Correction to: J Nanobiotechnol (2021) 19:11 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-020-00753-9
Following publication of this article [1] the authors identified mistakes in Fig. 2a, d, g (and its caption) and Fig. 5g. Errors in the representative SEM images of CS scaffolds, CePO4/CS scaffolds and CePO4/CS/GO scaffolds were found, which were possibly made during image collection. The correction of these figures does not affect the results and conclusion of the article and all authors agree to these corrections.
The incorrect and correct Figs. 2 and 5 are published in this Correction article. The original article has been updated.
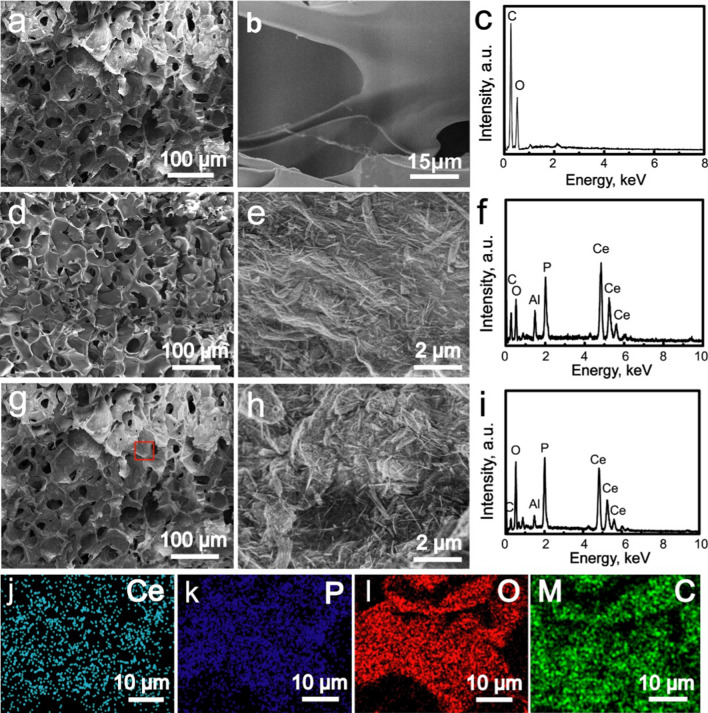
Fig. 2.
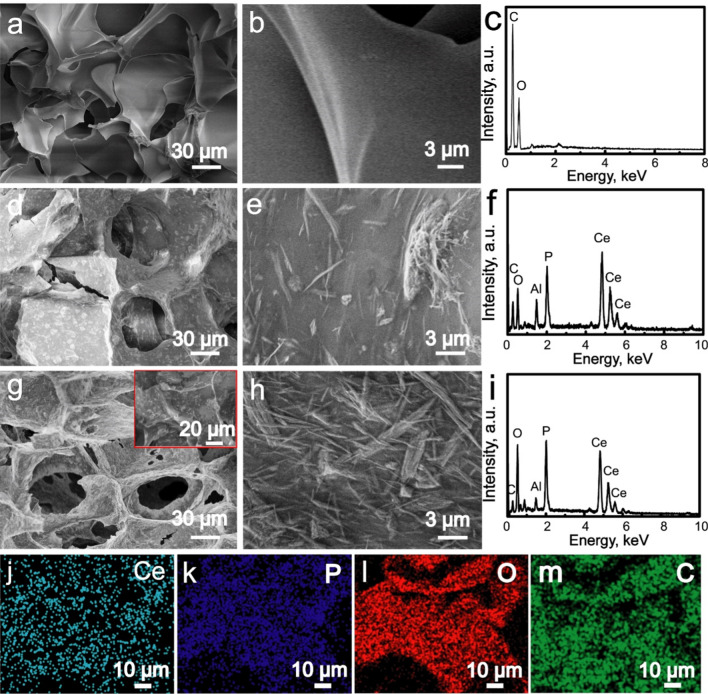
a, b SEM images and c EDS pattern of CS scaffolds; d, e SEM images and f EDS pattern of CePO4/CS scaffolds; g, h SEM images, i EDS pattern, j–m Ce, P, O and C element distribution images of CePO4/CS/GO scaffolds which corresponded to the red block in image (g)
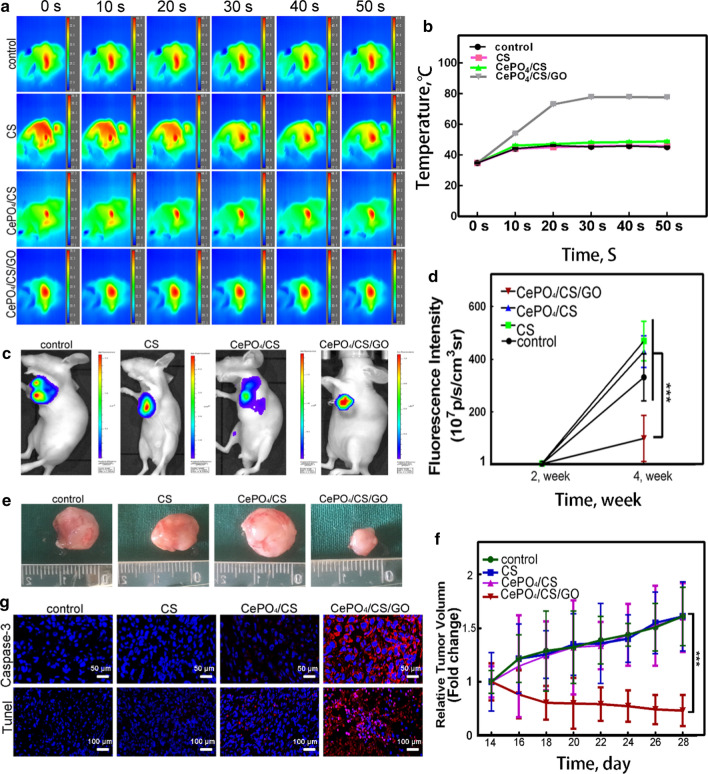
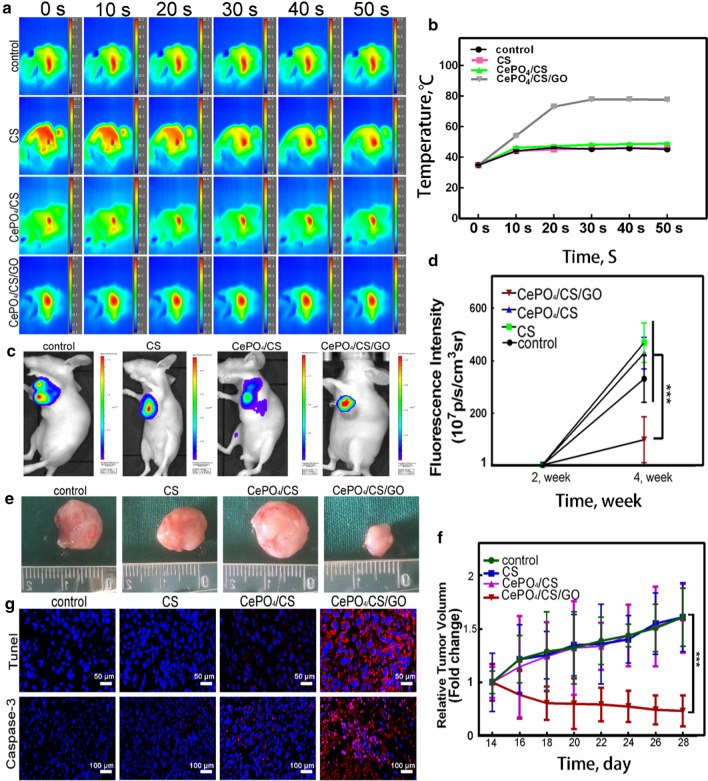
Fig. 5.
a, b The temperature changes after exposure to NIR radiation. c, d Fluorescence detection on nude mice after NIR laser irradiation by IVIS Lumina K Series III and fluorescence intensity of the CePO4/CS/GO group was significantly lower than the blank, CS and CePO4/CS groups. e, f Optical picture of tumors in nude mice, and quantitative analysis of tumor volume. g Histomorphological observation of tumors. Tunel represented apoptosis (blue: nucleus, red: apoptosis), and Caspase-3 represented the most important terminal cleavage enzyme in the process of apoptosis
Figure 2 before correction (Fig. 2a, d, g contained an error caused by the disordered sequence of pictures before submission).
Fig. 2 a, b The temperature changes after exposure to NIR radiation. c, d Fluorescence detection on nude mice after NIR laser irradiation by IVIS Lumina K Series III and fluorescence intensity of the CePO4/CS/GO group was significantly lower than the blank, CS and CePO4/CS groups. e, f Optical picture of tumors in nude mice, and quantitative analysis of tumor volume. g Histomorphological observation of tumors. Tunel represented apoptosis (blue: nucleus, red: apoptosis), and Caspase-3 represented the most important terminal cleavage enzyme in the process of apoptosis
Corrected Fig.2:
Figure 5 before correction (Fig. 5g was distorted and incorrectly labeled).
Fig. 5 a, b The temperature changes after exposure to NIR radiation. c, d Fluorescence detection on nude mice after NIR laser irradiation by IVIS Lumina K Series III and fluorescence intensity of the CePO4/CS/GO group was significantly lower than the blank, CS and CePO4/CS groups. e, f Optical picture of tumors in nude mice, and quantitative analysis of tumor volume. g Histomorphological observation of tumors. Tunel represented apoptosis (blue: nucleus, red: apoptosis), and Caspase-3 represented the most important terminal cleavage enzyme in the process of apoptosis
Corrected Fig. 5:
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Yu-Wei Ge, Xiao-Liang Liu and De-gang Yu contributed equally to this work
Contributor Information
Yuan-Qing Mao, Email: yuanqingmao@163.com.
Ya-Ping Guo, Email: ypguo@shnu.edu.cn.
Jing-Wei Zhang, Email: zjw_ys@163.com.
Reference
- 1.Ge YW, Liu XL, Yu DG, Zhu ZA, Ke QF, Mao YQ, Guo YP, Zhang JW. Graphene-modified CePO4 nanorods effectively treat breast cancer-induced bone metastases and regulate macrophage polarization to improve osteo-inductive ability. J Nanobiotechnol. 2021;19:11. doi: 10.1186/s12951-020-00753-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]