The evidence is clear: Black and Asian minority ethnic groups in the UK have experienced poorer outcomes in relation to the COVID-19 pandemic. People of Black and Asian ethnicity have faced higher diagnostic rates, higher intensive care admission rates, and ultimately higher death rates compared to the White population.1–3 Despite comprising the minority of the workforce, Black and Asian healthcare staff make up approximately two-thirds of the deaths observed in this setting.4
A LACK OF TRUST AND HISTORICAL MARGINALISATION
In the light of the statistical evidence, there have been increasing calls among experts for the government to categorise Black and Asian ethnicity as ‘extremely vulnerable’ and ensure these groups are next in the priority line for the COVID-19 vaccine.5 Nevertheless, action to address the growing prevalence of COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy in Black and Asian communities appears to be feeble.
A recent publication by the Scientific Advisory Group for Emergencies (SAGE) regarding data from the UK Household Longitudinal Study suggests that Black ethnic groups are the most COVID-19 vaccine hesitant, followed by the Pakistani and Bangladeshi groups.6 In fact, 72% of Black participants expressed being unlikely or very unlikely to accept the vaccine. For the Pakistani and Bangladeshi groups, it was 42%.6
The most likely explanation for this disparity appears to be centred around trust, or rather the lack of it. Previous research has highlighted the important role that trust in government institutions plays in fostering vaccine confidence.6
It is evident that vaccine hesitancy is yet another symptom of the pathology of historical marginalisation, structural racism, systematic discrimination, and under-representation in health research.
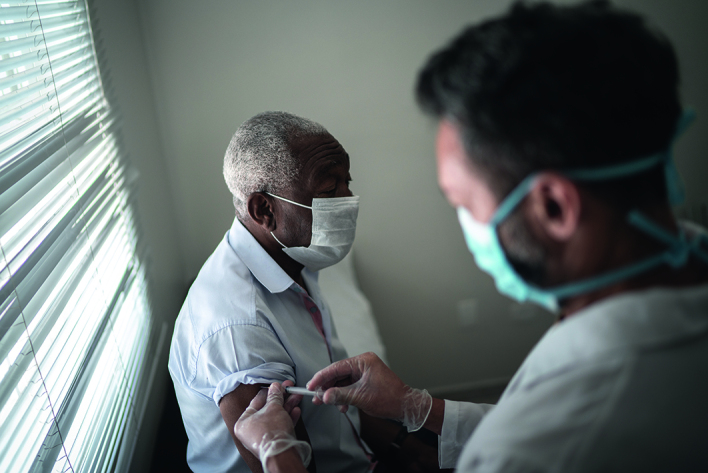
HISTORICAL TRAUMA
In response to this challenge, scientific and government experts have suggested improving trust and confidence in the COVID-19 vaccine through increased community partnership strategies such as deploying community champions to promote local engagement.6 Unfortunately, such initiatives will fail to deliver the necessary results because there is an even bigger elephant in the room that continues to be ignored. Until society, led by its government, is committed to undoing the longstanding damage of historical discrimination and disempowerment, trust will not be restored.
Minority ethnic groups that have been perpetually disenfranchised, should not be expected to readily forsake a lack of trust in the authorities that have caused them to face longstanding injustices with regards to health, education, wealth, freedom, and safety.
To presume that the symptoms of deeply-rooted historical trauma can be overcome simply through the dissemination of several well-meaning grassroots projects is to be ignorant of the magnitude of the problem and the scale of the solution it requires.
If the UK government wishes to tackle the disproportionate risk of COVID-19 infection among ethnic minority groups, it cannot delay in spearheading wide-reaching structural change to pave the way for truly equitable societal norms and practices. Only then can meaningful trust grow and vaccine hesitancy wane.
Footnotes
This article was first posted on BJGP Life on 26 January 2021: https://bjgplife.com/elephant
REFERENCES
- 1.Public Health England COVID-19: review of disparities in risks and outcomes. 2020 https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/covid-19-review-of-disparities-in-risks-andoutcomes (accessed 9 Mar 2021).
- 2.Intensive Care National Audit & Research Centre ICNARC report on COVID-19 in critical care: England, Wales and Northern Ireland 5 March 2021. 2021 https://www.icnarc.org/Our-Audit/Audits/Cmp/Reports (accessed 9 Mar 2021).
- 3.Harrison EM, Docherty AB, Barr B, et al. Ethnicity and outcomes from COVID-19: the ISARIC CCP-UK prospective observational cohort study of hospitalised patients. SSRN Electronic Journal. 2020 doi: 10.2139/ssrn.3618215.. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cook T, Kursumovic E, Lennane S. Exclusive: deaths of NHS staff from covid-19 analysed. Health Service Journal. 2020 Apr 22; https://www.hsj.co.uk/exclusive-deaths-of-nhsstaff-from-covid-19-analysed/7027471.article (accessed 9 Mar 2021).
- 5.Razai MS, Kankam HKN, Majeed A, et al. Mitigating ethnic disparities in covid-19 and beyond. BMJ. 2021;372:m4921. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m4921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Scientific Advisory Group for Emergencies Factors influencing COVID-19 vaccine uptake among minority ethnic groups, 17 December 2020. 2021 https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/factors-influencing-covid-19-vaccine-uptake-among-minority-ethnicgroups-17-december-2020 (accessed 9 Mar 2021).


