Important Compound Classes
Title
Pyrimidine-5-carboxamide Compound
Patent Publication Number
WO 2021/025975 A1
Publication Date
February 11, 2021
Priority Application
EP 19382686.4 and EP 19382744.1
Priority Date
August 6, 2019 and September 2, 2019
Inventors
Ruenoplaza, G.
Assignee Company
Eli Lilly and Company, USA
Disease Area
Diabetes
Biological Target
Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT)
Summary
Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT) is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a methyl group from the universal methyl donor S-(5′-adenosyl)-l-methionine (SAM) onto nicotinamide (NAM), resulting in the formation of 1-methylnicotinamide (1-MeNAM). NNMT is a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Analogues of nicotinamide have been reported as NNMT inhibitors. Small molecule inhibitors of NNMT for treating metabolic disorders are described. NNMT inhibitors which are efficacious and orally bioavailable are desired.
Increased expression and activity of NNMT has been linked to various disease pathologies including metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, neurodegeneration, and cancer. Of particular interest is the correlation exhibited between adipose NNMT activity and insulin resistance. This mechanism appears to be reversible, as adipose NNMT activity was reduced following interventions that improve insulin resistance. Genetic knockdown of the NNMT gene in mice showed protective effects against diet-induced obesity, and the animals displayed enhanced insulin sensitization, validating its potential utility as a therapeutic target for metabolic disorder and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Amelioration of hyperhomocysteinemia in these patients, via NNMT inhibition may serve as a valuable therapeutic mechanism for the treatment of chronic kidney disease (CKD).
The present application describes a series of novel pyrimidine-5-carboxamide compounds as NNMT inhibitors for the treatment of diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and chronic kidney disease. Further, the application discloses compounds and their preparation, use, pharmaceutical composition, and treatment.
Definitions
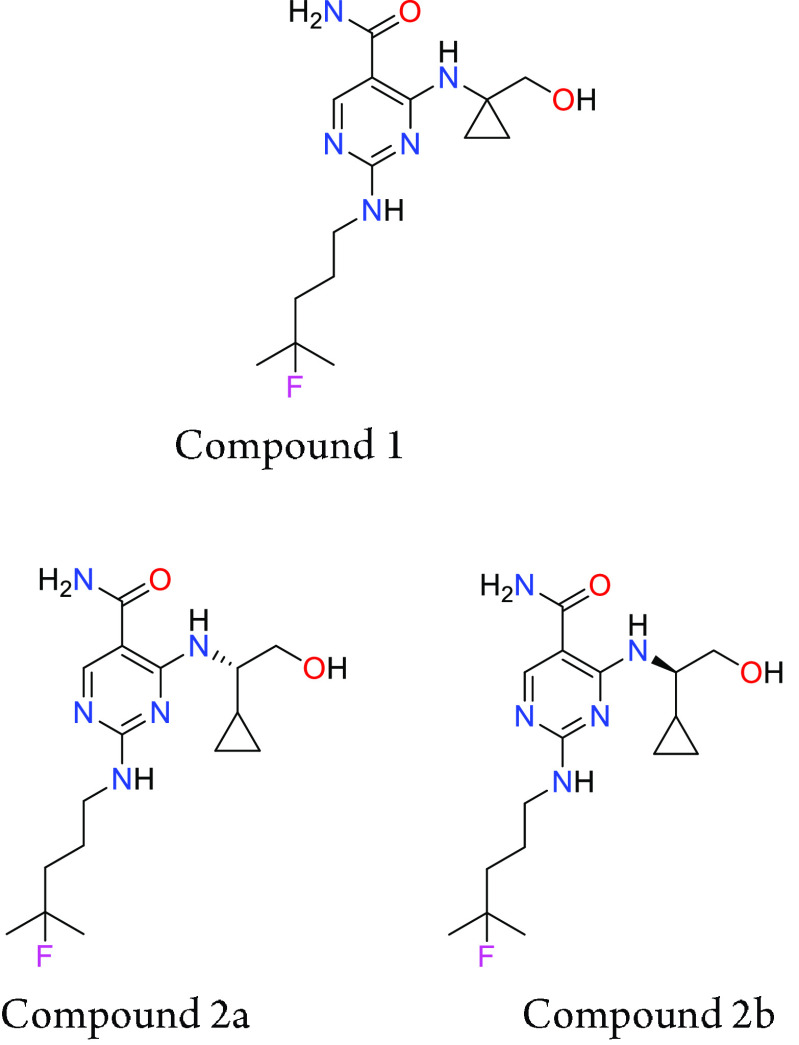
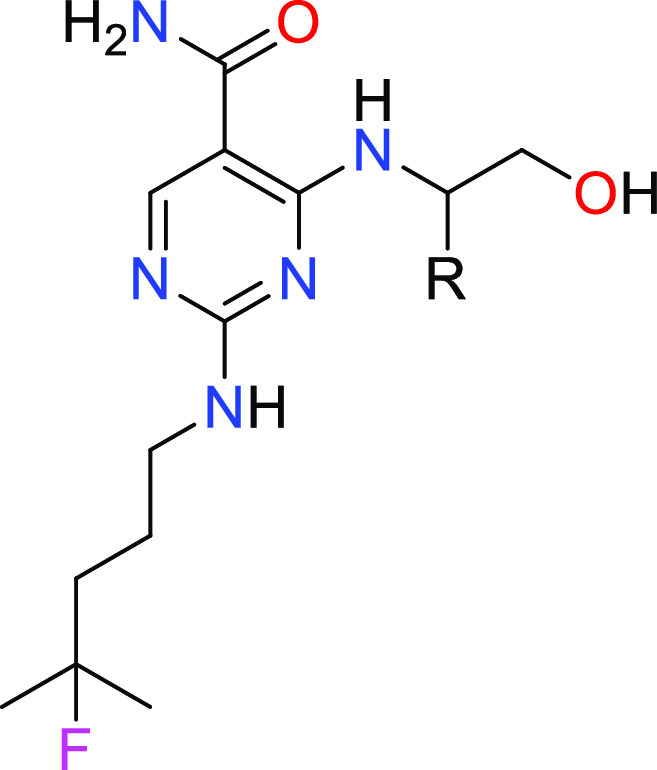
R = cyclopropyl and geminal cyclopropyl.
Key Structures
Biological Assay
The biochemical NNMT inhibition assay in human and mouse was performed. The compounds described in this application were tested for their ability to inhibit NNMT. The NNMT IC50 (nM) are shown in the following table.
Biological Data
The table below shows representative
compounds were tested for NNMT inhibition. The biological data obtained
from testing representative examples are listed in the following table.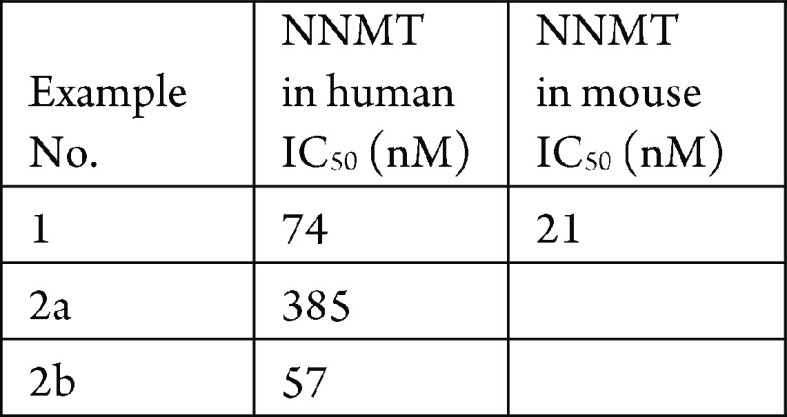
Claims
Total claims: 21
Compound claims: 9
Pharmaceutical composition claims: 1
Method of treatment claims: 7
Use of compound claims: 4
Recent Review Articles
-
1.
Fan L.; Cacicedo J. M.; Ido Y.. J. Diabetes Invest. 2020, 11, 1403.
-
2.
Roberti A.; Fernandez A. F.; Fraga M. F.. Mol. Metab. 2021, 45, 101165.
-
3.
Amjad S.; Nisar S.; Bhat A. A.; Shah A. R.; Frenneaux M. P.; Fakhro K.; Haris M.; Reddy R.; Patay Z.; Baur J.; Bagga P.. Mol. Metab. 2021, 49, 101195.
-
4.
Chandra S.; Srinivasan S.; Batra J.. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 1791.
-
5.
Tang Z.; Xu Z.; Zhu X.; Zhang J.. Cancer Commun. 2021, 41, 16.
The author declares no competing financial interest.