Abstract
Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) is a non-receptor kinase belonging to the Tec family of kinases. The role of BTK in B cell receptor signaling is well defined and is known to play a key role in the proliferation and survival of malignant B cells. Moreover, BTK has been found to be expressed in cells of the myeloid lineage. BTK has been shown to contribute to a variety of cellular pathways in myeloid cells including signaling in the NLRP3 inflammasome, receptor activation of nuclear factor-κβ and inflammation, chemokine receptor activation affecting migration, and phagocytosis. Myeloid cells are crucial components of the tumor microenvironment and suppressive myeloid cells contribute to cancer progression, highlighting a potential role for BTK inhibition in the treatment of malignancy. The increased interest in BTK inhibition in cancer has resulted in many preclinical studies that are testing the efficacy of using single-agent BTK inhibitors. Moreover, the ability of tumor cells to develop resistance to single-agent checkpoint inhibitors has resulted in clinical studies utilizing BTK inhibitors in combination with these agents to improve clinical responses. Furthermore, BTK regulates the immune response in microbial and viral infections through B cells and myeloid cells such as monocytes and macrophages. In this review, we describe the role that BTK plays in supporting suppressive myeloid cells, including myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) and tumor-associated macrophages (TAM), while also discussing the anticancer effects of BTK inhibition and briefly describe the role of BTK signaling and BTK inhibition in microbial and viral infections.
Keywords: Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, BTK, Myeloid-derived suppressor cells, Tumor-associated macrophage
Introduction
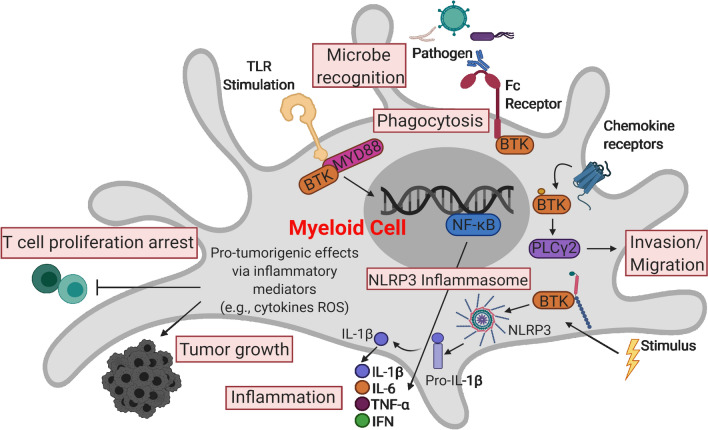
Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) is a non-receptor intracellular kinase that belongs to the Tec (tyrosine kinase expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma) family [1, 2]. Generally, BTK is located in a cytoplasmic position, yet it can be briefly recruited to the cell membrane via interaction with phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3), a phospholipid effector activated by phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K) [3]. BTK is known for its role in B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling, which is critical for normal B cell development and survival as well as its involvement in the signaling of Toll-like receptors (TLRs), chemokine receptors, and growth factor receptors. However, the expression of BTK is not restricted to B cells [2, 4–8]. Many myeloid cell lineages including monocytes, macrophages, thrombocytes, neutrophils, dendritic cells, and other cell types also express BTK, although the role that BTK plays in myeloid cell function is less defined [9, 10]. Recently, our group and others have shown that BTK is involved in the function, maturation, and trafficking of myeloid cells and plays an important role in the regulation of myeloid cell signal transduction [9–13]. BTK has an impact on a variety of myeloid cell pathways, including signaling through the NLRP3 inflammasome in neutrophils and macrophages, receptor activation of nuclear factor-κβ (NF-κB in osteoclasts, and the function and activation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) (Fig. 1) [14–18]. Research has shown that BTK also plays a key role in the oncogenic signaling that is critical for the survival and proliferation of several B cell malignancies [19]. BTK has been identified as a therapeutic target in several hematological malignancies, which has driven the development of small-molecule inhibitors that were efficacious in preclinical studies and have gone on to testing and approval in the clinical setting [20, 21]. Finally, it is important to note that BTK is also expressed by T cells and NK cells and is significant in their activation [22, 23]. However, the focus of this review is on the role of BTK in myeloid cells and the therapeutic implications of targeting BTK in cancer and microbial infections.
Fig. 1.
An overview of the roles of BTK in myeloid cells. The processes highlighted in red boxes indicate roles of BTK signaling in myeloid cells that have been reported in human or mice in the setting of microbial infection and cancer. Details regarding each cellular process are outlined in the text. Abbreviations: BTK, Bruton’s tyrosine kinase; TLR, Toll-like receptors; MYD88, myeloid differentiation primary response 88; PLCγ2, phospholipase C gamma 2; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; NO, nitric oxide; IL-1β, interleukin 1 beta; IL-6, interleukin 6; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IFN, interferon
BTK in BCR signaling and B cell malignancies and disorders
BTK is critical for B cell development and BCR signaling. The BCR signaling pathway is important in regulating the ability of B cells to survive, mature, adhere, and produce antibodies as plasma B cells [19, 24–26]. Upon BCR engagement, a signaling cascade involving Lyn, Syk, and BTK results in the activation of phospholipase Cγ2 (PLCγ2). In turn, the transcription factor NF-κB is activated resulting in the stimulation of survival and proliferative pathways [27–30]. In the absence of BTK, BCR-induced survival and proliferative signals are diminished [27–29].
BTK also contributes to tumor cell proliferation and survival in B cell leukemia and lymphoma [31]. Evidence suggests that overactive signaling supports the development of the tumor microenvironment through aberrant chemokine-controlled integrin-mediated adhesion and migration of malignant cells [26, 32]. Various small molecule inhibitors have been developed to target protein kinases in the BCR signaling cascade, and these have shown promising clinical effectiveness in multiple disease settings [2, 33]. Overall, this emphasizes the potential of targeting molecules associated with the BCR signaling pathway.
Defects in BTK have been implicated in abnormal B cell function. One major consequence of BTK impairment is the developmental delay of pro-B cells to pre-B cells and onto mature B lymphocytes. In 1993, BTK was identified as the gene defective in X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA), an inherited immunodeficiency disease in humans characterized by a drastic deficiency in B lymphocytes, low levels of immunoglobulin (Ig), and recurring infections [34–37]. Mutations in the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain reduce the binding activity of BTK and eliminate downstream signaling, which was identified in the murine version of BTK deficiency known as X-linked immunodeficient (XID). XID presents with a set of physiological manifestations similar to that of XLA in humans, yet is not as severe [34–38]. Both XLA in humans and XID in mice result in the depletion of B cells.
BTK in immune regulation and function
BTK is also expressed by other immune cell populations and has been implicated in the immune regulation and function of myeloid cells. BTK has been shown to play an important role in many TLR signaling pathways. TLRs are both extracellular and intracellular pattern recognition receptors that are expressed in B cells and myeloid cells. They recognize structurally conserved molecules from bacteria and viruses [19]. Upon activation by pathogens, most TLRs recruit the adaptor myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88) which activates interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase1 (IRAK1). This results in the activation, proliferation, antibody secretion, class switch recombination, and pro-inflammatory cytokine production in B cells [19, 39–41]. Studies investigating non-canonical pathways activated downstream of TLRs have shown that BTK can interact with the adapter molecules MyD88 and MAL downstream of TLR4, 6, 8, and 9 ultimately resulting in the production of IL-6 and TNF-α (Fig. 1) [42, 43]. Additionally, BTK is required for TLR-mediated IL-10 production in B cells and the cooperation between BCR and TLR signaling in the enhancement of IL-6 expression [38]. Kawakami et al. reported that BTK is required for IL-10 secretion by DCs and subsequent activation of STAT3 [13]. Notably, in the setting of BTK deficiency, dendritic cell cytokine production is impaired in response to viral single-stranded RNAs that activate TLR-8-mediated TNF-α and IL-6 production (Fig. 1) [6].
Furthermore, BTK is a contributor to chemokine receptor signaling pathways. Integrin α4β (VLA-4)-mediated adhesion of B cells to vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and fibronectin is dependent on BTK, as are B cell responses to various chemokines like stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1) and chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 13 (CXCL-13) [44–46]. Chemokine receptors are G-protein-coupled receptors that are composed of seven transmembrane regions, an extracellular N-terminus contributing to ligand specificity, and intracellular hetero-trimeric G proteins comprised of α, β, and γ subunits (Gα, Gβ, and Gγ [47, 48]. After a chemokine binds to the extracellular domain of the receptor, downstream activation of PI3K leads to the activation of BTK (Fig. 1) [49]. Furthermore, the Gα and Gβγ subunits can both interact with the PH and the Tec homology (TH) domain to directly bind to BTK [50, 51]. However, the Gα subunit has been shown to directly activate BTK alone [52]. B cells express chemokine receptors such as CXCR4 and CXCR5, and BTK is critical in acting downstream to mediate chemokine-controlled migration and maintain cell homeostasis [45].
The Fc receptor is an antibody receptor expressed by a multitude of cells including B cells, macrophages, mast cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and neutrophils. These receptors recognize the constant region of immunoglobulin G, known as the Fc (fragment, crystallizable) region. Among others, the Fc epsilon receptor (FCεRI)-mediated cross-linking in mast cells strongly activates BTK, which plays a role in many Fc receptors [12, 52, 53]. An activating Fc receptor (FcεRI) and immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs) recruit downstream messengers to activate various kinases such as SYK and BTK upon antigen recognition and cross-linking, but if an inhibitory Fc receptor such as FcγRIIB recognizes an antigen, immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs) recruit phosphatases to inhibit the effector function of BTK and eliminate downstream signaling (Fig. 1) [54]. Importantly, Bolland et al. reported that membrane recruitment of SHIP is responsible for the inhibitory signal generated by FcγRIIB to the BCR [55].
There is evidence that BTK can play a role in the cellular process of phagocytosis (Fig. 1). It was reported in a murine macrophage cell line RAW 264.7 that BTK was activated throughout phagocytosis and inhibition of BTK resulted in significantly inhibited FcγR-mediated phagocytosis [56]. BTK also contributes to phagocytosis in rodent microglia and human monocyte-derived macrophages as well as in cells from patients with XLA, a condition caused by a BTK mutation [57, 58]. However, further studies are needed to determine whether these effects are a result of a direct effect of the BTK inhibition.
BTK inhibition
Due to its role in B cell development, the BCR signaling cascade, and other immune-related pathways, BTK serves as a unique therapeutic target for many B cell malignancies and other disease states. Multiple agents have been developed for BTK inhibition, [33, 59] but this review will focus on the BTK inhibitors ibrutinib and acalabrutinib which have been tested extensively in the clinical realm.
Ibrutinib or PCI-32765 (brand name Imbruvica) is an orally available, irreversible inhibitor of BTK that binds to the cysteine at position 481 in the kinase domain where it blocks BTK kinase activity [60, 61]. Ibrutinib has been evaluated in several preclinical studies since its initial discovery in 2007. Ibrutinib inhibits the autophosphorylation of BTK, the phosphorylation of its substrate PLCγ2, and the downstream extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK), leading to reduced activation of NF-κB signal transduction [33, 62]. Furthermore, ibrutinib has a potent (inhibitory concentration 50 (IC50) = 0.5 nM) selectivity for BTK in B cells as opposed to other Tec kinases, making it an attractive therapeutic approach for B cell malignancies [33]. An important in vivo study of ibrutinib by Honiberg et al. reported objective clinical responses in dogs with spontaneous B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma [55]. Furthermore, the report indicated that ibrutinib-targeted BTK yet displayed off-target effects on other kinases with a corresponding cysteine residue in the ATP-binding site including JAK and ITK. These off-target effects of ibrutinib could explain unique toxicities and why ibrutinib has been found useful in other diseases [63–68]. Clinical efficacy was first reported in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) [69]. Ibrutinib received breakthrough designation and was later approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treatment of MCL in 2013 and CLL in 2014 [20, 21].
Acalabrutinib or ACP-196 (brand name Calquence) is an orally available, more selective second-generation irreversible BTK inhibitor that was designed to improve the safety and efficacy of first-generation inhibitors like ibrutinib [70]. Acalabrutinib binds irreversibly to cysteine 481 in the BTK kinase domain and blocks kinase activity, but results in less off-target activity on kinases like EGFR and is predicted to have fewer adverse events (AEs) than ibrutinib, such as antiplatelet activity [70, 71]. Acalabrutinib has shown success in clinical trials, including the first clinical use of the BTK inhibitor for patients with relapsed CLL such as those with chromosome 17p13.1 deletion. In this clinical setting, a 95% overall response rate was reported [72]. Furthermore, a phase II trial in refractory MCL patients reported a complete response in 40% of patients [73]. Acalabrutinib became FDA approved for adult patients with MCL in 2017 and CLL in 2019. An ongoing phase III clinical study investigating the relative effectiveness of acalabrutinib and ibrutinib in previously treated subjects with CLL (NCT02477696) has pending results [74].
The role of BTK in myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC)
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) are a population of heterogeneous myeloid progenitor cells that can inhibit T cell function and have been identified as contributors to the progression of many different types of cancer [75, 76]. MDSC are known to expand and activate as the result of two distinct signals. The first signal functions to expand immature myeloid cell populations, while the second signal is an activation signal, primarily mediated by the transcription factor NF-κB [77]. After activation, MDSC are responsible for producing various anti-inflammatory cytokines, nitric oxide, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and arginase-1, all of which function to suppress immune function [75, 76]. BTK plays an important role in the maturation and function of myeloid cells, and targeting BTK in malignant B cells has been shown to inhibit NF-κB signal transduction [14, 15, 17, 62]. Notably, NF-κB is a demonstrated mediator of MDSC expansion and function [78, 79]. MDSC expansion can cause loss of immune effector cell function and reduce the efficacy of immune-based cancer treatments, highlighting the therapeutic benefit of potentially targeting BTK in the MDSC population [17].
Stiff et al. found that MDSC isolated from Balb/c mice bearing EMT6 and 4T1 mammary carcinoma tumors, human MDSC generated in vitro, and MDSC isolated from metastatic melanoma patients all expressed BTK [17]. Furthermore, treatment of human MDSC and the murine MDSC cell line MSC2 with the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib led to inhibition of BTK phosphorylation in these cells [17]. Notably, ibrutinib also significantly inhibited the in vitro generation of MDSC, impaired MDSC migration, reduced mRNA expression of the immunosuppressive factor indolamine 2,3-dioxygenase, and halted production of the immunosuppressive molecule nitric oxide (NO) [17]. Our group has previously shown that cancer patient MDSC produce NO which significantly inhibits NK cell Fc receptor-mediated functions, and eliminating MDSC in vivo significantly improved monoclonal antibody treatment in an EMT6–HER2 mammary carcinoma model [80]. Ibrutinib treatment in wild-type mice bearing B16F10 melanoma tumors also resulted in a significant reduction of MDSC [17]. In Balb/c mice bearing EMT6 murine mammary carcinoma tumors, treatment with ibrutinib resulted in a significant reduction of MDSC in both the spleen and tumor and was shown to significantly enhance anti-PD-L1 therapy [17]. Taken together, these results demonstrated that targeting BTK with ibrutinib can modulate MDSC function, generation, and migration, revealing a promising strategy for enhancing immune modulation for solid tumor therapies.
The ability of ibrutinib to modulate MDSC has also been demonstrated utilizing an orthotopic mouse breast cancer model [81]. Varikuti et al. reported that ibrutinib treatment inhibited the proliferation of the E0.2 breast cancer cell line in vitro, while additionally demonstrating through a proliferation assay with CFSE-treated cells (carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester) that T cells co-cultured with MDSC from the spleens of ibrutinib-treated mice can proliferate significantly more compared to controls while promoting effector functions leading to the induction of anti-tumor T helper type 1 (Th1) and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) immune responses [17, 81]. Additionally, the spleens and tumors of ibrutinib-treated mice had significantly reduced levels of monocytic MDSC (M-MDSC), but the levels of granulocytic MDSC (PMN-MDSC) exhibited no significant change [81]. High levels of M-MDSC have been correlated with breast cancer metastasis and progression in human breast cancer patients [82]. Thus, it was not surprising for this group to find that ibrutinib-treated mice had a significant reduction in tumor metastasis to the lungs, a lower tumor burden, and reduced breast tumor progression compared to controls [81]. Treatment with ibrutinib also increased the frequency of mature dendritic cells (DCs) in the spleens and tumors of mice by converting MDSC to mature DCs, which are known to play a critical role in anti-tumor immunity [81–83]. These findings were confirmed via an ex vivo treatment of MDSC with ibrutinib which significantly enhanced expression of CD11c and MHCII molecules, indicating a change in phenotype to mature DCs [81]. These findings suggest the BTK pathway negatively regulates the conversion of MDSC into mature DCs [81]. Overall, these results demonstrate that ibrutinib inhibits tumor development and metastasis in an E0.2 breast cancer mouse model by inducing the transformation of mature DCs from MDSC, providing a novel, promising approach for the treatment of human breast cancer [81].
It is hypothesized that MDSC could limit the effectiveness of checkpoint inhibitors and that BTK inhibition could improve the effectiveness of checkpoint inhibitors by eliminating the negative effects of MDSC. As a result, combination clinical studies are being performed with BTK and checkpoint inhibition in patients with solid malignancies (Table 1). Overman et al. recently conducted a phase II, multicenter, open-label, randomized (1:1) clinical trial (NCT02362048) evaluating the BTK inhibitor acalabrutinib alone or in combination with the anti-PD-1 antibody pembrolizumab in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer [84]. Overall, 77 patients (37 monotherapy, 40 combination therapy) with a median age of 64 years received 100 mg of oral acalabrutinib twice daily with (combination therapy) or without (monotherapy) 200 mg of intravenous pembrolizumab on day 1 of each 3-week cycle, as peripheral blood and some tumors were analyzed [84]. The elevation of peripheral MDSC has been correlated with disease progression in patients with solid tumors treated with anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein-4 (anti-CTLA-4), anti-PD-1, or anti-PD-L1 therapies [85, 86]. Flow cytometric analysis of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) demonstrated durable reductions in the levels of PMN-MDSC, with a median reduction of greater than 50% achieved after 2–3 weeks of therapy in both arms of the study, suggesting this effect was likely facilitated by the BTK inhibitor acalabrutinib [84]. Furthermore, two exceptional responders in the study were shown to have low tumor mutational burden and no defects in the homologous DNA repair pathway [84]. Overall, the Overman et al. study showed that combination therapy with ibrutinib and pembrolizumab was well tolerated in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer, but limited clinical benefit was achieved in both arms of the study [84]. However, the study did demonstrate the strong effect on eliminating peripheral PMN-MDSC levels, emphasizing the importance of further studying the role of MDSC in the tumor microenvironment. Furthermore, a phase I clinical trial (NCT03525925), studying the effect of ibrutinib and anti-PD-1 inhibitor nivolumab on the levels of circulating MDSC in patients with metastatic solid tumors, is ongoing at our institution. Early results from this study show an initial increase in circulating MDSC levels with single-agent ibrutinib followed by reductions with the combination regimen. Plasma levels of chemokines (IL-8, CCL2, CCL3, and CCL4) associated with MDSC recruitment and migration significantly decreased following ibrutinib treatment and T cell function significantly improved with the combination therapy. Taken together, these results demonstrate the ability of ibrutinib to modulate MDSC in the setting of cancer and provide biological evidence to support the expansion of strategies to target MDSC in combination with immune checkpoint inhibition [87]. Overall, BTK inhibition has shown a favorable benefit in solid tumors with anti-tumor activity; however, these data are still preliminary, and it is possible that these effects are a result of the off-target effects of BTK inhibitors on other kinases.
Table 1.
An overview of BTK and checkpoint inhibition combination clinical trials in solid malignancies
| Combination | Setting | Phase | NCI identifier | Recruitment status | Effect | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BTK inhibitor | Checkpoint inhibitor | |||||
| Ibrutinib | Pembrolizumab | Advanced refractory colorectal cancers | I/II | NCT03332498 | Active, not recruiting | |
| Ibrutinib | Pembrolizumab | Stage III–IV melanoma that cannot be removed by surgery | II | NCT03021460 | Recruiting | |
| Ibrutinib | Pembrolizumab | Gastrointestinal and genitourinary tumors | I/II | NCT02599324 | Recruiting | |
| Ibrutinib | Nivolumab | Metastatic solid tumors | I | NCT03525925 | Active, not recruiting | |
| Ibrutinib | Nivolumab | Non-small cell lung cancer | II | NCT02950038 | Withdrawn | |
| Ibrutinib | Nivolumab | Previously treated metastatic kidney cancer | I/II | NCT02899078 | Recruiting | |
| Ibrutinib | Nivolumab | Recurrent/metastatic HNSCC | II | NCT03646461 | Recruiting | |
| Ibrutinib | Durvalumab | Relapsed or refractory solid tumors | I/II | NCT02403271 | Completed | 122 patients were enrolled and the combination had an acceptable safety profile. Overall response rates (complete or partial responses) were 2% for pancreatic cancer, 3% for breast cancer, and 0% for NSCLC |
| Acalabrutinib | Pembrolizumab | Advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer | II | NCT02362048 | Completed | 77 patients were enrolled (37 monotherapy; 40 combination therapy) and the combination was well tolerated. The overall response rate was 0% with monotherapy and 7.9% with combination therapy |
| Acalabrutinib | Pembrolizumab | Advanced non-small cell lung cancer | II | NCT02448303 | Completed | 31 patients and 28 patients were enrolled in the monotherapy and combination therapies, respectively, with overall response rates of 12.9% and 14.3% |
| Acalabrutinib | Pembrolizumab | Advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | II | NCT02454179 | Completed | 37 patients and 30 patients were enrolled in the monotherapy and combination therapies, respectively, with overall response rates of 18.9% and 16.7% |
| Acalabrutinib | Pembrolizumab | Ovarian cancer | II | NCT02537444 | Completed | 35 patients and 33 patients were enrolled in the monotherapy and combination therapies, respectively, with overall response rates of 2.9% and 9.1% |
| Acalabrutinib | Pembrolizumab | Metastatic urothelial carcinoma | II | NCT02351739 | Completed | 31 patients and 34 patients were enrolled in the monotherapy and combination therapies, respectively, with overall response rates of 29% and 23.5% |
The role of BTK in tumor-associated macrophages (TAM)
In cancer, macrophages can be recruited to the tumor microenvironment, and their function modified by tumor-derived factors. These tumor-resident macrophages may be roughly characterized as tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) [88]. Importantly, TAM can promote tumor growth and metastasis, enhance cancer cell resistance to chemotherapy, activate immunosuppression pathways, and inactivate T cell effector functions [88, 89]. Sousa et al. demonstrated in a study of human breast cancer that higher levels of TAM were correlated with increased tumor cell proliferation, augmented tumor growth, significant immunosuppression, and a subsequent increase in disease burden [90]. TAM are one of the most abundant tumor-infiltrating immune cells in the tumor microenvironment and play an important role in suppressing the anticancer immune response. Thus, TAM have become an attractive therapeutic target [91].
One mechanism by which TAM protect cancer cells and promote pro-survival signaling is through the secretion of chemokines such as CXCL12 and CXCL13, which bind to the G-protein-coupled receptors CXCR4 and CXCR5, respectively, found on malignant cells [92]. Due to the role that BTK plays in macrophage production of many pro-inflammatory chemokines and cytokines, Ping et al. investigated the immunomodulatory effects of BTK inhibition on macrophages [92]. This group discovered that BTK inhibition with ibrutinib or with PLS-123 (targets BTK catalytic activity and its auto-activation) in LPS-stimulated THP-1 differentiated macrophages efficiently downregulated the secretion of the homeostatic chemokines CXCL12, CXCL13, and CCL19, as well as the angiogenic cytokine VEGF [92]. Inhibition of these factors also occurred at the mRNA level, demonstrating the role of BTK in regulating the transcription of these genes [92]. In addition to targeting BTK pharmacologically, Ping et al. performed siRNA-mediated knockdown of BTK which also significantly impaired the secretion of CXCL12, CXCL13, CCL19, and VEGF [92]. Moreover, macrophages co-cultured with malignant B cell lymphoma cells (Namalwa or OCI-Ly7 cell lines) exhibited diminished adhesion to fibronectin compared to control [92]. A transwell migration assay demonstrated that malignant B cell and T cell lymphoma cells had diminished ability to migrate and invade when cultured with the supernatants of ibrutinib-treated cells [92]. Further experiments in macrophages revealed that BTK inhibitors impede downstream signaling pathways such as PLCγ2 and MAP kinases and the activity of specific transcription factors important for controlling chemokine and cytokine production such as NF-κB, STAT3, and AP-1 [92]. These results suggest that BTK inhibitors can be used to target TAM in the tumor microenvironment and modify the immune landscape via modulation of the chemokine and cytokine milieu.
Others have studied the role of TAM in murine models of cancer, particularly in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC)-bearing mice [93]. One characteristic feature of PDAC is the infiltration of various lymphoid and myeloid cell lineages, like TAM, which exert a strong effect on the tumor microenvironment and often contribute toward the ineffectiveness of various therapies [94]. Gunderson et al. investigated the role of the BTK signaling pathway based on data indicating that B cells and TAM can contribute to PDAC disease progression and tumorigenesis by inhibiting cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses. This group found that PDAC tumor growth requires crosstalk between B cells and TAM, resulting in pro-tumor Th2-type macrophage polarization via activation of the BTK signaling cascade [93]. In fact, one of the main features of an immunosuppressive environment was the lack of functional CTL due to macrophage polarization into a Th2-type phenotype [2]. Treatment of PDAC-bearing mice with ibrutinib reprogrammed macrophages toward a Th1-type macrophage phenotype which led to the enhancement of CD8+ CTL responses, improvement of a chemotherapeutic intervention with gemcitabine, and suppression of PDAC tumor progression. Thus, BTK appears to serve as a key regulator of TAM crosstalk and anti-tumor immune responses [93]. Unfortunately, in some cases in vivo ibrutinib is rapidly cleared, and thus, the low accumulation of ibrutinib results in the tumor, rendering these targeted therapies ineffective [95]. Qiu et al. have designed, synthesized, and investigated a sialic acid–stearic acid (SA) conjugate that encapsulates the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib within amphiphilic egg phosphatidylglycerol (EPG) as a novel immunotherapeutic approach to allow for prolonged exposure of TAM to ibrutinib [95]. Immunofluorescence staining demonstrated that the SA/IBR/EPG nanocomplex accumulated in TAM both in vitro and in vivo. This agent inhibited angiogenesis, Th2 tumorigenic cytokine secretion, and tumor progression and represents a promising targeted approach for targeting BTK in TAM [95].
Benner et al. have also studied the role that the BTK signaling pathway may have in modulating TAM-produced inflammatory processes [15]. The NLRP3 inflammasome is a multi-protein complex involved in innate immunity. It is composed of NLRP3, the adaptor protein ASC, and caspase-1 and is responsible for the production of the potent inflammatory cytokine IL-1β [96]. Due to the inherent role of BTK in myeloid cell signal transduction, it was hypothesized that in vitro generated TAM would express BTK and that this enzyme would participate in NLRP3 inflammasome activity [15, 97]. Murine and human TAM (both in vitro generated and tumor-derived) were utilized to establish that TAM express both BTK and the NLRP3 inflammasome [15]. Moreover, it was demonstrated that BTK physically associates with the NLRP3 inflammasome and promotes its activation and subsequent ability to mediate the production of IL-1β [15]. IL-1β production could be induced in TAM using LPS and ATP co-stimulation and ibrutinib inhibited the phosphorylation of BTK, prevented the association of BTK with the NLRP3 inflammasome, and reduced inflammasome activation as evidenced by a decrease in IL-1β production [15]. Furthermore, compared to controls, systemic ibrutinib therapy led to reduced expression of IL-1β expression in murine EMT6 and 4T1 tumors. These results suggest that BTK plays an important role in TAM-mediated inflammation within the tumor microenvironment that involves around IL-1β [15].
Other groups have studied the association between BTK and the NLRP3 inflammasome in different disease settings. Liu et al. used proteome-wide phosphoproteomics to identify and study BTK as a novel regulator of the NLRP3 inflammasome [18]. Utilizing bone marrow-derived macrophages from BTK-deficient mice and PBMC from patients with X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA), this group found reduced IL-1β production and impaired inflammasome activation within mutant myeloid cells [18]. Also, BTK inhibition impaired IL-1β processing and release in human primary macrophages from healthy donors, ibrutinib-treated cancer patients, and patients with Muckle–Wells syndrome—an autoinflammatory disease characterized by excessive production of IL-1β [18]. Inflammasome activation has also been implicated in the post-ischemic inflammation that occurs after stroke [98, 99]. Using a murine model of brain ischemia/reperfusion, Ito et al. reported that BTK inhibition by genetic and pharmacologic means impaired inflammasome activation in brain infarct macrophages and exerted a neuroprotective effect [14]. Immunofluorescence staining demonstrated that BTK inhibition suppressed caspase-1 activation in the brain infarct and correlated with the reduced maturation of IL-1β [14]. These studies offer further evidence for BTK as a crucial mediator of myeloid cell function and NLRP3 inflammasome activation and point toward the potential for BTK inhibition as a means of improving clinical outcomes in cancer and other diseases.
Targeting BTK beyond the tumor microenvironment
Myeloid cell lineages contribute to inflammation and infection, making BTK an interesting candidate for therapeutic intervention in a variety of disease settings [100]. TLR signaling plays an important role in innate immunity and TLRs are expressed in many myeloid cell populations including dendritic cells, mast cells, and macrophages, which are all essential for the recognition and elimination of microbial pathogens [101]. BTK promotes TLR signaling, leading to the activation of pro-inflammatory cytokines resulting in robust immune responses in many bacterial infections like pneumococcal pneumonia [102]. Murine models have demonstrated the protection BTK confers from endotoxin shock caused by the Gram-negative bacteria Escherichia coli [40]. Furthermore, BTK regulates macrophage responses to the Gram-positive bacteria Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus infections [103, 104]. In filarial infections, Mukhopadhyay et al. revealed that BTK-mutant CBA/N mice showed delayed clearance of microfilaria compared to wild-type CBA/N mice and that BTK regulates macrophage effector functions such as bactericidal activity and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines [10, 105]. However, the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib has been shown to impair immune mechanisms dedicated to controlling the Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection [106].
BTK is also involved in the clearance of fungal infections. Specifically, BTK contributes to the dectin-1-dependent phagocytosis of Candida albicans by macrophages [107]. Furthermore, Shahan et al. demonstrated that BTK is activated in the presence of spores from the fungal species Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus candidus, and Eurotium amstelodami [108]. BTK-deficient XID mice had enhanced susceptibility to Cryptococcus neoformans infection, a fungal pathogen that can affect immunocompromised patients [109]. In other studies, inhibition of the BTK signaling pathway with ibrutinib led to reduced NF-κB signaling and resulted in an increased risk of developing Aspergillus fumigatus, an invasive fungus largely found in organ transplant recipients [110, 111]. Recently, others have also demonstrated that second-generation BTK inhibitors impair the antifungal response of macrophages [112].
Various inflammatory diseases are implicated with the BTK signaling pathway. BTK regulates osteoclast differentiation by linking receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB (RANK) and immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) signals, and inhibiting BTK protects against osteoclast-mediated bone loss disorders [16, 113]. Other groups have shown that BTK is needed to drive macrophage activation and could be a potential target for patients with rheumatoid arthritis and sepsis [114, 115]. BTK inhibition ameliorates autoimmune arthritis and treatsTLR7/IFN-driven murine lupus, while BTK-deficient XID mice show reduced severity in many inflammatory disease models such as autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), colitis, and acute edema [97, 116, 117]. Finally, Mao et al. demonstrated that BTK regulates NLRP3 inflammasome activity in the setting of Crohn’s disease [118].
In addition to inflammatory diseases, bacterial and fungal infections, BTK plays a critical role in initiating antiviral responses [119]. In some pulmonary viral infections, the macrophage response driven by BTK can lead to tissue damage and unfavorable outcomes. For example, in murine models of influenza viral infection BTK inhibition with ibrutinib decreased lung injury and led to reduced alveolar macrophage activation [120]. Recently, Chong et al. and others discussed the potential that BTK inhibition may have in treating the novel virus SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) [121–123]. Pulmonary failure is the main cause of mortality related to COVID-19 infection, and BTK inhibition may mitigate the hyper-inflammatory pulmonary response through attenuation of M1-macrophage polarization [121, 124, 125]. Our group presented that the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib could inhibit inflammasome activation in TAMs and reduce the release of IL-1β (see below) [15]. These findings suggest a potential mechanism by which ibrutinib can inhibit macrophage activation, lower the production of IL-1β, and alter the pulmonary inflammatory landscape in patients infected with COVID-19. Furthermore, one clinical study utilized the BTK inhibitor acalabrutinib in COVID-19 patients. Administration of acalabrutinib led to improved oxygenation in a majority of patients over the 10–14-day treatment course and was well tolerated. Measures of inflammation such as C-reactive protein and IL-6 rapidly returned to normal in most patients, as did lymphopenia [122]. These findings support the hypothesis that the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines by pulmonary macrophages in COVID-19 is a major contributor to pulmonary failure and that BTK inhibition could provide some degree of protection against lung injury in this setting. BTK plays a large role in macrophage polarization, and through a variety of transcription factors, it may effectively regulate the hyperinflammatory state associated with many microbial infections and inflammatory disease settings.
Conclusion
Much progress has been made in understanding the mechanism by which BTK regulates innate immunity. Targeting BTK in CLL could have significant clinical efficacy via inhibition of the BCR signaling pathway in addition to the significant effects of BTK inhibition on B cell adhesion and chemotaxis. Moreover, targeting BTK in myeloid cells has shown recent progress and holds therapeutic promise for modulating the tumor microenvironment. However, more work is needed to determine the clinical efficacy of BTK inhibition in various disease states. One avenue of particular interest is utilizing BTK inhibition in combination with other immune-modulating agents to combat resistance to single-agent therapies. A greater understanding of the differences in safety profiles and clinical benefit of available BTK inhibitors in different disease states is needed in order to design effective treatment strategies.
Acknowledgments
BioRender was utilized for figure development.
Authors' contributions
LG, BB, and WEC conceptualized and designed the manuscript. LG and BB wrote the first draft and WEC provided an editorial review.
Funding
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grants P01CA95426, K24 CA93670 (W.E. Carson), and T32CA90338-27 (W.E. Carson).
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Logan Good and Brooke Benner contributed equally to this manuscript.
References
- 1.Hussain A, Yu L, Faryal R, et al. TEC family kinases in health and disease—loss-of-function of BTK and ITK and the gain-of-function fusions ITK–SYK and BTK–SYK. FEBS J. 2011;278:2001–2010. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Molina-Cerrillo J, Alonso-Gordoa T, Gajate P, Grande E (2017) Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) as a promising target in solid tumors. Cancer Treat Rev [DOI] [PubMed]
- 3.Hendriks RW, Yuvaraj S, Kil LP. Targeting Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in B cell malignancies. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014;14:219–232. doi: 10.1038/nrc3702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Genevier HC, Hinshelwood S, Gaspar HB, et al. Expression of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase protein within the B cell lineage. Eur J Immunol. 1994;24:3100–3105. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830241228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Marron TU. The role of BTK in TLR signaling. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;123:S92–S92. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2008.12.329. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Levy O. Bruton tyrosine kinase (Btk): key for signaling via Toll-like receptor 8. Blood. 2007;109:2273–2274. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-12-064642. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Seda V, Mraz M. B-cell receptor signalling and its crosstalk with other pathways in normal and malignant cells. Eur J Haematol. 2015;94:193–205. doi: 10.1111/ejh.12427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Smith CI, Baskin B, Humire-Greiff P, et al. Expression of Bruton’s agammaglobulinemia tyrosine kinase gene, BTK, is selectively down-regulated in T lymphocytes and plasma cells. J Immunol. 1994;152:557–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Horwood NJ, Mahon T, McDaid JP, et al. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase is required for lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor α production. J Exp Med. 2003;197:1603–1611. doi: 10.1084/jem.20021845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mukhopadhyay S, Mohanty M, Mangla A, et al. Macrophage effector functions controlled by Bruton’s Tyrosine kinase are more crucial than the cytokine balance of T cell responses for microfilarial clearance. J Immunol. 2002;168:2914–2921. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.6.2914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sochorová K, Horváth R, Rožková D, et al. Impaired Toll-like receptor 8-mediated IL-6 and TNF-α production in antigen-presenting cells from patients with X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Blood. 2007;109:2553–2556. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-07-037960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kawakami Y, Yao L, Miura T, et al. Tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of Bruton tyrosine kinase upon Fc epsilon RI cross-linking. Mol Cell Biol. 1994;14:5108–5113. doi: 10.1128/MCB.14.8.5108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kawakami Y, Inagaki N, Salek-Ardakani S, et al. Regulation of dendritic cell maturation and function by Bruton’s tyrosine kinase via IL-10 and Stat3. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2006;103:153–158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0509784103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ito M, Shichita T, Okada M, et al. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase is essential for NLRP3 inflammasome activation and contributes to ischaemic brain injury. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7360. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Benner B, Scarberry L, Stiff A et al (2019) Evidence for interaction of the NLRP3 inflammasome and Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in tumor-associated macrophages: implications for myeloid cell production of interleukin-1beta. Oncoimmunology 1659704. 10.1080/2162402X.2019.1659704 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 16.Shinohara M, Koga T, Okamoto K, et al. Tyrosine kinases Btk and Tec regulate osteoclast differentiation by linking RANK and ITAM signals. Cell. 2008;132:794–806. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.12.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Stiff A, Trikha P, Wesolowski R, et al. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells express Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase and can be depleted in tumor-bearing hosts by Ibrutinib treatment. Cancer Res. 2016;76:2125–2136. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-1490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Liu X, Pichulik T, Wolz O-O, et al. Human NACHT, LRR, and PYD domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activity is regulated by and potentially targetable through Bruton tyrosine kinase. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;140:1054–1067.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.01.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pal Singh S, Dammeijer F, Hendriks RW. Role of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in B cells and malignancies. Mol Cancer. 2018;17:57. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0779-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Byrd JC, Brown JR, O’Brien S, et al. Ibrutinib versus Ofatumumab in previously treated chronic lymphoid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:213–223. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1400376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wang Y, Eldridge N, Metersky ML, et al. National trends in patient safety for four common conditions, 2005–2011. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:341–351. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa1300991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Xia S, Liu X, Cao X, Xu S. T-cell expression of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase promotes autoreactive T-cell activation and exacerbates aplastic anemia. Cell Mol Immunol. 2020;17:1042–1052. doi: 10.1038/s41423-019-0270-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bao Y, Zheng J, Han C, et al. Tyrosine kinase Btk is required for NK cell activation. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:23769–23778. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.372425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wiestner A. Emerging role of kinase-targeted strategies in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2012;120:4684–4691. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-05-423194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Reth M, Nielsen P. Signaling circuits in early B-cell development. Adv Immunol. 2014;122:129–175. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800267-4.00004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dal Porto JM, Gauld SB, Merrell KT, et al. B cell antigen receptor signaling 101. Mol Immunol. 2004;41:599–613. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2004.04.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Takata M, Sabe H, Hata A, et al. Tyrosine kinases Lyn and Syk regulate B cell receptor-coupled Ca2+ mobilization through distinct pathways. EMBO J. 1994;13:1341–1349. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Petro JB, Rahman SMJ, Ballard DW, Khan WN. Bruton’s Tyrosine kinase is required for activation of Iκb Kinase and nuclear factor κb in response to B cell receptor engagement. J Exp Med. 2000;191:1745–1754. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.10.1745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bajpai UD, Zhang K, Teutsch M, et al. Bruton’s Tyrosine kinase links the B Cell receptor to nuclear factor κb activation. J Exp Med. 2000;191:1735–1744. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.10.1735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Petro JB, Khan WN. Phospholipase C-γ2 couples Bruton’s tyrosine kinase to the NF-κB signaling pathway in B lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:1715–1719. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M009137200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Dühren-von Minden M, Übelhart R, Schneider D, et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia is driven by antigen-independent cell-autonomous signalling. Nature. 2012;489:309–312. doi: 10.1038/nature11309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.de Rooij MFM, Kuil A, Geest CR, et al. The clinically active BTK inhibitor PCI-32765 targets B-cell receptor- and chemokine-controlled adhesion and migration in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2012;119:2590–2594. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-11-390989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Aalipour A, Advani RH. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors and their clinical potential in the treatment of B-cell malignancies: focus on ibrutinib. Ther Adv Hematol. 2014;5:121–133. doi: 10.1177/2040620714539906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rawlings D, Saffran D, Tsukada S et al (1993) Mutation of unique region of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in immunodeficient XID mice. Science261 (80):358–361. 10.1126/science.8332901 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 35.Thomas J, Sideras P, Smith C, et al (1993) Colocalization of X-linked agammaglobulinemia and X-linked immunodeficiency genes. Science 261(80):355–358. 10.1126/science.8332900 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 36.Tsukada S, Saffran DC, Rawlings DJ, et al. Deficient expression of a B cell cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase in human X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Cell. 1993;72:279–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90667-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Vetrie D, Vořechovský I, Sideras P, et al. The gene involved in X-linked agammaglobulinaemia is a member of the src family of protein-tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1993;361:226–233. doi: 10.1038/361226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Satterthwaite AB. Bruton’s Tyrosine kinase, a component of B cell signaling pathways, has multiple roles in the pathogenesis of Lupus. Front Immunol. 2018;8:1986. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gray P, Dunne A, Brikos C, et al. MyD88 adapter-like (Mal) is phosphorylated by Bruton’s tyrosine kinase during TLR2 and TLR4 signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:10489–10495. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M508892200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Liu X, Zhan Z, Li D, et al. Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining activation of the kinase Btk. Nat Immunol. 2011;12:416–424. doi: 10.1038/ni.2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Jefferies CA, Doyle S, Brunner C, et al. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase is a Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain-binding protein that participates in nuclear factor kappaB activation by Toll-like receptor 4. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:26258–26264. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M301484200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Doyle SL, Jefferies CA, Feighery C, O’Neill LAJ. Signaling by Toll-like receptors 8 and 9 requires Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:36953–36960. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M707682200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Horwood NJ, Page TH, McDaid JP, et al. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase is required for TLR2 and TLR4-induced TNF, but Not IL-6, production. J Immunol. 2006;176:3635–3641. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.6.3635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Spaargaren M, Beuling EA, Rurup ML, et al. The B cell antigen receptor controls integrin activity through Btk and PLCgamma2. J Exp Med. 2003;198:1539–1550. doi: 10.1084/jem.20011866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.de Gorter DJJ, Beuling EA, Kersseboom R, et al. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase and phospholipase Cgamma2 mediate chemokine-controlled B cell migration and homing. Immunity. 2007;26:93–104. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2006.11.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Halcomb KE, Contreras CM, Hinman RM, et al. Btk and phospholipase C gamma 2 can function independently during B cell development. Eur J Immunol. 2007;37:1033–1042. doi: 10.1002/eji.200636451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ritter SL, Hall RA. Fine-tuning of GPCR activity by receptor-interacting proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10:819–830. doi: 10.1038/nrm2803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Park SH, Das BB, Casagrande F, et al. Structure of the chemokine receptor CXCR1 in phospholipid bilayers. Nature. 2012;491:779–783. doi: 10.1038/nature11580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lowry WE, Huang X-Y. G Protein beta gamma subunits act on the catalytic domain to stimulate Bruton’s agammaglobulinemia tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:1488–1492. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110390200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Langhans-Rajasekaran SA, Wan Y, Huang XY. Activation of Tsk and Btk tyrosine kinases by G protein beta gamma subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1995;92:8601–8605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.19.8601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Tsukada S, Simon MI, Witte ON, Katz A. Binding of beta gamma subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins to the PH domain of Bruton tyrosine kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1994;91:11256–11260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.11256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Bence K, Ma W, Kozasa T, Huang XY. Direct stimulation of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase by G(q)-protein alpha-subunit. Nature. 1997;389:296–299. doi: 10.1038/38520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Bournazos S, Wang TT, Ravetch JV (2016) The role and function of Fcγ receptors on myeloid cells. Microbiol Spectr 4. 10.1128/microbiolspec.MCHD-0045-2016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 54.Nimmerjahn F, Ravetch JV. Fcgamma receptors as regulators of immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:34–47. doi: 10.1038/nri2206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bolland S, Pearse RN, Kurosaki T, Ravetch JV. SHIP modulates immune receptor responses by regulating membrane association of Btk. Immunity. 1998;8:509–516. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80555-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Jongstra-Bilen J, Puig Cano A, Hasija M, et al. Dual functions of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase and Tec Kinase during Fcγ receptor-induced signaling and phagocytosis. J Immunol. 2008;181:288–298. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.1.288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Marron TU, Rohr K, Martinez-Gallo M, et al. TLR signaling and effector functions are intact in XLA neutrophils. Clin Immunol. 2010;137:74–80. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2010.06.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Keaney J, Gasser J, Gillet G, et al. Inhibition of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase modulates microglial phagocytosis: therapeutic implications for Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019;14:448–461. doi: 10.1007/s11481-019-09839-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Burger JA. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) inhibitors in clinical trials. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2014;9:44–49. doi: 10.1007/s11899-013-0188-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Tai Y-T, Chang BY, Kong S-Y, et al. Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibition is a novel therapeutic strategy targeting tumor in the bone marrow microenvironment in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2012;120:1877–1887. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-12-396853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Akinleye A, Chen Y, Mukhi N, et al. Ibrutinib and novel BTK inhibitors in clinical development. J Hematol Oncol. 2013;6:59. doi: 10.1186/1756-8722-6-59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Herman SEM, Mustafa RZ, Gyamfi JA, et al. Ibrutinib inhibits BCR and NF-κB signaling and reduces tumor proliferation in tissue-resident cells of patients with CLL. Blood. 2014;123:3286–3295. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-02-548610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Zwolanek F, Riedelberger M, Stolz V, et al. The non-receptor Tyrosine Kinase Tec controls assembly and activity of the noncanonical Caspase-8 inflammasome. PLoS Pathog. 2014;10:e1004525. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Massó-Vallés D, Jauset T, Serrano E, et al. Ibrutinib exerts potent antifibrotic and antitumor activities in mouse models of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2015;75:1675–1681. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-2852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Gao W, Wang M, Wang L et al (2014) Selective antitumor activity of Ibrutinib in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer cells. JNCI J Natl Cancer Inst 106. 10.1093/jnci/dju204 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 66.Soucek L, Buggy JJ, Kortlever R et al (2011) Modeling pharmacological inhibition of mast cell degranulation as a therapy for Insulinoma. Neoplasia 13:1093-IN43. 10.1593/neo.11980 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 67.Grabinski N, Ewald F. Ibrutinib (ImbruvicaTM) potently inhibits ErbB receptor phosphorylation and cell viability of ErbB2-positive breast cancer cells. Invest New Drugs. 2014;32:1096–1104. doi: 10.1007/s10637-014-0141-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Honigberg LA, Smith AM, Sirisawad M, et al. The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor PCI-32765 blocks B-cell activation and is efficacious in models of autoimmune disease and B-cell malignancy. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2010;107:13075–13080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1004594107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Advani RH, Buggy JJ, Sharman JP, et al. Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib (PCI-32765) has significant activity in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell malignancies. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2013;31:88–94. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.42.7906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Owen C, Berinstein NL, Christofides A, Sehn LH. Review of Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma. Curr Oncol. 2019;26:e233–e240. doi: 10.3747/co.26.4345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Bye AP, Unsworth AJ, Desborough MJ, et al. Severe platelet dysfunction in NHL patients receiving ibrutinib is absent in patients receiving acalabrutinib. Blood Adv. 2017;1:2610–2623. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2017011999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Byrd JC, Harrington B, O’Brien S, et al. Acalabrutinib (ACP-196) in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:323–332. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1509981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Wang M, Rule S, Zinzani PL, et al. Acalabrutinib in relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (ACE-LY-004): a single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet (London, England) 2018;391:659–667. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33108-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.ClinicalTrials.gov Study of Acalabrutinib (ACP-196) Versus Ibrutinib in previously treated subjects with high risk CLL
- 75.Melani C, Chiodoni C, Forni G, Colombo MP. Myeloid cell expansion elicited by the progression of spontaneous mammary carcinomas in c-erbB-2 transgenic BALB/c mice suppresses immune reactivity. Blood. 2003;102:2138–2145. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-01-0190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Lechner MG, Liebertz DJ, Epstein AL. Characterization of cytokine-induced myeloid-derived suppressor cells from normal human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 2010;185:2273–2284. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Gabrilovich DI, Nagaraj S. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9:162–174. doi: 10.1038/nri2506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Yu J, Wang Y, Yan F, et al. Noncanonical NF-κB activation mediates STAT3-stimulated IDO upregulation in myeloid-derived suppressor cells in breast cancer. J Immunol. 2014;193:2574–2586. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1400833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Flores RR, Clauson CL, Cho J, et al. Expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells with aging in the bone marrow of mice through a NF-κB-dependent mechanism. Aging Cell. 2017;16:480–487. doi: 10.1111/acel.12571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Stiff A, Trikha P, Mundy-Bosse B, et al. Nitric oxide production by myeloid-derived suppressor cells plays a role in impairing Fc receptor-mediated natural killer cell function. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:1891–1904. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-0691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Varikuti S, Singh B, Volpedo G, et al. Ibrutinib treatment inhibits breast cancer progression and metastasis by inducing conversion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells to dendritic cells. Br J Cancer. 2020;122:1005–1013. doi: 10.1038/s41416-020-0743-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Bergenfelz C, Larsson A-M, von Stedingk K, et al. Systemic monocytic-MDSCs are generated from monocytes and correlate with disease progression in breast cancer patients. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0127028. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Fuertes MB, Kacha AK, Kline J, et al. Host type I IFN signals are required for antitumor CD8+ T cell responses through CD8{alpha}+ dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 2011;208:2005–2016. doi: 10.1084/jem.20101159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Overman M, Javle M, Davis RE et al (2020) Randomized phase II study of the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor acalabrutinib, alone or with pembrolizumab in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. J Immunother Cancer 8. 10.1136/jitc-2020-000587 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 85.Weide B, Martens A, Zelba H, et al. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells predict survival of patients with advanced melanoma: comparison with regulatory T cells and NY-ESO-1- or melan-A-specific T cells. Clin cancer Res an Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2014;20:1601–1609. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-2508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Meyer C, Cagnon L, Costa-Nunes C-M et al (2013) Frequencies of circulating MDSC correlate with clinical outcome of melanoma patients treated with ipilimumab. Cancer Immunol Immunother 63. 10.1007/s00262-013-1508-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 87.Benner B, Quiroga DM, Good L, et al. A pilot study of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib alone and in combination with PD-1 inhibitor nivolumab in patients with metastatic solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:3111–3111. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2020.38.15_suppl.3111. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Chen Y, Song Y, Du W, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages: an accomplice in solid tumor progression. J Biomed Sci. 2019;26:78. doi: 10.1186/s12929-019-0568-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Yang L, Zhang Y. Tumor-associated macrophages: from basic research to clinical application. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10:58. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0430-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Sousa S, Brion R, Lintunen M, et al. Human breast cancer cells educate macrophages toward the M2 activation status. Breast Cancer Res. 2015;17:101. doi: 10.1186/s13058-015-0621-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Dehne N, Mora J, Namgaladze D, et al. Cancer cell and macrophage cross-talk in the tumor microenvironment. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2017;35:12–19. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2017.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Ping L, Ding N, Shi Y et al (2017) The Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib exerts immunomodulatory effects through regulation of tumor-infiltrating macrophages. Oncotarget 8:39218–39229. 10.18632/oncotarget.16836 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 93.Gunderson AJ, Kaneda MM, Tsujikawa T, et al. Bruton tyrosine kinase-dependent immune cell cross-talk drives pancreas cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016;6:270–285. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-0827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Shibuya KC, Goel VK, Xiong W, et al. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma contains an effector and regulatory immune cell infiltrate that is altered by multimodal neoadjuvant treatment. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e96565. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Qiu Q, Li C, Song Y, et al. Targeted delivery of ibrutinib to tumor-associated macrophages by sialic acid-stearic acid conjugate modified nanocomplexes for cancer immunotherapy. Acta Biomater. 2019;92:184–195. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.05.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Lee J, Wan J, Lee L, et al. Study of the NLRP3 inflammasome component genes and downstream cytokines in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with carotid atherosclerosis. Lipids Health Dis. 2017;16:217. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0595-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Chang BY, Huang MM, Francesco M, et al. The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor PCI-32765 ameliorates autoimmune arthritis by inhibition of multiple effector cells. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13:R115. doi: 10.1186/ar3400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Eltzschig HK, Eckle T. Ischemia and reperfusion—from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 2011;17:1391–1401. doi: 10.1038/nm.2507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Iadecola C, Anrather J. The immunology of stroke: from mechanisms to translation. Nat Med. 2011;17:796–808. doi: 10.1038/nm.2399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Ye B, Zhou C, Guo H, Zheng M. Effects of BTK signalling in pathogenic microorganism infections. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23:6522–6529. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Brunner C, Müller B, Wirth T (2005) Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase is involved in innate and adaptive immunity. Histol Histopathol 20:945–955. 10.14670/HH-20.945 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 102.de Porto AP, Liu Z, de Beer R, et al. Btk inhibitor ibrutinib reduces inflammatory myeloid cell responses in the lung during murine pneumococcal pneumonia. Mol Med. 2019;25:3. doi: 10.1186/s10020-018-0069-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Olsson S, Sundler R. Different roles for non-receptor tyrosine kinases in arachidonate release induced by zymosan and Staphylococcus aureus in macrophages. J Inflamm (Lond) 2006;3:8. doi: 10.1186/1476-9255-3-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Köprülü AD, Kastner R, Wienerroither S, et al. The tyrosine kinase Btk regulates the macrophage response to Listeria monocytogenes infection. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e60476. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Mukhopadhyay S, Sahoo PK, George A, et al. Delayed clearance of filarial infection and enhanced Th1 immunity due to modulation of macrophage APC functions in xid mice. J Immunol. 1999;163:875–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Colado A, Genoula M, Cougoule C, et al. Effect of the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib on macrophage- and γδ T cell-mediated response against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Blood Cancer J. 2018;8:100. doi: 10.1038/s41408-018-0136-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Strijbis K, Tafesse FG, Fairn GD, et al. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) and Vav1 contribute to Dectin1-dependent phagocytosis of Candida albicans in macrophages. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9:e1003446. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Shahan TA, Sorenson WG, Simpson J, et al. Tyrosine kinase activation in response to fungal spores is primarily dependent on endogenous reactive oxygen production in macrophages. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:10175–10181. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.14.10175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Szymczak WA, Davis MJ, Lundy SK et al (2013) X-linked immunodeficient mice exhibit enhanced susceptibility to Cryptococcus neoformans Infection. MBio 4. 10.1128/mBio.00265-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 110.Herbst S, Shah A, Mazon Moya M et al (2015) Phagocytosis-dependent activation of a TLR9-BTK-calcineurin-NFAT pathway co-ordinates innate immunity to Aspergillus fumigatus. EMBO Mol Med 7:240–258. 10.15252/emmm.201404556 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 111.Bercusson A, Colley T, Shah A, et al. Ibrutinib blocks Btk-dependent NF-ĸB and NFAT responses in human macrophages during Aspergillus fumigatus phagocytosis. Blood. 2018;132:1985–1988. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-12-823393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Colado A, Marín Franco JL, Elías EE, et al. Second generation BTK inhibitors impair the anti-fungal response of macrophages and neutrophils. Am J Hematol. 2020;95:E174–E178. doi: 10.1002/ajh.25816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Shinohara M, Chang BY, Buggy JJ, et al. The orally available Btk inhibitor ibrutinib (PCI-32765) protects against osteoclast-mediated bone loss. Bone. 2014;60:8–15. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2013.11.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Hartkamp LM, Fine JS, van Es IE, et al. Btk inhibition suppresses agonist-induced human macrophage activation and inflammatory gene expression in RA synovial tissue explants. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:1603–1611. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Zhou P, Ma B, Xu S, et al. Knockdown of Burton’s tyrosine kinase confers potent protection against sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014;70:1265–1275. doi: 10.1007/s12013-014-0050-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Bender AT, Pereira A, Fu K, et al. Btk inhibition treats TLR7/IFN driven murine lupus. Clin Immunol. 2016;164:65–77. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2016.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Mangla A, Khare A, Vineeth V, et al. Pleiotropic consequences of Bruton tyrosine kinase deficiency in myeloid lineages lead to poor inflammatory responses. Blood. 2004;104:1191–1197. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-01-0207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Mao L, Kitani A, Hiejima E, et al. Bruton tyrosine kinase deficiency augments NLRP3 inflammasome activation and causes IL-1β-mediated colitis. J Clin Invest. 2020;130:1793–1807. doi: 10.1172/JCI128322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Lee K-G, Xu S, Kang Z-H, et al. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase phosphorylates Toll-like receptor 3 to initiate antiviral response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:5791–5796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1119238109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Florence JM, Krupa A, Booshehri LM, et al. Inhibiting Bruton’s tyrosine kinase rescues mice from lethal influenza-induced acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Cell Mol Physiol. 2018;315:L52–L58. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00047.2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Chong EA, Roeker LE, Shadman M et al (2020) BTK inhibitors in cancer patients with COVID19: “The winner will be the one who controls that chaos”; (Napoleon Bonaparte). Clin Cancer Res clincanres.1427.2020. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-1427 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 122.Roschewski M, Lionakis MS, Sharman JP et al (2020) Inhibition of Bruton tyrosine kinase in patients with severe COVID-19. Sci Immunol 5:eabd0110. 10.1126/sciimmunol.abd0110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 123.Treon SP, Castillo JJ, Skarbnik AP, et al. The BTK inhibitor ibrutinib may protect against pulmonary injury in COVID-19-infected patients. Blood. 2020;135:1912–1915. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020006288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, et al. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel Coronavirus-infected Pneumonia in Wuhan. China JAMA. 2020;323:1061. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Bhatraju PK, Ghassemieh BJ, Nichols M et al (2020) Covid-19 in critically Ill patients in the Seattle region—case series. N Engl J Med NEJMoa2004500. 10.1056/NEJMoa2004500 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]