Abstract
Unpasteurized milk is used to produce aged artisanal cheeses, which presents a safety concern due to possible contamination with foodborne pathogens, especially Listeria monocytogenes. The objective of this study was to examine the composition of the bacterial community in unpasteurized milk used to prepare Gouda cheese artificially contaminated with L. monocytogenes (~1 log CFU/ml) and assess the community dynamics and their potential interaction with L. monocytogenes during a 90-day ripening period using targeted 16S rRNA sequencing. The diversity of bacterial taxa in three batches of unpasteurized milk was not significantly different, and the microbiomes were dominated by species of Lactococcus, Streptomyces, Staphylococcus, and Pseudomonas. The highest relative abundances were observed for Pseudomonas fluorescens (31.84–78.80%) and unidentified operational taxonomic units (OTUs) of Pseudomonas (7.56–45.27%). After manufacture, both with and without L. monocytogenes-contaminated unpasteurized milk, Gouda cheese was dominated by starter culture bacteria (including Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris, lactis, lactis bv. diacetylactis, and Streptococcus thermophilus), in addition to unassigned members in the taxa L. lactis and Streptococcus. During ripening there was an overall decrease in L. lactis abundance and an increase in the number of taxa with relative abundances >0.1%. After 90-day ripening, a total of 82 and 81 taxa were identified in the Gouda cheese with and without L. monocytogenes, respectively. Of the identified taxa after ripening, 31 (Gouda cheese with L. monocytogenes) and 56 (Gouda cheese without L. monocytogenes) taxa had relative abundances >0.1%; 31 were shared between the two types of Gouda cheese, and 25 were unique to the Gouda cheese without added L. monocytogenes. No unique taxa were identified in the Gouda cheese with the added L. monocytogenes. This study provides information on the dynamics of the bacterial community in Gouda cheese during ripening, both with and without the addition of L. monocytogenes.
Keywords: microbiome, Gouda cheese, Listeria monocytogenes, unpasteurized milk, dairy
Introduction
Microbes and cheesemaking have been intertwined for hundreds of years, with the first description of cheese microorganisms dating back to 1665 (Donnelly, 2014). Many cheeses that are still consumed today originated hundreds of years ago: Cheddar, Parmesan, and Gouda and Gloucester, for example, were first documented in 1500, 1579, and 1697, respectively. Cheese serves as a long-standing dietary component in many countries around the world. Since the introduction of cheese microorganisms to science, studies have continued to shed light on the identities and roles of the organisms traditionally used in cheesemaking. The knowledge gained from these studies has resulted in a more controlled, standardized, and safe process for producing many of these cheese types (Donnelly, 2014).
Cheeses obtain their unique flavors from defined starter cultures and aging (ripening) conditions in an industrial setting that yields a predictable and replicable result. Artisanal cheesemaking, i.e., small batch, specialty-made, region-specific cheeses, relies on the selection and use of indigenous microorganism in the milk used as the base for the cheese. Supporters of artisanal cheeses argue that the high taxonomic diversity of the native microbiota in unpasteurized milk is important for developing the flavor profile unique to these cheeses. Additionally, it is debated that the diverse microbial profile of these cheeses presents competition and limits foodborne pathogens. Unfortunately, current data contradict this belief: Listeria monocytogenes and Shiga-toxin producing Escherichia coli have been identified in both unpasteurized milk and cheeses prepared using unpasteurized milk (U. S. FDA, 2016). In several studies, L. monocytogenes was identified in a substantial portion of the silos and bulk tanks used to house unpasteurized milk, ranging from 2.3 to 50% of the samples examined (Van Kessel et al., 2004; Jayarao et al., 2006; D’Amico et al., 2008; Jackson et al., 2012). The resident bacteria of unpasteurized milk originate from a variety of sources, including the animal’s teat canal and skin, equipment and personnel hygiene, transport and storage, and processing conditions (Verdier-Metz et al., 2009; Braem et al., 2012; Quigley et al., 2013; Kergourlay et al., 2015). Without pasteurization and proper process and post-process handling, the incidence of L. monocytogenes contamination may be increased. Pathogenic E. coli contamination of Gouda cheese and/or the unpasteurized milk that was used for manufacture has led to multiple outbreaks between 1998 and 2011 (Gould et al., 2014), and in 2013, it was responsible for 23 illnesses, five hospitalizations, and one death (Currie et al., 2018).
As the potential of foodborne illnesses remains a threat, and the consumption of artisanal cheeses increases, the interstate commerce of unpasteurized milk and cheese made with unpasteurized milk remains closely monitored and is illegal except under certain guidelines. Under U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulations in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 21 (U. S. FDA, 2018), specific standards allow cheese to be made from unpasteurized milk, but must be cured (aged) at a temperature not lower than 1.7°C (35°F) and for a minimum of 60 days, in an effort to reduce pathogen presence. However, multiple studies have indicated that in aged cheese, such as Cheddar and Gouda, the presence of a pathogen can extend well beyond the recommended 60-day ripening period (Reitsma and Henning, 1996; Schlesser et al., 2006; Salazar et al., 2020).
The demand for high-quality artisanal and traditional cheeses likely will not diminish, nor will the incidence of foodborne pathogens in these products. Little knowledge exists on how the resident microbiota impacts pathogen survival and whether altering specific taxa can aid in pathogen prevention measures in the artisanal cheese industry. The present study, complementing previous research (Salazar et al., 2020), assesses the microbial composition of Gouda cheese made with unpasteurized milk during a 90-day ripening process. The goals of this study were to determine the change in abundance of the taxa present (both from the starter culture, as well as those naturally residing in the milk) and to observe dynamic changes in the presence of L. monocytogenes, in an effort to provide information that may prove valuable for the development of future guidelines and risk assessments.
Materials and Methods
Strains and Inoculum Preparation
A cocktail of four L. monocytogenes dairy-related strains were used in this study: LM1240, LM1257, LM-6E, and LM-2F (van der Veen et al., 2008; Wemmenhove et al., 2013). Strains were cultured individually aerobically in Brain Heart Infusion (BHI; Becton, Dickinson and Co., Sparks, MD) broth at 37°C for 16–18 h. Cultures were normalized to an OD600 of 0.8, washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; pH 7.4), and combined to form a cocktail. The cocktail was serially diluted using PBS and plated onto Brilliance Listeria agar (BLA; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA) to verify initial inoculum levels.
Gouda Cheese Manufacture
Three batches of unpasteurized bovine milk (AB, CD, and EF) were sourced from a local dairy in Illinois on different concurrent weeks. Each batch of unpasteurized milk received was comprised of milk from multiple farms in Illinois. A total of three trials and six Gouda cheeses were prepared (labeled A through F). Trial 1 used batch AB unpasteurized milk to manufacture control uninoculated cheese A and L. monocytogenes-contaminated cheese B. Trial 2 used batch CD unpasteurized milk to manufacture control uninoculated cheese C and L. monocytogenes-contaminated cheese D. Trial 3 used batch EF unpasteurized milk to manufacture control uninoculated cheese E and L. monocytogenes-contaminated cheese F.
Gouda cheese was manufactured in a biocontainment pilot plant using a commercial cheese pasteurization vat (V15005, Northwestern Tools, Dayton, OH) as previously described (Salazar et al., 2020). Briefly, 10 gallons (37.9 L) of unpasteurized milk was added to the vat and was left uninoculated (in the case of cheeses A, C, and E) or was inoculated with 1.05 ± 0.24 log CFU/ml of the L. monocytogenes cocktail (in the case of cheeses B, D, and F). The milk was then heated to 30°C, followed by the addition of 2.4 Direct Culture Unit (DCU) of starter cultures consisting of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis, L. lactis subsp. cremoris, L. lactis subsp. lactis bv. diacetylactis, and Streptococcus thermophilus (CHOOZIT MA 4001 Lyo 25 DCU, Danisco, Thomson, IL). After 30 min at 30°C, 6.2 ml of rennet (PF 55 coagulant, GetCulture, Madison, WI) was added to the milk, mixed, and the temperature was maintained for 45–55 min. Curds were cut in up and down directions with a 1 inch2 cheese knife, with a 5 min wait between cuts. One third of the whey was drained, followed by the addition of an equal amount of water at 50°C, which aided in increasing the overall temperature of the mixture to 38°C. The curds were “cooked” at 38°C for 30 min with constant stirring. Curd were placed into molds (M19, New England Cheesemaking Supply Co., Deerfield, MA) and pressed with sequential increasing weights as described previously (Salazar et al., 2020). The resulting cheese wheel was brined in 20% (w/v) sodium chloride (Thermo Fisher Scientific) for 48 h, followed by 72 h ambient drying prior to waxing.
Waxing, Storage, and Sampling of Gouda Cheese During Ripening
Gouda cheese was waxed, stored, and sampled as described previously (Salazar et al., 2020). Cheese wheels were waxed with two coats of red cheese wax (New England Cheesemaking Supply Co.) and aged at 10°C for up to 90 days. At 0, 7, 28, 42, 60, 77, and 90 days, a 25-g pie-shaped wedge of cheese was removed from the wheel for sampling. The cheese was re-waxed after each sampling with two coats of cheese wax. All Gouda cheeses prepared in this study conformed to the standard of identity of Gouda cheese (U. S. FDA, 2018; Salazar et al., 2020).
Sample Processing and Sequencing
DNA was extracted from 1 ml of each of the three batches of unpasteurized milk (AB, CD, and EF) prior to the manufacture of the Gouda cheese to determine the composition and relative abundance of bacterial taxa. After the Gouda cheese was prepared, individual 25-g cheese samples, consisting of two 5-g pie-shaped wedges were evaluated. Each 5-g sample was homogenized with 10 ml of Buffered Listeria Enrichment Broth (BLEB; Oxoid, Basingstoke, England), and DNA was extracted immediately from 1 ml of each homogenate using the DNeasy PowerFood Microbial Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Total DNA was quantified using the Qubit dsDNA BR Assay Kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). PCR was conducted with 3 ng of template DNA and one of four 16S rDNA primer pairs to amplify the V4 region as previously described (Salazar et al., 2018). Amplicons were purified using AMPure XP beads (Beckman-Coulter, Indianapolis, IN) and quantified using the Qubit dsDNA BR Assay Kit. Samples were indexed using the Nextera XT Kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA) as described previously (Salazar et al., 2018), pooled, spiked with 10% of 12.5 pM PhiX, and sequenced using an Illumina MiSeq and 600 cycles of V3 chemistry.
Data Analyses
Raw paired-end sequences were quality filtered, merged, and taxonomically profiled using miniKraken and Kraken2 (Wood et al., 2019). Relative abundances were determined using Bracken 2.5 (Lu et al., 2017). Sequence counts were rarefied to 10,000 sequences for each independent sample. NCBI BLAST+ 2.9.0 was used to differentiate between the L. lactis subspecies (i.e., lactis, cremoris, and lactis bv. diacetylactis) using the BLAST V5 database. The vegan package 2.5–6 (Oksanen et al., 2019) in R 3.6.2 was used to determine alpha and beta diversity of the microbial population in the three unpasteurized milk batches (AB, CD, and EF), the six Gouda cheeses (A, B, C, D, E, and F), and the two types of cheeses (ACE, uninoculated; BDF, inoculated). Alpha diversity was estimated using Shannon, Simpson, inverse Simpson, and Chao1 diversity indices. Beta diversity was evaluated using Bray-Curtis dissimilarity matrix. A multilevel pairwise comparison using Adonis (~Permanova) was calculated using package pairwiseAdonis (Martinez Arbizu, 2020). A value of p less than 0.05 was considered as significant.
Accession Numbers
Metagenomic sequence data have been deposited in NCBI under Bioproject PRJNA643290, Biosamples SAMN15409189-409233.
Results
Native Bacteria in the Unpasteurized Milk
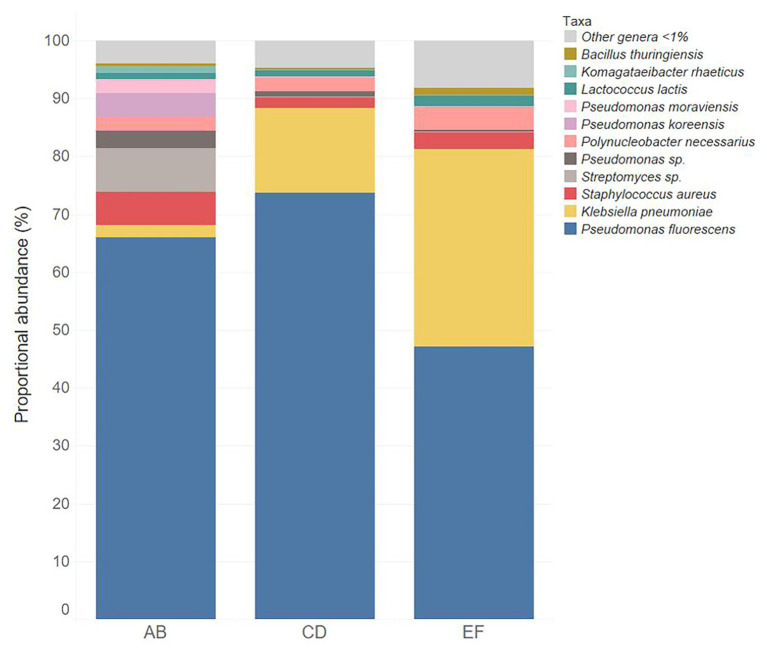
Three batches of unpasteurized milk were used to manufacture the six Gouda cheeses in this study. From plate count assays conducted previously (Salazar et al., 2020), the average populations of Enterobacteriaceae, yeasts and molds, lactic acid bacteria, and mesophilic bacteria in the unpasteurized milk were 0.95, 3.53, 3.33, and 3.09 log CFU/ml, respectively. In this study, a total of 193, 206, and 176 unique operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were identified in unpasteurized milk batch AB, CD, and EF, respectively (Table 1). Although differences were observed in the total OTUs, alpha and beta diversity metrics were not significantly different between batches (Tables 1 and 2). The bacterial genera Lactococcus, Pseudomonas, Polynucleobacter, Streptomyces, and Staphylococcus dominated the milk microbiomes (Figures 1, 2). A total of 11 different taxa were identified with relative abundances >1% in at least one of the three milk batches and included L. lactis, Pseudomonas fluorescens, P. koreensis, P. moraviensis, Polynucleobacter necessarius, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus thuringiensis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Komagataeibacter rhaeticus, as well as unclassified members in the genera of Streptomyces and Pseudomonas. The highest relative abundance was observed for P. fluorescens (47.06–73.76%). Lactococcus lactis was present in all three milk batches at relative abundances of 1.03–1.81%. Differences in the relative abundances of some taxa were more pronounced than others in the three batches of milk (Figures 1, 2). Klebsiella pneumoniae was present in all three milk batches but at different relative abundances (2.24–34.17%). A high abundance of Streptomyces (7.60%) was observed in milk batch AB, whereas this taxon had a relative abundance <1% in the other two batches. Staphylococcus aureus was also present in all three milk batches at 2.03–5.60%. No native Listeria spp. were detected in the unpasteurized milk via 16S rRNA sequencing. In addition, no native Listeria spp. were detected in the unpasteurized milk through enrichments (Salazar et al., 2020).
Table 1.
Observed operational taxonomic units (OTUs) and alpha diversity metrics of the three batches of unpasteurized milk (AB, CD, and EF) used for Gouda cheese manufacture.
| Milk batch | Observed OTUs | Chao1a | Shannonb | Simpsonc | Inverse Simpsonc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AB | 193 ± 51 | 465 ± 89 | 1.35 ± 0.11 | 0.64 ± 0.04 | 2.89 ± 0.55 |
| CD | 206 ± 72 | 449 ± 52 | 1.02 ± 0.04 | 0.55 ± 0.01 | 2.23 ± 0.04 |
| EF | 176 ± 43 | 486 ± 96 | 1.04 ± 0.27 | 0.36 ± 0.24 | 1.62 ± 0.95 |
Chao1 diversity index indicates the microbial richness for the three different batches of unpasteurized milk.
Shannon diversity index indicates the richness and evenness of the microbial community in the three different batches of unpasteurized milk.
Simpson and Inverse Simpson diversity indices indicate the diversity of the microbial community in the three batches of unpasteurized milk.
Table 2.
Pairwise Adonis of the three batches of unpasteurized milk used for Gouda cheese manufacture.
| Comparison | Sums of Squaresa | F.Modelb | r2c | p | Adjusted value of pd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AB vs. CD | 0.41 | 1.56 | 0.24 | 0.07 | 0.21 |
| AB vs. EF | 0.38 | 1.31 | 0.25 | 0.133 | 0.4 |
| CD vs. EF | 0.32 | 1.28 | 0.30 | 0.1 | 0.3 |
Sums of Squares expresses the total variation.
F.Model expresses the variation between the two unpasteurized milk batches compared.
r2, coefficient of determination.
Adjusted value of p, the value of p obtained using Bonferroni correction.
Figure 1.
Relative abundance of bacterial taxa in the three batches of unpasteurized milk (AB, CD, and EF) used in this study used to make Gouda cheese.
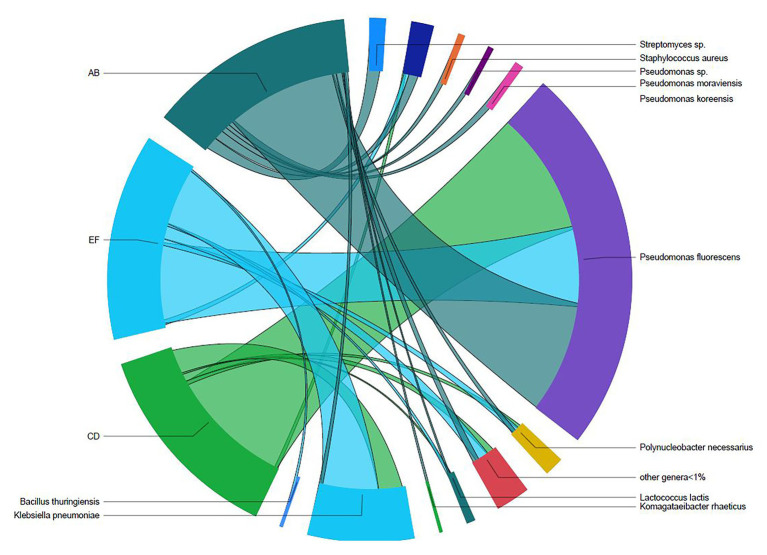
Figure 2.
Shared taxa between the three batches of unpasteurized milk (AB, CD, and EF) used to manufacture Gouda cheese.
Native and Starter Bacteria in Manufactured Gouda Cheese Prior to Ripening
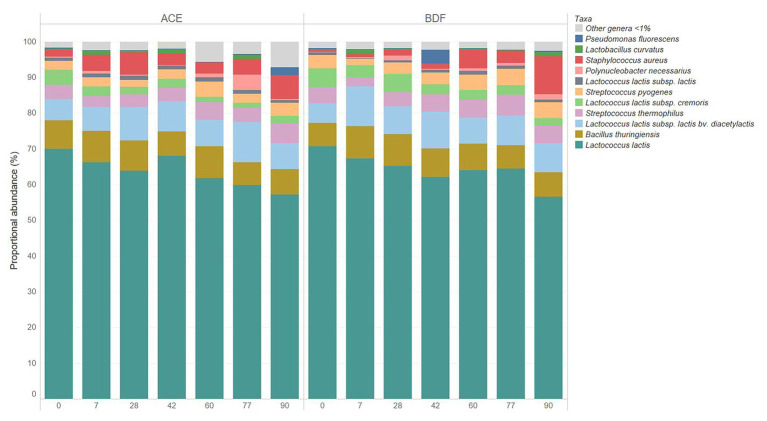
Two types of Gouda cheese were manufactured in this study: one type was manufactured with unpasteurized milk without addition of L. monocytogenes (cheese ACE) and one manufactured with unpasteurized milk containing 1.05 ± 0.24 log CFU/ml of L. monocytogenes (cheese BDF). From plate count assays conducted previously (Salazar et al., 2020), the average populations of Enterobacteriaceae, yeasts and molds, lactic acid bacteria, and mesophilic bacteria in the manufactured cheeses prior to ripening were 2.07, 3.06, 8.98, and 8.83 log CFU/g, respectively. Relative abundances of native and starter bacteria in the two types of Gouda cheeses (ACE and BDF) were determined at day 0 (after manufacture) and during ripening at 10°C for up to 90 days. At day 0, a total of 85 different taxa were identified in cheese ACE. Similarly, 85 different taxa were also identified in cheese BDF. Excluding starter culture bacteria, only two (B. thuringiensis and P. fluorescens) of the 11 taxa identified in the unpasteurized milk >1% (Figure 1) were present in both types of Gouda cheese at relative abundances >1% (Figures 3, 4). Bacillus thuringiensis was present in cheese ACE and cheese BDF at relative abundances of 7.97 and 6.58%, respectively. Pseudomonas fluorescens, which was identified in the unpasteurized milk at 47.06–73.76%, had reduced relative abundances of 0.23 (cheese ACE) and 0.26% (cheese BDF). Staphylococcus aureus was present in cheese ACE at a relative abundance of 2.12%, however, it was <1% in cheese BDF.
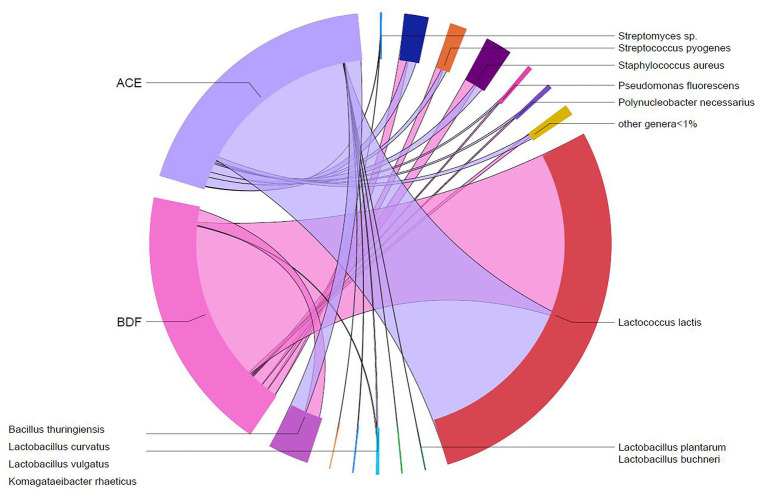
Figure 3.
Shared taxa between the two types of Gouda cheeses (ACE, uninoculated and BDF, inoculated) produced in this study.
Figure 4.
Relative abundance of bacterial taxa during 10°C aging of Gouda cheese manufactured with unpasteurized milk (cheese ACE) or with unpasteurized milk inoculated with 1 log CFU/mL of Listeria monocytogenes (cheese BDF).
The starter culture used for Gouda cheese manufacture consisted of four different bacteria: L. lactis subsp. lactis, L. lactis subsp. cremoris, L. lactis subsp. lactis bv. diacetylactis, and S. thermophilus. No differences in relative abundances of the starter culture bacteria were observed between the two types of Gouda cheeses (ACE and BDF) on day 0 (Figures 3, 4). Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis bv. diacetylactis was present at an average relative abundance of 5.73%, followed by L. lactis subsp. cremoris and subsp. lactis at 4.68 (cheese ACE) and 0.78% (cheese BDF). A high abundance of L. lactis that was not categorized into subtypes was present in both types of Gouda cheeses at an average abundance of 70.32%. Streptococcus thermophilus, another starter culture bacterium, was identified at an average relative abundance of 4.28%.
Influence of Listeria monocytogenes-Contaminated Milk on the Gouda Cheese Microbiome During Ripening
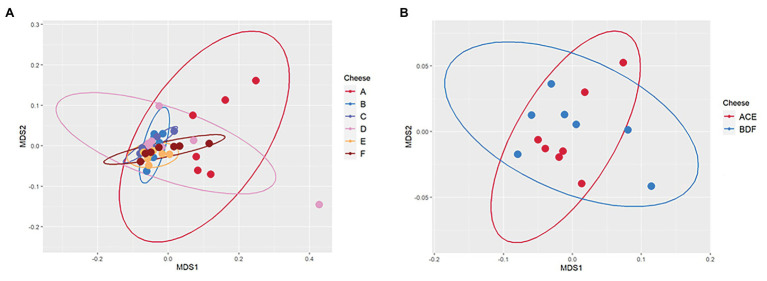
During 90-day ripening, beta diversity analysis determined that there were significant differences between the microbiomes of cheeses A and C as well as A and E, all of which were uninoculated (Table 3 and Figure 5). No significant differences were observed between the microbiomes of any of the three inoculated cheeses (B, D, and F). In addition, there was a significant difference between the microbiomes of the two types of cheeses manufactured in this study (ACE and BDF; Table 3 and Figure 5).
Table 3.
Pairwise Adonis of the six individual Gouda cheeses (A, B, C, D, E, and F) as well as the two types of cheeses (ACE, uninoculated and BDF, inoculated) manufactured in this study.
| Comparison | Sums of Squaresa | F.Modelb | r2c | p | Adjusted value of pd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A vs. B | 0.15 | 2.48 | 0.17 | 0.02 | 0.3 |
| A vs. C | 0.30 | 6.23 | 0.34 | 0.001 | 0.015* |
| A vs. D | 0.19 | 3.47 | 0.22 | 0.008 | 0.12 |
| A vs. E | 0.29 | 5.98 | 0.32 | 0.002 | 0.03* |
| A vs. F | 0.23 | 4.98 | 0.29 | 0.004 | 0.06 |
| B vs. C | 0.07 | 1.94 | 0.14 | 0.072 | 1 |
| B vs. D | 0.05 | 1.10 | 0.08 | 0.371 | 1 |
| B vs. E | 0.14 | 3.47 | 0.21 | 0.004 | 0.06 |
| B vs. F | 0.07 | 1.99 | 0.14 | 0.071 | 1 |
| C vs. D | 0.05 | 1.65 | 0.12 | 0.128 | 1 |
| C vs. E | 0.06 | 2.29 | 0.15 | 0.033 | 0.495 |
| C vs. F | 0.04 | 1.80 | 0.13 | 0.103 | 1 |
| D vs. E | 0.10 | 3.06 | 0.19 | 0.012 | 0.18 |
| D vs. F | 0.04 | 1.32 | 0.10 | 0.025 | 1 |
| E vs. F | 0.03 | 1.00 | 0.07 | 0.402 | 1 |
| ACE vs. BDF | 0.07 | 1.96 | 0.14 | 0.042 | 0.042* |
Indicates a significant difference.
Sums of Squares expresses the total variation.
F.Model expresses the variation between the two cheeses compared.
r2, coefficient of determination.
Adjusted value of p, the value of p obtained using Bonferroni correction.
Figure 5.
Principal Component Analysis Plot (PCA) using Bray Curtis distance matrix to measure beta diversity of (A) the six individual Gouda cheeses (A, B, C, D, E, and F) and (B) the two types of Gouda cheeses (ACE, uninoculated and BDF, inoculated) manufactured in this study.
The relative abundances of native, starter, and L. monocytogenes were determined during the 90-day ripening of the two types of Gouda cheeses (Figures 3, 4). L. monocytogenes was identified at relative abundances less than 0.001% in Gouda cheese BDF during ripening, which was consistent with previously determined plate count enumeration data (Salazar et al., 2020); after 90-day ripening, the population of L. monocytogenes was 1.11, 0.95, and 1.26 log CFU/g in cheeses B, D, and F, respectively. L. monocytogenes was not identified in cheese ACE (uninoculated) at any timepoint during ripening using 16S rRNA gene sequencing or via enrichments (Salazar et al., 2020).
Non-starter culture bacteria identified during ripening at relative abundances >1% for at least one timepoint in either type of Gouda cheese included B. thuringiensis, Lactobacillus curvatus, Po. necessarius, P. fluorescens, S. aureus, and Str. pyogenes (Figures 3, 4). Lactobacillus curvatus was identified at relative abundances of 0.03–2.25% and <0.1–1.26% in cheeses ACE and BDF during ripening, respectively. Polynucleobacter necessarius was identified at relative abundances of 0.24–4.35% and 0.15–1.41% in cheeses ACE and BDF during ripening, respectively. Bacillus thuringiensis (6.30–9.11%) and Str. pyogenes (1.78–4.63%) were the only two taxa present in both ACE and BDF cheeses at all timepoints during ripening. S. aureus was also present in both cheeses at all timepoints and increased during ripening at relative abundances of 2.13–10.73% with the exception of 0 and 7 days for cheeses BDF in which the relative abundances were 0.81 and 0.82%, respectively. From initial relative abundances of 2.13 and 0.81% on day 0, the abundance of S. aureus after 90 days ripening was 6.61 and 10.73% for cheeses ACE and BDF, respectively.
Less difference was observed in the relative abundances of starter culture bacteria between the two types of cheeses during ripening (Table 4). In general, the relative abundance of L. lactis subsp. lactis remained fairly constant during ripening. The relative abundance of L. lactis subsp. cremoris was observed to decrease during ripening. Conversely, the relative abundance of L. lactis subsp. lactis bv. diacetylactis increased over the 90-day ripening period. The greatest increase in relative abundance (2.71%) was observed by L. lactis subsp. lactis bv. diacetylactis in cheese BDF, whereas the greatest decrease (14.05%) was observed by unassigned L. lactis members, also in cheese BDF.
Table 4.
Average relative abundances of starter culture bacteria during 10°C ripening of Gouda cheese manufactured with unpasteurized milk (cheeses ACE) or with unpasteurized milk inoculated with 1 log CFU/ml of Listeria monocytogenes (cheese BDF).
| Starter culture bacteria | Relative abundance (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 day | 28 days | 60 days | 90 days | |
| Cheese ACE | ||||
| Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris | 4.17 | 2.11 | 1.45 | 2.20 |
| Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis | 0.90 | 1.17 | 1.14 | 0.84 |
| Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis bv. diacetylactis | 5.97 | 9.23 | 7.54 | 7.29 |
| Lactococcus lactis unassigned OTUs | 69.97 | 63.83 | 61.78 | 57.19 |
| Streptococcus thermophilus | 3.96 | 3.64 | 4.86 | 5.47 |
| Cheese BDF | ||||
| Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris | 5.18 | 5.08 | 2.74 | 2.09 |
| Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis | 0.66 | 0.69 | 0.99 | 0.82 |
| Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis bv. diacetylactis | 5.50 | 7.63 | 7.36 | 8.21 |
| Lactococcus lactis unassigned OTUs | 70.67 | 65.23 | 64.08 | 56.62 |
| Streptococcus thermophilus | 4.59 | 4.05 | 4.97 | 4.92 |
When comparing cheeses ACE and BDF, after 28, 60, and 90 days ripening, a total of 98, 130, and 81 taxa were identified in Gouda cheese ACE, respectively, whereas 95, 77, and 82 were identified in cheeses BDF. Out of the 81 taxa identified in cheese ACE after 90 days, 25, 47, and 9 taxa had relative abundances <0.1%, 0.1–0.5, and >0.5%, respectively. In contrast, out of 82 taxa identified in cheese BDF after 90 days, 51, 26, and 5 taxa had relative abundances <0.1%, 0.1–0.5, and >0.5%. Of the taxa with relative abundances 0.1–0.5%, 26 were shared between both types of cheeses and 21 were only identified in cheese ACE; no taxa were unique to cheese BDF, with the exception of the inoculated L. monocytogenes (Table 5). Genera with the most unique species identifications included Bacteroides and Prevotella.
Table 5.
Taxa present at relative abundances of 0.1–0.5% in Gouda cheese manufactured with unpasteurized milk (cheese ACE) or with unpasteurized milk inoculated with 1 log CFU/ml of Listeria monocytogenes (cheese BDF) after 90 days aging at 10°C.
| Taxa unique to ACE | Taxa present in both ACE and BDF |
|---|---|
|
Aerococcus christensenii Amycolatopsis mediterranei Anaerotignum propionicum Bacteroides cellulosilyticus Bacteroides dorei Bacteroides helcogenes Bacteroides heparinolyticus Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron Basilea psittacipulmonis Flavobacterium johnsoniae Lactobacillus crispatus Limnohabitans spp. Macrococcus caseolyticus Photobacterium damselae Porphyromonas gingivalis Prevotella dentalis Prevotella fusca Prevotella intermedia Prevotella melaninogenica Prevotella ruminicola Prevotella scopos |
Bacillus thuringiensis Bacteroides ovatus Denitrovibrio acetiphilus Faecalibacterium prausnitzii Fimbriimonas ginsengisoli Haemophilus parainfluenzae Ketobacter alkanivorans Lactiplantibacillus pentosus Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Levilactobacillus brevis Ligilactobacillus acidipiscis Ligilactobacillus murinus Limosilactobacillus fermentum Loigolactobacillus coryniformis Odoribacter splanchnicus Paenisporosarcina spp. Propionibacterium freudenreichii Pseudomonas koreensis Pseudomonas mandelii Sporosarcina spp. Streptococcus anginosus Streptococcus halotolerans Streptococcus pyogenes Streptomyces spp. Syntrophus aciditrophicus |
No unique taxa were identified in cheese BDF, with the exception of the inoculated Listeria monocytogenes.
Discussion
This study used metagenomic sequencing to profile the microbiomes of unpasteurized milk and the resulting Gouda cheese after manufacture and throughout a 90-day ripening period. Although previous studies have examined the resident bacterial populations of unpasteurized cheeses after manufacture and during the ripening process (Delbès et al., 2007; Casalta et al., 2009; Lusk et al., 2012; Quigley et al., 2012; Fuka et al., 2013; Delcenserie et al., 2014; Alessandria et al., 2016; Escobar-Zepeda et al., 2016), this is the first study to assess the community dynamics both with and without the addition of a foodborne pathogen. Contamination of unpasteurized milk can occur on the farm due to poor hygiene or unsanitary conditions, or during processing. L. monocytogenes has been identified in unpasteurized milk in various studies (Van Kessel et al., 2004; Jayarao et al., 2006; D’Amico et al., 2008; Jackson et al., 2012). Therefore, in this study L. monocytogenes was added to unpasteurized milk used to produce Gouda cheese to understand the dynamics and interactions of this pathogen with the bacterial community present during ripening.
In this study, the microbiomes of the three batches of unpasteurized milk utilized for Gouda cheese manufacture had similar bacterial diversity and were dominated by Lactococcus, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, Staphylococcus, and Streptococcus species. These genera have all been previously identified in unpasteurized milk (Correa et al., 2011; Quigley et al., 2013; Sudarwanto et al., 2015; Kable et al., 2016; Rodrigues et al., 2017) and Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, and Pseudomonas have been identified at abundances >30% in unpasteurized milk tanker trucks (Kable et al., 2016). Specifically, P. fluorescens, which was identified in the unpasteurized milk batches at abundances of 32–79%, is a known dairy spoilage organism and is responsible for blue discoloration in different types of cheeses (Ternstrom et al., 1993; Martin et al., 2011; del Olmo et al., 2018). These bacteria have also been shown to be inhibitory to L. monocytogenes in co-cultures (Buchanan and Bagi, 1999). It is noted that the unpasteurized milk batches used in this study were sourced from only one dairy; however, milk from multiple farms within the same geographic region comprised the batches. Although the microbiome of unpasteurized milk would likely vary based on the types of cattle at each farm, differences attributed to the geographic location were minimized.
After manufacture both with and without the addition of L. monocytogenes in the unpasteurized milk, the Gouda cheese bacterial communities were dominated by the starter culture members L. lactis subsp. lactis, L. lactis subsp. cremoris, L. lactis subsp. lactis bv. diacetylactis, and Str. thermophilus, as well as L. lactis that was not classified into subspecies and unclassified species in the genus Streptococcus. This finding was expected, as high population levels of starter culture bacteria are common in cheeses after manufacture (Montel et al., 2014). The strains in starter cultures play an important role in the cheese manufacturing and ripening process by influencing sensory, flavor, and texture profiles. This study utilized a commercially-available Gouda cheese starter culture. During cheese manufacture, the main contribution of these lactic acid bacteria is in milk acidification. During ripening, these bacteria are also involved in lipolysis, proteolysis, and the conversion of amino acids to flavor compounds (Yvon et al., 1997; Copan et al., 2007). Since the relative abundances of the strains in the starter cultures were similar between cheeses ACE and BDF during ripening, it can be inferred that L. monocytogenes is not inhibitory to the starter culture bacteria and vice versa.
After manufacture, the Gouda cheeses made with unpasteurized milk, both with and without the addition of L. monocytogenes (cheeses BDF and ACE, respectively), were ripened at 10°C for 90 days. Diversity analysis determined that the microbiomes of these two cheese types were significantly different, indicating that the presence of L. monocytogenes may alter the microbial community of Gouda cheese. Overall, the relative abundances of the major identified taxa in both types of cheeses trended similarly during ripening. Starter culture bacteria, along with non-subspecies classified L. lactis, decreased in abundance during ripening, yet remained the dominant taxa throughout the 90-day period. Other bacterial taxa identified during ripening with relative abundances >1% included B. thuringiensis, Lb. curvatus, S. aureus, and Str. pyogenes. These genera have previously been isolated from Danbo, Stilton, and Gouda cheeses (Antonsson et al., 2003; Ercolini et al., 2003; Hajikhani et al., 2007; Salazar et al., 2018) and have either originated from the milk used to make the cheese (as with this study) or from post-process contamination. S. aureus and Str. pyogenes, which were identified in both types of cheeses at relative abundances >3.60% after 90-day ripening, are both human foodborne pathogens. Although both of these strains were identified in the unpasteurized milk used to make the Gouda cheese in this study, this finding also highlights the need for proper cheese ripening conditions and personnel hygiene.
Although the abundances of the dominant bacterial community members of Gouda cheeses ACE and BDF were similar during ripening, notable differences in the relative abundances of non-dominant taxa were observed. With relative abundances of 0.1–0.5%, a total of 47 and 26 taxa were identified in cheeses ACE and BDF after 90-day ripening, respectively. Interestingly, no taxa were unique to cheese BDF since all the 26 taxa identified at an abundance of 0.1–0.5% in cheese BDF were also identified in cheese ACE. Twenty-one taxa (species from 11 different genera) having relative abundances 0.1–0.5% were unique to cheese ACE after 90 days (see Table 3). The unique taxa included, for example, five species in the genus Bacteroides, one species in each of the genera Flavobacterium, Macrococcus, Photobacterium, and Porphyromonas, and six species in the genus Prevotella.
Within a food matrix, there is a complex interaction between the microbial communities. The addition of a foodborne pathogen, in this case L. monocytogenes, may promote growth or hinder the survival of other community members. In contrast, the community members may promote or hinder the survival of L. monocytogenes. It is known that certain bacterial taxa, including Bacillus spp., Chryseobacterium spp., Enterococcus spp., Lactococcus spp., and P. fluorescence, possess anti-listerial properties or can readily out-complete L. monocytogenes for nutrients (Carpentier and Chassaing, 2004; Saubusse et al., 2007; Renye et al., 2009). On the other hand, L. monocytogenes possesses a bacteriocin, which can target Prevotella (Rolhion et al., 2019). In a study assessing the bacterial communities of floor drains in a food production facility both with and without resident Listeria spp., Prevotella populations were highest in these communities in the absence of Listeria spp. (Fox et al., 2014). The lack of identification of certain taxa in cheese BDF after 90 days may be due to inhibition of these bacteria by L. monocytogenes or by other community members.
Optimization of L. monocytogenes enrichment techniques for a particular food product is often necessary due to co-enriching and competitor resident microbiota. Rapid and accurate enrichment of L. monocytogenes from food matrices is essential to outbreak and recall investigations and public health. Some of the taxa present in relative abundances >0.1% in the Gouda cheese after 90 day ripening, regardless of L. monocytogenes addition, included Bacillus, Ketobacter, eight species of Lactobacillus, two species of Pseudomonas, Streptomyces, and Staphylococcus. Bacillus, Lactobacillus, Pseudomonas, and Staphylococcus species are known to co-enrich and, at times, hinder L. monocytogenes detection when cultured in typical Listeria enrichment broths (Dallas et al., 1991; Millet et al., 2006). The identification of the bacteria present in Gouda cheese during the ripening process can be used to develop appropriate enrichment procedures for L. monocytogenes for this food product.
In conclusion, this study examined the dynamics of the bacterial community in Gouda cheese after manufacture and 90-day ripening when made with unpasteurized milk both with and without the addition of L. monocytogenes. Although no microbial community differences were observed in the three batches of unpasteurized milk used to make Gouda cheese in this study, there were significant differences between the microbiomes of these two types of cheeses during ripening. While each type of cheese shared community members, a large number of bacterial taxa were unique to cheese ACE (made without L. monocytogenes) after 90-day ripening, indicating that L. monocytogenes may influence the microbial community. These data are important to understanding the impact of L. monocytogenes on the microbiome of Gouda cheese and vice versa. It is noted that these results are specific to the unpasteurized milk sourced in this study and that future studies could examine metataxonomic changes in Gouda cheese based on the seasonality, farm and cattle, and geographic location of the milk utilized.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/supplementary material.
Author Contributions
JS, KS, and MT conceived and designed the experiments. JS, LG, and MF performed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. JS, MF, and PR analyzed the data. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We thank Arlette Shazer and Karl Reineke for assistance with cheese manufacture experiments.
Footnotes
Funding. LG and MF were supported by the Oak Ridge Institute for Science and Education Research Participation Program through a contract from the U. S. Food and Drug Administration. The sponsors had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- Alessandria V., Ferrocino I., De Filippis F., Fontana M., Rantsiou K., Ercolini D., et al. (2016). Microbiota of an Italian Granalike cheese during manufacture and ripening, unraveled by 16S rRNA-based approaches. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 82, 3988–3995. 10.1128/AEM.00999-16, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonsson M., Molin G., Ardo Y. (2003). Lactobacillus strains isolated from Danbo cheese as adjunct cultures in a cheese model system. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 85, 159–169. 10.1016/S0168-1605(02)00536-6, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braem G., De Vliegher S., Verbist M., Heyndrickx F., Leroy L., De Vuyst L. (2012). Culture-independent exploration of the teat apex microbiota of dairy cows reveals a wide bacterial species diversity. Vet. Microbiol. 157, 383–390. 10.1016/j.vetmic.2011.12.031, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan R. L., Bagi L. K. (1999). Microbial competition: effect of Pseudomonas fluorescens on the growth of Listeria monocytogenes. Food Microbiol. 16, 523–529. 10.1006/fmic.1998.0264 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Carpentier B., Chassaing D. (2004). Interactions in biofilms between Listeria monocytogenes and resident microorganisms from food industry premises. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 97, 111–122. 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2004.03.031, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casalta E., Sorba J. M., Aigle M., Ogier J. C. (2009). Diversity and dynamics of the microbial community during the manufacture of Calenzana, an artisanal Corsican cheese. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 133, 243–251. 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2009.05.022, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copan T. M., Beresford T. P., Steele J., Broadbent J., Shah N. P., Ustunol Z. (2007). Invited review: advances in starter cultures and cultured foods. J. Dairy Sci. 90, 4005–4021. 10.3168/jds.2006-765, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correa A. P., Daroit D. J., Velho R. V., Brandelli A. (2011). Hydrolytic potential of a psychrotrophic Pseudomonas isolated from refrigerated raw milk. Braz. J. Microbiol. 42, 1479–1484. 10.1590/S1517-83822011000400034, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie A., Galanis E., Chacon P. A., Murray R., Wilcott L., Kirkby P., et al. (2018). Outbreak of Escherichia coli O157:H7 infections linked to aged raw milk Gouda cheese, Canada, 2013. J. Food Prot. 81, 325–331. 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-17-283, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas H. L., Tran T. T., Poindexter C. E., Hitchins A. D., Romanell L. J. (1991). Competition of food bacteria with Listeria monocytogenes during enrichment culture. J. Food Safety 11, 293–301. 10.1111/j.1745-4565.1991.tb00060.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- D’Amico D. J., Groves E., Donnelly C. W. (2008). Low incidence of foodborne pathogens of concern in raw milk utilized for farmstead cheese production. J. Food Prot. 71, 1580–1589. 10.4315/0362-028X-71.8.1580, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delbès C., Ali-Mandjee L., Montel M. C. (2007). Monitoring bacterial communities in raw milk and cheese by culture-dependent and -independent 16S rRNA gene-based analyses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73, 1882–1891. 10.1128/AEM.01716-06, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delcenserie V., Taminiau B., Delhalle L., Nezer C., Doyen P., Crevecoeur S., et al. (2014). Microbiota characterization of a Belgian protected designation of origin cheese, Herve cheese, using metagenomic analysis. J. Dairy Sci. 97, 6046–6056. 10.3168/jds.2014-8225, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Olmo A., Calzada J., Nunez M. (2018). The blue discoloration of fresh cheeses: a worldwide defect associated to specific contamination by Pseudomonas fluorescens. Food Control 86, 359–366. 10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.12.001 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly C. (2014). “From pasteur to probiotics: a historical overview of cheese and microbes” in Cheese and microbes. ed. Donnelly C. (Washington, DC: ASM Press; ). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ercolini D., Hill P. J., Dodd C. E. (2003). Bacterial community structure and location in Stilton cheese. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69, 3540–3548. 10.1128/AEM.69.6.3540-3548.2003, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobar-Zepeda A., Sanchez-Flores A., Quirasco Baruch M. (2016). Metagenomic analysis of a Mexican ripened cheese reveals a unique complex microbiota. Food Microbiol. 57, 116–127. 10.1016/j.fm.2016.02.004, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. M., Solomon K., Moore J. E., Wall P. G., Fanning S. (2014). Phylogenetic profiles of in-house microflora in drains at a food production facility: comparison and biocontrol implications of Listeria-positive and -negative bacterial populations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 80, 3369–3374. 10.1128/AEM.00468-14, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuka M. M., Wallisch S., Engel M., Welzl G., Havranek J., Schloter M. (2013). Dynamics of bacterial communities during the ripening process of different Croatian cheese types derived from raw ewe’s milk cheeses. PLoS One 8:e80734. 10.1371/journal.pone.0080734, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould L. H., Mungai E., Behravesh C. B. (2014). Outbreaks attributed to cheese: differences between outbreaks caused by unpasteurized and pasteurized dairy products, United States, 1998-2011. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 11, 545–551. 10.1089/fpd.2013.1650, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajikhani R., Beyatli Y., Aslim B. (2007). Antimicrobial activity of enterococci strains isolated from white cheese. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 60, 105–108. 10.1111/j.1471-0307.2007.00304.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson E. E., Erten E. S., Maddi N., Graham T. E., Larkin J. W., Blodgett R. J., et al. (2012). Detection and enumeration of four foodborne pathogens in raw commingled silo milk in the United States. J. Food Prot. 75, 1382–1393. 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-11-548, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayarao B. M., Donaldson S. C., Straley B. A., Sawant A. A., Hegde N. V., Brown J. L. (2006). A survey of foodborne pathogens in bulk tank milk and raw milk consumption among farm families in Pennsylvania. J. Dairy Sci. 89, 2451–2458. 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(06)72318-9, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kable M. E., Srisengfa Y., Laird M., Zaragoza J., McLeod J., Heidenreich J., et al. (2016). The core and seasonal microbiota of raw bovine milk in tanker trucks and the impact of transfer to a milk processing facility. MBio 7, e000836–e0008316. 10.1128/mBio.00836-16, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kergourlay G., Taminiau B., Daube G., Champomier Vergès M. C. (2015). Metagenomic insights into the dynamics of microbial communities in food. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 213, 31–39. 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2015.09.010, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu J., Breitwieser F. P., Thielen P., Salzberg S. L. (2017). Bracken: estimating species abundance in metagenomics data. PeerJ Computer Sci. 3:e104. 10.7717/peerj-cs.104 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lusk T. S., Ottesen A. R., White J. R., Allard M. W., Brown E. W., Kase J. A. (2012). Characterization of microflora in Latin-style cheeses by next-generation sequencing technology. BMC Microbiol. 12:254. 10.1186/1471-2180-12-254, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin N. H., Murphy S. C., Ralyea R. D., Wiedmann M., Boor K. J. (2011). When cheese gets the blues: Pseudomonas fluorescens as the causative agent of cheese spoilage. J. Dairy Sci. 94, 3176–3183. 10.3168/jds.2011-4312, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez Arbizu P. (2020). pairwiseAdonis: Pairwise multilevel comparison using adonis. R package version 0.4. Available at: https://github.com/pmartinezarbizu/pairwiseAdonis (Accessed February 1, 2021).
- Millet L., Saubusse M., Didienne R., Tessier L., Montel M. C. (2006). Control of Listeria monocytogenes in raw-milk cheeses. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 108, 105–114. 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2005.11.004, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montel M. C., Buchin S., Mallet A., Delbes-Paus C., Vuitton D. A., Desmasures N., et al. (2014). Traditional cheeses: rich and diverse microbiota with associated benefits. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 177, 136–154. 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2014.02.019, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen J., Blanchet F. G., Friendly M., Kindt R., Legendre P., McGlinn D., et al. (2019). Vegan: Community Ecoloy Package. R package version 2.5–6. Available at: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (Accessed December 7, 2020).
- Quigley L., McCarthy R., O’Sullivan O., Beresford T. P., Fitzgerald G. F., Ross R. P., et al. (2013). The microbial content of raw and pasteurized cow milk as determined by molecular approaches. J. Dairy Sci. 96, 4928–4937. 10.3168/jds.2013-6688, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley L., O’Sullivan O., Beresford T. P., Ross R. P., Fitzgerald G. F., Cotter P. D. (2012). High-throughput sequencing for detection of subpopulations of bacteria not previously associated with artisanal cheeses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 78, 5717–5723. 10.1128/AEM.00918-12, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitsma C., Henning D. (1996). Survival of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 during the manufacture and curing of cheddar cheese. J. Food Prot. 59, 460–464. 10.4315/0362-028X-59.5.460, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renye J. A., Jr., Somkuti G. A., Paul M., Van Hekken D. L. (2009). Characterization of antilisterial bacteriocins produced by Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus durans isolates from Hispanic-style cheeses. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 36, 261–268. 10.1007/s10295-008-0494-7, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues M. X., Lima S. F., Canniatti-Brazaca S. G., Bicalho R. C. (2017). The microbiome of bulk tank milk: characterization and associations with somatic cell count and bacterial count. J. Dairy Sci. 100, 2536–2552. 10.3168/jds.2016-11540, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolhion N., Chassaing B., Nahori M. A., de Bodt J., Moura A., Lecuit M., et al. (2019). A Listeria monocytogenes bacteriocin can target the commensal Prevotella copri and modulate intestinal infection. Cell Host Microbe 26, 691–e5-701.e5. 10.1016/j.chom.2019.10.016, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salazar J. K., Carstens C. K., Ramachandran P., Shazer A. G., Narula S. S., Reed E., et al. (2018). Metagenomics of pasteurized and unpasteurized Gouda cheese using targeted 16S rDNA sequencing. BMC Microbiol. 18:189. 10.1186/s12866-018-1323-4, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salazar J. K., Gonsalves L. J., Natarajan V., Shazer A., Reineke K., Mhetras T., et al. (2020). Population dynamics of Listeria monocytogenes, Escherichia coli O157:H7, and native microflora during manufacture and aging of Gouda cheese made with unpasteurized milk. J. Food Prot. 266–276. 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-18-480, PMID: [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Saubusse M., Millet L., Delbès C., Callon C., Montel M. C. (2007). Application of single strand conformation polymorphism --PCR method for distinguishing cheese bacterial communities that inhibit Listeria monocytogenes. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 116, 126–135. 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2006.12.024, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesser J. E., Gerdes R., Ravishankar S., Madsen K., Mowbray J., Teo A. Y. (2006). Survival of a five-strain cocktail of Escherichia coli O157:H7 during the 60-day aging period of Cheddar cheese made from unpasteurized milk. J. Food Prot. 69, 990–998. 10.4315/0362-028X-69.5.990, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudarwanto M., Akineden O., Odenthal S., Gross M., Usleber E. (2015). Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in bulk tank milk from dairy farms in Indonesia. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 12, 585–590. 10.1089/fpd.2014.1895, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ternstrom A., Lindberg A. M., Molin G. (1993). Classification of the spoilage flora of raw and pasteurized bovine milk, with special reference to Pseudomonas and Bacillus. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 75, 25–34. 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1993.tb03403.x, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- U. S. FDA (2016). FY 2014–2016 Microbiological sampling assignment summary report: raw milk cheese aged 60 days. Available at: https://www.fda.gov/food/sampling-protect-food-supply/microbiological-surveillance-sampling-fy14-16-raw-milk-cheese-aged-60-days (Accessed September 9, 2018).
- U. S. FDA (2018). Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 21. Available at: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfCFR/CFRSearch.cfm (Accessed September 9, 2018).
- van der Veen S., Moezelaar R., Abee T., Wells-Bennik M. H. (2008). The growth limits of a large number of Listeria monocytogenes strains at combinations of stresses show serotype--and niche-specific traits. J. Appl. Microbiol. 105, 1246–1258. 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2008.03873.x, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Kessel J. S., Karns J. S., Gorski L., McCluskey B. J., Perdue M. L. (2004). Prevalence of Salmonellae, Listeria monocytogenes, and fecal coliforms in bulk tank milk on US dairies. J. Dairy Sci. 87, 2822–2830. 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(04)73410-4, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdier-Metz I., Michel V., Delbes C., Monetl M. C. (2009). Do milking practices influence the bacterial diversity of raw milk? Food Microbiol. 26, 305–310. 10.1016/j.fm.2008.12.005, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wemmenhove E., Stampelou I., van Hooijdonk A. C. M., Zwietering M. H., Wells-Bennk M. H. J. (2013). Fate of Listeria monocytogenes in Gouda microcheese: no growth, and substantial inactivation after extended ripening times. Int. Dairy J. 32, 192–198. 10.1016/j.idairyj.2013.05.004 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. E., Lu J., Langmead B. (2019). Improved metagenomic anaysis with Kraken 2. Genome Biol. 20:257. 10.1186/s13059-019-1891-0, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yvon M., Thirouin S., Rijnen L., Fromentier D., Gripon J. C. (1997). An aminotransferase from Lactococcus lactis initiates conversion of amino acids to cheese flavor compounds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63, 414–419. 10.1128/AEM.63.2.414-419.1997, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/supplementary material.