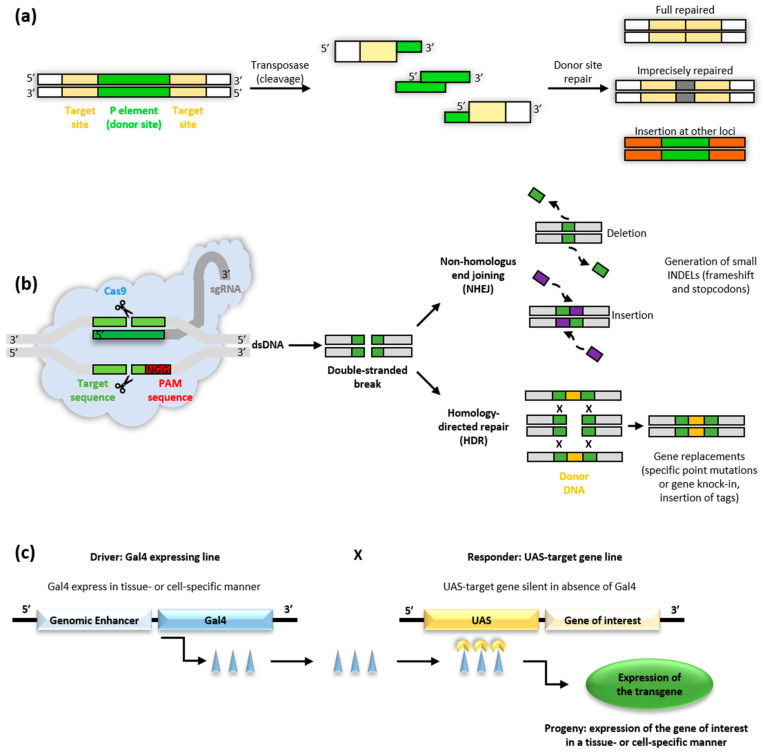
Figure 5.
Approaches to model diseases in Drosophila. Schematic view of the principal genetic approaches adopted to manipulate the Drosophila genome in a reverse approach. (a) P-element excision can generate a deletion or a mutation, can exit leaving the region fully intact or produce insertion in other sites. (b) The combination of the bacterial endonuclease Cas9 with a small guide RNA (gRNA) can drive the Cas9 to a genomic target site 5′ to an NGG protospacer adjacent motif (PAM). Repair of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated DNA double-strand breaks can occur by error-prone non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) or by homology-directed repair (HDR). (c) The UAS-GAL4 binary system allows the expression of the desired construct under the control of GAL4 protein. The system combined two transgenic lines, the driver line carrying the GAL4 expressed under a genomic enhancer and the responder line carrying the UAS promoter upstream of a gene of interest.