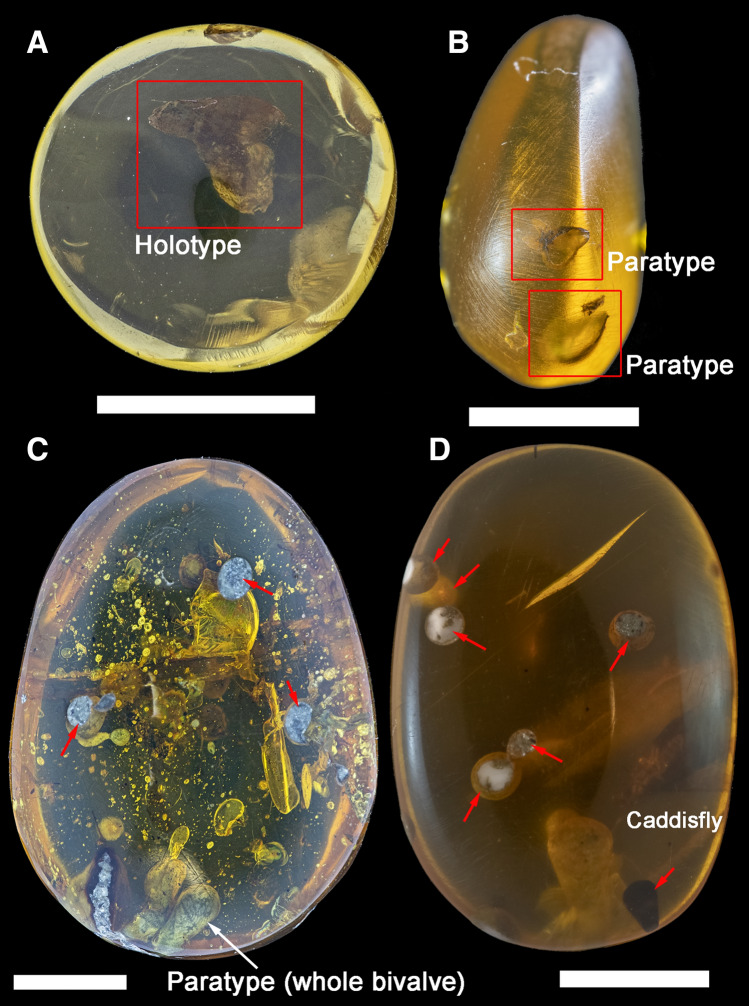
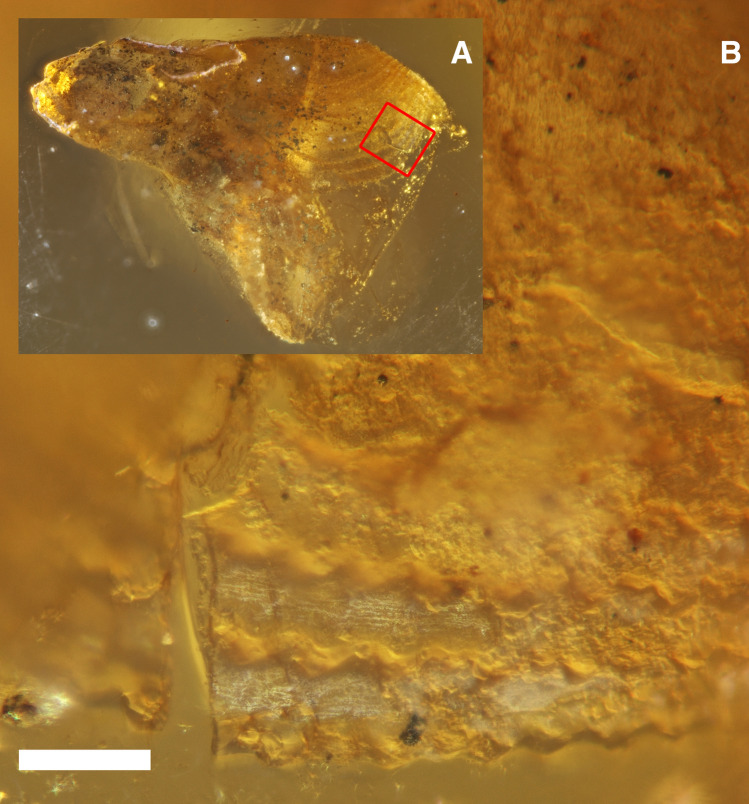
Figure 1.
Lower Cenomanian Kachin amber samples with specimens and borings of †Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov. from northern Myanmar used in this study. (A) RMBH biv1115 (frontal view with the holotype). (B) RMBH biv1101 (lateral view with two paratypes and a shell fragment). (C) RMBH biv1116 (frontal view with the fossilized paratype). (D) RMBH biv1100 (frontal view with borings). The red frames indicate position of the type specimens (holotype and some paratypes). The red arrows indicate bivalve borings. Scale bars = 5 mm. (Photos: Ilya V. Vikhrev).
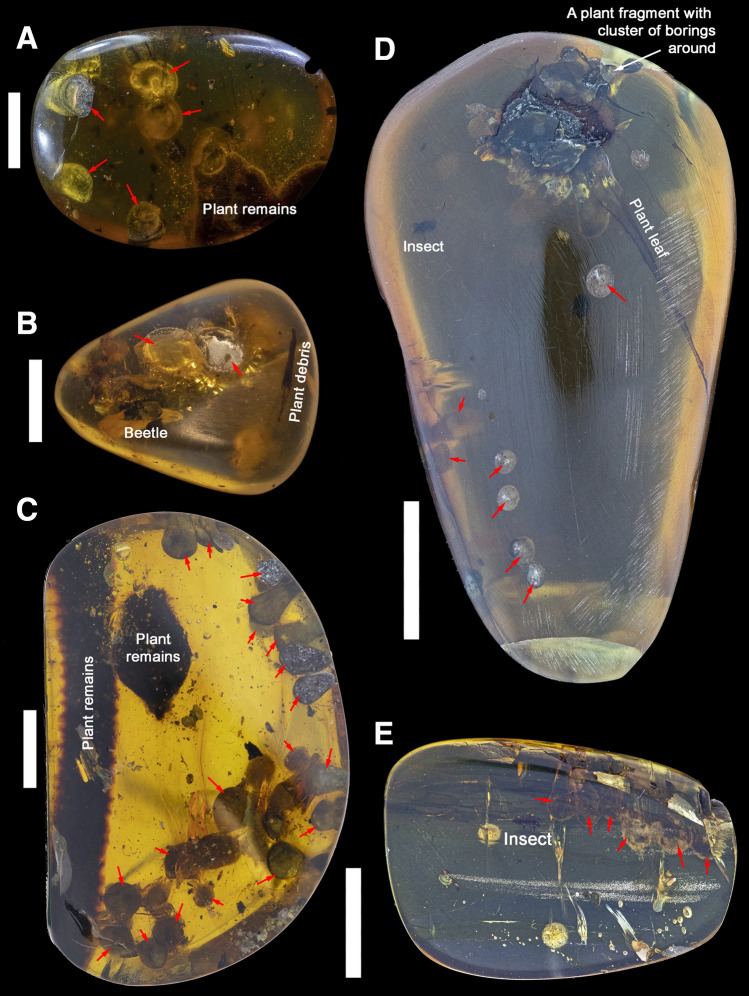
Figure 2.
Lower Cenomanian Kachin amber samples with borings of †Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov. from northern Myanmar used in this study. (A) RMBH biv1102 (frontal view). (B) RMBH biv1103 (frontal view). (C) RMBH biv1114 (frontal view). (D) RMBH biv1118 (frontal view). (E) RMBH biv1117 (frontal view). The red arrows indicate bivalve borings. Scale bars = 5 mm. (Photos: Ilya V. Vikhrev).
RMBH biv1115: Size 8.5 × 5.8 × 8.1 mm (Fig. 1A). Inclusions: articulated shell of †Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov., “floating” in the resin (the holotype).
RMBH biv1101: Size 15.6 × 6.4 × 11.5 mm (Fig. 1B). Inclusions: two complete articulated shells (paratypes) and a shell fragment of †Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov., “floating” in the resin.
RMBH biv1116: Size 22.5 × 8.3 × 16.5 mm (Fig. 1C). Inclusions: fossilized shell of †Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov. (paratype), borings of this species (filled with fine gray sand), unidentified fly specimens (Insecta: Diptera), and unidentified organic fragments (probably, plant debris).
RMBH biv1100: Size 17.5 × 4.9 × 12.0 mm (Fig. 1D). Inclusions: borings of †Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov. (filled with fine gray sand), and an unidentified caddisfly specimen (Insecta: Trichoptera).
RMBH biv1102: Size 15.6 × 5.1 × 12.7 mm (Fig. 2A). Inclusions: borings of †Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov. (filled with fine gray sand), and unidentified organic fragments (probably, plant debris).
RMBH biv1103: Size 19.6 × 4.7 × 14.3 mm (Fig. 2B). Inclusions: borings of †Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov. (filled with fine gray sand), an unidentified beetle specimen (Insecta: Coleoptera), and unidentified organic fragments (probably, plant debris).
RMBH biv1114: Size 33.1 × 7.8 × 21.7 mm (Fig. 2C). Inclusions: multiple borings of †Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov. (filled with fine gray sand), and unidentified plant remains.
RMBH biv1118: Size 25.1 × 8.4 × 14.3 mm (Fig. 2D). Inclusions: separate borings of †Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov. (filled with fine gray sand), a plant fragment with a cluster of borings around, and an unidentified insect specimen.
RMBH biv1117: Size 15.5 × 3.9 × 10.7 mm (Fig. 2E). Inclusions: borings of †Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov. (filled with fine gray sand), and an unidentified insect specimen.
Additionally, six amber samples containing adult and sub-adult specimens of †Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov. were examined using photographs in published works as follows: BMNH 20205 (Department of Palaeontology, Natural History Museum, London, UK)15, NIGP 169623 and NIGP 169624 (Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Nanjing, China)20, RS.P1450 (Ru D. A. Smith collection, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia)19, and AMNH (Division of Invertebrates, American Museum of Natural History, New York, NY, United States of America)16.
Based on morphological analyses of the fossil piddock shells, it was found to be a genus and species new to science, which is described here.
Systematic paleontology
Phylum Mollusca Linnaeus, 1758
Class Bivalvia Linnaeus, 1758
Family Pholadidae Lamarck, 1809
Subfamily Martesiinae Grant & Gale, 1931
†Palaeolignopholas gen. nov
LSID: http://zoobank.org/urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:1D686DCE-A5E9-41DA-9504-2EC58C93D988
Type species: †Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov.
Etymology. This name is derived from the prefix ‘Palaeo-’ (ancient), and ‘-lignopholas’, the name of a recent genus of estuarine and freshwater piddocks boring into wood, mudstone rocks, brickwork, laterites, etc.11,13. Masculine in gender.
Diagnosis. The new monotypic genus is conchologically similar to several other piddock genera such as Lignopholas, Martesia, and Diplothyra Tryon 1862 but can be distinguished from these taxa by the following combination of characters: mesoplax relatively small, triangular, divided longitudinally, posterior slope without concentric sculpture, sculptured valve with concave parallel ridges (Martesia-like “rasping teeth”) curved anteriorly, periostracal lamellae dense, fine, hair-like. The fossil genus †Opertochasma Stephenson, 1952 shares a divided mesoplax but it clearly differs from both †Palaeolignopholas gen. nov. and Lignopholas by having two radial grooves on the shell surface21.
Distribution. Kachin State, northern Myanmar; Upper Cretaceous (lower Cenomanian)15,19,22.
Comments. Both †Palaeolignopholas gen. nov. and Lignopholas appear to be closely related to each other because they share a longitudinally divided mesoplax and periostracal lamellae, which are considered diagnostic features distinguishing this clade from Martesia + Diplothyra. Based on available conchological characters, we assume that †Palaeolignopholas gen. nov. might be placed on the ancestral stem lineage of the Lignopholas clade, although a possibility of homeomorphy could not entirely be excluded.
†Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov
= Plant Antheridia or Fungal Sporangia indet. sensu Grimaldi et al. (2002): 9, fig. 2a,b (bivalve specimens), fig. 3 (borings), fig. 5 (shell reconstruction of an immature specimen), figs. 6 and 7 (SEMs of borings surface showing rasped ornament at different magnifications)16.
= Palaeoclavaria burmitis Poinar & Brown (2003): 765, figs. 1–4 (borings) [this fungal taxon was introduced using a trace fossil (boring) as the holotype]17; Poinar (2016): 2, figs. 10, 15, 16 (borings)18.
= Martesiinae indet. sensu Smith & Ross (2018): 4, figs. 1a–c, 2a,b, 3a–d (borings), 4a,b, 5a–e (bivalve specimens)19.
= Pholadidae indet. sensu Mao et al. (2018): 99, figs. 8a–f (borings), 8g,h (bivalve specimens)20.
= Martesia sp. 2 sensu Mayoral et al. (2020): 10, figs. 4a (borings), 7b, 8a–l (bivalve specimens)15.
= Pholadidae indet. sensu Balashov (2020): 623.
Figures 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7.
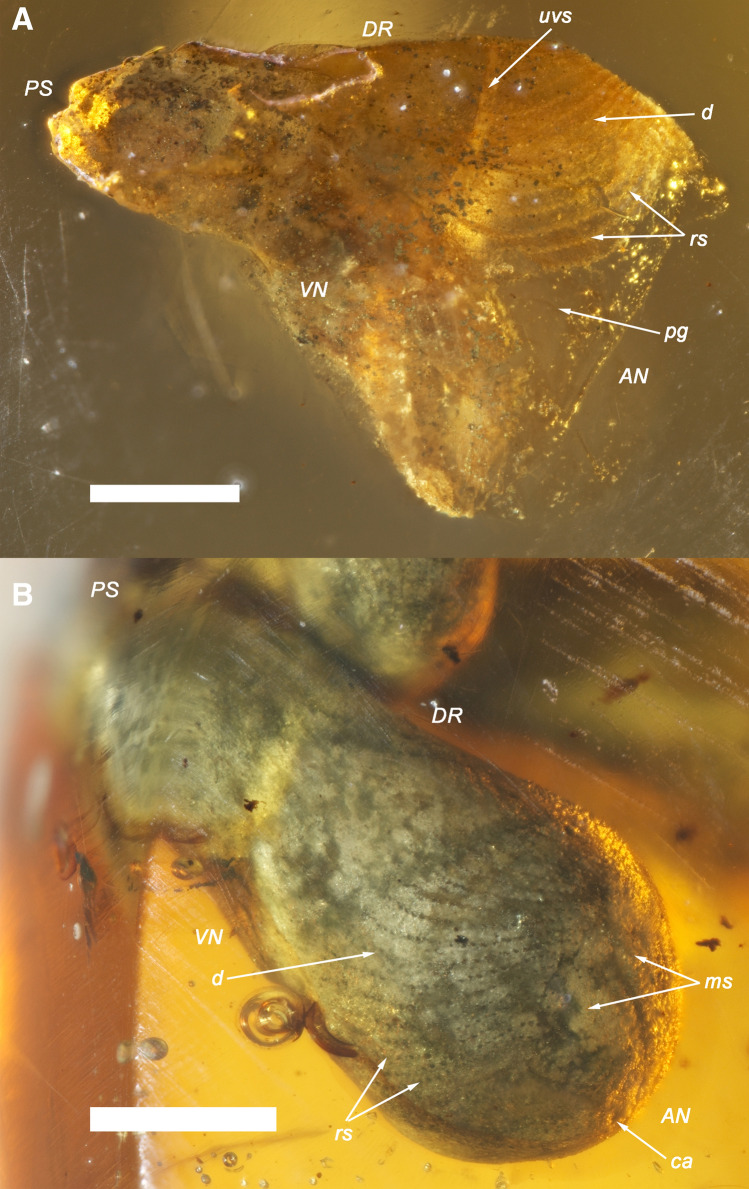
Figure 3.
Holotype and a paratype of †Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov. from lower Cenomanian Kachin amber, northern Myanmar. (A) Holotype: ventro-lateral view of articulated shell. (B) Paratype: anterio-lateral view of fossilized shell. VN ventral margin; DR dorsal margin; AN anterior margin; PS posterior margin; d disc; rs rasping surface of the valve; uvs umbonal ventral sulcus; pg pedal gape; pl periostracal lamellae. Scale bars = 500 µm. (Photos: Ilya V. Vikhrev).
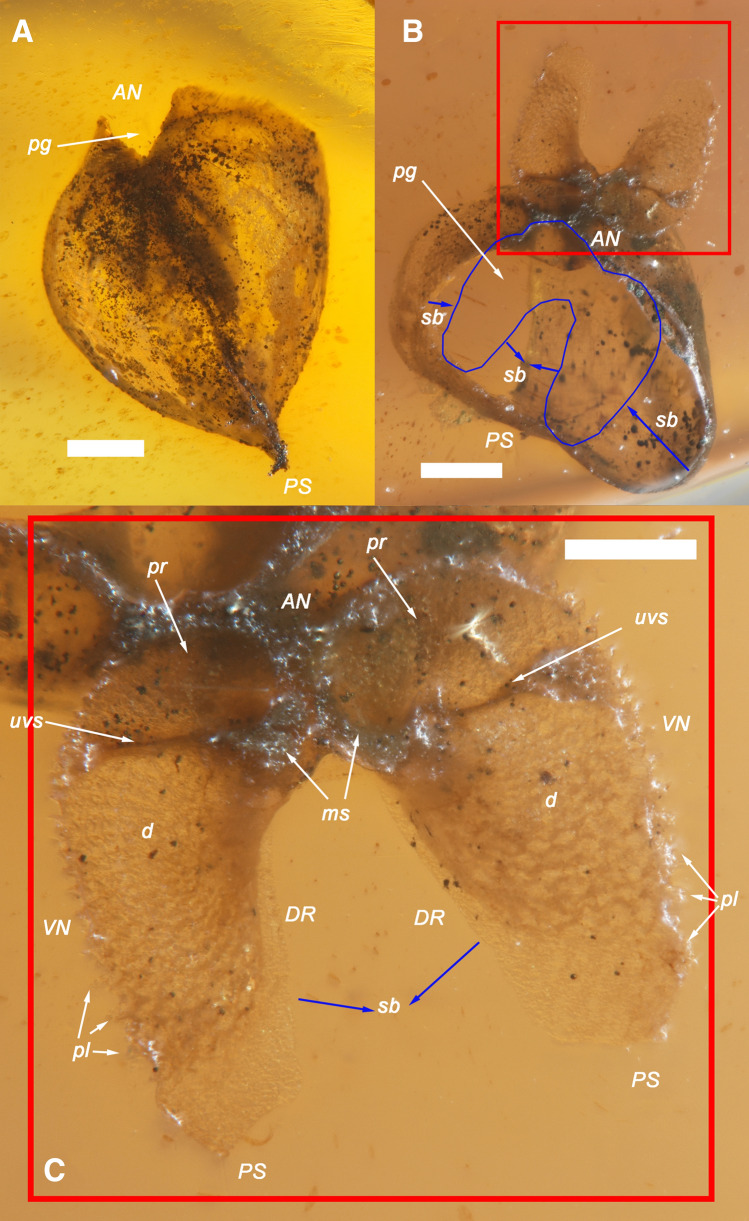
Figure 4.
Paratypes of †Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov. from lower Cenomanian Kachin amber, northern Myanmar. (A) Paratype: dorsal view of articulated shell. Scale bar = 500 µm. (B) Paratype: dorsal view of articulated shell. The detached and deflected umbonal paired fragment of the valves is framed by red square. The blue contour indicates the lifetime position of this fragment. The blue arrows show the shell breakages. Scale bar = 200 µm. (C) Umbonal paired fragment of the holotype valves (inner view). The blue arrows show the shell breakage. Scale bar = 200 µm. VN ventral margin; DR dorsal margin; AN anterior margin; PS posterior margin; ms longitudinally divided mesoplax (inner view); pr prora; d disc; rs rasping surface of the valve; uvs umbonal ventral sulcus; pg pedal gape; pl periostracal lamellae; sb shell breakage. (Photos: Ilya V. Vikhrev).
Figure 5.
Rasping surface of †Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov. shell. (A) Holotype shell. The red frame marks position of the enlarged area. (B) Undulated micro-sculpture of the rasping surface. Scale bar = 100 µm. (Photos: Ilya V. Vikhrev).
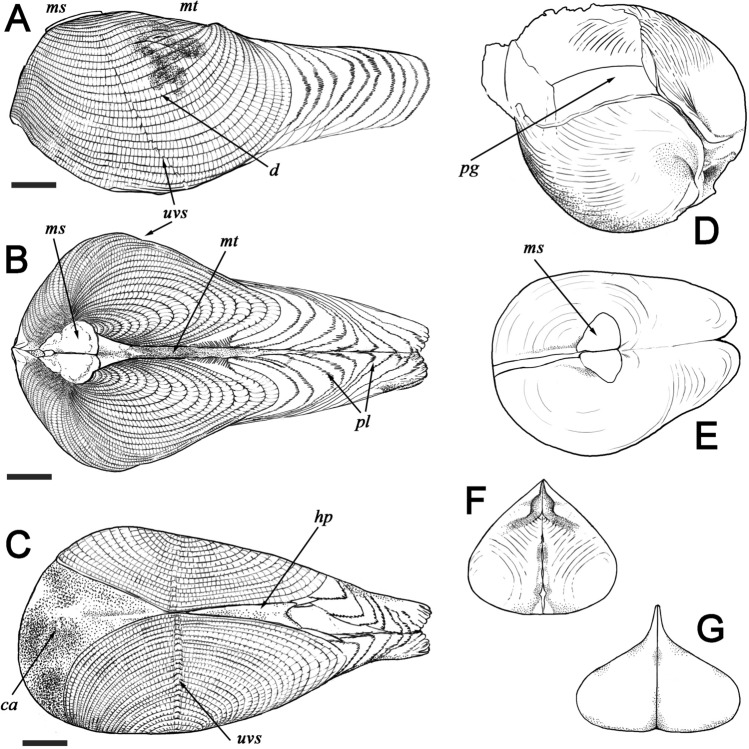
Figure 6.
Schematic reconstruction of †Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov. from lower Cenomanian Kachin amber, northern Myanmar based on the type series and other fossil material15,16,19,20. (A) Lateral view of adult specimen. (B) Dorsal view of adult specimen. (C) Ventral view of adult specimen (based on a paratype BMNH 2020515). (D) Anterio-ventral view of immature specimen. (E) Dorsal view of immature specimen. (F) Mesoplax of adult specimen. (G) Mesoplax of immature specimen. d disc; mt metaplax; ms mesoplax; hp hypoplax; ca callum; uvs umbonal ventral sulcus; pg pedal gape; pl periostracal lamellae. Scale bars = 1 mm (A–C). (Line graphics: Yulia E. Chapurina).
Figure 7.
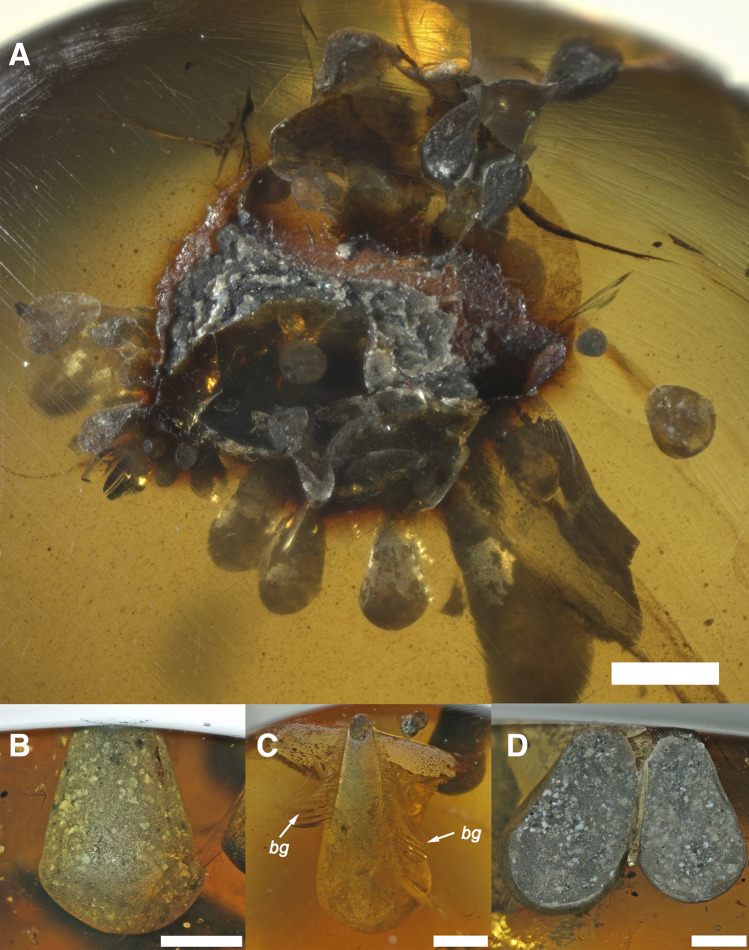
Clavate borings of †Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov. from lower Cenomanian Kachin amber, northern Myanmar. (A) Cluster of borings. It marks drilling of immature piddocks into soft resin from the unidentified plant (wood?) fragment. (B–D) Clavate borings of adult piddocks. Scale bars = 1 mm. Abbreviation: bg a characteristic bioglyph indicating the shell rotation inside hardening resin. (Photos: Ilya V. Vikhrev).
LSID: http://zoobank.org/urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:F6659EBF-B0A4-4B21-A99B-2C56BDB7EC9B.
Common name. Kachin Amber Piddock.
Holotype. RMBH biv1115, the adult shell with length 3.07 mm and width 1.13 mm “floating” in the resin (Figs. 1A, 3A, 5A,B), local collector leg., Russian Museum of Biodiversity Hotspots, N. Laverov Federal Center for Integrated Arctic Research of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Arkhangelsk, Russia.
Paratypes. RMBH biv1116, the fossilized adult shell with length 4.05 mm and width 1.83 mm (Figs. 1C, 3B); RMBH biv1101, the immature specimen with articulated shell (width 1.86 mm) sharing a detached and deflected umbonal paired fragment of the valves due to the shell breakage (Figs. 1B, 4B,C); RMBH biv1101, the other immature specimen with shell length 2.68 mm and shell width 2.52 mm in this amber piece (Figs. 1B, 4A); BMNH 20205, adult specimen [illustrated in Mayoral et al. (2020): fig. 7B15], Department of Palaeontology, Natural History Museum, London, UK; NIGP 169623, adult specimen [illustrated in Mao et al. (2018): 100, fig. 8G20], and NIGP 169624, two adult specimens [illustrated in Mao et al. (2018): 100, fig. 8H20], Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Nanjing, China; RS.P1450, two sub-adult specimens [illustrated in Smith & Ross (2018): 5, fig. 4A,B19], Ru D. A. Smith collection, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
Type locality and strata. The Noije Bum Hill mines, Hukawng Valley, near Tanai (26.3593°N, 96.7200°E), Kachin State, northern Myanmar; Upper Cretaceous (lower Cenomanian; absolute age of youngest zircons in enclosing marine sediment: 98.79 ± 0.62 Ma)19,22.
Etymology. The name of this species reflects its type locality, which is situated in the Kachin State of Myanmar.
Diagnosis. As for the genus.
Description. Shell small (up to 9.3 mm in length15,19,20), conical, with a rounded anterior margin, tapering posteriorly (Figs. 3A,B, 4A–C, 6A–E); its shape is similar to those in the recent Lignopholas, Martesia, and Diplothyra. Valve sculptured, with concave parallel ridges (Martesia-like “rasping teeth”) curved anteriorly (Fig. 5A,B). The ridges share a characteristic wave-like micro-sculpture (Fig. 5B). Sulcus deep (Figs. 3A, 4C, 6A–C). Mesoplax longitudinally divided, relatively small, triangular, tapering or lobed anteriorly (Fig. 3A, 6B,F), in immature specimens sometimes with lateral lobes (Figs. 4C, 6E,G). Metaplax and hypoplax long, narrow, not longitudinally divided but sometimes slightly bifurcated posteriorly (Fig. 6A–C). Periostracum densely covered by fine, hair-like lamellae (Figs. 4B,C and 6D). Umbonal reflection with large flattened ridge. Pedal gape presents in immature (Figs. 4A,B, 6D) and some adult specimens (Fig. 3A) but it is covered by callum in older specimens (Figs. 3B, 6C). Morphological details of the new species were also presented in a series of micro-CT images published Mayoral et al. (see Fig. 8 in that paper15) and in the reconstruction of Grimaldy et al. (see Fig. 5 in that work16).
Figure 8.
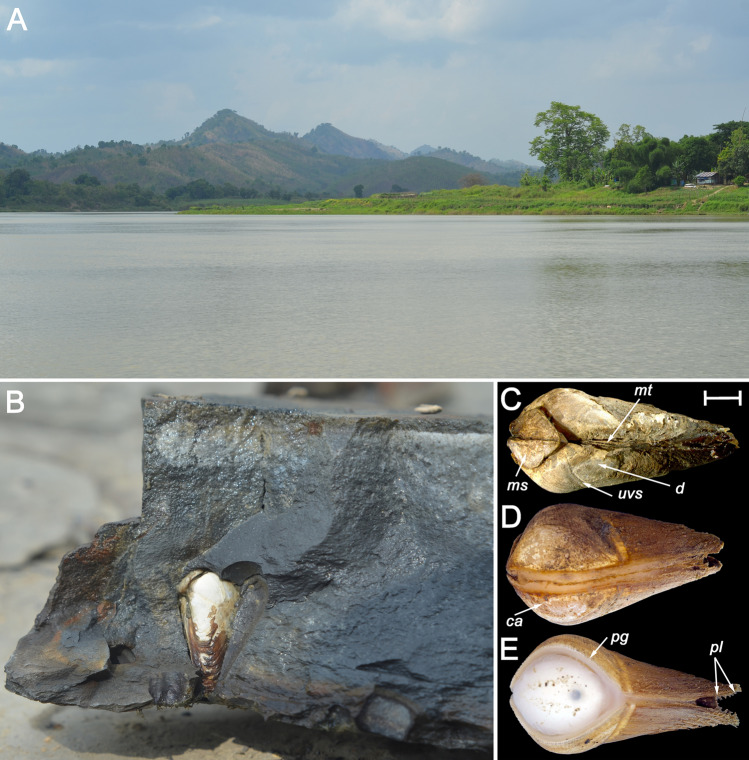
Recent freshwater piddock Lignopholas fluminalis (Blanford, 1867) in the middle reaches of the Kaladan River, Rakhine State, Myanmar13. (A) Habitat of the freshwater piddock: river pool with siltstone rocks at the bottom, a possible modern analogue of the Mesozoic riverine ecosystem with †Palaeolignopholas. (B) Siltstone rock fragment with living freshwater piddocks inside their clavate borings. (C) Ethanol-preserved piddock (dorsal view). (D) Living piddock with fully developed callum (ventral view). (E) Living piddock with pedal gape (ventral view). Abbreviations: d disc; mt metaplax; ms mesoplax; ca callum; uvs umbonal ventral sulcus; pg pedal gape; pl periostracal lamellae. Scale bar = 2 mm. (Photos: Olga V. Aksenova).
Borings and corresponding ichnotaxon. The borings produced by †Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov. represent club-shaped (clavate) structures (Figs. 1C,D, 2A–E, 7A–D), sometimes with a characteristic bioglyph revealing the shell rotation in hardening resin (Fig. 7C). These borings were illustrated in detail15–17,19,20, and were considered belonging to Teredolites clavatus Leymerie, 184215. Initially, the trace fossils produced by the Kachin amber piddock were described as sporocarps of Palaeoclavaria burmitis Poinar & Brown, 2003, a non-gilled hymenomycete taxon17. The holotype of this taxon represents a club-shaped piddock crypt labelled as follows: “Amber from the Hukawng Valley in Burma; specimen (in piece B with accession number B-P-1) deposited in the Poinar amber collection maintained at Oregon State University (holotype)17”. Hence, Palaeoclavaria Poinar & Brown, 2003 and P. burmitis Poinar & Brown, 2003 must be considered ichnogenus and ichnospecies, respectively. New ichnotaxonomic synonymies are formally proposed here as follows: Teredolites Leymerie, 1842 (= Palaeoclavaria Poinar & Brown, 2003 syn. nov.), and Teredolites clavatus Leymerie, 1842 (= Palaeoclavaria burmitis Poinar & Brown, 2003 syn. nov.).
Discussion
Taxonomic placement of the Kachin amber piddock
Previously, †Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov. was considered a member of the recent genus Martesia15. However, the latter genus does not share a divided mesoplax and periostracal lamellae11, hence, the new species cannot be placed in Martesia (nor Diplothyra). In its turn, these characters are diagnostic for the genus Lignopholas11–13. Conversely, Lignopholas shares a posterior slope with concentric sculpture, a smooth valve, and a specific shape of periostracal lamellae (being large, flat, and fringed). Therefore, we prefer to place the fossil species from Cretaceous Kachin amber within the new genus †Palaeolignopholas that appears to be on the stem lineage of the recent Lignopholas clade. The †Palaeolignopholas differs from Lignopholas by having a posterior slope without concentric sculpture, a sculptured valve with Martesia-like “rasping teeth”, and fine, hair-like lamellae.
Taphonomy of the new fossil taxon
All available specimens and trace fossils of †Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov. are characterized by very small size15–17,19,20. The shell length of the largest specimen ever known is 9.3 mm20, while other samples are much smaller15,19. For example, the maximum length was 4.2 mm in a comprehensive sample of shells and borings (N = 131) examined by Mayoral et al.15. At first glance, such a small size might be a diagnostic feature of this taxon, as species from conchologically similar genera such as Lignopholas, Martesia, and Diplothyra share much larger size, usually up to 20–30 mm in length11,12. However, Lignopholas chengi Turner & Santhakumaran, 1989 was described based on a series of small (possible immature) specimens, the largest of which was 11.5 mm long11 that agrees with our dataset on †Palaeolignopholas.
It should be noted that fossil specimens of †Palaeolignopholas kachinensis gen. & sp. nov. commonly occur “floating” in the amber (see Figs. 1A,B, 3A, 4A–C) indicating that they often bored into freshly produced (liquid or soft) resin15,19. Smith & Ross19 assumed that these “floating” clams died within 1–2 weeks since their settlement on the resin, while larger examples bored into hardened resin. Mayoral et al.’s taphonomic model15 predicts that at first stage the bivalves bored into a living resin-secreting tree, which was periodically immersed in seawater. Later, when the resin hardens, wood can partially decay, being replaced by episodic flows of resin, while the bivalves could repeatedly bore the resin after its hardening15. Among recent pholadid taxa, Martesia nairi Turner & Santhakumaran, 1989 bores into living mangroves, and damages the trees11. However, it was shown that the Kachin amber was produced by Taxodiaceae and Araucariaceae and that several conifer families were the primary sources of Cretaceous amber globally19,24. There is not much evidence that conifers such as taxodioids and araucarians could survive in seawater/brackish tidal environments, while the presence of Taxodiaceae pollen in the Noije Bum’s amber horizon25 could indicate riparian and freshwater wetland communities26. Pyrite inclusions in the Kachin amber pieces19 consistent with low oxygenated environments of freshwater and brackish sediments27. There are several possible ways of the pyrite origin in freshwater settings, e.g. diagenetic formation from slow oxidation of acid volatile sulphide by organic matter27. Hence, we could assume that †Palaeolignopholas clams were boring the resin dropped into the water from trunks and branches of conifer trees growing along the downstream river valley, probably having a tidal influence. Our novel records of a bunch of borings situated around a small plant (wood?) inclusion in the amber (see Fig. 7A) and a boring of adult piddock with a specific bioglyph revealing the shell rotation in hardening resin (Fig. 7C) also support this hypothesis.
Regional paleo-environmental reconstruction
Rare discoveries of supposed marine taxa in the Kachin amber20,28,29 were used as a basis to establish the hypothesis on a close proximity of the amber-producing forest to the coastal marine20 or brackish water habitats19. Records of a juvenile ammonite shell29 and several isopods of possible saltwater (littoral or supralittoral) affinities28,29 might reveal that the amber was produced from coastal trees located close to a marine bay or other kind of shoreline environments29. Numerous records of piddocks and their traces in the amber were also used as a robust evidence supporting the hypothesis on coastal origin of the resin15,19. It should be noted that alleged marine gastropods from the Burmese amber30 were found to be terrestrial snails from the operculate family Pupinidae (Cyclophoroidea)31. A few occurrences of marine oysters, corals, and crinoids adhering to the amber pieces20 are not relevant to the paleoenvironmental discussion since they post-date reworking of the amber into a marine environment.
Conversely, the Kachin amber houses a diverse assemblage of freshwater taxa such as caddisflies32–35, mayflies36–39, stoneflies40, chironomids41, water measurers42,43, odonates44–48 and their stem lineage49. It is known that insects rarely occur in marine and brackish environments50, although recent saltwater-tolerant or even marine species exist among several orders, e.g. Hemiptera51–53, Odonata54–56, and Trichoptera57. Hence, a species-rich and abundant fauna of freshwater insects occurring in the amber could indicate rather a proximity of resin-producing trees to freshwater habitats than to coastal marine environments. Frogs and amphibian egg masses discovered in the Kachin amber58,59 are also hardly correspond to saltwater environments.
Based on our new results and the published data, outlined above, we could assume that the Kachin amber-producing forest was partly situated near a downstream (estuarine to freshwater) section of a tropical river. Furthermore, we could hypothesize that these forests as a whole extended across a variety of freshwater and estuarine environments such as coastal rivers, river deltas, lakes, lagoons, and coastal bays. It is known that environmental conditions in downstream sections of rivers draining into the sea are changing periodically from freshwater to slightly brackish or brackish due to the tidal influence60,61. There is a possibility of seasonal changes driven by rainfall, when the salinity in lower tidal parts of coastal rivers significantly decreases during the rainy season62. Although the Hukawng Valley is currently a mainland site, which is far from the sea, the Burma Terrain (i.e. a microplate covering a large part of Myanmar with amber deposits west of the Sagaing fault) was a tropical island during the Albian–Cenomanian63,64. In general, the hypothesis that the resin-producing forest in northern Myanmar was partially situated near a largely freshwater body such as a downstream riverine section could explain the high diversity of freshwater taxa discovered in the Kachin amber. The scarce presence of saltwater (chiefly estuarine) fauna can be explained through occasional marine ingressions into the system. At first glance, habitats of the recent freshwater piddocks Lignopholas fluminalis in the middle reaches of the Kaladan River in Myanmar13,14 (Fig. 8A–C) can be considered a remote modern analogue of the Mesozoic ecosystem inhabited by †Palaeolignopholas. It is known that †Palaeolignopholas bored into the amber and wood15, while Lignopholas fluminalis bores into the bottom rocks13,14. The fossil species probably occurred in a downstream (estuarine to freshwater) riverine section, while the recent taxon is known to occur in the middle reaches of a river but may present itself in the estuary as well13. Besides, we do not know if they are really related, as the age difference between them is 100 Myr and there is no direct evidence on the missing link available. Theoretically, it could be a homeomorphy. There are other Mesozoic taxa with a portioned mesoplax21, providing candidates for an ancestry.
Finally, our novel results not only establish a taxonomic concept for a fossil amber-preserved piddock but also show that the bivalves on their own do not necessarily indicate the presence of brackish to normal marine salinity water.
Methods
Data collecting
This study is based on a series of fossil specimens and borings discovered in nine samples of Upper Cretaceous Kachin amber deposited in the Russian Museum of Biodiversity Hotspots, N. Laverov Federal Center for Integrated Arctic Research of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Arkhangelsk, Russia. Additional piddock fossils from Natural History Museum, London, UK; Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Nanjing, China; Ru D. A. Smith collection, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia; and Division of Invertebrates, American Museum of Natural History, New York, NY, United States of America were examined using photographs presented in published works15,16,19,20. The amber samples were collected by local miners in the Hukawng Valley, Kachin State, northern Myanmar. Based on U–Pb dating of zircons from enclosing sediment, the Kachin amber shares the early Cenomanian age22.
Morphological study
Measurements of amber pieces were performed using a digital caliper (Digimatic Coolant Proof, Mitutoyo, Japan). Images of amber pieces were taken using a Canon EOS 6D digital camera (Canon Inc., Japan) with Canon EF 100 mm f/2.8L IS USM macro lens (Canon Inc., Japan). Morphological study of fossil bivalve specimens was based on an approach of Turner & Santhakumaran11 with a special focus to the shell shape, size, valve shape and sculpture, the shape of mesoplax, metaplax, hypoplax, and umbonal reflection, and the character of periostracal lamellae. Images and measurements of specimens and trace fossils were taken with a Leica M165C microscope (Leica, Germany).
Nomenclatural acts
The electronic edition of this article conforms to the requirements of the amended International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), and hence the new name and synonymy contained herein are available under that Code from the electronic edition of this article. This published work and the nomenclatural acts it contains have been registered in ZooBank (http://zoobank.org), the online registration system for the ICZN. The LSID for this publication is: urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:C14A4E2F-9280-48A6-9C95-8298BD1F964F. The electronic edition of this paper was published in a journal with an ISSN and has been archived and is available from PubMed Central.
Acknowledgements
We are deeply grateful to Dr. Ru Smith (Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia) and an anonymous reviewer for their valuable comments on earlier versions of this paper. The Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation partly supported this work (project 0793-2020-0005 to I.N.B and O.V.A.; and project AAAA-A18-118012390161-9 to I.V.V. and E.S.K.). The Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project 18-44-292001) supported morphological investigation of the Cretaceous amber samples by A.V.K. The Northern Arctic Federal University covered an open access fee for this article.
Author contributions
I.N.B. developed the concept of this study. O.V.A., I.V.V., E.S.K., Y.E.C., and A.V.K. processed samples and prepared figures. I.N.B. wrote a first draft of the manuscript with input from O.V.A., I.V.V., E.S.K., Y.E.C., and A.V.K. All the co-authors discussed the final version of the paper.
Data availability
The amber samples containing the type series and borings of the new piddock species are available in the RMBH, Russian Museum of Biodiversity Hotspots, N. Laverov Federal Center for Integrated Arctic Research of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences (Arkhangelsk, Russia); Natural History Museum (London, UK); Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Nanjing, China); Ru D. A. Smith private collection (Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia), and Division of Invertebrates, American Museum of Natural History (New York, NY, United States of America).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Kennedy GL. New Cretaceous and Tertiary Pholadidae (Mollusca: Bivalvia) from California. J. Paleontol. 1993;67:397–404. doi: 10.1017/S0022336000036878. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Monari S. Phylogeny and biogeography of pholadid bivalve Barnea (Anchomasa) with considerations on the phylogeny of Pholadoidea. Acta Palaeontol. Pol. 2009;54:315–335. doi: 10.4202/app.2008.0068. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Distel DL, et al. Molecular phylogeny of Pholadoidea Lamarck, 1809 supports a single origin for xylotrophy (wood feeding) and xylotrophic bacterial endosymbiosis in Bivalvia. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2011;61:245–254. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2011.05.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Holmes, A., Fenwick, D., Gainey, P. & Williams, T. Martesia fragilis Verrill & Bush, 1898 in the north-east Atlantic. Overlooked and a recent new discovery. J. Conchol.42, 183–186 (2015).
- 5.Warme, J. E. Borings as trace fossils, and the processes of marine bioerosion. in The Study of Trace Fossils 181–227, 10.1007/978-3-642-65923-2_11 (Springer, 1975).
- 6.Voight JR. Experimental deep-sea deployments reveal diverse Northeast Pacific wood-boring bivalves of Xylophagainae (Myoida: Pholadidae) J. Molluscan Stud. 2007;73:377–391. doi: 10.1669/0883-1351(2004)019<0565:BBIPCA>2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tapanila, L., Roberts, E. M., Bouare, M. L., Sissoko, F. & O’Leary, M. A. Bivalve borings in phosphatic coprolites and bone, Cretaceous–Paleogene, northeastern Mali. Palaios19, 565–573, https://www.jstor.org/stable/3515875 (2004).
- 8.Pinn EH, Thompson RC, Hawkins SJ. Piddocks (Mollusca: Bivalvia: Pholadidae) increase topographical complexity and species diversity in the intertidal. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008;355:173–182. doi: 10.3354/meps07248. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Blanford, W. T. Contributions of Indian Malacology, No. VIII. List of estuary shells collected in the delta of the Irawady, in Pegu, with descriptions of new species. J. Asiatic Soc. Bengal36, 51–72 (1867).
- 10.Annandale N. Bivalve molluscs injuring brickwork in Calcutta docks. J. Asiatic Soc. Bengal. 1922;18:555–557. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Turner RD, Santhakumaran LN. The genera Martesia and Lignopholas in the Indo-Pacific (Mollusca: Bivalvia: Pholadidae) Ophelia. 1989;30:155–186. doi: 10.1080/00785326.1989.10430842. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Turner, R. D. The family Pholadidae in the western Atlantic. Part II—Martesiinae, Jouannetiinae and Xylophaginae. Johnsonia3, 65–160 (1955).
- 13.Bolotov IN, et al. Discovery of a silicate rock-boring organism and macrobioerosion in fresh water. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:1–11. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05133-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Daval D, et al. Symbiotic cooperation between freshwater rock-boring bivalves and microorganisms promotes silicate bioerosion. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:1–10. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70265-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mayoral E, et al. Bivalve bioerosion in Cretaceous-Neogene amber around the globe, with implications for the ichnogenera Teredolites and Apectoichnus. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2020;538:109410. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2019.109410. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Grimaldi, D. A., Engel, M. S. & Nascimbene, P. C. Fossiliferous Cretaceous amber from Myanmar (Burma): Its rediscovery, biotic diversity, and paleontological significance. Am. Mus. Novitates3361, 1–71; http://hdl.handle.net/2246/2914 (2002).
- 17.Poinar GO, Brown AE. A non-gilled hymenomycete in Cretaceous amber. Mycol. Res. 2003;107:763–768. doi: 10.1017/s0953756203007895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Poinar G. Fossil fleshy fungi (“mushrooms”) in amber. Fungal Genomics Biol. 2016;6:1000142. doi: 10.4172/2165-8056.1000142. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Smith RD, Ross AJ. Amberground pholadid bivalve borings and inclusions in Burmese amber: Implications for proximity of resin-producing forests to brackish waters, and the age of the amber. Earth Environ. Sci. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. 2018;107:239–247. doi: 10.1017/S1755691017000287. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mao, Y. et al. Various amberground marine animals on Burmese amber with discussions on its age. Palaeoentomology1, 91–103, 10.11646/palaeoentomology.1.1.11 (2018).
- 21.Haga, T. & Kase, T. Opertochasma somaensis n. sp. (Bivalvia: Pholadidae) from the Upper Jurassic in Japan: A perspective on pholadoidean early evolution. J. Paleontol.85, 478–488, 10.1666/10-008.1 (2011).
- 22.Shi G, et al. Age constraint on Burmese amber based on U-Pb dating of zircons. Cretac. Res. 2012;37:155–163. doi: 10.1016/j.cretres.2012.03.014. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Balashov, I. An inventory of molluscs recorded from mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber, with the description of a land snail, Euthema annae sp. nov. (Caenogastropoda, Cyclophoroidea, Diplommatinidae). Cretaceous Res.118, 104676, 10.1016/j.cretres.2020.104676 (2020). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 24.Stilwell JD, et al. Amber from the Triassic to Paleogene of Australia and New Zealand as exceptional preservation of poorly known terrestrial ecosystems. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:5703. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62252-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cruikshank RD, Ko K. Geology of an amber locality in the Hukawng Valley, Northern Myanmar. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2003;21:441–455. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(02)00044-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Peyrot D, Barron E, Polette F, Batten DJ, Néraudeau D. Early Cenomanian palynofloras and inferred resiniferous forests and vegetation types in Charentes (southwestern France) Cretac. Res. 2019;94:168–189. doi: 10.1016/j.cretres.2018.10.011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Davison W, Lishman JP, Hilton J. Formation of pyrite in freshwater sediments: Implications for C/S ratios. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 1985;49:1615–1620. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(85)90266-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Xing L, et al. A gigantic marine ostracod (Crustacea: Myodocopa) trapped in mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:1365. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19877-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Yu T, et al. An ammonite trapped in Burmese amber. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2019;116:11345–11350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1821292116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yu TT, Wang B, Jarzembowski E. First record of marine gastropods (wentletraps) from mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber. Palaeoworld. 2019;28:508–513. doi: 10.1016/j.palwor.2018.12.004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Neubauer, T. A., Páll-Gergely, B., Jochum, A. & Harzhauser, M. Striking case of convergence—Alleged marine gastropods in Cretaceous Burmese amber are terrestrial cyclophoroids. Comment on Yu et al. Palaeoworld28, 572–575, 10.1016/j.palwor.2019.05.015 (2019).
- 32.Wichard, W., Ross, E. & Ross, A. J. Palerasnitsynus gen. n. (Trichoptera, Psychomyiidae) from Burmese amber. ZooKeys130, 323–330, 10.3897/zookeys.130.1449 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 33.Wichard, W., Espeland, M. & Wang, B. Caddisflies with unusual hair-fans on the legs in Cretaceous Burmese amber (Insecta, Trichoptera). Palaeodiversity11, 21–28, 10.18476/pale.11.a3 (2018).
- 34.Wichard W, Wang B. New Cretaceous caddisflies from Burmese amber (Insecta, Trichoptera) Cretac. Res. 2016;61:129–135. doi: 10.1016/j.cretres.2016.01.004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wang J, Zhang W, Wang L, Ren D. A new caddisfly (Trichoptera: Polycentropodidae) from Upper Cretaceous amber of Myanmar. Cretac. Res. 2019;99:347–351. doi: 10.1016/j.cretres.2019.01.021. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sinitshenkova D. The first fossil prosopistomatid mayfly from Burmese amber (Ephemeroptera; Prosopistomatidae) Bull. Nat. Hist. Mus. (Geol. Ser.) 2000;56:25–28. [Google Scholar]
- 37.McCafferty WP, Santiago-Blay JA. A new Cretaceous mayfly from Burmese amber (Ephemeroptera: Australiphemeridae) Entomol. News. 2008;119:492–496. doi: 10.3157/0013-872X-119.5.492. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Poinar, G. Vetuformosa buckleyi n. gen., n. sp. (Ephemeroptera: Baetidae; Vetuformosinae n. subfam.), a new subfamily of mayflies in Early Cretaceous Burmese amber. Hist. Biol.23, 369–374, 10.1080/08912963.2011.559084 (2011).
- 39.Lin Q, Shih C, Zhao Y, Ren D. A new genus and species of Prosopistomatidae (Insecta: Ephemeroptera) from mid-Cretaceous Myanmar amber. Cretac. Res. 2018;84:401–406. doi: 10.1016/j.cretres.2017.11.020. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sroka P, Staniczek AH, Kondratieff BC. ‘Rolling’ stoneflies (Insecta: Plecoptera) from mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber. PeerJ. 2018;6:e5354. doi: 10.7717/peerj.5354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Baranov V, Góral T, Ross A. A new genus of Buchonomyiinae (Diptera, Chironomidae) from Upper Cretaceous Burmese amber, with the phylogeny of the subfamily revisited. Cretac. Res. 2017;79:146–152. doi: 10.1016/j.cretres.2017.07.007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Andersen NM, Grimaldi D. A fossil water measurer from the mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber (Hemiptera: Gerromorpha: Hydrometridae) Insect Syst. Evolut. 2001;32:381–392. doi: 10.1163/187631201x00263. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Huang DY, Garrouste R, Azar D, Engel MS, Nel A. The fourth Mesozoic water measurer discovered in mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber (Heteroptera: Hydrometridae: Hydrometrinae) Cretac. Res. 2015;52:118–126. doi: 10.1016/j.cretres.2014.09.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Schädel, M. & Bechly, G. First record of Anisoptera (Insecta: Odonata) from mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber. Zootaxa4103, 537–549, 10.11646/zootaxa.4103.6.4 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 45.Zheng D, Zhang Q, Chang SC, Wang B. A new damselfly (Odonata: Zygoptera: Platystictidae) from mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber. Cretac. Res. 2016;63:142–147. doi: 10.1016/j.cretres.2016.03.006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Zheng D, Nel A, Jarzembowski EA, Wang J, Zhang H, Wang B. New gomphaeschnid dragonflies (Odonata: Anisoptera: Aeshnoptera) from mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber. Cretac. Res. 2019;100:138–144. doi: 10.1016/j.cretres.2019.03.027. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Zheng, D. et al. Mesostictinae subfam. nov., an archaic group of platystictid damselflies (Odonata: Zygoptera) from mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber. J. Syst. Palaeontol.17, 1–8, 10.1080/14772019.2017.1348395 (2019).
- 48.Zheng D, Jarzembowski EA. A brief review of Odonata in mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber. Int. J. Odonatol. 2020;23:13–21. doi: 10.1080/13887890.2019.1688499. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Schädel, M., Mueller, P. & Haug, J. T. Two remarkable fossil insect larvae from Burmese amber suggest the presence of a terminal filum in the direct stem lineage of dragonflies and damselflies (Odonata). Riv. Ital. Paleontolx. Stratigr.126, 13–35, 10.13130/2039-4942/12720 (2020).
- 50.Vermeij GJ. The ecology of marine colonization by terrestrial arthropods. Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2020;56:100930. doi: 10.1016/j.asd.2020.100930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Polhemus JT, Cheng L. Notes on marine water-striders with descriptions of new species. Pac. Insects. 1982;24:219–227. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Andersen NM. A new genus of marine water striders (Hemiptera, Veliidae) with five new species from Malesia. Insect Syst. Evolut. 1991;22:389–404. doi: 10.1163/187631291X00192. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Andersen NM. The evolution of marine insects: Phylogenetic, ecological and geographical aspects of species diversity in marine water striders. Ecography. 1999;22:98–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0587.1999.tb00458.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Dunson WA, Travis J. Patterns in the evolution of physiological specialization in salt-marsh animals. Estuaries. 1994;17:102–110. doi: 10.2307/1352338. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Potapov, G. S., Kolosova, Y. S., Gofarov, M. Y. & Bolotov, I. N. Dragonflies and damselflies (Odonata) from Flores Island, Lesser Sunda Archipelago: New occurrences in extreme environments and an island-level checklist of this group. Ecol. Montenegr.35, 5–25, 10.37828/em.2020.35.2 (2020)
- 56.Wilson KDP. Marine dragonfly under threat at Lantau, Hong Kong (Odonata: Orthetrum poecilops) Agrion. 2020;24:162–168. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Cheng L, Frank JH. Marine insects and their reproduction. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 1993;31:479–506. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Xing L, Stanley EL, Bai M, Blackburn DC. The earliest direct evidence of frogs in wet tropical forests from Cretaceous Burmese amber. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:8770. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26848-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Xing, L. et al. Possible egg masses from amphibians, gastropods, and insects in mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber. Hist. Biol. 1–10, 10.1080/08912963.2019.1677642 (2019).
- 60.Xu L, Wang M, Xin C, Liu C, Wang W. Mangrove distribution in relation to seasonal water salinity and ion compartmentation: A field study along a freshwater-dominated river. Hydrobiologia. 2020;847:549–561. doi: 10.1007/s10750-019-04119-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Zhang Y, Fan D, Qin R. Estuary-shelf interactions off the Changjiang Delta during a dry-wet seasonal transition. Mar. Geol. 2020;426:106211. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106211. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Dwyer RG, et al. Niche partitioning between river shark species is driven by seasonal fluctuations in environmental salinity. Funct. Ecol. 2020;34:2170–2185. doi: 10.1111/1365-2435.13626. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Poinar G. Burmese amber: Evidence of Gondwanan origin and Cretaceous dispersion. Hist. Biol. 2019;31:1304–1309. doi: 10.1080/08912963.2018.1446531. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Licht A, et al. Magmatic history of central Myanmar and implications for the evolution of the Burma Terrane. Gondwana Res. 2020;87:303–319. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2020.06.016. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The amber samples containing the type series and borings of the new piddock species are available in the RMBH, Russian Museum of Biodiversity Hotspots, N. Laverov Federal Center for Integrated Arctic Research of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences (Arkhangelsk, Russia); Natural History Museum (London, UK); Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Nanjing, China); Ru D. A. Smith private collection (Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia), and Division of Invertebrates, American Museum of Natural History (New York, NY, United States of America).