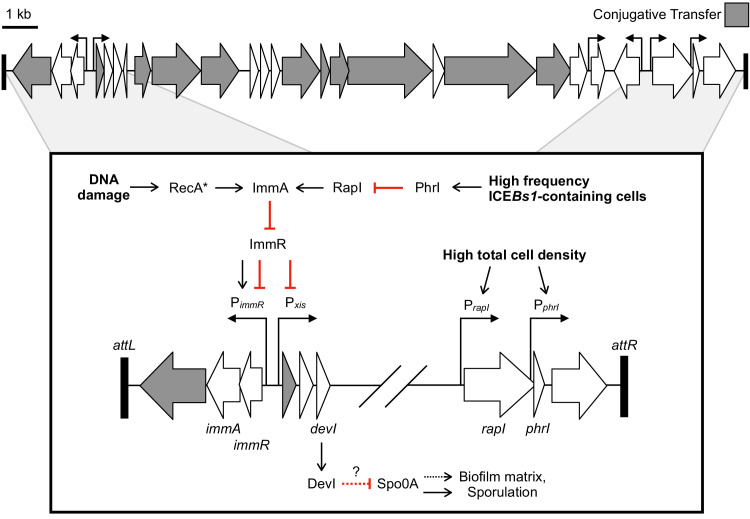
Figure 1. Genetic map and regulatory pathways of ICEBs1.
Genes are represented by horizontal block arrows indicating the direction of transcription. Vertical right-angle arrows mark the positions of promoters, and the arrowhead indicates the direction of transcription. Genes known to be involved in the conjugative life cycle of ICEBs1 are shaded in gray. The 60 bp direct repeats that mark the ends of ICEBs1 are shown as black rectangles. (Inset) A partial genetic map that highlights factors involved in the regulation of ICEBs1. The major promoter Pxis drives expression of most genes in ICEBs1. Pxis is repressed by the ICE-encoded repressor ImmR. Repression is relieved when ImmR is cleaved by the protease ImmA, and proteolytic cleavage is stimulated by activated RecA (RecA*) in response to DNA damage, or, independently by the cell signaling regulator RapI. RapI is made when cells are crowded by potential recipients, but repressed by the ICE-encoded secreted peptide PhrI if the neighboring cells already contain a copy of ICEBs1. devI (formerly ydcO) is the third open-reading frame downstream of Pxis. DevI inhibits sporulation and expression of biofilm matrix genes, likely by inhibiting Spo0A (directly or indirectly). In the genetic pathways, black arrows indicate activation and red T-bars indicate inhibition.