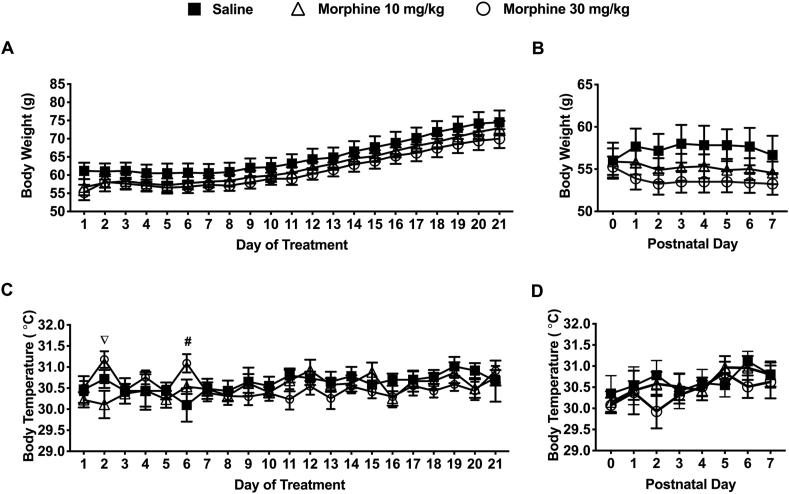
Figure 2.
Maternal changes during the gestational treatment period and early post-partum period (PND 0–7). a) There was no significant difference between treatment groups on the body weights of dams during gestation or during the early postpartum period (PND 0–7) parturition (AUC [Weight] – Saline: 1302 21.12; 10 mg/kg: 1251 17.38; 30 mg/kg: 1225 18.66). (b) During the early postpartum period (PND 0–7), 10 mg/kg morphine (N = 9) and 30 mg/kg morphine (N = 9) treated dams had lower (non-significant) body weights compared to saline-treated controls (N = 6) (AUC [Weight] – Saline: 402.5 9.82; 10 mg/kg: 386.3 7.95; 30 mg/kg: 375.3 6.64). (c) On the 2nd day of treatment, dams treated with 30 mg/kg morphine (N = 9) had significantly higher body temperatures compared to 10 mg/kg morphine (N = 9) treated dams. On the 6th day of treatment, spiny mice treated with 30 mg/kg morphine (N = 9) had significantly higher body temperatures than compared to saline-treated controls (N = 6) (AUC [Temperature] – Saline: 612.5 1.99; 10 mg/kg: 610.6 2.11; 30 mg/kg: 610.3 1.85). (d) During the early postpartum period (PND 0–7) there was no significant difference in body temperatures between treatment groups (AUC [Temperature] – Saline: 214.6 1.61; 10 mg/kg: 214.3 1.52; 30 mg/kg: 212.8 1.73). Data are presented as means totals (±SEM) during an approximate 21-day treatment/gestation period and a PND 0–7 period. An pound symbol (# = saline vs. 30 mg/kg morphine) or nabla symbol (∇ = 10 mg/kg morphine vs. 30 mg/kg morphine) are used to indicate a significant difference between groups, P < 0.05.