Figure 8.
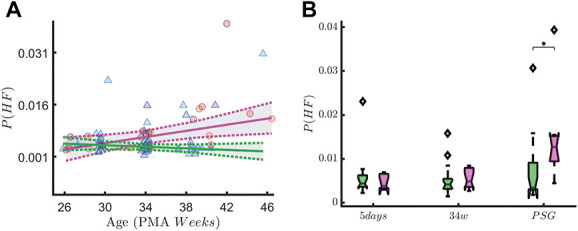
High-frequency oscillations in early-GA patients. The figure shows the association with the vagal tone (P(HF)) and early skin-breaking procedures (SBPs). Data are reported for the patients with gestational age below 29 weeks (n = 31) during QUIET sleep (QS). The left panel shows how the P(HF) maturational trend differs in case of high SBPs (magenta curve, SBP ≥50) compared to low SBPs (green curve, SBP <50). SBPs seem to increase the power of HF oscillations. The right panel shows the boxplot trend as output of the two-way ANOVA: the division between HIGH SBPs and LOW SBPs is reported for each recording time. The P-value associated to the ANOVA is reported on y-axis, whereas the output of the Tukey–Kramer multiple comparison test is reported below each boxplots group. A significant SBP-by-measuring point interaction on P(HF) is found in quiet sleep (F(2,67) = 3.49, P = 0.04). High-frequency oscillations also increases over time (main effect of measuring point: F(2,67) = 6.49, P ≤ 0.01). Post hoc analysis showed this difference in HF oscillations between the HIGH and LOW SBP group is only significantly different at the last, PSG, recording (P = 0.04, indicated as * in the figure). ANOVA, analysis of variance; GA, gestational age; HF, high-frequency.
