Important Compound Classes
Title
Heteroaryl Compounds for Treating Huntington’s Disease
Patent Publication Number
WO 2020/005877 A1
Publication Date
January 2, 2020
Priority Application
US 62/690,540
Priority Date
June 27, 2018
Inventors
Zhang, N.; Babu, S.; Barraza, S. J.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Chen, G.; Karp, G. M.; Kassick, A. J.; Mazzotti, A. R.; Moon, Y.; Narasimhan, J.; Sydorenko, N.; Turpoff, A.; Woll, M. G.; Yan, W.
Assignee Company
PTC Therapeutics, Inc., USA
Disease Area
Huntington’s disease
Biological Target
Huntington protein
Summary
Huntington’s disease (HD) is a progressive, autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disorder of the brain, having symptoms characterized by involuntary movements, cognitive impairment, and mental deterioration. Death, typically caused by pneumonia or coronary artery disease, usually occurs 13–15 years after the onset of symptoms. The prevalence of HD is between 3 and 7 individuals per 100 000 in populations of western European descent. In North America, an estimated 30 000 people have HD, while an additional 200 000 people are at risk of inheriting the disease from an affected parent. The disease is caused by an expansion of uninterrupted trinucleotide CAG repeats in the “mutant” huntingtin (Htt) gene, leading to production of HTT (Htt protein) with an expanded polyglutamine (polyQ) stretch, also known as a “CAG repeat” sequence. There are no current small molecule therapies targeting the underlying cause of the disease, leaving a high unmet need for medications that can be used for treating or ameliorating HD.
The present application describes a series of novel substituted benzothiazole compounds of Formula (I) or Formula (II), useful for treating or ameliorating Huntington’s disease. Further, the application discloses compounds, their preparation, use, pharmaceutical composition, and treatment.
Definitions
W1, W2 and W3 = C-Ra, or N;
Ra = H, CN, halogen, OH, C1–6alkyl, halo-C1–6alkyl, C1–6alkylcarbonyl, C1–6alkoxy, halo-C1–6alkoxy, C1–6alkoxy-C1–6alkyl, C1–6alkoxy-carbonyl, amino, C1–6alkyl-amino, (C1–6alkyl)2-amino, and hydroxyl-C1–4alkyl;
X = N-Rb, O or a bond;
Rb = H and C1–6alkyl;
R1 = C3–10cycloalkyl and heterocyclyl;
wherein heterocyclyl is a saturated or partially unsaturated 3–7 membered monocyclic, 6–10 membered bicyclic or 13–16 membered polycyclic ring system having 1, 2, or 3 heteroatom ring members independently selected from N, O or S; and
wherein C3–10cycloalkyl and heterocyclyl is optionally substituted with one, two, three or four R3 substituents and optionally, with one additional R4 substituent, or
wherein C3–10cycloalkyl and heterocyclyl is optionally substituted with one, two, three, four, or five R3 substituents; and
R2 = phenyl or heteroaryl;
wherein heteroaryl is a 3–7 membered monocyclic, 6–10 membered bicyclic ring system having 1,2,3,or 4 heteroatom ring members independently selected from N, O, or S;
wherein phenyl and heteroaryl is optionally substituted with one, two, or three R5 substituents and optionally, with one additional R6 substituent, or,
wherein phenyl and heteroaryl is optionally substituted with one, two, three, or four R5 substituent.
Key Structures
Biological Assay
The endogenous Huntington protein assay was performed. The compounds described in this application were tested, and their IC50 (μM) values are shown in the following table.
Biological Data
The table below
shows representative
compounds that were tested. The biological data obtained from testing
representative examples are listed in the following table. For IC50: (*) means between >3.0 and ≤9.0 μM; (**)
means
between >1.0 and ≤3.0 μM; (***) means between >0.5
and
≤1.0 μM; (****) means between >0.1 and ≤0.5
μM;
(*****) means ≤0.1 μM.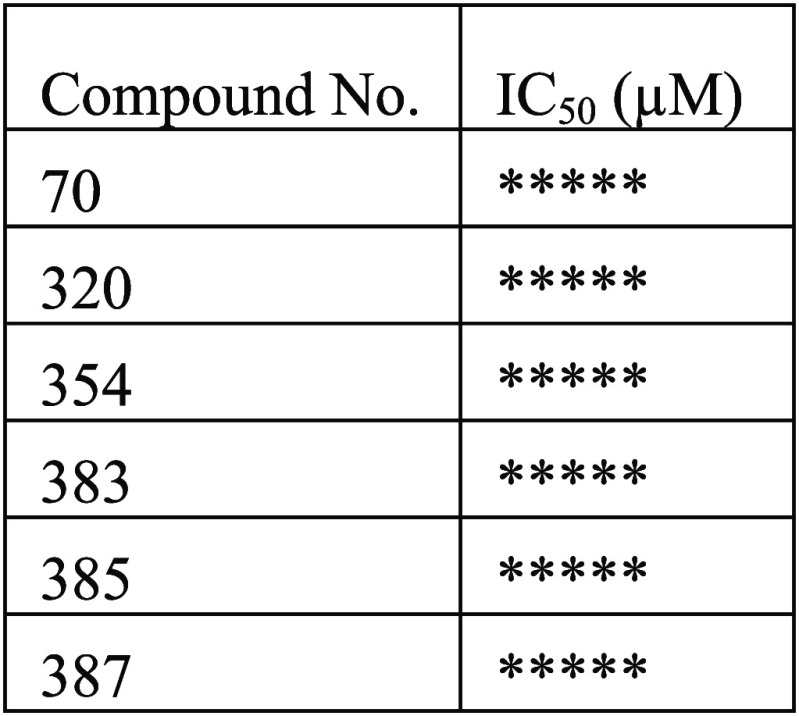
Claims
Total claims: 17
Compound claims: 7
Pharmaceutical composition claims: 2
Method of treatment claims: 2
Use of compound claims: 6
Recent Review Articles
-
1.
Moldovean S. N.; Chis V.. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 105.
-
2.
Kumar A.; Kumar V.; Singh K.; Kumar S.; Kim Y.; Lee Y.; Kim J.. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 43.
-
3.
Lebouc M.; Richard Q.; Garret M.; Baufreton J.. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 145, 105076.
-
4.
Karagas N. E.; Rocha N. P.; Stimming E. F.. J. Huntington's Dis. 2020, 9, 107.
-
5.
Stahl C. M.; Feigin A.. Neurol. Clin. 2020, 38, 367.
-
6.
Taran A. S.; Shuvalova L. D.; Lagarkova M. A.; Alieva I. B.. Cells 2020, 9, 1514.
The author declares no competing financial interest.




