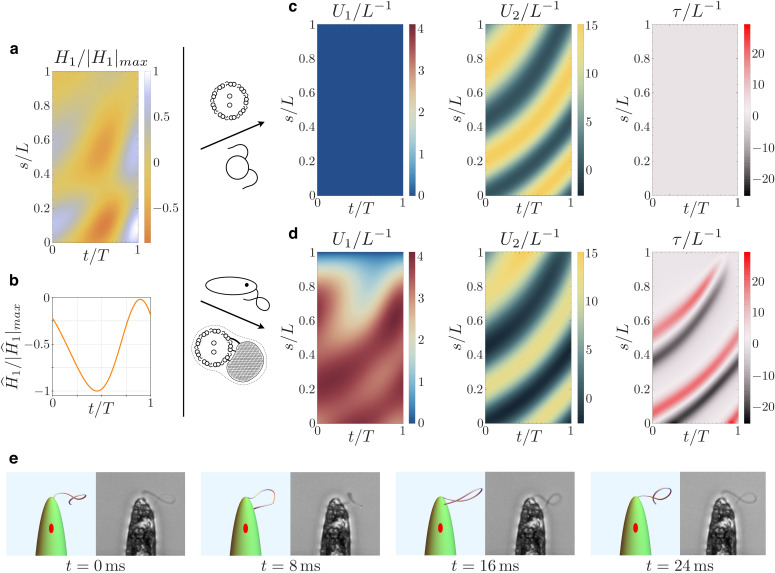
Figure 7. Kinematics of the beating euglenid flagellum: comparison between theoretical model and experiments.
(a-b) Dyneins’ shear forces. (c) Resulting bending strains and torsion for an Ax actuated by the force pattern (a–b), beating in a viscous fluid, and free of extra-axonemal structures. The beat is planar (Chlamydomonas-like). (d) Resulting bending strains and torsion for an euglenid flagellum (composite structure Ax+PFR) actuated by (a–b) and beating in a viscous fluid. The Ax-PFR interaction generates torsional peaks with alternate sign traveling from the proximal to the distal end of the flagellum. (e) Resulting shapes for the euglenid flagellum at different instants within a beat, and comparison with experimental observations.