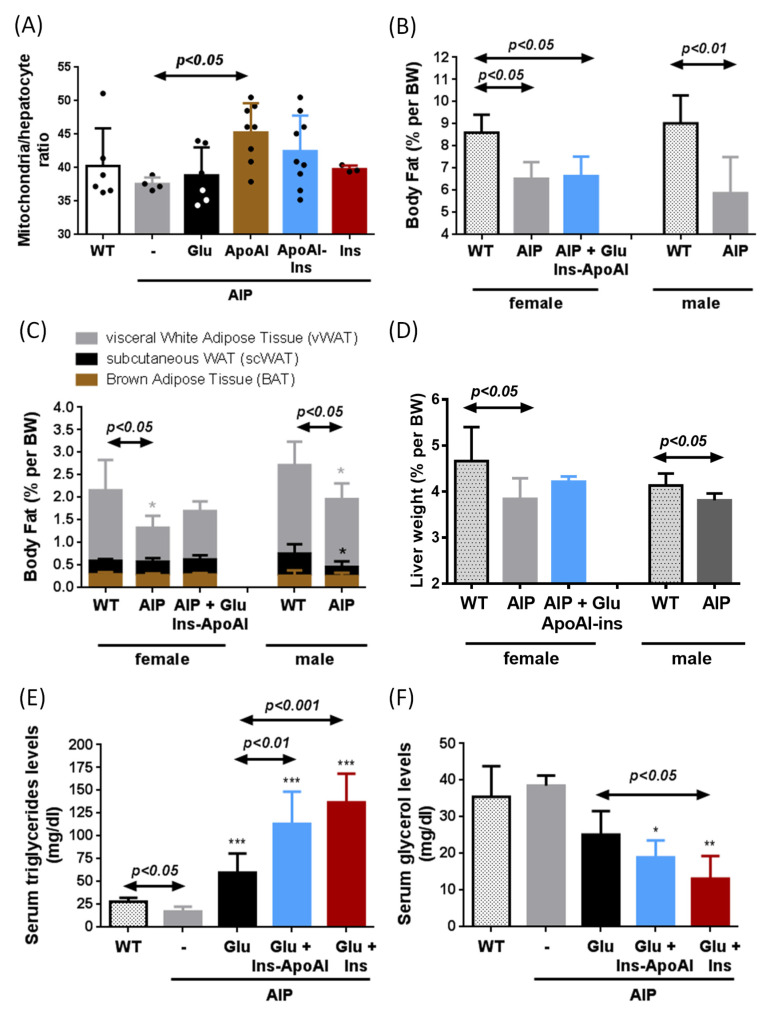
Figure 5.
Changes in mitochondrial count per hepatocyte, serum levels of triglycerides and glycerol and body mass composition of WT and AIP mice after repeated administration of glucose and exogenous insulin. (A) The ratio of mitochondria per hepatocyte was measured in AIP mice treated with glucose combined or not with fast-acting insulin, ApoAI or Ins-ApoAI. (B) Body fat composition, (C) brown adipose tissue (BAT), visceral white adipose tissue (vWAT), and subcutaneous white adipose tissue (scWAT) measured in fasted mice after 15 h of starvation using quantitative magnetic resonance. (D) Liver weight in WT and AIP mice. Serum (E) triglyceride and (F) glycerol levels measured in male mice treated with glucose for 10 days combined or not with four doses of either fast-acting insulin or Ins-ApoAI. All the assays presented in this figure were performed in mice not challenged with phenobarbital to avoid interference from the barbiturate effect. WT: wild type; AIP: acute intermittent porphyria; Glu: glucose; Ins: fast-acting insulin; Ins-ApoAI: Apolipoprotein AI conjugated with insulin. Data are mean ± s.d. of four mice per group. Comparisons were performed by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-test. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 vs. control untreated AIP mice. Glu: glucose; Ins-ApoAI: the fusion protein of a single chain insulin and apolipoprotein A-I; Ins: fast-acting insulin.