Abstract
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic continues its global spread. Coordinated effort on a vast scale is required to halt its progression and to save lives. Electronic health record (EHR) data are a valuable resource to mitigate the COVID-19 pandemic. We review how the EHR could be used for disease surveillance and contact tracing. When linked to “omics” data, the EHR could facilitate identification of genetic susceptibility variants, leading to insights into risk factors, disease complications, and drug repurposing. Real-time monitoring of patients could enable early detection of potential complications, informing appropriate interventions and therapy. We reviewed relevant articles from PubMed, MEDLINE, and Google Scholar searches as well as preprint servers, given the rapidly evolving understanding of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Abbreviations and Acronyms: COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; EHR, electronic health record; eMERGE, Electronic Medical Records and Genomics; GWAS, genome-wide association study; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
Article Highlights.
-
•
This review summarizes the potential of the electronic health record for COVID-19 surveillance, contact tracing, identification of genetic susceptibility variants, risk stratification, and real-time monitoring.
-
•
We discuss how such approaches can be useful in gaining insights into COVID-19 risk factors, pathophysiologic changes, disease complications, and drug repurposing.
-
•
We describe how new consortia are assembling to identify factors influencing susceptibility to COVID-19 and disease severity through linkage of “omics” data to electronic health record data.
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), an ongoing worldwide pandemic disease caused by infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has a wide spectrum of disease severity with diverse presentation and organ system involvement. More than 148 million cases have been documented and more than 3.1 million deaths have resulted worldwide as of April 27, 2021.1 A coordinated scientific effort on a vast scale is necessary to mitigate the widespread misery, morbidity, and mortality inflicted by the pandemic.
Many similarities have been drawn between the current pandemic and the influenza pandemic of 1918. However, one major difference is the availability of several data sources to track and to mitigate the effects of the pandemic. In this review, we examine use of the electronic health record (EHR) to address the COVID-19 pandemic. EHR data can facilitate disease surveillance and contact tracing; enable risk stratification and real-time monitoring for early detection and management of severe disease; identify risk factors and disease complications, including long-term sequelae; provide insights into the pathophysiologic process using “omics” approaches; and serve as a platform for innovations related to artificial intelligence, remote monitoring, and early detection of pandemics.
Disease Surveillance and Contact Tracing
Outbreaks of infectious diseases are traditionally monitored by active surveillance and contact tracing. Contact tracing is a time-consuming process whereby the individual representing the index case detected by surveillance is asked to provide details about other people who were in close contact during the time frame that puts them at risk of acquiring infection. Public health officials then trace these contacts and inform them about the possible exposure, leading to quarantine and testing.2 Given the extent of the COVID-19 pandemic and its rapid spread, conventional contact tracing is not feasible in most regions; however, mobile device data linked to the EHR are a potential alternative. Various apps for mobile devices have been developed to collect and to share COVID-19–related tracking information.3 App users can enter information when they test positive with COVID-19, and other users are then alerted if they were close to an infected individual during a prespecified amount of time before testing positive.4
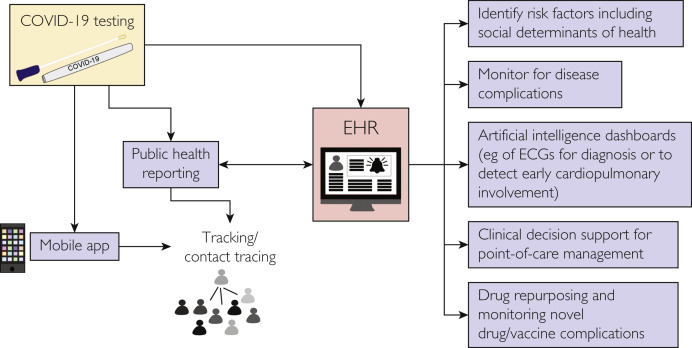
This information can also be shared with public health officials, depending on the permissions and capabilities of the app,5 and it could be linked to the EHR of health systems, triggering an alert in the system when an individual tests positive for COVID-19 (Figure 1 ). The public-private collaboration Sync for Science is an example of how individuals could share such EHR data with researchers.6 These approaches may improve modeling of COVID-19 transmission as shown in studies from Brazil7 and the United States8 that used mobile phone geolocation data. However, it is important to balance public good with personal privacy in employing such techniques.9 Tracking of cases and data on infection rates, deaths, hospitalization, and patient recovery metrics at the local/county, state/district, national, and global levels is critical to inform policy and strategy related to the pandemic. This has led to creation of publicly available online tracking tools such as the COVID-19 Dashboard developed by the Johns Hopkins University.1
Figure 1.
Using the electronic health record (EHR) and mobile apps in managing the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. ECGs, electrocardiograms.
Electronic Health Record–Based Algorithms for Risk Stratification
Risk Stratification
Phenotyping algorithms can be deployed across EHR systems to rapidly ascertain comorbidities, multiorgan complications, and disease severity in patients with COVID-19. Predictive electronic algorithms could identify patients heading toward invasive ventilator support and allow early interventions to reduce risk of progression. These algorithms leverage rule-based strategies or machine learning to help identify patients with a particular clinical profile by querying a wide spectrum of EHR data elements, such as coded diagnoses and procedures or clinical notes through natural language processing, laboratory tests, medications, and imaging studies.10 As case numbers continue to rise throughout the world, substantial EHR data are being generated for patients who have tested positive for COVID-19 and subsequently developed related complications. One study11 used data from the health system in Ontario, Canada, to develop a logistic regression–based model that included age and the presence of certain comorbidities (diabetes, renal disease, and immunocompromised state) to predict mortality. In UK Biobank participants, a model including clinical risk factors and 64 single-nucleotide variants was developed to predict risk of severe COVID-19.12
Phenotyping and Common Data Models
The Electronic Medical Records and Genomics (eMERGE) network has created the Phenotype KnowledgeBase13 to catalog and to share electronic phenotyping algorithms across different institutions and to conduct large-scale genomic studies.14 To date, 94 phenotyping algorithms have been validated, and 53 of those are finalized and publicly available. Whereas many of these are relevant to COVID-19, the eMERGE network is currently developing phenotyping algorithms specific for COVID-19–related complications, including acute myocardial injury, arrhythmias, ischemic stroke, thromboembolic disease, bleeding diathesis, acute kidney injury and progression to chronic kidney disease, and interstitial lung disease, among others. A challenge is to develop algorithms that detect these complications within a narrow window temporally related to acute COVID-19 infection.
Portability of phenotyping algorithms across platforms can be challenging because of heterogeneity of data representations in different institutions and biorepositories.15, 16, 17 Recently, PhenX18 , 19 (Phenotypes and eXposures)—a catalog of measurement protocols and bioinformatics tools to promote unified study design, data integration, and analyses among researchers—added a COVID-19 page20 for compiling and distributing COVID-19 protocols currently in use. Common data models,21 such as the Informatics for Integrating Biology and the Bedside (i2b2)22 and the Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership,23 may help harmonize data from diverse EHR systems. Tools to standardize the execution of computable phenotype representations,24 , 25 tools to assess and to quantify the portability of phenotyping algorithms,10 and machine learning–based methodologies26 for constructing and sharing phenotype classifiers across sites are being developed to facilitate COVID-19 research.
Risk Factors and Complications
Social Determinants of Health
Numerous studies have demonstrated that COVID-19 is not evenly distributed among the population, with higher rates of COVID-19 positivity, hospitalizations, and deaths in individuals with any of the following characteristics: male sex, older age, nonwhite ethnicity, higher body mass index, lower income, and smokers.27, 28, 29, 30, 31 Reasons for these disparities are likely to include factors such as increased number and severity of comorbid conditions, inability to work from home, and lack of access to health care. Indeed, mobile phone geolocation data8 reveal that increased rates of infection among disadvantaged socioeconomic groups are in part due to the inability of these groups to reduce mobility to the degree of other groups. Documenting social determinants of health in the EHR can increase our understanding of how these factors are associated with risk of infection and severity of illness.
Comorbidities Associated With Complications of Severe COVID-19
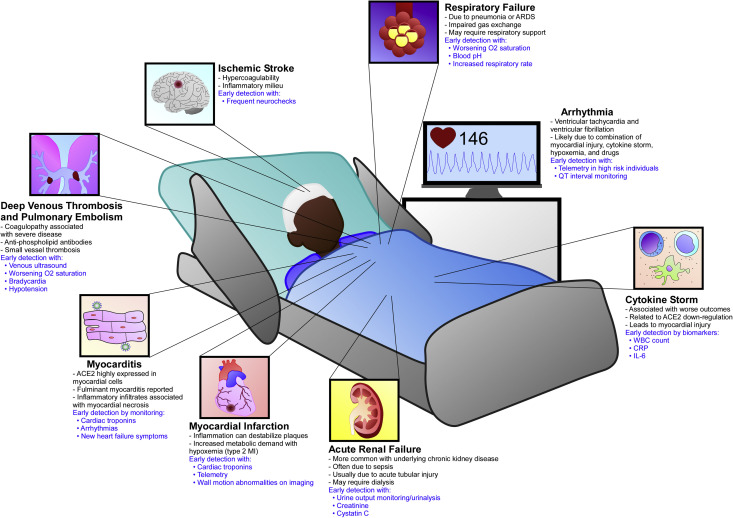
The EHR can aid in the identification of comorbidities related to disease severity and associated complications. Elderly patients with multiple comorbidities make up most of the severely ill patients with COVID-19.32, 33, 34 These comorbid conditions include obesity, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease,35 and their presence increases risk of myocardial injury and myocardial infarction, malignant arrhythmias, thromboembolic disease including pulmonary embolism and stroke, acute kidney injury, acute respiratory distress syndrome, cytokine storm, and death.33 , 34 Table 1 summarizes these complications and highlights how electronic algorithms linked to clinical decision support can be used for their early detection and management. Figure 2 depicts multisystemic complications that can occur in an infected patient.
Table 1.
Managing Complications of Severe COVID-19 With Use of EHR Data
| Complication | Pathogenesis | Imaging and laboratory data | Early detection | Clinical decision support | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immunopathology and cytokine storm | Proposed causes include down-regulation of ACE2 leading to unopposed angiotensin II in the setting of direct viral infection, genetic variation in inflammatory cascades, and antibody-dependent enhancement from prior exposure to other coronaviruses. | Elevated CRP, IL-6, leukocyte count | Baseline leukocyte count and CRP | Electronic algorithms incorporating vital signs, laboratory values of inflammatory markers, supplemental oxygen requirements, decline in oxygen saturation could prompt anti-inflammatory therapies (ie, dexamethasone, colchicine, or canakinumab) or cardioprotective therapies (ie, angiotensin receptor blockers) if trials prove these to be effective. | 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44 |
| Leads to multiorgan damage including myocardial injury and ARDS | |||||
| May be involved in multisystem inflammatory syndrome | |||||
| Myocardial injury | Defined by elevated troponin levels | Elevated levels of troponin, NT-proBNP | Baseline troponin and NT-proBNP in all individuals at time of hospitalization/emergency department evaluation | Periodic monitoring of troponin or NT-proBNP during hospitalization in high-risk individuals could inform decisions on length of stay and need for higher or lower level of care. Electronic algorithms incorporating multiple markers will provide useful prognostication and risk stratification information. | 34,35,45 |
| Presumably due to hostile inflammatory milieu in many cases, but may be due to direct viral infection, myocardial infarction, or malignant arrhythmias | Could be used to identify high-risk individuals who should be admitted for close observation rather than discharged home | ||||
| Associated with adverse outcomes and death in COVID-19 patients | |||||
| Myocarditis | Presumed direct myocyte infection by SARS-CoV-2 through ACE2 receptor | Cardiac MRI, ECG, and echocardiography | Requires high index of clinical suspicion | NLP of imaging reports, ECG monitoring, development of new heart failure symptoms, and real-time incorporation of laboratory data | 46, 47, 48 |
| Elevated levels of troponin, NT-proBNP | Baseline troponin and NT-proBNP would support this in the right clinical context. | ||||
| Myocardial infarction | Prothrombotic, systemic inflammatory milieu and elevated shear stress due to increased coronary blood flow requirements can precipitate plaque rupture, resulting in type 1 acute myocardial infarction. | ECG, echocardiography, cardiac stress tests, coronary angiography | Modifications of existing diagnostic protocols examining patient history, ECG, telemetry, age, risk factors, and cardiac troponin levels | Real-time review of troponin levels, telemetry monitoring, and NLP of ECG and imaging reports could identify individuals requiring either coronary angiography or anticoagulation for type 1 or 2 acute myocardial infarctions, respectively. | 49,50 |
| Increases in metabolic demand from systemic infection coupled with decreased oxygen supply from viral lung disease or ARDS can lead to demand ischemia and type 2 acute myocardial infarction. | Elevated troponin levels | ||||
| Malignant arrhythmia | Thought to be due to a combination of myocardial injury, hypoxemia from lung injury, cytokine storm, heightened inflammatory milieu, genetic predisposition, or medication adverse effects | ECG and telemetry | Telemetry monitoring in high-risk individuals, especially if prolonged QT is observed on ECG or the patient is taking high-risk medications | Rapid detection of malignant arrhythmias by telemetry monitoring should prompt medical and electrical defibrillation therapy. | 34,45,51 |
| Coagulopathy and pulmonary vessel thrombosis | Likely multifactorial: inflammatory cytokines, endothelial dysfunction, and oxidative stress, exacerbated by increased unopposed angiotensin II; some cases are associated with antiphospholipid antibodies. | Chest CT angiography, V/Q scan, Doppler ultrasound | Detection of decreased oxygen saturation/increased oxygen requirements, bradycardia, hypotension, and new symptoms of dyspnea or lower extremity swelling | Algorithms including real-time incorporation of laboratory values, vital signs, oxygen saturation/supplemental oxygen requirements, and NLP of patient’s symptoms documented in the EHR detecting high risk of venous thromboembolism should prompt imaging or anticoagulation initiation. | 34,35,52, 53, 54, 55, 56 |
| Can range from microangiopathy and DIC to larger-vessel thrombosis (coronary artery, DVT, PE) | Abnormalities in D-dimer, fibrinogen, PT, aPTT, platelets | Home-going oxygen saturation monitoring for individuals with elevated risk who are not admitted to the hospital | |||
| Thrombocytopenia is common and associated with poor outcomes. | |||||
| Ischemic stroke | Higher incidence of stroke in patients with severe COVID-19 may result from hypercoagulable and proinflammatory state. | Brain MRI, head CT | Evidence of hypercoagulability or elevated inflammatory markers could prompt more frequent neurochecks in hospitalized patients or admission of patients for close monitoring who otherwise might be dismissed from emergency departments. | Real-time NLP of nursing notes for neurochecks could prompt stroke pager activation for early imaging and subsequent treatment with fibrinolytic therapy. | 54,57, 58, 59 |
| Elevated levels of D-dimer, CRP, IL-6 | |||||
| Acute renal failure | More common with underlying chronic kidney disease | Increased serum creatinine or cystatin C | Obtain baseline serum creatinine or cystatin C level. Closely monitor urine output in hospitalized patients. These are especially important in patients with underlying chronic kidney disease or who present with sepsis. | Automated algorithms tracking urine output and creatinine or cystatin C trends can alert providers of likely acute renal failure and highlight any nephrotoxic medications that could be held. | 60,61 |
| Occurs frequently when patients are in sepsis or shock and usually is due to acute tubular injury | Urinalysis/microscopy | ||||
| Associated with poor outcome and may require dialysis | |||||
| Respiratory failure | Likely multifactorial, including direct infection of alveolar cells, inflammation including cytokine storm, pulmonary embolism, and neurologic involvement. This can lead to dyspnea with adequate oxygenation, hypoxemia requiring supplemental oxygen or PAP therapy, or ARDS requiring mechanical ventilation, prone positioning, and ECMO. | Chest radiograph, chest CT, ultrasound | Oxygen saturation at home, physician’s office, emergency department, or hospital | Real-time electronic monitoring of oxygen saturation, supplemental oxygen requirements, arterial or venous blood gases with pH, and respiratory rate can alert providers of the high likelihood of impending respiratory failure prompting consideration of escalation to intensive care. | 62, 63, 64 |
| Arterial and venous blood gas determinations with pH |
ACE2, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; AI, artificial intelligence; aPTT, activated partial thromboplastin time; ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; CRP, C-reactive protein; CT, computed tomography; DIC, disseminated intravascular coagulation; DVT, deep venous thrombosis; ECG, electrocardiography; ECMO, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; EHR, electronic health record; IL-6, interleukin 6; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; NLP, natural language processing; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro–B type natriuretic peptide; PAP, positive airway pressure; PE, pulmonary embolism; PT, prothrombin time; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Figure 2.
Electronic health record–based strategies for early detection of complications in severe COVID-19. Complications include pulmonary, cardiovascular, renal, and neurologic. Myocardial injury in COVID-19 can occur through several nonmutually exclusive mechanisms, including myocarditis, myocardial infarction, cytokine storm, heart strain from pulmonary embolism, and malignant arrhythmias. Blue text highlights areas where early detection through informatics approaches can lead to improvement in patient care. ACE2, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome; CRP, C-reactive protein; IL-6, interleukin 6; MI, myocardial infarction; WBC, white blood cell.
Laboratory Markers of Severe Disease
Clinical laboratory results are present as structured data in the EHR and can be mined with relative ease, cross-sectionally as well as to profile temporal changes.65 The Consortium for Clinical Characterization of COVID-19 by EHR (4CE) consortium,66 the eMERGE network, and other consortia are studying the association of laboratory abnormalities with outcomes in COVID-19. Laboratory findings associated with poor outcomes include an increasing white blood cell count with lymphopenia; prolonged prothrombin time; and elevated levels of liver enzymes, lactate dehydrogenase, D-dimer, interleukin 6, C-reactive protein, and procalcitonin.7 , 67 , 68 Markers of cardiac,69 immune,70 coagulation,71 muscle,72 hepatic,32 and renal73 injury or dysfunction are also associated with severe disease. Electronic algorithms incorporating real-time laboratory data, especially cardiac troponins and inflammatory markers, could be useful in early detection of complications and linked to clinical decision support for appropriate escalation of care to decrease morbidity and mortality.
Target Organ Damage
Although most individuals appear to recover completely after infection with SARS-CoV-2, some have persistent target organ damage. Whereas there are significant data on acute and short-term complications, not much is known about long-term target organ damage in COVID-19 survivors. EHR data will be important for tracking and understanding of persistent target organ damage consequent to COVID-19. Target organ damage can include cardiovascular (eg, myocarditis, pericarditis, microvascular angina, arrhythmias), pulmonary (eg, interstitial lung disease, chronic pulmonary emboli), neurologic (eg, myelopathy, neuropathy, neurocognitive disorders), renal (eg, chronic kidney disease), and others (eg, multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children).74 For example, in a study47 of patients who had recovered from COVID-19 with initial diagnosis occurring between 64 and 92 days previously, most continued to have elevated high-sensitivity troponin levels, lower left ventricular systolic function, and imaging evidence of ongoing myocardial inflammation.
"Long COVID"
Many individuals experience persistent symptoms and a decline in health-related quality of life after COVID-19.75 , 76 These can include a variety of nonspecific symptoms, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, headache, loss of taste and smell, and brain fog.74 , 75 , 77 Whether COVID-19 survivors will completely recover from these persistent symptoms is not yet clear.78 Congress recently allocated $1.15 billion for the National Institutes of Health to support research into "long COVID".79 This includes efforts to develop an EHR-based registry detailing symptoms that is linked to blood, tissue, and other samples from patients. The EHR data will be valuable to further characterize "long COVID."
Electronic Health Record–Based Omics Approaches
Viral Genomics
The SARS-CoV-2 is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus with a genome of about 30 kilobases. It has a high mutation rate similar to other RNA viruses,80 potentially allowing altered infectivity, pathogenesis, and development of drug resistance and vaccine evasion. Presently, EHR systems do not track the genetic variants detected in patients, but as sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 genomes becomes more common, such information could be incorporated in the EHR to trace clusters of community-acquired transmission and to identify specific concerning variants.81 This information can also be used to monitor success of control measures, treatments, and vaccination efforts.82 Tracing mutation hot spots and conserved regions in the viral genome could inform future drug and vaccine development and appropriate contact and travel restrictions to curb spread of new variants.
Host Genomic Studies
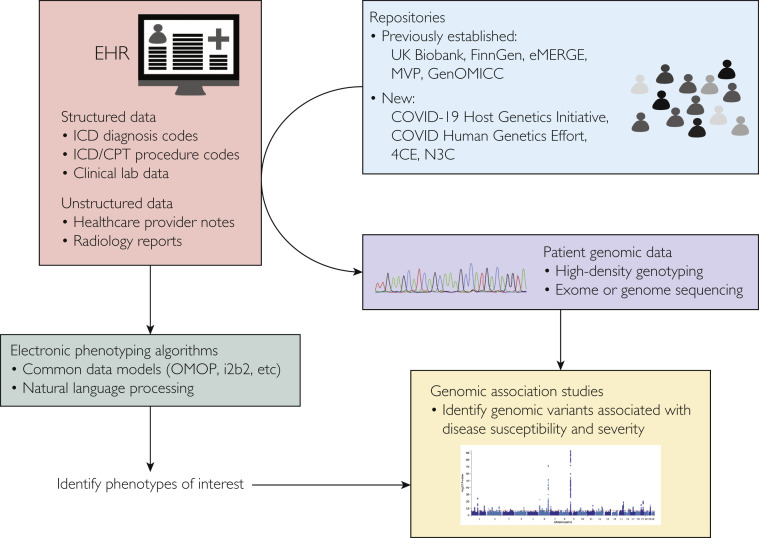
Host genomes influence disease severity for many respiratory pathogens,83 including COVID-19. Early studies primarily addressed epidemiologic84, 85, 86 and clinical characteristics7 , 84 , 87 of COVID-19 and the characteristics of the SARS-CoV-2 genome.88, 89, 90 As interindividual variation in COVID-19 disease severity became apparent, a search began for host genetic variants that may underlie this variability. The linkage of EHR data to patient genotype/sequence data from DNA biorepositories allowed rapid assembly of large national and international consortia to better understand the contribution of common DNA sequence variants to COVID-19 disease severity91 , 92 (Table 2 ; Figure 3 ).
Table 2.
Repositories of Genomic Data Linked With EHR Data Relevant to Study of COVID-19
| Repository | Description | Citations |
|---|---|---|
| Previously existing repositories | ||
| UK Biobank | Contains patient health information, clinical laboratory and radiology information, genomic data, and other relevant information from more than 500,000 participants in the United Kingdom. Data regarding COVID-19 are updated frequently and are available to researchers through an application process. Summary statistics are freely available. | https://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/93 |
| https://pan.ukbb.broadinstitute.org/94 | ||
| http://pheweb.sph.umich.edu/SAIGE-UKB/95 | ||
| FinnGen | A public-private collaborative effort that brings together Finnish universities, hospital and hospital districts, and a nationwide network of Finnish biobanks to combine genome information with digital health care data from national health registries. FinnGen contains data of more than 135,000 participants (data freeze 3) and is actively collecting data on COVID-19 status of participants based on the Finnish National Infectious Diseases Register and regularly updates this information. Data access can be obtained through collaboration with a FinnGen partner. Summary statistics are freely available. | https://www.finngen.fi/en96 |
| eMERGE | A consortium of multiple academic medical centers throughout the United States with EHR and genotype data for more than 136,000 participants. As part of phase 4, several sites are developing phenotyping algorithms for the early detection of complications from COVID-19. Data can be accessed through collaboration with an eMERGE partner. Electronic phenotyping algorithms from eMERGE are posted to the PheKB website. | https://emerge-network.org/97 |
| http://phekb.org13,14 | ||
| MVP | A research program that links EHR and genomic data from more than 825,000 US military veterans registered at the Veterans Health Administration. Investigators are analyzing complications of COVID-19 infection; disease severity and outcomes; and response to various medications, including the influence of race and ethnicity on disease susceptibility, severity, and outcomes. | https://www.research.va.gov/mvp/98 |
| GenOMICC | A global community of scientists and physicians established in 2016 to gather genomic information on patients with critical illness, including COVID, Middle Eastern respiratory syndrome virus, and influenza. They have partnered with the UK-wide COG viral sequencing group and have published a GWAS examinng associations of COVID-19 with disease severity as discussed in the main text. | https://genomicc.org/99 |
| New consortia assembled in the COVID-19 era | ||
| COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative | A consortium created to foster the sharing of resources, such as protocols to facilitate COVID-19 host genetics research; to organize and coordinate analyses across participating sites; and to provide a platform to share summary-level and individual-level data among the scientific community. This initiative currently includes ~190 individual studies, a number that will grow as more biobanks/EHR-linked biorepositories contribute COVID-19–related data. | https://www.covid19hg.org/100, 101, 102 |
| N3C | A repository of patient-level data from many clinical centers within the United States that will use common data models to reveal patterns of risk factors, comorbidities, and testing among COVID-19 patients. This collaborative currently includes more than 120,000 positive COVID-19 patients and hundreds of thousands of negative controls. | https://ncats.nih.gov/n3c103 |
| 4CE | A consortium that collects COVID-19 cases from 96 hospitals in 5 countries including France, Germany, Italy, Singapore, and the United States. It seeks to standardize information sharing and storage for patients’ characteristics as well as laboratory values of renal function, liver function, systemic inflammation, coagulopathy, and immune responses in these patients by using the Informatics for Integrating Biology and the Bedside (i2b2) and Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership (OMOP) platforms to produce a common data model across institutions to increase power in future analyses. | https://covidclinical.net/66,104 |
| COVID Human Genetic Effort | An international consortium focused on identifying rare and common genetic variants causing inborn errors of immunity that predispose to severe cases of COVID-19 as well as monogenic variants that provide resistance to the SARS-CoV-2 infection. | https://www.covidhge.com105 |
| SPHERES | A United States–based national open genomics consortium for COVID-19 that allows public health experts to monitor genetic changes within the circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants and to support contact tracing as well as advance public health research in transmission dynamics, host responses, and virus evolution. | https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/cases-updates/spheres.html106 |
4CE, Consortium for Clinical Characterization of COVID-19 by EHR; COG, COVID-19 Genomics; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; eMERGE, Electronic Medical Records and Genomics; EHR, electronic health record; GenOMICC, Genetics of Mortality in Critical Care; GWAS, genome-wide association study; MVP, Million Veteran Program; N3C, National COVID Cohort Collaborative; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; SPHERES, SARS-CoV-2 Sequencing for Public Health Emergency Response.
Figure 3.
Use of linked electronic health record (EHR) and patient genomic data to identify genomic variants influencing coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) susceptibility and severity. 4CE, Consortium for Clinical Characterization of COVID-19 by EHR; CPT, Current Procedural Terminology; eMERGE, Electronic Medical Records and Genomics; GenOMICC, Genetics of Mortality in Critical Care; i2b2, Informatics for Integrating Biology and the Bedside; ICD, International Classification of Diseases; MVP, Million Veteran Program; N3C, National COVID Cohort Collaborative; OMOP, Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership.
The first genome-wide association study (GWAS)91 of COVID-19 severity included approximately 2000 COVID-19 patients with respiratory failure from 7 hospitals in Europe. Genetic variants in loci involved in inflammation pathways that functionally interact with the SARS-CoV-2 cellular receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and the ABO blood groups were associated with severe disease; risk was higher in patients with blood group A than in patients with other blood groups, and lower risk was found in patients with blood group O compared with other blood groups, consistent with previous studies implicating the ABO locus in susceptibility to infection with SARS-CoV-2.91 , 107 , 108 An additional GWAS and transcriptome-wide association study from the Genetics of Mortality in Critical Care (GenOMICC) consortium in the United Kingdom109 included 2244 patients with severe disease and identified variants in multiple genes, many of which are known to be involved in innate immunity, to be associated with disease severity. Some of these variants hint at specific targets for novel drug development. A GWAS102 meta-analysis of 46 studies including 49,562 case patients and more than 2,000,000 controls with diverse ancestries found 15 variants (13 of them novel) associated with COVID-19. This study differed from the prior GWAS in that it examined infection susceptibility in addition to hospitalization and severe illness. The 25 genetic susceptibility variants discovered to date are listed in the Supplemental Table (available online at http://www.mayoclinicproceedings.org). As additional genetic susceptibility loci are discovered, it may be possible to combine these into a polygenic risk score for severe disease that could be integrated in the EHR for risk stratification.110 , 111
Rare variant analyses have been enabled by exome and genome sequencing data. The COVID Human Genetic Effort discovered 24 rare, deleterious genetic variants in 8 genes mediating type I interferon antiviral immunity that are enriched in patients who develop life-threatening COVID-19 compared with patients with mild or asymptomatic presentations of COVID-19.38 In a study of 2 families112 with multiple young, previously healthy men who developed severe COVID-19 in The Netherlands, separate mutations in TLR7 leading to loss of function of an important innate immunity–sensing protein were identified. These studies highlight that rare genetic variants in various key genes and pathways could have an impact on COVID-19 disease susceptibility.
Mendelian Randomization
Existing GWAS summary data can further be leveraged for 2-sample mendelian randomization analyses to infer causal risk factors. By use of this approach, a variety of factors have been shown to be causally related to severe COVID-19, including elevated body mass index, smoking, lung tissue–specific expression of CCR2, and circulating levels of numerous proteins.109 , 113, 114, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119 Of particular interest is a study demonstrating decreased disease severity with genetically predicted interleukin 6 receptor inhibition, which mimics clinically used therapies (eg, sarilumab, tocilizumab, and siltuximab).92
Proteomic and Metabolomic Studies
Integration of various omics approaches could provide novel insights into COVID-19 pathogenesis. Certain metabolomic profiles can distinguish COVID-19–positive patients from uninfected controls,120 whereas others can predict risk of death from COVID-19.121 Proteomic and metabolomic data can be combined with genotype expression data as demonstrated in a study116 that investigated whether commonly used drugs affect angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and transmembrane protease serine 2 and therefore might alter risk of infection with SARS-CoV-2. Shen et al122 applied metabolomics and proteomic profiling to serum from 46 patients with COVID-19 and 53 controls to demonstrate that 93 proteins were differentially expressed in patients with severe COVID-19 and 204 metabolites correlated with COVID-19 severity. Furthermore, pathway analysis showed metabolic and immune dysregulation in COVID-19 patients, consistent with findings from other studies with different designs.
Treatment
Repurposing Drugs and Vaccines
The EHR captures medication data, providing an opportunity to evaluate the benefit of therapies for COVID-19 as well as adverse effects and complications of novel therapies. Such data may also be useful for profiling patients for clinical trial eligibility and for insights into drug repurposing. Using EHR data from the French National Health Data System, Semenzato et al123 showed that COVID-19 patients receiving angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers had a lower risk of hospitalization, intubation, and death than patients using calcium channel blockers as their antihypertensive medications. Gupta et al124 used EHR data from hospitals in the United States to make the observation that hospitalized patients with COVID-19 receiving statins had lower mortality than those not taking statins. Castro et al125 used the EHR for an agnostic approach to identify ibuprofen, naproxen, and valacyclovir use as being associated with lower risk of hospitalization in patients with COVID-19. Data from the Mayo Clinic EHR revealed that individuals who received various vaccines (high-dose influenza, measles-mumps-rubella, Haemophilus influenzae type B, pneumococcal conjugate, hepatitis A, hepatitis B, or varicella) within the previous 5 years had decreased rates of COVID-19.126 The EHR-based omics studies mentioned may provide useful insights into new drug development or drug repurposing.
Targeted Medical Therapy
Variants can be associated with either improved therapeutic outcomes or adverse reactions for drugs being trialed for COVID-19; these variants are being tracked by the Pharmacogenomics Knowledge Base.127 These variants can be placed in the EHR to inform decisions related to selection of drug therapy.128 In addition, EHR-based algorithms and clinical decision support can be used to notify medical providers if patients meet preset criteria for use of certain medical therapies to improve care; these might include dexamethasone (if supplemental oxygen is required), monoclonal antibody therapy (on the basis of age and presence of certain comorbidities), or potential eligibility for experimental therapeutics and clinical trials.
Electronic Health Record–Based Innovations
Artificial Intelligence and the EHR
Artificial intelligence is being integrated into dashboards within the EHR to assist clinicians in real-time monitoring. Wagner et al129 used deep neural networks to examine clinical notes in the EHR for patients who eventually developed COVID-19. They identified multiple symptoms predictive of subsequent development of COVID-19 and included these in an augmented intelligence platform, allowing an EHR tool to assist clinicians for early diagnosis of COVID-19. The US Food & Drug Administration issued an Emergency Use Authorization130 for artificial intelligence–enhanced electrocardiography to detect left ventricular dysfunction in patients with COVID-19, and this has been successfully used in the clinical setting.131 In addition, artificial intelligence–enhanced electrocardiography for diagnosis of COVID-19,132 possibly even in presymptomatic patients, is being explored for potential use in portable devices to rapidly screen individuals.
Remote Monitoring
Infectious pandemics such as COVID-19 can overwhelm medical facilities, and there is a need for hospital-at-home models to care for less severely ill patients at home, thus decreasing transmission risk and freeing up hospital beds for more critically ill patients.133 Telemedicine can be used to manage not only mild disease but also severe disease by providing expanded access to critical care.134 Electronic phenotyping algorithms, including “real-time” natural language processing, can detect complications in patients with COVID-19, facilitate timely triage to intensive care units, and determine clinical trial eligibility. Such alerts can be linked to clinical decision support tools to provide guidance at the point-of-care and can identify individuals at high risk who may benefit from home oximetry, hospitalization, or early escalation of level of care in the hospital to the intensive care unit as well as identify individuals for clinical trials and drug repurposing. A critical care physician could monitor patients in small rural hospitals remotely, guiding local nurses, respiratory therapists, and hospitalists to adjust medications or ventilators and to perform interventions as needed.135
Early Detection of the Next Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of early detection of outbreaks, rapid response, and mitigation strategies to prevent escalation. The International Society for Infectious Diseases created ProMED,136 which allows various public health agencies to post information about potential or confirmed outbreaks of known or novel infectious diseases for the global community to view. The sobering experience with the COVID-19 pandemic should motivate a global data collaborative for early detection of outbreaks that may lead to pandemics. This can include data from a variety of sources, including the EHR, Internet search engine queries of symptoms, and artificial intelligence monitoring of news reports around the world. Indeed, the Big Data and the Global Public Health Intelligence Network137 and the Meaningful Integration of Data Analytics and Services platform138 are exploring strategies for early recognition of the next pandemic.
Conclusion
To mitigate global pandemics such as COVID-19, international collaborations that share EHR data using common data models are key. Phenotyping algorithms based on billing codes, laboratory and medication data, and natural language processing of clinical notes are useful for monitoring disease epidemiology and severity. Such algorithms enable rapid automated phenotyping for genomic studies and drug repurposing efforts. Data sharing between EHRs of health systems, public health entities, and patients through mobile apps can improve disease tracking and contact tracing to limit spread. By linkage to clinical decision support tools for point-of-care patient management, EHR algorithms for early detection of complications can improve patient outcomes. Such surveillance can detect high-risk individuals who may benefit from increased monitoring either at home or through early hospitalization. Together, various EHR-centered approaches can improve patient care and advance the scientific understanding needed to combat and to end the COVID-19 pandemic.
Footnotes
Grant Support: This work was funded by a supplemental award HG006379-09S1 from the National Human Genome Research Institute. I.J.K. is supported by National Human Genome Research Institute grant HG006379 and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute award K24 HL130710. B.A.S. was supported by the Mayo Clinic Clinician-Investigator Training Program.
Potential Competing Interests: The authors report no competing interests.
Supplemental material can be found online at http://www.mayoclinicproceedings.org. Supplemental material attached to journal articles has not been edited, and the authors take responsibility for the accuracy of all data.
Supplemental Online Material
References
- 1.Johns Hopkins University and Medicine COVID-19 dashboard. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu Accessed April 27, 2021.
- 2.Kretzschmar M.E., Rozhnova G., Bootsma M.C.J., van Boven M., van de Wijgert J., Bonten M.J.M. Impact of delays on effectiveness of contact tracing strategies for COVID-19: a modelling study. Lancet Public Health. 2020;5(8):e452–e459. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(20)30157-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ye J. The role of health technology and informatics in a global public health emergency: practices and implications from the COVID-19 pandemic. JMIR Med Inform. 2020;8(7):e19866. doi: 10.2196/19866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Abeler J., Bäcker M., Buermeyer U., Zillessen H. COVID-19 contact tracing and data protection can go together. JMIR mHealth uHealth. 2020;8(4):e19359. doi: 10.2196/19359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Mahmood S., Hasan K., Carras M.C., Labrique A. Global preparedness against COVID-19: we must leverage the power of digital health. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2020;6(2):e18980. doi: 10.2196/18980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sync for Science. http://healthit.gov/topic/sync-science Accessed April 27, 2021.
- 7.Zhou F., Yu T., Du R., et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395(10229):1054–1062. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3. [erratum appears in Lancet. 2020;395(10229):1038] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chang S., Pierson E., Koh P.W., et al. Mobility network models of COVID-19 explain inequities and inform reopening. Nature. 2021;589(7840):82–87. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2923-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kapa S., Halamka J., Raskar R. Contact tracing to manage COVID-19 spread—balancing personal privacy and public health. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020;95(7):1320–1322. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.04.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Shang N., Liu C., Rasmussen L.V., et al. Making work visible for electronic phenotype implementation: lessons learned from the eMERGE network. J Biomed Inform. 2019;99:103293. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2019.103293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fisman D.N., Greer A.L., Hillmer M., Tuite R. Derivation and validation of clinical prediction rules for COVID-19 mortality in Ontario, Canada. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2020;7(11):ofaa463. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofaa463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dite G.S., Murphy N.M., Allman R. An integrated clinical and genetic model for predicting risk of severe COVID-19: a population-based case-control study. PLoS One. 2021;16(2):e0247205. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.eMERGE-Network PheKB. Phenotype KnowledgeBase. http://phekb.org Accessed April 27, 2021.
- 14.Kirby J.C., Speltz P., Rasmussen L.V., et al. PheKB: a catalog and workflow for creating electronic phenotype algorithms for transportability. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2016;23(6):1046–1052. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocv202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Newton K.M., Peissig P.L., Kho A.N., et al. Validation of electronic medical record–based phenotyping algorithms: results and lessons learned from the eMERGE network. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2013;20(e1):e147–e154. doi: 10.1136/amiajnl-2012-000896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Conway M., Berg R.L., Carrell D., et al. Analyzing the heterogeneity and complexity of Electronic Health Record oriented phenotyping algorithms. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2011;2011:274–283. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mo H., Thompson W.K., Rasmussen L.V., et al. Desiderata for computable representations of electronic health records–driven phenotype algorithms. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2015;22(6):1220–1230. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocv112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.PhenX (Phenotypes and eXposures) Toolkit. https://www.phenxtoolkit.org Accessed April 27, 2021.
- 19.Hamilton C.M., Strader L.C., Pratt J.G., et al. The PhenX Toolkit: get the most from your measures. Am J Epidemiol. 2011;174(3):253–260. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwr193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.PhenX (Phenotypes and eXposures) Toolkit. COVID-19 protocol library. https://www.phenxtoolkit.org/covid19 Accessed April 27, 2021.
- 21.Hripcsak G., Shang N., Peissig P.L., et al. Facilitating phenotype transfer using a common data model. J Biomed Inform. 2019;96:103253. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2019.103253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Murphy S.N., Weber G., Mendis M., et al. Serving the enterprise and beyond with Informatics for Integrating Biology and the Bedside (i2b2) J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2010;17(2):124–130. doi: 10.1136/jamia.2009.000893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hripcsak G., Duke J.D., Shah N.H., et al. Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI): opportunities for observational researchers. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2015;216:574–578. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Brandt P.S., Kiefer R.C., Pacheco J.A., et al. Toward cross-platform electronic health record–driven phenotyping using Clinical Quality Language. Learn Health Syst. 2020;4(4):e10233. doi: 10.1002/lrh2.10233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chapman M., Rasmussen L.V., Pacheco J.A., Curcin V. Phenoflow: a microservice architecture for portable workflow-based phenotype definitions. medRxiv. March 23, 2021. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.07.01.20144196v3 Accessed March 27, 2021. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 26.Kashyap M., Seneviratne M., Banda J.M., et al. Development and validation of phenotype classifiers across multiple sites in the observational health data sciences and informatics network. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2020;27(6):877–883. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocaa032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Phillips N., Park I.W., Robinson J.R., Jones H.P. The perfect storm: COVID-19 health disparities in US blacks. J Racial Ethn Health Disparities. 2020 Sep 23:1–8. doi: 10.1007/s40615-020-00871-y. [Online ahead of print] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Burström B., Tao W. Social determinants of health and inequalities in COVID-19. Eur J Public Health. 2020;30(4):617–618. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/ckaa095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rollston R., Galea S. COVID-19 and the social determinants of health. Am J Health Promot. 2020;34(6):687–689. doi: 10.1177/0890117120930536b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Williamson E., Walker A.J., Bhaskaran K., et al. OpenSAFELY: factors associated with COVID-19–related hospital death in the linked electronic health records of 17 million adult NHS patients. medRxiv. May 7, 2020. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.05.06.20092999v1 Accessed August 3, 2020.
- 31.OpenSAFELY platform. https://opensafely.org/ Accessed April 27, 2021.
- 32.Yang X., Yu Y., Xu J., et al. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(5):475–481. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5. [erratum appears in Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(4):e26] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Shi S., Qin M., Shen B., et al. Association of cardiac injury with mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Cardiol. 2020;5(7):802–810. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.0950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Guo T., Fan Y., Chen M., et al. Cardiovascular implications of fatal outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) JAMA Cardiol. 2020;5(7):811–818. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1017. [erratum appears in JAMA Cardiol. 2020;5(7):848] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yang J., Zheng Y., Gou X., et al. Prevalence of comorbidities in the novel Wuhan coronavirus (COVID-19) infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Infect Dis. 2020;94:91–95. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.03.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tersalvi G., Vicenzi M., Calabretta D., Biasco L., Pedrazzini G., Winterton D. Elevated troponin in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: possible mechanisms. J Card Fail. 2020;26(6):470–475. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2020.04.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Peiro C., Moncada S. Substituting angiotensin-(1-7) to prevent lung damage in SARS-CoV-2 infection? Circulation. 2020;41(21):1665–1666. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zhang Q., Bastard P., Liu Z., et al. Inborn errors of type I IFN immunity in patients with life-threatening COVID-19. Science. 2020;370(6515):eabd4570. doi: 10.1126/science.abd4570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Bastard P., Rosen L.B., Zhang Q., et al. Autoantibodies against type I IFNs in patients with life-threatening COVID-19. Science. 2020;370(6515):eabd4585. doi: 10.1126/science.abd4585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Mehta P., McAuley D.F., Brown M., et al. COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet. 2020;395(10229):1033–1034. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Yang Y., Shen C., Li J., et al. Exuberant elevation of IP-10, MCP-3 and IL-1ra during SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with disease severity and fatal outcome. medRxiv. March 6, 2020. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.02.20029975v1 Accessed August 15, 2020.
- 42.Viner R.M., Whittaker E. Kawasaki-like disease: emerging complication during the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet. 2020;395(10239):1741–1743. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31129-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Licciardi F., Pruccoli G., Denina M., et al. SARS-CoV-2–induced Kawasaki-like hyperinflammatory syndrome: a novel COVID phenotype in children. Pediatrics. 2020;146(2):e20201711. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-1711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Chowdhary A., Joy E., Plein S., Abdel-Rahman S.E.D. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in an adult with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020 Sep 4:jeaa232. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jeaa232. [Online ahead of print] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wang D., Hu B., Hu C., et al. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 2020;323(11):1061–1069. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.1585. [erratum appears in JAMA. 2021;325(11):1113] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Zhou W., Nielsen J.B., Fritsche L.G., et al. Efficiently controlling for case-control imbalance and sample relatedness in large-scale genetic association studies. Nat Genet. 2018;50(9):1335–1341. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0184-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Puntmann V.O., Carerj M.L., Wieters I., et al. Outcomes of cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging in patients recently recovered from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) JAMA Cardiol. 2020;5(11):1265–1273. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.3557. [erratum appears in JAMA Cardiol. 2020;5(11):1308] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Hu H., Ma F., Wei X., Fang Y. Coronavirus fulminant myocarditis treated with glucocorticoid and human immunoglobulin. Eur Heart J. 2021;42(2):206. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa190. [erratum appears in Eur Heart J. 2021;42(2):191] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Musher D.M., Abers M.S., Corrales-Medina V.F. Acute infection and myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(2):171–176. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1808137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Mahler S.A., Lenoir K.M., Wells B.J., et al. Safely identifying emergency department patients with acute chest pain for early discharge: HEART pathway accelerated diagnostic protocol. Circulation. 2018;138(22):2456–2468. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.036528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kochi A.N., Tagliari A.P., Forleo G.B., Fassini G.M., Tondo C. Cardiac and arrhythmic complications in patients with COVID-19. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2020;31(5):1003–1008. doi: 10.1111/jce.14479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Zhang Y., Xiao M., Zhang S., et al. Coagulopathy and antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(17):e38. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2007575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Ullah W., Saeed R., Sarwar U., Patel R., Fischman D.L. COVID-19 complicated by acute pulmonary embolism and right-sided heart failure. JACC Case Rep. 2020;2(9):1379–1382. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2020.04.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Klok F.A., Kruip M., van der Meer N.J.M., et al. Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19. Thromb Res. 2020;191:145–147. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Lippi G., Plebani M., Henry B.M. Thrombocytopenia is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infections: a meta-analysis. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;506:145–148. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.03.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Banerjee I., Sofela M., Yang J., et al. Development and Performance of the Pulmonary Embolism Result Forecast Model (PERFORM) for computed tomography clinical decision support. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(8):e198719. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.8719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Wu Y., Xu X., Chen Z., et al. Nervous system involvement after infection with COVID-19 and other coronaviruses. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;87:18–22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.03.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Mao L., Jin H., Wang M., et al. Neurological manifestations of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Neurol. 2020;77(6):683–690. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.1127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Li Y., Li M., Wang M., et al. Acute cerebrovascular disease following COVID-19: a single center, retrospective, observational study. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2020;5(3):279–284. doi: 10.1136/svn-2020-000431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Raza A., Estepa A., Chan V., Jafar M.S. Acute renal failure in critically ill COVID-19 patients with a focus on the role of renal replacement therapy: a review of what we know so far. Cureus. 2020;12(6):e8429. doi: 10.7759/cureus.8429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Ali H., Daoud A., Mohamed M.M., et al. Survival rate in acute kidney injury superimposed COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ren Fail. 2020;42(1):393–397. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2020.1756323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Li Y.C., Bai W.Z., Hashikawa T. The neuroinvasive potential of SARS-CoV2 may play a role in the respiratory failure of COVID-19 patients. J Med Virol. 2020;92(6):552–555. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Gattinoni L., Coppola S., Cressoni M., Busana M., Rossi S., Chiumello D. Covid-19 does not lead to a “typical” acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;201(10):1299–1300. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202003-0817LE. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Matthay M.A., Aldrich J.M., Gotts J.E. Treatment for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome from COVID-19. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(5):433–434. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30127-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Pawlowski C., Wagner T., Puranik A., et al. Inference from longitudinal laboratory tests characterizes temporal evolution of COVID-19-associated coagulopathy (CAC) Elife. 2020;9:e59209. doi: 10.7554/eLife.59209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Brat G.A., Weber G.M., Gehlenborg N., et al. International electronic health record–derived COVID-19 clinical course profiles: the 4CE consortium. NPJ Digit Med. 2020;3(1):109. doi: 10.1038/s41746-020-00308-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Lippi G., Plebani M. Laboratory abnormalities in patients with COVID-2019 infection. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020;58(7):1131–1134. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2020-0198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Lippi G., Plebani M. Procalcitonin in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;505:190–191. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.03.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Bonow R.O., Fonarow G.C., O'Gara P.T., Yancy C.W. Association of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) with myocardial injury and mortality. JAMA Cardiol. 2020;5(7):751–753. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Ahmadpoor P., Rostaing L. Why the immune system fails to mount an adaptive immune response to a COVID-19 infection. Transpl Int. 2020;33(7):824–825. doi: 10.1111/tri.13611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Thachil J. The versatile heparin in COVID-19. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18(5):1020–1022. doi: 10.1111/jth.14821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Jin M., Tong Q. Rhabdomyolysis as potential late complication associated with COVID-19. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26(7):1618–1620. doi: 10.3201/eid2607.200445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Pan X.W., Xu D., Zhang H., Zhou W., Wang L.H., Cui X.G. Identification of a potential mechanism of acute kidney injury during the COVID-19 outbreak: a study based on single-cell transcriptome analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46(6):1114–1116. doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-06026-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Gorna R., MacDermott N., Rayner C., et al. Long COVID guidelines need to reflect lived experience. Lancet. 2021;397(10273):455–457. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32705-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Logue J.K., Franko N.M., McCulloch D.J., et al. Sequelae in adults at 6 months after COVID-19 infection. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(2):e210830. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Garrigues E., Janvier P., Kherabi Y., et al. Post-discharge persistent symptoms and health-related quality of life after hospitalization for COVID-19. J Infect. 2020;81(6):e4–e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.08.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Carfì A., Bernabei R., Landi F. Persistent symptoms in patients after acute COVID-19. JAMA. 2020;324(6):603–605. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.12603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Del Rio C., Collins L.F., Malani P. Long-term health consequences of COVID-19. JAMA. 2020;324(17):1723–1724. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.19719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.National Institutes of Health NIH launches new initiative to study “long COVID.”. https://www.nih.gov/about-nih/who-we-are/nih-director/statements/nih-launches-new-initiative-study-long-covid Accessed March 4, 2021.
- 80.Shen Z., Xiao Y., Kang L., et al. Genomic diversity of severe acute respiratory syndrome–coronavirus 2 in patients with coronavirus disease 2019. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71(15):713–720. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Mahase E. Covid-19: what new variants are emerging and how are they being investigated? BMJ. 2021;372:n158. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Meredith L.W., Hamilton W.L., Warne B., et al. Rapid implementation of SARS-CoV-2 sequencing to investigate cases of health-care associated COVID-19: a prospective genomic surveillance study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020;20(11):1263–1271. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30562-4. [erratum appears in Lancet Infect Dis. 2021;21(3):e36] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Horby P., Nguyen N.Y., Dunstan S.J., Baillie J.K. The role of host genetics in susceptibility to influenza: a systematic review. PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33180. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Huang C., Wang Y., Li X., et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):497–506. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. [erratum appears in Lancet. 2020;395(10223):496] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Onder G., Rezza G., Brusaferro S. Case-fatality rate and characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID-19 in Italy. JAMA. 2020;323(18):1775–1776. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4683. [erratum appears in JAMA. 2020;323(16):1619] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Chan J.F., Yuan S., Kok K.H., et al. A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: a study of a family cluster. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):514–523. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30154-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Deng Y., Liu W., Liu K., et al. Clinical characteristics of fatal and recovered cases of coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective study. Chin Med J (Engl) 2020;133(11):1261–1267. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Lu R., Zhao X., Li J., et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet. 2020;395(10224):565–574. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Zhou P., Yang X.L., Wang X.G., et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 2020;579(7798):270–273. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Shen Z., Xiao Y., Kang L., et al. Genomic diversity of SARS-CoV-2 in coronavirus disease 2019 patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71(15):713–720. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Ellinghaus D., Degenhardt F., Bujanda L., et al. Genomewide association study of severe Covid-19 with respiratory failure. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(16):1522–1534. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2020283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Larsson S.C., Burgess S., Gill D. Genetically proxied interleukin-6 receptor inhibition: opposing associations with COVID-19 and pneumonia. Eur Respir J. 2021;57(1):2003545. doi: 10.1183/13993003.03545-2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.UK Biobank. https://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/ Accessed April 27, 2021.
- 94.Pan-UK Biobank. https://pan.ukbb.broadinstitute.org/ Accessed April 27, 2021.
- 95.UKBiobank ICD PheWeb. http://pheweb.sph.umich.edu/SAIGE-UKB/ Accessed April 27, 2021.
- 96.FinnGen. https://www.finngen.fi/en Accessed April 27, 2021.
- 97.eMERGE Network Electronic Medical Records and Genomics Network. https://emerge-network.org/ Accessed April 27, 2021.
- 98.U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Million Veteran Program. https://www.research.va.gov/mvp/ Accessed April 27, 2021.
- 99.GenOMICC Genetics of Mortality in Critical Care. https://genomicc.org/ Accessed April 27, 2021.
- 100.The COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative. https://www.covid19hg.org/ Accessed April 27, 2021.
- 101.The COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative, a global initiative to elucidate the role of host genetic factors in susceptibility and severity of the SARS-CoV-2 virus pandemic. Eur J Hum Genet. 2020;28(6):715–718. doi: 10.1038/s41431-020-0636-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Ganna A. Mapping the human genetic architecture of COVID-19 by worldwide meta-analysis. medRxiv. March 12, 2021. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.03.10.21252820v1 Accessed March 15, 2021.
- 103.National COVID Cohort Collaborative. https://ncats.nih.gov/n3c Accessed April 27, 2021.
- 104.4CE. Consortium for Clinical Characterization of COVID-19 by EHR. https://covidclinical.net/ Accessed April 27, 2021.
- 105.COVID Human Genetic Effort. https://www.covidhge.com Accessed April 27, 2021.
- 106.SPHERES. SARS-CoV-2 Sequencing for Public Health Emergency Response, Epidemiology, and Surveillance. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/cases-updates/spheres.html Accessed April 27, 2021.
- 107.Zhao J., Yang Y., Huang H., et al. Relationship between the ABO blood group and the COVID-19 susceptibility. Clin Infect Dis. 2020 Aug 4:ciaa1150. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1150. [Online ahead of print] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Tanigawa Y., Rivas M. Initial review and analysis of COVID-19 host genetics and associated phenotypes. Preprints. 2020 2020030356 2020. [Google Scholar]
- 109.Pairo-Castineira E., Clohisey S., Klaric L., et al. Genetic mechanisms of critical illness in COVID-19. Nature. 2021;591(7848):92–98. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-03065-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Kullo I.J., Jarvik G.P., Manolio T.A., Williams M.S., Roden D.M. Leveraging the electronic health record to implement genomic medicine. Genet Med. 2013;15(4):270–271. doi: 10.1038/gim.2012.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Safarova M.S., Kullo I.J. Using the electronic health record for genomics research. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2020;31(2):85–93. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.van der Made C.I., Simons A., Schuurs-Hoeijmakers J., et al. Presence of genetic variants among young men with severe COVID-19. JAMA. 2020;324(7):663–673. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.13719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Ponsford M.J., Gkatzionis A., Walker V.M., et al. Cardiometabolic traits, sepsis, and severe COVID-19: a Mendelian randomization investigation. Circulation. 2020;142(18):1791–1793. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.050753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Sun Y., Zhou J., Ye K. Prioritizing causal risk factors for severe COVID-19: an exhaustive Mendelian randomization study. In Review. January 25, 2021. https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-149087/v1 Accessed March 5, 2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 115.Zhou S., Butler-Laporte G., Nakanishi T., et al. A Neanderthal OAS1 isoform protects individuals of European ancestry against COVID-19 susceptibility and severity. Nat Med. 2021 February 25 doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01281-1. [Online ahead of print] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Gill D., Arvanitis M., Carter P., et al. ACE inhibition and cardiometabolic risk factors, lung ACE2 and TMPRSS2 gene expression, and plasma ACE2 levels: a Mendelian randomization study. R Soc Open Sci. 2020;7(11):200958. doi: 10.1098/rsos.200958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Butler-Laporte G., Nakanishi T., Mooser V., et al. Vitamin D and Covid-19 susceptibility and severity: a Mendelian randomization study. medRxiv. December 22, 2020. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.09.08.20190975v3 Accessed January 20, 2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 118.Zhu J., Wu C., Wu L. Associations between genetically predicted protein levels and COVID-19 severity. J Infect Dis. 2021;223(1):19–22. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Zhou S., Butler-Laporte G., Nakanishi T., et al. Circulating proteins influencing COVID-19 susceptibility and severity: a Mendelian randomization study. medRxiv. October 29, 2020. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.10.13.20212092v3 Accessed January 5, 2021.
- 120.Song J.W., Lam S.M., Fan X., et al. Omics-driven systems interrogation of metabolic dysregulation in COVID-19 pathogenesis. Cell Metab. 2020;32(2):188–202.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.06.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Migaud M., Gandotra S., Chand H.S., Gillespie M.N., Thannickal V.J., Langley R.J. Metabolomics to predict antiviral drug efficacy in COVID-19. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2020;63(3):396–398. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2020-0206LE. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Shen B., Yi X., Sun Y., et al. Proteomic and metabolomic characterization of COVID-19 patient sera. Cell. 2020;182(1):59–72.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Semenzato L., Botton J., Drouin J., et al. Antihypertensive drugs and COVID-19 risk: a cohort study of 2 million hypertensive patients. Hypertension. 2021;77(3):833–842. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.16314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Gupta A., Madhavan M.V., Poterucha T.J., et al. Association between antecedent statin use and decreased mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):1325. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21553-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Castro V.M., Ross R.A., McBride S.M., Perlis R.H. Identifying common pharmacotherapies associated with reduced COVID-19 morbidity using electronic health records. medRxiv. August 28, 2020. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.11.20061994v2 Accessed September 30, 2020.
- 126.Pawlowski C., Puranik A., Bandi H., et al. Exploratory analysis of immunization records highlights decreased SARS-CoV-2 rates in individuals with recent non–COVID-19 vaccinations. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):4741. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83641-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.PharmGKB. COVID-19. https://www.pharmgkb.org/disease/PA166197121/overview Accessed April 27, 2021.
- 128.van der Graaf P.H., Giacomini K.M. COVID-19: a defining moment for clinical pharmacology? Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2020;108(1):11–15. doi: 10.1002/cpt.1876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Wagner T., Shweta F., Murugadoss K., et al. Augmented curation of clinical notes from a massive EHR system reveals symptoms of impending COVID-19 diagnosis. Elife. 2020;9:e58227. doi: 10.7554/eLife.58227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Emergency use of the ELEFT during the COVID-19. https://www.fda.gov/media/137930/download Accessed April 27, 2021.
- 131.Attia Z.I., Kapa S., Noseworthy P.A., Lopez-Jimenez F., Friedman P.A. Artificial intelligence ECG to detect left ventricular dysfunction in COVID-19: a case series. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020;95(11):2464–2466. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.09.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Siontis K.C., Noseworthy P.A., Attia Z.I., Friedman P.A. Artificial intelligence–enhanced electrocardiography in cardiovascular disease management. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2021 Feb 1:1–14. doi: 10.1038/s41569-020-00503-2. [Online ahead of print] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Arias–de la Torre J., Alonso J., Martín V., Valderas J.M. Hospital-at-home as an alternative to release the overload of healthcare systems during the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2020;21(7):990–991. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2020.04.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Barbash I.J., Sackrowitz R.E., Gajic O., et al. Rapidly deploying critical care telemedicine across states and health systems during the Covid-19 pandemic. NEJM Catalyst. 2020;1(4) [Google Scholar]
- 135.Lilly C.M., Thomas E.J. Tele-ICU: experience to date. J Intensive Care Med. 2010;25(1):16–22. doi: 10.1177/0885066609349216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.ProMED International Society for Infectious Diseases. https://promedmail.org/ Accessed April 27, 2021.
- 137.Dion M., AbdelMalik P., Mawudeku A. Big data and the Global Public Health Intelligence Network (GPHIN) Can Commun Dis Rep. 2015;41(9):209–214. doi: 10.14745/ccdr.v41i09a02. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Costa J.P., Grobelnik M., Fuart F., et al. Meaningful big data integration for a global COVID-19 strategy. IEEE Comput Intell Mag. 2020;15(4):51–61. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.