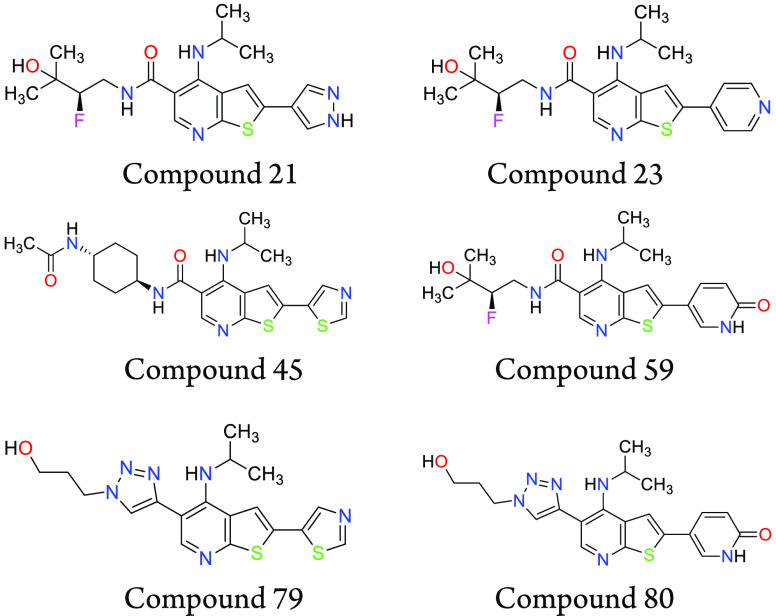
Important Compound Classes
Title
Thienopyridinyl and Thiazolopyridinyl Compounds Useful as IRAK4 Inhibitors
Patent Publication Number
WO 2021/016289 A1
Publication Date
January 28, 2021
Priority Application
US 62/877,334
Priority Date
July 23, 2019
Inventors
Ahmad, S.; Li, L.; Wu, H.; Hynes, J.
Assignee Company
Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, USA
Disease Area
Inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, cancer
Biological Target
Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4)
Summary
Toll/IL-1 receptor family members are important regulators of inflammation and host resistance. The Toll-like receptor (TLR) family recognizes molecular patterns derived from infectious organisms including bacteria, fungi, parasites, and viruses. With the exception of TLR3, all TLRs recruit the adaptor molecule MyD88. Members of the interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) family of serine/threonine kinases are recruited to the receptor via interactions with MyD88. The family consists of four members. Several lines of evidence indicate that IRAK4 plays a critical and nonredundant role in initiating signaling via MyD88 dependent TLRs and IL-1R family members. IRAK4 directly interacts with MyD88 and subsequently recruits either IRAK1 or IRAK2 to the receptor complex to facilitate downstream signaling.
IRAK4 is the only member of the IRAK family whose kinase activity has been shown to be required for initiation of signaling. IRAK4 inhibitors will block all MyD88 dependent signaling. MyD88 dependent TLRs have been shown to contribute to the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, sepsis, systemic lupus erythematosus, inflammatory bowel diseases including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, autoimmune uveitis, asthma, allergy, type I diabetes, and allograft rejection.
Oncogenically active MyD88 mutations in diffuse large B cell lymphomas have been identified that are sensitive to IRAK4 inhibition. Whole genome sequencing also identified mutations in MyD88 associated with chronic lymphatic leukemia suggesting that IRAK4 inhibitors have utility in treating leukemias.
The present application describes a series of novel thienopyridinyl and thiazolopyridinyl compounds as IRAK4 inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory diseases, autoimmune diseases, and cancer. Further, the application discloses compounds and their preparation, use, pharmaceutical composition, and treatment.
Definitions
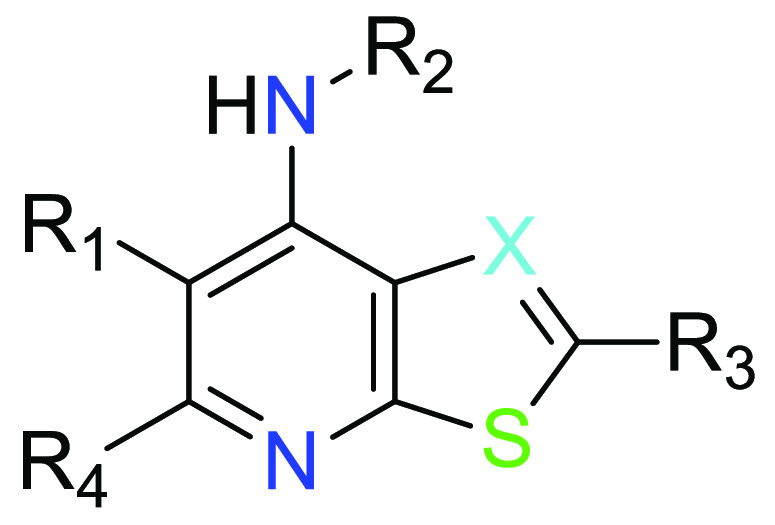
X = CR4 or N;
R1 = (i) −C(O)NHR1a or −C(O)NH(CH2)1–3R1b; or
(ii) pyrazolyl, imidazolyl, isooxazolyl, or triazolyl, each substituted with 0 or 1 R1c;
R2 = (i) C1–6 alkyl substituted with 0 to 4 substituents independently selected from F, Cl, OH and CN; or
(ii) a cyclic group selected from C3–6 cycloalkyl, oxetanyl, tetrahydrofuranyl, tetrahydropyranyl, and pyrazolyl, wherein said cyclic group is substituted with 0 to 3 substituents independently selected from F, OH, CN, C1–2 alkyl, C1–2 fluoroalkyl and C1–2 hydroxyalkyl;
R3 = R3a or -NHR3a; and
R4 = H, F, Cl, CH3 or CF3.
Key Structures
Biological Assay
The IRAK4 inhibition assay was performed. The compounds described in this application were tested for their ability to inhibit IRAK4. The IRAK4 IC50 (μM) are shown in the following table.
Biological Data
The table below shows representative
compounds were tested for IRAK4 inhibition. The biological data obtained
from testing representative examples are listed in the following table.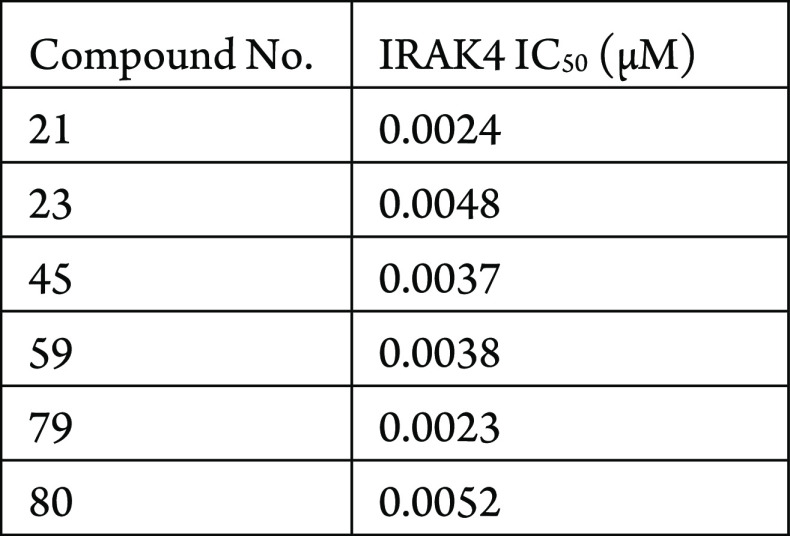
Claims
Total claims: 10
Compound claims: 9
Pharmaceutical composition claims: 1
Recent Review Articles
-
1.
Zheng J.; Wu J.; Ding X.; Shen H. C.; Zou G.. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 38, 127862.
-
2.
Su L.; Xu W.; Huang A.. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102461.
-
3.
Patra M. C.; Shah M.; Choi S.. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 64, 61.
-
4.
Fitzgerald K. A.; Kagan J. C.. Cell 2020, 180, 1044.
-
5.
Bu L.; Baba H.; Yasuda T.; Uchihara T.; Ishimoto T.. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 3468.
-
6.
Robertson S. A.; Hutchinson M. R.; Rice K. C.; Chin P.; Modenhauer L. M.; Stark M. J.; Olson D. M.; Keelan J. A.. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2020, 9, e1121.
The author declares no competing financial interest.