In the article titled “A Case of Epistaxis as the First Sign of Acute Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura” [1], Figure 1 was formatted incorrectly. The authors have corrected this error and provided the correct Figure 1 as follows:
Figure 1.
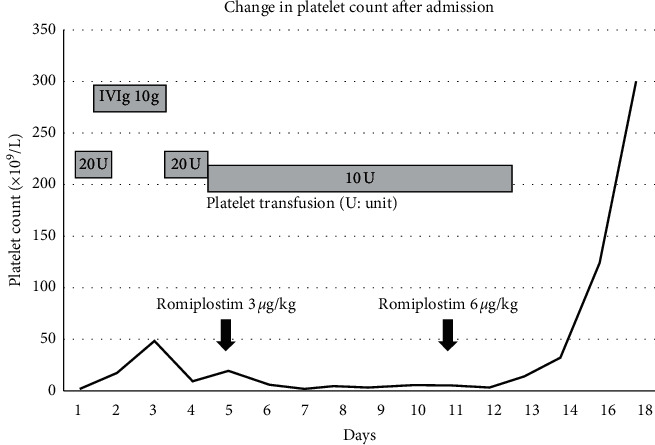
Change in platelet count after admission. The patient underwent treatment with platelet transfusion, high-dose intravenous gamma-globulin (IVIG), and romiplostim. Platelet counts increased about 14 days after admission.
References
- 1.Tajima S., Matsumoto F., Anzai T., Hara S., Suzuki Yo, Ikeda K. A Case of Epistaxis as the First Sign of Acute Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Case Reports in Otolaryngology. 2021;2021:4. doi: 10.1155/2021/6612939.6612939 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


