To the editor:
International recommendations on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccine distribution have given priority to immunocompromised patients, including kidney transplant recipients (KTRs).1 , 2 Unfortunately, this guidance has been released without inclusion of this clinical population in vaccine clinical trials. In an effort to shed light on the efficacy and safety of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in KTRs, this preliminary study was undertaken to investigate the anti–severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) antibody response after the first injection.
We examined 242 KTRs who received the first injection of the Moderna mRNA-1273 vaccine (100 μg) at the Strasbourg University Hospital (Strasbourg, France) between January 21 and 28, 2021. All had a negative history for COVID-19 and tested negative for anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibodies on the day of the first injection. The anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibody response against the spike protein was assessed at 28 days after injection using the ARCHITECT IgG II Quant test (Abbott, Abbott Park, IL), with titers >50 arbitrary units (AUs)/ml being considered as positive (detection range, 6.8–40,000 AUs/ml; positive agreement, 99.4%; negative agreement, 99.6%).
One patient developed mild symptomatic COVID-19 7 days after injection, and only 26 (10.8%) KTRs had a positive serology at 28 days after injection. The median IgG titer was 224 AUs/ml (interquartile range, 76−496 AUs/ml), whereas the median IgG titer in the seronegative group was <6.8 AUs/ml (Figure 1 ). Patients who seroconverted had longer time from transplantation, received less immunosuppression, and had a better kidney function (Table 1 ).
Figure 1.
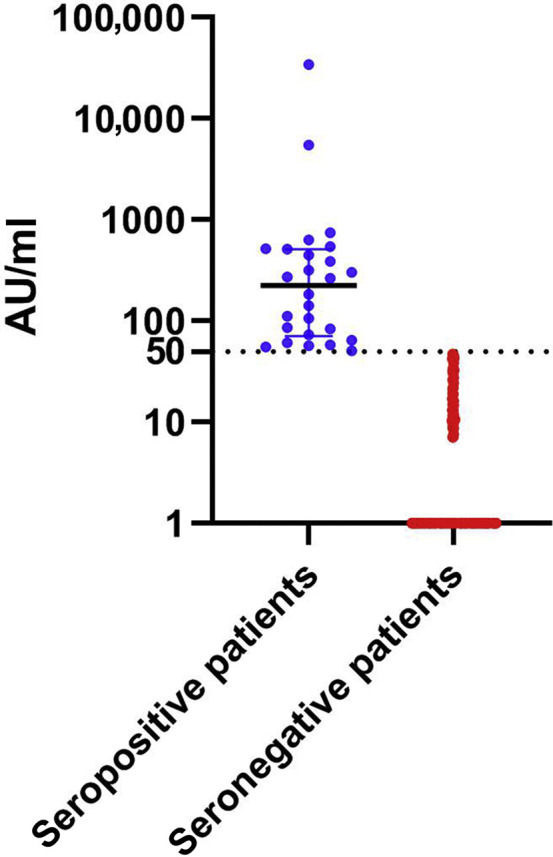
Anti-spike IgG antibody titers measured at 28 days after vaccination in 215 seronegative kidney transplant recipients (median titer, <6.8 arbitrary units [AUs]/ml [interquartile range, <6.8−<6.8 AUs/ml]) and 26 seropositive kidney transplant recipients (median titer, 224 AUs/ml [interquartile range, 76−496 AUs/ml]). The dotted line indicates the cutoff for positivity (50 AUs/ml).
Table 1.
Characteristics of kidney transplant recipients, according to serologic response after the first dose of the Moderna mRNA-1273 vaccine
| Characteristics | Entire cohort (n=241)a | SARS-CoV-2 seronegative patients (n=215) | SARS-CoV-2 seropositive patients (n=26) | P value | Missing data |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, yr | 57.7 (49.3–67.6) | 57.7 (49.6–67.7) | 58.4 (43.3–66.9) | 0.51 | 0 |
| Male sex | 156 (64.7) | 142 (66.1) | 14 (53.9) | 0.28 | 0 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 25.7 (22.6–29.5) | 25.7 (22.8–29.4) | 26.4 (21.9–29.9) | 0.73 | 2 |
| Time from kidney transplantation, yr | 6.4 (2.9–13) | 5.8 (2.8–11.9) | 15.4 (8.6–25.9) | <0.001 | 2 |
| First transplantation | 202 (83.8) | 176 (81.8) | 26 (100) | 0.01 | 0 |
| Deceased donor | 192 (79.6) | 172 (80) | 20 (76.9) | 0.8 | 0 |
| ABO group | 0.02 | 2 | |||
| O | 94 (39.3) | 82 (38.5) | 12 (46.2) | ||
| A | 101 (42.3) | 93 (43.7) | 8 (30.8) | ||
| B | 30 (12.6) | 29 (13.6) | 1 (3.9) | ||
| AB | 14 (5.9) | 9 (4.2) | 5 (19.2) | ||
| Induction treatment | 0.001 | 7 | |||
| Anti-thymocyte globulin | 138 (59.5) | 127 (60.8) | 11 (47.8) | 9 | |
| Anti-CD25 | 88 (37.9) | 80 (38.3) | 8 (34.8) | ||
| No induction | 6 (2.6) | 2 (1) | 4 (17.4) | ||
| CNI | 0.06 | 0 | |||
| Tacrolimus | 133 (55.2) | 124 (57.7) | 9 (34.6) | ||
| Ciclosporin | 82 (34) | 69 (32.1) | 14 (50) | ||
| No CNI | 26 (10.8) | 22 (10.2) | 4 (15.4) | ||
| MMF/MPA | 191 (79.3) | 177 (82.3) | 14 (53.9) | 0.002 | 0 |
| Azathioprine | 7 (2.9) | 4 (1.86) | 3 (11.5) | 0.03 | 0 |
| mTOR inhibitors | 35 (14.5) | 32 (14.9) | 3 (11.6) | 1 | 0 |
| Steroids | 142 (58.9) | 133 (61.9) | 9 (34.6) | 0.01 | 0 |
| Belatacept | 9 (3.8) | 9 (4.2) | 0 | 0.26 | 0 |
| eGFR, ml/min per 1.73 m2 | 51.6 (38.1–68) | 51 (37.9–66.5) | 64.9 (39.9–72.2) | 0.08 | 0 |
| Serum creatinine, μmol/L | 118 (99–158) | 120 (101–159) | 104 (85–134) | 0.05 | 0 |
BMI, body mass index; CD, cluster of differentiation; CNI, calcineurin inhibitor; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; MMF, mycophenolate mofetil; MPA, mycophenolic acid; mTOR, mechanistic target of rapamycin; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Continuous variables are presented as medians (interquartile ranges), whereas categorical variables are given as n (%).
The patient who developed coronavirus disease 2019 after the first injection was excluded from the analysis.
In summary, the burden of immunosuppression may induce a weak anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibody response in KTRs after the first injection of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. This finding is strikingly different compared with immunocompetent subjects, who invariably seroconverted after the first injection.3 , 4 We highlight the need not to delay the second vaccine injection in immunocompromised patients. Close surveillance is also recommended to discuss the opportunity of a third dose in less responsive patients.
Footnotes
see commentary on page 1275
References
- 1.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 vaccination program operational guidance. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/covid-19/covid19-vaccination-guidance.html
- 2.ECD. COVID-19 vaccination and prioritisation strategies in the EU/EEA. Available at: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/COVID-19-vaccination-and-prioritisation-strategies.pdf
- 3.Jackson L.A., Anderson E.J., Rouphael N.G. An mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 — preliminary report. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1920–1931. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2022483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Prendecki M., Clarke C., Brown J. Effect of previous SARS-CoV-2 infection on humoral and T-cell responses to single-dose BNT162b2 vaccine. Lancet. 2021;397:1178–1181. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00502-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


