Figure 5. Functional associations with emotion metacognition.
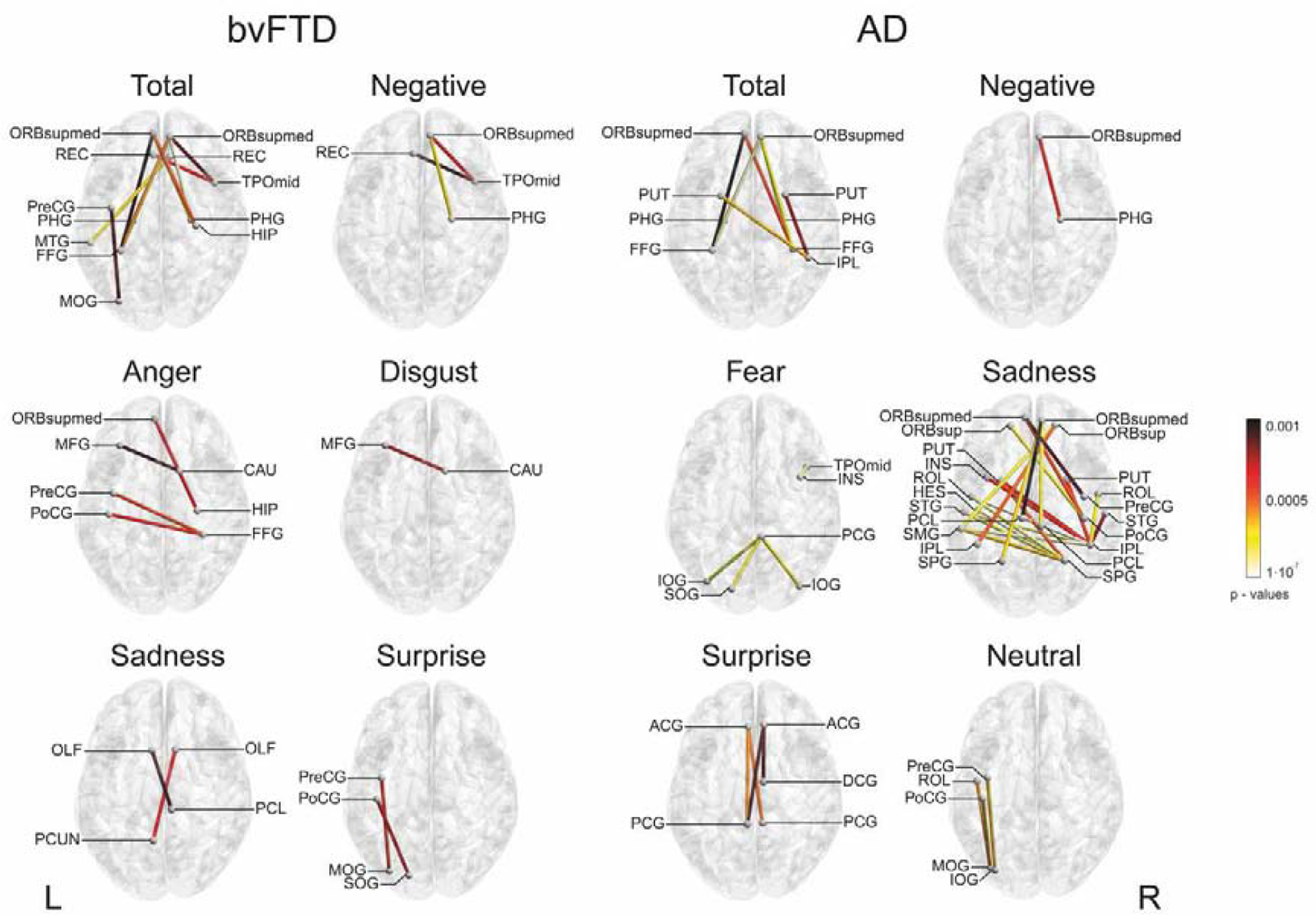
Spearman’s correlations were performed between resting-state functional connectivity of bvFTD-controls and AD-controls and the MI in each patient group and emotion (p < 0.001). Only negative correlations were considered. ACG = anterior cingulate gyrus; CAU = caudate nucleus; DCG = dorsal cingulate gyrus; FFG fusiform gyrus; HES = Heschl’s gyrus; HIP = hippocampus; INS = insula; IOG = inferior occipital gyrus; IPL = inferior parietal gyrus; MFG = middle frontal gyrus; MOG = middle occipital gyrus; MTG = middle temporal gyrus; OLF = olfactory cortex; ORBsup = superior frontal gyrus; ORBsupmed = orbitofrontal gyrus; PCG = posterior cingulate gyrus; PCL = paracentral lobule; PCUN = precuneus; PHG = parahipocampal gyrus; PoCG = postcentral gyrus; PreCG = precentral gyrus; PUT = putamen; REC = gyrus rectus; ROL = Rolandic operculum; SMG = supramarginal gyrus; SOG = superior occipital gyrus; SPG = superior parietal gyrus; STG = superior temporal gyrus; TPOmid =middle temporal pole; L = left, R = right.
