Figure 2.
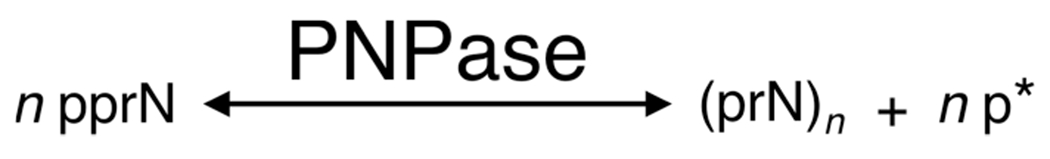
Proposed pathway of PNPase RNA synthesis and degradation. From left to right, 5′ diphosphate ribonucleosides (pprN) drive the reaction toward PNPase catalysis of RNA (n monomers long), with the release of orthophosphate. At high concentrations, phosphate byproduct (p*) drives the reaction (right to left) toward phosphorolysis, degrading RNA into its 5′ diphosphate ribonucleoside monomers.23
