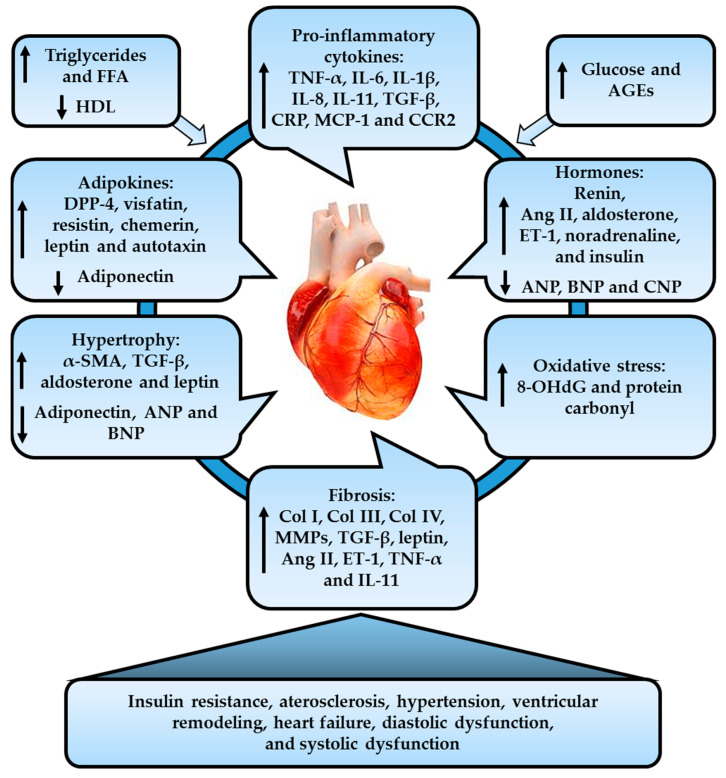
Figure 1.
Pathophysiology involved in cardiovascular disease (CVD). Obesity-related cardiac tissue injury induces dysregulation in the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, adipokines, and hormones, leading to oxidative stress, inflammation, systemic insulin resistance, atherosclerosis, as well as cardiac fibrosis and hypertrophy, and ultimately cardiac dysfunction. FFA: free fatty acids; HDL: high-density lipoprotein; CRP: higher C-reactive protein; MCP-1: monocyte chemotactic protein 1; CCR2: chemokine re-ceptor 2; AGEs: advanced glycation end products; DPP-4: dipeptidyl peptidase 4; ET-1: endo-thelin-1; OHdG: 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine; MMPs: matrix metalloproteinase; ANP: atrial natriuretic peptide; BNP: B-type natriuretic peptide; CNP: C-type natriuretic peptide.