Abstract
Objective
It is estimated that up to 75% of patients with severe mental illness (SMI) also have substance use disorder (SUD). The aim of this systematic review was to explore the scope, quality and inclusivity of international clinical guidelines on mental health and/or substance abuse in relation to diagnosis and treatment of co-existing disorders and considerations for wider social and contextual factors in treatment recommendations.
Method
A protocol (PROSPERO CRD42020187094) driven systematic review was conducted. A systematic search was undertaken using six databases including MEDLINE, Cochrane Library, EMBASE, PsychInfo from 2010 till June 2020; and webpages of guideline bodies and professional societies. Guideline quality was assessed based on ‘Appraisal of Guidelines for Research & Evaluation II’ (AGREE II) tool. Data was extracted using a pre-piloted structured data extraction form and synthesized narratively. Reporting was based on PRISMA guideline.
Result
A total of 12,644 records were identified. Of these, 21 guidelines were included in this review. Three of the included guidelines were related to coexisting disorders, 11 related to SMI, and 7 guidelines were related to SUD. Seven (out of 18) single disorder guidelines did not adequately recommend the importance of diagnosis or treatment of concurrent disorders despite their high co-prevalence. The majority of the guidelines (n = 15) lacked recommendations for medicines optimisation in accordance with concurrent disorders (SMI or SUD) such as in the context of drug interactions. Social cause and consequence of dual diagnosis such as homelessness and safeguarding and associated referral pathways were sparsely mentioned.
Conclusion
Despite very high co-prevalence, clinical guidelines for SUD or SMI tend to have limited considerations for coexisting disorders in diagnosis, treatment and management. There is a need to improve the scope, quality and inclusivity of guidelines to offer person-centred and integrated care.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12888-021-03188-0.
Keywords: Severe mental illness, Substance use disorders, Substance misuse, Substance abuse, Coexisting disorders, Dual diagnosis
Background
It is estimated that up to 75% of patients with severe mental illness (SMI) also have substance use disorder (SUD) and about 60% of adults with SUD have at least one type of SMI [1–4], with one being either the cause or consequence of the other or various social issues leading to both issues at the same time [5, 6]. Genetic factors for such co-morbidity including variations in how people respond to treatments have also been suggested [7]. Coexisting disorders can result in greater incidence of adverse health outcomes, suicide, unplanned hospital admissions [2, 8–10] and early mortality [11–13]. Social consequences include violence, homelessness, involvement with criminal justice system, and relationship breakdowns have also been suggested [14–17]. For example, between a quarter and a third of prison populations in the Western countries are known to have a dual diagnosis [15, 18]. Involvement with criminal justice system is also known to adversely impact patient access to SMI and SUD services [19].
Assessment and treatment of patients in regard to dual diagnosis presents a challenge for care providers. Care providers can face challenges in managing psychiatric symptoms, substance craving, and social issues as a result of coexisting disorders [20]. In addition, fragmentation of care, for example, physical separation of services can result in barrier to access and provision of care [21–23]. Different opinion and divergent views of health care providers about treatment plan are also other known challenges [24, 25]. Parallel and separate care provided for each disorder within the same or different healthcare settings for patients with coexisting disorders are likely to be ineffective. This can lead to fragmentation of care, lack of timely access to treatment, withdrawal from treatment, physical multi-morbidity, and early deaths [9, 26, 27]. The advantage of considering both disorders together is that both SMI and SUD are simultaneously addressed and are given due attention [28]. However, practices are often patchy. Despite the known effectiveness of integrated treatment models for patients with coexisting disorders, integrated services availability remains sparse. A study conducted in the United States sampled programs from all over the US and showed that only 18% of addiction treatment and 9% of mental health programs had sufficient capacity to provide simultaneous services for patients with coexisting disorder [29].
A previous systematic review published in 2010 evaluated SMI and SUD guidelines to investigate whether or not they addressed co-occurring disorders [30]. The review considered guidelines published until 2007 and was limited to the inclusion of guidelines published in the National Guideline Clearinghouse database. Guidelines developed by the professional societies and clinical excellence committees are important decision tools that guide health care professionals’ care of their patients. Evidence-based guidelines allow practitioners to follow the best available evidence and also speeds up the adaptation of new treatment approaches. While practitioners may utilize professional judgements and conduct their own evidence search to inform person-centred care, guidelines are cornerstones in healthcare practice and adherence to clinical guidelines is often taken synonymous to evidence based practice [31]. The aim of this systematic review was to explore the scope, quality and inclusivity of international clinical guidelines on mental health and/or substance abuse in relation to diagnosis and treatment of such co-existing disorders and consideration of wider social and contextual issues in treatment recommendations.
Methodology
Protocol and registration
The study protocol registered in PROSPERO (CRD42020187094). The review was conducted as per PRISMA checklist and statement [32] (Electronic supplementary material 1).
Criteria for considering guidelines for this review
The research for this review focused international guidelines which related to the assessment and treatment of either SUD, SMI or on concurrent disorders. The search was limited to guidelines published from 2010 until June 2020. To make sure that included guidelines represented current practice, guidelines published before 2010 were not considered. The search was restricted to guidelines published in the English language.
Search and selection of guidelines
The research for guidelines was conducted using the following databases: MEDLINE, Cochrane Library, EMBASE, and PsychInfo, Google, Google scholar, Guideline Central; and national clinical guidelines and professional organizations’ web pages including National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) and the American Psychiatric Association (APA) .
The search terms used related to SUD and SMI MeSH terms (electronic supplemental material 2). The screening process was performed in three distinct stages including title, summary or abstract and full texts. The selection of guidelines done independently by two reviewers (RA and VP) and any discrepancies were resolved by consensus. We searched reference list of included guidelines to identify any further guidelines.
Search definitions
We considered the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) definition of, ‘substance use disorder’ which is a single term combines both abuse and dependence [33]. Such substances include legal drugs such as alcohol, illicit drugs such as heroin and cocaine, and prescription drugs such as oxycodone [34]. The SMIs considered in this review were psychosis and other associated types of schizophrenia, as well as bipolar disorder. The terms coexisting disorder, co-occurring disorder, or dual diagnosis are frequently used to describe the existence of both conditions of SMI and SUD simultaneously.
Data extraction
After identification of eligible guidelines, data were extracted using a Microsoft Excel® spreadsheet. Data were extracted in relation to guideline characteristics, targeted patient population and health care providers, screening and management of co-existing disorders including recommendations for treatment adjustments and consideration of monitoring of physical health or drug interactions. Consideration of offending behavior, risks of homelessness, violence, and suicide were also extracted. Data extraction was done by two authors (RA and VP) in duplicate and independently and any disagreements were resolved by further discussion.
Quality assessment
The included guidelines are appraised by using the Appraisal of Guidelines for Research & Evaluation II (AGREE II) tool. The assessment of each guideline is carried out by following the users’ instruction manual for AGREE II instruments [35]. The assessment for the following domains: ‘scope and purpose, stakeholder involvement, rigor of development, clarity of presentation, applicability, and editorial independence’ [36]. Each of the 23 items is scored 1 to 7 where 1 signals strong disagreement and 7 signals strong agreement and the final score is rated from 0 to 100%. In addition, there are two overall assessments of each guideline. The first one reflects the overall quality of each guideline. The second overall assessment allows assessment of whether or not the guideline is recommended for application in practice. Three distinct choices; namely, ‘Yes’, ‘Yes with modification’, or ‘No’ are utilized in relation to recommendation for use. Score sheet is demonstrated in Electronic supplemental material 3. Two reviewers independently assessed the included guidelines.
In order to calculate domain rate, the following equation from AGREE II users’ manual was used:
The rate of each domain = (total score of all items within the domain − lowest score of all items within the domain) / (highest score of all items within the domain − lowest score of all items within the domain) × 100.
A narrative synthesis was used to present the findings. Comparisons between guidelines are pre-identified in accordance with the particular objectives of the review.
Results
The search and selection of guidelines
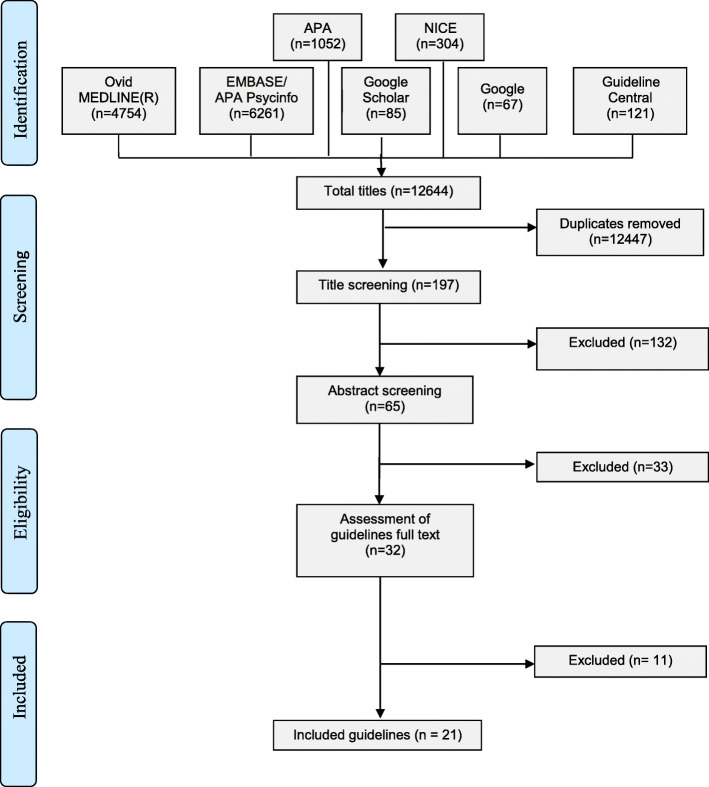
In total, 12,644 records were identified through the searching of various databases. After the exclusion of data de-duplication and both title and abstract screening, 32 guidelines were screened for eligibility. Twenty-one guidelines were included in this study (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
PRISMA* diagram of guidelines selection process
General characteristics of the included guidelines
Of the 21 included, three guidelines related to coexisting disorders [37–39], seven guidelines related to SUD including alcohol use disorder and opioid disorder (Table 1) [40–46]. Eleven guidelines related to SMI (six of them were related to schizophrenia, and five of them were related to bipolar disorder) [47–57]. The aim of each guideline is illustrated in Table 1.
Table 1.
General characteristic of the guidelines
| Guideline title | Organization | Country | Publication year |
Target disorders | Aim | For which patient population is this guideline intended for? | For which healthcare provider is this guideline intended for? | Clinical setting for which this is applicable |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coexisting severe mental illness (psychosis) and substance misuse: assessment and management in healthcare settings [37] | NICE | UK | 2011 | Psychosis + SUD | To provide diagnosis and treatment recommendations for both disorders. | For all patients above 14 years old with both disorders. | For professionals who provide care in all clinical settings. | All clinical settings and medical services that commissioned by NHS |
| Coexisting severe mental illness and substance misuse: community health and social care services overview [38] | NICE | UK | 2016 | Psychosis + SUD | To offer a number of integrated services to meet people’s requirements and solve other related problems, such as lack of housing and joblessness. | For patients above 14 years old with both disorders. | All professionals and commissioners, Workers who have direct contact with patients, The criminal justice system, Voluntary organizations and other third-party sectors, Targeted patients and their families and carers. | Community settings |
| Guidelines on the management of cooccurring alcohol and other drug and mental health conditions in alcohol and other drug treatment settings [39] | Australian government | Australia | 2016 | Co-occurring alcohol and other drug and mental health conditions | To provide directives in relation to the management of AOD and co-occurring mental health conditions. | Patients with AOD and co-occurring mental health conditions. | AOD workers, including nurses, medical practitioners, psychiatrists, psychologists, counsellors, social workers, and other AOD workers. | AOD treatment settings |
| Management of schizophrenia [47] | SIGN | UK | 2013 | Schizophrenia | To provide recommendations for managing schizophrenia. | Adults with schizophrenia | Healthcare providers | Not mentioned specifically |
| Psychosis and schizophrenia in adults: prevention and management [48] | NICE | UK | 2014 | Psychosis and schizophrenia | To provide diagnosis and treatment recommendations psychosis and schizophrenia. | Adults with psychosis and schizophrenia | Health care providers who provide services in primary, community, secondary and tertiary clinical settings. | All clinical settings and medical services that commissioned by NHS |
| Guidelines for Biological Treatment of Schizophrenia. Part 3: Update 2015 Management of special circumstances: Depression, Suicidality, substance use disorders and pregnancy and lactation [49] | WFSBP | International | 2015 | Schizophrenia | To issue guidelines relating to the management of schizophrenia and the assessment of pharmacological agents. | Patients with schizophrenia. | Physicians | Not mentioned specifically |
| Clinical practice guidelines for the management of schizophrenia and related disorders [50] | RANZCP | Australia and New Zealand | 2016 | Schizophrenia and related disorders | To provide guidance for the treatment of schizophrenia and to provide care for schizophrenic patients. | For patients with schizophrenia and related disorders. | Clinicians such as psychiatrists and GPs, psychiatry trainees, mental health nurses, clinicians who have contact with this patient group, and policymakers. | Not mentioned specifically |
| Evidence-based guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of schizophrenia [51] | BAP | UK | 2019 | Schizophrenia | To provide recommendations for the management of schizophrenia. | Patients with schizophrenia | Clinicians | Not mentioned specifically |
| Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with schizophrenia [52] | APA | US | 2020 | Schizophrenia | To help clinicians optimize care for their patients and improve quality of care. | Patients with schizophrenia | Clinicians | Not mentioned specifically |
| Management of Bipolar Disorder in Adults (BD) [53] | VA/DoD | US | 2010 | Bipolar disorder | To manage patients with bipolar disorder. | People aged 18 years old and older with bipolar disorder. | Healthcare professionals | Not mentioned specifically |
| Bipolar disorder [54] | Singapore MOH | Singapore | 2011 | Bipolar disorder | To manage patients with bipolar disorder. | Older patients with bipolar disorder | GP and clinicians | Not mentioned specifically |
| The assessment and management of bipolar disorder in adults, children and young people in primary and secondary care [55] | NICE | UK | 2014 | Bipolar disorders | To manage patients with bipolar disorder. | Children, young adults (aged above 13 years old), and adults. | Professionals who provide care in all clinical settings. | All clinical settings and medical services that commissioned by NHS |
| Evidence-based guidelines for treating bipolar disorder [56] | BAP | UK | 2016 | Bipolar disorder | To assess and manage patients with bipolar disorder. | Patients with bipolar disorder. | Practitioners | Not mentioned specifically |
| Guidelines for the management of patients with bipolar disorder [57] | CANMAT and ISBD | Canada | 2018 | Bipolar disorder | To manage patients with bipolar disorder. | Patients with bipolar disorder | Psychiatrists and primary care providers | Not mentioned specifically |
| Evidence-based guidelines for the pharmacological management of substance abuse, harmful use, addiction and comorbidity [40] | BAP | UK | 2012 | SUD | To provide treatment recommendations in order to help clinicians in prescribing medication for patients with SUD alone and those with psychiatric comorbidities. | Young adults and adults with SUD. | Clinicians such as psychiatrists and GPs, professionals in this field, non-specialists, patients and their families. | Not mentioned specifically |
| Guidelines for biological treatment of substance use and related disorders, part 1: Alcoholism, first revision [41] | WFSBP | International | 2017 | Substance use and related disorders | To provide recommendations for the treatment of AUD that help clinicians in clinical decision making and subsequently improvement of care | Adult with AUD | Professionals who provide care for patients with AUD. | Not mentioned specifically |
| Drug misuse and dependence UK guidelines on clinical management [42] | gov.uk | UK | 2017 | Substance misuse | To provide guidance on managing drug abuse and dependency in the UK. | Drug misusers | Healthcare professionals, Regulatory bodies, Targeted patients, and their families and carers. | Drug misuse services |
| German Guidelines on Screening, Diagnosis and Treatment of Alcohol Use Disorders [43] | DGPPN and DG-Sucht | Germany | 2017 | Alcohol use disorder | To provide screening, diagnosis, and treatment recommendations for patients with alcohol misuse disorder. | Patients with alcohol misuse disorder and comorbidity psychiatric disorders. | Clinicians | In- and outpatient settings |
| Alcohol use disorders: diagnosis, assessment and management of harmful drinking and alcohol dependence [44] | NICE | UK | 2011 | Alcohol use disorder | To provide recommendations for managing patients with alcohol misuse disorder. | Younger children and young adults 10–17 years old with alcohol use disorder. | Professionals who provide care in all clinical settings. | All clinical settings and medical services that commissioned by NHS |
| Practice guideline for the Pharmacological Treatment of Patients with Alcohol Use Disorder [45] | APA | US | 2018 | Alcohol use disorder | To provide recommendations that help in improving the quality of care and quality of life for patients with AUD. | Patients with AUD | Clinicians | Not mentioned specifically |
| National Practice Guideline for the Use of Medications in the Treatment of Addiction Involving Opioid Use [46] | ASAM | US | 2015 | Opioid use disorder | To provide recommendations for managing patients with opioid use disorder. | Patients with opioid use disorder | Physicians; other healthcare providers, medical educators, trainee; and clinical care managers. | Not mentioned specifically |
AOD Alcohol and other drug, APA American Psychiatric Association, ASAM American society of addiction medicine, AUD alcohol use disorder, BAP British Association of psychopharmacology, CANMAT and ISBD Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments and International Society for Bipolar Disorders, DGPPN and DG-Sucht German Association for Psychiatry, Psychotherapy, and Psychosomatics and the German Association for Addiction Research and Therapy, gov.UK United Kingdom guidelines on clinical management, NICE National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, NIH National health service, RANZCP Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists, SIGN Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, Singapore MOH Singapore Ministry of Health, SMI Severe mental illness, SUD Substance use disorder, UK United Kingdom, US United States, VA/DoD Department of Veterans Affairs and The Department of Defense, WFSBP World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry
Most of the included guidelines were produced by NICE in England (n = 5), followed by guidelines produced by British Association of Psychopharmacology in the UK (n = 3). Two of the included guidelines were published by APA in the USA, two of them were produced by the World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) which developed by a group of experts from different countries, and nine guidelines were published by government departments of health [39, 42, 43, 46, 47, 50, 53, 54, 57] (Table 1).
Quality assessment of guidelines
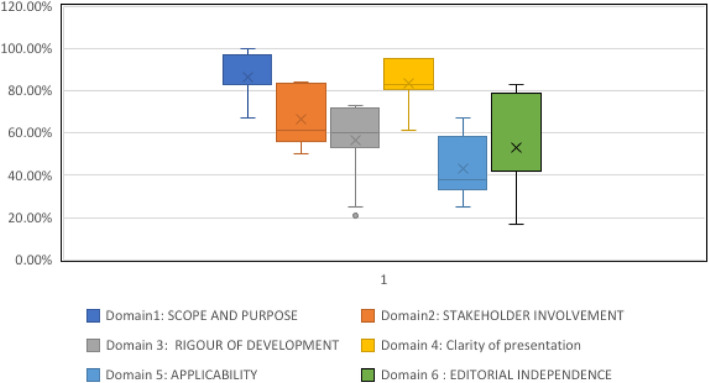
The scores of each guideline against the criteria of the AGREE II tool are displayed in Table 2. In terms of ‘scope and purpose’, first domain had the highest domain score. Only four guidelines scored below 80% [39, 46, 54, 57] (Table 2). In the second domain, ‘stakeholder involvement’, the guidelines that were developed by NICE and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) demonstrated the highest score; 84 and 83%, respectively [37, 38, 44, 47, 48, 55] (Table 2). The ‘Rigour of development’ domain scores were generally low (Fig. 2). Fifteen out of 21 included guidelines rated below 70% (Table 2). Most of the guidelines scored higher in ‘Clarity of presentation’ domain (Fig. 2). The guidelines that were developed by NICE and SIGN obtained the highest scores [37, 38, 44, 47, 48, 55] (Table 2). Figure 2 shows that the ‘Applicability’ domain has the lowest domain score. Fifteen guidelines were graded below 50% (Table 2). With regard to the ‘Editorial independence’ domain, the highest score was reported with the NICE guidelines, this being 83%. The rest of the included guidelines were graded below 80% (Table 2, Fig. 2).
Table 2.
Quality assessment of guidelines
| Guideline | Domain1: Scope and purpose | Domain2: Stakeholder involvement | Domain 3: Rigour of development | Domain 4: Clarity of presentation | Domain 5: Applicability | Domain 6: Editorial independence | Overall quality | Recommendation of use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NICE 2011 [37] | 100.00% | 84.00% | 73.00% | 95.00% | 67.00% | 83.00% | 7 | Recommended |
| NICE 2014 [55] | 100.00% | 84.00% | 73.00% | 95.00% | 67.00% | 83.00% | 7 | Recommended |
| RANZCP 2016 [50] | 83.00% | 72.00% | 35.00% | 83.00% | 33.00% | 42.00% | 4 | Recommended with modification |
| BAP 2012 [40] | 83.00% | 61.00% | 54.00% | 83.00% | 42.00% | 42.00% | 5 | Recommended with modification |
| WFSBP 2017 [41] | 83.00% | 50.00% | 60.00% | 67.00% | 25.00% | 42.00% | 4 | Recommended with modification |
| gov.uk 2017 [42] | 94.00% | 67.00% | 60.00% | 72.00% | 33.00% | 33.00% | 7 | Recommended |
| DGPPN and DG-Sucht 2017 [43] | 83.00% | 56.00% | 63.00% | 78.00% | 33.00% | 50.00% | 4 | Recommended with modification |
| NICE 2011 [44] | 100.00% | 84.00% | 73.00% | 95.00% | 67.00% | 83.00% | 7 | Recommended |
| ASAM 2015 [46] | 67.00% | 72.00% | 52.00% | 83.00% | 38.00% | 58.00% | 5 | Recommended with modification |
| APA 2018 [45] | 89.00% | 56.00% | 65.00% | 83.00% | 42.00% | 75.00% | 6 | Recommended |
| Singapore MOH 2011 [54] | 67.00% | 56.00% | 25.00% | 89.00% | 38.00% | 17.00% | 3 | Not recommended |
| VA/DoD 2010 [53] | 83.00% | 56.00% | 58.00% | 83.00% | 38.00% | 17.00% | 4 | Recommended with modification |
| CANMAT & ISBD 2018 [57] | 67.00% | 61.00% | 31.00% | 61.00% | 29.00% | 42.00% | 3 | Not recommended |
| SIGN 2013 [47] | 94.00% | 83.00% | 71.00% | 95.00% | 50.00% | 50.00% | 7 | Recommended |
| WFSBP 2015 [49] | 83.00% | 50.00% | 60.00% | 67.00% | 25.00% | 42.00% | 4 | Recommended with modification |
| NICE 2016 [38] | 100.00% | 84.00% | 73.00% | 95.00% | 67.00% | 83.00% | 7 | Recommended |
| NICE 2014 [48] | 100.00% | 84.00% | 73.00% | 95.00% | 67.00% | 83.00% | 7 | Recommended |
| BAP 2019 [51] | 83.00% | 61.00% | 54.00% | 83.00% | 33.00% | 42.00% | 5 | Recommended with modification |
| BAP 2016 [56] | 83.00% | 61.00% | 54.00% | 83.00% | 33.00% | 42.00% | 5 | Recommended with modification |
| APA 2020 [52] | 89.00% | 56.00% | 65.00% | 83.00% | 42.00% | 75.00% | 6 | Recommended |
| Australian government 2016 [39] | 78.00% | 56.00% | 21.00% | 89.00% | 38.00% | 25.00% | 3 | Not recommended |
APA American Psychiatric Association, ASAM American society of addiction medicine, BAP British Association of psychopharmacology, CANMAT and ISBD Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments and International Society for Bipolar Disorders, gov.UK United Kingdom guidelines on clinical management, DGPPN and DG-Sucht German Association for Psychiatry, Psychotherapy, and Psychosomatics and the German Association for Addiction Research and Therapy, NICE National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, RANZCP Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists, SIGN Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, Singapore MOH Singapore Ministry of Health, VA/DoD Department of Veterans Affairs and The Department of Defense, WFSBP World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry
Fig. 2.
Combined AGREE II assessment of guidelines
Assessment of concurrent problems
All of the included coexisting disorders guidelines emphasized that a comprehensive assessment should be carried out for patients with either SMI or SUD for dual diagnosis [37–39]. However, five out of eleven (45%) SMI guidelines did not highlight the assessment of coexisting disorders [47, 48, 54, 55, 57]. In addition, one SUD guidelines (14%) did not highlight the assessment of coexisting disorders [41] (Table 3).
Table 3.
Consideration of concurrent problems
| Guideline | Is the link between mental health and misuse of substances mentioned as part of the background? | Does the guideline mention that either SMI or SUD can worsen the outcome of another? | Does the guideline provide recommendations about Screening/Assessment for coexisting disorders? | Does the guideline mention the competence of healthcare professionals in recognition the existence of the other comorbidity (i.e. either substance misuse or mental health problems)? | Does the guideline requests healthcare professionals to seek advice or training from the other service i.e. training from substance misuse service staff to staff in mental health services? | Does the guideline specifically mention not to exclude patients who misuse substance from age-appropriate treatment settings of mental illness due to use of substances? | Does the guideline specifically mention not to exclude patients who have mental illness from age-appropriate treatment setting of substance misuse due to mental health problems? | Who refers patients to a mental health setting or to the substance misuse/alcohol misuse services? | If a guideline is for mental health, does it mention not to discharge patients from inpatient services because of their substance misuse? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
NICE 2011 (coexisting disorders) [37] |
Yes | Yes | Mentioned. Suspected patients should be asked about any drugs and alcohol drinking including: its type, quantity, frequency, route of administration, and duration of use. | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Mentioned. All staff who have direct contact with patients, including professionals in primary care and educational settings. | Yes |
|
NICE 2016 (coexisting disorders) [38] |
Yes | Yes | Mentioned. A Full evaluation for suspected patients. | No | Yes | Yes | No | Mentioned. All staff who have direct contact with patients, including professionals in primary care and educational settings. | No |
| Australian government 2016 [39] | Yes | Yes | Mentioned. After abstinence, a full assessment of the patient should ideally occur. | Yes | Yes | No | No | Not mentioned | Not applicable |
| SIGN 2013 [47] | Yes | Yes | Not mentioned | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Not mentioned | No |
| NICE 2014 [48] | Yes | Yes | Not mentioned | No | Yes | No | No | Mentioned. Primary healthcare professionals | No |
| WFSBP 2015 [49] | Yes | Yes | Mentioned. Detailed assessment of substance use disorder should be obtained. | No | No | No | No | Not mentioned | No |
| RANZCP 2016 [50] | Yes | Yes | Mentioned. Any suspicions regarding the use of stimulant drugs should be raised if there are recurrent episodes of psychosis. | Yes | Yes | No | No | Mentioned. Health care professionals and any other professionals involved in providing care for patients, such as GPs and social counsellors. | No |
| BAP 2019 [51] | Yes | Yes | Mentioned. A detailed assessment of substance use disorder should be obtained. | No | No | No | No | Not mentioned | No |
| APA 2020 [52] | Yes | Yes | Mentioned. Any initial assessment of a patients with a possible psychotic disorder should include an assessment of their tobacco use and other substance misuse. | Yes | Yes | No | No | Not mentioned | No |
| VA/DoD 2010 [53] | Yes | Yes | Mentioned. A complete clinical assessment should be obtained. | No | No | No | No | Not mentioned | Yes |
| Singapore MOH 2011 [54] | Yes | Yes | Not mentioned | No | No | No | No | Not mentioned | No |
| NICE 2014 [55] | Yes | Yes | Not mentioned | No | Yes | No | No | Mentioned. Primary healthcare professionals | No |
| BAP 2016 [56] | No | Yes | Mentioned. The clinician should assess to what extent does substance misuse contribute to bipolar symptoms. | No | Yes | No | No | Not mentioned | No |
| CANMAT and ISBD 2018 [57] | Yes | Yes | Not mentioned | Yes | No | No | No | Not mentioned | No |
| BAP 2012 [40] | Yes | Yes | Mentioned. Substance history, family history, urinalysis and blood tests, as well as an assessment of psychiatric disorder onset, and the misuse of substances should be carried out. | No | No | No | No | Not mentioned | Not applicable |
| WFSBP 2017 [41] | Yes | Yes | Not mentioned | No | No | No | No | Not mentioned | Not applicable |
| gov.uk 2017 [42] | Yes | Yes | Mentioned. Identifying any current or previous psychological problems | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Mentioned. GPs | Not applicable |
| DGPPN and DG-Sucht 2017 [43] | Yes | Yes | Mentioned. The assessment process derived from alcohol use disorder identification test guidelines | No | No | No | No | Not mentioned | Yes |
| NICE 2011 [44] | Yes | Yes | Mentioned. Patients should be referred to a psychiatrist for effective assessment and treatment. | Yes | Yes | No | No | Mentioned. Whole range of healthcare such as a GP. | Not applicable |
| APA 2018 [45] | Yes | Yes | Mentioned. Patients should be assessed for alcohol use disorder and comorbid mental health disorder. | No | No | No | No | Not mentioned | No |
| ASAM 2015 [46] | Yes | Yes | Mentioned. A comprehensive assessment of the patient and any ideas related to suicide should be evaluated. The patient’s full medical history and a physical examination should also be obtained. | Yes | Yes | No | No | Not mentioned | Not applicable |
AOD Alcohol and other drug, APA American Psychiatric Association, ASAM American society of addiction medicine, AUD alcohol use disorder, BAP British Association of psychopharmacology, CANMAT and ISBD Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments and International Society for Bipolar Disorders, gov.UK United Kingdom guidelines on clinical management, GPs General practitioners, DGPPN and DG-Sucht German Association for Psychiatry, Psychotherapy, and Psychosomatics and the German Association for Addiction Research and Therapy, NICE National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, RANZCP Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists, SIGN Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, Singapore MOH Singapore Ministry of Health, SMI Severe mental illness, SUD Substance use disorder, UK United Kingdom, US United States, VA/DoD Department of Veterans Affairs and The Department of Defense, WFSBP World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry
Three guidelines explicitly stated that patients with SMI with coexisting SUD who completed their SMI treatment course should stay in the hospital to avoid exacerbation of psychotic symptoms and future risk due to substance abuse not be discharged from a healthcare setting due to their substance abuse [37, 43, 53]. Of the SMI guidelines, four guidelines highlighted the competency need of healthcare providers in each health care setting to consider for the co-existing disorders [47, 50, 52, 57]. Three out of seven SUD guidelines similarly covered competency aspects [42, 44, 46]. All coexisting disorder guidelines requested healthcare providers to gain training and expertise from other specialist staff in regards to either SMI or SUD [37–39] (Table 3).
Treatment of coexisting disorders
All of the guidelines related to SMI or coexisting disorders described the importance of screening and/or treatment for both problems simultaneously [37–39]. Three (27%) SMI guidelines stipulated SUD clinical guidelines and vice versa when recommending treatment of the other co-existing disorder (Table 4) [53, 55, 56]. One SUD guideline (14%) [45] however, did not explicitly provide recommendation regarding treatment of both disorders.
Table 4.
Consideration of treatment adjustments
| Guideline | Does the recommendation address the management of coexisting disorders? | What treatment adjustment should be considered? (such as a change of antipsychotic medication in patients who have alcohol use disorder) | Recommendation for monitoring of physical health | Recommendation about drug interactions | Psychological and psychosocial interventions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
NICE 2011 (coexisting disorders) [37] |
No recommendations regarding the benefits of one antipsychotic over another are given. Refers the reader to the NICE guidelines for related disorders. | Mentioned. Use of long-acting injectable antipsychotic medication | Mentioned | Mentioned. Substance misuse practically alcohol may affect the metabolism of medication | Mentioned |
|
NICE 2016 (coexisting disorders) [38] |
Not mentioned. Refers the reader to a NICE guideline for the management of coexisting disorders. | Not mentioned | Mentioned | Not included | Not mentioned |
| Australian government 2016 [39] | Mentioned. Detailed treatment plan for both psychosis and bipolar disorder are provided | Not mentioned | Mentioned | Included | mentioned |
| SIGN 2013 [47] | Mentioned. The treatment of both disorders requires a joint consultative approach between the services provided from both mental health and substance use settings. | Not mentioned | Mentioned | Not included | Mentioned |
| NICE 2014 [48] | Mentioned. Monitoring for coexisting conditions particularly in the early phases of treatment. | Not mentioned | Mentioned | Not included | Mentioned |
| WFSBP 2015 [49] | Mentioned. Consider the addition of clozapine for coexisting disorder. | Mentioned. Patients with a history of non-adherence to their medication should be treated with long-acting depot formulations of antipsychotic medications. | Not mentioned | Not included | Mentioned |
| RANZCP 2016 [50] | Mentioned. Treatment of comorbid substance use. Urine or saliva drug testing for the presence of substance misuse should also be employed. | Not mentioned | Mentioned | Not included | Mentioned |
| BAP 2019 [51] | Mentioned. Optimization of antipsychotic medication and one should consider the addition of clozapine for the patients with dual diagnosis. | Not mentioned | Mentioned | Included | Mentioned |
| APA 2020 [52] | Mentioned. Treatment for both disorders should be provided by the same clinician team. However, if an integrated treatment is unavailable, the treatment plan should address both disorders with communication and collaboration among the clinicians treating the patient. | Not mentioned | Mentioned | Included | Mentioned |
| VA/DoD 2010 [53] | For the management of substance misuse, the reader should refer to the VA/DoD guideline for other related disorders. Treatment of bipolar disorder should be based on this guideline. | Not mentioned | Mentioned | Included | Mentioned |
| Singapore MOH 2011 [54] | Mentioned. Patients with both addiction and bipolar disorders should be treated. | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | Not included | Mentioned |
| NICE 2014 [55] | The reader should refer to the NICE guideline for other related disorders. Moreover, bipolar disorder treatment should be in accordance with this guideline. | Not mentioned | Mentioned | Included | Mentioned |
| BAP 2016 [56] | For alcohol use disorder, this guideline refers the reader to another BAP guideline. The practitioner should assess to what extent substance misuse contributes to bipolar disorder symptom. | Not mentioned | Mentioned | Included | Mentioned |
| CANMAT and ISBD 2018 [57] | Mentioned. For patients with both bipolar disorder and substance misuse, lithium can reduce using of substance. Patients with both bipolar disorder and substance misuse may benefit from the use of N-acetylcysteine. | Mentioned. Reduce bipolar disorder symptoms with olanzapine. Reduce cravings for alcohol and cocaine use with aripiprazole. | Mentioned | Not included | Mentioned |
| BAP 2012 [40] | Treatment of bipolar disorder as recommended in other guidelines and the impact of harmful substance use should be assessed. | Mentioned. Add sodium valproate for bipolar disorder patients who are on lithium only, and limit alcohol drinking with Naltrexone. Clozapine should be considered in patients with both schizophrenia and substance misuse. | Mentioned | Not included | Not mentioned |
| WFSBP 2017 [41] | It is difficult to provide treatment recommendations for managing patients with both schizophrenia and coexisting alcohol use disorder. |
Mentioned. Suggest the use of second generation antipsychotics for managing patients with both schizophrenia and coexisting alcohol use disorder. However, evidence recommends the use of clozapine. |
Not mentioned | Not included | Mentioned |
| gov.uk 2017 [42] | Mentioned. Dual focused treatments | Not mentioned | Mentioned | Included | Mentioned |
| DGPPN and DG-Sucht 2017 [43] | Mentioned. Pharmacological treatment should be based on schizophrenia guidelines. | Mentioned. Treatment of patients with schizophrenia and comorbid alcohol use disorder with atypical antipsychotics (AAP). | Not mentioned | Not included | Mentioned |
| NICE 2011 [44] | Mentioned. For the treatment of comorbid mental health disorders, the reader is referred to the other related disorder’s NICE guideline. | Not mentioned | Mentioned | Included | Mentioned |
| APA 2018 [45] | Not mentioned. | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | Not included | Not mentioned |
| ASAM 2015 [46] | Mentioned. Use of mood stabilizers for the treatment of patients with bipolar disorder. Patients with schizophrenia should be treated with suitable antipsychotic therapy along with treatment of opioid use disorder. Patients with a history of non-adherence to their medication should be treated with long-acting depot formulations of antipsychotic medications. Methadone, buprenorphine, or naltrexone for mental status stabilization. | Not mentioned | Mentioned | Included | Mentioned |
AOD Alcohol and other drug, APA American Psychiatric Association, ASAM American society of addiction medicine, AUD alcohol use disorder, BAP British Association of psychopharmacology, CANMAT and ISBD Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments and International Society for Bipolar Disorders, gov.UK United Kingdom guidelines on clinical management, DGPPN and DG-Sucht German Association for Psychiatry, Psychotherapy, and Psychosomatics and the German Association for Addiction Research and Therapy, NICE National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, RANZCP Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists, SIGN Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, Singapore MOH Singapore Ministry of Health, SMI Severe mental illness, SUD Substance use disorder, UK United Kingdom, US United States, VA/DoD Department of Veterans Affairs and The Department of Defense, WFSBP World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry
Only two out of the 11 (18%) SMI guidelines mentioned recommendation about treatment adjustments when considering dual diagnosis and treatment [49, 57]. Similarly, only three of the seven (43%) SUD guidelines mentioned recommendation about treatment adjustment [40, 41, 43] (Table 4). Examples of treatment adjustments included recommendation for the use of long-acting injectable antipsychotic medication in cases where there was a history of non-adherence to medication in place of regular antipsychotic medication [49]. Only one (33%) guideline of the coexisting disorders guidelines recommended the use of long-acting injectable antipsychotic medication accordingly [37]. Two (67%) of the guidelines related to coexisting disorders [37, 39], five (45%) of SMI guidelines [51–53, 55, 56] and three (43%) of the SUD guidelines [42, 44, 46] considered potential drug interaction in patients with SMI and coexisting SUD. For example, the NICE (2011) guideline recommends that caution be exercised during the prescribing of medication for patients demonstrating substance abuse particularly that of alcohol, since alcohol will affect the metabolism of other medications and either diminish their efficacy or increase the risk of side effects [37] (Table 4).
Importance of physical health monitoring were described by all guidelines related to coexisting disorders, nine (82%) SMI guidelines, and four of the seven (57%) SUD guidelines. These included monitoring and management of diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidemia (Table 4).
Care pathway and integrated care provision
All of the coexisting disorders guidelines, seven (64%) of the SMI guidelines, and three (43%) of SUD guidelines mentioned the importance of continuity of care. For example, the Australian government guideline advised that it is important to develop systems in order to facilitate the transition of patients with coexisting disorders by providing them with much-needed services and helping them to address their complex needs [39] (Table 5).
Table 5.
Care pathway and integrated care provision
| Guideline | Does the guideline mention continuity of care i.e. importance of same health or key worker in managing the substance misuse or mental health/ continuity of care? | Where should integrated services be provided | Is there a mention of the role of emergency department or A&E and what they should do if patients present there? |
|---|---|---|---|
|
NICE 2011 (coexisting disorders) [37] |
Yes |
Secondary care mental health services, CAMHS |
Yes |
|
NICE 2016 (coexisting disorders) [38] |
Yes | Mental health services | No |
| Australian government 2016 [39] | Yes | AOD settings | No |
| SIGN 2013 [47] | No | Not mentioned | No |
|
NICE 2014 [48] |
Yes | secondary care settings | No |
| WFSBP 2015 [49] | No | Not mentioned | No |
| RANZCP 2016 [50] | Mentions continuity but not link key worker | Dual diagnosis service | No |
| BAP 2019 [51] | No | Not mentioned | No |
| APA 2020 [52] | Yes | Not mentioned | No |
| VA/DoD 2010 [53] | Yes | Urgent/emergent mental health settings | No |
| Singapore MOH 2011 [54] | Yes | In an integrated specialist treatment centre. | No |
| NICE 2014 [55] | Yes | Not mentioned | No |
| BAP 2016 [56] | No | Not mentioned | No |
| CANMAT and ISBD 2018 [57] | Yes | inpatient hospital or community residential treatment | No |
| BAP 2012 [40] | No | Not mentioned | No |
| WFSBP 2017 [41] | No | Not mentioned | No |
| gov.uk 2017 [42] | Yes | In drug misuse services and mental health services | Yes |
| DGPPN and DG-Sucht 2017 [43] | No | Inpatient treatment | No |
| NICE 2011 [44] | Yes | Not mentioned | Yes |
| APA 2018 [45] | Yes | Not mentioned | No |
| ASAM 2015 [46] | No | Hospitals | Yes |
AOD Alcohol and other drug, APA American Psychiatric Association, ASAM American society of addiction medicine, AUD alcohol use disorder, BAP British Association of psychopharmacology, CANMAT and ISBD Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments and International Society for Bipolar Disorders, gov.UK United Kingdom guidelines on clinical management, DGPPN and DG-Sucht German Association for Psychiatry, Psychotherapy, and Psychosomatics and the German Association for Addiction Research and Therapy, NICE National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, RANZCP Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists, SIGN Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, Singapore MOH Singapore Ministry of Health, SMI Severe mental illness, SUD Substance use disorder, UK United Kingdom, US United States, VA/DoD Department of Veterans Affairs and The Department of Defense, WFSBP World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry
Only one (33%) of the guidelines pertaining to coexisting disorders mentioned that healthcare providers in the emergency department should regularly ask patients about any potential substance abuse [37]. Three (43%) of the guidelines related to SUD mentioned the role of the emergency department [42, 44, 46]. Such consideration was missing from SMI guidelines (Table 5).
Equity consideration and person-centered care
Three guidelines pertaining to coexisting disorders, ten (91%) SMI guidelines, and six (86%) SUD guidelines described the essential role played by ‘significant others’ such as families and carers and encouraged their involvement along with any integrated care plans provided to patients (Table 6). All of the three guidelines pertaining to coexisting disorders were explicit in reporting the need for assessment of any children cared for by patients with both disorders, according to safeguarding procedures. However, only three (27%) of the SMI guidelines and two (29%) of the SUD guidelines provided recommendations about children cared for by patients with both disorders (Table 6).
Table 6.
Equity considerations and person-centered care
| Guideline | Does the guideline mention the importance of involving family and carers? | Dose the guideline mention children cared for by patient with mental health conditions or substance misuse? | Does the guideline mention the importance of engaging with various ethnicities and cultural needs? | Does the guideline mention allaying patient fear about being detained or forcefully put into care or rehabilitation? | Is there consideration for people with physical, sensory or learning disabilities in the guideline? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
NICE 2011 (coexisting disorders) [37] |
Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
NICE 2016 (coexisting disorders) [38] |
Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Australian government 2016 [39] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| SIGN 2013 [47] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
|
NICE 2014 [48] |
Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| WFSBP 2015 [49] | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| RANZCP 2016 [50] | Yes | No | Yes | No | No |
| BAP 2019 [51] | Yes | No | No | No | Yes |
| APA 2020 [52] | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| VA/DoD 2010 [53] | Yes | No | No | No | Yes |
| Singapore MOH 2011 [54] | No | No | No | No | No |
| NICE 2014 [55] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| BAP 2016 [56] | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| CANMAT and ISBD 2018 [57] | Yes | No | No | No | Yes |
| BAP 2012 [40] | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| WFSBP 2017 [41] | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| gov.uk 2017 [42] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| DGPPN and DG-Sucht 2017 [43] | No | No | No | No | No |
| NICE 2011 [44] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| APA 2018 [45] | Yes | No | No | No | Yes |
| ASAM 2015 [46] | Yes | No | No | No | Yes |
AOD Alcohol and other drug, APA American Psychiatric Association, ASAM American society of addiction medicine, AUD alcohol use disorder, BAP British Association of psychopharmacology, CANMAT and ISBD Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments and International Society for Bipolar Disorders, gov.UK United Kingdom guidelines on clinical management, DGPPN and DG-Sucht German Association for Psychiatry, Psychotherapy, and Psychosomatics and the German Association for Addiction Research and Therapy, NICE National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, RANZCP Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists, SIGN Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, Singapore MOH Singapore Ministry of Health, SMI Severe mental illness, SUD Substance use disorder, UK United Kingdom, US United States, VA/DoD Department of Veterans Affairs and The Department of Defense, WFSBP World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry
All of the guidelines pertaining to coexisting disorders, five (45%) of the SMI guidelines, and two (29%) of the SUD guidelines mentioned the importance of ensuring that healthcare providers who provide care to patients with coexisting disorders should engage with patients from different ethnicities and cultural backgrounds (Table 6). Only the NICE 2011 offered advice to healthcare providers to solve access to care issues in patients [37] (Table 6).
Consideration of multiple social disadvantage
All of the guidelines pertaining to coexisting disorders, nine (82%) of the SMI guidelines, and five (71%) of the SUD guidelines considered the assessment of risks of violence, suicide, and self-harm (Table 7). Two (67%) of the guidelines pertaining to coexisting disorders highlighted the risk of certain getting involved with criminal justice system and the importance of prevention actions [37, 38]. Only the SMI guideline by Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists (RANZCP) [50] and three (45%) of the SUD guidelines [42, 44, 46] highlighted the risk of patients being registered in the criminal justice system (Table 7).
Table 7.
Inclusivity in relation to consideration of homelessness and contextual factors
| Guideline | Does the guideline mention that concurrent problems can increase risk of self-harm, suicide, violence, injury or offending behaviour? | Is the risk of criminal justice system/offending/prison for those affected mentioned? | Does the guideline recommend providing health care for prison offender in rehabilitation centre | Is the risk of homelessness for those affected mentioned? | Does the guideline provide suggestions for healthcare professionals to refer patients to housing assistance or homelessness services if patients are found at risk of homelessness | Does the screening mentions patient history of sexual or other forms of abuse? | Is there mention of or consideration about stigma and discrimination in healthcare setting? | Does the guideline mention the importance of working with voluntary, charity or No? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
NICE 2011 (coexisting disorders) [37] |
Yes | Yes | Yes, in case of diverted treatment | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
NICE 2016 (coexisting disorders) [38] |
Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Australian government 2016 [39] | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| SIGN 2013 [47] | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
|
NICE 2014 [48] |
No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| WFSBP 2015 [49] | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| RANZCP 2016 [50] | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| BAP 2019 [51] | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| APA 2020 [52] | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| VA/DoD 2010 [53] | Yes | No | No | No | No | Yes, but as risk factor for suicide in patients with bipolar disorder | No | No |
| Singapore MOH 2011 [54] | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| NICE 2014 [55] | Yes | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| BAP 2016 [56] | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| CANMAT and ISBD 2018 [57] | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| BAP 2012 [40] | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| WFSBP 2017 [41] | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| gov.uk 2017 [42] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| DGPPN and DG-Sucht 2017 [43] | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| NICE 2011 [44] | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| APA 2018 [45] | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| ASAM 2015 [46] | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No |
AOD Alcohol and other drug, APA American Psychiatric Association, ASAM American society of addiction medicine, AUD alcohol use disorder, BAP British Association of psychopharmacology, CANMAT and ISBD Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments and International Society for Bipolar Disorders, gov.UK United Kingdom guidelines on clinical management, DGPPN and DG-Sucht German Association for Psychiatry, Psychotherapy, and Psychosomatics and the German Association for Addiction Research and Therapy, NICE National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, RANZCP Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists, SIGN Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, Singapore MOH Singapore Ministry of Health, SMI Severe mental illness, SUD Substance use disorder, UK United Kingdom, US United States, VA/DoD Department of Veterans Affairs and The Department of Defense, WFSBP World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry
All of the guidelines pertaining to coexisting disorders, four (36%) of the SMI guidelines [47, 49, 50, 52], and two (29%) of the SUD guidelines [42, 44] attempted to inform the healthcare providers about the risk of homelessness as being a negative social outcome for individuals affected by SMI or SUD. However, only the Australian government mentioned the risk of homelessness in patients with coexisting disorders, but did not provide further recommendations about how such patients could receive support [39] (Table 7). Assessment of the history of any kind of abuse suffered by the patient, including sexual abuse were only rarely considered [37, 39, 42, 44, 52, 53, 55] (Table 7).
Issue of stigma and discrimination from healthcare providers were covered well by guidelines for co-existing disorders but less so by either SMI or SUD guidelines (Table 7).
Two (67%) of the guidelines pertaining to coexisting disorders, two (18%) of the SMI guidelines, and two (29%) of the SUD guidelines seemed to encourage seeking support from voluntary organizations [37, 38, 42, 44, 48, 50] (Table 7).
Discussion
This study provides an up-to-date assessment of the scope, quality and inclusivity of international clinical guidelines on mental health and/or substance abuse in relation to diagnosis and treatment of such co-existing disorders and consideration of wider social and contextual issues in treatment recommendations.
The overall quality of the included guidelines rated from a high to moderate quality. The ‘scope and purpose’ and ‘clarity of presentation’ domains were well addressed by the included guidelines. Previous systematic reviews have also demonstrated that clinical guidelines often score high in these domains [58–60]. For the ‘Stakeholder involvement’, it was noticed that there was a lack of incorporation of patient or public preferences in the guidelines development process. The ‘applicability’ domain was rated low amongst all the guidelines.
This review has demonstrated that there is a lack of clinical guidelines aimed to help healthcare professionals manage the dual diagnosis. More importantly any existing single disorder guidelines should incorporate coexisting disorders in diagnosis and treatment recommendations. These guidelines need to be consistent with current evidence that supported development of integral treatment model, strengthen the connection between mental health care setting and substance abuse services, and providing care for patients’ multiple disadvantages including wider social and contextual factors such as homelessness, involvement with criminal justice system [2, 15, 17].
Implication of practice and research
Until recently, most of the guidelines and recommendations addressed a single disorder; namely, either SMI or SUD. The result of this review suggests that a greater number of guidelines are required in order to cover dual diagnosis given the high overlap of the concurrent disorders.
Most single disorder guidelines included in this review did emphasize the importance of assessment of dual diagnosis. However, treatment adjustment for dual diagnosis was rarely described. Barriers of access to medicines, adherence issues requiring long acting depot injections, and drug interactions (including interactions with drug and substance of abuse) are key issues that require further considerations in single disorder guidelines.
There needs to be better emphasis on the integrated and inclusive care to be offered to the patients with dual diagnosis. Evidence suggests significant reductions in substance abuse, improvement in psychiatric symptoms, quality of life as well as social outcomes in relation to integrated models of management [61, 62]. However, traditional culture of specialist treatment centres that are focused on the treatment of a single condition, lack of expertise and resources are some of the barriers to provision of integrated care as described in the literature [29]. This review suggests that lack of clinical guidelines to offer integrated care could be contributing to the fragmented care. The need for liaison with emergency department, primary care, drug and alcohol services and hospital and specialist treatment centers also require further emphases. There is also scope to enhance cultural and ethnic specific issues in treatment recommendations.
It is well documented in the evidence that the treatment of coexisting disorders multifaceted and requires the continued assessment of many social and contextual issues of a patient. Social and contextual factors were not however uniformly addressed in the included guidelines. While risk of homelessness in patients with SMI, SUD or dual diagnosis was commonly described, further information to health providers to support prevention actions were often missing. It is imperative to signpost patients to housing assistance, volunteer sectors and social benefits system in order to prevent homelessness including repeat cycle of homelessness. Adequate evidence exist on the overlap between homelessness, SUD, SMI and dual diagnosis [63]. Persons who are homeless or risk facing homelessness often find accessing services difficult and future guidelines should consider addressing access issues better [21–23]. These include perceived stigma and discrimination in healthcare setting. Some guidelines described risks of homelessness with dual diagnosis. There are various barriers which patients experiencing homelessness and SUD must overcome in order to obtain housing due to their criminal record and economic status, all of which make them more susceptible to being submerged in their current negative environment and seem to increase the risk of relapse [64, 65].
Only a limited number of guidelines considered the continuity of care of offenders in community settings. It is known that treatment failure can trigger a return back to the patient’s offending behavior after their release from prison [66, 67].
There needs to be better emphases on the integrated and inclusive care to be offered to the patients with dual diagnosis. Liaison with emergency department, primary care, drug and alcohol services and hospital and specialist treatment centers require further emphases. There is also scope to enhance cultural and ethnic specific issues in treatment recommendations. Roles of community based services such as community pharmacy and voluntary sectors should be better stipulated in the guidelines [68–71].
Future research is need needed to cover healthcare professional, patient, carer and payer’s perspectives to identify ways to strengthen the guidelines and limitations and improve patient experiences of care and outcomes. It is also imperative to compare practices against the guideline recommendations. For example, research suggest that patients prescribed antipsychotic medicines are often poorly followed up for their cardiovascular and metabolic health in contrary to the recommendations from the guidelines [72]. Guideline development procedures should learn and share best practices being adopted in other countries.
The assessment of the quality of the guidelines using Agree II checklist suggested that the ‘Rigour of development’ domain scores were generally low as 15 out of 21 included guidelines rated below 70%. This domain captures how well did the guidelines provide evidence in relation to systematic search of relevant body of evidence-based literature, critical appraisal and expert review of the evidence. Further systematic and transparent approach needs to be adopted around the use and reporting of how evidence informed the guideline development.
In summary, this study reinforces the need for adaptation of international clinical guidelines so that healthcare professionals in diverse settings can undertake comprehensive assessment of patient with either SMI or SUD for dual diagnosis, consider assessment of wider social circumstances and consequences that are relevant to the dual diagnosis and adapt their treatment plans accordingly allowing better outcomes for patients, mitigate relapse of SMI, prevent repeat cycles of substance abuse and social consequences such as homelessness. This in turn have the potential to minimize healthcare costs and resource implications. Stakeholder should be involved in development of guidelines.
Study strengths and limitations
This is the first systematic review to discuss coexisting disorders and aspects of their different complex needs. A comprehensive search was undertaken using databases and professional body web pages. Validated appraisal tool (AGREE II) was used for quality assessment. However, our search was restricted to English language guidelines only. In addition, we did not assess any supplementary patient screening, risk assessment and patient placement criteria that were not included or appended within the published guidelines.
Conclusion
Treatment guidelines for management of either SUD or SMI have tend to have limited considerations for dual diagnosis. There is a need for the guidelines to be more inclusive in order to enable better diagnosis and treatment and cover social cause and consequences of dual diagnosis such as homelessness. Further emphasis is also needed to promote effective transition of care across services and promotion of self-care after discharge. Professional societies should better communicate the guideline development process as well as rigour in relation to the inclusion and appraisal of evidence base in the guideline development process.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1. Electronic supplemental material 1: PRISMA Checklist.
Additional file 2. Electronic supplemental material 2: Search strategy.
Additional file 3. Electronic supplemental material 3: AGREE II Score Sheet.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Data availability
All data associated with the manuscript has been reported in the manuscript and supplemental materials.
Conflict of interest
No authors have any conflicts of interests to disclose.
Abbreviations
- SMI
Severe mental illness
- SUD
Substance use disorder
- NICE
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
- APA
American Psychiatric Association
- US
United States
- UK
United Kingdom
- GPs
General practitioners
- DSM-5
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-5
- BAP
British Association of psychopharmacology
- AUD
Alcohol use disorder
- PRISMA
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
- PROSPERO
International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews
- SIGN
Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network
- AGREE II
Appraisal of Guidelines for Research & Evaluation II
- AOD
Alcohol and other drug
- WFSBP
World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry
- DGPPN and DG-Sucht
German Association for Psychiatry, Psychotherapy, and Psychosomatics and the German Association for Addiction Research and Therapy
- ASAM
American society of addiction medicine
- Singapore MOH
Singapore Ministry of Health
- VA/DoD
Department of Veterans Affairs and The Department of Defense
- CANMAT and ISBD
Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments and International Society for Bipolar Disorders
- RANZCP
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists
- Gov.uk
United Kingdom guidelines on clinical management
- CAMHS
Child and adolescent mental health services
Authors’ contributions
This work related to RA’s Master of Science in Toxicology study. DS, SA, and VP were the supervisors to the study. RL contributed through expert advice, critical review and significant input in the write up. RA led the write up to which all authors contributed through editing and recommendations. All authors agreed to the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Carrà G, Bartoli F, Brambilla G, Crocamo C, Clerici M. Comorbid addiction and major mental illness in Europe: a narrative review. Subst Abus. 2015;36(1):75–81. doi: 10.1080/08897077.2014.960551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fantuzzi C, Mezzina R. Dual diagnosis: a systematic review of the organization of community health services. Int J Soc Psychiatry. 2020;66(3):300–310. doi: 10.1177/0020764019899975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.McCreadie RG. Use of drugs, alcohol and tobacco by people with schizophrenia: case–control study. Br J Psychiatry. 2002;181(4):321–325. doi: 10.1192/bjp.181.4.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Temmingh HS, Williams T, Siegfried N, Stein DJ. Risperidone versus other antipsychotics for people with severe mental illness and co-occurring substance misuse. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 5.Elliott I. Poverty and mental health: a review to inform the Joseph Rowntree Foundation’s Anti-Poverty Strategy. Available from: http://www.patient.co.uk/doctor/Poverty-and-Mental-Health.htm. Accessed 07 Feb 2021.
- 6.Wade D, Harrigan S, Edwards J, Burgess PM, Whelan G, McGorry PD. Substance misuse in first-episode psychosis: 15-month prospective follow-up study. Br J Psychiatry. 2006;189(3):229–234. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.105.017236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.National Institute on Drug Abuse. Comorbidity: substance use disorders and other mental illnesses drugfacts. Available from: https://www.drugabuse.gov/drug-topics/publications/drug-facts. Accessed 07 Feb 2021.
- 8.Antai-Otong D, Theis K, Patrick DD. Dual diagnosis: coexisting substance use disorders and psychiatric disorders. Nurs Clin. 2016;51(2):237–247. doi: 10.1016/j.cnur.2016.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Brunette MF, Mueser KT, Drake RE. A review of research on residential programs for people with severe mental illness and co-occurring substance use disorders. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2004;23(4):471–481. doi: 10.1080/09595230412331324590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lambert-Harris C, Saunders EC, McGovern MP, Xie H. Organizational capacity to address co-occurring substance use and psychiatric disorders: assessing variation by level of care. J Addict Med. 2013;7(1):25–32. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0b013e318276e7a4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hjorthøj C, Østergaard MLD, Benros ME, Toftdahl NG, Erlangsen A, Andersen JT, Nordentoft M. Association between alcohol and substance use disorders and all-cause and cause-specific mortality in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and unipolar depression: a nationwide, prospective, register-based study. Lancet Psychiatry. 2015;2(9):801–808. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(15)00207-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lynskey MT, Kimber J, Strang J. Drug-related mortality in psychiatric patients. Lancet Psychiatry. 2015;2(9):767–769. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(15)00372-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fridell M, Bäckström M, Hesse M, Krantz P, Perrin S, Nyhlén A. Prediction of psychiatric comorbidity on premature death in a cohort of patients with substance use disorders: a 42-year follow-up. BMC Psychiatry. 2019;19(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s12888-019-2098-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fekadu W, Mihiretu A, Craig TKJ, Fekadu A. Multidimensional impact of severe mental illness on family members: systematic review. BMJ Open. 2019;9(12). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 15.Lukasiewicz M, Blecha L, Falissard B, Neveu X, Benyamina A, Reynaud M, Gasquet I. Dual diagnosis: prevalence, risk factors, and relationship with suicide risk in a nationwide sample of French prisoners. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2009;33(1):160–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2008.00819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Polcin DL. Co-occurring substance abuse and mental health problems among homeless persons: suggestions for research and practice. J Soc Distress Homeless. 2016;25(1):1–10. doi: 10.1179/1573658X15Y.0000000004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Schütz C, Choi F, Jae Song M, Wesarg C, Li K, Krausz M. Living with dual diagnosis and homelessness: marginalized within a marginalized group. J Dual Diagn. 2019;15(2):88–94. doi: 10.1080/15504263.2019.1579948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Buckley PF. Prevalence and consequences of the dual diagnosis of substance abuse and severe mental illness. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006;67:5. doi: 10.4088/JCP.0706e01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.McLeod KE, Butler A, Young JT, Southalan L, Borschmann R, Sturup-Toft S, et al. Global prison health care governance and health equity: a critical lack of evidence. Am J Public Health. 2020;110(3):303–308. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2019.305465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kelly TM, Daley DC. Integrated treatment of substance use and psychiatric disorders. Soc Work Public Health. 2013;28(3–4):388–406. doi: 10.1080/19371918.2013.774673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gunner E, Chandan SK, Yahyouche A, Paudyal V, Marwick S, Saunders K, et al. Provision and accessibility of primary healthcare services for people who are homeless: a qualitative study of patient perspectives in the UK. Br J Gen Pract. 2019;69(685):E526–E536. doi: 10.3399/bjgp19X704633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Paudyal V, Maclure K, Forbes-McKay K, McKenzie M, McLeod J, Smith ASD. If I die, I die, I don’t care about my health’: perspectives on self-care of people experiencing homelessness. Health Soc Care Community. 2020;28(1):160–172. doi: 10.1111/hsc.12850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Paudyal V, MacLure K, Buchanan C, Wilson L, Macleod J, Stewart D. ‘When you are homeless, you are not thinking about your medication, but your food, shelter or heat for the night’: behavioural determinants of homeless patients’ adherence to prescribed medicines. Public Health. 2017;148:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2017.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Pinderup P. Challenges in working with patients with dual diagnosis. Adv Dual Diagn. 2018;11(2):60–75. doi: 10.1108/ADD-11-2017-0021. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sorsa M, Greacen T, Lehto J, Åstedt-Kurki P. A qualitative study of barriers to care for people with co-occurring disorders. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 2017;31(4):399–406. doi: 10.1016/j.apnu.2017.04.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ducharme LJ, Knudsen HK, Roman PM. Availability of integrated care for co-occurring substance abuse and psychiatric conditions. Community Ment Health J. 2006;42(4):363–375. doi: 10.1007/s10597-005-9030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Murthy P, Chand P. Treatment of dual diagnosis disorders. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2012;25(3):194–200. doi: 10.1097/YCO.0b013e328351a3e0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Stewart SH, Conrod PJVO-19 State-of-the-art in cognitive-behavioral interventions for substance use disorders: introduction to the special issue. J Cogn Psychother. 2005;19(3):195. [Google Scholar]
- 29.McGovern MP, Lambert-Harris C, Gotham HJ, Claus RE, Xie H. Dual diagnosis capability in mental health and addiction treatment services: an assessment of programs across multiple state systems. Adm Policy Ment Health Ment Health Serv Res. 2014;41(2):205–214. doi: 10.1007/s10488-012-0449-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Perron BE, Bunger A, Bender K, Vaughn MG, Howard MO. Treatment guidelines for substance use disorders and serious mental illnesses: do they address co-occurring disorders? Subst Use Misuse. 2010;45(7–8):1262–1278. doi: 10.3109/10826080903442836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.De Brún C. Finding the evidence: a key step in the information production process. Inf Stand Guid. 2013.
- 32.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, The PRISMA Group Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed1000097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.American Pyschiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5®): American Psychiatric Association; 2013. https://www.psychiatry.org/psychiatrists/practice/dsm. Accessed 07 Feb 2021
- 34.Mclellan AT. Substance misuse and substance use disorders: why do they matter in healthcare? Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 2017;128:112. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Brouwers MC, Kho ME, Browman GP, Burgers JS, Cluzeau F, Feder G, et al. AGREE II: Advancing guideline development, reporting and evaluation in health care. CMAG. 2010;182(18). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 36.Brouwers MC, Kerkvliet K, Spithoff K, Consortium ANS. The AGREE reporting checklist: a tool to improve reporting of clinical practice guidelines. BMG. 2016;352:i1152. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i1152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Psychosis with coexisting substance misuse: assessment and management in adults and young people. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK109783/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK109783.pdf. Accessed 07 Feb 2021.
- 38.NICE. Coexisting existing severe mental illness and substance misuse : community health and social care services. Available from: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng58. Accessed 07 Feb 2021.
- 39.Marel C, Mills KL, Kingston R, Gournay K, Deady M, Kay-Lambkin F, et al. Co-occurring alcohol and other drug and mental health conditions in alcohol and other drug treatment settings. Illustrations; 2016.
- 40.Lingford-Hughes AR, Welch S, Peters L, Nutt DJ. BAP updated guidelines: evidence-based guidelines for the pharmacological management of substance abuse, harmful use, addiction and comorbidity: Recommendations from BAP. J Psychopharmacol. 2012;26(7):899–952. doi: 10.1177/0269881112444324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Soyka M, Kranzler HR, Hesselbrock V, Kasper S, Mutschler J, Möller HJ. Guidelines for biological treatment of substance use and related disorders, part 1: alcoholism, first revision. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2017;18(2):86–119. doi: 10.1080/15622975.2016.1246752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Gov.uk. Drug misuse and dependence: UK guidelines on clinical management. 2021. Available from: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/drug-misuse-and-dependence-uk-guidelines-on-clinical-management. Accessed 07 Feb 2021.
- 43.Preuss UW, Gouzoulis-Mayfrank E, Havemann-Reinecke U, Schäfer I, Beutel M, Hoch E, et al. Psychiatric comorbidity in alcohol use disorders: results from the German S3 guidelines. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2018;268(3):219–29. 10.1007/s00406-017-0801-2. Accessed 07 Feb 2021. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 44.NICE. Alcohol-use disorders: diagnosis, assessment and management of harmful drinking (high-risk drinking) and alcohol dependence. Available https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg115. Accessed 07 Feb 2021.
- 45.Reus VI, Laura Fochtmann CJ, Oscar Bukstein M, Evan Eyler MA, Donald Hilty MM, Horvitz-Lennon M, et al. The american psychiatric association practice guideline for the pharmacological treatment of patients with alcohol use disorder guideline writing group systematic review group steering committee on practice guidelines APA assembly liaisons. 2018. Available from: https://psychiatryonline.org/doi/pdf/10.1176/appi.books.9781615371969. Accessed 07 Feb 2021.
- 46.Comer S, Cunningham C, Fishman MJ, Gordon FA, Kampman FK, Langleben D, et al. National practice guideline for the use of medications in the treatment of addiction involving opioid use. Am Soc Addicit Med. 2015;66.
- 47.Scottish Intercollegiate Guideline Network. SIGN 131 • Management of schizophrenia key to evidence statement and grades of recommendations Available from: http://sign.ac.uk/pdf/sign131.pdf.
- 48.NICE. Psychosis and schizophrenia in adults: treatment and management. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg178. Accessed 07 February 2021.
- 49.Hasan A, Falkai P, Wobrock T, Lieberman J, Glenthoj B, Gattaz WF, et al. World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) guidelines for biological treatment of schizophrenia part 3: update 2015 management of special circumstances: depression, Suicidality, substance use disorders and pregnancy and lactation. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2015;16(3):142–170. doi: 10.3109/15622975.2015.1009163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Castle DJ, Galletly CA, Dark F, Humberstone V, Morgan VA, Killackey E, et al. The 2016 royal australian and New Zealand college of psychiatrists guidelines for the management of schizophrenia and related disorders. Med J Aust. 2017;206(11):501–5. 10.5694/mja16.01159. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 51.Barnes TRE, Drake R, Paton C, Cooper SJ, Deakin B, Ferrier IN, et al. Evidence-based guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of schizophrenia: updated recommendations from the British Association for Psychopharmacology. J Psychopharmacol. 2020;34(1):3–78. 10.1177/0269881119889296. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 52.Keepers GA, Anzia JM, Benjamin S, Lyness JM, Mojtabai R, Servis M, et al. The American Psychiatric Association practice guideline for the treatment of patients with schizophrenia Guideline .https://www.psychiatry.org/psychiatrists/practice/clinical-practice-guidelines. Accessed 07 Feb 2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 53.Department of Veterans Affairs, Department of Defense . VA/DoD clinical practice guidline for management of bipolar disorder in adults. 2009. pp. 1–176. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Mok YM, Chan HN, Chee KS, Chua T-E, Lim BL, Marziyana AR, et al. MOH clinical practice guidelines: bipolar disorder. Ministry of Health. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22159936/. Accessed 07 Feb 2021. [PubMed]
- 55.NICE. Bipolar disorder: assessment and management. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg185/resources/bipolar-disorder-assessment-and-management-pdf-35109814379461 . Accessed 07 Feb 2021.
- 56.Goodwin GM, Haddad PM, Ferrier IN, Aronson JK, Barnes TRH, Cipriani A, et al. Evidence-based guidelines for treating bipolar disorder: revised third edition recommendations from the British Association for Psychopharmacology. J Psychopharmacol. 2016;30(6):495–553. 10.1177/0269881116636545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 57.Yatham LN, Kennedy SH, Parikh SV, Schaffer A, Bond DJ, Frey BN, et al. Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments (CANMAT) and International Society for Bipolar Disorders (ISBD) 2018 guidelines for the management of patients with bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord. 2018;20(2):97–170. 10.1111/bdi.12609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 58.Keating D, McWilliams S, Schneider I, Hynes C, Cousins G, Strawbridge J, Clarke M. Pharmacological guidelines for schizophrenia: a systematic review and comparison of recommendations for the first episode. BMJ Open. 2017;7(1):e013881. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-013881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Johnston A, Hsieh S-C, Carrier M, Kelly SE, Bai Z, Skidmore B, et al. A systematic review of clinical practice guidelines on the use of low molecular weight heparin and fondaparinux for the treatment and prevention of venous thromboembolism: implications for research and policy decision-making. PLoS One. 2018;13(11):e0207410. 10.1371/journal.pone.0207410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 60.Zhang P, Lu Q, Li H, Wang W, Li G, Si L, Ding Y. The quality of guidelines for diabetic foot ulcers: a critical appraisal using the AGREE II instrument. PLoS One. 2019;14(9):e0217555. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Ziedonis DM, Smelson D, Rosenthal RN, Batki SL, Green AI, Henry RJ, et al. Improving the care of individuals with schizophrenia and substance use disorders: consensus recommendations. J Psychiatr Pract. 2005;11(5):315–339. doi: 10.1097/00131746-200509000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Morrens M, Dewilde B, Sabbe B, Dom G, De Cuyper R, Moggi F. Treatment outcomes of an integrated residential programme for patients with schizophrenia and substance use disorder. Eur Addict Res. 2011;17(3):154–163. doi: 10.1159/000324480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Bowen M, Marshall T, Yahyouche A, Paudyal V, Marwick S, Saunders K, et al. Multimorbidity and emergency department visits by a homeless population: a database study in specialist general practice. Br J Gen Pract. 2019;69(685):E515–E525. doi: 10.3399/bjgp19X704609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Moxley VBA, Hoj TH, Novilla MLB. Predicting homelessness among individuals diagnosed with substance use disorders using local treatment records. Addict Behav. 2020;102:106160. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2019.106160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Padgett DK, Stanhope V, Henwood BF, Stefancic A. Substance use outcomes among homeless clients with serious mental illness: comparing housing first with treatment first programs. Community Ment Health J. 2011;47(2):227–232. doi: 10.1007/s10597-009-9283-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Field G. Continuity of offender treatment for substance use disorders from institution to community: treatment improvement protocol (TIP) series 30. Washington, DC: Department of Health and Human Services; 1998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Peters RH, Bartoi MG, Sherman PB. Screening and assessment of co-occurring disorders in the justice system. https://www.ce-credit.com/articles/100958/Screening_Assessment_Mono.pdf. Accessed 18 Mar 2021.
- 68.Paudyal V, Gibson Smith K, MacLure K, Forbes-McKay K, Radley A, Stewart D. Perceived roles and barriers in caring for the people who are homeless: a survey of UK community pharmacists. Int J Clin Pharm. 2019;41(1):215–27. 10.1007/s11096-019-00789-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 69.Jagpal P, Saunders K, Plahe G, Russell S, Barnes N, Lowrie R, et al. Research priorities in healthcare of persons experiencing homelessness: outcomes of a national multi-disciplinary stakeholder discussion in the United Kingdom. Int J Equity Health. 2020;19(1):1–7 10.1186/s12939-020-01206-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 70.Jagpal P, Barnes N, Lowrie R, Banerjee A, Paudyal V. Clinical pharmacy intervention for persons experiencing homelessness: evaluation of patient perspectives in service design and development. Pharmacy. 2019;7(4):153. doi: 10.3390/pharmacy7040153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Alenezi A, Yahyouche A, Paudyal V. Interventions to optimize prescribed medicines and reduce their misuse in chronic non-malignant pain: a systematic review. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2021;77(4):467–490. doi: 10.1007/s00228-020-03026-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Ali RA, Jalal Z, Paudyal V. Barriers to monitoring and management of cardiovascular and metabolic health of patients prescribed antipsychotic drugs: a systematic review. BMC Psychiatry. 2020;20(1) 10.1186/s12888-020-02990-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1. Electronic supplemental material 1: PRISMA Checklist.
Additional file 2. Electronic supplemental material 2: Search strategy.
Additional file 3. Electronic supplemental material 3: AGREE II Score Sheet.
Data Availability Statement
All data associated with the manuscript has been reported in the manuscript and supplemental materials.
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].