Abstract
Interstitial pregnancy is a rare, life-threatening condition that requires high clinical suspicion for diagnosis. Most cases are discovered after complications have occurred. Many authors have described laparoscopic management. Although previous systematic reviews have compared the attributes and complications associated with interstitial pregnancy, we endeavored to complete the first systematic review and meta-analysis to compare the laparoscopic treatment of interstitial pregnancy with the open approach in the modern age of laparoscopic surgery. We systematically searched PubMed, ClinicalTrials.gov, Scopus, Web of Science, and Cochrane until June 2020 using relevant keywords and screened them for eligibility. We found a statistically significant difference in blood loss between laparoscopic and open surgery (168 mL compared to 1,163 mL). Further, cumulative meta-analysis has revealed that blood loss in laparoscopy has been decreasing over time from 1991 to 2020. Laparoscopic patients took less operative time (63.2 minutes) compared to laparotomy patients (78.2 minutes). Patients in the laparoscopic group spent less time hospitalized (3.7 days) compared to laparotomy patients (5.2 days). Our findings add strength to the position that laparoscopic approaches to interstitial pregnancy can be considered first-line in most situations. The laparoscopic approach was found to have a mean blood loss of 168 mL, and this blood loss seems to decrease over time. Increased gravidity and duration of amenorrhea are positive factors that increase bleeding during the procedure. We are unable to find enough high-quality data to significantly compare successful pregnancy following surgery or risk of mortality in these populations.
Keywords: Ectopic, Laparoscopy, Laparotomy, Meta-analysis
Introduction
Ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy due to implantation outside the normal endometrium, and it is a rare occurrence representing about 2% of all pregnancies [1]. Many risk factors contribute to increasing the incidence of ectopic pregnancy, such as a history of ectopic gestation, tubal adhesions, history of endometriosis or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), the use of some contraceptive devices, and previous tubal surgeries [2]. The most common sites within the fallopian tube include the ampulla (69.9%), isthmus (12%), and interstitium (2.4%) [2,3]. The term “interstitial pregnancy” is used interchangeably with “cornual pregnancy” to describe a pregnancy in the interstitium, although interstitial pregnancy may be considered a more accurate description [4]. Some authors believe the term “cornual pregnancy” should be reserved to refer to gestations in a horn of a bicornuate uterus [5-7].
Symptoms of interstitial pregnancy vary from asymptomatic to non-specific symptoms of suprapubic pain, nausea, vomiting, and vaginal bleeding [5,8]. Therefore, diagnosing interstitial pregnancy presents a challenge for obstetricians; it requires high clinical suspicion, especially in women with the aforementioned risk factors. In the last two decades, there has been a noticeable rise in the incidence of interstitial pregnancies, mainly due to the increased use of contraceptive devices and increased prevalence of PID, in addition to the major advances in imaging technologies and ultrasound [9].
Treatment of cases of interstitial pregnancy range from medical treatment to surgical interventions. Local and systemic methotrexate is the mainline for medical treatment, mainly indicated in young nulliparous women desiring future fertility [9]. Surgical interventions include laparotomy and laparoscopic management.
Recently, laparoscopy has become more common for gynecologic and obstetric procedures as a safe approach with less bleeding and improved surgical outcomes [10,11]. A study by Gyr et al. [12] compared traditional abdominal hysterectomy with minimally invasive laparoscopic hysterectomy with an ultrasonic scalpel and found that the latter reduces the need for analgesia and improves postoperative outcomes. Laparoscopy has also shown considerable efficacy in the management of mild to moderate endometriosis [13] and is considered one of the safest gynecologic operations for removing ovarian masses in adolescents [14].
We aimed to conduct this systematic review and meta-analysis to provide an updated insight into the use of laparoscopy in interstitial pregnancy, in addition to measuring its effectiveness in reducing blood loss and other complications compared to traditional techniques. We endeavored to complete the first systematic review and meta-analysis to compare the laparoscopic treatment of interstitial pregnancy with the open approach in the modern age of laparoscopic surgery.
Methods
We conducted this systematic review and meta-analysis following the guidelines reported in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions [15] and Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement [16].
Literature search
We searched for published studies in four electronic databases: PubMed, ClinicalTrials.gov, Web of Science, Scopus, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) up to June 2020. We used the following strategy for our search: (Laparoscop* OR cornuostomy OR cornu* OR laparotomy OR “cornual evacuation” OR “cornual resection” OR “cornual excision” OR “wedge resection” OR “loop ligature” OR “Vicryl loop placement” OR “conical exeresis” OR hysterectomy OR salping* OR traditional OR classic* OR conventional) AND (“interstitial pregnancy” OR “cornual pregnancy” OR “cornual gestation” OR “interstitial gestation” OR “cornual ectopic”).
Eligibility criteria
All studies that met the following criteria were included: 1) patients=women with interstitial or cornual pregnancy; 2, 3) intervention with or without a comparator=all types of laparoscopic surgeries, open surgeries, or both, 4) outcomes=all reported outcomes, especially those regarding bleeding, operation time, and hospital stay; and 5) study design=all interventional and observational studies (cohort, case-control, cross-sectional, case series, and case reports). We excluded conference abstracts, non-English studies, reviews, and studies that report the effect of only one type of surgery. No restriction on age, place, or publication date was implemented.
Screening and studies selection
Retrieved citations were screened for eligibility in two steps: title and abstract screening in which preliminary eligible records from the first step entered the second one; followed by full-text screening in which the articles were assessed for all criteria to be included in our study. In addition, we manually screened the references of the included studies and previous systematic reviews for additional or missed citations.
Data extraction
After the screening step, we extracted the following data from the eligible studies using a formatted data extraction sheet: 1) summary and baseline characteristics of the patients in each study, including study design, type of operation, number of patients, groups, age, parity, gravidity, previous ectopic pregnancy, and duration of amenorrhea, and 2) any repeated outcomes (reported by two or more studies) including postoperative hospital stay (days), operation time (minutes), blood loss (mL), postoperative pregnancy rate, and ruptured ectopic pregnancy. Data for continuous outcomes were extracted as mean and standard deviation, and dichotomous outcomes were extracted as event and total.
Quality assessment
The quality of the included studies was assessed using four tools according to the study design. We assessed the quality of cohort, case series, and case control studies using three different tools developed by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute [17]. Each tool consisted of questions to assess the risk of bias and confounders. These questions were answered by “yes,” “no,” “not applicable,” “cannot determine,” or “not reported,” and then each study was given a score to guide the overall rating of the quality as “good,” “fair,” or “poor.”
We also assessed the quality of the included case reports using the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) critical appraisal tool for case reports. The tool is composed of some questions developed according to the CARE Guidelines for reporting case reports. These questions were answered by “yes,” “no,” “not applicable,” or “unclear” [18]. We could not assess publication bias due to the small number of included studies according to Egger’s funnel-plot-based methodologies [19].
Data synthesis
Comprehensive meta-analysis and open meta-analyst software were used to perform this meta-analysis. Continuous outcomes were pooled as the mean and standard deviation (SD). Whenever studies provided median and range, we used the methods described by Hozo et al. [20]. to transform these data to mean and SD. Dichotomous data were pooled as proportions. A random-effects model was used. We employed meta-regression models and leave-one-out metaanalysis whenever there was significant heterogeneity. In addition, a cumulative meta-analysis was used to reveal trends in the data over time.
Results
1. Literature search
We identified 96 records after searching PubMed, ClinicalTrials.gov, Web of Science, Scopus, and CENTRAL. The remaining records after removing duplicates were screened for eligibility. Two hundred studies were included in the fulltext screening. We finally included 96 studies. We did not find any missing papers after screening the references of the included trials and previous systematic reviews.
2. Characteristics of the included studies
Our review included 96 studies: 65 case reports, 23 cohort studies, 6 case series, and 2 casecontrol studies conducted between 1992 and 2020 [7-115]. The included studies enrolled 885 patients. A total of 723 patients underwent laparoscopy, while 132 underwent operative laparotomy for the management of ectopic pregnancy. The median age of the included participants ranged from 19 to 42 years. A summary of the included studies and their findings and baseline characteristics of the enrolled patients is shown in Table 1.
Table 1.
Study characteristics
| Study | Type of operation | Study design | Number of patients | Age (yr) | Gravidity | Parity | Duration of amenorrhea | Previous ectopics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Api and Api [74] (2010) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 38 | 3 | 0+2 | 1 | |
| Attia et al. [75] (2005) | Laparotomy | Case report | 1 | 34 | 17 | |||
| Bremner et al. [76] (2000) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 36 | 4 | 1 | 8.5 | 2 |
| Cai et al. [77] (2009) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 32 | 5 | 0+4 | 9.5 | |
| Casadio et al. [78] (2009) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 27 | 3 | 2 | ||
| Chachan et al. [79] (2011) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 36 | 3 | 1 | ||
| Chauhan et al. [80] (2006) | Laparotomy | Case report | 1 | 40 | 3 | 12 | ||
| Chen et al. [94] (2019) | Laparoscopy | Retrospective (cohort/analysis) | 14 | 32.8±5.9 | ||||
| Laparoscopy | 26 | 33.0±5.5 | 1±0.9 | |||||
| Cheng et al. [81] (2009) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 22 | 2 | 0 | ||
| Chin et al. [82] (2004) | Laparotomy | Case report | 1 | 29 | 2 | 0 | 12 | |
| Laparotomy | 1 | 34 | 1 | 0 | 17 | |||
| Choi et al. [96] (2009) | Laparoscopy | Retrospective (cohort/analysis) | 8 | 7.6 | ||||
| Corić et al. [83] (2004) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 42 | 3 | 2 | 5 | |
| Cucinella et al. [86] (2012) | Laparoscopy | Retrospective (cohort/analysis) | 5 | 32 | 1.8 | 7.2 | 1 | |
| Dendas et al. [84] (2017) | Laparotomy | Case report | 1 | 35 | ||||
| Di Tizio et al. [85] (2018) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 26 | ||||
| Laparoscopy | 1 | 30 | ||||||
| Laparoscopy | 1 | 38 | ||||||
| Divry et al. [21] (2007) | Laparotomy | Case report | 1 | 32 | ||||
| Dumesic et al. [22] (2001) | Laparotomy | Case report | 1 | 37 | 3 | 1 | ||
| Faioli et al. [112] (2016) | Laparoscopy | Case series | 3 | |||||
| Gao et al. [88] (2019) | Laparoscopy | Retrospective (cohort/analysis) | 9 | 30.1 | 4.3 | |||
| Garretto et al. [23] (2015) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | |||||
| Garzon et al. [24] (2019) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 30 | 2 | 1 | 12 | |
| Gezer and Mutlu [25] (2004) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 36 | 2 | 1 | 7 | |
| Grant et al. [100] (2017) | Laparoscopy | Retrospective (cohort/analysis) | 44 | 32.6 (NR) | 3 | 4 | 6 | |
| Grimbizis et al. [26] (2004) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 28 | 3 | 2 | 7 | |
| Grobman and Milad [27] (1998) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 31 | 3 | 4 | 7 | |
| Ghazali et al. [106] (2018) | Laparoscopy | Retrospective (cohort/analysis) | 7 | 29.3±5.9 | 2.9±0.7 | 8.4±2.1 | 3 | |
| Laparotomy | 7 | 31.4±7.3 | 2.7±1.5 | 11.0±4.6 | 1 | |||
| Huang et al. [108] (2005) | Laparoscopy | Case series | 4 | 9 | ||||
| Hwang et al. [113] (2011) | Laparoscopy | Case control | 54 | 32.74±5.11 | 0.98±0.74 | 7.7±1.5 | 6 | |
| Laparoscopy | 34 | 31.12±5.99 | 0.82±0.90 | 8±2 | 8 | |||
| Kahramanoglu et al. [110] (2017) | Laparotomy | Case series | 1 | 25 | 4 | 2 | ||
| Laparoscopy | 1 | 28 | 1 | 0 | 7 | |||
| Kalchman and Meltzer [28] (1966) | Laparotomy | Case report | 1 | 28 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Laparotomy | 1 | 29 | 8 | 1 | ||||
| Kasum et al. [29] (1998) | Laparotomy | Case report | 1 | 38 | 5 | 0 | 14 | 2 |
| Kim et al. [114] (2015) | Laparoscopy | Case control | 26 | 32 | 0 | 6 (3-8) | ||
| Laparoscopy | 80 | 31 | 0 | 6 (4-10) | ||||
| Kim et al. [101] (2016) | Laparoscopy | Retrospective (cohort/analysis) | 13 | 31 (25-33) | 1 (1-6) | 0 (0-1) | 7 (5) | |
| Ko et al. [30] (2007) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 32 | 3 | 0 | ||
| Koukoura et al. [31] (2020) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 39 | 1 | 0 | 9 | |
| Kumakiri et al. [32] (2005) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 38 | 2 | 0 | 7.4 | |
| Lai et al. [33] (2016) | Laparotomy | Case report | 1 | 22 | 2 | 1 | 12 | |
| Lam et al. [34] (2004) | Laparotomy | Case report | 1 | 32 | 12 | 1 | ||
| Laparotomy | 1 | 32 | 9 | 2 | ||||
| Lam and Tulandi [8] (1999) | Laparoscopy | Retrospective (cohort/analysis) | 22 | |||||
| Lazard et al. [107] (2011) | Laparoscopy | Case series | 1 | 41 | 4 | 3 | 7 | |
| Laparoscopy | 1 | 32 | 6 | 3 | 8 | |||
| Lee et al. [35] (2011) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 28 | 3 | 1 | ||
| Lialios et al. [36] (2008) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 29 | 3 | 2 | 6.8 | |
| Liao and Ding [37] (2009) | Laparotomy | Case report | 1 | 29 | 6 | 0 | 13 | |
| MacRae et al. [89] (2009) | Laparoscopy | Prospective cohort | 10 | 30 (7.5) | 1 | |||
| Laparotomy | 1 | 24 | ||||||
| Maher and Grimwade [38] (1982) | Laparotomy | Case report | 1 | 31 | 3 | 2 | 6 | |
| Laparotomy | 1 | 36 | 5 | 2 | 13 | |||
| Marfori and Kotzen [39] (2018) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 33 | 3 | 1 | 7.8 | |
| Morita et al. [40] (1997) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 39 | 4 | 2 | 6 | |
| Laparoscopy | 1 | 29 | 0 | 7 | ||||
| Mavrelos et al. (1996) | Laparoscopy | Retrospective (cohort/analysis) | 12 | 37 | 15 | |||
| Moon et al. [103] (2000) | Laparoscopy | Retrospective (cohort/analysis) | 24 | 33.4±5.8 | ||||
| Moon et al. [104] (2010) | Laparoscopy | Retrospective (cohort/analysis) | 20 | 28 (NR) | 6.7 | |||
| Nabeshima et al. [41] (2010) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 38 | 2 | |||
| Ng et al. [98] (2009) | Laparoscopy | Retrospective (cohort/analysis) | 53 | 19-40 | ||||
| Nirgianakis et al. [105] (2017) | Laparoscopy | Retrospective (cohort/analysis) | 10 | 34.5±6.21 | 2.6±1.58 | 1.0±1.05 | 2 | |
| Oelsner et al. [42] (1993) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 29 | ||||
| Laparoscopy | 1 | 21 | ||||||
| Olagundoye et al. [97] (2000) | Laparotomy | Retrospective (cohort/analysis) | 7 | |||||
| Laparoscopy | 66 | |||||||
| Both | 33 | |||||||
| Oral et al. [43] (2014) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 27 | ||||
| Osuga et al. [44] (2001) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 3 | 32 | 3 | 0 | 7 | |
| Pasic et al. [45] (2002) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 21 | 1 | 0 | 8 | |
| Pedroso et al. [46] (2014) | Laparotomy | Case report | 1 | 19 | 1 | 0 | 15 | |
| Pluchino et al. [47] (2009) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 34 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 1 |
| Poujade et al. [48] (2009) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 32 | 5 | 9 | ||
| Pramayadi et al. (2018) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 35 | 2 | 1 | ||
| Quinlan and Newcombe [54] (2007) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 40 | 6 | |||
| Raheem and Afifi [53] (2008) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 35 | 1 | 8 | ||
| Rheinboldt and Ibrahim [52] (2013) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 20 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Ron-el et al. [50] (1988) | Laparotomy | Case report | 1 | 38 | 14 | 1 | ||
| Ross et al. [55] (2006) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 27 | 3 | 1 | 11 | |
| Laparoscopy | 1 | 30 | 2 | 1 | 6 | |||
| Sagiv et al. [51] (2001) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 21 | 3 | 1 | 8 | 1 |
| Sagiv et al. [93] (2013) | Laparotomy | Retrospective (cohort/analysis) | 5 | 33 (20-47) | 5 (1-9) | 2 (0-5) | 6-17 | |
| Laparotomy | 8 | |||||||
| Sahoo et al. [56] (2009) | Laparotomy | Case report | 1 | 28 | 7 | 5+1 | 5 | |
| Said [111] (2016) | Laparoscopy | Case series | 1 | 23 | 1 | |||
| Laparoscopy | 1 | 30 | 4 | 1+2 | 2 | |||
| Laparoscopy | 1 | 25 | 10 | |||||
| Laparoscopy | 1 | 26 | 1 | 0 | 7 | |||
| Sant and Andersen [57] (2012) | Laparotomy | Case report | 1 | 30 | 2 | 0 | 21 | |
| Sarmini and Tate [58] (2005) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 22 | 2 | 0 | ||
| Sherer et al. [59] (1995) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 32 | 2 | 1 | 7 | |
| Soriano et al. [6] (2008) | Laparoscopy | Retrospective (cohort/analysis) | 11 | 34.3±5.8 | 3.7±1.8 | 1.5±1.4 | 59.1±14.7 | 0.5 |
| Laparotomy | 11 | 35.2±4.3 | 4.3±2.1 | 1.7±1.3 | 49.7±8.4 | |||
| Takeda et al. [60] (2009) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 29 | 3 | 2 | 7 | |
| Tinelli et al. [61] (2010) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 34 | ||||
| Laparoscopy | 1 | 37 | 2 | 11 | ||||
| Laparoscopy | 1 | 31 | 7 | |||||
| Tulandi and Al-Jaroudi [90] (2004) | Laparotomy | Retrospective (cohort/analysis) | 32 | 13 | ||||
| Laparotomy | 13 | 7.3±0.4 | ||||||
| Laparoscopy | 11 | 5.4±1.0 | ||||||
| Ugwumadu et al. [62] (1997) | Laparotomy | Case report | 1 | 1 | 33 | |||
| Uludag et al. [92] (2018) | Laparoscopy | Retrospective (cohort/analysis) | 3 | 30.6 (NR) | 1 | 6 | ||
| Vicino et al. [63] (2000) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 39 | 7 | 3 | ||
| Vilos [64] (1995) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 31 | 4 | 2 | 7 | |
| Vilos [65] (2001) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 31 | 8 | |||
| Walid et al. (2010) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 27 | ||||
| Wang et al. [99] (2014) | Laparoscopy | Retrospective (cohort/analysis) | 9 | 30.4 | 7.2 | |||
| Watanabe et al. [91] (2014) | Laparoscopy | Prospective cohort | 13 | 34.6±10.2 | 7.6±1.3 | |||
| Weissman and Fishman [67] (1992) | Laparotomy | Case report | 1 | 34 | 2 | 1 | 20 | |
| Wood and Hurley [68] (1992) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 27 | 6 | |||
| Woodland et al. [69] (1996) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 23 | 8 | |||
| Xu et al. [95] (2018) | Laparoscopy | Retrospective (cohort/analysis) | 14 | 30.9 | 2.21 | 0.14 | 5±7.1 | |
| Yalçın et al. [70] (2015) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 36 | 5 | 3 | 6 | |
| Yang and Song [71] (2018) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 1 | 41 | 7 | |||
| Yoong et al. [109] (2020) | Laparoscopy | Case series | 12 | 31 (20-44) | ||||
| Zhang et al. [72] (2004) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 18 | 5-12 | ||||
| Zhang et al. [73] (2013) | Laparoscopy | Case report | 2 | 30.43 (NR) | 4,2 | 1.1 | 8, 12 | |
| Zuo et al. [87] (2012) | Laparoscopy | Retrospective (cohort/analysis) | 17 | 26.8 (20-35) | 7.8±0.7 |
Data are reported as median (range) or mean ± standard deviation, number.
NR, not reported.
3. Results of risk of bias assessment
According to JBI critical appraisal tool for case reports, the quality of the included reports ranged from moderate to high. Most of the included case reports did not clearly describe patient demographics. However, most of them have clearly reported patients’ history, clinical presentation, diagnostic method, intervention, post-intervention status, and side effects, and provided takeaway lessons for clinical practice.
According to different NIH quality assessment tools for each study design, all case-control studies were of poor quality, while four case series were of fair quality, and the remaining two studies were of poor quality. Regarding cohort studies, 13 studies were of fair quality, and 10 were poor quality.
4. Analysis of the outcomes
1) Blood loss
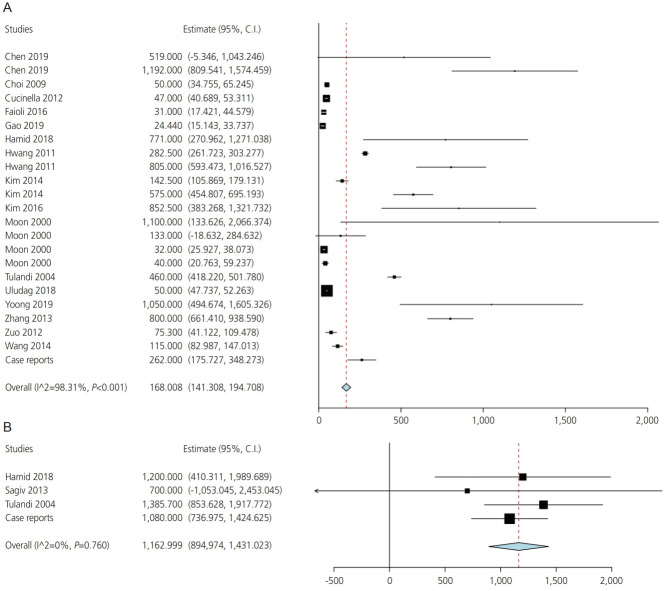
Laparoscopy group
Eighty-three studies reported blood loss in the laparoscopy group. The overall mean blood loss was 168 mL (confidence interval [CI] [141.3, 194.7], P<0.001) (Fig. 1A). There was significant heterogeneity among these studies (I2=98.3%, P<0.001); therefore, a meta-regression model was employed. Gravidity and the duration of amenorrhea explained most of the heterogeneity among the included studies (R2=44% and 51%, respectively) (Supplementary Fig. 1). In addition, the cumulative meta-analysis showed a reduction in blood loss over time from 2000 to 2019 (Supplementary Fig. 2).
Fig. 1.
Blood loss in the laparoscopy (A) and laparotomy (B) groups.
Laparotomy group
Data reported from 27 studies revealed a mean blood loss of 1,163 mL (CI [894.974, 1431.023], P<0.001) in the laparotomy group (Fig. 1B). There was no heterogeneity among the data obtained from these studies (I2= 0%, P=0.8).
2) Operative time
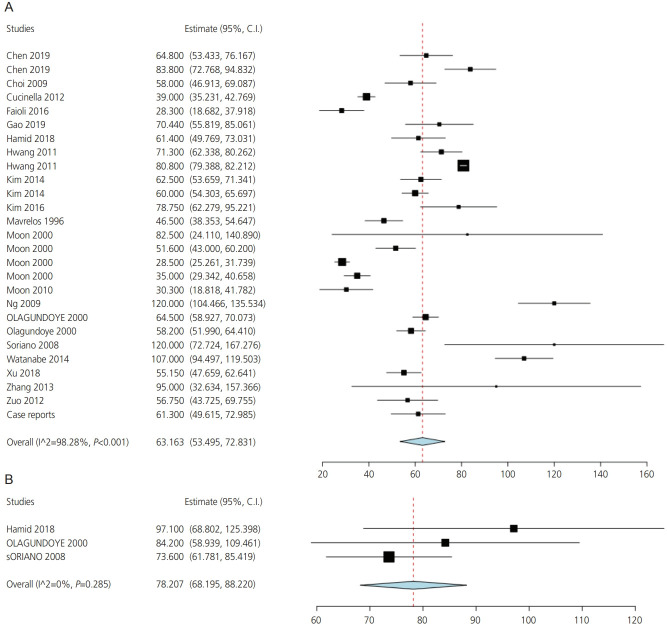
Laparoscopy group
Data on operative time in the laparoscopy group were reported by 52 studies. The overall mean operative time was 63.2 minutes (CI [53.5, 72.8], P<0.001) (Fig. 2A). However, data from these studies showed significant heterogeneity (I2=98.3%, P<0.001). Interestingly, a meta-regression model that included “duration of amenorrhea” as a covariate explained 81% of the between-studies variance (R2=81%) (Supplementary Fig. 3). Cumulative meta-analysis of operative time showed a trend increase in the cumulative mean operative time from 46.5 minutes in 1996 to 63.3 minutes in 2019 (Supplementary Fig. 4).
Fig. 2.
Operative time in the laparoscopy (A) and laparotomy (B) groups.
Laparotomy group
Three studies reported data on operative time in the laparotomy group. No significant heterogeneity (I2= 0%, P=0.3) was found among these studies, and the overall mean operative time was 78.2 minutes (CI [68.2, 88.2], P<0.001) (Fig. 2B).
3) Hospital stay
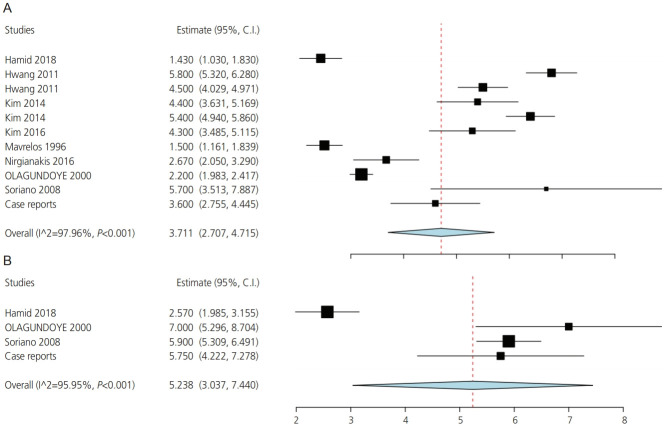
Laparoscopy group
Data on hospital stay in the laparoscopy group were reported by 48 studies. The overall mean hospital stay was 3.7 days (CI [2.7, 4.7], P<0.001) (Fig. 3A). Considerable heterogeneity existed among the included studies (I2=98%, P<0.001). A meta-regression model that included “gravidity” and “year of the study” as covariates explained 95% of the between-studies heterogeneity (R2=0.95) (Supplementary Fig. 5).
Fig. 3.
Length of hospital stay in the laparoscopy (A) and laparotomy (B) groups.
Laparotomy group
Fifteen studies (12 case reports and 3 case series) were included in the meta-analysis for hospital stay in the laparotomy group (Supplementary Fig. 6). The summary estimate for mean hospital stay was 5.2 days (CI [3, 7.4], P<0.001) (Fig. 3B). There was significant heterogeneity among these studies (I2=96%, P<0.001). When the study by Ghazali et al. [106] (2018) was removed in a leave-one-out meta-analysis, heterogeneity was minimal (I2=0%, P=0.5) (Supplementary Fig. 7).
4) Incidence of rupture
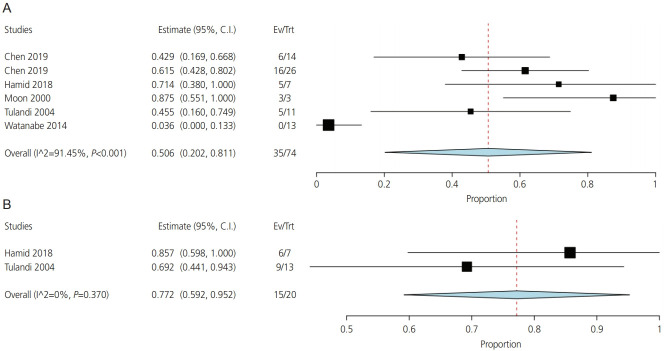
Laparoscopy group
Six studies provided analyzable data for the incidence of rupture in the laparoscopy group. The summary effect size was 0.51 (CI [0.2, 0.8], P<0.001) (Fig. 4A). There was significant heterogeneity among these studies (I2=91%, P<0.001). When the study of Watanabe et al. (2014) [91] was removed in a leave-one-out meta-analysis, heterogeneity was minimal (I2=0%, P=0.7) (Supplementary Fig. 8).
Fig. 4.
Incidence of rupture in the laparoscopy (A) and laparotomy (B) groups.
Laparotomy group
Only two studies that included 20 patients reported data on the incidence of ectopic rupture in the laparotomy group. The overall effect estimate was 0.77 (CI [0.59, 0.95], P<0.001). No significant heterogeneity was found (I2=0%, P=0.4) (Fig. 4B).
5) Future pregnancy rate
Laparoscopy group
Data on future pregnancy rates were provided by 10 studies. The summary effect estimate was 0.62 (CI [0.42, 0.82], P<0.001). Significant heterogeneity was observed among these studies (I2=86.4%, P<0.001), and a meta-regression model was fitted to explain this heterogeneity. The duration of amenorrhea and sample size were responsible for almost all the heterogeneity among the effect estimates (R2=1).
Laparotomy group
The available studies provided no data on the future pregnancy rate in the laparotomy group.
Discussion
Our analysis showed less blood loss in the laparoscopic group (168 mL) than in laparotomy patients (1,163 mL). An increased duration of amenorrhea and gravidity is associated with increased blood loss in laparoscopic patients. Interestingly, blood loss in laparoscopy has been decreasing over time, as shown by cumulative meta-analysis. This is consistent with the nature of laparoscopic operations. Laparoscopic patients took less operative time (63.2 minutes) compared to laparotomy patients (78.2 minutes). However, the mean operative time for the laparoscopic approach is actually increasing over time. Patients in the laparoscopic group spent less time hospitalized (3.7 days) compared to laparotomy patients who spent 5.2 days in the hospital on average. More recently performed studies and women with higher gravidity were both associated with a shorter hospital stay for patients in the laparoscopic group.
Laparotomy patients had a higher incidence of ectopic pregnancy rupture (77%) than patients who underwent laparoscopic surgery (51%). However, we could not employ a meta-regression model because of the low number of studies. The study by Watanabe et al. [91] (2014) significantly contributed to this heterogeneity as it reported a much lower incidence of ruptured ectopic pregnancy (0/13) than in other studies.
Only two previous systematic reviews have discussed the different management strategies, including laparoscopy and laparotomy [103,104]. These studies discussed and compared most medical and surgical options, but stopped short of a direct meta-analysis of the laparoscopic versus open approach. This is likely because these systematic reviews predate most of the high-quality data we were able to utilize to complete this analysis, being published in 2000 and 2010, respectively. Outside of isolating for interstitial pregnancy, many authors have completed reviews comparing open and laparoscopic ectopic pregnancies. For example, a meta-analysis by Gao et al. [116] compared laparoscopy and laparotomy for ectopic pregnancy and showed similar results regarding blood loss. However, they found no difference between laparoscopy and laparotomy in terms of operation time, which we found was lower in the laparoscopic group.
Both techniques have some advantages and drawbacks. Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgery and is associated with improved cosmesis, shorter hospital stay, faster recovery, less postoperative pain, and a higher rate of preservation of the uterus [6,98,117]. A laparoscopic approach, however, also has some drawbacks such as higher incidences of hematomas of the abdominal and abdominal or pelvic infections, although major complications are rarely reported [118]. There was not sufficient data to meaningfully analyze all possible laparoscopic techniques separately, and it is likely that the increased operative time for laparoscopic procedures from 1996 to 2019 was a result of more complex procedures and the advent of robotic-assisted laparoscopy.
Laparotomy is also a widely used management technique, especially when adequate closure or hemostasis cannot be achieved by laparoscopy, and when surgeons without laparoscopic expertise are available. Laparotomy, however, has multiple risks including the general risks of anesthesia and surgery, incisional hernia, serious infections, bleeding, and injury of pelvic or abdominal organs. All of these are reported more often in open approaches [106,113].
We included all studies reporting data regarding the safety and efficacy of laparoscopic surgery or laparotomy (or both) in the management of interstitial or cornual ectopic pregnancy patients, as indicated in our PRISMA flow chart (Supplementary Fig. 9). Additionally, most of the heterogeneity detected among the studies was managed. The quality of most of the included studies was fair, and a large number of studies entered the analysis, which increases the generalizability of the results. A cumulative meta-analysis was also used to reveal trends in the data over time.
Limitations of this study would include the lack of data regarding long-term effects, as we were able to find little or no data regarding late complications or overall survival. We reported what little we did find with regard to future pregnancy following surgical intervention. Another limitation is that all of the included studies were observational, which is generally considered at a low level of evidence. Lastly, the authors admit that the possibility of publication bias affecting results also exists.
Conclusion
Our analysis supports laparoscopy as the mainline surgical option for patients with interstitial pregnancy. Laparoscopy was associated with an average blood loss of 168 mL, a mean operative time of one hour, and an average hospitalization time of 3.7 days. Our review shows that complications decrease over time. Interestingly, our analysis showed that both increased gravidity and duration of amenorrhea are positive risk factors leading to increased bleeding. Compared with laparotomy, management with laparoscopic surgery is associated with less blood loss, less operative time, and a shorter hospital stay. Laparotomy is also associated with a higher incidence of rupture of ectopic pregnancy.
Further interventional studies with a larger sample size and longer follow-up duration are needed to produce more valid results. We believe as the first systematic review to address this topic, our findings add strength to the position that laparoscopic approaches to interstitial pregnancy can be considered first-line in most situations.
Acknowledgments
The Marchand Institute for Minimally Invasive Surgery would like to acknowledge all the researchers, students, residents, and fellows who put time and effort without compensation into our projects for the benefit of women’s health, and firmly assure them that the future of medicine belongs to them.
Footnotes
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Ethical approval
The study was performed in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Patient consent
Written informed consent and the use of images from patients are not required for the publication.
Funding information
None.
Condensation
Many authors have described laparoscopic management of interstitial pregnancy. We performed the first systematic review of modern laparoscopy to assess the appropriateness of the laparoscopic approach as first-line management.
IRB approval
Found exempt at the Marchand Institute July 2020 IRB Meeting (2020-04-855).
Prospero registration number
CRD42020185248.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary materials associated with this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.5468/ogs.20299
Meta-regression model of blood loss in the laparoscopy group.
Cumulative meta-analysis of blood loss. CI, confidence interval.
Meta-regression model of operative time in the laparoscopy group.
Cumulative meta-analysis of operative time. CI, confidence interval.
Meta-regression model of hospital stay in the laparoscopy group.
Meta-regression model of the future pregnancy rate in the laparoscopy group.
Cumulative meta-analysis of hospital stay. CI, confidence interval.
Cumulative meta-analysis of incidence of rupture. CI, confidence interval.
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) flow chart.
References
- 1.Jones T, Ho JR, Gualtieri M, Bruno-Gaston J, Chung K, Paulson RJ, et al. Clomiphene stair-step protocol for women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131:91–5. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000002418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Attar E. Endocrinology of ectopic pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2004;31:779–94. doi: 10.1016/j.ogc.2004.08.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Stulberg DB, Cain LR, Dahlquist I, Lauderdale DS. Ectopic pregnancy rates and racial disparities in the Medicaid population, 2004-2008. Fertil Steril. 2014;104:1671–6. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2014.08.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ghaneie A, Grajo JR, Derr C, Kumm TR. Unusual ectopic pregnancies: sonographic findings and implications for management. J Ultrasound Med. 2015;34:951–62. doi: 10.7863/ultra.34.6.951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Habana A, Dokras A, Giraldo JL, Jones EE. Cornual heterotopic pregnancy: contemporary management options. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000;182:1264–70. doi: 10.1067/mob.2000.103620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Soriano D, Vicus D, Mashiach R, Schiff E, Seidman D, Goldenberg M. Laparoscopic treatment of cornual pregnancy: a series of 20 consecutive cases. Fertil Steril. 2008;90:839–43. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2007.07.1288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Faraj R, Steel M. Management of cornual (interstitial) pregnancy. Obstet Gynaecol. 2007;9:249–55. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lau S, Tulandi T. Conservative medical and surgical management of interstitial ectopic pregnancy. Fertil Steril. 1999;72:207–15. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(99)00242-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Moawad NS, Mahajan ST, Moniz MH, Taylor SE, Hurd WW. Current diagnosis and treatment of interstitial pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2010;202:15–29. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2009.07.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Levine DJ. Safety and efficacy of laparoscopy for benign gynecologic conditions. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2001;184:1585–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tadir Y, Fisch B. Operative laparoscopy: a challenge for general gynecology? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993;169:7–12. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(93)90122-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gyr T, Ghezzi F, Arslanagic S, Leidi L, Pastorelli G, Franchi M. Minimal invasive laparoscopic hysterectomy with ultrasonic scalpel. Am J Surg. 2001;181:516–9. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(01)00636-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sulewski JM, Curcio FD, Bronitsky C, Stenger VG. The treatment of endometriosis at laparoscopy for infertility. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1980;138:128–32. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(80)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Grabowski A, Korlacki W, Pasierbek M. Laparoscopy in elective and emergency management of ovarian pathology in children and adolescents. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2014;9:164–9. doi: 10.5114/wiitm.2014.41626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Higgins JP, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, et al. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. 2nd ed. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6:e1000097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.National Institute of Health National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute . Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Health National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute; c2020. Quality Assessment Tools [Internet] [cited 2020 Aug 2]. Available from: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/study-quality-assessment-tools. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Moola S, Munn Z, Tufanaru C, Aromataris E, Sears K, Sfetcu R, et al. Adelaide: JBI; c2020. Chapter 7: Systematic reviews of etiology and risk. [Internet] [cited 2020 Aug 2]. Available from: https://wiki.jbi.global/display/MANUAL/Chapter+7%3A+Systematic+reviews+of+etiology+and+risk. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315:629–34. doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2005;5:13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-5-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Divry V, Hadj S, Bordes A, Genod A, Salle B. Case of progressive intrauterine twin pregnancy after surgical treatment of cornual pregnancy. Fertil Steril. 2007;87:190.e1–3. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2006.04.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Dumesic DA, Damario MA, Session DR. Interstitial heterotopic pregnancy in a woman conceiving by in vitro fertilization after bilateral salpingectomy. Mayo Clin Proc. 2001;76:90–2. doi: 10.4065/76.1.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Garretto D, Lee LN, Budorick NE, Figueroa R. Interstitial twin pregnancy: a unique case presentation. J Clin Ultrasound. 2015;43:447–50. doi: 10.1002/jcu.22209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Garzon S, Laganà AS, Pomini P, Raffaelli R, Ghezzi F, Franchi M. Laparoscopic reversible occlusion of uterine arteries and cornuostomy for advanced interstitial pregnancy. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2019;28:359–62. doi: 10.1080/13645706.2018.1547764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gezer A, Mutlu H. Laparoscopic management of cornual pregnancy without sutures. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2004;270:194–6. doi: 10.1007/s00404-003-0501-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Grimbizis GF, Tsalikis T, Mikos T, Zepiridis L, Athanasiadis A, Tarlatzis BC, et al. Case report: laparoscopic treatment of a ruptured interstitial pregnancy. Reprod Biomed Online. 2004;9:447–51. doi: 10.1016/s1472-6483(10)61282-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Grobman WA, Milad MP. Conservative laparoscopic management of a large cornual ectopic pregnancy. Hum Reprod. 1998;13:2002–4. doi: 10.1093/humrep/13.7.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kalchman GG, Meltzer RM. Interstitial pregnancy following homolateral salpingectomy. Report of 2 cases and a review of the literature. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1966;96:1139–43. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(66)90524-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kasum M, Grizelj V, Simunic V. Combined interstitial and intrauterine pregnancies after in-vitro fertilization and embryo transfer. Hum Reprod. 1998;13:1547–9. doi: 10.1093/humrep/13.6.1547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ko ML, Jeng CJ, Chou CS, She BC, Chen SC, Tzeng CR. Laparoscopic electrodessication of an interstitial pregnancy. Fertil Steril. 2007;88:705.e19–20. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2006.11.140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Koukoura O, Dragoumis G, Gorila G, Gkorezi-Ntavela I, Dafopoulos K, Pistofidis G. Spontaneous intraoperative rupture of a large interstitial pregnancy: laparoscopic management. Case Rep Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Apr 14; doi: 10.1155/2020/5626783. [Epub]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kumakiri J, Takeuchi H, Kitade M, Kikuchi I, Shimanuki H, Kubo M, et al. Interstitial pregnancy with huge adenomyosis uteri managed laparoscopically by using pre-operative and intra-operative imaging: case report. BJOG. 2005;112:1578–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2005.00738.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lai YJ, Lin CH, Hou WC, Hwang KS, Yu MH, Su HY. Pregnancy in a noncommunicating rudimentary horn of a unicornuate uterus: prerupture diagnosis and management. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;55:604–6. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2016.06.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lam PM, Lok IH, Yip SK. Two cases of heterotopic cornual pregnancy with initially missed diagnosis. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2004;44:256–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1479-828X.2004.00179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lee ES, Hahn HS, Park BJ, Ro DY, Kim JH, Kim YW. Single-port laparoscopic cornual resection for a spontaneous cornual ectopic pregnancy following ipsilateral salpingectomy. Fertil Steril. 2011;96:e106–10. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2011.05.097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lialios GA, Kallitsaris A, Kabisios T, Messinis IE. Ruptured heterotopic interstitial pregnancy: rare case of acute abdomen in a Jehovah’s Witness patient. Fertil Steril. 2008;90:1200.e15–7. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2007.11.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Liao CY, Ding DC. Repair of uterine rupture in twin gestation after laparoscopic cornual resection. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2009;16:493–5. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2009.03.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Maher PJ, Grimwade JC. Cornual pregnancy--diagnosis before rupture a report of 2 cases. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 1982;22:172–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1479-828x.1982.tb01437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Marfori CQ, Kotzen M. Angular vs. interstitial pregnancy: a case report highlighting diagnostic nuances with stark management differences. Case Rep Womens Health. 2018;19:e00068. doi: 10.1016/j.crwh.2018.e00068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Morita Y, Tsutsumi O, Momoeda M, Taketani Y. Cornual pregnancy successfully treated laparoscopically with fibrin glue hemostasis. Obstet Gynecol. 1997;90(4 Pt 2):685–7. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(97)00398-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Nabeshima H, Nishimoto M, Utsunomiya H, Arai M, Ugajin T, Terada Y, et al. Total laparoscopic conservative surgery for an intramural ectopic pregnancy. Diagn Ther Endosc. 2010 Oct 11; doi: 10.1155/2010/504062. [Epub]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Oelsner G, Admon D, Shalev E, Shalev Y, Kukia E, Mashiach S. A new approach for the treatment of interstitial pregnancy. Fertil Steril. 1993;59:924–5. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)55883-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Oral S, Akpak YK, Karaca N, Babacan A, Savan K. Cornual heterotopic pregnancy after bilateral salpingectomy and uterine septum resection resulting in term delivery of a healthy infant. Case Rep Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Nov 5; doi: 10.1155/2014/157030. [Epub]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Osuga Y, Tsutsumi O, Fujiwara T, Kugu K, Fujimoto A, Taketani Y. Usefulness of long-jaw forceps in laparoscopic cornual resection of interstitial pregnancies. J Am Assoc Gynecol Laparosc. 2001;8:429–32. doi: 10.1016/s1074-3804(05)60344-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Pasic RP, Hammons G, Gardner JS, Hainer M. Laparoscopic treatment of cornual heterotopic pregnancy. J Am Assoc Gynecol Laparosc. 2002;9:372–5. doi: 10.1016/s1074-3804(05)60420-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Pedroso C, Lermann R, Amaral N, Condeço P. Interstitial pregnancy rupture at 15 weeks of pregnancy. BMJ Case Rep. 2014 Aug 25; doi: 10.1136/bcr-2014-203979. [Epub]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Pluchino N, Ninni F, Angioni S, Carmignani A, Genazzani AR, Cela V. Spontaneous cornual pregnancy after homolateral salpingectomy for an earlier tubal pregnancy: a case report and literature review. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2009;16:208–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2008.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Poujade O, Ducarme G, Luton D. Cornual heterotopic pregnancy: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2009 Jun 23; doi: 10.4076/1752-1947-3-7233. [Epub]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Tsuchiya A, Komatsu Y, Matsuyama R, Tsuchiya H, Takemura Y, Nishii O. Intraoperative and postoperative clinical evaluation of the hysteroscopic morcellator system for endometrial polypectomy: a prospective, randomized, single-blind, parallel group comparison study. Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther. 2018;7:16. doi: 10.4103/GMIT.GMIT_6_17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ron-el R, Langer R, Herman A, Caspi E, Bukovsky Y. Term delivery following mid‐trimester ruptured cornual pregnancy with combined intrauterine pregnancy. Case report. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1988;95:619–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1988.tb09495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Sagiv R, Golan A, Arbel-Alon S, Glezerman M. Three conservative approaches to treatment of interstitial pregnancy. J Am Assoc Gynecol Laparosc. 2001;8:154–8. doi: 10.1016/s1074-3804(05)60567-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Rheinboldt M, Ibrahim S. Atypical presentation of a large interstitial pregnancy. Emerg Radiol. 2013;20:251–4. doi: 10.1007/s10140-012-1096-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Raheem M, Afifi Y. Laparoscopic selective ipsilateral uterine artery ligation for the management of a cornual ectopic pregnancy. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2008;15:260–1. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2008.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Quinlan D, Newcombe M. Cornual ectopic pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2007;29:537–8. doi: 10.1016/s1701-2163(16)32512-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Ross R, Lindheim SR, Olive DL, Pritts EA. Cornual gestation: a systematic literature review and two case reports of a novel treatment regimen. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2006;13:74–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2005.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Sahoo S, Jose J, Shah N, Opemuyi I. Recurrent cornual ectopic pregnancies. Gynecol Surg. 2009;6:389–91. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Sant CLH, Andersen PE. Misdiagnosed uterine rupture of an advanced cornual pregnancy. Case Rep Radiol. 2012 Apr 3; doi: 10.1155/2012/289103. [Epub]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Sarmini RO, Tate D. Ruptured left cornual gestation in an unstable patient. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2005;12:383. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2005.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Sherer DM, Scibetta JJ, Sanko SR. Heterotopic quadruplet gestation with laparoscopic resection of ruptured interstitial pregnancy and subsequent successful outcome of triplets. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1995;172:216–7. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(95)90119-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Takeda A, Koyama K, Imoto S, Mori M, Sakai K, Nakamura H. Successful management of interstitial pregnancy with fetal cardiac activity by laparoscopicassisted cornual resection with preoperative transcatheter uterine artery embolization. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2009;280:305–8. doi: 10.1007/s00404-008-0896-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Tinelli A, Malvasi A, Pellegrino M, Pontrelli G, Martulli B, Tsin DA. Laparoscopical management of cornual pregnancies: a report of three cases. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2010;151:199–202. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2010.03.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Ugwumadu AHN, Hamid R, Ross LD. Live infant salvaged from a ruptured cornual (interstitial) pregnancy at 33-weeks gestation. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 1997;58:247–9. doi: 10.1016/s0020-7292(97)00089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Vicino M, Loverro G, Resta L, Bettocchi S, Vimercati A, Selvaggi L. Laparoscopic cornual excision in a viable large interstitial pregnancy without blood flow detected by color Doppler ultrasonography. Fertil Steril. 2000;74:407–9. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(00)00636-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Vilos GA. Laparoscopic resection of a heterotopic cornual pregnancy followed by term vaginal delivery. J Am Assoc Gynecol Laparosc. 1995;2:471–3. doi: 10.1016/s1074-3804(05)80073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Vilos GA. Laparoscopic ligation and resection of two ipsilateral interstitial pregnancies in the same patient. J Am Assoc Gynecol Laparosc. 2001;8:299–302. doi: 10.1016/s1074-3804(05)60595-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Chopra S, Keepanasseril A, Rohilla M, Bagga R, Kalra J, Jain V. Obstetric morbidity and the diagnostic dilemma in pregnancy in rudimentary horn: retrospective analysis. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2009;280:907–10. doi: 10.1007/s00404-009-1013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Weissman A, Fishman A. Uterine rupture following conservative surgery for interstitial pregnancy. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1992;44:237–9. doi: 10.1016/0028-2243(92)90105-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Wood C, Hurley V. Ultrasound diagnosis and laparoscopic excision of an interstitial ectopic pregnancy. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 1992;32:371–2. doi: 10.1111/j.1479-828x.1992.tb02855.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Woodland MB, DePasquale SE, Molinari JA, Sagullo CC. Laparoscopic approach to interstitial pregnancy. J Am Assoc Gynecol Laparosc. 1996;3:439–41. doi: 10.1016/s1074-3804(96)80079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Yalçın Y, Tatar B, Erdemoğlu E, Akkurt MÖ, Yavuz A, Erdemoğlu E. Laparoscopic systemic devascularization of uterine cornu for cornual resection in interstitial pregnancy. Turk J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;12:182–4. doi: 10.4274/tjod.23500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Yang H, Song T. Temporary simultaneous 2 arterial occlusions during laparoscopic management for cornual ectopic pregnancy. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2018;25:961–2. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2018.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Zhang X, Liu X, Fan H. Interstitial pregnancy and transcervical curettage. Obstet Gynecol. 2004;104(5 Pt 2):1193–5. doi: 10.1097/01.AOG.0000132807.44055.f5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Zhang K, Yuan P. Laparoscopy-assisted vaginal cornual resection for the treatment of large interstitial pregnancy. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2013;23:783–6. doi: 10.1089/lap.2013.0177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Api M, Api O. Laparoscopic cornuotomy in the management of an advanced interstitial ectopic pregnancy: a case report. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2010;26:208–2. doi: 10.1080/09513590903215524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Attia M, Karuppaswamy J, Griffith H. Management of interstitial (cornual) pregnancy at 17 weeks’ gestation: conservation of a ruptured uterus. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2005;25:722–3. doi: 10.1080/01443610500307391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Bremner T, Cela V, Luciano AA. Surgical management of interstitial pregnancy. J Am Assoc Gynecol Laparosc. 2000;7:387–9. doi: 10.1016/s1074-3804(05)60483-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Cai Z, Wang F, Cao H, Xia Q. Transcervical suction of interstitial pregnancy under laparoscopic and hysteroscopic guidance. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2009;16:761–4. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2009.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Casadio P, Formelli G, Spagnolo E, De Angelis D, Marra E, Armillotta F, et al. Laparoscopic treatment of interstitial twin pregnancy. Fertil Steril. 2009;92:390.e13–7. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.03.063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Chachan S, Waters N, Kent A. Laparoscopic management of cornual heterotopic pregnancy with the use of Harmonic ACE®-a case report. Gynecol Surg. 2011;8:243–6. [Google Scholar]
- 80.Chauhan M, Chaudhary P, Dahiya P, Sangwan K, Sen J. Molar cornual ectopic pregnancy. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2006;85:625–6. doi: 10.1080/00016340600604302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Cheng Z, Xu L, Zhu Y, Dai H, Qu X, Gong J. Laparoscopic uterine vessels occlusion for the treatment of interstitial pregnancy. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2009;19:509–12. doi: 10.1089/lap.2008.0361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Chin HY, Chen FP, Wang CJ, Shui LT, Liu YH, Soong YK. Heterotopic pregnancy after in vitro fertilizationembryo transfer. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2004;86:411–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijgo.2004.05.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Corić M, Barisić D, Strelec M. Laparoscopic approach to interstitial pregnancy. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2004;270:287–9. doi: 10.1007/s00404-003-0499-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Dendas W, Schobbens JC, Mestdagh G, Meylaerts L, Verswijvel G, Van Holsbeke C. Management and outcome of heterotopic interstitial pregnancy: case report and review of literature. Ultrasound. 2017;25:134–42. doi: 10.1177/1742271X17710965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Di Tizio L, Spina MR, Gustapane S, D’Antonio F, Liberati M. Interstitial pregnancy: from medical to surgical approach-report of three cases. Case Rep Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Oct 15; doi: 10.1155/2018/2815871. [Epub]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Cucinella G, Rotolo S, Calagna G, Granese R, Agrusa A, Perino A. Laparoscopic management of interstitial pregnancy: the “purse-string” technique. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2012;91:996–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0412.2012.01437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Zuo X, Shen A, Chen M. Successful management of unruptured interstitial pregnancy in 17 consecutive cases by using laparoscopic surgery. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2012;52:387–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1479-828X.2012.01455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Gao B, Cheng C, Pan Q, Johnson G, Qin X, Xu D. Laparoscopic strategy for heterotopic interstitial pregnancy following assisted reproductive techniques. JSLS. 2019 Apr-Jun; doi: 10.4293/JSLS.2018.00109. [Epub]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.MacRae R, Olowu O, Rizzuto MI, Odejinmi F. Diagnosis and laparoscopic management of 11 consecutive cases of cornual ectopic pregnancy. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2009;280:59–64. doi: 10.1007/s00404-008-0872-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Tulandi T, Al-Jaroudi D. Interstitial pregnancy: results generated from the society of reproductive surgeons registry. Obstet Gynecol. 2004;103:47–50. doi: 10.1097/01.AOG.0000109218.24211.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Watanabe T, Watanabe Z, Watanabe T, Fujimoto K, Sasaki E. Laparoscopic cornuotomy for interstitial pregnancy and postoperative course. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2014;40:1983–8. doi: 10.1111/jog.12422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Uludag SZ, Kutuk MS, Dolanbay M, Ozgun MT, Eliyeva G, Altun O. Conservative management of interstitial pregnancies: experience of a single centre. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2018;38:848–53. doi: 10.1080/01443615.2017.1417979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Sagiv R, Debby A, Keidar R, Kerner R, Golan A. Interstitial pregnancy management and subsequent pregnancy outcome. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2013;92:1327–30. doi: 10.1111/aogs.12239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Chen PL, Lin HH, Hsiao SM. Predictors of subsequent pregnancy in women who underwent laparoscopic cornuostomy or laparoscopic wedge resection for interstitial pregnancy. J Chin Med Assoc. 2019;82:138–42. doi: 10.1097/JCMA.0000000000000016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Xu W, Lin X, Huang D, Zhang S. Laparoscopic treatment of cornual heterotopic pregnancy: a retrospective cohort study. Int J Surg. 2018;53:98–102. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.03.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Choi YS, Eun DS, Choi J, Shin KS, Choi JH, Park HD. Laparoscopic cornuotomy using a temporary tourniquet suture and diluted vasopressin injection in interstitial pregnancy. Fertil Steril. 2009;91:1933–7. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Olagundoye V, Adeghe J, Guirguis M, Cox C, Murphy D. Laparoscopic surgical management of ectopic pregnancy: a district general hospital experience. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2000;20:620–3. doi: 10.1080/01443610020001495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Ng S, Hamontri S, Chua I, Chern B, Siow A. Laparoscopic management of 53 cases of cornual ectopic pregnancy. Fertil Steril. 2009;92:448–52. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.08.072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Wang YL, Weng SS, Huang WC, Su TH. Laparoscopic management of ectopic pregnancies in unusual locations. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2014;53:466–70. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2014.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Grant A, Murji A, Atri M. Can the presence of a surrounding endometrium differentiate eccentrically located intrauterine pregnancy from interstitial ectopic pregnancy? J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2017;39:627–34. doi: 10.1016/j.jogc.2017.03.087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Kim MJ, Jung YW, Cha JH, Seok HH, Han JE, Seong SJ, et al. Successful management of heterotopic cornual pregnancy with laparoscopic cornual resection. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2016;203:199–203. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2016.04.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Mencaglia L, Tiso E, Tantini C, Bianchi R. Risks of virus transmission during diagnostic hysteroscopy. J Am Assoc Gynecol Laparosc. 1996;3(4, Supplement):S30. doi: 10.1016/s1074-3804(96)80237-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Moon HS, Choi YJ, Park YH, Kim SG. New simple endoscopic operations for interstitial pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000;182:114–21. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(00)70499-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Moon HS, Kim SG, Park GS, Choi JK, Koo JS, Joo BS. Efficacy of bleeding control using a large amount of highly diluted vasopressin in laparoscopic treatment for interstitial pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2010;203:30, e1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2010.02.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Nirgianakis K, Papadia A, Grandi G, McKinnon B, Bolla D, Mueller MD. Laparoscopic management of ectopic pregnancies: a comparison between interstitial and “more distal” tubal pregnancies. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2017;295:95–101. doi: 10.1007/s00404-016-4191-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Ghazali WAHW, Abidin NHZ, Muda AM, Hamid HA. Comparative study on surgical outcomes between laparoscopic and open cornuotomy in urban tertiary center of Malaysia. Gynecol Minim invasive Ther. 2018;7:22–6. doi: 10.4103/GMIT.GMIT_7_17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Lazard A, Poizac S, Courbiere B, Cravello L, Gamerre M, Agostini A. Cornual resection for interstitial pregnancy by laparoendoscopic single-site surgery. Fertil Steril. 2011;95:2432, e5–8. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2011.03.056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Huang MC, Su TH, Lee MY. Laparoscopic management of interstitial pregnancy. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2005;88:51–2. doi: 10.1016/j.ijgo.2004.09.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Yoong W, Neophytou C, de Silva L, Adeyemo A, Lodhi W. Novel laparoscopic cornual resection of interstitial pregnancy using the Endo GIATM Universal Stapler (Medtronic): a series of 12 cases. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2020;60:130–4. doi: 10.1111/ajo.13082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Kahramanoglu I, Mammadov Z, Turan H, Urer A, Tuten A. Management options for interstitial ectopic pregnancies: a case series. Pak J Med Sci. 2017;33:476–82. doi: 10.12669/pjms.332.12093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Said TH. Laparoscopic management of interstitial ectopic using simple and safe technique: case series and review of literature. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2016;66(Suppl 1):482–7. doi: 10.1007/s13224-016-0862-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Faioli R, Berretta R, Dall’Asta A, Di Serio M, Galli L, Monica M, et al. Endoloop technique for laparoscopic cornuectomy: a safe and effective approach for the treatment of interstitial pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2016;42:1034–7. doi: 10.1111/jog.13005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Hwang JH, Lee JK, Lee NW, Lee KW. Open cornual resection versus laparoscopic cornual resection in patients with interstitial ectopic pregnancies. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2011;156:78–82. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2010.12.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Kim MK, Kim JJ, Choi JS, Eom JM, Lee JH. Prospective comparison of single port versus conventional laparoscopic surgery for ectopic pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2015;41:590–5. doi: 10.1111/jog.12595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Cucinella G, Calagna G, Rotolo S, Granese R, Saitta S, Tonni G, et al. Interstitial pregnancy: a ‘road map’ of surgical treatment based on a systematic review of the literature. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2014;78:141–9. doi: 10.1159/000364869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Gao M, Gao Q, Jia J, Bao L, Zhang P, Tian JH, et al. Laparoscopy versus laparotomy for ectopic pregnancy: a systematic review. Chinese Journal of Evidence-Based Medicine. 2009;9:994–1000. [Google Scholar]
- 117.Ehrenberg-Buchner S, Sandadi S, Moawad NS, Pinkerton JS, Hurd WW. Ectopic pregnancy: role of laparoscopic treatment. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2009;52:372–9. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0b013e3181b0be24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Rempen A, Dietl J. Complication rates after surgical treatment of ectopic pregnancy. Hum Reprod. 1999;14:1401–3. doi: 10.1093/humrep/14.5.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Meta-regression model of blood loss in the laparoscopy group.
Cumulative meta-analysis of blood loss. CI, confidence interval.
Meta-regression model of operative time in the laparoscopy group.
Cumulative meta-analysis of operative time. CI, confidence interval.
Meta-regression model of hospital stay in the laparoscopy group.
Meta-regression model of the future pregnancy rate in the laparoscopy group.
Cumulative meta-analysis of hospital stay. CI, confidence interval.
Cumulative meta-analysis of incidence of rupture. CI, confidence interval.
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) flow chart.