Abstract
Background
Orthotopic liver transplantation has become the procedure of choice for end-stage liver disease. There are 3 commonly used methods of vena cava anastomosis. Here, we report a new technique for native hepatectomy.
Material/Methods
The data of 12 patients who underwent orthotopic liver transplantation using a new surgical technique were retrospectively collected for analysis. The new separation and reconstruction surgical technique mainly involved the second portal isolation and hepatectomy that followed. We performed recipient liver resection without the occlusion of the inferior vena cava, which was then followed by classic, piggyback, modified piggyback, or side-to-side orthotopic liver transplantation. The graft function index and complications were collected after transplantation.
Results
The length of the anhepatic phase was 30.92±9.1 min. Alanine transaminase (ALT) levels were 138 to 2027 U/L, with a median of 361.5 U/L. The ALT levels of all patients gradually decreased to normal levels 7 to 10 days after surgery. Only 2 recipients had elevated levels of ALT higher than 1000 U/L. Four of 12 patients did not require red blood cell transfusion during surgery. Four patients appeared to have early allograft dysfunction, while others recovered smoothly.
Conclusions
This new surgical technique may shorten the anhepatic phase and decrease blood loss volume, aiding the success of liver transplant surgery. It can be used for most patients and does not increase the risk of complications or impair prognosis.
Keywords: Hepatectomy; Liver Transplantation; Surgical Procedures, Operative
Background
Liver transplantation is a successful therapy that helps many patients with end-stage liver disease recover from critical illness, giving them a nearly normal quality of life [1]. Since the first reported human liver transplantation performed by Starzl in 1963 [2], liver transplantation surgery has been performed worldwide, with more than 20 000 procedures conducted yearly in recent years [3]. With improvements in surgical techniques and immunosuppression therapy, the 1-year and 5-year patient survival rates (82% and 70%, respectively) and 1-year and 5-year graft survival rates (73% and 61%, respectively) have improved [4]. Although the 1-year survival rate reached 91.6% in benchmark liver transplantation cases (patients having a model for end-stage liver disease score ≤20, a balance of risk score ≤9, and receiving a primary graft by donation after brain death [DBD]), half of benchmark patients developed severe complications during the 1-year follow-up [5]. Twenty percent of benchmark patients developed biliary complications in the 6 months after surgery [5]. Therefore, improvements are still needed in the liver transplantation procedure.
The technique for orthotopic liver transplantation is based on 3 different methods of caval reconstruction: classic, piggyback, and side-to-side caval anastomosis [6–8]. The classic technique requires cross-clamping of the suprahepatic and intrahepatic inferior vena cava (IVC) and excision of the retrohepatic vena cava. The piggyback and side-to-side caval anastomosis procedures only partially occlude the IVC and allow some venous return in the anhepatic phase [7,8]. The classic technique may prolong the anhepatic phase and increase the incidence of kidney failure and unstable hemodynamics during or after surgery. Although the piggyback technique may prove beneficial for hemodynamic stability, the transfusion requirements increase because of the incomplete cross-clamping of the vena cava [7,8]. In all of these methods, the anhepatic phase and volume of blood loss are the crucial measures of surgical outcome. It has been shown that an anhepatic phase longer than 100 min is a significant independent predictive factor for primary nonfunction or initial poor function [9]. As surgeons, we are most concerned with the blood loss volume and the anhepatic phase during surgery, because these factors directly affect the patient’s recovery of graft function after transplantation. It has been shown that previous abdominal surgery increases hepatectomy time and bleeding with a consequent reduction in long-term overall survival. Here, we report a new technique of liver transplantation that offers benefits including easier intraoperative exposure, shorter anhepatic phase, and decreased blood loss. This technique might provide a new surgical mode of liver transplantation. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first procedure of its kind described to date. Furthermore, no previous reports have focused on the liver isolation technique or the completion of a native hepatectomy.
Material and Methods
Patients
The data of 12 patients who underwent liver transplantation from January 2018 to May 2018 at the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China, were analyzed retrospectively. All patients had the new technique performed by the same transplant surgeon. Recipient characteristics including age, sex, weight, operative blood loss, hepatic venous anastomosis technique, cold ischemia and warm ischemia time, duration of anhepatic phase, type of graft, duration of surgery, and primary transplant were obtained from the database. Some data were collected from retrospective paperwork and electronic medical records. The pretransplant model of end-stage liver disease (MELD) score was used as a marker of disease severity. The amount of intraoperative blood loss and volume resuscitation were chosen to identify the extent of surgical difficulty. The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, and informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Procedure of Surgical Isolation Technique
Our separation and reconstruction surgical technique was conducted as follows. The new technique involved recipient liver resection without occlusion of the IVC, which was then followed by classic, piggyback, modified piggyback, or side-to-side orthotopic liver transplantation.
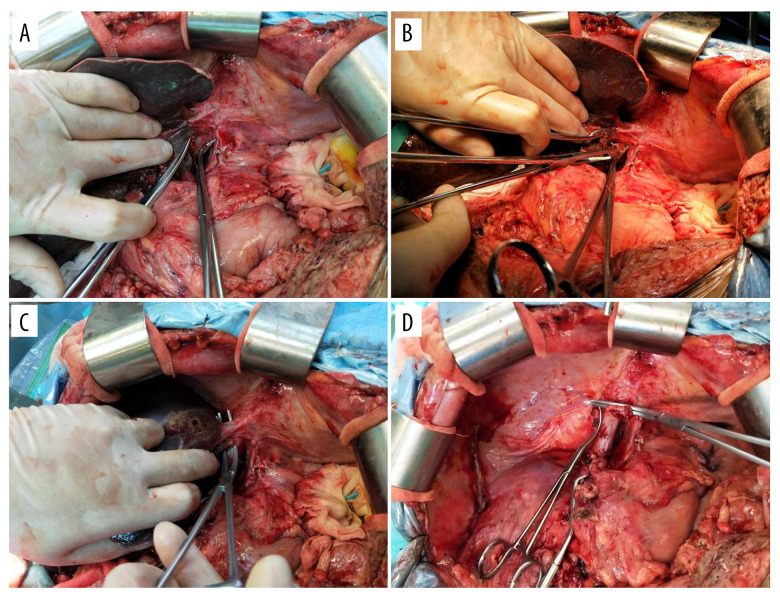
First, following laparotomy and mobilization of the tissue around the liver, the hepatic artery and portal vein were isolated for inflow control, and the right liver ligament and hepatogastric ligament were detached. Then, the surgeon lifted the left lateral lobe of liver to separate the caudate lobe from the retrohepatic IVC, and the hepatic short veins in the posterior vena cavity of the liver were separated completely or incompletely. Most importantly, a separation channel was established between the liver and the retrohepatic IVC using abdominal aortic forceps or other surgical instruments. This channel is from the interval of the right hepatic vein and middle hepatic vein to the left lateral side of the IVC.
In the anhepatic phase, the portal vein was first interrupted, followed by the occlusion of the left hepatic vein and middle hepatic vein together. The liver was then moved up superiorly, making it easier to work with the hepatic short vein and right hepatic vein with good exposure. Native liver hepatectomy was performed completely (Figure 1), and then the surgeon could easily select the classic, piggyback, or side-to-side caval anastomosis style for the donor liver. Depending on the feasibility of the technique, surgeon preference, and intraoperative situation, the surgeon could decide whether or not to employ complete cross-clamping of the vena cava. For most recipients, we preferred using the classic style; however, it increases hemodynamic instability, blood loss, and transfusion requirements.
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the division technique for resection of native liver with preservation of the inferior vena cava (IVC). (A) Separation of the caudate lobe from retrohepatic IVC. (B) Find the interval of right hepatic vein and middle hepatic vein in the front of retrohepatic IVC. (C) Preparation for occlusion of both lateral hepatic vein. (D) Image after removal of native liver.
Finally, the donor liver was placed back in the original position for caval and portal vein reconstruction. Next, we proceeded to reperfusion by declamping the portal vein and hepatic vein or IVC. End-to-end arterial anastomosis was performed using a branch patch with polypropylene 8-0 interrupted sutures under an operating microscope. Biliary reconstruction was anastomosed with a microsurgical technique.
Data Collection and Follow-Up
The data collected during surgery for analysis included warm ischemia time, cold ischemia time, anhepatic phase, anesthesia time, blood transfusion amount, and blood loss volume. The length of intensive care unit (ICU) stay, hospital stay, liver function test results, and complications were also recorded. Patients will receive life-long follow-up. Basic descriptive statistics were used for the statistical analyses.
Results
Twelve liver transplantation patients were included in this study. The patient characteristics are summarized in Table 1. The main etiologies of liver disease leading to the transplantation were hepatocellular carcinoma, hilar cholangiocarcinoma, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, acute-on-chronic liver failure, decompensated liver cirrhosis caused by alcohol, hepatitis B or hepatitis C virus, and decompensated cryptogenic cirrhosis. Two patients had both hepatocellular carcinoma and concurrent liver cirrhosis. The disease severity was measured by the MELD score (12.08±2.28, median 12). Most livers were derived from DBD donors and 2 were from donation after circulatory death (DCD). Four patients had normal platelet counts before transplantation, while 8 had low platelet counts. The preoperative coagulation parameter international normalized ratio (INR) was higher than 3 in 1 recipient. All patients had normal renal function results before surgery.
Table 1.
Patient demographic data and clinical characteristics.
| Patient number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 62 | 62 | 35 | 52 | 45 | 68 | 38 | 59 | 57 | 54 | 50 | 65 |
| Sex (M/F) | F | M | F | M | M | M | M | M | M | M | M | M |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.7 | 29.8 | 25 | 23.1 | 24.3 | 28.6 | 21.6 | 24.7 | 18.4 | 26.6 | 21.3 | 21.7 |
| Diagnosis | HCC | HCC | LF | LC | HCC | LC | LC | LC | CHOL | HCC | CHOL | LC |
| Hemoglobin pretransplant (g/dL) | 107 | 153 | 99 | 64 | 152 | 103 | 101 | 94 | 139 | 74 | 147 | 100 |
| Leukocytes pretransplant (×109/L) | 2.93 | 5.02 | 6.02 | 1.2 | 5.05 | 5.03 | 3.12 | 3.54 | 13.09 | 2.68 | 9.34 | 3.89 |
| Platelets pretransplant (×109/L) | 57 | 147 | 27 | 46 | 154 | 75 | 41 | 74 | 362 | 43 | 229 | 37 |
| Prothrombin time INR | 2.34 | 0.97 | 3.68 | 1.71 | 0.99 | 1.73 | 1.84 | 1.26 | 1.01 | 1.47 | 0.98 | 1.11 |
| Serum sodium pretransplant (mmol/L) | 138 | 139 | 133 | 138 | 142 | 141 | 133 | 140 | 133 | 139 | 141 | 140 |
| ALT pretransplant (U/L) | 11 | 44 | 71 | 39 | 588 | 70 | 39 | 22 | 209 | 38 | 35 | 16 |
| AST pretransplant (U/L) | 58 | 24 | 72 | 73 | 986 | 92 | 37 | 31 | 82 | 91 | 21 | 26 |
| Total bilirubin pretransplant (mg/dL) | 299.3 | 20.4 | 829 | 90.1 | 25.7 | 178.8 | 51.8 | 19.7 | 28.1 | 23.4 | 9.7 | 23.1 |
| Urea pretransplant (mmol/L) | 2.7 | 5.1 | 8.3 | 6.4 | 3.8 | 6 | 5.5 | 3.1 | 4.5 | 5 | 6.1 | 3.7 |
| Serum creatinine pretransplant (mg/dL) | 44 | 76 | 47 | 62 | 66 | 88 | 53 | 79 | 55 | 96 | 85 | 50 |
| Child-Pugh points in hospitalization | C | A | C | C | A | C | C | A | B | B | A | B |
| Child-Pugh points pretransplant | C | A | C | C | A | C | C | A | B | B | A | B |
| MELD score in hospitalization | 24 | 5 | 25 | 13 | 6 | 21 | 10 | 8 | 14 | 13 | 5 | 4 |
| MELD score pretransplant | 20 | 5 | 28 | 15 | 11 | 21 | 13 | 8 | 4 | 13 | 4 | 3 |
| Donor type | DBD | DBD | DBD | DBD | DBD | DCD | DBD | DCD | DBD | DBD | DBD | DBD |
| Length of ICU stay (days) | 3 | 1 | 5 | 1.5 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 12 | 0.9 | 2.3 | 0.5 | 0.8 |
| Length of hospital stay (days) | 63 | 22 | 50 | 30 | 23 | 29 | 31 | 12 | 20 | 21 | 16 | 15 |
ALT – alanine aminotransferase; AST – aspartate aminotransferase; BMI – body mass index; CHOL – cholangiocarcinoma; DCD – donation after circulatory death; DBD – donation after brain death; HCC – hepatocellular carcinoma; INR – international normalized ratio; LC – liver cirrhosis; LF – liver failure; MELD – model for end-stage liver disease.
The new technique was performed in all patients. We used modified piggyback transplantation with 1 patient and the classic piggyback transplantation with the remaining 11 patients. We did not perform the side-to-side technique, portocaval shunts, or veno-veno bypass in any patients. The length of ICU stay was 2.833±0.908 days, with a median of 2 days. The length of hospital stay was 27.667±4.321 days, with a median of 22.5 days.
The intraoperative data are summarized in Table 2. The warm ischemia time of the 2 patients with DCD donation was 5 min and 8 min, respectively. The other donor livers came from DBD donation without warm ischemia time. The cold ischemia time was from 156 min to 728 min, with a median of 344 min. The anhepatic phase was 21 min to 53 min, with a median of 28 min (30.92±9.1 min). The anhepatic time was longer than 33 min in only 3 patients. Intraoperative transfusion of red blood cells (RBC) was 6.916±7.831 units, with a median of 7 units. Four of 12 patients did not require RBC transfusion during liver transplantation. Fresh frozen plasma transfusion was 600 mL to 2500 mL, with a median of 1200 mL. Blood loss volume was 600 mL to 5000 mL, with a median of 1000 mL. Anesthesia time was 5 h to 8.4 h, with a median of 6.25 h. One patient had cardiac arrest after reperfusion and recovered after 4 min of cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Table 2.
Operation-related characteristics.
| Patient number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-clamping of IVC | no | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| Warm ischemia time (min) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cold ischemic time | 4h28 | 12h08 | 6h43 | 5h22 | 6h06 | 9h33 | 4h59 | 5h06 | 6h25 | 11h07 | 4h30 | 2h36 |
| Anhepatic phase (min) | 27 | 40 | 26 | 39 | 53 | 33 | 29 | 21 | 27 | 23 | 29 | 24 |
| Red blood cells (u) | 4 | 0 | 16 | 15 | 0 | 16 | 8 | 6 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 10 |
| Fresh frozen plasma (ml) | 1100 | 700 | 2450 | 2200 | 800 | 1200 | 1200 | 900 | 1400 | 1250 | 600 | 2500 |
| Platelet counts (u) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Cryoprecipitate (u) | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| Urine volume (ml) | 1200 | 900 | 1400 | 800 | 2300 | 1200 | 1500 | 800 | 750 | 500 | 2300 | 2300 |
| Blood loss volume (ml) | 600 | 800 | 5000 | 2400 | 700 | 3500 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 600 | 900 | 2000 |
| Anesthesia time (min) | 306 | 372 | 366 | 372 | 8.4 | 7.5 | 5.3 | 7 | 6.3 | 6.5 | 7 | 5 |
IVC – inferior vena cava.
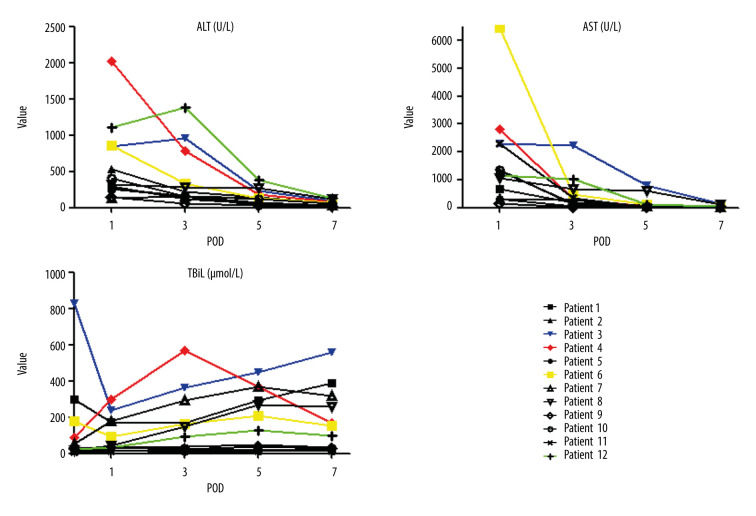
Postoperative laboratory values are shown in Figure 2. The alanine transaminase (ALT) value in the first postoperative day was 138 to 2027 U/L, with a median of 361.5 U/L (599.9±547.4 U/L). The ALT levels of all patients gradually decreased to normal levels in the 7 to 10 days after surgery. Only 4 recipients showed levels of ALT higher than 600 U/L, and 2 of them had levels higher than 1000 U/L. Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels were 142 U/L to 6448 U/L, with a median of 1243.5 U/L. The total bilirubin level in the first week after surgery fluctuated, which was related to the patients’ preoperative disease and ischemia reperfusion injury. A total of 4 patients showed early allograft dysfunction, while 8 patients recovered smoothly.
Figure 2.
Recovery of liver function in the first week after liver transplantation, including alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and total bilirubin (TBIL) value variation. The colored lines represent 4 of 12 recipients with the highest ALT values.
Discussion
Liver transplantation is a mature surgical technique for end-stage liver disease. There are 3 vena cave anastomosis methods: classical, piggyback, or side-to-side caval anastomosis. Surgeons may choose their preferred technique based on their evaluation of a patient’s circulation stability and the complexity of the surgical procedure. Unfortunately, there are no reported studies focusing on the efficiency of native liver hepatectomy. Here, we report a new technique to divide and remove native liver. The advantages of this new technique include a wide view of the operation field, decreased blood loss, increased convenience for the caval anastomosis style, and a shortened anhepatic phase. This technique can also benefit anatomical teaching.
Classic liver transplantation and modified piggyback liver transplantation require the occlusion of the IVC, while the piggyback liver transplantation and side-to-side liver transplantation do not. The major difference between those anastomosis styles is whether they completely block the IVC or not, since occlusion of the IVC might cause adverse impact to hemodynamic stability, renal insufficiency, blood loss, and transfusion requirements [10]. In certain situations, the surgeon is obligated to use the classic liver transplantation technique, such as in an extremely hypertrophic caudate lobe or a retrohepatic vena cava removal for oncologic reasons [11]. In the classic technique, the only major shortcoming is the high risk of postoperative acute renal failure. A retrospective study with 184 consecutive orthotopic liver transplants showed that the classic technique appeared to be an independent risk factor for postoperative acute renal failure [12]. However, subsequent reports confirmed that there were no significant differences in postoperative creatinine levels, intraoperative blood pressure, transfusion amount, total operating time, warm ischemia time, cold ischemia time, graft function, total hospital stay, or survival rates between the classic technique and the piggyback technique [7,10,13]. Furthermore, about 2% to 11% of classic piggyback recipients have hepatic outflow obstruction, compared with 1.8% to 5% of recipients of the side-to-side cavocaval anastomosis technique [14,15]. In the present study, none of the 11 classical liver transplantation patients had outflow obstruction complications.
In addition to providing options in transplant modes, this new technique could provide a wide view of the operation field for surgeons, shorten the anhepatic phase, decrease blood loss, and increase convenience for the caval anastomosis style. In the present study, we had a lower blood loss volume (1625±1381 mL), which is more conducive to the recovery of graft function after liver transplantation. Lower blood loss volume also results in less blood transfusion. The intraoperative transfusion of RBC for the 12 patients was 6.916±7.831 units, with a median of 7 units. Four patients did not require RBC transfusion during liver transplantation, and the transfusion of RBC for 12 patients in our study was 6.9±6.3 units, which is far less than the amount of blood transfusion needed with conventional surgery. The anhepatic phase is defined as the period of time that the donor liver is off of ice until reperfusion in the recipient, which is another type of warm ischemic time. This kind of prolonged rewarming time during implantation is reported to be associated with severe hepatitis C recurrence and decreased graft and patient survival [16,17]. When blocking of the portal vein exceeds 1 h without veno-venous bypass, portal hypertension and edema of the bowel occurs. This might result in biliodigestive anastomosis leakage [11]. Nikeghbalian et al [7] reported that anhepatic time in the piggyback technique group was 45.07±9.54 min compared with 51.76±8.28 min in the classic technique group. Our study showed that, except for 1 patient who received the modified piggyback technique of orthotopic liver transplantation and had 53 min of anhepatic time, the other 11 piggyback group patients had 28.91±6.16 min of anhepatic time. We have reported a new technique to shorten the warm ischemia time to 30 min, which is almost half the time of reported cases. To date, there is one other recently reported technique that would decrease warm ischemia time by using stapler devices. Akbulut et al [15] reported that they were able to perform cavocavostomy within 4 min using a linear stapler, compared with a mean of 15 min using standard manual suturing, thereby reducing the warm ischemic time. This technique could be of particular importance with marginal grafts.
Conclusions
The presented new technique of complete recipient hepatectomy with preservation of the IVC could be safely used in a wide variety of situations. Although the choice of the surgical vena cava anastomosis method had no significant effect on the outcome of liver transplantation, this new technique could shorten the anhepatic phase and decrease blood loss volume. Therefore, we recommend this procedure technique in all liver transplant recipients for the convenience of the surgery and improved patient prognosis.
Footnotes
Conflict of interest
None.
Source of support: This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81401324 and 81770410) and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2020A1515011557, 2020A1515010903), China
References
- 1.Dutkowski P, Linecker M, DeOliveira ML, et al. Challenges to liver transplantation and strategies to improve outcomes. Gastroenterology. 2015;148(2):307–23. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.08.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Starzl TE, Marchioro TL, Vonkaulla KN, et al. Homotransplantation of the liver in humans. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1963;117:659–76. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Carpenter DJ, Chiles MC, Verna EC, et al. Deceased brain dead donor liver transplantation and utilization in the United States: Nighttime and weekend effects. Transplantation. 2019;103(7):1392–404. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000002533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Agopian VG, Petrowsky H, Kaldas FM, et al. The evolution of liver transplantation during 3 decades: Analysis of 5347 consecutive liver transplants at a single center. Ann Surg. 2013;258(3):409–21. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3182a15db4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Muller X, Marcon F, Sapisochin G, et al. Defining benchmarks in liver transplantation: A multicenter outcome analysis determining best achievable results. Ann Surg. 2018;267(3):419–25. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Calne RY, Williams R. Liver transplantation in man. I. Observations on technique and organization in five cases. Br Medical J. 1968;4(5630):535–40. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5630.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nikeghbalian S, Toutouni MN, Salahi H, et al. A comparative study of the classic and piggyback techniques for orthotopic liver transplantation. Electron Physician. 2014;6:741–46. doi: 10.14661/2014.741-746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chan T, DeGirolamo K, Chartier-Plante S, Buczkowski AK. Comparison of three caval reconstruction techniques in orthotopic liver transplantation: A retrospective review. Am J Surg. 2017;213(5):943–49. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2017.03.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ijtsma AJ, van der Hilst CS, de Boer MT, et al. The clinical relevance of the anhepatic phase during liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2009;15(9):1050–55. doi: 10.1002/lt.21791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Vieira de Melo PS, Miranda LE, Batista LL, et al. Orthotopic liver transplantation without venovenous bypass using the conventional and piggyback techniques. Transplant Proc. 2011;43(4):1327–33. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2011.03.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Salizzoni M, Andorno E, Bossuto E, et al. Piggyback techniques versus classical technique in orthotopic liver transplantation: A review of 75 cases. Transplant Proc. 1994;26(6):3552–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cabezuelo JB, Ramirez P, Acosta F, et al. Does the standard vs piggyback surgical technique affect the development of early acute renal failure after orthotopic liver transplantation? Transplant Proc. 2003;35(5):1913–14. doi: 10.1016/s0041-1345(03)00598-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Khan S, Silva MA, Tan YM, et al. Conventional versus piggyback technique of caval implantation; without extra-corporeal veno-venous bypass. A comparative study. Transpl Int. 2006;19(10):795–801. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-2277.2006.00331.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lerut J, Ciccarelli O, Roggen F, et al. Cavocaval adult liver transplantation and retransplantation without venovenous bypass and without portocaval shunting: A prospective feasibility study in adult liver transplantation. Transplantation. 2003;75(10):1740–45. doi: 10.1097/01.TP.0000061613.66081.09. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Akbulut S, Wojcicki M, Kayaalp C, Yilmaz S. Liver transplantation with piggyback anastomosis using a linear stapler: A case report. Transplant Proc. 2013;45(3):1031–33. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2013.02.098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Velidedeoglu E, Mange KC, Frank A, et al. Factors differentially correlated with the outcome of liver transplantation in hcv+ and HCV– recipients. Transplantation. 2004;77(12):1834–42. doi: 10.1097/01.tp.0000130468.36131.0d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Baron PW, Sindram D, Higdon D, et al. Prolonged rewarming time during allograft implantation predisposes to recurrent hepatitis C infection after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2000;6(4):407–12. doi: 10.1053/jlts.2000.7581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]