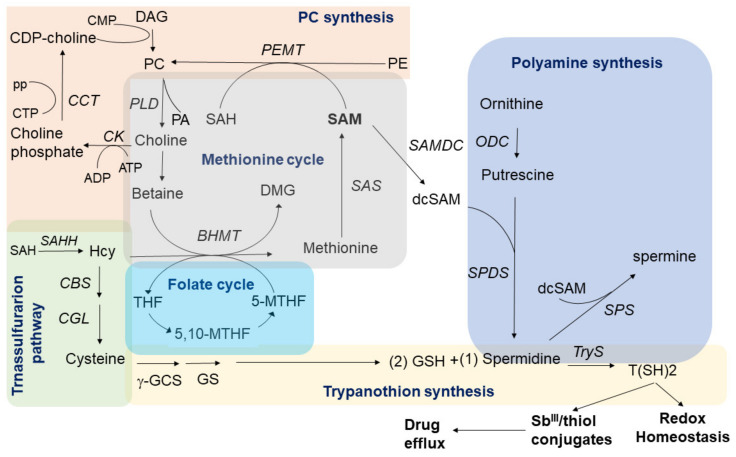
Figure 11.
Summarized interconnection between PC synthesis, trans-sulfuration pathway, folate cycle, methionine cycle, polyamine pathway, and trypanothion synthesis. In antimony resistant parasites a decrease in PC biosynthesis and/or the activation of the PC hydrolysis via phospholipase D (PLD) can potentially contribute to increase the SAM levels and other methyl group donors, which can be addressed to feed the polyamine pathway and improve the trypanothione T(SH)2 synthesis. In Leishmania, T(SH)2 is the main antioxidant molecule and can interact with SbIII. It is commonly accepted that this complex can be transported via ABC (ATP-binding cassette) transporters and released during drug efflux. 5,10-MTHF: 5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate; 5-MTHF: 5-methyltetrahydrofolate; 5-MTHF: 5-methyltetrahydrofolate; ADP: Adenosine diphosphate; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; BHMT: Betaine Homocysteine Methyltransferase; CBS: Cystathionine b-synthase; CCT: phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase; CEPT: choline/ethanolamine phosphotransferase; CGL: Cystathionine gamma-lyase; CK: Choline kinase; CMP: Cytidine monophosphate; CPT: CDP-choline phosphotransferase; CTP: Cytidine triphosphate; DAG: Diacylglycerol; dcSAM: decarboxylated S-adenosyl-L-methionine; DMG: Dimethylglycine; ODC: Ornithine decarboxylase; PA: phosphatidic acid; PC: phosphatidylcholine; PE: phosphatidylethanolamine; PEMT: Phosphatidylethanolamine methyltransferase; pp: pyrophosphate; SAH: S-adenosyl homocysteine; SAHH: S -adenosyl- L -homocysteine hydrolase; SAM: S-adenosyl-L-methionine; SAMDC: SAM decarboxylase; SAS: S-adenosylmethionine synthetase; SPDS: Spermidine synthase; SPS: Spermine synthase; T(SH)2: Trypanothione; THF: tetrahydrofolate; TryS: Trypanothione synthase.