Abstract
Despite decades of study, debate persists over the role of inflammation, fibrosis, and prostaglandins in the histopathology of androgenic alopecia (AGA). This brief review proposes that inconsistent findings across histological studies are a consequence of three inadequately controlled variables: 1) biopsy location, 2) hair diameter diversity (HDD), and 3) relative hair follicle miniaturization (HFM) within and across subjects. We suggest new methodological considerations to improve AGA histopathological research, as well as a novel classification system to quantify HFM by its stages. Finally, we hypothesize a dynamic relationship between inflammation, fibrosis, and prostaglandin activity dependent on relative HFM.
Keywords: androgenic alopecia, hair diameter diversity, inflammation, fibrosis, prostaglandins
Introduction
AGA is a progressive hair loss disorder that predominantly affects skin tissues above the galea aponeurotica. It is well-established that AGA is mediated by androgens and genetics.1 However, there is less consensus surrounding its histopathology – particularly in regard to the presence of inflammation, fibrosis, and prostaglandin activity in balding tissues.
In his landmark study, Whiting discovered inflammation and/or fibrosis in 70% of AGA-affected biopsied vertices compared to 40.9% of non-balding controls.2 These findings were corroborated in a follow-up investigation demonstrating inflammation and/or fibrosis in 71.4% versus 37% of balding and non-balding controls, respectively.3 Since then, histological studies have built on and conflicted with Whiting’s work (Table 1).4–15 For instance, Goyal et al found no evidence of inflammation or fibrosis in men with moderate AGA.14 El-Domyati et al found that the magnitude of fibrosis increased alongside Norwood gradients – with follicular destruction observed in AGA’s advanced stages.11 Recently, Valdebran et al noted fibrosis in 68% of AGA biopsies and 82% of non-balding controls – calling into question the role of inflammation and fibrosis in AGA.15
Table 1.
A Summary of Investigations Reporting Inflammation and/or Fibrosis in AGA Biopsies
| Author (Year) | Subjects | Biopsy Methodologies | Balding Subjects | Control Subjects | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Age (Years) | Sex | Hamilton-Norwood/Ludwig Gradient | Inflammation (%) | Fibrosis (%) | Inflammation (%) | Fibrosis (%) | ||
| Lattanand & Johnson (1975)4 | 23 (347 specimens) | 21–48 | Male | Not specified | Biopsies from hair transplants | 50% | NE | NE; no control group | |
| Kligman (1988)5 | 13 | 21–48 | Male | 7 with early AGA; 6 with late AGA | Transverse and vertical | NE; early AGA: inflammation in the infundibulum, sebaceous gland, and follicular streamers; late AGA: inflammation still present | NE; early AGA: collagen bundles and fibroblasts noted in follicular streamers; late AGA: fibrosis more evident in follicular streamers with some becoming fibrous tracts | NE; inflammation absent in specimens derived from senescent balding scalps; sparse, mild inflammation noted in normal scalps. | NE |
| Abell (1988)6 | 603 | Not specified | 600 male, 3 female | Not specified | 3–6mm punch biopsy; transverse | 77% | 25% | NE; no control group | |
| Sperling & Winton (1990)7 | 5 | Not specified | Male | Not specified | 3.5mm punch biopsy; transverse and vertical | 100% | NE; increased dermal collagen surrounding follicular groups | NE; no control group | |
| Jaworsky et al (1992)8 | 4 | 25–67 years | 3 males, 1 female | Segmented samples by location: samples were obtained from the most affected region, transitional region (perimeter of affected pattern regions), and non-alopecic regions | Not specified | NE; significant inflammation in the infundibulum of specimens derived from transitional scalp | NE; balding samples: mature collagen noted in adventitial sheath; transitional samples: collagen noted in adventitial sheath, but less pronounced | NE; inflammation and fibrous tract remnants scarce among non-alopecic regions | |
| Whiting (1993)2 | 106 | 16–70, average 37 years | Male | Not specified | 4mm punch biopsy; horizontal and vertical | 70% (inflammation and fibrosis grouped together) | 40.9% (inflammation and fibrosis grouped together) | ||
| Whiting (1996)3 | 412 | 15–80, average 40 years | 193 male, 219 female | Not specified | 4mm punch biopsy; horizontal and vertical | 71.4% (inflammation and fibrosis grouped together); moderate inflammation and/or fibrosis found in 37% | 40% (inflammation and fibrosis grouped together); moderate inflammation and/or fibrosis found in 11% | ||
| Deloche et al (2004)9 | 40 | 19–51 in male group, 21–65 in female group | 21 male, 19 female | Norwood I: 2 Norwood II: 10 Norwood III: 3 Norwood IV: 5 Norwood VI: 1 Ludwig I: 4 Ludwig II: 12 Ludwig III: 3 |
One 4mm punch biopsy, one 2mm punch biopsy; horizontal and vertical | 100% in males, 100% in females | 62% of males, 51% of females | NE; no control group | |
| Won et al (2008)10 | 10 | 20–35 | Male | Norwood III to Norwood IV, specimens were taken from both balding vertex and non-balding occipital region | 4mm punch biopsy; horizontal | NE; significantly increased numbers of mast cells | NE; significantly increased collagen bundles and elastic fibers in vertex samples correlated with higher mast cells | NE; collagen and/or elastic fiber deposition absent in non-balding occipital samples | |
| El-Domyati et al (2009)11 | 40 | 20–80 | Male | Norwood I: 3 Norwood II: 4 Norwood IIa: 3 Norwood III: 1 Norwood IIIa: 1 Norwood IIIv: 5 Norwood IV: 3 Norwood IVa: 3 Norwood V: 5 Norwood Va: 2 Norwood VI: 8 Norwood VII: 2 |
4mm punch biopsy; biopsies taken from balding area, non-balding occipital area, and frontal area from control subjects; horizontal and transverse | 90% | 60% | 17.5% | |
| Aslani et al (2018)12 | 61 | 11–50 years in the female group, 18–37 in the male group | 46 female, 15 male | Not specified | 4mm punch biopsy; horizontal, vertical, and transverse | 66.7% of males, 35.7% of females | NE | NE; no control group | |
| Tandon et al (2019)13 | 30 | 28–45 years | Female | Not specified | 4mm punch biopsy | 56% | 30% | NE; no control group | |
| Goyal et al (2019)14 | 9 | 26–30 in men, 25–48 in women | 5 male, 4 female | Norwood II: 1 Norwood IV: 2 Norwood VI: 2 Ludwig I: 2 Ludwig II: 2 |
4mm punch biopsies; transverse | 0% in males, 0% in females | 0% in males, 25% in females | NE; no control group | |
| Valdebran et al (2020)15 | 37 | Not specified | Not specified | Not specified | Examined specimens with at least one vertical section | 73% | 68% | 84% | 82% |
Abbreviation: NE, not estimated.
Conflicting histological reports have also emerged regarding prostaglandin activity in balding scalps. In 2012, Garza et al found that prostaglandin D2 (PGD2) and prostaglandin J2 (PGJ2) levels were elevated in balding scalps, and that prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) levels were higher in non-balding scalps.16 However, follow-up investigations by Villarreal-Villarreal et al found no significant differences in PGD2 levels across balding and non-balding subjects, and concluded that PGE2 synthase was only elevated in biopsies of early-stage AGA subjects.17 Most recently, Chovarda et al found higher PGD2 and PGI2 and lower PGE2 and PGF2a in balding scalps – further elucidating a complex relationship between prostaglandins and AGA.18
Some authors suggest that inconsistent histological findings are due to differences across study subject demographics (ie, age, sex, and/or race) and methodologies (ie, transverse versus horizontal biopsies and/or the use of demographic-matched, non-balding controls).19,20 These are plausible considerations. Nonetheless, three additional variables may greatly influence study outcomes, none of which are adequately controlled for in histological investigations: biopsy location, HDD, and relative HFM.
We propose the hypothesis that biopsy location, HDD, and relative HFM are responsible for the majority of conflicting findings across AGA histological studies. We introduce a classification system to quantify relative HFM and control for these variables. Finally, we hypothesize a dynamic relationship between inflammation, fibrosis, and prostaglandin activity in AGA that attempts to make sense of conflicting histopathological reports: a model dependent on relative HFM.
Discussion
Histopathological Challenges
AGA progresses through reductions in hair diameter, also known as HFM.21 HFM is considered a single step-process; it is believed to occur during reentry into anagen and worsen with each subsequent hair cycle.21 In AGA, hair cycling rates are not uniform. As such, AGA-affected locations often present with hair diameters ranging from full-thickness to miniaturized to vellus – even within 1mm zones. This phenomenon is termed anisotrichosis, also known as HDD.22 When terminal HDD varies by more than 20%, it is used as a diagnostic tool for AGA.23 In all likelihood, HDD of less than 20% may also indicate early-stage AGA, albeit at cosmetically imperceptible levels.24
HDD is ubiquitous but variable across AGA locations, gradients, and subjects.23 As such, its presence poses a unique challenge in histopathological research. Current understandings of AGA histology come from analyses of 2–4mm punch biopsies. Biopsies are conducted on subjects with cosmetic AGA – often at gradients of Norwood 2–4. Due to concerns of scarring, investigators often biopsy regions where incisions are less conspicuous, like the vertex (Table 1).
Under these circumstances, a 4mm vertex biopsy may contain anywhere from 10 to 50 hairs – 80% of which are terminal.2 However, within each biopsy, terminal HDD varies: some terminal hairs appear unaffected by HFM, while others appear toward the final stages of HFM. Resultantly, 1mm adjustments to biopsy location can skew HDD and HFM toward earlier or later miniaturization cycles (Figure 1). As such, HDD and relative HFM are phenomena that reduce the usefulness of standardizing biopsies based only on subject demographics, general location (ie, vertex), and Norwood gradient – particularly if research objectives involve elucidating histological changes throughout AGA’s multi-stage progression.
Figure 1.
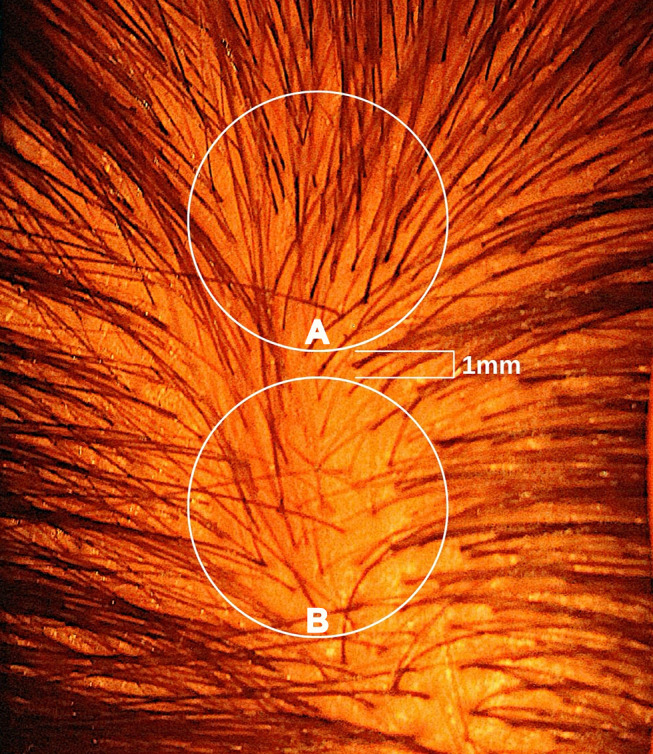
A photograph of a male vertex in the early stages of AGA. Zones represent potential biopsy locations separated by approximately 1 mm. Zone A features relatively high hair counts, low HDD, and terminal hair follicles skewed toward earlier cycles of HFM. Zone B features relatively low hair counts, high HDD, and terminal hair follicles skewed toward later cycles of HFM.
Abbreviations: AGA, androgenic alopecia; HDD, hair diameter diversity; HFM, hair follicle miniaturization.
Dermatopathologists stress the importance of performing biopsies at the edge of disease onset to capture both affected and unaffected tissue.25 However, AGA’s slow and widespread progression often obfuscates an early diagnosis due to change blindness. Therefore, by the time AGA becomes a cosmetic concern, HDD is already greater than 20%, HFM has already occurred over several hair cycles, and its initial edge of onset is difficult to discern. Therefore, as investigators continue to preferentially select for AGA subjects with visual hair loss, histological research continues to underrepresent AGA in its earliest of stages (Table 1).
Lastly, in private conversations with dermatologists, trichoscopic examinations tend to show some degree of HDD in nearly all post-pubertal patients. If true, this suggests that the incidence of AGA is higher than previously reported, that AGA initiates much earlier than it cosmetically presents, and that inflammation in non-balding controls may actually indicate early-stage AGA – albeit with HDD of less than 20%. This draws into question the utility of comparing biopsies of balding scalps to location- and demographic-matched non-balding controls – at least without intrasubject evaluations to measure hair diameter in balding-prone versus donor-safe scalp regions.
Methodological Considerations
It is imperative that future histopathological AGA investigations not only control for Norwood gradient and biopsy location, but also HDD and relative HFM within and across subjects. Without accounting for HDD and relative HFM, conflicting reports regarding the presence of inflammation, fibrosis, and prostaglandins in AGA are likely to persist.
Historically, HDD is used as a binary measurement: it is present if an arbitrary examination zone shows hair diameter variations greater than 20%. Measuring HDD is simple; however, its usefulness in histological research is limited without also capturing relative HFM. For example, HDD is often undetectable in biopsies of early- and late-stage AGA where hair diameters present uniformly as near-full thickness or near-completely miniaturized, respectively. Therefore, in addition to HDD, we propose that research teams also control for relative HFM within balding and non-balding controls.
Relative HFM can be established for each subject by averaging terminal hair diameters in a biopsied region, 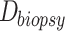 , to compare against average terminal diameters in a donor-safe region,
, to compare against average terminal diameters in a donor-safe region, 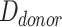 . Preferably, donor-safe hairs would be measured in occipital zones A1, B1, and C1, where Yun et al found the widest hair diameters.24
. Preferably, donor-safe hairs would be measured in occipital zones A1, B1, and C1, where Yun et al found the widest hair diameters.24
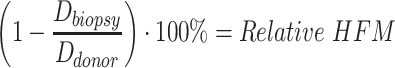 |
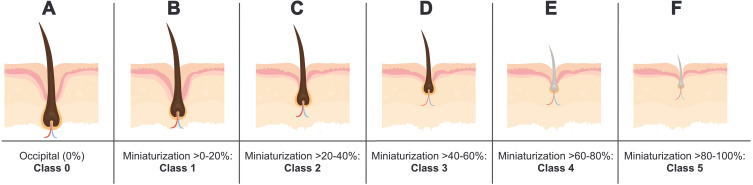
Finally, relative HFM can be segmented by 20% increments and denoted by five classes to distinguish magnitudes of miniaturization (Figure 2). In adult male scalps, the average diameter of terminal hair versus AGA-affected vellus hair ranges from 70 to 90 μm and 25 to 35 μm, respectively.24,26,27 Thus, a five-stage classification system would allow for histological observations across three stages of terminal HFM (Figure 2B and C) and two stages of vellus HFM (Figure 2E and F) in relation to a hair follicle unaffected by AGA (Figure 2A).
Figure 2.
A proposed classification system to quantify relative HFM within the same subject. (A) Class 0 represents full-thickness hairs unaffected by AGA. (B–F) Classes 1–5 represent AGA-affected hairs benchmarked to Class 0, with miniaturization segmented by 20% increments per class.
Abbreviations: HFM, hair follicle miniaturization; AGA, androgenic alopecia.
Altogether, controlling for HDD and relative HFM would serve to (1) identify balding subjects inadvertently featured as non-balding controls, and (2) clarify the histological role of inflammation, fibrosis, and prostaglandin activity across all classes of HFM, and thereby multiple stages of AGA.
Hypothetical Model
Conflicting histological reports regarding inflammation and fibrosis have stirred debate over whether AGA should be considered a scarring or nonscarring alopecia – with many investigators settling on a biphasic definition.28 Inconsistent findings regarding prostaglandin activity have led Villarreal-Villarreal et al to suggest that PGE2 synthase is upregulated in the early stages of AGA in order to protect hair follicles from miniaturization.17 Taking these stances into consideration, we hypothesize a dynamic relationship between AGA and the presence of inflammation, fibrosis, and prostaglandins dependent on relative HFM (Figure 3).
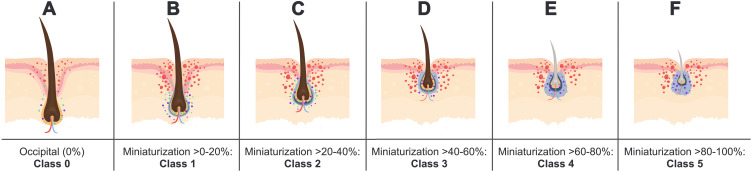
Figure 3.
A hypothetical model showing a dynamic relationship between AGA and the presence of inflammation, fibrosis, and prostaglandin activity based on relative HFM. Inflammation is denoted by red markings; PGE2 synthase is denoted by green markings; PGD2 and PGJ2 are denoted by purple markings; fibrosis is denoted by blue perifollicular shading. (A) Class 0 hair follicles unaffected by AGA show no fibrosis and relatively low levels of inflammation, PGE2 synthase, PGD2, and PGJ2. (B and C): Class 1–2 hair follicles in the early stages of HFM show relatively low levels of fibrosis but increased inflammation, PGE2 synthase, PGD2, and PGJ2. (D–F) Class 3–5 hair follicles in the mid- to late-stages of HFM show increasing levels of fibrosis, decreased activity of PGE2 synthase, and sustained levels of PGD2 and PGJ2.
Abbreviations: AGA, androgenic alopecia; HFM, hair follicle miniaturization; PGE2, Prostaglandin E2; PGD2, Prostaglandin D2; PGJ2, Prostaglandin J2.
In the absence of HFM, our model suggests that hair follicles show no fibrosis and relatively low levels of inflammation, PGE2 synthase, PGD2, and PGJ2 (Figure 3A). During early stages of HFM (ie, hair diameter reductions greater than 0% and up to 40%), hair follicles show relatively low levels of fibrosis but increased inflammation, PGE2 synthase, PGD2, and PGJ2 (Figure 3B and C). During mid- to late-stages of HFM (ie, hair diameter reductions greater than 40%), hair follicles show increasing levels of fibrosis, decreased activity of PGE2 synthase, and sustained levels of PGD2 and PGJ2 (Figure 3D–F). This hypothetical model would help make sense of decades worth of conflicting histological reports without undermining or dismissing any past findings.
Testing the Hypothesis
Testing our hypothesis would require, for each participant, the collection of five datapoints from both affected and unaffected AGA scalp regions: hair counts, hair diameters, and histological assessments of inflammation, fibrosis, and prostaglandin activity. Hair counts and hair diameters could be established non-invasively through dermoscopy and image analysis software. However, to the best of our knowledge, determining the presence and magnitude of inflammation, fibrosis, and prostaglandin activity in scalp skin would require a biopsy. This poses a methodological challenge: most AGA patients are not diagnosed through biopsies, nor are they eager to undergo invasive procedures that potentiate scarring. Thus, to improve the testability of our hypothesis, there is a need to develop non-invasive methods to measure inflammation, fibrosis, and prostaglandins in cutaneous tissues.
There are non-invasive devices to assess inflammatory, proliferative, and remodeling phases of wound-healing in vivo for cutaneous tissues.29 Some of these technologies may soon evolve to support hair loss research. Recently, Mogensen et al demonstrated that optical coherence tomography – in combination with topical gold nanoshells – enhanced the contrast of hair follicles and allowed for in vivo histological analysis at a resolution of 2 to 6 μm, but only to a depth of 1.2 mm.30 Çildağ and Çildağ found that sonoelastography could assess the magnitude of skin fibrosis in subjects with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis, albeit with lower accuracy in early stages of disease development.31 Laistler et al found that magnetic resonance imaging alongside highly-sensitive superconducting surface coils could achieve in vivo skin images that distinguished cutaneous layers and blood vessel walls, but only up to a resolution of 80 μm.32 Interestingly, magnetic resonance imaging has demonstrated utility in diagnosing AGA, determining hair follicle depth, and measuring epidermal, dermal, and hypodermal layer thickness.33 Finally, Mize et al found that non-invasive reverse iontophoresis could measure, in vivo, changes to cutaneous PGE2 from drug-induced irritation, but not from agents that induced vasodilation or vasoconstriction.34 With continued advancements, optical coherence tomography, sonoelastography, magnetic resonance imaging, and reverse iontophoresis may allow for real-time in vivo monitoring of inflammation, fibrosis, and prostaglandins in AGA – thereby accelerating histopathological research across a variety of hair loss disorders.
Conclusion
In AGA, the ubiquitous but variable presence of HDD and relative HFM undermine the utility of controlling histological investigations only for subject demographics and biopsy locations. We hypothesize that biopsy location, HDD, and relative HFM are responsible for the majority of conflicting findings across AGA histopathological investigations – and that a dynamic relationship exists between inflammation, fibrosis, and prostaglandins dependent upon relative HFM. We propose methodological considerations to account for HDD and relative HFM, as well as a novel classification system to establish relative HFM within each subject. Controlling for HDD and relative HFM can be accomplished by (1) measuring hair diameters within a biopsy to establish HDD, and (2) comparing biopsied hair diameters to those found in regions protected from AGA (ie, the occipital) to establish relative HFM. Such methodologies would not significantly complicate any investigation. They might, however, clarify decades worth of conflicting reports regarding AGA’s histopathology.
Author Contributions
All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; agreed to submit to the current journal; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Disclosure
Robert English and Sophia Ruiz have no conflicts to declare.
References
- 1.Cash T. The psychosocial consequences of androgenetic alopecia. Rev Res Lit. 1999;141:398–405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Whiting DA. Diagnostic and predictive value of horizontal sections of scalp biopsy specimens in male pattern androgenetic alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;28(5 Pt 1):755–763. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(93)70106-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Whiting DA. Chronic telogen effluvium: increased scalp hair shedding in middle-aged women. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35(6):899–906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lattanand A, Johnson WC. Male pattern alopecia a histopathologic and histochemical study. J Cutan Pathol. 1975;2(2):58–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.1975.tb00209.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kligman AM. The comparative histopathology of male-pattern baldness and senescent baldness. Clin Dermatol. 1988;6(4):108–118. doi: 10.1016/0738-081x(88)90074-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Abell E. Histologic response to topically applied minoxidil in male-pattern alopecia. Clin Dermatol. 1988;6(4):191–194. doi: 10.1016/0738-081x(88)90086-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sperling LC, Winton GB. The transverse anatomy of androgenic alopecia. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1990;16(12):1127–1133. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4725.1990.tb00024.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jaworsky C, Kligman AM, Murphy GF. Characterization of inflammatory infiltrates in male pattern alopecia: implications for pathogenesis. Br J Dermatol. 1992;127(3):239–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1992.tb00121.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Deloche C, de Lacharriere O, Misciali C, et al. Histological features of peripilar signs associated with androgenetic alopecia. Arch Dermatol Res. 2004;295(10):422–428. doi: 10.1007/s00403-003-0447-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Won CH, Kwon OS, Kim YK, et al. Dermal fibrosis in male pattern hair loss: a suggestive implication of mast cells. Arch Dermatol Res. 2008;300(3):147–152. doi: 10.1007/s00403-007-0826-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.El-Domyati M, Attia S, Saleh F, Abdel-Wahab H. Androgenetic alopecia in males: a histopathological and ultrastructural study. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2009;8(2):83–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1473-2165.2009.00439.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sari Aslani F, Heidari Esfahani M, Sepaskhah M. Non-scarring Alopecias in Iranian Patients: a Histopathological Study With Hair Counts. Iran J Pathol Summer. 2018;13(3):317–324. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Tandon S, Arora P, Gautam RK, Bhardwaj M, Garga U, Sharma N. Correlation between clinical features, biochemical parameters, and histopathological findings in women with patterned baldness: a study from North India. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2019;12(1):42–48. doi: 10.4103/JCAS.JCAS_30_18 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Goyal M, Khandpur S, Ramam M, Sharma VK, Singh MKA. Study of the histopathological features of alopecias on transverse sections of scalp biopsies. Indian J Dermatol. 2019;64(1):47–54. doi: 10.4103/ijd.IJD_477_17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Valdebran M, Mo J, Elston DM, Doan L. Pattern hair loss: assessment of inflammation and fibrosis on histologic sections. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(3):757–758. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2019.09.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Garza LA, Liu Y, Yang Z, et al. Prostaglandin D2 inhibits hair growth and is elevated in bald scalp of men with androgenetic alopecia. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4(126):126ra34. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003122 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Villarreal-Villarreal CD, Sinclair RD, Martinez-Jacobo L, et al. Prostaglandins in androgenetic alopecia in 12 men and four female. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33(5):e214–e215. doi: 10.1111/jdv.15479 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chovarda E, Sotiriou E, Lazaridou E, Vakirlis E, Ioannides D. The role of prostaglandins in androgenetic alopecia. Int J Dermatol. 2021. doi: 10.1111/ijd.15378 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sadick N, Magro C. Response to Letter to the Editor. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.176 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Valdebran M, Doan L, Elston DM. Reply to comment on: pattern hair loss. Assessment of inflammation and fibrosis on histologic sections. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.05.040 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Krajcik RA, Vogelman JH, Malloy VL, Orentreich N. Transplants from balding and hairy androgenetic alopecia scalp regrow hair comparably well on immunodeficient mice. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48(5):752–759. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2003.95 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sewell LD, Elston DM, Dorion RP. “Anisotrichosis”: a novel term to describe pattern alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56(5):856. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2007.01.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.de Lacharriere O, Deloche C, Misciali C, et al. Hair diameter diversity: a clinical sign reflecting the follicle miniaturization. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137(5):641–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yun SS, Park JH, Na YC. Hair diameter variation in different vertical regions of the occipital safe donor area. Arch Plast Surg. 2017;44(4):332–336. doi: 10.5999/aps.2017.44.4.332 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Vidal CI. Overview of Alopecia: a Dermatopathologist’s Perspective. Mo Med. 2015;112(4):308–312. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Leerunyakul K, Suchonwanit P. Evaluation of hair density and hair diameter in the adult thai population using quantitative trichoscopic analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:2476890. doi: 10.1155/2020/2476890 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lee MS, Kossard S, Wilkinson B, Doyle JA. Quantification of hair follicle parameters using computer image analysis: a comparison of androgenetic alopecia with normal scalp biopsies. Australas J Dermatol. 1995;36(3):143–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-0960.1995.tb00956.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Stefanato CM. Histopathology of alopecia: a clinicopathological approach to diagnosis. Histopathology. 2010;56(1):24–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2009.03439.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ud-Din S, Bayat A. Non-invasive objective devices for monitoring the inflammatory, proliferative and remodelling phases of cutaneous wound healing and skin scarring. Exp Dermatol. 2016;25(8):579–585. doi: 10.1111/exd.13027 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mogensen M, Bojesen S, Israelsen NM, et al. Two optical coherence tomography systems detect topical gold nanoshells in hair follicles, sweat ducts and measure epidermis. J Biophotonics. 2018;11(9):e201700348. doi: 10.1002/jbio.201700348 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cildag S, Cildag MB. The relationship between the degree of skin fibrosis by sonoelastography and the degree of pulmonary involvement in scleroderma. Turk J Med Sci. 2017;47(5):1555–1559. doi: 10.3906/sag-1702-44 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Laistler E, Poirier-Quinot M, Lambert SA, et al. In vivo MR imaging of the human skin at subnanoliter resolution using a superconducting surface coil at 1.5 Tesla. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015;41(2):496–504. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24549 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Soga S, Koyama T, Mikoshi A, et al. Quantitative analysis of the anatomical changes in the scalp and hair follicles in androgenetic alopecia using magnetic resonance imaging. Skin Res Technol. 2021;27(1):56–61. doi: 10.1111/srt.12908 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Mize NK, Buttery M, Daddona P, Morales C, Cormier M. Reverse iontophoresis: monitoring prostaglandin E2 associated with cutaneous inflammation in vivo. Exp Dermatol. 1997;6(6):298–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.1997.tb00176.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]