Abstract
Colorectal cancer (CRC) represents the third leading cause of death among cancer patients below the age of 50, necessitating improved treatment and prevention initiatives. A crude methanol extract from the wood pulp of Artocarpus heterophyllus was found to be the most bioactive among multiple others, and an enriched extract containing 84% (w/v) artocarpin (determined by HPLC–MS–DAD) was prepared. The enriched extract irreversibly inhibited the activity of human cytochrome P450 CYP2C9, an enzyme previously shown to be overexpressed in CRC models. In vitro evaluations on heterologously expressed microsomes, revealed irreversible inhibitory kinetics with an IC50 value of 0.46 µg/mL. Time- and concentration-dependent cytotoxicity was observed on human cancerous HCT116 cells with an IC50 value of 4.23 mg/L in 72 h. We then employed the azoxymethane (AOM)/dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) colitis-induced model in C57BL/6 mice, which revealed that the enriched extract suppressed tumor multiplicity, reduced the protein expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen, and attenuated the gene expression of proinflammatory cytokines (Il-6 and Ifn-γ) and protumorigenic markers (Pcna, Axin2, Vegf, and Myc). The extract significantly (p = 0.03) attenuated (threefold) the gene expression of murine Cyp2c37, an enzyme homologous to the human CYP2C9 enzyme. These promising chemopreventive, cytotoxic, anticancer and anti-inflammatory responses, combined with an absence of toxicity, validate further evaluation of A. heterophyllus extract as a therapeutic agent.
Subject terms: Biochemistry, Cancer, Plant sciences, Diseases, Molecular medicine
Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) ranks as the third most commonly diagnosed cancer in the US1 and in Jamaica2, and it is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in both sexes in the US1. While CRC is affected by modifiable factors such as environment, physical activity, Quetelet's index, diet, cigarette smoking, and alcohol consumption3, it is of noteworthy concern that it ranks as the third leading cause of death among young cancer patients aged 20–49 in the US4. Approximately 20% of patients diagnosed with colorectal cancer in Jamaica between 2008 and 2012 were younger than 50 years old5. A recent study on a murine model showed that moving away from a Western diet even after carcinogenesis may reduce tumor burden6, demonstrating that incorporating dietary compounds containing anticancer, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties may have added benefits in treating and preventing colorectal cancer. Given that nature has inspired significant solutions to cancer therapy in the past four decades7 and the demonstrated reliance and confidence on ethnomedicines by cancer patients8, it is imperative that nature’s sources be fully evaluated as novel therapeutic options for the treatment and prevention of CRC.
Cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes are ubiquitous enzymes considered highly important in the metabolism of pharmaceutical drugs9,10, as well as in the activation of environmental carcinogens11. The upregulation of CYP enzymes in cancer tissue in comparison to surrounding tissue implies their vital role in carcinogenesis, as well as in drug resistance12. The overexpression of CYP2C enzymes in murine induced CRC models, as well as in human CRC cell lines13 and human CRC tissue samples14, in comparison to their normal counterparts, suggests a role for these enzymes in pathogenesis, due most likely to the increased amount of carcinogenic metabolites derived from their activities. Indeed, elevated levels of epoxygenated fatty acids in the plasma of mice with induced CRC provide evidence for such biomarker upregulation13. These findings lend support to the search for targeted CYP2C inhibitors that could mitigate enzyme activities, thus functioning as chemopreventors15, in addition to the search for prodrugs that rely on activation from elevated metabolic enzyme activity16.
The Artocarpus genus, comprising nutrient-rich fruits with ethnomedicinal uses in Southeast Asia, Africa, Central America, and the Caribbean, demonstrates numerous potential health benefits. Isolated phytochemicals including artocarpin, isoartocarpin, cyloartocarpin, artocarpetin, and norartocarpetin were found to have anti-inflammatory, anticancer, chemopreventive, and antioxidant properties, as well as inhibit the cellular production of melanin17. A previous study18 revealed the targeted impact of isolated artocarpin on the phosphoinositide 3 -kinase/Akt pathway, suggesting a chemopreventive role. Yet, there is a dearth of information on its impact on cytochrome P450 2C enzymes, previously found to have elevated levels in CRC models14. Furthermore, a more rigorous in vivo study examining the inflammatory response is still needed, particularly through the evaluation of a bioactive extract that can display a high safety profile. Hence, we employed a multitarget study design to better understand the potential colon cancer-reducing effects of an A. heterophyllus extract. Following numerous in vitro evaluations using heterologously expressed human CYP enzymes, as well as human cancer cell lines, we used the AOM/DSS model, a chemically induced colitis-associated cancer (CAC) mouse model employing azoxymethane (AOM) and dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) carcinogens, which mimics a form of inflammatory colorectal cancer in humans, to assess the impact of the A. heterophyllus extract on colon tumor development19,20.
Results
Identification and standardization of bioactive A. heterophyllus extract
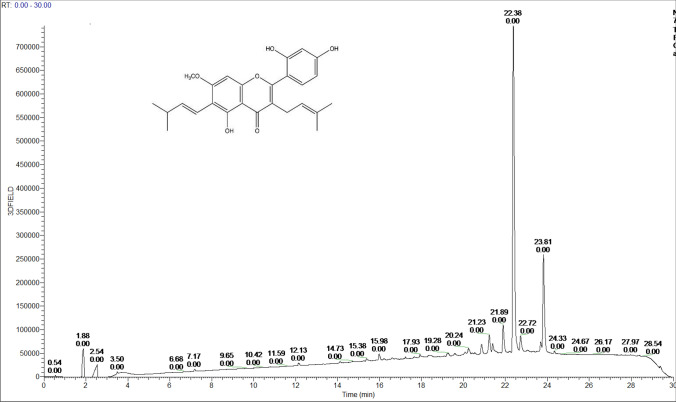
Eight crude extracts were prepared from various parts of the A. heterophyllus Lam. plant with n-hexane and methanol. Then, after an initial screen for cytotoxicity potential, the crude methanol extract from the wood was identified as the most potent. This crude extract was fractionated using column chromatography, which led to 14 semi-purified fractions. Through the application of a cytotoxic assay using a panel of three cell lines (Supplementary Table S1), those with potent bioactivity was identified. Accordingly, an enriched extract was prepared using solvent extraction. The final enriched extract (simply referred to as the A. heterophyllus extract from here on) was quantified as containing 84% (w/v) artocarpin using LC–MS (Fig. 1). This was confirmed by NMR analysis and a standard curve using the UV absorption of pure artocarpin.
Figure 1.
HPLC–MS chromatogram of the A. heterophyllus Lam. extract containing artocarpin (inset).
The prepared A. heterophyllus extract was then evaluated for cytotoxicity using the aggressive, human CRC cell line, HCT116. Cell viability decreased in a concentration- and time-dependent manner in the presence of the A. heterophyllus extract. After 24 h of treatment with the A. heterophyllus extract, an IC50 value of 9.38 ± 1.26 mg/L was obtained, while, after 48 h and 72 h of exposure, the IC50 decreased by 31% and 55% to 6.48 ± 0.63 and 4.23 ± 0.08 mg/L, respectively (Fig. 2).
Figure 2.
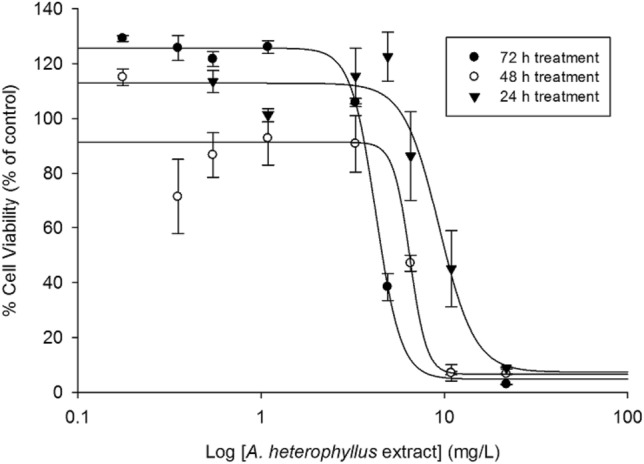
Cytotoxicity of the A. heterophyllus extract toward human colon adenocarcinoma HCT116 cells. The cells were treated with the A. heterophyllus extract for 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h, and the cell viability, as a percentage relative to the solvent (ethanol)-treated control, was measured using the MTT assay as detailed in the methods. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments.
Impact of A. heterophyllus extract on CYP2C enzyme activity in vitro and in vivo
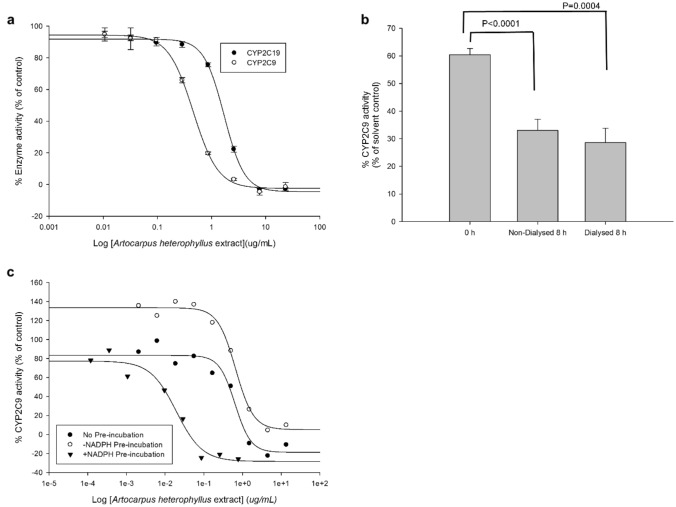
Given the putative role of CYP2C enzymes in the pathogenesis of CRC in humans and mice 13, we evaluated the inhibitory potential of the A. heterophyllus extract on the activities of human CYP2C9 and 2C19 enzymes. Potent, concentration-dependent inhibition was observed against the activity of heterologously expressed human CYP2C9 with an IC50 of 0.46 ± 0.02 µg/mL, while moderate inhibition was observed against the activity of CYP2C19, with an IC50 value of 1.71 ± 0.09 µg/mL (Fig. 3a). Further characterization of the inhibition revealed irreversible kinetics against CYP2C9 with no return in activity, even after 8 h of dialysis following exposure to the extract (Fig. 3b). A shift in IC50 of 33 units (Fig. 3c) following a 30-min preincubation is suggestive of time-dependent kinetics, although further timepoint evaluations are needed to validate such assertions.
Figure 3.
Inhibitory effects of the A. heterophyllus extract on human CYP2C9-mediated 7-methoxy-4-trifluoromethylcoumarin demethylase (80 µM) and CYP2C19-catalyzed 3-cyano-7-ethoxycoumarin deethylase (25 µM) in vitro activities. (a) A. heterophyllus extract concentration-dependent inhibition of CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 activities. Control activities performed with methanol (mean ± SEM) for CYP2C9 and 2C19 were 5.84 × 10−4 ± 3.56 × 10−5 and 8.01 × 10−3 ± 2.83 × 10−4 µM metabolite formed per min/pmol of CYP, respectively. (b) Effect of dialysis on the inactivation of human recombinant CYP2C9 activity by the A. heterophyllus extract. For (a) and (b), each data point is the mean percentage of control enzyme activity for three independent experiments. A p value ≤ 0.05 was considered statistically significant. (c) Effect of preincubation in the presence or absence of NADPH on the inhibition of human recombinant CYP2C9 activity by the A. heterophyllus extract.
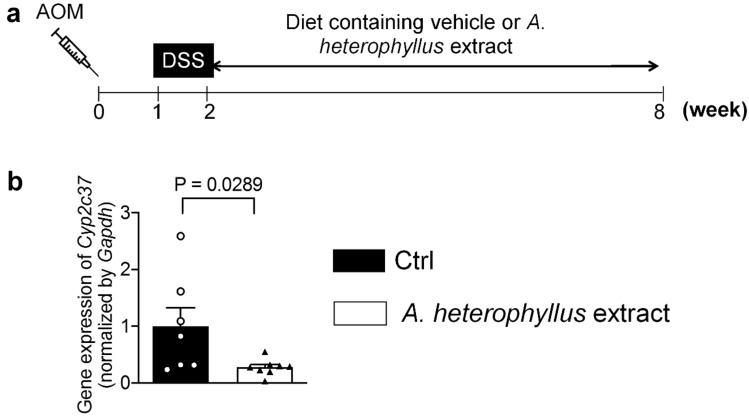
The above in vitro evaluations pointed to an effective and potent impact of the wood extract of A. heterophyllus Lam. on markers of chemoprevention and cytotoxicity, motivating its further evaluation using an in vivo model. We, therefore, implemented the AOM/DSS colitis-induced cancer mouse model to gain additional insight into in-vivo efficacy (see scheme of animal experiment in Fig. 4a).
Figure 4.
qRT-PCR evaluation of the Cyp2c37 gene expression in vivo. (a) Scheme of animal experiment. (b) qRT-PCR analysis of Cyp2c37 gene expression in colon tissues. The results are expressed as the mean ± SEM, n = 11 mice in Ctrl group and n = 10 mice in the A. heterophyllus group. Ctrl, vehicle control.
The mice with AOM/DSS colitis-induced cancer who were administered the A. heterophyllus extract displayed a marked threefold reduction (p = 0.02) in the expression of Cyp2c37 gene throughout the colon (Fig. 4b), gauged by qRT-PCR, in comparison to the vehicle control diet group. This gene was selected due to its high homology with the human CYP2C9 gene (as cyp2c9 is not found in mice). The observed reduction in Cyp2c37 gene expression, along with an inhibitory effect toward the enzyme activity of the human protein product (CYP2C9), suggests a potential role for the A. heterophyllus extract in chemoprevention via the CYP2C pathway.
Impact of A. heterophyllus extract on AOM/DSS-induced colon tumorigenesis
The effect of the A. heterophyllus extract containing artocarpin was tested on AOM/DSS-induced colon tumorigenesis in mice. The mutagenic activity of AOM requires metabolic activation by CYP2E121. Thus, the A. heterophyllus extract was included in the diet, after allowing the colonic mutagen AOM enough time to be activated by CYP2E1, coupled with DSS-induced colonic inflammation, thereby mimicking colitis-associated tumorigenesis (see scheme of animal experiment in Fig. 4a).
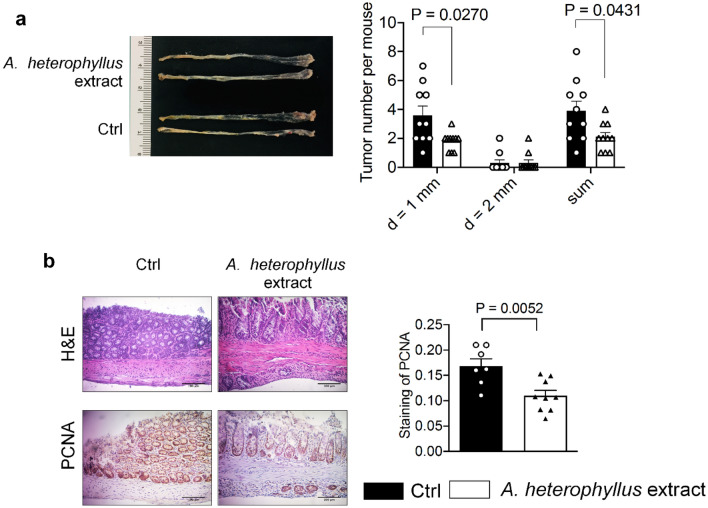
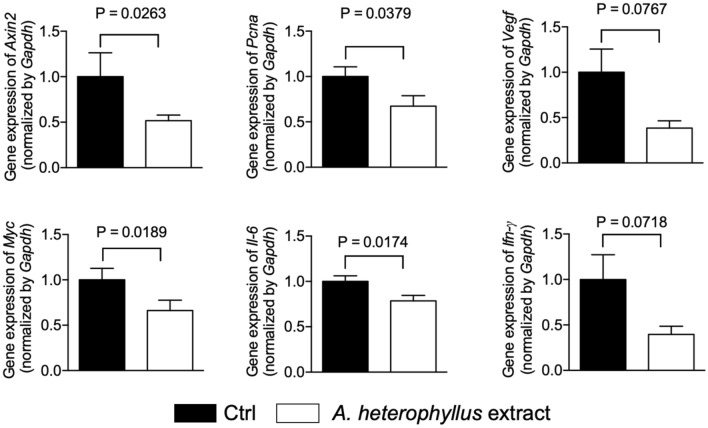
Oral administration of 480 ppm A. heterophyllus extract suppressed AOM/DSS-induced colon tumorigenesis by 46.2%. Compared with vehicle-treated AOM/DSS mice, the A. heterophyllus extract-treated mice had a significantly (p = 0.0270) lower number of tumors per mouse, particularly those with a diameter of ~ 1 mm (Fig. 5a). The extract was well tolerated, with no fatalities observed within the test group. Immunohistochemical staining showed that treatment with the A. heterophyllus extract reduced the protein expression of tumorigenic marker proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) in the colon tissues (Fig. 5b). Furthermore, treatment with the A. heterophyllus extract significantly reduced the gene expression of a series of protumorigenic and proinflammatory genes (Axin2 (p = 0.0379), Pcna (p = 0.0263), Il-6 (p = 0.0174), and Myc (p = 0.0189)), while a substantial (albeit nonsignificant) decrease in the expression of Ifn-γ (p = 0.0718) and Vegf (p = 0.0767) was seen (Fig. 6). Overall, these results demonstrate the anti-CRC effects of the A. heterophyllus extract.
Figure 5.
The Artocarpus heterophyllus extract suppresses AOM/DSS-induced colon tumorigenesis in mice. (a) Quantification of colon tumorigenesis in mice. Dissected colons were examined for number and dimension of tumors in each group and categorized on the basis of diameter (approximately 1 mm, 2 mm, and total sum). (b) H&E staining and immunochemical staining of PCNA in the colon scale bar=100μm. The results are expressed as the mean ± SEM, n = 11 mice in Ctrl group and n = 10 mice in the A. heterophyllus group. Ctrl, vehicle control; d, diameter.
Figure 6.
Expression of proinflammatory and protumorigenic genes in the colon after treatment with the Artocarpus heterophyllus extract. The results are expressed as the mean ± SEM, n = 11 mice in Ctrl group and n = 10 mice in the A. heterophyllus group. Ctrl, vehicle control.
Discussion
Using numerous in vitro and in vivo tools, we herein demonstrate the promising application of a prepared botanical wood extract (A. heterophyllus extract, 84% (w/v) artocarpin) in the reduction of tumor multiplicity, proinflammatory biomarkers, and gene expression and activities of cytochrome P450 2C enzymes, indicative of potential chemoprevention.
The extract was well tolerated in mice with 100% survival for the duration of this study, similar to previous studies involving the active component artocarpin, which suggests an acceptable safety profile18. Furthermore, cytotoxicity to cancer cells was observed using HCT116 colorectal cells with IC50 values < 10 mg/L (6.48 mg/L), along with less than half such impact on normal colon cell line CCD-18Co with an IC50 value of 17.8 mg/L, over a 48 h period. These values compared well with previous estimations of IC50 for purified artocarpin treated-colorectal cell lines SW480, HT-29, HCT15, and HCT116 with IC50 values of ~ 15 µM (or 6.55 mg/L) at 48 h, along with a nominal impact on the normal colon cell line CCD-18Co18. A time- and concentration-dependent effect on HCT116 cells was illustrated by the drop in IC50 after 48 h (6.48 ± 0.63 mg/L) and 72 h (4.23 ± 0.08 mg/L) in comparison to the value at 24 h (9.38 ± 1.26 mg/L), suggesting the likely exploitation of a pathway impacting cellular replication by the extract or its metabolites. Previously, artocarpin was proven to be cytotoxic toward a wide range of other cancer cells lines, including breast (T47D and MCF-7), bone (U-2 OS, MG63, and HOS), colon (SW480, HT-29, and HCT15), lung (A549), prostate (PC-3), and the CNS (U-87, MGU87, and U118)18,22–26, in addition to in vivo efficacy in breast, bone, colon, and prostate models18,22,26–28.
Recently, Wang and colleagues13 found that the expression of CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 (both mRNA and protein) was elevated in human colon cancer HCT116 and Caco-2 cells in comparison to the normal cell line CCD-18Co; they also demonstrated that targeted inhibitors could aid in mitigating tumorogenesis in mice. Our current results provide evidence that the presence of the A. heterophyllus extract could mitigate the in vivo gene expression of Cyp2c37 and reduce the in vitro activities of human recombinant CYP2C9 and 2C19 isoforms, thereby providing strong evidence for its inhibitory and antagonistic effect on CYP2C9’s role in CRC. Modulation of CYP gene expression, as well as the direct binding to and inhibition of overexpressed enzymes in cancer, could lead to mitigation of carcinogenesis and tumor progression29. We also found that the extract behaves as an irreversible inhibitor (Fig. 3), providing it with the potential advantage of a lasting impact. Future studies considering chronic exposure and its impact on co-administered drugs reliant on CYP2C9 metabolism9 would allow expanding its safety profile.
Following the promising in vitro results, we embarked on a study of the impact of the A. heterophyllus extract in the AOM/DSS mouse model. The results obtained herein show that oral administration of the A. heterophyllus extract, as the component of a diet fed to AOM/DSS-induced colon tumorigenesis mice, reduced tumor multiplicity, consistent with the findings of a previous study utilizing a pure artocarpin gavage18. Moreover, according to Fig. 6, the expression of proinflammatory and protumorigenic genes (Axin2, Ifn-γ, and C-myc) was downregulated, partially supporting a previous murine study which showed that topical application of artocarpin resulted in the decreased protein expression of proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β and TNF-α30. While there was a decrease in the genetic expression of Il-1β and Tnf-α in this study, it was not significant (data not shown).
Previous research has suggested the arachidonic acid/COX-2 pathway via CYP activation as a key player in the inflammatory response driving colitis-associated colon tumorigenesis13,30. Furthermore, a previous in vitro experiment determined that artocarpin, like celecoxib, acts as a COX-2 inhibitor with anti-inflammatory properties, which, in the presence of AOM/DSS, results in an increase in inflammatory response18,31. DSS-induced colitis, caused by the microrupture of colon epithelial tissue, is characterized by the infiltration of immune cells as an inflammatory response32,33. We identified a decrease in the gene expression of proinflammatory cytokine Il-6 and chemokine Ifn-γ (Fig. 6) in mice fed the A. heterophyllus extract. Artocarpin, as one of numerous Artocarpus spp.-derived phytochemicals, has been shown in numerous studies to behave as an anti-inflammatory and anticancer agent, which suggests a potential role in addressing the inflammation seen in colitis-associated cancer27,34. These results demonstrate that, while the extract could repress the proinflammatory response, its antitumor effects, similar to celecoxib, may not depend solely on its anti-inflammatory properties31,35.
There was a significant reduction in tumor proliferation, as well as a reduction in crypt cells marked by PCNA staining. Additionally, H&E staining of colon tissue showed greater inflammation in control mice, suggesting that treatment with the A. heterophyllus extract aids in the recovery from AOM/DSS-associated colitis tumorigenesis.
In summary, the administration of an extract from A. heterophyllus Lam., standardized to contain 84% (w/v) artocarpin, effectively suppressed tumor multiplicity and inflammation in AOM/DSS-induced mouse colon via decreasing the expression of cytokine Il-6. Additionally, the reduced expression of the Cyp2c37 gene in mice and the potent inhibition toward the activity of human CYP2C9, an upregulated isoform in colon cancer cells, point to the chemopreventive potential of this extract. Taken together, the A. heterophyllus extract with its active component, artocarpin, displays promising anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and chemopreventive properties and may be a lead molecule for treating colitis-associated tumorigenesis.
Materials and methods
Preparation of crude polar and nonpolar plant extracts
Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. (Voucher # 36378), collected at the Botany Gardens, the University of the West Indies, Mona-Campus, Jamaica, was authenticated by Mr Patrick Lewis, the local herbarium curator. Oven-dried wood chips (1200 g), fruit rind chips (323 g), ground testa (24 g), and seeds (170 g) were exhaustively extracted with n-hexane and then methanol, at least 3 times. Crude extracts were concentrated to dryness in vacuo on a rotary evaporator (Heidolph Laborota 4000 efficient and BUCHI water bath B-481) below 55 °C, and they were stored at − 20 °C in aluminum-wrapped glass vials until reconstituted in appropriate solvents for cytotoxicity evaluation.
Semi-purification of crude methanol extract via silica gel column chromatography
Following the determination of optimum cytotoxicity, the methanol crude extract of the wood chips (red–orange gum, 3 g) was subjected to further separation using silica gel 60 Å (230–400 mesh (40–63 μm) particle size, SiliCycle Inc., Quebec City, QC, Canada) gravity column chromatography. The crude methanol wood extract was added to the column (60 × 6 cm) and eluted with 90% n-hexane with increasing concentrations of ethyl acetate. This was followed by neat ethyl acetate, which was gradually enriched with methanol to a maximum concentration of 75% (v/v), to produce 14 different semi-purified fractions (I–XIV). These were monitored using TLC via molybdenum spray detection and combined according to Rf values. The fractions were concentrated, and the resulting powdered extracts were stored as previously described, before subsequent use in cytotoxicity evaluation against colorectal (HT29), prostate (PC3), and liver (HepG2) cancer cell lines (Table S1), subject to the quantity of material available.
Preparation and standardization of an enriched A. heterophyllus extract
Guided by the conditions that yielded the most potent fractions from chromatographic separation (above), an enriched extract was prepared, as briefly described elsewhere36. Oven-dried wood chips (2.5 kg) of A. heterophyllus Lam. were exhaustively defatted with n-hexane and then differentially re-extracted in methanol in amber containers. The methanol crude extract (21.2 g, yield: 0.85%), concentrated as previously described, was suspended in water and subjected to successive portioning with equivalent volumes of n-hexane followed by methylene chloride. The methylene chloride portion was subsequently recrystallized with ethyl acetate/hexane, producing a yellow-orange powder (referred to as the A. heterophyllus extract, 4.5 g, yield: 0.18%), standardized for artocarpin (Fig. 1) and stored at − 20 °C in an aluminum-wrapped glass vial until further use.
To quantitatively determine artocarpin content in the extract, it was dissolved to a concentration of 1.53 mg/mL in methanol, before injecting 2 µL into a quantitative high-performance liquid chromatograph (HPLC) mass spectrometer (MS) equipped with UV diode array detection (DAD) (Velos-Pro, Thermo Fisher Scientific). A Phenomenex C18 column (150 × 3 mm, 3 μm particle size) was used as the stationary phase, and the mobile phase at a flow rate of 0.4 mL/min was applied as follows: 0–1 min = isocratic gradient 10% acetonitrile in H2O; 1–20 min = linear gradient 10% acetonitrile in H2O to 10% acetonitrile in methanol. Pure artocarpin (BOC Sciences NY, USA) was used to produce a calibration curve at concentrations of 1.1 mg/mL, 0.55 mg/mL, and 0.257 mg/mL, using 2 µL injections. Concentrations were calculated from the integrated UV peak areas at a wavelength of 256 nm. HPLC-grade solvents were used.
In vitro CYP P450 enzyme assays
High-throughput fluorometric inhibition assays performed in 96-well microtiter plates were used to evaluate the inhibitory capacity of the A. heterophyllus extract on human CYP2C enzyme activity. Catalytic activities describing the CYP2C9-mediated conversion of 7-methoxy-4-trifluoromethylcoumarin (MFC) demethylase (80 µM) to fluorescent 7-hydroxy-4-trifluoromethyl-coumarin (HFC) and 3-cyano-7-ethoxycoumarin (CEC) deethylase (25 µM) to fluorescent 3-cyano- 7-hydroxycoumarin (CHC)37,38 were monitored. For inhibition assays, the incubating mixture contained CYP2C9 (Cypex Ltd.) (2.5 pmol) and CYP2C19 (Cypex Ltd.) (1.0 pmol), in 0.1 M potassium phosphate buffer (KPB, pH 7.4) in a final volume of 0.2 mL, which was prewarmed for 10 min, unless otherwise stated37. Following the appropriate incubation period (CYP2C9, 45 min and CYP2C19, 30 min), 75 μL of 80% acetonitrile/20% Tris base (0.5 M) was added to stop the reaction. Fluorescence generated from the formation of CHC or HFC was recorded using a Varian Cary Eclipse Fluorescence Spectrophotometer microplate reader with excitation/emission wavelengths of 409/460 nm and 405/530 nm, respectively. Methanol (1.5% v/v) was used as a negative control.
Direct inhibition studies (IC50 determination)
The prewarmed A. heterophyllus extract was serially diluted (23.27–0.01 µg/mL) in tubes containing human CYP2C enzymes and their respective substrates, at concentrations equal to their Km values37. NADPH (43 µM) was added to initiate the reaction. After terminating the reaction, fluorescence data were measured and converted to CYP activity ± SEM as a percentage of the control using Microsoft Excel (2002). IC50 values were determined by fitting the average % CYP activity ± SEM with a four-parameter logistic (4PL) nonlinear regression model, using SigmaPlot 10.0 from Systat Software Inc., San Jose California USA, www.systatsoftware.com.
where Min and Max are the minimal and maximal observed effects, respectively, x is the concentration of the test agent, and IC50 is the half-maximal inhibitory concentration.
In order to determine the kinetics of the A. heterophyllus extract on CYP2C9 activity, dialysis, and IC50 shift assays were carried out. To evaluate reversibility, CYP2C9 was preincubated with an IC75 concentration of extract in a Pur-A-Lyzer™ Midi 60,010 dialysis unit (Sigma Aldrich) or microcentrifuge tube for 8 h at 4 °C. The residual enzyme activity of the incubation mixtures pre and post dialysis was expressed as a percentage of their respective vehicle controls (0.18% methanol). For the IC50 shift assay, the A. heterophyllus extract in the presence of CYP2C9 (5 pmol) was directly incubated with substrate (160 µM) or first preincubated with or without NADPH for 30 min.
Cell lines and culture
The human colon adenocarcinoma cell line HCT116 (ATCC, CCL-247) and normal cell line CCD-18Co (ATCC, CRL-1459) were cultured in DMEM, supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, and maintained under standard cell culture conditions at 37 °C and 5% CO2 in a humidified incubator39. To rule out specificity to one type of colon cancer cell, the aggressive HCT116 cell line was used, as HT29 cells were employed earlier in the study (Table S1).
Cell viability assay
Viable cells were quantified using a tetrazolium-based colorimetric 3‐(4,5‐dimethylthiazol‐2‐yl)‐2,5‐diphenyl‐2H‐tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, by determining the amount of formazan crystals produced by metabolically active cells40,41. Following 24 h of incubation, cells seeded into 96-well plates (1–1.5 × 103 cells per well) were exposed to the A. heterophyllus extract or ethanol (3% v/v) for a further 24, 48, or 72 h. After disposal of used medium, MTT in fresh medium (0.5 mg/mL) was added to each well. The plate was incubated for 1–2 h, after which the medium was discarded and the formed formazan crystals were dissolved in DMSO (100 µL). The absorbance of cells was measured at 570 nm using a BioTek Synergy 2 microplate spectrophotometer with Gen5 Software (Bio-Tek). The data are presented as the percentage of viable cells using SigmaPlot 10.0, and the IC50 values were determined.
Animal experiments
The mouse experiments were conducted in accordance with the protocols approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of Massachusetts Amherst (protocol number: 2017–0019) with mice maintained in a specific pathogen-free (SPF) facility of the University of Massachusetts (Amherst, MA). C57BL/6 male mice (age: 6 weeks) were purchased from Charles River (Cambridge, MA). All methods involving animals are reported in accordance with ARRIVE guidelines42.Upon arrival, the mice were allowed free access to water and a chow diet for 1 week acclimation. Afterward, mice were treated with 10 mg/kg AOM (Sigma Aldrich) via intraperitoneal injection, and at week 1 post AOM injection, they were given 2% DSS (36–50 kDa, MP Biochemicals) in drinking water for 1 week. Mice were then randomly assigned to two groups (n = 11 in control group, (mean ± SEM) body weight = 23.02 ± 0.39 g; and n = 10 in A. heterophyllus group, (mean ± SEM) body weight = 22.94 ± 0.46 g) and maintained ad libitum on a modified AIN-9G diet (containing 10% fat). Corn oil was the only source of fat content, and the diet composition, as described in Supplementary Table S2, contained 480 mg of A. heterophyllus extract/kg diet dissolved in polyethylene glycol 400 (PEG 400, Millipore) as a vehicle (0.1% in diet, v/w) or vehicle alone for 6 weeks. All ingredients except the corn oil and A. heterophyllus extract were purchased from Dyets Inc. Bethlehem, PA. The diets were freshly prepared and changed twice weekly. At week 8 post AOM injection, the mice were sacrificed, and colon tissues were collected for analysis. Colon tissues were cut open longitudinally, washed in PBS, and inspected under a dissecting microscope. The size of the tumors was determined using the following formula: tumor size = π × d2/4, where d is the diameter of each tumor. Tissue staining and qRT-PCR analysis of gene expression in colon tissues were carried out according to protocols described in the Supplementary Materials and Methods using the RT-PCR primers listed in Supplementary Table S3.
Statistical analysis
Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. Significance comparisons for in vitro data were performed using a two-tailed Student t-test with data analysis performed using SigmaPlot 10.0, while comparisons between two groups (in vivo) were performed using the Mann–Whitney test with data analysis performed using Prism 6 (GraphPad Software). A p value < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
Supplementary Information
Acknowledgements
We graciously acknowledge the assistance of Patrick Lewis, curator of herbarium at the University of the West Indies (UWI Mona), for plant identification and Marc Collins, who aided in extractions and separations of extracts at the Department of Chemistry, UWI, Mona. We are also grateful to Professor Eric A. Decker for facilitating collaborative partnerships and Prof. Hang Xiao and Prof. Margie Clapper for helpful discussions. We are very grateful to Dr. William Irvine for editorial support. The authors are also grateful for the funding support from the following agencies: to R.D., Caribbean Public Health Agency (CARPHA) via US National Cancer Institute (NCI) grant (#62798), University of the West Indies Development Fund (UWIDEF), National Health Fund, Jamaica, and National Commission for Science and Technology and Jamaica–South Africa bilateral agreement; to I.J.M., University of the West Indies Graduate Studies and Research, Graduate Research Grant; to G.Z., USDA/Hatch, MAS00556.
Author contributions
I.J.M. and J.Z. contributed equally to this work and conducted the major portion of the experiments; J.L. and J.E.M. assisted in the acquisition of data; M.K.L., N.J.S., and J.B. conducted and interpreted the HPLC–MS data; R.D., R.P., and G.Z. conceptualized and designed the experiments; I.J.M. and R.D. wrote the manuscript and all authors contributed to and reviewed the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These authors contributed equally: Isaac J. Morrison and Jianan Zhang.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41598-021-86040-5.
References
- 1.Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020;70:7–30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gibson T, Hanchard B, Waugh N, McNaughton D. Age-specific incidence of cancer in Kingston and St Andrew, Jamaica, 2003–2007. West Indian Med. J. 2010;59:456–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wu A, Paganini-Hill A, Ross R, Henderson B. Alcohol, physical activity and other risk factors for colorectal cancer: A prospective study. Br. J. Cancer. 1987;55:687–694. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bhandari A, Woodhouse M, Gupta S. Colorectal cancer is a leading cause of cancer incidence and mortality among adults younger than 50 years in the USA: A SEER-based analysis with comparison to other young-onset cancers. J. Investig. Med. 2017;65:311–315. doi: 10.1136/jim-2016-000229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Plummer JM, et al. Colorectal cancer survival in Jamaica. Ann. Med. Surg. 2016;6:26–29. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2016.01.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gröschel C, et al. Switching to a healthy diet prevents the detrimental effects of western diet in a colitis-associated colorectal cancer model. Nutrients. 2020;12:45. doi: 10.3390/nu12010045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Newman DJ, Cragg GM. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020 doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b01285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Foster K, Younger N, Aiken W, Brady-West D, Delgoda R. Reliance on medicinal plant therapy among cancer patients in Jamaica. Cancer Causes Control. 2017;28:1349–1356. doi: 10.1007/s10552-017-0924-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Delgoda R, Westlake AC. Herbal interactions involving cytochrome P450 enzymes. Toxicol. Rev. 2004;23:239–249. doi: 10.2165/00139709-200423040-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Furge LL, Guengerich FP. Cytochrome P450 enzymes in drug metabolism and chemical toxicology: An introduction. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2006;34:66–74. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.49403402066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yamazaki H, Shaw PM, Guengerich FP, Shimada T. Roles of cytochromes P450 1A2 and 3A4 in the oxidation of estradiol and estrone in human liver microsomes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1998;11:659–665. doi: 10.1021/tx970217f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kim JH, et al. Expression of cytochromes P450 1A1 and 1B1 in human lung from smokers, non-smokers, and ex-smokers. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004;199:210–219. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2003.11.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wang W, et al. Targeted metabolomics identifies the cytochrome P450 monooxygenase eicosanoid pathway as a novel therapeutic target of colon tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2019 doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-3221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Enayetallah AE, French RA, Grant DF. Distribution of soluble epoxide hydrolase, cytochrome P450 2C8, 2C9 and 2J2 in human malignant neoplasms. J. Mol. Histol. 2006;37:133–141. doi: 10.1007/s10735-006-9050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Francis S, Delgoda R. A patent review on the development of human cytochrome P450 inhibitors. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2014;24:699–717. doi: 10.1517/13543776.2014.899583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dihal AA, et al. Quercetin, but not its glycosidated conjugate rutin, inhibits azoxymethane-induced colorectal carcinogenesis in F344 rats. J. Nutr. 2006;136:2862–2867. doi: 10.1093/jn/136.11.2862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wei B-L, et al. Antiinflammatory flavonoids from Artocarpus heterophyllus and Artocarpus communis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005;53:3867–3871. doi: 10.1021/jf047873n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sun G, et al. Chemoprevention of colorectal cancer by artocarpin, a dietary phytochemical from Artocarpus heterophyllus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017;65:3474–3480. doi: 10.1021/jf047873n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Stastna M, Janeckova L, Hrckulak D, Kriz V, Korinek V. Human colorectal cancer from the perspective of mouse models. Genes (Basel) 2019;10:788. doi: 10.3390/genes10100788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tanaka T, et al. A novel inflammation-related mouse colon carcinogenesis model induced by azoxymethane and dextran sodium sulfate. Cancer Sci. 2003;94:965–973. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2003.tb01386.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sohn OS, Fiala ES, Requeijo SP, Weisburger JH, Gonzalez FJ. Differential effects of CYP2E1 status on the metabolic activation of the colon carcinogens azoxymethane and methylazoxymethanol. Cancer Res. 2001;61:8435–8440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lee CW, Chi MC, Chang TM, Liu JF. Artocarpin induces cell apoptosis in human osteosarcoma cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress and reactive oxygen species. J. Cell Physiol. 2019;234:13157–13168. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lee C-W, et al. Extracts of Artocarpus communis induce mitochondria-associated apoptosis via pro-oxidative activity in human glioblastoma cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2018;9:411. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Arung ET, et al. Cytotoxic effect of artocarpin on T47D cells. J. Nat. Med. 2010;64:423–429. doi: 10.1007/s11418-010-0425-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tsai M-H, et al. Artocarpin, an isoprenyl flavonoid, induces p53-dependent or independent apoptosis via ROS-mediated MAPKs and Akt activation in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2017;8:28342. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Di X, et al. New phenolic compounds from the twigs of Artocarpus heterophyllus. Drug Discov. Ther. 2013;7:24–28. doi: 10.5582/ddt.2013.v7.1.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chan EWC, et al. Chemistry and pharmacology of artocarpin: An isoprenyl flavone from Artocarpus species. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2018;8:86–91. doi: 10.5530/srp.2018.1.12. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zheng Z-P, et al. Characterization of antiproliferative activity constituents from Artocarpus heterophyllus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014;62:5519–5527. doi: 10.1021/jf500159z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.D'Uva G, Baci D, Albini A, Noonan DM. Cancer chemoprevention revisited: Cytochrome P450 family 1B1 as a target in the tumor and the microenvironment. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018;63:1–18. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2017.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lee C-W, et al. Artocarpin attenuates ultraviolet B-induced skin damage in hairless mice by antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effect. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013;60:123–129. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.07.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Coudry, R. A. et al. Correlation of inhibition of colitis-associated dysplasia by celecoxib with degree of inflammation in the mouse model of DSS-induced colitis (2004).
- 32.Parang B, Barrett CW, Williams CS. Gastrointestinal Physiology and Diseases. Springer; 2016. pp. 297–307. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Pastorelli L, De Salvo C, Mercado JR, Vecchi M, Pizarro TT. Central role of the gut epithelial barrier in the pathogenesis of chronic intestinal inflammation: Lessons learned from animal models and human genetics. Front. Immunol. 2013;4:280. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ock CY, et al. Prevention of colitis-associated colorectal cancer with 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila) 2011;4:1507–1521. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-11-0161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Saud SM, et al. Chemopreventive activity of plant flavonoid isorhamnetin in colorectal cancer is mediated by oncogenic Src and β-catenin. Cancer Res. 2013;73:5473–5484. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-0525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yeh C-J, et al. The effects of artocarpin on wound healing: In vitro and in vivo studies. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:1–13. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15876-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Murray J, et al. Significant inhibitory impact of dibenzyl trisulfide and extracts of Petiveria alliacea on the activities of major drug-metabolizing enzymes in vitro: An assessment of the potential for medicinal plant-drug interactions. Fitoterapia. 2016;111:138–146. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2016.04.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Crespi CL, Miller VP, Penman BW. Microtiter plate assays for inhibition of human, drug-metabolizing cytochromes P450. Anal. Biochem. 1997;248:188–190. doi: 10.1006/abio.1997.2145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Campbell S, Murray J, Delgoda R, Gallimore W. two new oxodolastane diterpenes from the Jamaican Macroalga Canistrocarpus cervicornis. Mar. Drugs. 2017;15:150. doi: 10.3390/md15060150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Alley MC, et al. Feasibility of drug screening with panels of human tumor cell lines using a microculture tetrazolium assay. Cancer Res. 1988;48:589–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Moghadam MH, et al. Anti-proliferative activity and apoptotic potential of britannin, a sesquiterpene lactone from Inula aucheriana. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2012;7:979–980. doi: 10.1177/1934578X1200700804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Percie du Sert N, et al. Reporting animal research: Explanation and elaboration for the ARRIVE guidelines 2.0. PLoS Biol. 2020;18:e3000411. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.