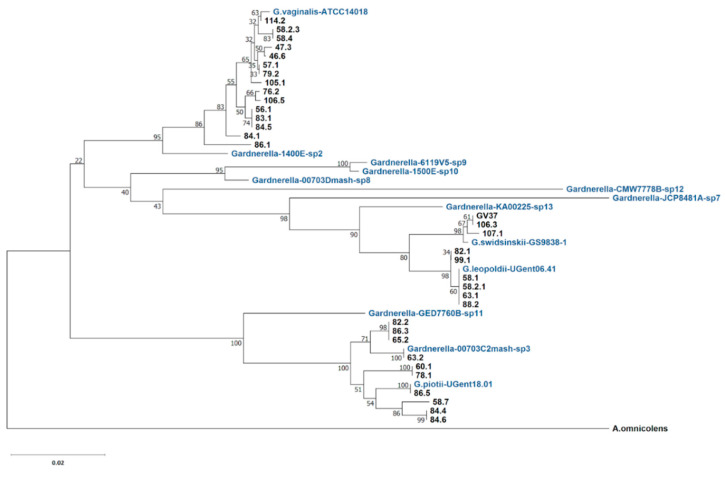
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic relationships of 34 Gardnerella spp. isolates based on cpn60 UT sequences. The type strains of G. vaginalis, G. piotii, G. swidsinskii, G. leopoldii species and nine genome species [13] were included. Evolutionary history was inferred using the neighbor-joining method [18]. The percentage of the replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test of 500 replicates is indicated. Alloscardovia omnicolens sequence was included as an outgroup [17]. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA X [19].