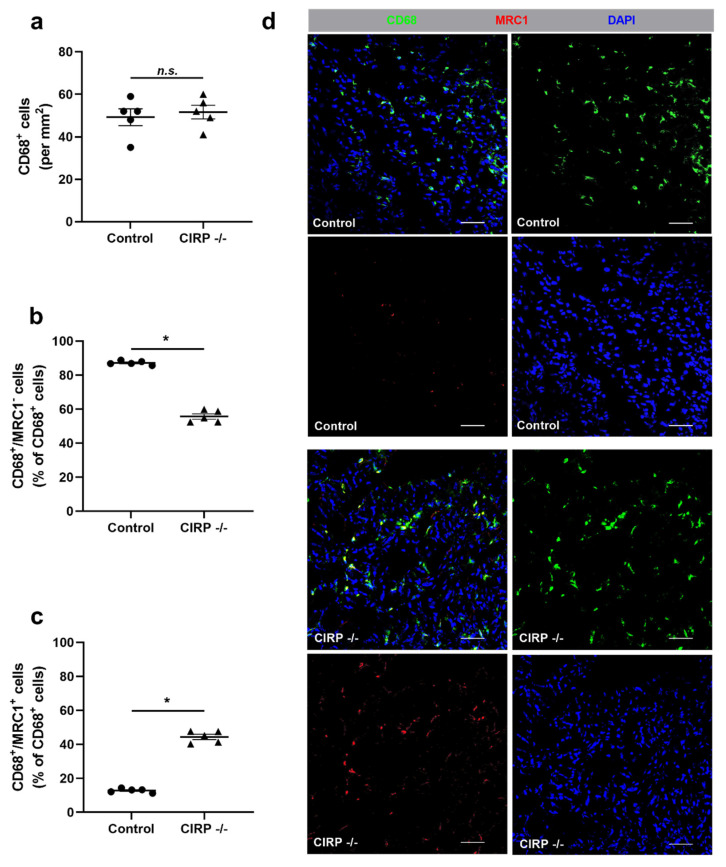
Figure 4.
Cold-inducible RNA-binding protein (CIRP) knockout affects macrophage polarization. (a) The scatter plots display the relative amount of CD68+ cells (macrophages) (per mm2), (b) CD68+/MRC1- (mannose receptor c-type 1) (M1-like polarized macrophages), and (c) CD68+/MRC1+ cells (M2-like polarized macrophages) in relation to all CD68+ cells (in%) in ischemic gastrocnemius muscles of CIRP wildtype control and CIRP -/- mice 7 days after femoral artery ligation (FAL). Data are means ± S.E.M., n = 5 per group. n.s. p > 0.05 ((a) CIRP -/- vs. control), * p < 0.05 ((b,c) CIRP -/- vs. control) by unpaired, two-sided student’s t-test. (d) Representative immunofluorescence staining of ischemic gastrocnemius muscle slices of wildtype control (above) and CIRP -/- mice (below) 7 days after FAL. Images show single and merged channels of CD68 and MRC1 labeled macrophages (anti-CD68, green; anti-MRC1, red) and nucleic acid (DAPI, blue). Scale bars 50 µm.