Figure 1.
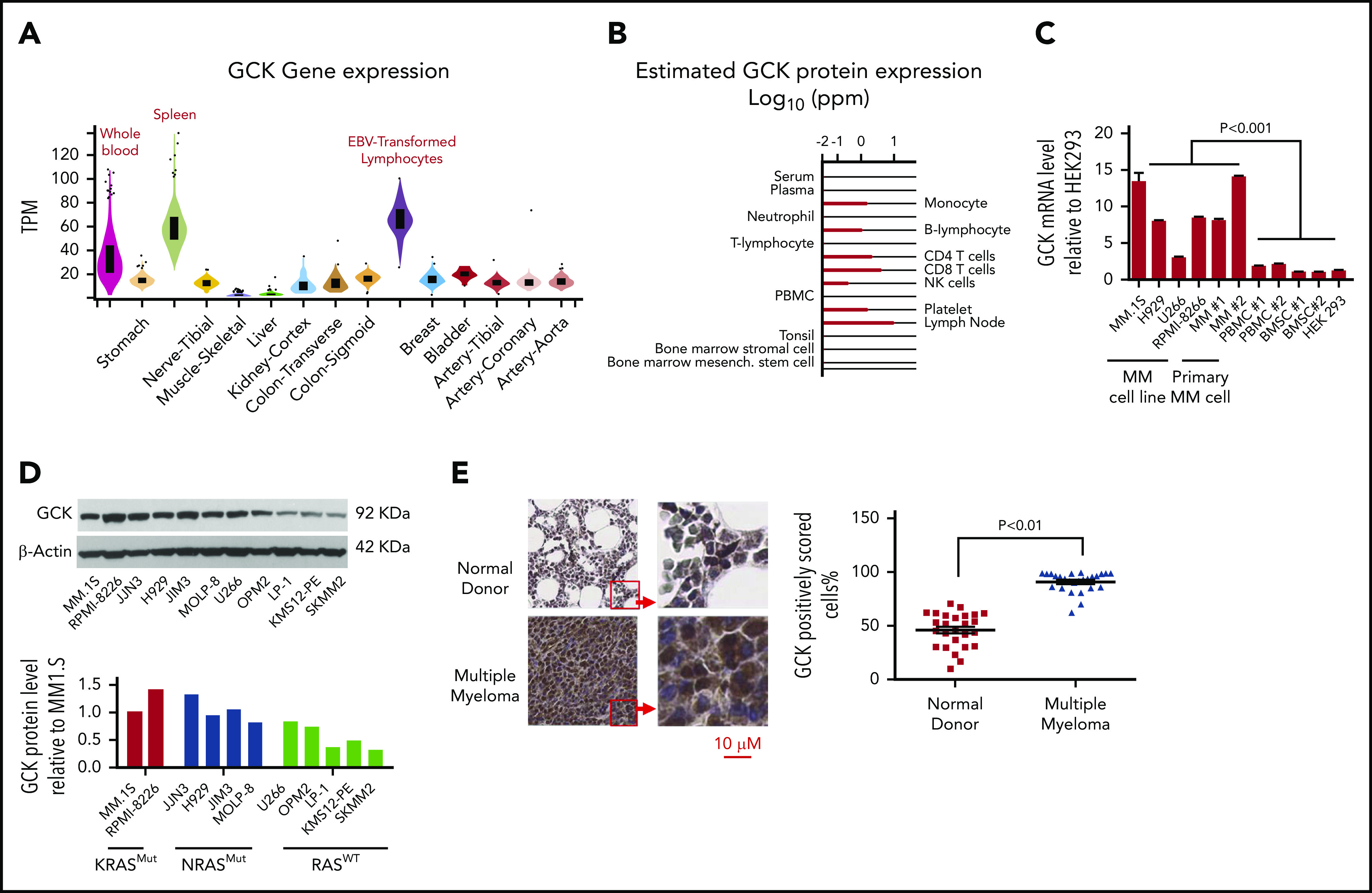
GCK expression is elevated in MM. (A) The GCK gene and transcript expression values were obtained from the publically available genotype-tissue expression portal on 30 June 2019 and shown as reads per kilobase transcript per million reads (RPKM). (B) The GCK protein expression values were obtained from the Human Integrated Protein Expression Database (HIPED) on 30 June 2019. Parts per million (PPM): each protein entity is enumerated relative to all other protein molecules in the sample. (C) mRNA from a panel of MM cell lines (MM.1S, H929, RPMI-8226, U266), primary MM cell (MM 1 and MM 2), PBMC#1 and PBMC #2, BMSC #1 and BMSC#2, and HEK-293 cells was extracted and GCK mRNA expression was analyzed by quantitative PCR with β-actin as control. GCK mRNA level was calculated relative to its level in HEK-293. (D) RASMut MM cell lines (MM.1S, RPMI-8226, JJN3, H929, JIM3, and MOLP-8) and RASWT cell lines (U266, OPM2, LP-1, KMS12-PE, and SKMM2) were analyzed for GCK protein levels by western blotting of whole cell extracts using β-actin as a loading control. GCK protein levels were quantified using ImageJ software. (E) Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded bone marrow biopsy sections for GCK expression (Brown staining) of normal donor (n = 26) and myeloma patients (n = 26). The slides were scanned using a high-resolution scanner (Leica SCN400 Slide Scanner) at ×40 magnification. Images were analyzed using Aperio ImageScope software (Aperio Technologies, Inc., Vista, CA). Statistical analysis was performed using the Aperio Positive Pixel Count algorithm in the ImageScope viewing software.
