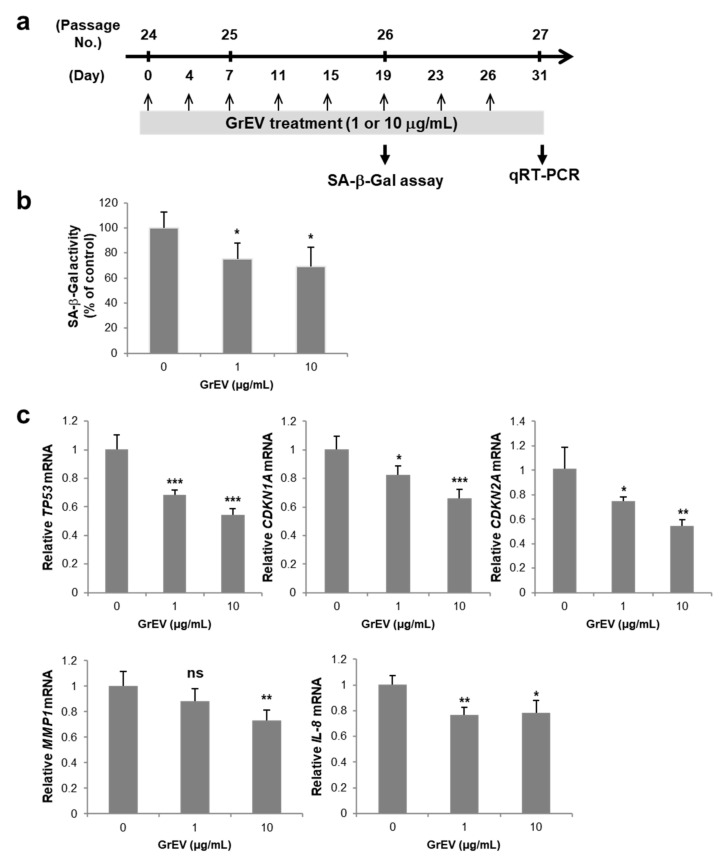
Figure 2.
Ginseng root-derived extracellular vesicles (GrEVs) caused an anti-senescence effect in replicative senescent human dermal fibroblasts (HDFs). (a) Scheme used to treat replicative senescent HDFs with GrEVs. HDFs (2 × 105), which were not treated (0 µg/mL; HEPES-buffered saline (HBS) buffer-treated) or were repeatedly treated with GrEVs at different doses (1 or 10 µg/mL) every third or fourth day, were harvested at passage numbers 26 and 27 (after > 50 population doublings). (b,c) The harvested cells were analyzed for senescence-associated beta-galactosidase (SA β-Gal) activity using a Mammalian β-Gal Assay Kit (b) and for gene expression by performing reverse transcriptase-quantitative polymerase chain reaction experiments using specific primers (c). SA β-Gal activity and gene expression levels were normalized to protein quantities and RPL13A expression, respectively. The data (in b and c) represent the means ± standard deviations of three independent experiments, using two independent senescent cell lines from one donor (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001; ns, non-significant).