Antibody tests for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, are widely available. These practice points help clinicians, patients, and public health professionals understand how to use and interpret these results on the basis of the available evidence. The practice points will be updated as more evidence becomes available.
Abstract
Description: The widespread availability of SARS-CoV-2 antibody tests raises important questions for clinicians, patients, and public health professionals related to the appropriate use and interpretation of these tests. The Scientific Medical Policy Committee (SMPC) of the American College of Physicians developed these rapid, living practice points to summarize the current and best available evidence on the antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 infection, antibody durability after initial infection with SARS-CoV-2, and antibody protection against reinfection with SARS-CoV-2.
Methods: The SMPC developed these rapid, living practice points based on a rapid and living systematic evidence review done by the Portland VA Research Foundation and funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Ongoing literature surveillance is planned through December 2021. When new studies are identified and a full update of the evidence review is published, the SMPC will assess the new evidence and any effect on the practice points.
Practice Points: Practice Point 1: Do not use SARS-CoV-2 antibody tests for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Practice Point 2: Antibody tests can be useful for the purpose of estimating community prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Practice Point 3: Current evidence is uncertain to predict presence, level, or durability of natural immunity conferred by SARS-CoV-2 antibodies against reinfection (after SARS-CoV-2 infection).
Key Question 1
What are the prevalence, level, and durability of detectable anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibodies among patients infected with or recovered from reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)–diagnosed SARS-CoV-2 infection?
Key Question 1a
Do the levels and durability of detectable antibodies vary by patient characteristics (for example, age, sex, race/ethnicity, and comorbidities), COVID-19 severity, presence of symptoms, time from symptom onset, or the characteristics of the immunoassay (sensitivity or specificity)?
Key Question 2
Do anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibodies confer natural immunity against reinfection?
Key Question 2a
Does natural immunity vary by such factors as initial antibody levels, patient characteristics, presence of symptoms, or severity of disease?
Key Question 2b
Is there a threshold level of detectable anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibodies necessary to confer natural immunity, and if so, does this threshold vary by patient characteristics (for example, age, sex, race/ethnicity, and comorbidities)?
Key Question 3
If anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibodies confer natural immunity against reinfection, how long does this immunity last?
Key Question 3a
Does the duration of natural immunity vary by such factors as initial antibody levels, patient characteristics, presence of symptoms, or severity of disease?
Key Question 4
What are the unintended consequences of antibody testing after SARS-CoV-2 infection?
Background
The widespread availability of SARS-CoV-2 antibody tests raises important questions for clinicians, patients, and public health professionals related to the appropriate use and interpretation of these tests. However, currently little is known about the relationship between SARS-CoV-2 antibodies and natural immunity. The potential for natural immunity to SARS-CoV-2 infection stems from the activation of B lymphocytes (humoral or antibody-mediated immunity) and T lymphocytes (cellular immunity). However, like with other viruses, the relationship between antibodies and natural immunity may vary on the basis of differences in the level and duration of antibodies produced as well as viral mutations of the infection. When persons are infected with SARS-CoV-2, uncertainty exists about whether the antibodies produced (IgM, IgG, IgA, or neutralizing) are protective against reinfection, and if so, for how long what levels of antibodies are needed for such protection (1). In addition, because antibodies to other coronaviruses have been shown to decline over time, how long such protection against reinfection may last also needs to be determined (2). As a step toward better understanding the immune response to SARS-CoV-2, the Scientific Medical Policy Committee (SMPC) of the American College of Physicians (ACP) developed these practice points on the basis of key questions related to the antibody-mediated natural immunity after SARS-CoV-2 infection. This article does not evaluate cellular immunity or artificial immunity conferred by vaccines, both of which are important areas of research.
The SMPC developed these rapid, living practice points (Table 1) on the basis of a rapid and living systematic evidence review done by the Portland VA Research Foundation and funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (3, 4). The details of our process can be found in the Appendix. This version of the practice points is based on an initial search to 4 August 2020 that was subsequently revised and updated through 15 December 2020. It was approved by ACP's Executive Committee of the Board of Regents on behalf of the Board of Regents on 22 February 2021 and submitted to Annals of Internal Medicine on 22 February 2021. Ongoing literature surveillance is planned through December 2021. The target audience for these practice points includes clinicians, patients, the public, and public health officials. The target patient population includes adults who have been previously infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Table 1. Practice Points.

Table 2 presents clinical considerations, the Figure and Table 3 summarize current evidence, and Table 4 identifies additional evidence gaps. The Appendix Table presents the data estimates supporting the practice points.
Table 2. Clinical Considerations.

Figure. Evidence description.
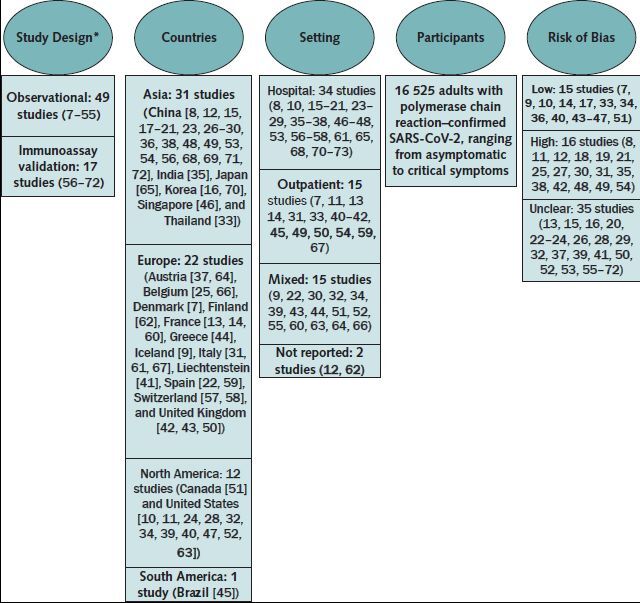
Evidence search and assessment done by the Portland VA Research Foundation (3, 4). Updated search for evidence updated through 15 December 2020.
* Observational studies include studies estimating seroprevalence among a given population that includes a small subpopulation known to have SARS-CoV-2 and cross-sectional or cohort studies characterizing the antibody response among adults with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Immunoassay validation studies include those validating the diagnostic performance of 1 or more immunoassays (3, 4).
Table 3. Evidence Summary for Patients With PCR-Confirmed SARS-CoV-2 Infection.
Table 4. Evidence Gaps.

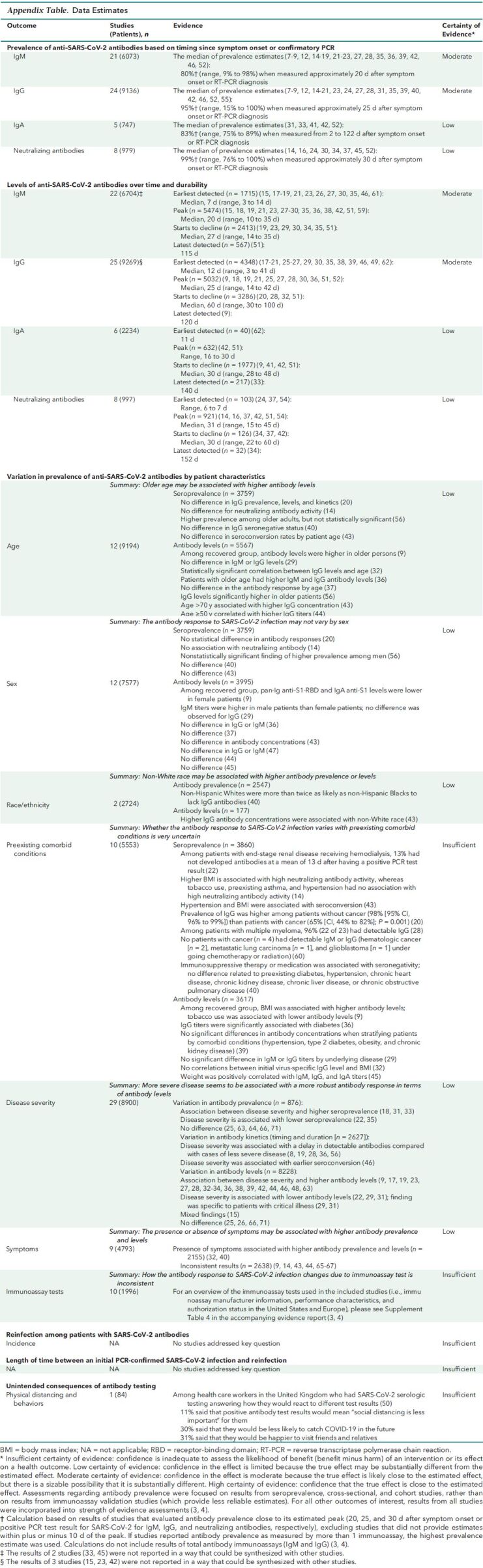
Appendix Table. Data Estimates.
Practice Points and Rationale
Prevalence, Level, and Durability of Antibodies Among Patients Infected With or Recovered From SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Practice Point 1: Do not use SARS-CoV-2 antibody tests for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Practice Point 2: Antibody tests can be useful for the purpose of estimating community prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Studies included in the evidence review focused on evaluating the trends in types of antibodies and their levels after symptom onset or confirmation of SARS-CoV-2 infection with a positive RT-PCR test result. Evidence from studies evaluating community prevalence in antibody response showed that patients develop an immune response after SARS-CoV-2 infection. This is evidenced by detectable IgA antibodies in most patients (low certainty), IgM in most patients (moderate certainty), IgG in nearly all patients (moderate certainty), and neutralizing antibodies in nearly all patients (low certainty). The antibody prevalence and levels may vary over time by certain patient characteristics (for example, age, sex, and race/ethnicity) and disease factors (for example, presence of symptoms and severity) (low certainty). The timing from symptom onset or PCR-confirmed infection of when antibodies first become detectable and the level at which they remain detectable vary depending on the type of antibody. At or around peak level, IgM, IgG, IgA, and neutralizing antibodies are estimated to be detectable in approximately 80%, 95%, 83%, and 99% of patients, respectively, after symptom onset or PCR-confirmed infection. Despite variation, each of these antibody types has its peak level on average between 20 and 31 days after symptom onset or PCR-confirmed infection. Evidence shows that antibodies may persist over time; IgM antibodies were detected up to 115 days (moderate certainty), IgG antibodies were detected up to 120 days (moderate certainty), IgA antibodies were detected up to 140 days (low certainty), and neutralizing antibodies were detected up to 152 days (low certainty).
Given that not all patients develop detectable antibodies early in the course of the infection and that the presence and levels may vary by patient and disease characteristics, antibody tests should not be used for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. It is also important for clinicians and patients to keep in mind that SARS-CoV-2 antibody test results may be falsely positive due to cross-reactivity with antibodies of other coronaviruses (74, 75). Furthermore, although a complete assessment of diagnostic accuracy of various antibody tests was beyond the scope of the evidence review, characteristics (for example, sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy) varied substantially among the antibody tests used in included studies (3, 4). Such variation can contribute to false-negative and false-positive test results and ultimately wrong conclusions (76, 77).
However, for the purposes of estimating community prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection, antibody testing is a feasible option, keeping in mind that antibody levels peak roughly 3 to 5 weeks after symptom onset or PCR diagnosis. Also, the usability and interpretation of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies will need to be evaluated in persons vaccinated against COVID-19, as vaccination will also affect the development of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies.
Reinfection Among Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies and Unintended Consequences of Antibody Testing
Practice Point 3: Current evidence is uncertain to predict presence, level, or durability of natural immunity conferred by SARS-CoV-2 antibodies against reinfection (after SARS-CoV-2 infection).
Current evidence is limited about natural immunity conferred by SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. As discussed earlier, asymptomatic or symptomatic patients may develop an antibody response consistent with natural immunity after having SARS-CoV-2 infection, but key individual-level differences depend on such variables as COVID-19 disease severity, patient factors, types of antibodies and amount developed, and how long the antibodies last. This is an area of rapidly emerging new evidence. No identified evidence directly evaluates the association between antibodies and natural immunity, although 2 studies are in progress (7, 78). In the evidence review, a study (8) of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 (n = 47) reported a potential case of reinfection during the “convalescence stage” of the disease in 1 patient who did not have detectable IgM or IgG antibodies at 4-week follow-up. However, the study was not designed to determine whether antibodies confer immunity. Evidence does show that there are detectable levels of IgA antibodies in most patients (low certainty), IgM in most patients (moderate certainty), IgG in nearly all patients (moderate certainty), and neutralizing antibodies in nearly all patients (low certainty). Evidence also shows that IgG antibodies probably remain detectable for at least 120 days (moderate certainty) and neutralizing antibodies may remain detectable for at least 152 days (low certainty). The antibody prevalence and levels over time may vary by certain patient characteristics (for example, age, sex, and race/ethnicity) and disease factors (for example, presence of symptoms and severity) (low certainty). The evidence review also identified 3 longitudinal studies (indirect evidence) that used serologic rather than RT-PCR testing as the index test and, thus, did not meet the inclusion criteria. These studies suggest that antibody presence may be associated with natural immunity (78–81); however, the evidence review has not critically appraised them. Given that there is no direct evidence to inform the question of reinfection, we will consider modifying future searches to formally incorporate additional sources of indirect evidence, including these studies.
Evidence is uncertain (insufficient) about the unintended consequences of antibody testing.
Given limited knowledge about the association between antibody levels and natural immunity, patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection and those with a history of SARS-CoV-2 infection should follow recommended infection prevention and control procedures to slow and reduce the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 (5, 6).
Appendix: Practice Points Development Process
The SMPC, in collaboration with staff from ACP's Department of Clinical Policy, developed these practice points on the basis of a rapid and living systematic evidence review done by the Portland VA Research Foundation and funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (3, 4). The SMPC comprises 11 internal medicine physicians representing various clinical areas of expertise and 1 public (nonclinician) member and includes members with expertise in epidemiology, evidence synthesis, health policy, and guideline development. In addition to contributing clinical, scientific, and methodological expertise, Clinical Policy staff provided administrative support and liaised among the SMPC, the evidence review funding entity and evidence team, and the journal. Clinical Policy staff and the SMPC reviewed and prioritized potential topic suggestions from ACP members, SMPC members, and ACP governance. A committee subgroup, including the SMPC chair, worked with staff to draft the key questions and led the development of the practice points. Clinical Policy staff worked with the subgroup and an independent evidence review team to refine the key questions and determine appropriate evidence synthesis methods for each key question. Via conference calls and e-mail, Clinical Policy staff worked with the committee subgroup to draft the practice points on the basis of the results of the rapid and living systematic evidence review. The full SMPC reviewed and approved the final practice points. Before journal submission, ACP's Executive Committee of the Board of Regents also reviewed and approved the practice points on behalf of the ACP Board of Regents. The evidence review team is planning ongoing literature surveillance at least through December 2021. When no new studies are identified, the SMPC will publish a comment on the most recent version of the practice points that indicates the date of the last search and that no new studies were identified. When new studies are identified but previous conclusions remain unchanged, the SMPC will publish an update alert letter that briefly summarizes the new evidence and updates the rationale and evidence tables for the practice points. When new studies are identified and a full update of the evidence review is published, the SMPC will assess the new evidence and reaffirm (via update alert letter) or revise and modify (via new version) the practice points. The SMPC will continually evaluate the priority level of each living topic and may decide to retire a topic early from living status if it determines that the topic is no longer considered a priority for decision making, if there is confidence that the conclusions are not likely to change with the emergence of new evidence or affect practice, or when it is unlikely that new evidence will emerge (82).
Footnotes
This article was published at Annals.org on 16 March 2021.
* This paper, written by Amir Qaseem, MD, PhD, MHA; Jennifer Yost, RN, PhD; Itziar Etxeandia-Ikobaltzeta, PharmD, PhD; Mary Ann Forciea, MD; George M. Abraham, MD, MPH; Matthew C. Miller, MD; Adam J. Obley, MD; and Linda L. Humphrey, MD, MPH, was developed for the Scientific Medical Policy Committee of the American College of Physicians. Individuals who served on the Scientific Medical Policy Committee from initiation of the project until its approval were Linda L. Humphrey, MD, MPH (Chair)†; Robert M. Centor, MD (Vice Chair)†; Elie A. Akl, MD, MPH, PhD†; Rebecca Andrews, MS, MD†; Thomas A. Bledsoe, MD†; Mary Ann Forciea, MD†; Ray Haeme†§; Janet A. Jokela, MD, MPH‡; Devan L. Kansagara, MD, MCR†; Maura Marcucci, MD, MSc‡; Matthew C. Miller, MD†; and Adam Jacob Obley, MD†. Approved by the ACP Executive Committee of the Board of Regents on behalf of the Board of Regents on 22 February 2021.
† Author.
‡ Nonauthor contributor.
§ Nonphysician public representative.
Update Alerts: The authors have specified in the Background section and the Appendix the interval and stop date for updates to this Practice Points article. As Annals receives updates, they will appear in the Comments section of the article on Annals.org. Reader inquiries about updates that are not available at approximately the specified intervals should be submitted as comments to the article.
Contributor Information
Collaborators: Linda L. Humphrey, Robert M. Centor, Elie A. Akl, Rebecca Andrews, Thomas A. Bledsoe, Mary Ann Forcia, Ray Haeme, Janet A. Jokela, Devan L. Kansagara, Maura Marcucci, Matthew Miller, and Adam Jacob Obley
References
- 1. World Health Organization. What we know about the COVID-19 immune response: the latest on COVID-19 immunity & the current global situation. Accessed at www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/risk-comms-updates/update-34-immunity-2nd.pdf?sfvrsn=8a488cb6_2 on 11 January 2021.
- 2. Kellam P , Barclay W . The dynamics of humoral immune responses following SARS-CoV-2 infection and the potential for reinfection. J Gen Virol. 2020;101:791-797. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001439 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Arkhipova-Jenkins I, Helfand M, Armstrong C, et al. Antibody response after SARS-CoV-2 infection and implications for immunity: a rapid living review. Ann Intern Med. XX March 2021. [Epub ahead of print]. doi:10.7326/M20-7547 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 4. 4. Mackey K, Arkhipova-Jenkins I, Armstrong C, et al. Antibody response following SARS-CoV-2 infection and implications for immunity: a rapid living review. (Prepared by the Portland VA Research Foundation under Contract No. 290-2017-00003-C). AHRQ Publication No. 21-EHC016. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. March 2021. Posted final reports are located on the Effective Health Care Program search page. doi:10.23970/AHRQEPCCOVIDIMMUNITY.
- 5. World Health Organization. Advice on the use of masks in the context of COVID-19: interim guidance, 5 June 2020. World Health Organization; 2020. Accessed at https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/332293 on 11 January 2021.
- 6. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Guidance for wearing masks. Accessed at www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/cloth-face-cover-guidance.html on 9 December 2020.
- 7. Iversen K , Bundgaard H , Hasselbalch RB , et al. Risk of COVID-19 in health-care workers in Denmark: an observational cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020;20:1401-1408. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30589-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Zhao G , Su Y , Sun X , et al. A comparative study of the laboratory features of COVID-19 and other viral pneumonias in the recovery stage. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020;34:e23483. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1002/jcla.23483 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Gudbjartsson DF , Norddahl GL , Melsted P , et al. Humoral immune response to SARS-CoV-2 in Iceland. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1724-1734. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2026116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Flannery DD , Gouma S , Dhudasia MB , et al. SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence among parturient women in Philadelphia. Sci Immunol. 2020;5. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abd5709 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Payne DC , Smith-Jeffcoat SE , Nowak G , et al; CDC COVID-19 Surge Laboratory Group. SARS-CoV-2 infections and serologic responses from a sample of U.S. Navy service members—USS Theodore Roosevelt, April 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:714-721. [PMID: ] doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6923e4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Xu X , Sun J , Nie S , et al. Seroprevalence of immunoglobulin M and G antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in China. Nat Med. 2020;26:1193-1195. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0949-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Blain H , Rolland Y , Tuaillon E , et al. Efficacy of a test-retest strategy in residents and health care personnel of a nursing home facing a COVID-19 outbreak. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2020;21:933-936. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2020.06.013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Fafi-Kremer S , Bruel T , Madec Y , et al. Serologic responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection among hospital staff with mild disease in eastern France. EBioMedicine. 2020;59:102915. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102915 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Hou H , Wang T , Zhang B , et al. Detection of IgM and IgG antibodies in patients with coronavirus disease 2019. Clin Transl Immunology. 2020;9:e01136. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1002/cti2.1136 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Ko JH , Joo EJ , Park SJ , et al. Neutralizing antibody production in asymptomatic and mild COVID-19 patients, in comparison with pneumonic COVID-19 patients. J Clin Med. 2020;9:2268. [PMID: ] doi: 10.3390/jcm9072268 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Zhao J , Yuan Q , Wang H , et al. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with novel coronavirus disease 2019. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71:2027-2034. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa344 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Liu X , Wang J , Xu X , et al. Patterns of IgG and IgM antibody response in COVID-19 patients [Letter]. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020;9:1269-1274. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1773324 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Qu J , Wu C , Li X , et al. Profile of immunoglobulin G and IgM antibodies against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71:2255-2258. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa489 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Shang Y , Liu T , Li J , et al. Factors affecting antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with severe COVID-19 [Letter]. J Med Virol. 2021;93:612-614. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1002/jmv.26379 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Shu H , Wang S , Ruan S , et al. Dynamic changes of antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19 patients at early stage of outbreak. Virol Sin. 2020;35:744-751. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1007/s12250-020-00268-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Stock da Cunha T, Gomá-Garcés E, Avello A, et al.. The spectrum of clinical and serological features of COVID-19 in urban hemodialysis patients. J Clin Med. 2020;9:2264. [PMID: ] doi: 10.3390/jcm9072264 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Sun B , Feng Y , Mo X , et al. Kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 specific IgM and IgG responses in COVID-19 patients. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020;9:940-948. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1762515 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Suthar MS , Zimmerman MG , Kauffman RC , et al. Rapid generation of neutralizing antibody responses in COVID-19 patients. Cell Rep Med. 2020;1:100040. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100040 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Van Elslande J, Decru B, Jonckheere S, et al.. Antibody response against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and nucleoprotein evaluated by four automated immunoassays and three ELISAs. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020;26:1557.e1-1557.e7. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.07.038 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Xie L , Wu Q , Lin Q , et al. Dysfunction of adaptive immunity is related to severity of COVID-19: a retrospective study. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2020;14:1753466620942129. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1177/1753466620942129 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Zhang B , Zhou X , Zhu C , et al. Immune phenotyping based on the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and IgG level predicts disease severity and outcome for patients with COVID-19. Front Mol Biosci. 2020;7:157. [PMID: ] doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.00157 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Li K , Huang B , Wu M , et al. Dynamic changes in anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies during SARS-CoV-2 infection and recovery from COVID-19. Nat Commun. 2020;11:6044. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19943-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Chen Y , Ke Y , Liu X , et al. Clinical features and antibody response of patients from a COVID-19 treatment hospital in Wuhan, China. J Med Virol. 2020. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1002/jmv.26617 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Bao Y , Ling Y , Chen YY , et al. Dynamic anti-spike protein antibody profiles in COVID-19 patients. Int J Infect Dis. 2021;103:540-548. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.12.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Bruni M , Cecatiello V , Diaz-Basabe A , et al. Persistence of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in non-hospitalized COVID-19 convalescent health care workers. J Clin Med. 2020;9. [PMID: ] doi: 10.3390/jcm9103188 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Chen Y , Zuiani A , Fischinger S , et al. Quick COVID-19 healers sustain anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody production. Cell. 2020;183:1496-1507.e16. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.10.051 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Chirathaworn C , Sripramote M , Chalongviriyalert P , et al. SARS-CoV-2 RNA shedding in recovered COVID-19 cases and the presence of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in recovered COVID-19 cases and close contacts, Thailand, April-June 2020. PLoS One. 2020;15:e0236905. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236905 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Crawford KHD , Dingens AS , Eguia R , et al. Dynamics of neutralizing antibody titers in the months after SARS-CoV-2 infection. J Infect Dis. 2020. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa618 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Dave M, Poswal L, Bedi V, et al. Study of antibody-based rapid card test in COVID-19 patients admitted in a tertiary care COVID hospital in Southern Rajasthan. Journal, Indian Academy of Clinical Medicine. 2020;21:7-11. Accessed at www.jiacm.in/pdf2020/jan_july_20_7_11.pdf on 9 December 2020.
- 36. Huang M , Lu QB , Zhao H , et al. Temporal antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients of coronavirus disease 2019. Cell Discov. 2020;6:64. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1038/s41421-020-00209-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Koblischke M , Traugott MT , Medits I , et al. Dynamics of CD4 T cell and antibody responses in COVID-19 patients with different disease severity. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020;7:592629. [PMID: ] doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.592629 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Kwon JS , Kim JY , Kim MC , et al. Factors of severity in patients with COVID-19: cytokine/chemokine concentrations, viral load, and antibody responses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020;103:2412-2418. [PMID: ] doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.20-1110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Lynch KL , Whitman JD , Lacanienta NP , et al. Magnitude and kinetics of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody responses and their relationship to disease severity. Clin Infect Dis. 2020. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa979 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Petersen LR , Sami S , Vuong N , et al. Lack of antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 in a large cohort of previously infected persons. Clin Infect Dis. 2020. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1685 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Schaffner A , Risch L , Weber M , et al. Sustained SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antibody levels in nonsevere COVID-19: a population-based study [Letter]. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020;59:e49-e51. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1515/cclm-2020-1347 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Seow J , Graham C , Merrick B , et al. Longitudinal observation and decline of neutralizing antibody responses in the three months following SARS-CoV-2 infection in humans. Nat Microbiol. 2020;5:1598-1607. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1038/s41564-020-00813-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Staines HM , Kirwan DE , Clark DJ , et al. IgG seroconversion and pathophysiology in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection. Emerg Infect Dis. 2021;27. [PMID: ] doi: 10.3201/eid2701.203074 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Terpos E , Politou M , Sergentanis TN , et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody responses in convalescent plasma donors are increased in hospitalized patients; subanalyses of a phase 2 clinical study. Microorganisms. 2020;8. [PMID: ] doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8121885 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Wendel S, Kutner JM, Fontao-Wendel R, et al. Screening for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in convalescent plasma (CCP) in Brazil: results from a voluntary convalescent donor program. Transfusion. 2020;60:296A-296A. Accessed at https://search.bvsalud.org/global-literature-on-novel-coronavirus-2019-ncov/resource/en/covidwho-838630 on 11 January 2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 46. Young BE , Ong SWX , Ng LFP , et al; Singapore 2019 Novel Coronavirus Outbreak Research team. Viral dynamics and immune correlates of COVID-19 disease severity. Clin Infect Dis. 2020. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1280 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Takahashi T , Ellingson MK , Wong P , et al; Yale IMPACT Research Team. Sex differences in immune responses that underlie COVID-19 disease outcomes. Nature. 2020;588:315-320. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2700-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Zheng Y , Yan M , Wang L , et al. Analysis of the application value of serum antibody detection for staging of COVID-19 infection. J Med Virol. 2021;93:899-906. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1002/jmv.26330 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Liu J , Guo J , Xu Q , et al. Detection of IgG antibody during the follow-up in patients with COVID-19 infection [Letter]. Crit Care. 2020;24:448. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03138-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Robbins T , Kyrou I , Laird S , et al. Healthcare staff perceptions & misconceptions regarding antibody testing in the United Kingdom: implications for the next steps for antibody screening. J Hosp Infect. 2020. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2020.11.019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Isho B , Abe KT , Zuo M , et al. Persistence of serum and saliva antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 spike antigens in COVID-19 patients. Sci Immunol. 2020;5. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abe5511 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Iyer AS , Jones FK , Nodoushani A , et al. Persistence and decay of human antibody responses to the receptor binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in COVID-19 patients. Sci Immunol. 2020;5. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abe0367 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Liu J , Lian R , Zhang G , et al. Changes in serum virus-specific IgM/IgG antibody in asymptomatic and discharged patients with reoccurring positive COVID-19 nucleic acid test (RPNAT). Ann Med. 2021;53:34-42. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1080/07853890.2020.1811887 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Wang K , Long QX , Deng HJ , et al. Longitudinal dynamics of the neutralizing antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2020. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1143 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Wang B , Van Oekelen O , Mouhieddine TH , et al. A tertiary center experience of multiple myeloma patients with COVID-19: lessons learned and the path forward. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13:94. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00934-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Shen B , Zheng Y , Zhang X , et al. Clinical evaluation of a rapid colloidal gold immunochromatography assay for SARS-Cov-2 IgM/IgG. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12:1348-1354. [PMID: ] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Andrey DO , Cohen P , Meyer B , et al. Head-to-head accuracy comparison of three commercial COVID-19 IgM/IgG serology rapid tests. J Clin Med. 2020;9. [PMID: ] doi: 10.3390/jcm9082369 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Andrey DO , Cohen P , Meyer B , et al; Geneva Centre for Emerging Viral Diseases. Diagnostic accuracy of Augurix COVID-19 IgG serology rapid test. Eur J Clin Invest. 2020;50:e13357. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1111/eci.13357 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. de la Iglesia J, Fernández-Villa T, Fegeneda-Grandes JM, et al.. Concordance between two rapid diagnostic tests for the detection of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. Semergen. 2020;46 Suppl 1:21-25. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1016/j.semerg.2020.06.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Dellière S , Salmona M , Minier M , et al; Saint-Louis CORE (COvid REsearch) group. Evaluation of the COVID-19 IgG/IgM rapid test from Orient Gene Biotech. J Clin Microbiol. 2020;58. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1128/JCM.01233-20 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Infantino M , Grossi V , Lari B , et al. Diagnostic accuracy of an automated chemiluminescent immunoassay for anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM and IgG antibodies: an Italian experience. J Med Virol. 2020;92:1671-1675. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1002/jmv.25932 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Jääskeläinen AJ , Kekäläinen E , Kallio-Kokko H , et al. Evaluation of commercial and automated SARS-CoV-2 IgG and IgA ELISAs using coronavirus disease (COVID-19) patient samples. Euro Surveill. 2020;25. [PMID: ] doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.18.2000603 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Theel ES , Harring J , Hilgart H , et al. Performance characteristics of four high-throughput immunoassays for detection of IgG antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. J Clin Microbiol. 2020;58. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1128/JCM.01243-20 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Traugott M , Aberle SW , Aberle JH , et al. Performance of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 antibody assays in different stages of infection: comparison of commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays and rapid tests. J Infect Dis. 2020;222:362-366. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa305 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Imai K , Tabata S , Ikeda M , et al. Clinical evaluation of an immunochromatographic IgM/IgG antibody assay and chest computed tomography for the diagnosis of COVID-19. J Clin Virol. 2020;128:104393. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104393 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Wolff F , Dahma H , Duterme C , et al. Monitoring antibody response following SARS-CoV-2 infection: diagnostic efficiency of 4 automated immunoassays. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020;98:115140. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2020.115140 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Pancrazzi A , Magliocca P , Lorubbio M , et al. Comparison of serologic and molecular SARS-CoV 2 results in a large cohort in Southern Tuscany demonstrates a role for serologic testing to increase diagnostic sensitivity. Clin Biochem. 2020;84:87-92. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2020.07.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Wang P . Combination of serological total antibody and RT-PCR test for detection of SARS-COV-2 infections. J Virol Methods. 2020;283:113919. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2020.113919 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Xiang F , Wang X , He X , et al. Antibody detection and dynamic characteristics in patients with coronavirus disease 2019. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71:1930-1934. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa461 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Choe JY , Kim JW , Kwon HH , et al. Diagnostic performance of immunochromatography assay for rapid detection of IgM and IgG in coronavirus disease 2019. J Med Virol. 2020;92:2567-2572. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1002/jmv.26060 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Liu R , Liu X , Yuan L , et al. Analysis of adjunctive serological detection to nucleic acid test for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection diagnosis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;86:106746. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106746 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Liu L , Liu W , Zheng Y , et al. A preliminary study on serological assay for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in 238 admitted hospital patients. Microbes Infect. 2020;22:206-211. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2020.05.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Xiang Y, Fan W, Zhou L, et al. PCV21 cost-effectiveness analysis of plus aspirin vs placebo plus aspirin in the treatment of ischemic stroke based on a randomized clinical trial. Value in Health. 2020;23:S93. doi:10.1016/j.jval.2020.04.126
- 74. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim guidelines for COVID-19 antibody testing. Accessed at www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/resources/antibody-tests-guidelines.html on 1 October 2020.
- 75. Infectious Diseases Society of America. IDSA COVID-19 antibody testing primer. Accessed at www.idsociety.org/globalassets/idsa/public-health/covid-19/idsa-covid-19-antibody-testing-primer.pdf on 1 October 2020.
- 76. Watson J , Richter A , Deeks J . Testing for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. BMJ. 2020;370:m3325. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1136/bmj.m3325 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Using antibody tests for COVID-19. Accessed at www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/resources/antibody-tests.html on 14 January 2021.
- 78. Lumley SF , O'Donnell D , Stoesser NE , et al; Oxford University Hospitals Staff Testing Group. Antibody status and incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection in health care workers. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:533-540. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2034545 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Addetia A , Crawford KHD , Dingens A , et al. Neutralizing antibodies correlate with protection from SARS-CoV-2 in humans during a fishery vessel outbreak with a high attack rate. J Clin Microbiol. 2020;58. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1128/JCM.02107-20 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. Lumley SF , Wei J , O'Donnell D , et al; Oxford University Hospitals Staff Testing Group. The duration, dynamics and determinants of SARS-CoV-2 antibody responses in individual healthcare workers. Clin Infect Dis. 2021. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81. Pray IW , Gibbons-Burgener SN , Rosenberg AZ , et al. COVID-19 outbreak at an overnight summer school retreat—Wisconsin, July-August 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:1600-1604. [PMID: ] doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6943a4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82. Akl EA , Meerpohl JJ , Elliott J , et al; Living Systematic Review Network. Living systematic reviews: [WEB_ONLY]4. Living guideline recommendations. J Clin Epidemiol. 2017;91:47-53. [PMID: ] doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.08.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


