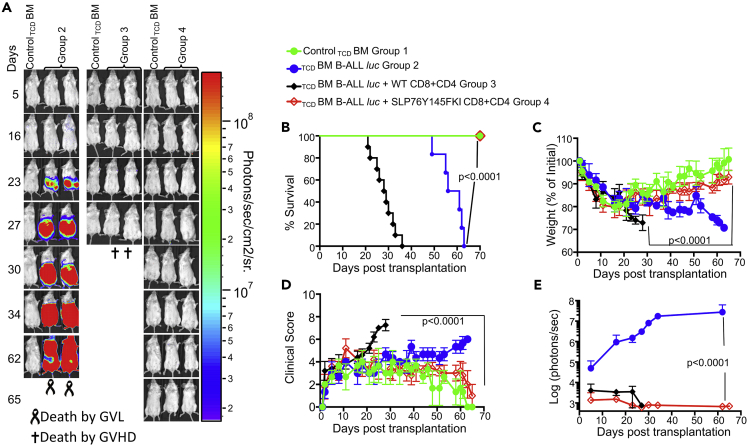
Figure 1.
Disruption of ITK → SLP76 Y145 signaling allows tumor clearance without inducing GVHD
1X106 purified CD8+ T cells and 1X106 purified CD4+ T cells from WT or SLP76 Y145FKI mice were mixed at a 1:1 ratio and transplanted with 2X105 B-ALL cells and 10 × 106 T cell-depleted bone marrow (TCDBM) cells transplanted into irradiated BALB/c mice. Host BALB/c mice were imaged using the IVIS 50 system three times a week.
(A) Group one received 10 × 106 T cell depleted bone marrow cells (TCDBM) only. Group one mice are used as negative controls while imaging other groups that have luciferase-expressing primary leukemia cells. Group two received 10X106TCDBM with 2X105 B-ALL-luc cells (TCDBM + B-ALL luc). The third group was transplanted with 10X106TCDBM cells and 1X106 purified WT CD8+ and 1X106 CD4+ T cells (1:1 ratio) along with 2X105 B-ALL -luc cells (TCDBM + B-ALL-luc + WT CD8+ and CD4+). Group four received 10X106TCDBM cells and 1X106 purified CD8+ and 1X106 CD4+ T cells (1:1 ratio from SLP76 Y145FKI) along with 2X105 B-ALL-luc B-ALL-luc cells (TCDBM + B-ALLluc + SLP76Y145F CD8+CD4).
(B–D) (B) We monitored the survival of recipient animals, (C) body weight changes, and (D) clinical score for 65 days post-BMT. For weight changes and clinical score, one representative of 2 independent experiments is shown (n = 3 mice/group for BM alone; n = 5 experimental mice/group for all three groups).
(E) We have quantitated tumor growth via luciferase bioluminescence. Statistical analysis for survival and the clinical score was performed using the log rank test and two-way ANOVA, respectively. Note: Controls are naive for cancer, but transplanted with 10 × 106T cell depleted bone marrow alone (TCDBM)and used as a negative control for BLI. See also Figures S1 and S2.