Abstract
The BRCA2 tumor suppressor is a DNA double‐strand break (DSB) repair factor essential for maintaining genome integrity. BRCA2‐deficient cells spontaneously accumulate DNA‐RNA hybrids, a known source of genome instability. However, the specific role of BRCA2 on these structures remains poorly understood. Here we identified the DEAD‐box RNA helicase DDX5 as a BRCA2‐interacting protein. DDX5 associates with DNA‐RNA hybrids that form in the vicinity of DSBs, and this association is enhanced by BRCA2. Notably, BRCA2 stimulates the DNA‐RNA hybrid‐unwinding activity of DDX5 helicase. An impaired BRCA2‐DDX5 interaction, as observed in cells expressing the breast cancer variant BRCA2‐T207A, reduces the association of DDX5 with DNA‐RNA hybrids, decreases the number of RPA foci, and alters the kinetics of appearance of RAD51 foci upon irradiation. Our findings are consistent with DNA‐RNA hybrids constituting an impediment for the repair of DSBs by homologous recombination and reveal BRCA2 and DDX5 as active players in their removal.
Keywords: BRCA2, DNA double‐strand breaks, DNA‐RNA hybrids, homologous recombination, R‐loops
Subject Categories: Chromatin, Epigenetics, Genomics & Functional Genomics; DNA Replication, Repair & Recombination; RNA Biology
Recruitment of RNA helicase DDX5 via direct interaction explains the BRCA2 role in suppressing DNA‐RNA hybrids, which is compromised in cells expressing the breast‐cancer variant T207A of this tumor suppressor.
Introduction
BRCA2 tumor suppressor protein is involved in genome maintenance mechanisms including DNA repair by homologous recombination (HR) (Moynahan et al, 2001; Jensen et al, 2010), protection of stalled replication forks (RFs) (Schlacher et al, 2011), and faithful segregation of chromosomes (Daniels et al, 2004; Ehlén et al, 2020). Recent reports have revealed that BRCA2‐deficient cells accumulate DNA‐RNA hybrids or R‐loops (Bhatia et al, 2014; Tan et al, 2017). Unscheduled hybrids may form during transcription representing an important source of genome instability by either the subsequent action of nucleases acting on the displaced ssDNA strand or, mainly, by blocking RF progression leading to transcription–replication conflicts (García‐Muse & Aguilera, 2019). On the other hand, DNA‐RNA hybrid accumulation is enhanced by both single‐strand DNA breaks (SSBs) and double‐strand DNA breaks (DSBs) (Aguilera & Gómez‐González, 2017) and recent reports indicate that DNA‐RNA hybrids accumulate in the proximity of DSBs (Li et al, 2016; Ohle et al, 2016; Cohen et al, 2018; Lu et al, 2018; Yasuhara et al, 2018).
Given the ability of R‐loops to compromise genome integrity, cells have developed different strategies to prevent the detrimental accumulation of these structures. Among these are particularly relevant nucleases such as RNases H1 and H2 and a number of recently characterized RNA helicases (García‐Muse & Aguilera, 2019). The latter include, in addition to Senataxin (Skourti‐Stathaki et al, 2011), AQR (Sollier et al, 2014), members of the DEAD‐box family of RNA helicases such as DDX1 (Li et al, 2008), DDX5 (Mersaoui et al, 2019), DDX21 (Song et al, 2017), DDX19 (Hodroj et al, 2017), UAP56/DDX39B (Pérez‐Calero et al, 2020) or DHX9 (Chakraborty & Grosse, 2011). Arguably, their mechanism of action is not completely elucidated and their functional specificity might be determined by the nucleic acid structural context and the co‐factors they interact with.
Several DNA repair proteins have been proposed to act in concert with helicases and nucleases to direct DNA‐RNA hybrid resolution. For example, BRCA2 and other related proteins such as BRCA1 or the Fanconi anemia (FA) canonical factors FANCD2, FANCJ, and FANCM reduce DNA‐RNA hybrids at transcription–replication conflicts (García‐Rubio et al, 2015; Schwab et al, 2015; Madireddy et al, 2016). Both BRCA1 and BRCA2 have also been reported to regulate RNA pol II transcription elongation (Shivji et al, 2018) or termination (Hatchi et al, 2015), which when defective result in R‐loop‐mediated DNA breaks. Interestingly, a connection between FA factors and splicing has been recently revealed (Moriel‐Carretero et al, 2017).
In this study, we find that BRCA2 interacts with DDX5, a known DEAD‐box RNA helicase (Hirling et al, 1989; Xing et al, 2017), and their association is particularly enriched in DNA damage conditions. BRCA2 stimulates the DNA‐RNA hybrid‐unwinding activity of DDX5 in vitro and promotes its association with DNA‐RNA hybrids located in the vicinity of DSBs. Both DDX5‐depleted cells and cells bearing a breast cancer missense variant (T207A), which reduces BRCA2 interaction with DDX5, exhibit increased DNA damage‐associated DNA‐RNA hybrids and delays kinetics of HR‐mediated DSB repair. Our results indicate that DNA‐RNA hybrids are an impediment for the repair of DSBs and reveal that BRCA2 and DDX5 are active players in their removal.
Results
BRCA2 physically interacts with DDX5
The N‐terminal region of BRCA2 is highly disordered (Julien et al, 2020). To get insight on its function, we used a mass spectrometry screen to identify the nuclear interacting partners of this region using HEK293T cells overexpressing a fusion protein comprising the first 1,000 aa of BRCA2 fused to a N‐terminal 2xMBP tag followed by two nuclear localization signals (NLS) (hereafter BRCA2NT) or the 2xMBP‐NLS alone (Fig EV1A). Among the potential protein partners, we found several RNA helicases including the DEAD‐box RNA helicase DDX5 (Xing et al, 2017), recently reported to suppress R‐loops (Mersaoui et al, 2019; Fig EV1B, Table EV1). In order to validate the interaction between BRCA2 and DDX5, we performed a pull‐down assay and Western blots from HEK293T whole cell extracts that showed an interaction between overexpressed BRCA2NT and endogenous DDX5 (Fig 1A). Exposure of the cells to DNA damage induced by γ‐irradiation (6 Gy) enhanced the interaction although the increase was moderate (Fig 1A). We then confirmed the interaction with the endogenous proteins BRCA2 and DDX5 by co‐immunoprecipitation (co‐IP) in both unchallenged or 4 h post‐irradiation (γ‐irradiation, 6 Gy) (Fig 1B). The association of the endogenous BRCA2 and DDX5 was not mediated by DNA or RNA as was not affected by benzonase (Fig 1B). While we could validate DDX5 interaction, we failed to confirm the interaction with other RNA‐binding proteins that were enriched by emPAI quantification (Ishihama et al, 2005; Fig EV1B) such as RBMX and DDX21 (Fig EV1C); thus, we focused on BRCA2‐DDX5 interaction. Consistently, using in situ proximity ligation assay (PLA) and specific antibodies and extraction conditions to reveal co‐localization specific to chromatin, we found that BRCA2 and DDX5 colocalized in U2OS cells and that their proximity was enhanced in cells exposed to γ‐irradiation (Fig 1C).
Figure EV1. Related to Fig 1. DEAD‐box proteins identified in the proteomics mass spectrometry screen.
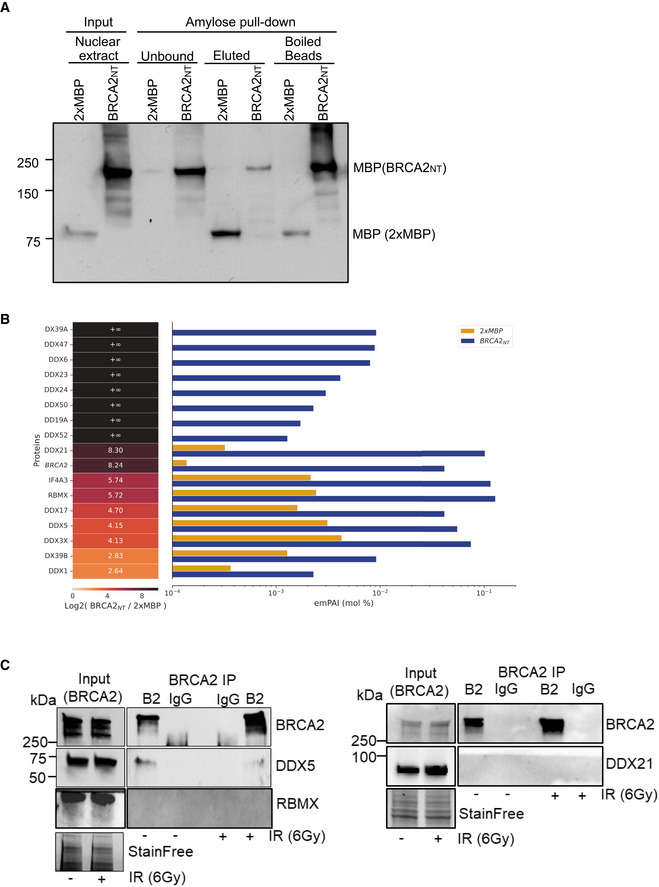
- Amylose pull‐down from HEK293T nuclear cell extracts expressing 2xMBP‐BRCA2NT (BRCA2NT) and 2XMBP, detected by immunoblot, showing the samples for mass spectrometry experiment. The loading for input and unbound fractions is 1%, for the elution fraction is 8%, and for boiled bead fraction is 35%.
- DEAD‐box helicases enriched in the BRCA2NT interactome. Label‐free protein quantification. (Left) BRCA2 (in italic) and DDX Protein ID present in the proteomics mass spectrometry screen. (Center) Heat‐map showing fold enrichment of each protein in BRCA2NT/2xMBP. Infinite‐fold indicates proteins that are only present in BRCA2NT sample and not in pull‐down performed with the 2xMBP. (Bottom) Heat‐map log2 color scale. (Right) Bar graph showing protein abundance in molar fraction percentage (mol %) in each pull‐down (yellow in 2xMBP, blue in BRCA2NT) based on label‐free emPAI quantification (see Materials and Methods section).
- Immunoprecipitation (IP) of endogenous BRCA2 from benzonase‐treated HEK293T whole cell lysates treated or not with IR (6 Gy), as indicated. Normal mouse IgG was used as negative control. Immunoblot of DDX5, DDX21 and RBMX and BRCA2. Stain‐Free images of the gels before transfer were used as loading control (cropped images are shown).
Figure 1. BRCA2 physically interacts with DDX5.
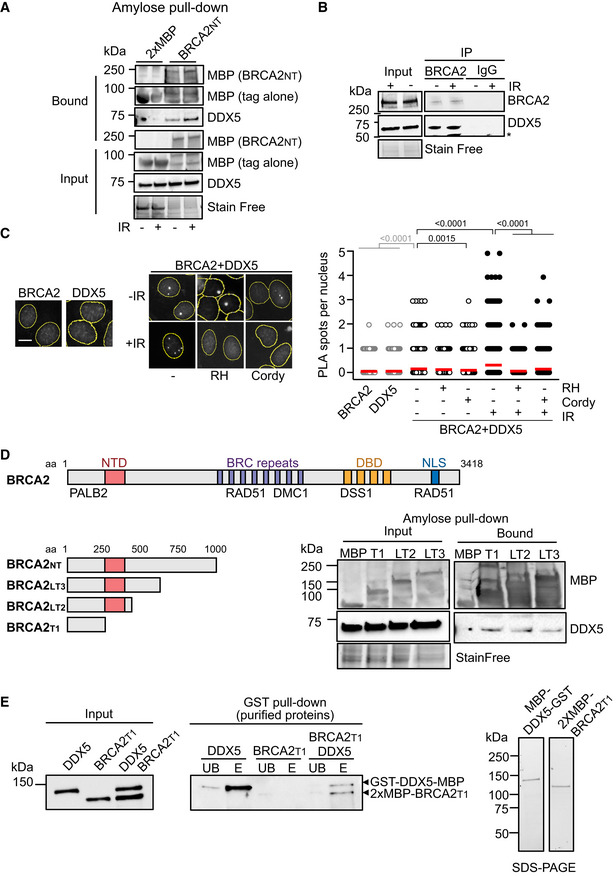
- Amylose pull‐down from benzonase‐treated HEK293T cell lysates expressing 2xMBP‐BRCA2NT in untreated or irradiated cells (6Gy; +IR). DDX5 and BRCA2NT (MBP) detected by immunoblot. Stain‐Free images of the gels before transfer were used as loading control (cropped image is shown).
- Immunoprecipitation (IP) of endogenous BRCA2 from benzonase‐treated HEK293T cell lysates left untreated or treated with IR (6 Gy) and harvested 4 h post‐IR, as indicated. Mouse IgG was used as negative control. Immunoblot of DDX5 and BRCA2. Stain‐Free image of the gels before transfer was used as loading control (cropped image is shown). Asterisk (*) indicates a non‐specific band detected by anti‐DDX5 antibody.
- Left: Representative images of in situ proximity ligation assay (PLA) between BRCA2 and DDX5 antibodies in U2OS cells either left untreated (−) or irradiated (4 h post‐IR; 6 Gy). Nuclei as defined by auto threshold plugin on the DAPI image (ImageJ) are outlined in yellow. When indicated, cells were transfected with a plasmid expressing RNase H1 (RH) 24 h before or treated with cordycepin (Cordy) for 2 h at 37°C before fixation. Single antibody controls from untreated siC cells are shown. Scale bar indicates 10 µm. Right: Quantification of the number of PLA spots per nucleus. For statistical comparison of the differences between the samples, we applied a Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test and the P‐values show significant differences. The red line in the plot indicates the median, and each symbol represents a single PLA spot.
- Diagram showing the BRCA2 N‐terminal truncations used in this study and amylose pull‐down from HEK293T whole cells extracts overexpressing the indicated BRCA2 N‐terminal truncations (BRCA2T1, BRCA2LT2, BRCA2LT3) or the 2xMBP tag. DDX5 and BRCA2 truncations were detected using specific antibodies against DDX5 and MBP, respectively. Stain‐Free images of the gels before transfer were used as loading control (cropped image is shown).
- Left: GST pull‐down assay using purified BRCA2T1 and DDX5; MBP antibody was used for the detection of both proteins. UB: unbound; E: eluate. Right: SDS–PAGE showing 300 ng of purified MBP‐DDX5‐GST and of 2xMBP‐tagged BRCA2T1 used in the pull‐down assay.
Source data are available online for this figure.
Given that both BRCA2‐ and DDX5‐deficient cells accumulate DNA‐RNA hybrids (Bhatia et al, 2014; Mersaoui et al, 2019), we assessed whether the interaction could be promoted by DNA‐RNA hybrids. As shown in Fig 1C, the proximity of BRCA2 and DDX5 in both untreated and irradiated cells was reduced after overexpression of RNase H1, a nuclease that specifically degrades the RNA moiety of DNA‐RNA hybrids, the effect being stronger under irradiated conditions. In addition, inhibition of transcription with cordycepin led to a substantial reduction in the proximity of BRCA2 and DDX5 in both untreated and irradiated conditions suggesting that their co‐localization is transcription‐dependent (Fig 1C).
Next, to define a smaller region of BRCA2 sufficient to bind DDX5 we used a series of truncated fragments contained in the BRCA2NT used in the proteomic mass spectrometry screen. We overexpressed three 2xMBP‐NLS‐tagged fragments comprising either BRCA2 aa 1–250, 1–500, or 1–750 or the 2XMBP‐NLS alone as control and performed an amylose pull‐down for the detection of DDX5 in complex with these fragments of BRCA2 (Fig 1D). Three BRCA2 fragments but not the control 2xMBP‐NLS were able to form a benzonase‐resistant complex with DDX5 indicating that the first 250 aa of BRCA2 (hereafter BRCA2T1) are sufficient to bind DDX5 (Fig 1D). To find out if the interaction was direct, we purified 2XMBP‐BRCA2T1 from HEK293T cells as we previously reported (von Nicolai et al, 2016) and MBP‐DDX5‐GST from bacteria as previously described (Xing et al, 2017) and performed a GST pull‐down assay. Importantly, BRCA2T1 was readily eluted from the glutathione resin only in the reaction containing GST‐DDX5‐MBP indicating that the interaction between BRCA2 and DDX5 is direct (Fig 1E).
Altogether, these results indicate that BRCA2 and DDX5 interact directly through the first 250 aa of BRCA2 and suggest that the interaction is enhanced particularly at DNA‐RNA hybrids and in cells exposed to γ‐irradiation.
DDX5 depletion leads to an increase of DNA‐RNA hybrids
It has previously been shown that depletion of BRCA2 (Bhatia et al, 2014) or DDX5 (Mersaoui et al, 2019) leads to DNA‐RNA hybrids accumulation; accordingly, we observed DNA‐RNA accumulation in the nucleus of U2OS depleted of BRCA2 or DDX5 visualized by immunofluorescence (IF) using the DNA‐RNA hybrid marker S9.6 (Boguslawski et al, 1986) after nuclei pre‐extraction and excluding signal from nucleoli (Fig EV2A). This signal was specific as it was sensitive to RNaseH1 treatment. Consistently, DDX5 overexpression rescued the DNA‐RNA hybrid accumulation observed in DDX5‐depleted cells but also of BRCA2‐depleted cells (Figs 2A and EV2B) confirming its role suppressing these hybrids.
Figure EV2. Related to Figs 1 and 2. DNA‐RNA hybrids levels in BRCA2‐ and DDX5‐depleted cells and localization of DDX5 at DNA‐RNA hybrids.
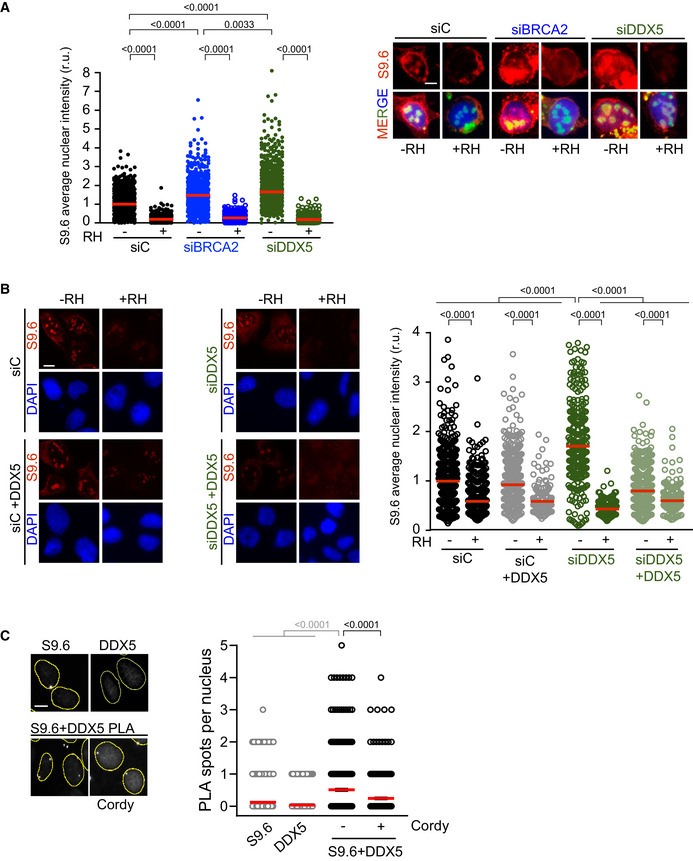
- Left: Quantification of the relative intensity of S9.6 staining. The data represent at least 500 cells per condition from three independent experiments. The red line in the scatter plot represents the median. For statistical comparison of the differences between the samples, we applied Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test and the P‐values show significant differences. Right: Representative immunofluorescence images of U2OS cells depleted of DDX5 (siDDX5), BRCA2 (siBRCA2), or control cells (siC) and stained with S9.6 antibody (DNA‐RNA hybrids) and counterstained with DAPI. When indicated, cells were transfected/treated with RNase H1 (RH) 24 h before fixation. Scale bar indicates 10 µm.
- Left: Representative images of S9.6 immunofluorescence of U2OS cells depleted of DDX5 (siDDX5) or control cells (siC) expressing RNaseH1‐GFP and/or DDX5‐GFP. Scale bar indicates 10 µm. Right: Quantification of S9.6 average nuclear intensity of U2OS cells depleted of DDX5 (siDDX5) or control cells (siC) expressing RNaseH1‐GFP and/or DDX5‐GFP. The red line in the plot indicates the median, and each symbol represents the value of a single cell. The statistical significance of the difference was calculated with Mann–Whitney U‐test; the P‐values show the significant difference. The data represent at least 170 cells per condition from one single experiment.
- Left: Representative images of in situ PLA experiment performed between DDX5 and S9.6 antibodies in U2OS cells. When indicated, cells were treated with cordycepin (Cordy) for 2 h at 37°C before fixation. Single antibody controls from untreated cells are shown. Scale bar indicates 10 µm. Nuclei as defined by auto threshold plugin on the DAPI image (ImageJ) are outlined in yellow. Right: Quantification of the number of PLA spots per nucleus in different conditions, as indicated. The data represent at least 200 cells per condition from three independent experiments. For statistical comparison of the differences between the samples, we applied a Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test and the P‐values show significant differences. The red line in the plot indicates the median, and each symbol represents a single PLA spot.
Figure 2. DDX5 depletion leads to a genome‐wide accumulation of DNA‐RNA hybrids particularly enriched at DSBs.
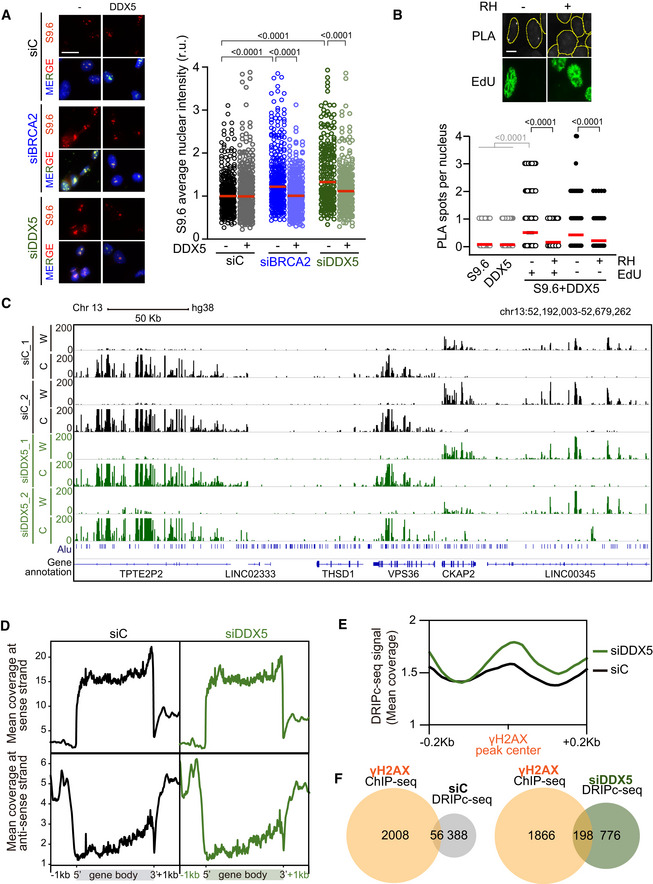
- Left: Representative images of S9.6 immunofluorescence of U2OS cells depleted of BRCA2 (siBRCA2), DDX5 (siDDX5), or control cells (siC) after transfection with either an empty plasmid or a plasmid expressing DDX5. The merged images show the signal of S9.6, nucleolin (nucleoli) antibodies and DAPI staining. Scale bar indicates 25 µm. Right: Quantification of S9.6 average nuclear intensity of U2OS cells depleted of BRCA2 (siBRCA2), DDX5 (siDDX5), or control cells (siC) after transfection with either an empty plasmid or a plasmid expressing DDX5. The red line in the plot indicates the median, and each symbol represents the value of a single cell. The statistical significance of the difference was calculated with Mann–Whitney U‐test, and the P‐values show the significant difference. The data represent at least 235 cells per condition from three independent experiments. See also Fig EV2B.
- Top: Representative images of in situ PLA performed with anti‐DDX5 and S9.6 antibodies in EdU‐labeled U2OS cells. Where indicated, cells were transfected with a plasmid expressing RNase H1 (RH). Nuclei as defined by auto threshold plugin on the DAPI image (ImageJ) are outlined in yellow. Bottom: Quantification of PLA spots per nucleus in each condition as indicated. At least 300 cells per condition were counted from three independent experiments. For statistical comparison of the differences between the samples, we applied a Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test and the P‐values show significant differences. The red line in the plot indicates the median, and each symbol represents a single PLA spot. See also Fig EV2C.
- Representative screenshot of a specific genomic region showing DRIPc‐seq profiles at Watson (W) and Crick (C) strands in K562 cells depleted of DDX5 (siDDX5) or control cells (siC) from two independent experiments. See also Fig EV3.
- DNA‐RNA hybrid distribution along protein‐coding genes containing DRIPc‐seq peaks in both conditions (siC and siDDX5) and replicates. Gene metaplots represent the mean of antisense or sense DRIPc‐seq signal from two independent experiments in K562 cells depleted of DDX5 (siDDX5) or control cells (siC) as indicated.
- DNA‐RNA hybrid metaplot distribution over γH2AX ChIP‐seq peaks. Peak metaplot shows the mean DRIPc‐seq signal from two independent experiments in K562 cells depleted of DDX5 (siDDX5) or control cells (siC).
- Venn diagram representing the overlap between γH2AX‐positive genes in K562 cells (γH2AX ChIP‐seq) and genes that specifically accumulate hybrids in control cells (top) or in DDX5‐depleted cells (bottom).
To test whether DDX5 associates with DNA‐RNA hybrids, we performed in situ PLA experiments and found that DDX5 was indeed in close proximity to them (Fig 2B). As expected for an association with DNA‐RNA hybrids, the proximity was reduced in cells transfected with a plasmid expressing RNase H1 (Fig 2B). Given that (i) DDX5 depletion leads to increased sensitivity to replication stress (Mersaoui et al, 2019) and (ii) unscheduled DNA‐RNA hybrids represent a barrier for replication (Kotsantis et al, 2016; Stork et al, 2016; Gómez‐González & Aguilera, 2019), we asked whether this association was particularly enriched in replicating cells. However, in our conditions, DDX5 association with hybrids was independent of replication, since both EdU‐ and non‐EdU‐stained cells displayed similar levels of DDX5‐S9.6 PLA signal (Fig 2B), but was dependent on transcription (Fig EV2C).
To analyze the genome‐wide effect of DDX5 depletion on DNA‐RNA hybrids, we performed DNA‐RNA hybrid immunoprecipitation (DRIP) followed by cDNA conversion coupled to high‐throughput sequencing (DRIPc‐seq) that provides high‐resolution and strand‐specific profiling of hybrids (Sanz et al, 2016) in K562 cells. To verify the specificity of the S9.6 immunoprecipitated signal before sequencing, we confirmed the presence of DNA‐RNA hybrids in this cell type by DRIP followed by qPCR (DRIP‐qPCR) at different loci (Fig EV3A). These included APOE, previously described to be hybrid‐prone in several conditions such as BRCA2‐depleted HeLa cells (Bhatia et al, 2014), HIST1H2BG, shown to accumulate DNA‐RNA hybrids in U2OS cells upon DDX5 loss (Mersaoui et al, 2019), and WDR90, shown to accumulate DNA‐RNA hybrids in HeLa cells depleted of DNA damage response (DDR) factors (Barroso et al, 2019). Importantly, all S9.6 signals were severely reduced after in vitro treatment with RNase H1 indicating that S9.6 immunoprecipitation was specific for DNA‐RNA hybrids. Consistent with the reliability of the DRIPc‐seq method (Sanz & Chédin, 2019), the data obtained from three biological replicates were reproducible (Fig EV3B). We compared the genome‐wide strand‐specific composite profile between two replicas (Figs 2C and EV3C) as well as with control cells (GEO, GSE127979) (Pérez‐Calero et al, 2020). Metaplot analysis of the strand‐specific composite profile across the average gene body revealed an enrichment of DNA‐RNA hybrids at the 3’ end of the template strand (Fig 2D), corresponding to sense transcription throughout the gene body, as well as an enrichment of DNA‐RNA hybrids at the 5’ end of the non‐template strand, corresponding to antisense transcription at the promoters, as previously reported (Sanz et al, 2016; Pérez‐Calero et al, 2020). Therefore, although DDX5 depletion led to an increase in DNA‐RNA hybrids, it did not alter their distribution pattern, consistent with a general role in RNA processing and R‐loop suppression.
Figure EV3. Related to Fig 2. Reproducibility of the DRIPc‐seq data.
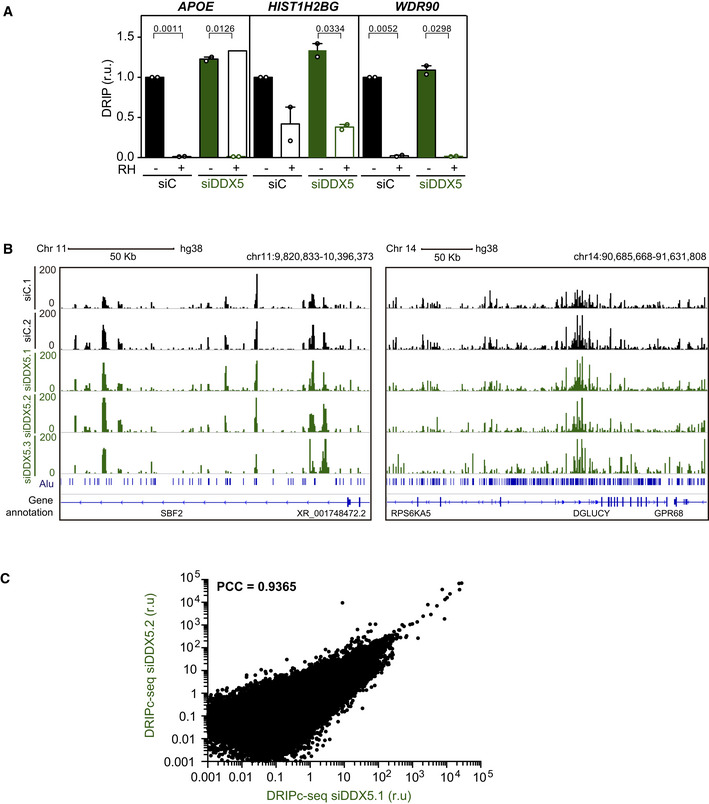
- Relative DRIP‐qPCR signal values (respect to the siC level at each locus) at the APOE, HIST1H2BG, and WDR90 loci in K562 cells transfected with the indicated siRNAs and treated in vitro with RNase H1 (RH) pre‐immunoprecipitation where indicated. The data represent the mean ± SEM from two independent experiments. The statistical significance of the difference was calculated with paired Student t‐test, and the P‐values show the significant difference.
- Representative screenshots of specific genomic regions showing the DRIPc‐seq profiles without DNA strand separation in K562 cells depleted of DDX5 (siDDX5) from three independent experiments as compared to data from control cells (siC). Two regions with different Alu sequence density are shown for comparison.
- xy correlation plot between the DRIPc signal intensity from two DRIPc‐seq independent experiments performed in DDX5‐depleted K562 cells (PCC, Pearson correlation coefficient).
DDX5‐ and BRCA2‐depleted cells accumulate DNA‐RNA hybrids at DSBs
Since the interaction between BRCA2 and DDX5 was enhanced after γ‐irradiation, we wondered whether DNA‐RNA hybrids were enriched at DSB sites in DDX5‐depleted cells. We compared our DRIPc‐seq data to a previously reported γH2AX ChIP‐seq analysis performed in the same cell line (GEO, GSE104800) (Kim et al, 2018). Interestingly, the signal of DRIPc‐seq was enriched in DDX5‐depleted cells around γH2AX ChIP‐seq peaks (Fig 2E). Moreover, the overlap of DNA‐RNA hybrid and γH2AX‐enriched regions was almost twofold larger in DDX5‐depleted cells compared to the control cells (20% in DDX5‐depleted cells compared to 13% in control cells) (Fig 2F). This 20% overlap was strongly significant (P < 0.0001, chi‐square test) when data were compared to the same number of regions randomly distributed, which led to almost fourfold smaller overlap. These results suggest that, in addition to the genome‐wide accumulation of DNA‐RNA hybrids along gene bodies in the absence of induced damage, DDX5 depletion leads to an enrichment of DNA‐RNA hybrids in the vicinity of DSBs. Consistent with this, DDX5 depletion caused a twofold increase in the number of PLA foci observed with the S9.6 and anti‐γH2AX antibodies used as a proxy of DNA‐RNA hybrid‐associated DSBs (Fig 3A). As expected, the increase was reduced by RNase H1 and cordycepin treatments (Fig 3A). Comparable results were obtained with S9.6 and the anti‐NBS1 antibody against a component of the MRN complex that is early recruited to DSBs (Bekker‐Jensen et al, 2006; Fig EV4A). Importantly, a similar increase of PLA signal was observed in BRCA2‐depleted cells suggesting that both DDX5 and BRCA2 depletion cause a transcription‐dependent increase in DNA‐RNA hybrids associated with DNA breaks.
Figure 3. DDX5‐ and BRCA2‐depleted cells accumulate DNA‐RNA hybrids at DSBs sites.
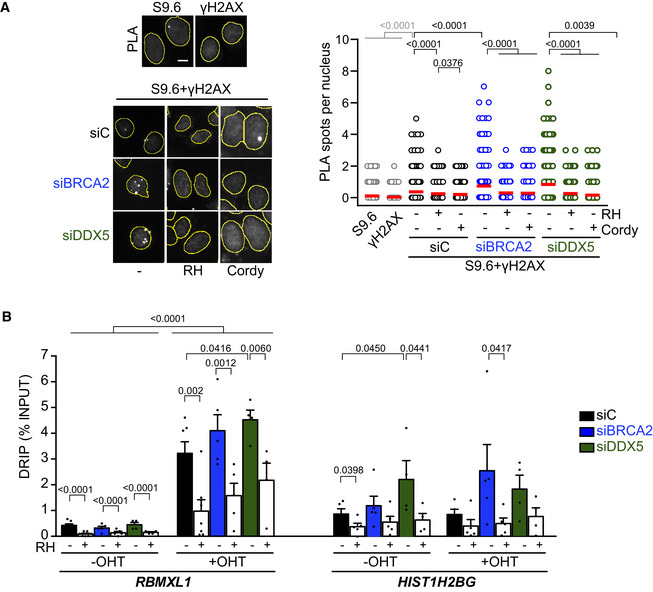
- Left: Representative images of in situ PLA between S9.6 and γH2AX antibodies in U2OS cells depleted of BRCA2 (siBRCA2), DDX5 (siDDX5), or control cells (siC). When indicated, cells were transfected with a plasmid expressing RNase H1 (RH) 24 h before or treated with cordycepin (Cordy) for 2 h at 37°C before fixation. Single antibody controls from non‐irradiated siC cells are shown. Scale bar indicates 10 µm. Nuclei as defined by auto threshold plugin on the DAPI image (ImageJ) are outlined in yellow. Right: Quantification of PLA spots per nucleus in each condition as indicated. At least 500 cells per condition were counted from three independent experiments. For statistical comparison of the differences between the samples, we applied a Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test and the P‐values show significant differences. The red line in the plot indicates the median, and each symbol represents a single PLA spot. See also Fig EV4A.
- DRIP‐qPCR signal values at RBMXL1 and HIST1H2BG loci in U2OS DIvA cells transfected with the indicated siRNAs and treated in vitro with RNase H1 (RH) pre‐immunoprecipitation where indicated. The experiment was performed in both untreated cells (−OHT) and after tamoxifen addition (+OHT). The data represent the mean ± SEM from at least four independent experiments. The statistical significance of the difference was calculated with unpaired one‐tailed t‐test, and the P‐values show the significant difference. See also Fig EV4B and C.
Figure EV4. Related to Fig 3. NBS1 co‐localization with DNA‐RNA hybrids in U2OS depleted of DDX5 or BRCA2 and DNA‐RNA hybrids, transcription levels, and DDX5 occupancy at different genomic locations in U2OS DIvA cells.
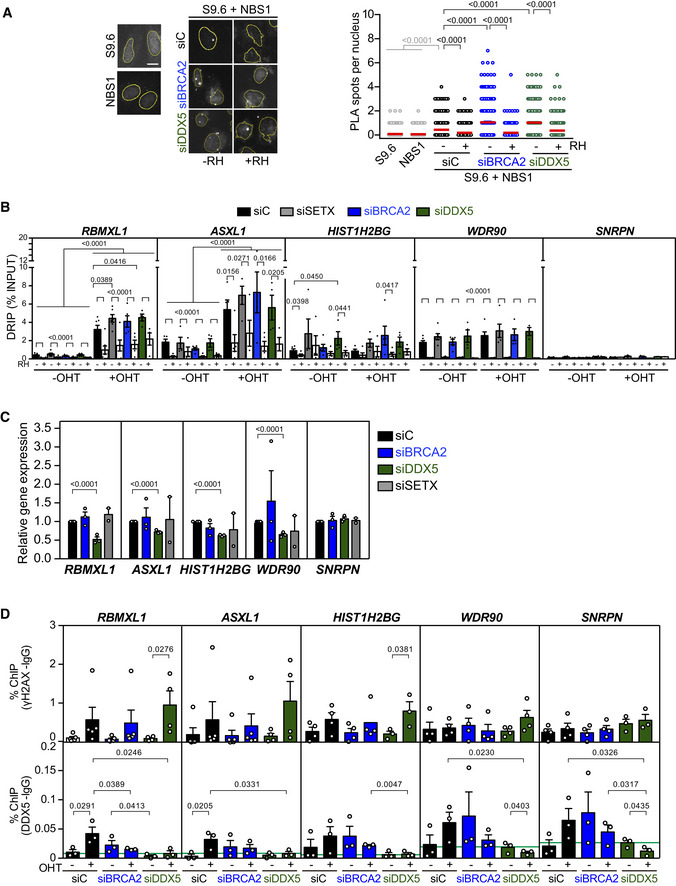
- Left: Representative images of in situ PLA experiment performed between NBS1 and S9.6 antibodies in U2OS cells transfected with either siRNA control (siC) or siRNA specific for DDX5 (siDDX5). When indicated, cells were transfected with RNAseH1 (RH) 24 h before fixation. Single antibody controls from untreated cells are shown. Scale bar indicates 10 µm. Nuclei as defined by auto threshold plugin on the DAPI image (ImageJ) are outlined in yellow. Right: Quantification of the number of PLA spots per nucleus in different conditions, as indicated. The data represent at least 400 cells per condition from three independent experiments. For statistical comparison of the differences between the samples, we applied a Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test and the P‐values show significant differences. The red line in the plot indicates the median, and each symbol represents a single PLA spot.
- DRIP‐qPCR signal values at RBMXL1, ASXL1, HIST1H2BG, WDR90, and SNPRN loci in U2OS DIvA cells transfected with the indicated siRNAs and treated in vitro with RNase H1 (RH) pre‐immunoprecipitation where indicated. The experiment was performed in both untreated cells (−OHT) and after tamoxifen addition (+OHT). The data represent the mean ± SEM from at least four independent experiments. The statistical significance of the difference was calculated with unpaired one‐tailed Student t‐test, and the P‐values show the significant differences.
- Relative RBMXL1, ASXL1, HIST1H2BG, WDR90, and SNPRN gene expression levels in U2OS DiVA cells transfected with the indicated siRNAs. The data represent the mean ± SEM from two or three independent experiments. The statistical significance of the difference was calculated with unpaired Student t‐test; the P‐values show the significant differences.
- γH2AX (top) and DDX5 (bottom) ChIP‐qPCR signal values at RBMXL1, ASXL1, HIST1H2BG, WDR90, and SNPRN loci in U2OS DiVA cells transfected with the indicated siRNAs and either left untreated (−OHT) or treated with tamoxifen (+OHT). The green line represents the background levels of DDX5 signal. The data represent the mean ± SEM from at least three independent experiments. The statistical significance of the difference was calculated with unpaired one‐tailed Student t‐test, and the P‐values show the significant differences.
These results, however, do not discriminate whether the DNA‐RNA hybrid leads to the break or vice versa. To add some light to this conundrum, we determined DNA‐RNA hybrid levels at DSBs induced in the previously described U2OS DIvA cell system (Aymard et al, 2014). In these cells, around 100 DSBs (detectable by γH2AX) are generated by the restriction enzyme AsiSI at specific sites upon treatment with tamoxifen (OHT). We focused the analysis on five different loci, including the RBMXL1 and ASXL1 genes containing AsiSI cut‐sites and other genes that do not contain any annotated AsiSI cut‐sites such as the WDR90 and HIST1H2BG hybrid‐prone regions, and the SNRPN gene, which is not prone to DNA‐RNA hybrids (D’Alessandro et al, 2018; Figs 3B and EV4B).
Quantification of DNA‐RNA hybrids in these cells by DRIP revealed that DSB induction (+OHT) led to a strong accumulation of DNA‐RNA hybrids at the RBMXL1 and ASXL1 genes (Figs 3B and EV4B). As previously reported (Cohen et al, 2018), we confirmed that depletion of the Senataxin (SETX) DNA‐RNA helicase further increased hybrids at the cut‐sites compared to the control cells (10.7‐fold versus 7.6‐fold in control cells) (Fig EV4B). Consistent with a previous report (D’Alessandro et al, 2018), BRCA2‐depleted cells also showed a similar trend further elevating this increase to 12.8‐fold. Similar to SETX depletion, DDX5 depletion led to a 10‐fold enrichment of DNA‐RNA hybrids upon induction of DSBs (Fig 3B). The levels of hybrids were strongly reduced by RNase H1 treatment demonstrating the specificity of the signal. Moreover, DRIP signals were not significantly affected by OHT addition in the HIST1H2BG, WDR90, or SNRPN regions (Figs 3B and EV4B), indicating that the effect observed depends on the induction of the break. In agreement with the data in U2OS cells (Fig EV2A; Mersaoui et al, 2019), a significant accumulation of spontaneous DNA‐RNA hybrids (−OHT) was also observed at the HIST1H2BG gene in DDX5‐depleted cells in the DIvA cell system (Figs 3B and EV4B). This increase was not due to a higher transcription, since siDDX5 cells exhibited reduced HIST1H2BG expression levels (Fig EV4C). Altogether, these results suggest that BRCA2 and DDX5 depletion cause a moderate increase in the levels of DNA‐RNA hybrids at DSB sites comparable to those reported for Senataxin depletion.
BRCA2 helps retain DDX5 at DNA damage sites
To determine whether BRCA2 could modulate DDX5 retention at damaged sites, we performed laser irradiation (405 nm) in U2OS live cells sensitized by Hoechst 33258 transfected with DDX5‐GFP and monitored the recruitment of DDX5 at DNA damage tracks as described before for DNA repair proteins (Bekker‐Jensen et al, 2006) and RNA‐binding proteins (RBPs) (Adamson et al, 2012). We verified the efficiency of our system to specifically recruit DSB repair proteins by monitoring under the same conditions the recruitment of the early DSB marker GFP‐53BP1. As expected, GFP‐53BP1 signal relocalized at laser tracks within 2 min post‐irradiation and the signal at the tracks increased over time reaching a maximum at around 10 min post‐irradiation (Fig 4A). Before laser irradiation, DDX5‐GFP exhibited a predominant nuclear staining as previously reported (Wang et al, 2009), although with some accumulation of signal at the nucleoli probably due to its overexpression (Fig 4A). In contrast to GFP‐53BP1, DDX5‐GFP signal decreased specifically at the DNA damage tracks, detected in 11% of the laser‐irradiated GFP+ cells immediately after micro‐irradiation (Fig 4A). This “anti‐stripe” pattern already reported before for other RBPs and DEAD‐box proteins (Chou et al, 2010; Adamson et al, 2012; Britton et al, 2014) started within the first 2 min post‐irradiation and reached 25% of the cells at 10 min post‐irradiation, whereas the rest of the cells showed DDX5 pan‐nuclear staining. While revising this manuscript, another report has also shown exclusion of GFP‐DDX5 from laser‐induced DNA damage using a different system (Yu et al, 2020). Interestingly, depletion of BRCA2 resulted in a widespread “anti‐stripe” pattern of DDX5‐GFP in the cell population reaching 63% of the cells at 6 min (Fig 4A). Thus, only 37% of the cells retained DDX5 at the laser tracks in BRCA2‐depleted cells compared to the 75% in cells expressing BRCA2.
Figure 4. BRCA2 enhances DDX5 retention at DNA damage sites.
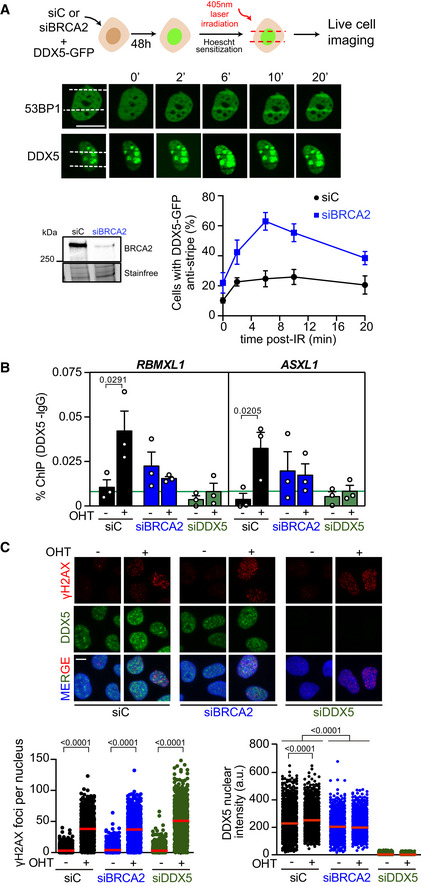
- Top: Scheme showing the experimental set up for laser irradiation in DDX5‐GFP transfected U2OS cells depleted of BRCA2 (siBRCA2) or control cells (siC). Middle: Live cell imaging of the recruitment of GFP‐53BP1 or DDX5‐GFP to DNA damage tracks at different time points as indicated. Exposure and processing were adjusted to best demonstrate stripes and anti‐stripes. Scale bar indicates 10 µm. Bottom left: Western blot showing the siRNA‐mediated knock‐down of BRCA2 from U2OS cells transfected with DDX5‐GFP. Bottom right: Quantification of the percentage of transfected cells that exhibit DDX5‐GFP “anti‐stripe” pattern (reduced GFP signal at DNA damage tracks compared to the signal in the nucleus) at the times indicated in cells depleted of BRCA2 (siBRCA2) or treated with control siRNA (siC). The data represent the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments.
- DDX5 ChIP‐qPCR signal values at RBMXL1 and ASXL1 loci in U2OS DIvA cells transfected with the indicated siRNAs and either untreated cells (−OHT) or after tamoxifen addition (+OHT). The data represent the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. The green line represents the background levels of DDX5 signal. The statistical significance of the difference was calculated with unpaired one‐tailed t‐test, and the P‐values show the significant differences between untreated cells (−OHT) and after tamoxifen addition (+OHT). See also Fig EV4D.
- Top: Representative images of immunofluorescence of U2OS DIvA cells depleted of BRCA2 (siBRCA2), DDX5 (siDDX5), or control cells (siC) and either untreated cells (−OHT) or after tamoxifen addition (+OHT), as indicated. Scale bar indicates 10 µm. Bottom: Quantification of the number of γH2AX foci per nucleus (left) and DDX5 nuclear intensity (right). The data represent at least 800 cells per condition from three independent experiments. The red line in the plot indicates the median, and each symbol represents the value of a single cell. The statistical significance of the difference was calculated with Mann–Whitney U‐test, and the P‐values show the significant difference.
Source data are available online for this figure.
Since DDX5 has been involved in transcription regulation in response to DNA damage (Nicol et al, 2013), the “anti‐stripe” pattern observed here suggests that DDX5 is excluded from the DNA damage sites probably due to the local repression of transcription concomitant to DNA damage (Chou et al, 2010; Shanbhag et al, 2010) and that BRCA2 retains or relocalizes DDX5 at laser‐induced DNA damage tracks. To confirm this possibility, we used the U2OS DIvA cell system (Aymard et al, 2014) and measured directly the presence of DDX5 at DSBs by chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). In addition, we performed γH2AX ChIP in the same conditions as a control for DSB induction (Fig EV4D). Importantly, the occupancy of DDX5 at the RBMXL1 and ASLX1 genes significantly increased upon DSB induction (+OHT) in control cells but not in BRCA2‐depleted cells (Fig 4B). In contrast, the occupancy of DDX5 in regions with no AsiSI cut‐sites (HIST1H2BG, WDR90, or SNRPN genes) did not change significantly between siC‐ and siBRCA2‐treated cells, although they followed a similar trend (Fig EV4D). In this line, we also monitored the nuclear fluorescence intensity of DDX5 to determine any difference upon DNA damage induction. As expected, DSB induction with OHT treatment resulted in a robust increase of γH2AX foci in all conditions (Fig 4C). Endogenous DDX5 displayed a distinct granular nuclear pattern as previously reported in interphase cells (Iggo et al, 1991; Fig 4C). In addition, DDX5 nuclear intensity increased upon DSB induction in control cells, whereas it remained unchanged in BRCA2‐depleted cells (Fig 4C). These results suggest that DDX5 nuclear localization increases upon DNA damage in a BRCA2‐dependent manner and that BRCA2 helps retain DDX5 at DNA damage sites.
BRCA2 stimulates the R‐loop‐unwinding activity of DDX5
DDX5 can unwind R‐loops and DNA‐RNA hybrids in vitro (Xing et al, 2017; Mersaoui et al, 2019) suggesting that its helicase activity might be required to process DNA‐RNA hybrids in cells. Thus, we next assessed whether DDX5 R‐loop‐unwinding activity was altered by BRCA2. We purified GFP‐MBP‐BRCA2 from human HEK293T cells following our standard protocol (von Nicolai et al, 2018) and assayed the unwinding activity of DDX5 on synthetic radiolabeled R‐loops substrates in vitro. The incubation of increasing concentrations of DDX5 (1–5 nM) with the R‐loop substrate for 30 min reached up to 40% of unwound product in a reaction that required ATP and Mg2+ (Fig 5A), consistent with a previous report (Mersaoui et al, 2019). Importantly, the addition of nearly stoichiometric concentration of purified BRCA2 relative to DDX5 (2 nM) stimulated DDX5 helicase activity up to twofold reaching 80% of unwound product (Fig 5A). To find out whether smaller fragments of BRCA2 containing the region of interaction, BRCA2LT3 and BRCA2T1 (Fig 1D and E), were sufficient to stimulate this activity, we conducted the same unwinding assay now in the presence of BRCA2LT3 or BRCA2T1. Interestingly, as with full‐length BRCA2, both BRCA2LT3 and BRCA2T1 were able to stimulate DDX5 R‐loop‐unwinding activity, although the concentration of protein required to achieve similar stimulation as the full‐length BRCA2 was ~ 5‐fold (BRCA2LT3) or ~ 25‐fold (BRCA2T1) higher (Fig 5A).This is perhaps not surprising given the disordered nature of the N‐terminal region in isolation (Julien et al, 2020). In contrast to BRCA2T1, BRCA2T2, which does not bind DDX5 but is able to interact with DNA (von Nicolai et al, 2016), inhibited the reaction (Fig EV5A). This is probably due to the ability of this fragment to compete for the substrate. Finally, BRCA2 also stimulated the unwinding activity of DDX5 on DNA‐RNA hybrids although with this substrate, the helicase activity of DDX5 was much more modest (Fig EV5B).
Figure 5. BRCA2 stimulates the R‐loop‐unwinding activity of DDX5.
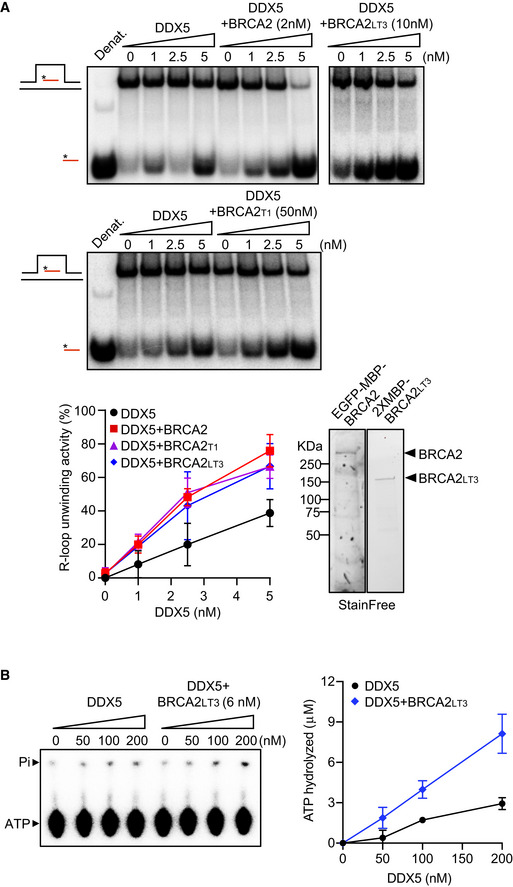
- Top: PAGE gel showing a representative unwinding assays in which purified MBP‐DDX5‐GST (1–5 nM) was incubated with 32P‐labeled synthetic R‐loop substrate in the presence or absence of 2 nM purified EGFP‐MBP‐BRCA2 (top gel left) or 10 nM purified BRCA2LT3 (top gel right) or 50 nM purified BRCA2T1 (bottom gel). Bottom: Quantification of the unwinding experiments showing the percentage of free RNA relative to the R‐loop substrate (unwound product) as a function of DDX5 concentration alone (black) or in the presence of BRCA2 (red) or BRCA2LT3 (blue) or BRCA2T1 (pink). The data represent the mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. Right: SDS–PAGE showing 500 ng of purified 2XMBP‐BRCA2LT3 and 150 ng of purified BRCA2 used in the unwinding assay. See also Fig EV5A and B.
- Left: Thin layer chromatography (TLC) plate showing a representative ATP hydrolysis assay in which purified MBP‐DDX5‐GST (50–200 nM) was incubated with R‐loop synthetic substrate and [γ32P] ATP in the presence or absence of or 6 nM purified BRCA2LT3. Right: Quantification of the ATP hydrolyzed in each condition. No protein control was used as background. The data represent the mean ± SD from three independent experiments.
Figure EV5. Related to Figs 5, 6, 7, 8. Effect of BRCA2T2 and BRCA2 on DDX5 R‐loop and DNA‐RNA hybrid‐unwinding activity; accumulation of DNA‐RNA hybrids in BRCA2‐deficient DLD1 cells; interaction of BRCA2T1‐T207A with DDX5; and kinetics of DNA damage accumulation in cells depleted of DDX5 or in cells bearing BRCA2‐T207A mutation.
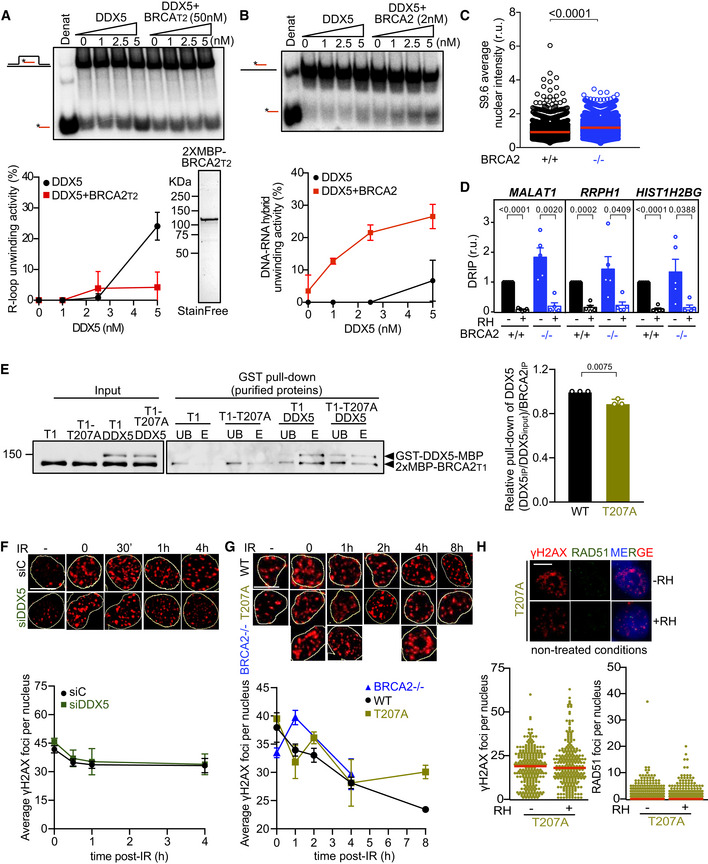
- Top: PAGE gel showing a representative unwinding assays in which purified MBP‐DDX5‐GST (1–5 nM) was incubated with 32P‐labeled synthetic R‐loop substrate in the presence or absence of 50 nM purified 2xMBP‐BRCA2T2. Bottom: Quantification of the unwinding experiments showing the percentage of free RNA relative to the R‐loop substrate (unwound product) as a function of DDX5 concentration alone (black) or in the presence of BRCA2T2 (red). Bottom right: SDS–PAGE gel showing 1 μg of purified 2xMBP‐BRCA2T2 used for the unwinding assay. The data represent the mean ± SD of two independent experiments.
- Top: PAGE gel showing a representative unwinding assays in which purified MBP‐DDX5‐GST (1–5 nM) was incubated with 32P‐labeled synthetic DNA‐RNA hybrid substrate in the presence or absence of 2 nM purified EGFP‐MBP‐BRCA2. Bottom: Quantification of the unwinding experiments showing the percentage of free RNA relative to the DNA‐RNA hybrid substrate (unwound product) as a function of DDX5 concentration alone (black) or in presence of BRCA2 (red). The data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
- Quantification of the average nuclear intensity of S9.6 antibody in DLD1 BRCA2+/+ (+/+) and BRCA2−/− (−/−) cells. The red line in the plot indicates the median, and each symbol represents the value of a single cell. The data represent at least 2,000 cells per condition from four independent experiments. The statistical significance of the difference was calculated with Mann–Whitney U‐test; the P‐values show the significant difference.
- Relative DRIP‐qPCR signal values (respect to the siC level at each locus) at the MALAT1, RRPH1, and HIST1H2BG loci in DLD1 BRCA2+/+ (+/+) and BRCA2−/− (−/−) cells and treated in vitro with RNase H1 (RH) pre‐immunoprecipitation where indicated. The data represent the mean ± SEM from five independent experiments. The statistical significance of the difference was calculated with unpaired Student t‐test, and the P‐values show the significant difference.
- GST pull‐down assay using purified BRCA2T1 (T1) or BRCA2T1‐T207A (T1‐T207A) and DDX5. MBP antibody was used for the detection of both proteins. UB: unbound; E: eluate. Right: Quantification of the GST pull‐down experiments calculated as the pulled‐down BRCA2T1 (WT and T207A) with DDX5 relative to the input levels of BRCA2T1 (WT and T207A) and the amount of pulled‐down MBP‐DDX5‐GST. Results are presented as the fold change compared to the BRCA2 WT clone. The data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. The statistical significance of the difference was calculated with unpaired t‐test, and the P‐values show the significant difference.
- Top: Representative immunofluorescence images of cells hybridized with anti‐γH2AX antibody in U2OS cells depleted of DDX5 (siDDX5) and in control cells (siC) in cells left untreated (−) or at different time points after exposure to IR (6 Gy), as indicated. Scale bar indicates 10 µm. Nuclei as defined by auto threshold plugin on the DAPI image (ImageJ) are outlined in yellow. Bottom: Graph showing the average number of γH2AX foci. The data represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments.
- Top: Representative immunofluorescence images of three independent experiments of nuclear γH2AX foci in BRCA2‐deficient DLD1 cells (BRCA2−/−) or BRCA2−/− bearing BRCA2 WT (WT) or BRCA2‐T207A (T207A) variant in cells left untreated or at different time points after exposure to IR (6Gy), as indicated. Scale bar indicates 10 µm. Nuclei as defined by auto threshold plugin on the DAPI image (ImageJ) are outlined in yellow. Bottom: Graph showing the average number of γH2AX foci. The data represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments.
- Top: Representative immunofluorescence images of DLD1 BRCA2‐T207A stained for γH2AX and RAD51 in non‐treated conditions. When indicated, cells were transfected with a plasmid expressing RNaseH1 (+RH) 48 h prior fixation. Right: Quantification of the number of γH2AX foci (left) or RAD51 foci (right) per nucleus. The data shown are from at least 400 cells per condition from three independent experiments. For statistical comparison of the differences between the samples, we applied a Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test and no statistically significant differences were found. The red line in the plot indicates the median, and each symbol represents a single focus.
To find out the mechanism of stimulation and given the ATP dependence of DDX5 helicase activity, we performed an in vitro ATPase assay with purified BRCA2LT3 and DDX5 in the presence of the same R‐loop synthetic substrate and 32P‐γATP. DDX5 showed little ATP hydrolysis activity; however, increasing concentrations of DDX5 (50–200 nM) resulted in the release of inorganic phosphate (Pi) reaching 3 μM of ATP hydrolyzed. Interestingly, addition of 6 nM BRCA2LT3, resulted in ~ 3‐fold increase in the levels of ATP hydrolyzed (Fig 5B).
Taken together, these results reveal that nearly stoichiometric amounts of BRCA2 stimulate the R‐loop and DNA‐RNA hybrid‐unwinding activity of DDX5 by enhancing its catalytic activity. Truncated BRCA2 fragments containing the DDX5 interacting region of BRCA2 (BRCA2LT3 (1–750 aa) and BRCA2T1 (1–250 aa) were sufficient to stimulate the reaction, whereas the 250–500 aa region containing a DNA binding domain (von Nicolai et al, 2016) failed to stimulate DDX5 unwinding activity and rather inhibited the reaction. Therefore, the stimulatory function of BRCA2 depends primarily on direct protein‐protein interaction through the first 250 aa of BRCA2.
BRCA2‐T207A reduces the interaction with DDX5 leading to increased DNA‐RNA hybrids in cells
Following the mapping of the interaction and the helicase stimulatory activity to the first 250 aa of BRCA2 (BRCA2T1), we searched for BRCA2 missense variants identified in breast cancer patients that could disrupt the interaction with DDX5. We selected T207A, a breast cancer variant of unknown clinical significance (VUS) (clinvar/variation/VCV000052028.2) affecting a highly conserved residue in the region of BRCA2T1 that we had characterized previously in the context of mitosis (Ehlén et al, 2020). Using DLD1 BRCA2‐deficient cells stably complemented with GFP‐tagged BRCA2 WT or BRCA2‐T207A, we performed a GFP‐trap pull‐down assay to detect bound DDX5. Although the levels of BRCA2 WT and BRCA2‐T207A were variable (see input levels in Fig 6A), the amount of pull‐down BRCA2 protein was equivalent in the two samples (GFP‐trap pull‐down). BRCA2‐T207A association with DDX5 was consistently reduced by twofold as compared to BRCA2 (Fig 6A).
Figure 6. Cells bearing BRCA2‐T207A show reduced BRCA2 interaction with DDX5 leading to increased DNA‐RNA hybrids.
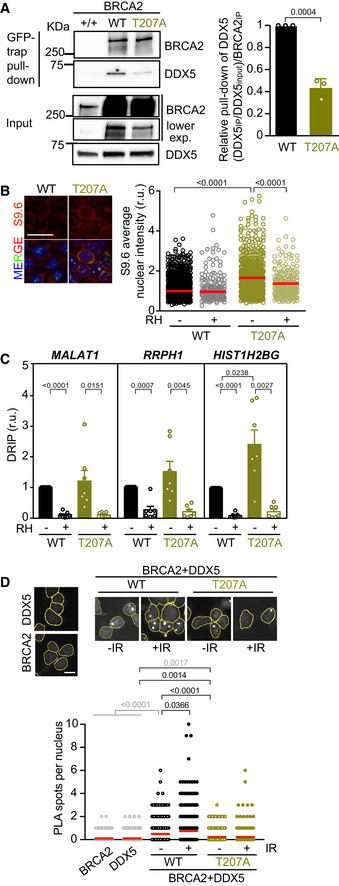
- Left: GFP pull‐down assay from whole cell extracts of BRCA2‐deficient DLD1 expressing BRCA2 (WT) or the variant T207A (T207A). DLD1 BRCA2+/+ (+/+) cell extracts were used as control for the GFP‐trap. DDX5 and BRCA2 were detected with specific antibodies against DDX5 and BRCA2, respectively. Stain‐Free images of the gels before transfer were used as loading control (cropped image is shown). Right: Quantification of the GFP‐trap pull‐down experiments calculated as the co‐immunoprecipitated DDX5 with either BRCA2 WT or BRCA2‐T207A relative to the input levels of DDX5 and the amount of immunoprecipitated EGFP‐MBP‐BRCA2. Results are presented as the fold change compared to the BRCA2 WT clone. The data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. The statistical significance of the difference was calculated with unpaired t‐test, and the P‐values show the significant difference.
- Left: Representative images of S9.6 immunofluorescence of DLD1 cells bearing BRCA2 (WT) or BRCA2‐T207A (T207A). The merged images show the signal of S9.6, nucleolin (nucleoli) antibodies, and DAPI staining. Scale bar indicates 25 µm. Right: Quantification of the average nuclear intensity of S9.6 antibody in DLD1 BRCA2‐WT (WT) or BRCA2‐T207A (T207A) cells transfected with either a plasmid expressing GFP alone (−RH) or GFP‐RNase H1 (+RH), as indicated. The red line in the plot indicates the median, and each symbol represents the value of a single cell. Data correspond to at least 170 cells per condition from two independent experiments. The statistical significance of the difference was calculated with Mann–Whitney U‐test; P‐values show the significant difference. See also Fig EV5C.
- Relative DRIP‐qPCR signal values (respect to the siC level at each locus) at the MALAT1, RRPH1, and HIST1H2BG loci in DLD1 BRCA2−/− cells bearing BRCA2 (WT) or BRCA2‐T207A (T207A) and treated in vitro with RNase H1 (RH) pre‐immunoprecipitation where indicated. The data represent the mean ± SEM from seven independent experiments. The statistical significance of the difference was calculated with paired Student t‐test; the P‐values show the significant difference. See also Fig EV5D.
- Top: Representative images of in situ PLA performed between BRCA2 and DDX5 antibodies in cells bearing BRCA2 (WT) or BRCA2‐T207A (T207A), as indicated. Cells were fixed directly or 4 h post‐irradiation (6 Gy). Single antibody controls in non‐irradiated BRCA2 WT cells are shown. Scale bar indicates 10 µm. Bottom: Quantification of the number of PLA spots per nucleus. At least 750 cells were counted per condition from three independent experiments. For statistical comparison of the differences between the samples, we applied a Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test and the P‐values show significant differences. The red line in the plot indicates the median, and each symbol represents a single PLA spot.
Source data are available online for this figure.
We next wondered whether cells bearing the T207A variant accumulated DNA‐RNA hybrids. In agreement with a previous report using BRCA2‐depleted cells (Bhatia et al, 2014) and reproduced in U2OS cells here (Fig EV2A), we found that DLD1 BRCA2‐deficient cells (BRCA2−/−) accumulated DNA‐RNA hybrids, as detected by an increase in S9.6 nuclear IF signal, compared to the DLD1 cells bearing endogenous BRCA2 (BRCA2+/+) (Fig EV5C). Importantly, BRCA2−/− cells stably expressing BRCA2‐T207A augmented the levels of DNA‐RNA hybrids by 1.5‐fold compared to the cells complemented with BRCA2 WT (Fig 6B). Consistently, a 2.4‐fold increase in the levels of DNA‐RNA hybrids was detected by DRIP at the HIST1H2BG locus (Fig 6C). A similar trend was observed at other loci previously shown to accumulate DNA‐RNA hybrids in U2OS cells upon DDX5 depletion (Mersaoui et al, 2019), such as MALAT1 and RRPH1 in both BRCA2−/− and BRCA2‐T207A cells (Fig 6C). Importantly, these increased levels were specific to DNA‐RNA hybrids as they were significantly reduced upon RNase H1 treatment (Figs 6B and C, and EV5D).
Given that BRCA2 interaction with DDX5 seemed to be enhanced upon DNA damage, we analyzed whether these conditions would promote DDX5 retention or localization to damaged sites by in situ PLA. As shown before in U2OS cells (Fig 1C), the proximity between BRCA2 and DDX5 was enhanced by irradiation in DLD1 cells bearing BRCA2 WT (Fig 6D). In contrast, cells bearing BRCA2‐T207A displayed consistently reduced proximity of BRCA2 and DDX5 in both conditions (Fig 6D).
Importantly, BRCA2‐T207A cells also exhibited a strong reduction of anti‐DDX5‐S9.6 PLA signal compared to the BRCA2 WT cells, particularly in cells exposed to DNA damage, a reduction that was equivalent to that of BRCA2−/− cells (Fig 7A). The signal was specific for DNA‐RNA hybrids as it was strongly reduced upon RNaseH1 treatment. We noticed that the signal of S9.6‐anti‐DDX5 PLA was lower in irradiated conditions than in untreated cells in both BRCA2−/− and BRCA2‐T207A cells but not in BRCA2 WT cells. This is likely due to the presence of DDX5 at DNA‐RNA hybrids independently of DNA damage as described (Mersaoui et al, 2019) and to the exclusion of DDX5 from DSBs due to the transcriptional reduction observed especially in the absence of BRCA2 (Fig 4A and B). Consistently, the levels of DDX5 at DSBs were reduced in cells bearing the BRCA2‐T207A variant as visualized by the reduced anti‐DDX5‐γH2AX PLA signal (Fig 7B). This reduction was not due to BRCA2‐T207A recruitment at DSBs as it can readily accumulate to laser‐induced DNA damage sites (Fig 7C).
Figure 7. BRCA2‐T207A bearing cells exhibit reduced localization of DDX5 at DSB‐associated DNA‐RNA hybrids.
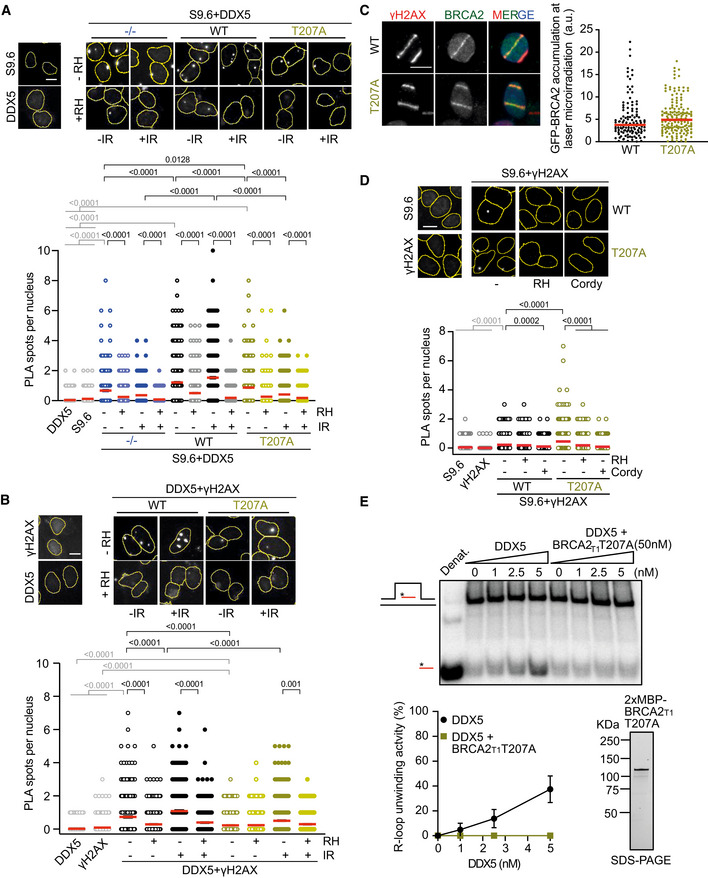
- Top: Representative images of in situ PLA performed between DDX5 and S9.6 (DNA‐RNA hybrids) antibodies in BRCA2‐deficient DLD1 cells (BRCA2−/−) or DLD1 stable clones expressing BRCA2 (WT) or BRCA2‐T207A (T207A). Cells were fixed directly or 4 h post‐irradiation (6 Gy). When indicated, cells were transfected/treated with RNase H1 (RH) prior to fixation. Single antibody controls in non‐irradiated BRCA2 WT cells are shown. Scale bar indicates 10 µm. Bottom: Quantification of the number of PLA spots per nucleus. At least 500 cells were counted per condition from three independent experiments. For statistical comparison of the differences between the samples, we applied a Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test and the P‐values show significant differences. The red line in the plot indicates the median, and each symbol represents a single PLA spot.
- Top: Representative images of in situ PLA performed between DDX5 and γH2AX antibodies in BRCA2‐deficient DLD1 cells (BRCA2−/−) bearing BRCA2 (WT) or BRCA2‐T207A (T207A). Cells were fixed directly or 4 h post‐irradiation (6 Gy). When indicated, cells were transfected/treated with RNase H1 (RH) prior to fixation. Single antibody controls in non‐irradiated BRCA2 WT cells are shown. Scale bar indicates 10 µm. Bottom: Quantification of the number of PLA spots per nucleus. At least 600 cells were counted per condition from three independent experiments. For statistical comparison of the differences between the samples, we applied a Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test and the P‐values show significant differences. The red line in the plot indicates the median, and each symbol represents a single PLA spot.
- Left: Representative images of the recruitment of transient transfected GFP‐MBP‐BRCA2 (WT and T207A) to DNA damage tracks at 5 min post‐irradiation in U2OS cells. γH2AX is used as a marker of DNA damage. Scale bar indicates 10 µm. Right: Quantification of the intensity of GFP signal at the laser tracks. At least 130 cells were counted per condition from three independent experiments. For statistical comparison of the differences between the two samples, we applied an unpaired t‐test. The red line in the plot indicates the median, and each symbol represents a single cell intensity value.
- Top: Representative images of in situ PLA performed between S9.6 (DNA‐RNA hybrids) and anti‐γH2AX antibodies in BRCA2‐deficient DLD1 cells (BRCA2−/−) bearing BRCA2 (WT) or BRCA2‐T207A (T207A). When indicated, cells were transfected/treated with RNase H1 (RH) or treated with cordycepin (Cordy) for 2 h at 37°C before fixation. Single antibody controls in non‐irradiated BRCA2 WT cells are shown. Scale bar indicates 10 µm. Nuclei as defined by auto threshold plugin on the DAPI image (ImageJ) are outlined in yellow. Bottom: Quantification of the number of PLA spots per nucleus. At least 600 cells were counted per condition from three independent experiments. For statistical comparison of the differences between the samples, we applied a Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test and the P‐values show significant differences. The red line in the plot indicates the median, and each symbol represents a single PLA spot.
- Top: PAGE gel showing a representative unwinding assays in which purified MBP‐DDX5‐GST (1–5 nM) was incubated with 32P‐labeled synthetic R‐loop substrate in the presence or absence of 50 nM purified BRCA2T1‐T207A (bottom right). Bottom left: Quantification of the unwinding experiments showing the percentage of free RNA relative to the R‐loop substrate (unwound product) as a function of DDX5 concentration alone (black) or in the presence of BRCA2T1‐T207A (green). The data represent the mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. Bottom right: SDS–PAGE showing 650 ng of purified 2XMBP‐BRCA2T1‐T207A used in the unwinding assay.
Altogether, these results confirm that a BRCA2‐DDX5 interaction promotes the localization/retention of DDX5 at DNA‐RNA hybrids accumulated at DNA breaks.
Given the lower occupancy of DDX5 at DNA‐RNA hybrid‐associated DSBs in cells bearing BRCA2‐T207A, we expected increasing levels of hybrids at breaks in these cells. Indeed, T207A bearing cells exhibited higher number of S9.6‐γH2AX PLA spots compared to control cells (Fig 7D). This effect was transcription‐dependent and specific to DNA‐RNA hybrids as shown by the dramatic signal reduction caused by cordycepin and RNase H1 treatments, respectively.
To find out whether this increase in DNA‐RNA hybrids was due to a defect in the unwinding activity of DDX5, we purified BRCA2T1‐T207A from human cells and tested how it affected the helicase activity of DDX5 as previously performed for BRCA2T1 (Fig 5A). Interestingly, BRCA2T1‐T207A inhibited the helicase activity of DDX5 (Fig 7E). This mutated fragment also reduced the interaction with DDX5 although to a lesser extent than the full‐length BRCA2‐T207A (Fig EV5E). These results favor the hypothesis that the fraction of BRCA2‐T207A that binds DDX5 results in a non‐productive interaction with DDX5 precluding its unwinding activity.
Thus, BRCA2‐T207A reduces BRCA2‐DDX5 productive interaction, impairing the localization of DDX5 at DNA‐RNA hybrids especially in cells exposed to DNA damage and inhibiting its unwinding activity.
DDX5‐BRCA2 interaction favors DSB repair by homologous recombination
Finally, we assessed the possible impact of the DNA‐RNA hybrids observed in DDX5‐depleted cells or BRCA2‐T207A cells on the repair of DSBs by HR. We used cells exposed to γ‐irradiation (6 Gy) at different time points and quantified the number of γH2AX foci as a marker of DSBs and RAD51 foci as a marker of HR repair. As expected, the number of γH2AX foci increased upon irradiation in both control and DDX5‐depleted U2OS cells (Fig EV5F). Interestingly, although the number of RAD51 foci gradually increased upon exposure to irradiation in both cell lines, the kinetics was clearly affected in DDX5‐depleted cells (Fig 8A). In control cells, the number of RAD51 foci reached a maximum 1 h after the irradiation and started recovering 4 h post‐irradiation, consistent with the repair of the damage. In contrast, 4 h were required to reach the same maximum levels in DDX5‐depleted cells. A delay in the kinetics of appearance of RAD51 foci post‐irradiation was also observed in DLD1 cells stably expressing BRCA2‐T207A variant versus BRCA2 WT (Figs 8B and EV5G). Of note, in agreement with the slower growth rate we observed in DLD1 cells compared to U2OS cells, the peak of RAD51 foci was observed only at 4 h post‐irradiation in DLD1 BRCA2 WT cells and was not reached even at 8 h post‐irradiation in BRCA2‐T207A cells. Consistent with previous reports (Yuan et al, 1999), the number of RAD51 foci was severely reduced in BRCA2−/− cells exposed to IR as compared to the BRCA2 WT cells (Fig 8B).
Figure 8. DDX5‐BRCA2 interaction favors DSB repair by homologous recombination.
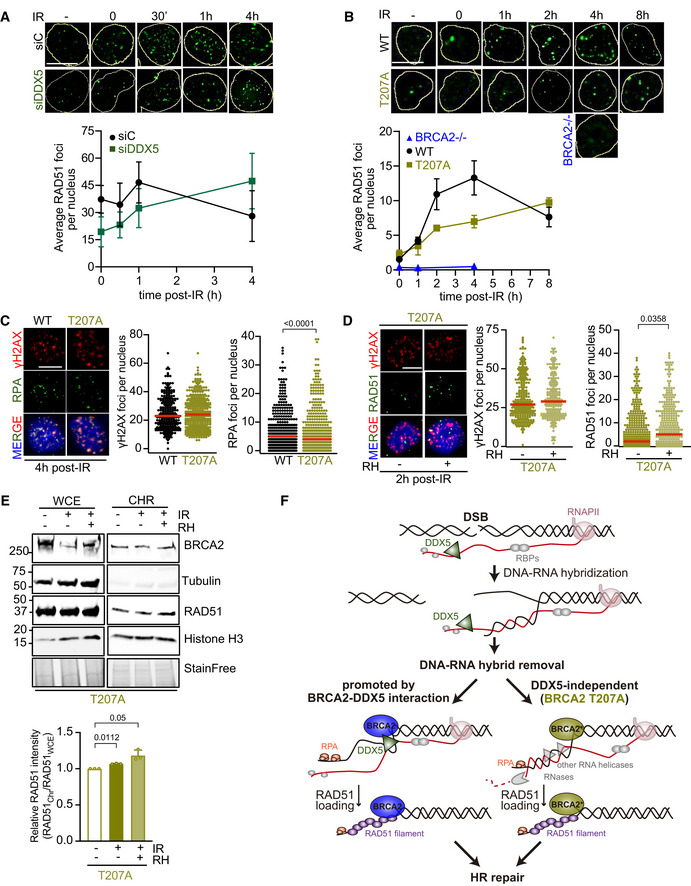
- Top: Representative immunofluorescence images of cells stained for RAD51 (green) in U2OS cells depleted of DDX5 (siDDX5) and in control cells (siC) in non‐treated (−) or different time points after exposure to IR (6 Gy), as indicated. Scale bar indicates 10 µm. Bottom: Graph showing the average number of RAD51 repair foci in both cell lines. The data represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. See also Fig EV5A.
- Top: Representative immunofluorescence images of DLD1 BRCA2‐deficient cells (BRCA2−/−) or BRCA2−/− cells expressing BRCA2 WT (WT) or BRCA2‐T207A (T207A) in non‐treated or at different time points post‐IR (6 Gy), as indicated; hybridized with anti‐RAD51 antibody (green). Scale bar indicates 10 µm. Bottom: Graph showing the average number of RAD51 repair foci in the three cell lines. The data represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. See also Fig EV5G.
- Left: Representative immunofluorescence images of DLD1 BRCA2 WT or BRCA2‐T207A cells 4 h post‐irradiation (6 Gy) hybridized with anti‐γH2AX and anti‐RPA antibodies. Right: Quantification of the number of γH2AX and RPA foci per nucleus, as indicated. The data represent at least 400 cells per condition from two independent experiments. For statistical comparison of the differences between the samples, we applied a Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test and the P‐values show significant differences. The red line in the plot indicates the median, and each symbol represents a single focus.
- Left: Representative immunofluorescence images of DLD1 BRCA2‐T207A cells 2 h post‐irradiation (6 Gy), as indicated, hybridized with anti‐γH2AX and anti‐RAD51 antibodies. (RH) RNase H. Right: Quantification of the number of γH2AX foci (left) or RAD51 foci (right) per nucleus. When indicated, cells were transfected with a plasmid expressing RNase H1 (RH) 48 h prior fixation. The data shown are from at least 400 cells per condition from three independent experiments. For statistical comparison of the differences between the samples, we applied a Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test and the P‐values show significant differences. The red line in the plot indicates the median, and each symbol represents a single focus. See also Fig EV5H.
- Top: Subcellular fractionation showing amount of RAD51 in DLD1 stable clones expressing BRCA2‐T207A (T207A) in chromatin fraction. When indicated, cells were irradiated (2 h treatment) and/or transfected with a plasmid expressing RNase H1 (RH) 48 h prior fixation. α‐Tubulin and histone H3 signals are shown as markers of cytoplasmic and chromatin fraction, respectively. Bottom: Quantification of RAD51 levels detected by Western blot with a RAD51‐specific antibody in chromatin fraction relative to RAD51 levels in WCE. Results are presented as the fold change compared to the untreated sample. The data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. The statistical significance of the difference was calculated with unpaired t‐test, and the P‐values show the significant difference.
- Model. DNA‐RNA hybrid formation may be enhanced in the vicinity of DSBs due to the DNA rotation freedom provided by the break. Left: Through its interaction with DDX5, BRCA2 helps retain DDX5 at DSBs and stimulates its helicase activity to resolve the DNA‐RNA hybrids. Removal of the RNA from the hybrid would trigger RPA binding to the exposed ssDNA followed by the subsequent loading of RAD51 by BRCA2 and the displacement of RPA to resume HR. Right: When the interaction of BRCA2 with DDX5 is impaired as in cells bearing the breast cancer variant BRCA2‐T207A, DDX5 would not mediate hybrid removal, leading to hybrids that persist longer delaying the coating of the ssDNA by RPA. Eventually, the RNA from the hybrids would be cleared by other nucleases and helicases such as RNase H1 or Senataxin in a likely less efficient manner.
Source data are available online for this figure.
DNA‐RNA hybrids that form at DSBs have been shown to alter the outcome of their repair by either promoting or impeding DNA‐end resection (Francia et al, 2012; Lu et al, 2018), one of the early steps of the HR pathway. To test the effect on DNA‐end resection of the DNA‐RNA hybrids accumulated due to the lack of BRCA2‐DDX5 interaction, we monitored the formation of RPA foci, a protein that coats ssDNA immediately upon resection (Chen et al, 2013), in irradiated DLD1 cells bearing BRCA2 WT or BRCA2‐T207A. Interestingly, cells bearing T207A mutation showed reduced number of RPA foci after γ‐irradiation compared to BRCA2 WT cells even if the levels of γH2AX were equivalent in both cell lines (Fig 8C) suggesting that end resection might be affected in these cells.
If the increased levels of DNA‐RNA hybrids observed in T207A cells are causing the delay observed in the appearance of RPA and RAD51 repair foci, reducing the DNA‐RNA hybrids should rescue this delay. To test this hypothesis, we overexpressed RNase H1 in cells bearing T207A and monitored the number of RAD51 foci upon γ‐irradiation as compared to non‐irradiated cells. Importantly, overexpression of RNase H1 partially restored the levels of RAD51 foci at 2 h after treatment without significantly changing the number of DSBs, as monitored by γH2AX foci (Figs 8D and EV5H). As an independent measure, we monitored the fraction of RAD51 bound to chromatin in irradiated cells bearing T207A. In agreement with the increase in RAD51 foci, the fraction of RAD51 bound to chromatin augmented upon RNase H1 overexpression (Fig 8E). Overall, these results suggest that the DNA‐RNA hybrids that accumulate in cells bearing BRCA2‐T207A variant interfere with the repair of DNA damage by HR.
Discussion
In this work, we establish that BRCA2 physically binds the RNA helicase DDX5 and demonstrate that this interaction plays an active role in the resolution of DNA‐RNA hybrids associated with DSBs that favors their repair by HR. BRCA2 retains DDX5 at DNA damage sites and stimulates its DNA‐RNA hybrid‐unwinding activity in vitro. We show that either depleting DDX5 or precluding the interaction of BRCA2 and DDX5, as observed in the breast cancer variant BRCA2‐T207A, reduce the efficiency of HR repair by altering the kinetics of appearance of RAD51 repair foci. Our findings suggest that DDX5 functions at DNA‐RNA hybrids that form in the vicinity of DSBs and its association with these structures is enhanced by BRCA2. Several observations support this interpretation: (i) DDX5‐depleted cells accumulate DNA‐RNA hybrids genome‐wide and particularly at DSBs; (ii) BRCA2 is required to retain/relocalize DDX5 at induced DSBs and laser micro‐irradiation tracks; and (iii) the proximity of DDX5 to DNA‐RNA hybrids under DNA damage conditions (IR) decreases in cells bearing a BRCA2 missense variant that impairs BRCA2‐DDX5 interaction.
DDX5 has been recently reported to suppress spontaneous R‐loops at R‐loop‐prone loci, an activity that requires DDX5 methylation by PRMT5 (Mersaoui et al, 2019). Here we show that the role of DDX5 preventing DNA‐RNA hybrids is ubiquitous, since the distribution of DNA‐RNA hybrids after depletion of DDX5, also described by a report that appeared while revising this manuscript (Villarreal et al, 2020), is similar genome‐wide. Furthermore, our strand‐specific (DRIPc‐seq) analysis shows that DDX5‐depleted cells accumulate DNA‐RNA hybrids at gene bodies and antisense transcripts at the promoters. Importantly, we find that DDX5‐depleted cells exhibit an enrichment of DNA‐RNA hybrids at γH2AX positive regions suggesting DNA‐RNA hybrids accumulating particularly at DSBs in these cells. These results are consistent with a recent report that appeared while revising this manuscript (Yu et al, 2020).
As its homolog in yeast Dbp2, DDX5 can unwind DNA‐RNA hybrids both alone and in the context of R‐loops in vitro (Xing et al, 2017; Mersaoui et al, 2019). Unlike canonical RNA helicases, DEAD‐box proteins such as DDX5 unwind duplex RNA by “bending” one of the RNA strands (Xing et al, 2019). Hence, it is not surprising that this type of non‐processive helicases rely on co‐factors for substrate specificity, whether an RNA or a DNA‐RNA hybrid, to enhance their activity (Xing et al, 2019). Indeed, we found that BRCA2 stimulates the R‐loop‐dependent unwinding activity of DDX5 by enhancing its ATP hydrolysis activity, thus defining a novel function for BRCA2. The modulation of the catalytic activity is not unprecedented for BRCA2 as it can also alter that of RAD51 (Carreira et al, 2009; Jensen et al, 2010).
Interestingly, these findings suggest a role of BRCA2 upstream its canonical position in the recombination process as the resolution of DNA‐RNA hybrids precedes the loading of RAD51 (Fig 8F). Regarding this possibility, a previous report showed that BRCA2 is recruited early to DNA damage sites through PolyADP‐ribose (PAR) binding (Zhang et al, 2015).
The consequences of DNA‐RNA hybrids at the break are controversial: Whereas some reports suggest that hybrids formed at DSBs may preclude the subsequent steps of the HR repair process (Li et al, 2016; Cohen et al, 2018), others have suggested that these structures could act as intermediates of the pathway (Ohle et al, 2016; Lu et al, 2018; D’Alessandro et al, 2018). In both scenarios however, DNA‐RNA hybrids need to be removed to license DNA repair by HR. DNA‐RNA hybrid resolution could be required at different stages. On the one hand, DNA‐RNA hybrids may form at the breaks before resection facilitated by the dsDNA rotation freedom conferred by a DSB (Aguilera & Gómez‐González, 2017). This would enable channeling repair toward NHEJ as it was shown in Senataxin‐depleted cells (Cohen et al, 2018). On the other hand, DNA‐RNA hybrids may form at the ssDNA generated upon resection, in a scenario in which HR is already committed. This would impede RPA binding as described in DDX1‐depleted cells (Li et al, 2016). Interestingly, DDX5 interaction with BRCA2 favored RPA coating and the timely repair of DSBs, as measured by RPA and RAD51 foci, which are not altered by Senataxin (Cohen et al, 2018). Moreover, RNase H1 treatment restored RAD51 foci formation in cells where the interaction of BRCA2 and RAD51 is reduced (BRCA2‐T207A), and this was concomitant with an augmented fraction of RAD51 bound to chromatin, suggesting that the DNA‐RNA hybrid resolution activity of BRCA2‐DDX5 directly favors HR. Thus, our results are consistent with DNA‐RNA hybrids associated with DNA damage being an impediment for the HR process and BRCA2‐DDX5 being active players in their resolution. Because the domains of interaction of RAD51 and of DDX5 on BRCA2 are separated, it is conceivable that the two proteins transiently co‐exist bound to BRCA2, presumably enabling the efficient repair of DSBs by HR.
Although enhanced, BRCA2 interaction with DDX5 is not restricted to DNA damage conditions. Based on the number of RNA helicases that came out in our mass spectrometry screen, and a previous report (Bhatia et al, 2014), it is possible that BRCA2 acts with other proteins to remove unscheduled DNA‐RNA hybrids both in the context of replication stress together with other components of the Fanconi anemia pathway (Schwab et al, 2015; García‐Rubio et al, 2015), or at induced DSBs. Along these lines, a recent work has reported the association of BRCA2 with the nuclease RNase H2 at DNA‐RNA hybrids in the vicinity of DSBs (D’Alessandro et al, 2018), although the phenotype of disrupting the interaction was not assessed in that study.
We show here that a single missense mutation in BRCA2 leads to a reduced and non‐productive interaction between BRCA2 and DDX5, inhibiting its helicase activity in vitro and increasing DNA damage‐dependent DNA‐RNA hybrids in cells. BRCA2‐T207A is a breast cancer variant previously characterized as being defective in the alignment of chromosomes due to its altered phosphorylation by PLK1 (Ehlén et al, 2020). In that study, a mild sensitivity of BRCA2‐T207A bearing cells to MMC was shown that could not be explained by the defect observed in mitosis. It is possible that sensitivity results from the fraction of DNA‐RNA hybrids at DSBs not resolved in BRCA2‐T207A cells. The fact that T207A alters DDX5 interaction and the removal of DNA‐RNA hybrids at DSBs with consequences in RAD51‐mediated repair exemplifies a missense BRCA2 variant that indirectly affects HR without impairing the canonical HR functional domains of BRCA2, that is, the BRC repeats and the C‐terminal DNA binding domain, previously associated with breast cancer risk (Guidugli et al, 2013; Shimelis et al, 2017). This and the cumulative impact of this variant on the functions of BRCA2 may have potential implications for cancer risk assessment.
In summary, our results agree with a model in which the removal of DNA‐RNA hybrids formed at DSBs is favored by the direct interaction between the DSB repair factor BRCA2 and the RNA helicase DDX5 (Fig 8F). We propose that BRCA2 interacts with and retains DDX5 at the DSB site at a DNA transcribed region harboring a DNA‐RNA hybrid, thus promoting its DNA‐RNA helicase activity to enable HR repair. Other proteins, such as RNA helicases or RNases, might also contribute to DNA‐RNA hybrid removal but, when BRCA2‐DDX5 interaction is impaired, as exemplified by the BRCA2‐T207A breast cancer variant, the reaction would either be delayed or less efficient.
Materials and Methods
Cell lines
The human cell lines HEK293T and U2OS cells (kind gift from Dr. Mounira Amor‐Gueret) were cultured in DMEM (Eurobio Abcys, Courtaboeuf, France) containing 25 mM sodium bicarbonate and 2 mM l‐Glutamine supplemented with 10% heat inactive FCS (Eurobio Abcys). The BRCA2‐deficient colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line DLD1 BRCA2−/− (Hucl et al, 2008) (HD 105–007) and the parental cell line DLD1 BRCA2+/+ (HD‐PAR‐008) were purchased from Horizon Discovery (Cambridge, England). The cells were cultured in RPMI media containing 25 mM sodium bicarbonate and 2 mM l‐Glutamine (Eurobio Abcys) supplemented with 10% heat inactivated fetal calf serum (Eurobio Abcys). The DLD1 BRCA2−/− cells were maintained in growth media containing 0.1 mg/ml hygromycin B (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The stable cell lines of DLD1−/− BRCA2‐deficient cells expressing BRCA2 WT or T207A generated as described (Ehlén et al, 2020) were cultured in growth media containing 0.1 mg/ml hygromycin B and 1 mg/ml G418 (Sigma‐Aldrich). DIvA cells (AsiSI‐ER‐U2OS) (kind gift from G. Legube) were cultured in DMEM (Gibco) supplemented with antibiotics, 10% FBS and 1 μg/ml puromycin. For AsiSI‐dependent induction of DSBs, cells were incubated for 4 h in medium containing 300 nM trans‐4‐Hydroxytamoxifen (4OHT) (Sigma, H7904). K562 cells (ATCC, CCL‐243) were cultured in Iscove's modified Dulbecco's medium (IMDM; GIBCO) supplemented with 10% heat inactivated fetal bovine serum (Sigma‐Aldrich) and 1% antibiotic‐antimycotic (BioWEST).
All cells were cultured at 37°C with 5% CO2 in a humidified incubator, and all cell lines used in this study have been regularly tested negatively for mycoplasma contamination (MycoAlert, Lonza).
Plasmids, transfections, and inhibitors
All BRCA2 N‐terminal expression constructs containing the sequence coding for BRCA2 amino acids 1–250 (BRCA2T1), 1–500 (BRCA2LT2), 1–750 (BRCA2LT3) or 1–1,000 (BRCA2NT) and EGFP‐MBP‐BRCA2 subcloning in phCMV1 expression vector were generated as described (von Nicolai et al, 2016). The point mutation T207A in the 2xMBP‐BRCA2T1 and EGFP‐MBP‐BRCA2 has been described before (Ehlén et al, 2020). The GFP‐53BP1 construct was obtained by Gateway cloning (Thermo Fisher Scientific) into pCDNA6.2‐GFP of a construct comprising the coding sequence of 53BP1 (kind gift of P. Bertrand, CEA, FR). The DDX5‐GFP construct was obtained by the insertion of DDX5 sequence from a pcDNA 6.2 CMV EmGFP vector in a pEGFP‐N3 vector (kind gift from Carsten Janke, Institut Curie, FR) using oAC953/967 primers (see Appendix Table S1). MBP‐DDX5‐GST construct for purification of human DDX5 was a kind gift from Elizabeth Tran (Purdue University, US). pCDNA3 CMV expressing RNAseH1 has been previously reported (ten Asbroek et al, 2002); the same as pEGFP‐M27 (Cerritelli et al, 2003).
Transfection of either U2OS or DLD1 cells with pCDNA3 CMV expressing RNAseH1 was performed with TurboFect (Thermo Fisher Scientific) 24 h before fixation (48 h before fixation in case of Figs 7A, B, and 8D, E). Transfection of U2OS cells with EGFP‐MBP‐BRCA2 (WT and T207A) was performed with jetPRIME (Ozyme) 48 h before fixation. Transfection of U2OS with DDX5‐GFP and of DLD1 BRCA2 WT and BRCA2‐T207A clones with either pEGFP‐C1 (−RH) or pEGFP‐M27 (+RH) was performed with Lipofectamine 3000 (Life Technologies) 24 h before fixation. For transcription inhibition in cells, cordycepin (100 μM, Sigma‐Aldrich C3394‐25MG) was added to the growth media for a 2‐h treatment at 37°C.
Ionizing radiation‐induced DNA damage
Cells were exposed to a 137Cs source (GSR D1; dose rate: 0.9 Gy/min) and subsequently incubated at 37°C for the indicated time.
siRNA transfections
For U2OS cells, siRNA transfections were performed using jetPRIME (Ozyme) with 100 nM of the indicated siRNAs following manufacturer’s instructions, except for Fig 2A, in which Lipofectamine 3000 (Life Technologies) was used. For BRCA2 depletion, we transfected a combination of the BRCA2 siRNA (SI00000966, Qiagen) and BRCA2 siRNA (Dharmacon D‐003462‐04) (100 nM each) (Figs 3A and EV2A) or the ON‐TARGETplus SMARTpool human BRCA2 (L‐021420‐00) (Dharmacon) (Fig 2A). For DDX5 depletion, we used siRNA targeting DDX5 (Mazurek et al, 2012) (Figs 3A and 8A, and EV2A and EV5F) (see Appendix Table S2). Experiments were performed 30 h or 72 h (Fig 2A) after transfection.
For experiments using K562 cells (Figs 2C–F and EV3), siRNA transfections were performed using Lipofectamine 3000 (Life Technologies) according to manufacturer’s instructions with 100 nM siRNA targeting DDX5 (Mazurek et al, 2012) (see Appendix Table S2) and experiments were performed 72 h after transfection.
For experiments using DIvA cells (Figs 3B and 4B, C, and EV4, EV5), siRNA transfections were performed using Lipofectamine 3000 (Life Technologies) according to manufacturer’s instructions with 100 nM of the indicated siRNAs (ON‐TARGETplus SMARTpool human SETX (L‐003462‐00) (Dharmacon), ON‐TARGETplus SMARTpool human BRCA2 (L‐021420‐00) (Dharmacon), or siRNA targeting DDX5 (Mazurek et al, 2012) (see Appendix Table S2) and experiments were performed 72 h after transfection.
The non‐targeting oligonucleotide (Dharmacon D‐001810‐04‐20, 100 nM) was used as control (siC) in all cells.
Expression and purification of 2xMBP‐BRCA2T1 (WT and T207A), 2xMBP‐BRCA2T2, 2xMBP‐BRCA2LT3, and EGFP‐MBP‐BRCA2
2xMBP‐BRCA2T1, 2xMBP‐BRCA2T2, 2xMBP‐BRCA2LT3, and EGFP‐MBP‐BRCA2 were purified as previously described (von Nicolai et al, 2016). Briefly, from ten to twenty 150 mm plates of HEK293 were transiently transfected with the 2xMBP‐BRCA21–250 (BRCA2T1) or the EGFP‐MBP‐BRCA2 using TurboFect (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The cells were harvested 30 h post‐transfection, lysed in lysis buffer H (50 mM HEPES (pH 7.5), 250 mM NaCl, 1% NP‐40, 5 mM EDTA, 1 mM ATP and 3 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, 1 mM PMSF and EDTA‐free Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (Roche)), and incubated with amylose resin (NEB) for 3 h at 4°C. The lysate was extensively washed with buffer H including 250 mM (EGFP‐MBP‐BRCA2) or 500 mM (BRCA2T1) NaCl, and the protein was eluted with 20 mM maltose. The eluate was further purified with Bio‐Rex 70 cation‐exchange resin (Bio‐Rad) by NaCl step elution. For the purification of 2xMBP‐BRCA2T1‐T207A, we followed the same steps as above except for the Bio‐Rex resin that was substituted by a HiTrap Q HP strong anion exchange column (GE Healthcare). The size and purity of the final nuclease‐free fractions were analyzed by SDS–PAGE and Western blotting using anti‐MBP antibody or anti‐BRCA2 antibody in the case of full‐length BRCA2 purification. Pooled protein was snap‐frozen in N2 and stored at −80°C. Concentrations were calculated measuring the intensity of the band on a Stain‐Free gel (Bio‐Rad) via ImageLab software and using the same protein at known concentration as a reference.
Expression and purification of MBP‐DDX5‐GST
MBP‐DDX5‐GST was purified as described (Xing et al, 2017). Briefly, expression of MBP‐DDX5‐GST in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) Star cells was induced using 0.2 mM IPTG at 16°C overnight. Cells were lysed in a buffer containing 50 mM HEPES (pH 7.5), 250 mM NaCl and 1% NP‐40 and disrupted using a French press. The crude lysate was clarified by centrifugation in a Beckmann Ti45 rotor at 150,650 g (RCF), 60 min, and the MBP‐DDX5‐GST was purified from the soluble lysate using glutathione resin (GE Healthcare) followed by cation‐exchange chromatography (SP sepharose, Sigma‐Aldrich). The protein was eluted with elution buffer 1 [50 mM Tris–HCl (pH 8.0), 300 mM NaCl, 20% glycerol]. Stain‐Free images of the gels before transfer were used as loading control for the input, and cropped image is shown in the figure. Nuclease‐free aliquots were snap‐frozen in N2 and stored at −80°C. Concentration was calculated measuring intensity of the band on Stain‐Free gel via ImageLab software and using Bradford assay.
Amylose and GFP pull‐down from whole cell extracts
For amylose pull‐down, cell pellets were resuspended in lysis buffer (50 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 250 mM NaCl) supplemented with 1× protease inhibitor cocktail (Complete, EDTA‐free; Roche), 1 mM PMSF, 1% NP‐40, 1 mM DTT, 1 mM MgCl2, and 250 units/ml benzonase (1.5 ml lysis buffer/2.5 × 107 cells). Cell suspension was sonicated and cleared by centrifugation. The supernatant was then incubated for O/N at 4°C with 60 µl amylose resin (New England Biolabs) per 2.5 × 107 cells. After four washes with washing buffer (50 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 500 mM NaCl, EDTA 5 mM), the bound proteins were eluted in washing buffer supplemented with 10 mM maltose (Sigma). Eluted proteins were separated by SDS–PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting. For all Western blots, the protein bands were visualized with ChemiDoc XRS + System (Bio‐Rad). Stain‐Free images of the gels before transfer were used as loading control for the input, and cropped image is shown in the figure.
For GFP pull‐down, DLD1 BRCA2+/+ parental cells and DLD1 BRCA2−/− stable clones expressing EGFP‐MBP‐BRCA2 (WT or T207A) pellets were resuspended in lysis buffer (50 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl) supplemented with 1× protease inhibitor cocktail (Complete, EDTA‐free; Roche), 1 mM PMSF, 1% NP‐40, 1 mM DTT, 1 mM MgCl2, and BSA 100 μg/ml. Cell suspension was sonicated and cleared by centrifugation. The supernatant was then incubated for 1, 5 h at 4°C with 25 µl of pre‐equilibrated GFP‐TRAP beads (Chromotek) to pull down EGFP‐MBP‐BRCA2. The beads were washed three times in lysis buffer with 250 mM NaCl. Bound proteins were eluted by boiling the samples for 4 min in 3× SDS–PAGE sample loading buffer (SB), and eluted proteins were separated by SDS–PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting. For all Western blots, the protein bands were visualized with ChemiDoc XRS + System (Bio‐Rad) and quantified by Image LabTM5.2.1 Software (Bio‐Rad). To calculate the relative co‐immunoprecipitation (co‐IP)/co‐pull‐down of a protein of interest, the intensity of the band in the co‐IP was divided by the intensity of the band in the input (ImageQuant TMTL software), and the ratio co‐IP: input of the protein of interest was then divided by the intensity of the band of the immunoprecipitated protein. Stain‐Free images of the gels before transfer were used as loading control for the input, and cropped image is shown in the figure.
Amylose pull‐down from nuclear cell extracts
Four plates of HEK293T exponentially growing cells were harvested, and the cell pellets were gently resuspended in nuclear isolation buffer (NIB; 10 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 10 mM KCl, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 10% glycerol, 350 mM sucrose) supplemented with 1× protease inhibitor cocktail (Complete, EDTA‐free; Roche), 1 mM PMSF, and 1 mM DTT (1.5 ml lysis buffer/2.5 × 107 cells). Samples were kept on ice for 10 min and centrifuged at 1,300 g for 5 min at 4°C. The pellet (nuclear fraction) was washed with NIB and sonicated. The pull‐down was performed as that of the whole cell extracts above.
Mass spectrometry
Amylose‐isolated samples were separated by SDS–PAGE and stained with colloidal blue (LabSafe GEL Blue G‐Biosciences). In‐gel digestion was performed, according to standard protocols. Briefly, 23–24 gel slices were excised, washed, and the proteins were reduced with 10 mM DTT (Sigma) and alkylated with 55 mM iodoacetamide (Sigma). The gel pieces were washed with 100% acetonitrile and incubated overnight with trypsin (Roche Diagnostics) in 25 mM ammonium bicarbonate at 30°C. Peptides extracted from each gel slice were used directly and analyzed by nano‐liquid chromatography‐coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (nanoLC‐MS/MS) for protein identification. Each sample was concentrated and then separated on a C18 reverse phase column, with a linear acetonitrile gradient (UltiMate 3000 System, Dionex, and column 75 μm inner diameter × 15 cm, packed with C18 PepMapTM, 3 μm, 100 Å; LC Packings) before MS and MS/MS. Spectra were recorded on an LTQ‐Orbitrap XL mass spectrometer (Thermo Electron). For identification, data were searched against the Swiss‐Prot “Homo sapiens” database using Mascot™ (version 2.5.1) one by one band or merged per conditions for emPAI abundance evaluation. Enzyme specificity was set to trypsin, and a maximum of two‐missed cleavage sites were allowed. Oxidized methionine, carbamidomethyl cysteine, and N‐terminal acetylation were set as variable modifications. Maximum allowed mass deviation was set to 2 ppm for monoisotopic precursor ions and 0.8 Da for MS/MS peaks. Result files were further processed using myProMS software (Poullet et al, 2007). FDR calculation used Percolator (Spivak et al, 2009) and was set to 1% at the peptide level for the whole study. To calculate protein abundance, we used the label‐free exponentially modified protein abundance index (emPAI) and molar % values obtained in the merged Mascot from each replicate as described (Ishihama et al, 2005). Mascot uses only peptides identified with score at or above homology or identity thresholds for the calculation of the emPAI values. Fold change ratios for identified proteins were calculated by dividing the calculated molar percentage value for an individual protein in the BRCA2NT condition with the cognate 2XMBP condition value.
Mass spectrometry datasets generated during this study are available at ProteomeXchange Consortium via the PRIDE (Perez‐Riverol et al, 2019) partner repository. Project Name: BRCA2‐N‐terminus interacting proteins in HEK293T cells.
Project accession: PXD018979.
Co‐immunoprecipitation
Cell pellets were resuspended in lysis buffer (50 mM HEPES pH7.5, 250 mM NaCl, 5 mM EDTA) supplemented with 1× protease inhibitor cocktail (Complete, EDTA‐free; Roche), 1 mM PMSF, 1% NP‐40, 1 mM DTT, 1 mM MgCl2, and 250 units/ml benzonase (1.5 ml lysis buffer/2.5 × 107 cells). The cell suspension was sonicated and cleared by centrifugation. The supernatant was then incubated for 2 h in a rotator at 4°C with 1 μg Dynabeads Protein G (Life Technologies) and 1 μg primary antibody (or normal IgG where indicated) per 2.5 × 107 cells. The beads were collected using a magnet and washed three times with washing buffer (50 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 250 mM NaCl, EDTA 5 mM). Boiled beads resuspended in 1× SDS–PAGE sample loading buffer (SB) were separated by SDS–PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting. For all Western blots, the protein bands were visualized with ChemiDoc XRS+ System (Bio‐Rad). Stain‐Free images of the gels before transfer were used as loading control for the input, and cropped image is shown in the figure.
In vitro pull‐down
Glutathione resin (GE Healthcare) was equilibrated with binding buffer: 50 mM HEPES (pH 7.5), 250 mM NaCl, and 1 mM DTT. Purified MBP‐DDX5‐GST (200 ng) was incubated with 200 ng of purified 2XMBP‐BRCA2T1 (WT and T207A) for 30 min at 37°C and then batch bound to 30 μl of glutathione resin for 1 h at 4°C under rotation. The complexes were washed three times with washing buffer (50 mM HEPES (pH 7.5), 500 mM NaCl, and 1 mM DTT) containing 0.1% Triton X‐100. Bound proteins were eluted with 30 μl 20 mM reduced Glutathione in binding buffer, resuspended in 3× SDS sample buffer, heated at 54°C for 5 min, and loaded onto a 10% SDS–PAGE gel. Proteins were analyzed by Western blotting. For all Western blots, the protein bands were visualized with ChemiDoc XRS + System (Bio‐Rad).
Subcellular fractionation
DLD1 stable clones expressing EGFP‐MBP‐BRCA2 T207A pellets were resuspended in BADT buffer (10 mM HEPES pH 7.9, 10 mM KCl, 10% glycerol, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 0.34 M sucrose, Triton X‐100 0.1%) supplemented with 1× protease inhibitor cocktail (Complete, EDTA‐free; Roche), 1 mM PMSF, 1 mM DTT, and 0.1 mM Na3VO4. Cell suspension was incubated 20 min on ice and cytoplasmic fraction separated by centrifugation (supernatant). After a wash with BAD buffer (same as BADT buffer, without Triton X‐100), the pellet was resuspended in NSB buffer (EDTA 3 mM, EGTA 0.2 mM) supplemented with 1× protease inhibitor cocktail (Complete, EDTA‐free; Roche), 1 mM PMSF, 1 mM DTT, and 0.1 mM Na3VO4. The suspension was incubated 30 min on ice with occasional vortexing, and nuclear soluble fraction (supernatant) was separated from the chromatin fraction by centrifugation. Chromatin fraction pellets were resuspended in lysis buffer (same as described for co‐Immunoprecipitation) and sonicated. Whole cell extracts (WCE) and chromatin fraction proteins were boiled for 5 min, separated by SDS–PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting. For all Western blots, the protein bands were visualized with ChemiDoc XRS+ System (Bio‐Rad). Stain‐Free images of the gels before transfer were used as loading control for the input, and cropped image is shown in the figure. For the quantification, the intensity of the RAD51 band from the chromatin fraction was divided by the intensity of the band in the input (WCE) (ImageQuant TMTL software) and normalized to the level of not Irradiated samples.
Antibodies used for Western Blotting
Antibodies used for Western blotting were as follows: mouse anti‐MBP (1:5,000, R29, Cat. #MA5‐14122, Thermo Fisher Scientific), mouse anti‐BRCA2 (1:1,000, OP95, EMD Millipore), mouse anti‐DDX5 (1:100 or 1:500, Cat. # sc‐166167 Santa Cruz Biotechnology), rabbit anti‐RAD51 (1:2,000, Cat. ab63801 Abcam), mouse anti‐α‐tubulin (1:5,000, Cat. GTX628802 Genetex GT114), and rabbit anti‐Histone H3 (1:5,000, Cat. A300‐823A, Bethyl Laboratories). Horseradish peroxidase (HRP)‐conjugated secondary antibodies used were as follows: mouse‐IgGκ BP‐HRP (IB: 1:5,000, Cat. #sc‐516102, Santa Cruz), mouse anti‐rabbit IgG‐HRP (IB: 1:5,000, Cat. sc‐2357, Santa Cruz), and goat anti‐mouse IgG‐HRP (1:10,000, Cat. # 115‐035‐003, Interchim).
In situ proximity ligation assay
Cells were seeded on coverslips pre‐coated with 1 μg/ml fibronectin (Sigma) and 20 μg/ml collagen (Sigma). In case of EdU incorporation, a pulse‐label nascent DNA was performed with 10 µM EdU for 5 min before fixation. Cells were washed with PBS and cytoskeleton (CSK) buffer [10 mM PIPES pH 6.8, 100 mM NaCl, 300 mM sucrose, 3 mM MgCl2 and 1× protease inhibitor cocktail (Complete, EDTA‐free; Roche)] and permeabilized with CSK‐T buffer (CSK supplemented with 0.5% Triton X‐100). After washes in CSK and PBS, the cells were fixed with 2% para‐formaldehyde (PFA) for 20 min at room temperature (RT). The cells were then washed three times with PBS. In case of EdU labeling, before incubation with primary antibodies, samples were incubated for 30 min at RT with a Click‐mix solution (Biotin‐azide 6 nM, Sodium ascorbate 10 mM, CuSO4 2 mM, diluted in PBS 1×) in order to allow EdU‐biotin conjugation. In this case, IF was combined to PLA, adding a primary antibody anti‐biotin (1:3,000, Bethyl laboratories, Cat. # BETA150‐109A) together with primary antibodies for PLA and secondary antibody (donkey anti‐rabbit Alexa 488, 1:1,000, Cat. # A‐21206, Life Technologies) together with PLA probes.
In situ PLA was performed following the manufacturer’s specifications (Duolink™, Sigma) except that the primary antibody was incubated for 1 h at 37°C. For quantification, particle analysis was done using ImageJ software (NIH Image). The nucleus was defined by an auto‐threshold (Huang, ImageJ) on DAPI, and a mask was generated and applied onto the Texas‐Red2 picture to count PLA spots within the nucleus using the plugin Find Maxima with a prominence of 1,000 for Fig 6D, 2,000 for Figs 1C and 7B, and EV4A, of 5,000 Figs 2B, 3A, and 7A, D. Primary antibodies used for PLA were as follows: BRCA2 (1:2,000 OP95 EMD Millipore), DDX5 (1:3,000 Cat. # ab10261 Abcam), S9.6 (1:100,000, Protein Expression and Purification Core facility, Institut Curie), γ‐H2AX (1:3,000 for Figs 3A and EV4A, and 1:100,000 for Fig 7B, Cat. # 07‐164, EMD Millipore), and NBS1 (1:2,000 for Fig EV4A, Cat. #NB100‐92610 Novus Biologicals).
Immunofluorescence microscopy
For immunofluorescence experiments in Figs 8A–D, and EV2A and EV5F–H, cells were seeded on coverslips pre‐coated with 1 μg/ml fibronectin (Sigma) and 20 μg/ml collagen (Sigma) the day before 6 Gy γ‐irradiation. At the time indicated after irradiation, the coverslips were washed twice in PBS followed by one wash in CSK buffer (10 mM PIPES, pH 6.8, 0.1 M NaCl, 0.3 M sucrose, 3 mM MgCl2, EDTA‐free Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (Roche)). The cells were permeabilized for 5 min at room temperature in CSK buffer containing 0.5% Triton X‐100 (CSK‐T) followed by one rinse in CSK buffer and one rinse in PBS before fixation for 20 min at room temperature with 2% PFA in PBS. After one rinse in PBS and one in PBS‐T, the cells were blocked for 5 min at room temperature with 5% BSA in PBS‐T.
For immunofluorescence experiments in Figs 2A, 4C, 6B, and EV2B and EV5C, cells grown on glass coverslips coated with poly‐l‐Lysine (Sigma) were rinsed with cold PBS and treated for 3 min with a Triton X‐100 extraction buffer (0.1% Triton X‐100, 20 mM HEPES‐KOH pH 7.9, 50 mM NaCl, 3 mM MgCl2, 300 mM sucrose). In the case of Figs 2A and 6B, and EV2B and EV5C, after extraction, cells were fixed for 8 min with methanol at −20°C; coverslips were then washed three times with PBS and blocked overnight at 4°C in blocking solution (PBS with 2% BSA). In the case of Fig 4C, after extraction, DIvA cells were fixed in 4% FA/2% sucrose in PBS for 10 min at room temperature (RT), washed twice in PBS and repermeabilized with PBS‐Triton X‐100 0.5% for 10 min at RT. Then, cells were blocked at RT for 1 h in blocking solution (3% BSA, 0.1% Triton X‐100 in PBS). For S9.6 immunofluorescence experiments in pre‐extracted cells (see Figs 2A and 6B, and EV2B and EV5C), consecutive treatments with RNase III and RNase H1 were performed before blocking, incubating each coverslip with 1.2 U of RNase III and 9 U of RNase H1, for 30 min at 37°C.
For all immunofluorescence experiments, cells were incubated overnight at 4°C in blocking solution with primary antibodies, except in case of Fig EV2A, when cells were incubated for 1 h at 37°C with S9.6 (1:500, Protein Expression and Purification Core facility, Institut Curie) and anti‐nucleolin (1:1,000 Cat. # ab22758, Abcam) antibodies. For Figs 8A–D and EV5F–H, cells were incubated with anti‐γH2AX (1:1,000 Cat. # 05‐636, EMD Millipore), anti‐RAD51 (1:100 for DLD1 cells, 1:1,000 for U2OS cells, Cat. # sc‐8349, Santa Cruz Biotechnology), or anti‐RPA (1:1,000, Cat. # 2208S, Ozyme (Cell Signaling) antibodies. For Figs 2A and 6B, and EV2A and B, the mouse S9.6 (1:2,000) and rabbit anti‐nucleolin (1:1,000 Cat. # ab50279, Abcam) primary antibodies were used except for the case of DDX5 transfected cells where the couple mouse S9.6 (1:2,000) and rabbit anti‐GFP (1:200, Cat. # ab6556 Abcam) were used. For Fig 4C, anti‐γH2AX (1:1,000, Cat. # ab2893, Abcam) or anti‐DDX5 (1:500, Cat. # sc‐166167 Santa Cruz) was used. After primary antibody incubation, the coverslips were rinsed in PBS‐T followed by two washes of 10 min in PBS‐T and blocked for 5 min at room temperature with 5% BSA in PBS‐T. Cells were incubated with appropriate secondary antibodies (conjugated with Alexa Fluor 488, 546, 568, 594, or 647), diluted in blocking solution for 1 h at RT. After rinsing, coverslips were mounted onto slides using ProLong Gold Antifade reagent (Invitrogen). Images in Figs 2A, 4C, 6B, and EV2B and EV5C were acquired using a Leica DM6000 wide‐field microscope equipped with a DFC390 camera (Leica) at ×63 magnification using the LAS AF software (Leica). For Figs 8A–D, and EV2A and EV5F–H, the camera used was a Hamamatsu Flash 4.0 sCMOS controlled with MetaMorph 2.1 software (Molecular Devices).
Quantification of S9.6 intensity was performed in the area of the nucleus as determined by DAPI and subtracting the intensity of S9.6 in nucleoli (stained with an antibody specific for nucleolin, see above). For Figs 2A, 4C, 6B, and EV2B and EV5C, automated quantification of foci and fluorescence intensities was performed using the MetaMorph v7.5.1.0 software (Molecular Probes). For Figs 8A–D and EV5AF–H Z‐stacks were taken at 0.5‐μm intervals to generate a Z‐projection image using ImageJ. For the analysis of γ‐H2AX, RAD51, and RPA foci, 26 Z‐stacks were taken at 0.2‐μm intervals to generate a maximal intensity projection using ImageJ. The number of γH2AX foci per nucleus was counted with a customized macro using a semi‐automated procedure; the nucleus was defined by an auto‐threshold (Otsu, ImageJ) on DAPI, and a mask was generated and applied onto the Z‐projection to count foci within the nucleus. For the definition of foci, we applied the threshold plugin IsoData (ImageJ) and for the quantification of foci, we used the tool Analyze Particles (ImageJ) setting a range of 5–100 pixels2 for Fig EV5F and a range of 5–1,000 for Figs 8D, and EV5AG and H to select only particles that correspond to the size of a focus. RAD51 and RPA foci were quantified using the plugin Find Maxima onto the Z‐projection with a prominence of 1,000 for Fig 8A and of 5,000 for Fig 8B–D.
Protein recruitment after laser‐induced damage
U2OS cells were seeded on glass coverslips pre‐coated with 1 μg/ml fibronectin (Sigma) and 20 μg/ml collagen (Sigma). For Fig 4A, cells were then co‐transfected with 2 μg of a DDX5‐GFP construct and BRCA2 siRNA and ON‐TARGET plus non‐targeting oligonucleotide (as described in siRNA section) 48 h prior to imaging; or with 2 μg of a construct expressing GFP‐53BP1 also 48 h prior imaging. For Fig 7C, cells were transfected with 5 μg of a construct expressing EGFP‐MBP‐BRCA2 (WT and T207A) 30h prior imaging. Cells were pre‐sensitized by adding 10 mg/ml of Hoechst dye 33258 to the medium for 5 min at 37°C. Live cell imaging of DDX5‐GFP or GFP‐53BP1 at laser tracks was carried out using an inverted Leica confocal laser scanning SP5 system equipped with a 37°C heating chamber attached to a DMI6000 stand using 63×/1.4 oil objective. DNA damage was generated using a 405 nm laser diode focused onto a single line (thickness: 1 pixel) within the nucleus to generate the damage. Specifically, we set the laser output to 70% of maximum power and the scan speed at 10 Hz. GFP signal was detected between 500–550 nm on PMdetector. All recordings were performed using the indicated sampling frequency (512 × 512 image size, line average of 4 and zooming set to 7.94). To reduce the time of image acquisition, the scan was used in bidirectional regime and the scan speed was set at 10 Hz (10,000 lines/s). The whole system was driven by LAS AF software (Leica). For Fig 4A, images were collected at 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 15, and 20 min after the DNA damage using a 488 nm argon laser.
For Fig 7C, DNA damage was induced the same way as described above, and cells were fixed 5 min after DNA damage. Permeabilization, fixation, and blocking were performed as described in “Immunofluorescence microscopy” section for Figs 8A–D, and EV2A and EV5F–H. Cells were incubated overnight at 4°C in blocking solution with primary antibodies mouse anti‐γH2AX (1:1,000 Cat. # 05‐636, EMD Millipore) and rabbit anti‐GFP (1:1,000, Cat. # A11122, Thermo Fisher Scientific (Life Technologies)). After primary antibody incubation, the coverslips were rinsed in PBS‐T followed by two washes of 10 min in PBS‐T and blocked for 5 min at room temperature with 5% BSA in PBS‐T. Cells were incubated with the appropriate secondary antibodies (conjugated with Alexa Fluor 488, 594), diluted in blocking solution for 1 h at RT. After rinsing, coverslips were mounted onto slides using ProLong Gold Antifade reagent (Invitrogen).
For Fig 4A, the quantification of cells showing a DDX5‐GFP “anti‐stripe” pattern at DNA damage tracks (reduced GFP signal at the laser tracks compared to the rest of the nucleus) was performed by manual counting in images visualized in ImageJ. For Fig 7C, intensity of recruited protein was measured drawing a rectangle comprising the laser track. The same size region in a zone adjacent in the nucleus was used to establish the background intensity. Finally, the background intensity was subtracted from that of the laser track and divided by the area of the rectangle to obtain the average intensity of each laser track.
In vitro unwinding assay
DNA substrates were purchased PAGE‐purified from MWG Eurofins and the RNA substrate was purchased from Sigma. The RNA oligonucleotide oAC864 (see Appendix Table S3) was 5′ end labeled with T4 polynucleotide kinase and [γ‐32P] ATP. R‐loops substrates were prepared by annealing 1 pmol of labeled oAC864 (RNA) to 2.5 pmol of DNA oligo oAC862 (see Appendix Table S3) and 2.5 pmol of DNA oligo oAC863 (see Appendix Table S3) in annealing buffer (1 mM EDTA, 10 mM Tris–HCl at pH 7.6) by heating for 2 min at 95°C followed by slow cooling to room temperature. To assess unwinding activity, 1.5 nM molecules of R‐loop or DNA‐RNA hybrid substrate were incubated with the indicated concentrations of purified MBP‐DDX5‐GST in 25 mM TrisAcO, 5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, 5 mM ATP, 100 μg/ml, and 40 U RNAse OUT (Thermo Fisher Scientific) alone or with the indicated concentration of purified 2XMBP‐BRCA2, 2XMBP‐BRCA2T1, 2XMBP‐BRCA2T2, 2XMBP‐BRCA2LT3. The mixture was incubated at 37°C for 30 min, and the reaction products were resolved on 10% PAGE in 1% TAE buffer (40 mM Tris Acetate, 0.5 mM EDTA) at 110 V for 45 min at room temperature. The gels were dried, visualized by phosphoimaging (Typhoon, GE Healthcare), and analyzed on Image Quant software (GE Healthcare). In all in vitro unwinding assays, DDX5 unwinding activity was calculated as the percentage of free radiolabeled RNA relative to the R‐loop signal.
ATP hydrolysis assay
DDX5 at the indicated concentrations was preincubated or not with the 2xMBP‐BRCA2LT3 (6 nM) for 15 min at 37°C, followed by addition of R‐loop substrate (5 μM) (see Appendix Table S3) in 10 μl of buffer containing 25 mM Tris–HCl (pH 7.5), 1 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, 1 mM ATP, and 20 μCi/ml [γ32P] ATP, and further incubated at 37°C for 60 min. Aliquots (1 μl) were spotted onto a polyethyleneimine (PEI) thin layer chromatography (TLC) plate (Millipore). The spots were air‐dried, and the plates were developed in 1 M formic acid and 0.5 M LiCl. The amount of ATP hydrolyzed was determined from dried plates using phosphoimaging (Typhoon, GE Healthcare). The amount of 32Pi and [γ32P] ATP was quantified using ImageQuant software.
DNA‐RNA immunoprecipitation
DNA‐RNA immunoprecipitation (DRIP) was performed in enzymatically digested DNA from U2OS DIvA cells after 72 h transfection, with or without 4‐h treatment with 4OHT for DSB induction, and treated or not with RNase H1 in vitro as previously described (Herrera‐Moyano et al, 2014). Analysis was performed by qPCR using primers located at each of the regions of interest: RBMXL1‐fw (GATTGGCTATGGGTGTGGAC), RBMXL1‐rv (CATCCTTGCAAACCAGTCCT), ASXL1‐fw (CCTAGCTGAGGTCGGTGCTA), ASXL1‐rv (GAAGAGTGAGGAGGGGGAGT), HIST1H2BG‐fw (TGTGACCAAGGCGCAGAAGA), HIST1H2BG‐rv (GAGCGCTTGTTGTAGTGGGC), WDR90‐fw (GTGCCAGGCTGTATTGCTT), WDR90‐rv (GGGAAATGCAGACGTGTCAT), MALAT1‐fw (ACGCAGGGAGAATTGCGTCAR), MALAT1‐rv (CCTTCCCGTACTTCTGTCTTCCA), RPPH1‐fw (GTGCGTCCTGTCACTCCACTR), RRPH1‐rv (TTCCAAGCTCCGGCAAAGGA), SNRNP‐fw (GCCAAATGAGTGAGGATGGT), and SNRNP‐rv (TCCTCTCTGCCTGACTCCAT). Means and SEM from 4 to 5 independent experiments were calculated, and the statistical significance was analyzed using unpaired t‐test.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
Cells were crosslinked with a formaldehyde solution added to the culture medium (1% formaldehyde final concentration) for 10 min at room temperature, with gentle agitation. Glycine (0.125 M) was added for 5 min to stop the reaction. Cells were washed twice with cold PBS in the presence of complete protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche) and PMSF and harvested by. Pelleted cells were lysed in two steps, first using 0.5% NP‐40 buffer for nucleus isolation followed by nuclear lysis in 1% SDS lysis buffer. Sonication was performed using Bioruptor (Diagenode, UCD‐200) at high intensity and two cycles of 8 min (30″ sonication, 30″ pause) to achieve DNA fragments of about 200–1,000 bp and chromatin was clarified by centrifugation (13,000 × g, 30 min, 4°C). For each IP, 20 μg of chromatin was diluted in IP buffer (0.01% SDS, 1.1% Triton X‐100, 1.2 mM EDTA pH 8, 16.7 mM Tris pH 8, 167 mM NaCl) and incubated overnight at 4°C on a rotating wheel with 4 μg antibody (anti‐DDX5 Santa Cruz sc‐166167; anti‐γH2AX Abcam ab2893; rabbit IgG SIGMA I8140; and mouse IgG SIGMA I8765 as controls), followed by 2‐h incubation with 30 μl pre‐cleared Dynabeads protein A and Dynabeads protein G (Thermo Fisher). Beads were sequentially washed with increasing salt concentrations (150–500 mM NaCl, 0.1% SDS, 1% Triton X‐100, 2 mM EDTA pH 8, 20 mM Tris pH 8), and LiCl buffer (0.25 M LiCl, 1% NP‐40, 1% sodium deoxycholate, 1 mM EDTA, 10 mM Tris pH 8). Immunoprecipitated complexes were resuspended in elution buffer (Tris 10 mM pH 8, EDTA 0.5 mM pH 8, 1% SDS) and incubated for 20 min at 65°C shaking. After removal of the beads, SDS concentration was brought to 0.5% by addition of 1× TE and samples were further incubated overnight at 65°C to revert crosslinking. After 1‐h proteinase K treatment, immunoprecipitated and input DNA was purified with phenol/chloroform and precipitated in ethanol at −20°C. Samples were resuspended in 50 μl water.
Quantitative PCR analysis
All real‐time (RT)–qPCR analysis was performed with iTaq Universal SYBR Green Supermix (Bio‐Rad) and analyzed on 7500 FAST Real‐Time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA). The oligos used were RBMXL1cDNA‐fw (GGTGGAAGTCGAGACAGTTACTCA), RBMXL1cDNA –rv (GCCAACCCTGTCACAACTTGA), ASXL1cDNA‐fw (TTTATAAACTGCCTGGCCGAAT), ASXL1cDNA‐rv (CCACTGCAGGGCATCCTT) HIST1H2BG‐fw (TGTGACCAAGGCGCAGAAGA), HIST1H2BG‐rv (GAGCGCTTGTTGTAGTGGGC), WDR90‐fw (GTGCCAGGCTGTATTGCTT), WDR90‐rv (GGGAAATGCAGACGTGTCAT), SNRPNcDNA‐fw (TTGATCCTCTGTGATTGTGATGAGT), and SNRPNcDNA‐rv (TTCTTCACGCTCTGGTTGCTT), and the results were normalized versus the results in the housekeeping gene HPRT1 with oligos HPRT1‐fw (GGACTAATTATGGACAGGACTG) and HPRT1‐rv (TCCAGCAGGTCAGCAAAGAA).
DRIPc‐seq
For genome‐wide detection of DNA‐RNA hybrids, DRIPc‐seq was performed essentially as described (Sanz & Chédin, 2019; Pérez‐Calero et al, 2020). Briefly, after DRIP, the eluted DNA from five immunoprecipitations of each sample was treated with 6 U of DNase I (New England BioLabs) for 45 min at 37°C to degrade all DNA. The resulting RNA was subjected to library construction using the TruSeq Stranded Total RNA protocol (Illumina) from the fragmentation step. The quality of the libraries was checked on a 2100 Agilent Bioanalyzer prior to sequencing on an Illumina NextSeq 500 platform.
DRIPc‐seq read mapping, peak calling, and annotation
Sequenced paired‐end reads were subjected to quality control pipeline using the FASTQ Toolkit v.1.0.0 software (Illumina) and aligned to the human reference genome hg38 canonical with Bowtie2 (Langmead & Salzberg, 2012). Reads were then sorted, and the potential PCR duplicates were removed using SAMTools (Li et al, 2009). Genome signal tracks were obtained using bamCoverage command from deepTools2 (Ramírez et al, 2016) with RPKM normalization and bin size of 10.
For DRIPc‐seq peaks calculation, reads were separated into Watson and Crick strand using SAMTools (Li et al, 2009). DRIPc‐seq peaks were called using MACS2 (Zhang et al, 2008) setting default parameters and FRD < 0.01 allowing broad region detection with a 0.1 cutoff. Next, regions covered by peaks in both replicates in both conditions were merged and fused when closer than 5kb distance for comparative analysis using BEDtools (Quinlan & Hall, 2010). The number of counts per peak was calculated using FeatureCounts and RPKM normalized. For further comparative analysis, R‐loop‐enriched peaks were established selecting peaks whose DRIPc signal fold change was higher than 2.5‐fold in siDDX5 with respect to the siC control cells in both replicates and vice versa for R‐loop‐enriched in siC cells. Finally, peaks were annotated to genes using ChIPseeker (Yu et al, 2015) and genes retrieved from Ensembl release 94 2018 (Zerbino et al, 2018) considering promoter as −2 Kb from the Transcription start site (TSS) and downstream as +2 Kb from the Transcription Termination Site (TTS). To determine the coincidence between DRIPc peaks and Alu repeats, DRIPc peaks from both replicates were merged and demanded to overlap Alu sequence. Peaks mapping entirely to Alu sequences were maintained in all analyses, as they did not provide further significant differences between siC and siDDX5 cells.
For gene metaplots and screenshots, bamCoverage was used to obtain Watson and Crick strands. In the case of gene metaplot representation, the mean of the signal of each strand from two biological replicates was calculated with the tool bigwigCompare from deepTools2. Finally, DRIPc signal representation of the corresponding protein‐coding genes from Watson or Crick strand with R‐loop in both conditions (siC and siDDX5) and replicates was made with computeMatrix and plotHeatmap tools from deepTools2. Genomic regions were scaled to 3 kb considering +1 kb from TTS and −1 kb from TTS.
For the γH2AX peak metaplot (Fig 2E), the mean DRIPc‐seq signal (mean coverage) from the two replicates in K562 cells was superimposed on the plot of γH2AX peaks from previously reported γH2AX ChIP‐seq analysis (GSE104800) (Kim et al, 2018) performed in the same cells. A smooth value of 40 was applied to DRIPc genomic signal tracks. For Venn diagrams, γH2AX peaks were annotated to genes as previously detailed. Comparisons between γH2AX positive genes and R‐loop‐enriched genes were established considering all genes.
The correlation plot in Fig EV3C was generated using multiBamSummary tool from deepTools2 package. Briefly, DRIPc‐seq coverage files were computed for equally sized bins, compared, and plotted in xy graph. The DRIPc‐seq datasets generated in this study are available at GEO repository (GSE150163).
Quantification and statistical analysis
The total number of replicates, mean, and error bars in graphs is explained in the figure legends. The statistical significance of differences was calculated with unpaired or paired two‐tailed t‐test, one/two‐way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test or Mann–Whitney two‐tailed test as indicated in the figure legends except for Figs 3B and 4B, and EV4, EV5, where unpaired one‐tailed t‐test was used. All analyses were conducted using GraphPad Prism (version Mac OS X 8.4.2). Only the P‐values with statistically significant differences are shown in the figures.
Author contributions
Conceptualization: GS, BG‐G, SV, AA and AC Methodology: GS, BG‐G, SS, CP‐C, SV, AA and AC; Experimentation: GS, BG‐G, SS, CP‐C, RB, SB, SM, AE, JSM, CM, BL and DL; Visualization and formal analysis: GS, BG‐G, CP‐C, AA and AC. Writing‐Original Draft: GS, BG‐G, AA and AC. Funding Acquisition, SV, AA, AC. Supervision, AA and AC.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Supporting information
Appendix
Expanded View Figures PDF
Table EV1
Review Process File
Source Data for Figure 1
Source Data for Figure 4
Source Data for Figure 6
Source Data for Figure 8
Acknowledgements
We thank Isaac Dumoulin for technical assistance on the MS experiments. We thank Elizabeth Tran (Purdue Univ., US) and Gaelle Legube (Toulouse, FR) for kindly providing the plasmid expressing DDX5 and the U2OS DIvA cell system, respectively; Robert Crouch (NIH, Bethesda) for providing plasmids expressing RNH; Laetitia Besse from the Cell and Tissue Imaging Facility of the Institut Curie (PICT), a member of the France BioImaging National Infrastructure (ANR‐10‐INBS‐04), Patricia Duchambon from the Protein Core Facility of Institut Curie (Orsay, FR) for helping with protein purification; Victor Laigle from the Mass Spectrometry facility of Institut Curie for helping with the graphical representation of the mass spectrometry data; and Eloisa Andújar and Mónica Pérez from the Genomic Unit of CABIMER for DNA sequencing of the DRIPc‐seq samples. Research was funded by grants from the Agence National de Recherche (ANR‐17‐CE12‐0016), Institut National du Cancer (INCa‐DGOS_8706), Ligue contre le Cancer and the "Avenir” Prize from the French Breast Cancer Association: “Ruban Rose” to A.C.; grants from the European Research Council (ERC2014 AdG669898 TARLOOP), the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (BFU2016‐75058‐P), Fundación Vencer el Cáncer and the European Union (FEDER) to A.A; and grants from Institut Curie and CNRS to S.V. A predoctoral Fellowship from Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer (ARC) and from French Ministry of Education supported G.S, B.G‐G. was recipient of a grant from the Asociación Española Contra el Cancer (AECC), S.S. and C.P‐C were the recipients of a Juan de la Cierva‐Incorporation grant and a predoctoral FPI fellowship, respectively, from the Spanish Ministry of Economy, Industry, and Competitiveness, and J.S.M. was supported by a postdoctoral Fellowship from Fondation de France.
The EMBO Journal (2021) 40: e106018.
Correction added on 1 April 2021, after first online publication: The title was changed from ‘BRCA2 promotes R‐loop resolution by DDX5 helicase at DNA breaks to facilitate their repair by homologous recombination’.
Contributor Information
Andrés Aguilera, Email: aguilo@us.es.
Aura Carreira, Email: aura.carreira@curie.fr.
Data availability
Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to A.A. or A.C. The datasets produced in this study are available in the following databases:
Protein interaction AP‐MS data: PRIDE PXD018979 (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD018979).
DRIPc‐seq data: Gene Expression Omnibus GSE150163 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE150163).
References
- Adamson B, Smogorzewska A, Sigoillot FD, King RW, Elledge SJ (2012) A genome‐wide homologous recombination screen identifies the RNA‐binding protein RBMX as a component of the DNA‐damage response. Nat Cell Biol 14: 318–328 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguilera A, Gómez‐González B (2017) DNA‐RNA hybrids: the risks of DNA breakage during transcription. Nat Struct Mol Biol 24: 439–443 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Asbroek ALMA, van Groenigen M, Nooij M, Baas F (2002) The involvement of human ribonucleases H1 and H2 in the variation of response of cells to antisense phosphorothioate oligonucleotides. Eur J Biochem 269: 583–592 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aymard F, Bugler B, Schmidt CK, Guillou E, Caron P, Briois S, Iacovoni JS, Daburon V, Miller KM, Jackson SP et al (2014) Transcriptionally active chromatin recruits homologous recombination at DNA double‐strand breaks. Nat Struct Mol Biol 21: 366–374 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barroso S, Herrera‐Moyano E, Muñoz S, García‐Rubio M, Gómez‐González B, Aguilera A (2019) The DNA damage response acts as a safeguard against harmful DNA–RNA hybrids of different origins. EMBO Rep 20: e47250 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bekker‐Jensen S, Lukas C, Kitagawa R, Melander F, Kastan MB, Bartek J, Lukas J (2006) Spatial organization of the mammalian genome surveillance machinery in response to DNA strand breaks. J Cell Biol 173: 195–206 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia V, Barroso SI, García‐Rubio ML, Tumini E, Herrera‐Moyano E, Aguilera A (2014) BRCA2 prevents R‐loop accumulation and associates with TREX‐2 mRNA export factor PCID2. Nature 511: 362–365 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boguslawski SJ, Smith DE, Michalak MA, Mickelson KE, Yehle CO, Patterson WL, Carrico RJ (1986) Characterization of monoclonal antibody to DNA.RNA and its application to immunodetection of hybrids. J Immunol Methods 89: 123–130 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton S, Dernoncourt E, Delteil C, Froment C, Schiltz O, Salles B, Frit P, Calsou P (2014) DNA damage triggers SAF‐A and RNA biogenesis factors exclusion from chromatin coupled to R‐loops removal. Nucleic Acids Res 42: 9047–9062 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carreira A, Hilario J, Amitani I, Baskin RJ, Shivji MKK, Venkitaraman AR, Kowalczykowski SC (2009) The BRC repeats of BRCA2 modulate the DNA‐binding selectivity of RAD51. Cell 136: 1032–1043 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerritelli SM, Frolova EG, Feng C, Grinberg A, Love PE, Crouch RJ (2003) Failure to produce mitochondrial DNA results in embryonic lethality in Rnaseh1 null mice. Mol Cell 11: 807–815 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty P, Grosse F (2011) Human DHX9 helicase preferentially unwinds RNA‐containing displacement loops (R‐loops) and G‐quadruplexes. DNA Repair 10: 654–665 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H, Lisby M, Symington LS (2013) RPA coordinates DNA end resection and prevents formation of DNA hairpins. Mol Cell 50: 589–600 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou DM, Adamson B, Dephoure NE, Tan X, Nottke AC, Hurov KE, Gygi SP, Colaiácovo MP, Elledge SJ (2010) A chromatin localization screen reveals poly (ADP ribose)‐regulated recruitment of the repressive polycomb and NuRD complexes to sites of DNA damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107: 18475–18480 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S, Puget N, Lin Y‐L, Clouaire T, Aguirrebengoa M, Rocher V, Pasero P, Canitrot Y, Legube G (2018) Senataxin resolves RNA:DNA hybrids forming at DNA double‐strand breaks to prevent translocations. Nat Commun 9: 533 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D’Alessandro G, Whelan DR, Howard SM, Vitelli V, Renaudin X, Adamowicz M, Iannelli F, Jones‐Weinert CW, Lee M, Matti V et al (2018) BRCA2 controls DNA:RNA hybrid level at DSBs by mediating RNase H2 recruitment. Nat Commun 9: 5376 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels MJ, Wang Y, Lee M, Venkitaraman AR (2004) Abnormal cytokinesis in cells deficient in the breast cancer susceptibility protein BRCA2. Science 306: 876–879 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlén Å, Martin C, Miron S, Julien M, Theillet F‐X, Ropars V, Sessa G, Beaurepere R, Boucherit V, Duchambon P et al (2020) Proper chromosome alignment depends on BRCA2 phosphorylation by PLK1. Nat Commun 11: 1819 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francia S, Michelini F, Saxena A, Tang D, de Hoon M, Anelli V, Mione M, Carninci P, d’Adda di Fagagna F (2012) Site‐specific DICER and DROSHA RNA products control the DNA‐damage response. Nature 488: 231–235 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García‐Muse T, Aguilera A (2019) R Loops: from physiological to pathological roles. Cell 179: 604–618 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García‐Rubio ML, Pérez‐Calero C, Barroso SI, Tumini E, Herrera‐Moyano E, Rosado IV, Aguilera A (2015) The Fanconi Anemia pathway protects genome integrity from R‐loops. PLoS Genet 11: e1005674 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez‐González B, Aguilera A (2019) Transcription‐mediated replication hindrance: a major driver of genome instability. Genes Dev 33: 1008–1026 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidugli L, Pankratz VS, Singh N, Thompson J, Erding CA, Engel C, Schmutzler R, Domchek S, Nathanson K, Radice P et al (2013) A classification model for BRCA2 DNA binding domain missense variants based on homology‐directed repair activity. Cancer Res 73: 265–275 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatchi E, Skourti‐Stathaki K, Ventz S, Pinello L, Yen A, Kamieniarz‐Gdula K, Dimitrov S, Pathania S, McKinney KM, Eaton ML et al (2015) BRCA1 recruitment to transcriptional pause sites is required for R‐Loop‐Driven DNA damage repair. Mol Cell 57: 636–647 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera‐Moyano E, Mergui X, García‐Rubio ML, Barroso S, Aguilera A (2014) The yeast and human FACT chromatin‐reorganizing complexes solve R‐loop‐mediated transcription‐replication conflicts. Genes Dev 28: 735–748 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirling H, Scheffner M, Restle T, Stahl H (1989) RNA helicase activity associated with the human p68 protein. Nature 339: 562–564 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodroj D, Recolin B, Serhal K, Martinez S, Tsanov N, Abou Merhi R, Maiorano D (2017) An ATR‐dependent function for the Ddx19 RNA helicase in nuclear R‐loop metabolism. EMBO J 36: 1182–1198 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hucl T, Rago C, Gallmeier E, Brody JR, Gorospe M, Kern SE (2008) A syngeneic variance library for functional annotation of human variation: application to BRCA2. Cancer Res 68: 5023–5030 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iggo RD, Jamieson DJ, MacNeill SA, Southgate J, McPheat J, Lane DP (1991) p68 RNA helicase: identification of a nucleolar form and cloning of related genes containing a conserved intron in yeasts. Mol Cell Biol 11: 1326–1333 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihama Y, Oda Y, Tabata T, Sato T, Nagasu T, Rappsilber J, Mann M (2005) Exponentially Modified Protein Abundance Index (emPAI) for estimation of absolute protein amount in proteomics by the number of sequenced peptides per protein. Mol Cell Proteomics 4: 1265–1272 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen RB, Carreira A, Kowalczykowski SC (2010) Purified human BRCA2 stimulates RAD51‐mediated recombination. Nature 467: 678–683 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julien M, Miron S, Carreira A, Theillet F‐X, Zinn‐Justin S (2020) 1H, 13C and 15N backbone resonance assignment of the human BRCA2 N‐terminal region. Biomol NMR Assign 14: 79–85 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J, Sturgill D, Sebastian R, Khurana S, Tran AD, Edwards GB, Kruswick A, Burkett S, Hosogane EK, Hannon WW et al (2018) Replication stress shapes a protective chromatin environment across fragile genomic regions. Mol Cell 69: 36–47.e7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotsantis P, Silva LM, Irmscher S, Jones RM, Folkes L, Gromak N, Petermann E (2016) Increased global transcription activity as a mechanism of replication stress in cancer. Nat Commun 7: 13087–13113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2012) Fast gapped‐read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Meth 9: 357–359 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L, Monckton EA, Godbout R (2008) A role for DEAD box 1 at DNA double‐strand breaks. Mol Cell Biol 28: 6413–6425 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R, 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup (2009) The sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25: 2078–2079 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L, Germain DR, Poon H‐Y, Hildebrandt MR, Monckton EA, McDonald D, Hendzel MJ, Godbout R (2016) DEAD Box 1 facilitates removal of RNA and homologous recombination at DNA double‐strand breaks. Mol Cell Biol 36: 2794–2810 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu W‐T, Hawley BR, Skalka GL, Baldock RA, Smith EM, Bader AS, Malewicz M, Watts FZ, Wilczynska A, Bushell M (2018) Drosha drives the formation of DNA:RNA hybrids around DNA break sites to facilitate DNA repair. Nat Commun 9: 532–613 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madireddy A, Kosiyatrakul ST, Boisvert RA, Herrera‐Moyano E, García‐Rubio ML, Gerhardt J, Vuono EA, Owen N, Yan Z, Olson S et al (2016) FANCD2 Facilitates replication through common fragile sites. Mol Cell 64: 388–404 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurek A, Luo W, Krasnitz A, Hicks J, Powers RS, Stillman B (2012) DDX5 regulates DNA replication and is required for cell proliferation in a subset of breast cancer cells. Cancer Discov 2: 812–825 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mersaoui SY, Yu Z, Coulombe Y, Karam M, Busatto FF, Masson J‐Y, Richard S (2019) Arginine methylation of the DDX5 helicase RGG/RG motif by PRMT5 regulates resolution of RNA:DNA hybrids. EMBO J 38: e100986 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriel‐Carretero M, Ovejero S, Gérus‐Durand M, Vryzas D, Constantinou A (2017) Fanconi anemia FANCD2 and FANCI proteins regulate the nuclear dynamics of splicing factors. J Cell Biol 216: 4007–4026 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moynahan ME, Pierce AJ, Jasin M (2001) BRCA2 is required for homology‐directed repair of chromosomal breaks. Mol Cell 7: 263–272 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicol SM, Bray SE, Black HD, Lorimore SA, Wright EG, Lane DP, Meek DW, Coates PJ, Fuller‐Pace FV (2013) The RNA helicase p68 (DDX5) is selectively required for the induction of p53‐dependent p21 expression and cell‐cycle arrest after DNA damage. Oncogene 32: 3461–3469 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Nicolai C, Ehlen A, Martin C, Zhang X, Carreira A (2016) A second DNA binding site in human BRCA2 promotes homologous recombination. Nat Commun 7: 12813 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Nicolai C, Ehlen A, Martinez JS, Carreira A (2018) Dissecting the recombination mediator activity of BRCA2 using biochemical methods. Meth Enzymol 600: 479–511 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohle C, Tesorero R, Schermann G, Dobrev N, Sinning I (2016) Transient RNA‐DNA hybrids are required for efficient double‐strand break repair. Cell 167: 1001–1013.e7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez‐Calero C, Bayona‐Feliu A, Xue X, Barroso SI, Muñoz S, González‐Basallote VM, Sung P, Aguilera A (2020) UAP56/DDX39B is a major cotranscriptional RNA‐DNA helicase that unwinds harmful R loops genome‐wide. Genes Dev 34: 898–912 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez‐Riverol Y, Csordas A, Bai J, Bernal‐Llinares M, Hewapathirana S, Kundu DJ, Inuganti A, Griss J, Mayer G, Eisenacher M et al (2019) The PRIDE database and related tools and resources in 2019: improving support for quantification data. Nucleic Acids Res 47: D442–D450 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poullet P, Carpentier S, Barillot E (2007) myProMS, a web server for management and validation of mass spectrometry‐based proteomic data. Proteomics 7: 2553–2556 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan AR, Hall IM (2010) BEDTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 26: 841–842 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez F, Ryan DP, Grüning B, Bhardwaj V, Kilpert F, Richter AS, Heyne S, Dündar F, Manke T (2016) deepTools2: a next generation web server for deep‐sequencing data analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 44: W160–W165 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanz LA, Hartono SR, Lim YW, Steyaert S, Rajpurkar A, Ginno PA, Xu X, Chédin F (2016) Prevalent, dynamic, and conserved R‐loop structures associate with specific epigenomic signatures in mammals. Mol Cell 63: 167–178 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanz LA, Chédin F (2019) High‐resolution, strand‐specific R‐loop mapping via S9.6‐based DNA‐RNA immunoprecipitation and high‐throughput sequencing. Nat Protoc 14: 1734–1755 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlacher K, Christ N, Siaud N, Egashira A, Wu H, Jasin M (2011) Double‐strand break repair‐independent role for BRCA2 in blocking stalled replication fork degradation by MRE11. Cell 145: 529–542 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab RA, Nieminuszczy J, Shah F, Langton J, Lopez Martinez D, Liang C‐C, Cohn MA, Gibbons RJ, Deans AJ, Niedzwiedz W (2015) The Fanconi Anemia pathway maintains genome stability by coordinating replication and transcription. Mol Cell 60: 351–361 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanbhag NM, Rafalska‐Metcalf IU, Balane‐Bolivar C, Janicki SM, Greenberg RA (2010) ATM‐dependent chromatin changes silence transcription in cis to DNA double‐strand breaks. Cell 141: 970–981 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimelis H, Mesman RLS, von Nicolai C, Ehlen A, Guidugli L, Martin C, Calléja FMGR, Meeks H, Hallberg E, Hinton J et al (2017) BRCA2 hypomorphic missense variants confer moderate risks of breast cancer. Cancer Res 77: 2789–2799 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivji MKK, Renaudin X, Williams ÇH, Venkitaraman AR (2018) BRCA2 regulates transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II to prevent R‐Loop accumulation. Cell Rep 22: 1031–1039 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skourti‐Stathaki K, Proudfoot NJ, Gromak N (2011) Human Senataxin resolves RNA/DNA hybrids formed at transcriptional pause sites to promote Xrn2‐dependent termination. Mol Cell 42: 794–805 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollier J, Stork CT, García‐Rubio ML, Paulsen RD, Aguilera A, Cimprich KA (2014) Transcription‐coupled nucleotide excision repair factors promote R‐Loop‐induced genome instability. Mol Cell 56: 777–785 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song C, Hotz‐Wagenblatt A, Voit R, Grummt I (2017) SIRT7 and the DEAD‐box helicase DDX21 cooperate to resolve genomic R loops and safeguard genome stability. Genes Dev 31: 1370–1381 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivak M, Weston J, Bottou L, Käll L, Noble WS (2009) Improvements to the percolator algorithm for Peptide identification from shotgun proteomics data sets. J Proteome Res 8: 3737–3745 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stork CT, Bocek M, Crossley MP, Sollier J, Sanz LA, Chédin F, Swigut T, Cimprich KA (2016) Co‐transcriptional R‐loops are the main cause of estrogen‐induced DNA damage. Elife 5: e17548 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan SLW, Chadha S, Liu Y, Gabasova E, Perera D, Ahmed K, Constantinou S, Renaudin X, Lee M, Aebersold R et al (2017) A Class of environmental and endogenous toxins induces BRCA2 haploinsufficiency and genome instability. Cell 169: 1105–1118.e15 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarreal OD, Mersaoui SY, Yu Z, Masson J‐Y, Richard S (2020) Genome‐wide R‐loop analysis defines unique roles for DDX5, XRN2, and PRMT5 in DNA/RNA hybrid resolution. Life Science Alliance 3: e202000762 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H, Gao X, Huang Y, Yang J, Liu Z‐R (2009) P68 RNA helicase is a nucleocytoplasmic shuttling protein. Cell Res 19: 1388–1400 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xing Z, Wang S, Tran EJ (2017) Characterization of the mammalian DEAD‐box protein DDX5 reveals functional conservation with S. cerevisiae ortholog Dbp2 in transcriptional control and glucose metabolism. RNA 23: 1125–1138 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xing Z, Ma WK, Tran EJ (2019) The DDX5/Dbp2 subfamily of DEAD‐box RNA helicases. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 10: e1519 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuhara T, Kato R, Hagiwara Y, Shiotani B, Yamauchi M, Nakada S, Shibata A, Miyagawa K (2018) Human Rad52 promotes XPG‐mediated R‐loop processing to initiate transcription‐associated homologous recombination repair. Cell 175: 558–570.e11 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu G, Wang L‐G, He Q‐Y (2015) ChIPseeker: an R/Bioconductor package for ChIP peak annotation, comparison and visualization. Bioinformatics 31: 2382–2383 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Z, Mersaoui SY, Guitton‐Sert L, Coulombe Y, Song J, Masson J‐Y, Richard S (2020) DDX5 resolves R‐loops at DNA double‐strand breaks to promote DNA repair and avoid chromosomal deletions. NAR Cancer 2: zcaa028 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan SS, Lee SY, Chen G, Song M, Tomlinson GE, Lee EY (1999) BRCA2 is required for ionizing radiation‐induced assembly of Rad51 complex in vivo . Cancer Res 59: 3547–3551 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerbino DR, Achuthan P, Akanni W, Amode MR, Barrell D, Bhai J, Billis K, Cummins C, Gall A, Girón CG et al (2018) Ensembl 2018. Nucleic Acids Res 46: D754–D761 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y, Liu T, Meyer CA, Eeckhoute J, Johnson DS, Bernstein BE, Nusbaum C, Myers RM, Brown M, Li W et al (2008) Model‐based analysis of ChIP‐Seq (MACS). Genome Biol 9: R137–R139 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang F, Shi J, Bian C, Yu X (2015) Poly(ADP‐Ribose) mediates the BRCA2‐dependent early DNA damage response. Cell Rep 13: 678–689 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Appendix
Expanded View Figures PDF
Table EV1
Review Process File
Source Data for Figure 1
Source Data for Figure 4
Source Data for Figure 6
Source Data for Figure 8
Data Availability Statement
Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to A.A. or A.C. The datasets produced in this study are available in the following databases:
Protein interaction AP‐MS data: PRIDE PXD018979 (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD018979).
DRIPc‐seq data: Gene Expression Omnibus GSE150163 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE150163).


