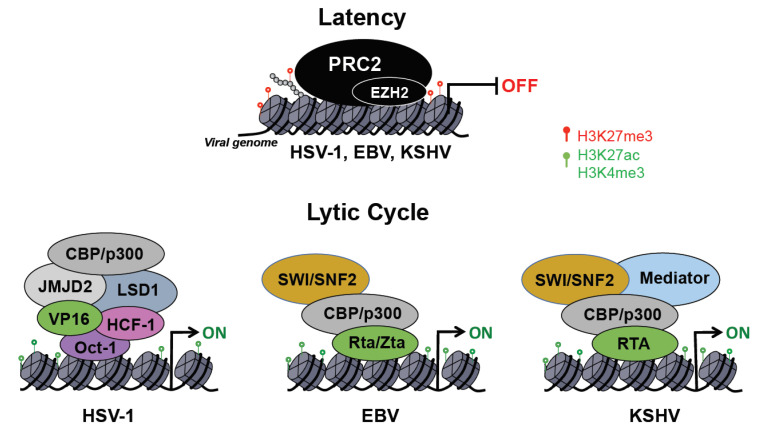
Figure 2.
Epigenetic regulation of herpesvirus infections. During latency, lytic viral gene expression is suppressed by the polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2). The enzymatic subunit of PRC2 is EZH2, which deposits the repressive histone mark H3K27me3 on the viral chromatin. PRC2-mediated inhibition of lytic gene expression during latency was reported for HSV-1, EBV, and KSHV as well. During the lytic cycle, herpesvirus lytic factors (e.g., HSV-1 VP16; EBV Zta and Rta; KSHV RTA) recruit epigenetic enzymes and chromatin remodeling complexes to the viral promoters, leading to the deposition of activating histone marks (e.g., H3K27ac, H3K4me3) and chromatin changes that activate transcription of lytic viral genes. Note: the illustration of epigenetic factors does not reflect their true biological interactions in every case.