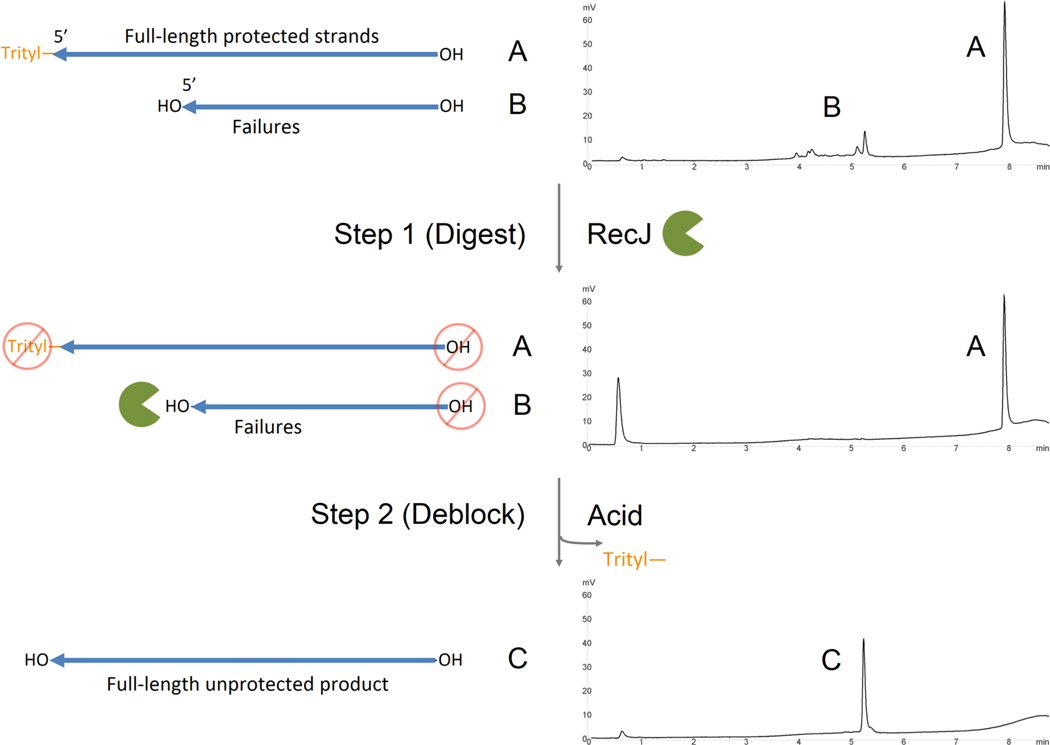
Figure 1.
Method of RecJ digestion of oligonucleotide truncated failure strands in aqueous solution. Here, oligonucleotides are first synthesized trityl-on, removed from the instrument, cleaved, and deprotected according to the manufacturer’s protocol. In step 1 of the enzymatic purification method, the crude sample is treated with RecJ (green Pac-Man character) at 37 °C; while the trityl-on FLP is untouched (A), only those ssDNA molecules with a free 5′-hydroxyl group are digested (hydrolyzed) by RecJ (B). In step 2, a weak acid [0.1 M NaOAc (pH 3.5)] is added to the reaction mixture to detritylate FLP, yielding a 5′-hydroxyl group (C). The sample is then passed through a Sephadex (G-50 fine) column to remove acetate, trityl, and hydrolysis product. This yields a purified, desalted sample ready for downstream application. Each step is accompanied by a RP HPLC chromatogram depicting various oligonucleotide species present in the reaction.