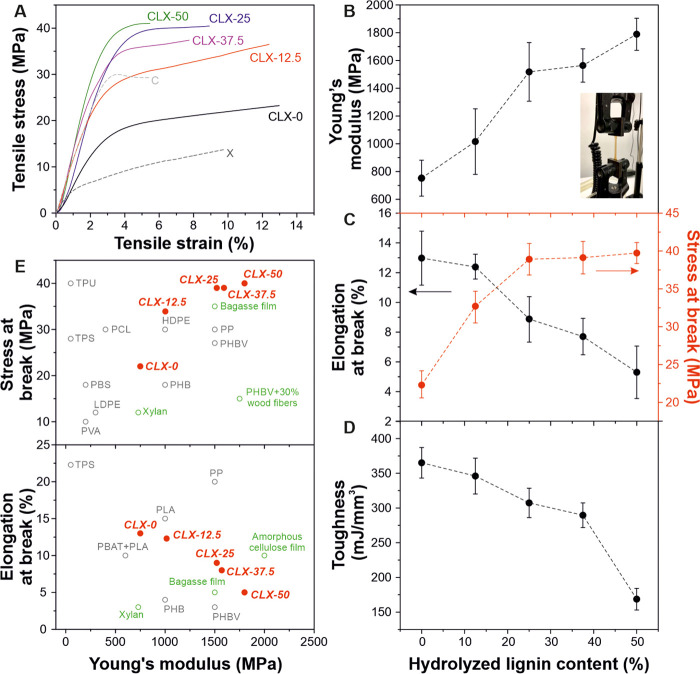
Figure 3.
(A) Typical stress–strain curves of CLX-0, CLX-12.5, CLX-25, CLX-37.5, and CLX-50 films and of C and X control samples. (B, C, D) Young’s modulus, elongation, and stress at break, and toughness parameters, respectively, for the lignin-based bioplastics. The inset in B shows a photo of a lignin-based bioplastic during a tensile test. (E) Ashby plots of stress and elongation at break versus Young’s Modulus data for CLX-0, CLX-12.5, CLX-25, CLX-37.5, and CLX-50 samples in comparison to petroleum-based and bio-based plastics (gray) such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE), low-density polyethylene, polypropylene (PP), thermoplastic polyurethane, thermoplastic starch, polycaprolactone, poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA), and polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) and to lignin-based composite materials (green) (i.e., bagasse film, xylan film, amorphous cellulose film, and PHB with wood fibers).11,21,43−45