Abstract
目的
研究LIM域结合蛋白2(LDB2)在肺腺癌中的表达模式及作用。
方法
从mRNA和蛋白表达数据库中分析在肺腺癌中表达下调基因的交集。通过qRT-PCR、Western blot和免疫组化的方法验证LDB2在肺腺癌中的表达模式。在GEO和TCGA数据库中分析LDB2与肺腺癌患者预后的相关性。在H1299细胞中过表达LDB2,通过细胞计数实验、软琼脂克隆实验及流式细胞术证明LDB2在肺腺癌中的作用。生信预测结合后期MeRIP-qPCR实验证实LDB2转录本上存在m6A结合位点。通过qRT-PCR和Western blot实验检测YTHDC2对LDB2的转录调控。RIP实验验证YTHDC2能否与LDB2转录本结合。
结果
通过分析TCGA、GEO及CPTAC 3个数据集中在肺腺癌中低表达的差异基因,最终聚焦于LDB2基因。免疫组化结果证实该基因在80例肺腺癌组织中的表达量也显著低于17例正常癌旁组织的表达量。与正常肺上皮细胞16HBE相比,LDB2在肺腺癌细胞中的表达量亦明显降低。生信分析提示高表达的LDB2与肺腺癌患者良好的预后正相关。在H1299细胞中过表达LDB2后,发现LDB2可诱导H1299细胞发生S期阻滞,从而抑制该细胞的增殖能力和软琼脂克隆形成能力。生信预测结合后期MeRIPqPCR实验证实LDB2转录本上存在m6A位点。GEPIA数据库提示YTHDC2在肺腺癌组织中低表达,且与LDB2在肺腺癌中表达正相关(r=0.22,P < 0.0001)。在H1299细胞中过表达YTHDC2,可明显增加LDB2的表达。最后,在过表达YTHDC2的H1299细胞中开展RIP实验,定量结果显示LDB2在YTHDC2组的含量是其在IgG组含量的19.35倍,YTHDC2可结合在LDB2转录本上调控其表达。双荧光素酶报告基因实验证实YTHDC2可上调野生型而不是缺失型报告基因载体活性。
结论
m6A编码器YTHDC2在肺腺癌中上调LDB2的表达。过表达LDB2可明显诱导肺腺癌细胞发生S期阻滞,抑制肺腺癌细胞增殖能力。
Keywords: LIM域结合蛋白2, N6-甲基腺嘌呤, 增殖, 肺腺癌
Abstract
Objective
To investigate the role and expression pattern of LIM-domain binding protein 2 (LDB2) in lung adenocarcinoma.
Methods
We studied the expression pattern of LDB2 in lung adenocarcinoma based on data from the online databases TCGA, GEO and CPTAC, and the results were verified in lung adenocarcinoma tissues and cells using immunohistochemistry, qRT-PCR and Western blotting. The relationship between LDB2 and the prognosis of patients with lung adenocarcinoma was analyzed using GEPIA and GEO databases. We further analyzed the role of LDB2 in regulating cell behaviors in a H1299 cell model over-expressing LDB2 using cell counting, soft agar colony forming assay and flow cytometry. The m6A binding sites on LDB2 were confirmed by bioinformatics analysis and MeRIP-qPCR assays. The effect of YTHDC2 on LDB2 was examined using qRT-PCR and Western blotting, and the binding of YTHDC2 to the transcript of LDB2 was verified with RIP-qPCR assays. Dual luciferase reporter assay was performed to verify YTHDC2 functioning via m6A sites.
Results
LDB2 expression was significantly decreased in lung adenocarcinoma in comparison with normal tissues based on data from TCGA, GEPIA and CPTAC, and the same results were obtained from 80 lung adenocarcinoma tissues and 17 adjacent normal tissues. Similarly, LDB2 expression was decreased in lung adenocarcinoma cells as compared with 16HBE cells. The data from Prognoscan and GEPIA suggested that a high LDB2 expression was positively correlated with a more favorable outcome of lung adenocarcinoma patients. LDB2-overexpressing H1299 cells showed a significant inhibition of proliferative activity with cell cycle arrest in S phage. Bioinformatics analysis and MeRIP-qPCR assay confirmed the presence of m6A sites on LDB2. The m6A reader YTHDC2 was positively related with LDB2 in lung adenocarcinoma based on data from GEPIA (r=0.22). Overexpression YTHDC2 significantly enhanced LDB2 expression in H1299 cells by about 19.35 folds. Dual luciferase reporter assay showed that YTHDC2 enhanced the promoter activity in the wild-type group but not in deletion group.
Conclusion
LDB2 expression can be up-regulated by m6A reader YTHDC2 in lung adenocarcinoma to inhibit the proliferation of the tumor cells in vitro.
Keywords: LIM-domain binding protein 2, N6-methyladenosine, proliferation, lung adenocarcinoma
肺癌是全球发病率和死亡率均居首位的恶性肿瘤。根据组织学分类,肺癌分为小细胞肺癌和非小细胞肺癌[1-2]。非小细胞肺癌中最常见的亚型为肺腺癌,约占肺癌总病例的40%[3]。与其他肺癌亚型相比,肺腺癌的发病率近年来明显增加[4]。肺腺癌由小的气道上皮,Ⅱ型肺泡细胞发展而来[2]。目前已鉴定了若干高频遗传变化(诸如EGFR、KRAS突变和ALK重排)与肺腺癌的发生发展相关,且针对这些靶点开发的药物能够有效抑制肺腺癌的进程[5-7]。近年来,在肺腺癌中针对程序性死亡配体1(PD-L1)和细胞毒性T淋巴细胞相关抗原4(CTLA-4)的免疫治疗备受瞩目[8-9]。但是,还有更多的患者既无上述遗传突变,且对免疫检查点治疗不敏感。因此,探究肺腺癌发生和进展过程中新的关键分子,有望为临床肺腺癌提供潜在的诊断标志物或有效的治疗靶标。
LIM域结合蛋白2(LDB2)属于LIM域家族蛋白。LIM结构域是一种特殊的双锌指基序,存在于多种蛋白质中。LIM域介导功能复合物成员之间的特定接触并调节某些组成蛋白的活性[10]。目前公认的几种重要的LIM蛋白均与细胞骨架有关,在粘附斑块和肌动蛋白微丝组织中起作用[10]。LDB家族蛋白包括LDB1、LDB2和LDB3。LDB1定位于细胞核,在细胞中组成型表达。LDB1在连接增强子和基因方面起着关键作用,它通过跨神经发育、心脏发生、视网膜发生和造血等多种发展途径形成具有细胞类型特异性的复合物[11]。LDB3特异性剪接会引起特发性扩张型心肌病[12]。许多研究表明,LDB2基因在视网膜发育和细胞周期中起调节作用[13]。LDB2通过与DLL4启动子区域结合调节该基因启动子活性,并且LDB2还介导VEGF诱导的内皮细胞中的DLL4表达,从而参与血管生成发芽和血管重塑等生理过程[14]。此外,LDB2还可驱动白细胞跨上皮迁移和动脉粥样硬化[13]。研究认为在乳腺癌中LDB2对ER受体活性有负调节作用,并破坏ERE依赖的转录[15]。在肝细胞癌中LDB2通过下调HEY1的表达抑制肿瘤细胞的增殖和迁移[16]。但是LDB2在肺腺癌中的作用尚未被阐明。
在本研究中,我们从多个数据库中预测LDB2在肺腺癌中低表达,且与患者不良预后负相关。在此基础上,本课题拟验证LDB2在肺腺癌中的表达模式,明确其在肺腺癌中的表达意义,探索其在肺腺癌中发挥的作用及潜在的分子机制。
1. 资料和方法
1.1. 细胞培养
正常肺上皮细胞16HBE和肺腺癌细胞(H1299、H1975、A549、H1650和PC9)均由本实验室自主保存提供,上述细胞均在含有10%胎牛血清(Gibco)的1640完全培养基中培养,将细胞置于37 ℃,5%培养箱中培养。
1.2. 标本收集
收集2013年3月~2018年12月来本院就诊的肺腺癌患者的癌组织80例和癌旁组织17例,置于RNA保存液中,在液氮中保存备用。
1.3. 转染
Lipofectamine 3000转染试剂购自Fermentas。将H1299细胞接种6孔板,次日进行脂质体转染。6孔板1孔的转染量如下:(1)质粒4 µg和5 µL p3000加入250 µL无血清培养基,(2)5 µL Lipofectamine 3000加入250 µL无血清培养基,分别混匀,将(1)加入(2)混合液中,轻柔混匀后室温静置15 min,将上述混合液加入6孔板中,48 h后用于后续研究。
1.4. qRT-PCR
使用Omega RNA提取试剂盒来获得目标细胞及组织总RNAs,并将其逆转录成cDNAs。SYBR法用于检测各基因mRNA水平的表达量。各基因引物序列见表 1。
1.
qRT-PCR所用的引物
Primers used for qRT-PCR
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5'-3') |
| GAPDH-F | ACAACTTTGGTATCGTGGAAGG |
| GAPDH-R | GCCATCACGCCACAGTTTC |
| LDB2-F | TCCAGCACACCACATGACC |
| LDB2-R | TCTCATAGATTCGGTACTCTGGC |
| YTHDC2-F | CAAAACATGCTGTTAGGAGCCT |
| YTHDC2-R | CCACTTGTCTTGCTCATTTCCC |
1.5. Western blot检测
使用含有蛋白酶抑制剂的细胞裂解液处理目标细胞,BCA法测定蛋白浓度。蛋白样品上样量是30 µg,蛋白样品经SDS-PAGE电泳后,转至PVDF膜上。5% BSA室温封闭2 h,一抗孵育过夜,HRP偶联二抗室温孵育2 h,ECL底物检测蛋白表达量。
1.6. 细胞计数
将5×103细胞种于12孔板中,混匀后置于37 ℃,5% 培养箱中培养,此后连续7 d用胰酶消化不同孔的细胞,混匀后吸出同等体积的细胞混合液,使用细胞计数仪计算细胞数目。
1.7. 软琼脂克隆
在6孔板中均匀铺入含有0.75%琼脂糖的完全培养基的下层胶,室温下冷却后,将2×103细胞加入含有0.375%琼脂糖的完全培养基中,混匀后铺入凝固的下层胶上,室温下冷却后置于37 ℃,5%培养箱中培养2周,显微镜下观察克隆大小并拍照。
1.8. 流式细胞检测
将5×105细胞均匀铺于六孔板中,使用含10%胎牛血清的1640完全培养基培养,并置于37 ℃,5%培养箱中。24 h后将完全培养基置换成无血清的1640进行饥饿处理24 h,随后换成完全培养基培养,按照说明书对处理后的细胞进行固定及染色,最后使用流式细胞仪分析细胞周期。
1.9. MeRIP-qPCR实验
购买Millipore的Magna RIPTM RNA-Binding Protein Immunoprecipitation Kit,按照说明书开展实验。RIP裂解液处理细胞后,使用anti-m6A抗体(RIPqPCR实验中用到的是YTHDC2抗体)孵育细胞裂解液,磁珠与上述混合物孵育,蛋白酶K处理相关蛋白,纯化RNA并逆转录成cDNA,qRT-PCR检测目标RNA的含量。
1.10. 双荧光素酶报告基因实验
购买TaKaRa的定点突变试剂盒MutanBest Kit,将LDB2转录本上“AGA(274 bp)CT”序列缺失,将野生型的序列(转录本1~400 bp)和缺失型的序列构建到报告基因载体pGL4 Basic,分别命名为“LDB2-WT”和“LDB2-DEL”。分别将野生型报告基因/缺失型报告基因与pRLTK(海肾荧光素酶报告基因载体,作为内参)、YTHDC2过表达质粒共转染H1299细胞。48 h后,1× passive lysis buffer裂解各组细胞30 min,将裂解液转移至白板,依次加入萤火虫荧光素酶底物和海肾荧光素酶底物(含有荧光猝灭剂),多功能酶标仪检测各孔化学发光值,计算各孔荧光素酶活性。
1.11. 生物信息学预测网址
Prognoscan(<a href="http://dna00.bio.kyutech.ac.jp/PrognoScan/" target="_blank">http://dna00.bio.kyutech.ac.jp/PrognoScan/</a>)
GEPIA(<a href="http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn/" target="_blank">http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn/</a>)
cBioPortal for Cancer Genomics (<a href="https://www.cbioportal.org/" target="_blank">https://www.cbioportal.org/</a>)
TCGA(<a href="http://www.tcga.org/" target="_blank">http://www.tcga.org/</a>)
SRAMP(<a href="http://www.cuilab.cn/sramp" target="_blank">http://www.cuilab.cn/sramp</a>)
1.12. 统计处理
所有实验重复3次以上,数据均用均数±标准差表示。两对基因表达的相关性通过SPSS 19.0软件包进行Pearson相关性分析。两组间比较采用独立样本t检验和卡方检验,P < 0.05认为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1. LDB2在肺腺癌中的表达模式
下载GEO、TCGA及CPTAC 3个数据库的肺腺癌中下调的基因表达信息,取交集分析后发现肺腺癌中有25个表达下调的基因(图 1A)。GEPIA数据库显示LDB2在483例肺腺癌组织中的表达量远低于其在347例肺正常组织中的表达量(图 1B)。GSE10072和GSE43767数据集均展示LDB2在肺腺癌组织中低表达;而在GSE32863数据集中发现LDB2在58例肺腺癌中的表达量显著低于其在配对癌旁组织中的表达量(图 1C)。CPTAC数据库证实LDB2蛋白在111例肺腺癌组织中的表达量低于其在111例正常组织中的表达量(图 1D)。我们通过免疫组化方法检测LDB2在80例肺腺癌组织和17例正常组织的表达量,亦获得相似的结果(图 1E)。最后,qRT-PCR方法显示LDB2在肺腺癌细胞株A549、H1299、H1975、H1650和PC9中的表达量均显著低于其在正常肺上皮细胞16HBE中的表达量(图 1F)。
1.
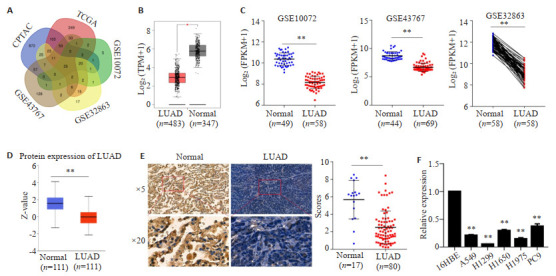
LDB2在肺腺癌中的表达模式
Expression pattern of LDB2 in LUAD. A: TCGA, GEO and CPTAC databases were searched for genes with low expressions in LUAD. B: Expression levels of LDB2 in LUAD and normal tissues were evaluated by GEPIA databank, **P < 0.01. C: GEO database analysis of LDB2 expression in LUAD and normal tissues, **P < 0.01. D: CPTAC databank analysis of the protein expression levels of LDB2 in LUAD and normal tissues, **P < 0.01. E: Immunohistochemical method was used to detect LDB2 expression in 80 LUAD tissues and 17 normal lung tissues, **P < 0.01. F: qRT-PCR for to estimating LDB2 expression in 16HBE and several LUAD cells, **P < 0.01.
2.2. LDB2在肺腺癌中低表达的临床意义
在GEPIA数据库中统计了273例LDB2高表达肺腺癌患者和144例LDB2低表达的肺腺癌患者的总生存率,结果发现LDB2高表达与肺腺癌患者较好的预后正相关(图 2A,P=0.049)。在线数据库Prognoscan预测到LDB2在多个数据集中与肺腺癌患者不良预后负相关。最后,将收集到的80例肺腺癌组织分为51例LDB2低表达的肺腺癌组织和29例高表达LDB2的肺腺癌组织,经统计分析:随着LDB2表达量越低,肺腺癌患者总的生存率越差,LDB2表达量与肺腺癌患者总的生存率表达负相关(P=0.0087,图 2C)。
2.
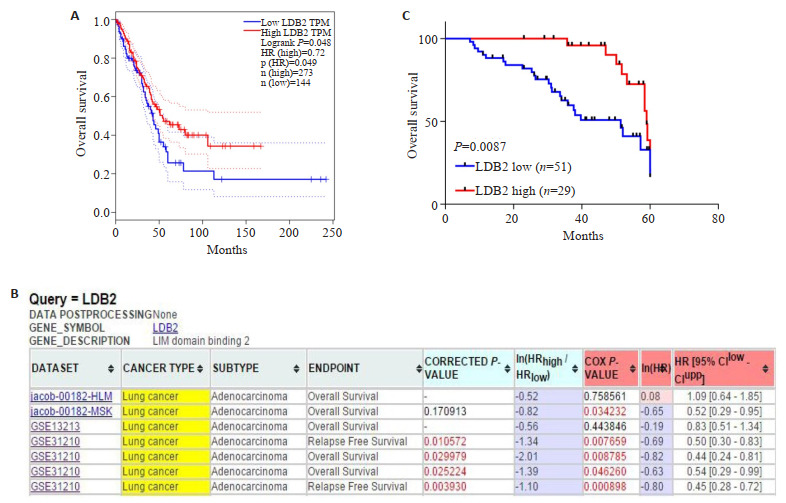
LDB2是肺腺癌患者预后良好的标志物
LDB2 is a prognosis biomarker for LUAD patients. The outcome of LUAD patients according to LDB2 expression was estimated by online databank GEPIA (A) and Prognoscan (B); C: The 80 cases of LUAD tissues were divided into 2 groups according to LDB2 expression. Kaplan-merier analysis were performed to estimate the relationship between LDB2 expression and prognosis of LUAD patients.
2.3. LDB2抑制肺腺癌细胞增殖
H1299中过表达LDB2,通过qRT-PCR及Western blot验证,H1299细胞株中过表达LDB2构建成功(图 3A)。体外细胞计数实验结果显示:与对照组对比,过表达LDB2可明显抑制H1299细胞的增殖能力(图 3B)。软琼脂克隆实验发现:与对照组相比,过表达LDB2组可显著抑制H1299细胞的克隆形成能力(图 3C)。流式细胞术证实:与对照组相比,过表达LDB2后将诱导肺腺癌细胞发生S期阻滞(图 3D)。
3.
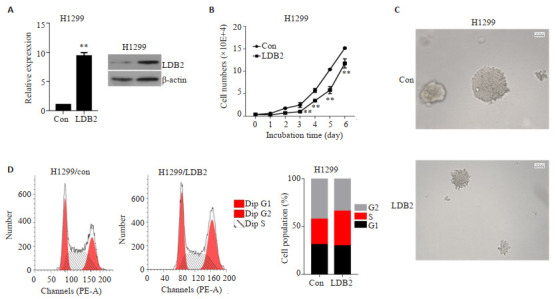
LDB2抑制肺腺癌细胞的增殖能力
LDB2 inhibits proliferation ability of LUAD cells. A: qRT-PCR and Western blot were performed to verify the expression level of LDB2 in H1299 cells. **P < 0.01 vs H1299-con. (B) Cell counting and (C) soft agar clone formation assays were used to analyze the cell proliferation ability. **P < 0.01 vs H1299-con. D: Cell cycle was detected by flow cytometry assay in H1299 cells.
2.4. m6A修饰调控LDB2表达
我们首先通过在线数据库SRAMP预测到LDB2转录本上存在多个m6A结合位点,其中274位点的m6A具有高度可靠性,后期重点验证该位点(图 4A)。在H1299细胞中开展MeRIP-qPCR实验,发现与IgG相比,其m6A组的LDB2含量显著升高(图 4B)。GEPIA数据库显示YTHDC2在肺腺癌中低表达,且与LDB2表达正相关(图 4C,r=0.22,P=1.2e-06)。在H1299细胞中过表达YTHDC2,qRT-PCR和WB检测结果均证实过表达细胞系构建成功(图 4D)。通过qRT-PCR和Western blot检测发现H1299细胞中过表达YTHDC2可增加LDB2的表达(图 4E)。H1299过表达YTHDC2的细胞中开展RIP实验,定量结果显示LDB2在YTHDC2组的含量是其在IgG组含量的19.35倍(图 4F)。双荧光素酶报告基因试验发现:与对照组相比,YTHDC2可上调野生型报告基因活性13.04倍;而当该位点m6A发生缺失后,YTHDC2对其活性调控也大幅度降低(图 4G)。
4.
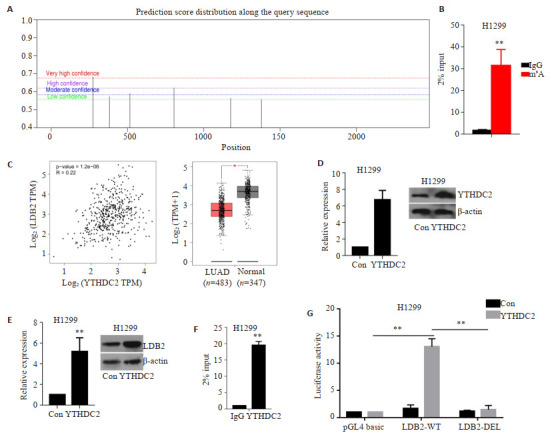
YTHDC2通过m6A修饰上调LDB2的表达
M6A modifies the expression of LDB2. A: The distribution of m6A sites on LDB2 RNA was predicted via online software SRAMP; B: MeRIP-qPCR assay was carried out to examine m6A sites on LDB2, **P < 0.01; C: Expression pattern of YTHDC2 in LUAD. Pearson correlation analysis was performed to discover the expression relationship between LDB2 and YTHDC2 in LUAD; YTHDC2 overexpression plasmid was transfected in H1299 cells, qRT-PCR and Western blot assays were implemented to detect the expression of YTHDC2 (D) and LDB2 (E), **P < 0.01; F: We performed RIP-qPCR assays to evaluate whether YTHDC2 could bind to the transcript of LDB2, **P < 0.01; G: Dual-luciferase report assay in 293T cells with wildtype or deletion reporter plasmid, **P < 0.01.
3. 讨论
尽管在研究肺腺癌的相关发病机制及临床治疗上取得了新的进展,但是肺腺癌仍然是最具侵袭性及快速致死性的肿瘤类型之一,总生存率不到5年[3]。因此探讨肺腺癌发生发展的分子机制是目前亟待解决的重大课题。在本研究中,我们前期通过数据库预测、组织学及细胞学水平验证,发现LDB2在肺腺癌中显著低表达。并且LDB2的表达与肺腺癌患者良好的临床预后呈正相关。细胞功能实验发现,过表达LDB2后可抑制肺腺癌细胞的增殖能力。深入探究后发现m6A修饰调控LDB2在肺腺癌中低表达。
m6A修饰是真核mRNA最常见的内部修饰,广泛参与许多细胞过程,例如RNA转录、剪接、核转运、降解和翻译[17]。大量研究发现m6A扮演了肿瘤启动子或抑制子的角色,通过调节肿瘤相关基因的表达,而参与肿瘤细胞的启动、增殖、分化、转移和代谢重编程等生命过程[17]。m6A修饰主要发生在DRACH基序上(D对应于A,G或U;R对应于G或A;H对应于A,C或U),通常在转录本的5'-UTR、3'-UTR和终止密码子附近[18]。m6A的效应器包括编码器、读码器和消码器。编码器(如METTL3、METTL14和WTAP等)通过S-腺苷甲硫氨酸(SAM)转移酶将甲基添加到目标RNA上,形成m6A甲基化位点[19]。FTO和ALKBH5是两种主要的m6A销码器,它们以Fe(Ⅱ)/α-酮戊二酸依赖性方式催化去除m6A修饰[20]。读码器(如YTHDF1-3、YTHDC1-2和HNRNPA2B1等)能够专门识别并结合带有m6A修饰的RNA,以控制其命运并调节下游功能[21]。
YTHDC2的YTH结构域优先通过保守的疏水口袋与含m6A的RNA结合,而锚蛋白重复序列介导与5'-3'外核糖核酸酶XRN1的RNA相互作用。YTHDC2与小核糖体亚基相互作用,接近mRNA进入/退出位点,从而调控特定基因的表达[22]。目前关于YTHDC2对转录本的调控尚未有定论。有报道指出YTHDC2能够结合到SLC7A11转录本上促进其降解[23]。也有文章发现YTHDC2在耐辐射的鼻咽癌细胞中高表达。生物信息学和机制研究发现,YTHDC2能结合到胰岛素样生长因子1受体(IGF1R)mRNA上,促进该转录本的翻译起始,进而激活IGF1R-AKT/S6信号通路,从而实现鼻咽癌放疗抵抗[24]。YTHDC2在肺腺癌中低表达,且与肺腺癌的低分化、淋巴结转移、肿瘤大小和临床分期等特征相关。YTHDC2能够抑制肺腺癌细胞的增殖和迁移能力[25]。与此不同的是,我们在研究中发现YTHDC2可以调控LDB2的mRNA丰度,也调控其蛋白丰度,我们优先考虑YTHDC2对LDB2转录活性有影响。由于LDB2的转录起始位点位于该转录本161位,274位点与转录起始位点比较接近,仍可作为启动子区域,因此构建启动子报告基因载体,双荧光素酶报告基因证实YTHDC2可识别LDB2上的m6A位点,从而转录活化该转录本。与这些数据相吻合的是,GEPIA数据库数据亦显示YTHDC2与LDB2在肺腺癌中表达正相关。在后续研究中,我们将进一步寻找LDB2转录本上m6A修饰的编码器和销码器。
因此,本研究阐述了LDB2在肺腺癌中表达量显著下降,其表达受m6A修饰调控抑制,且LDB2可诱导肺腺癌细胞发生S期阻滞,抑制其增殖能力。LDB2调控肺腺癌细胞周期的分子机制有待于进一步研究。
Biography
翟东凤,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: Z159162468542020@163.com
Funding Statement
国家自然科学基金(81902846);广东省医学科学技术研究基金项目(B2018274,A2020492)
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81902846)
Contributor Information
翟 东凤 (Dongfeng ZHAI), Email: Z159162468542020@163.com.
尹 江 (Jiang YIN), Email: yinjiang20@gzhmu.edu.cn.
References
- 1.van Meerbeeck JP, Fennell DA, de Ruysscher DK. Small-cell lung cancer. Lancet. 2011;378(9804):1741–55. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60165-7. [van Meerbeeck JP, Fennell DA, de Ruysscher DK. Small-cell lung cancer[J]. Lancet, 2011, 378(9804): 1741-55.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hirsch FR, Scagliotti GV, Mulshine JL, et al. Lung cancer: current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet. 2017;389(10066):299–311. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30958-8. [Hirsch FR, Scagliotti GV, Mulshine JL, et al. Lung cancer: current therapies and new targeted treatments[J]. Lancet, 2017, 389(10066): 299-311.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Denisenko TV, Budkevich IN, Zhivotovsky B. Cell death-based treatment of lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(2):117. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0063-y. [Denisenko TV, Budkevich IN, Zhivotovsky B. Cell death-based treatment of lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9(2): 117.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Meza R, Meernik C, Jeon J, et al. Lung cancer incidence trends by gender, race and histology in the United States, 1973-2010. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0121323. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121323. [Meza R, Meernik C, Jeon J, et al. Lung cancer incidence trends by gender, race and histology in the United States, 1973-2010[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(3): e0121323.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Du RL, Shen WZ, Liu Y, et al. TGIF2 promotes the progression of lung adenocarcinoma by bridging EGFR/RAS/ERK signaling to cancer cell stemness. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2019;4:60. doi: 10.1038/s41392-019-0098-x. [Du RL, Shen WZ, Liu Y, et al. TGIF2 promotes the progression of lung adenocarcinoma by bridging EGFR/RAS/ERK signaling to cancer cell stemness[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2019, 4: 60.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hu K, Li K, Lv J, et al. Suppression of the SLC7A11/glutathione axis causes synthetic lethality in KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. J Clin Invest. 2020;130(4):1752–66. doi: 10.1172/JCI124049. [Hu K, Li K, Lv J, et al. Suppression of the SLC7A11/glutathione axis causes synthetic lethality in KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinoma[J]. J Clin Invest, 2020, 130(4): 1752-66.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gillette MA, Satpathy S, Cao S, et al. Proteogenomic characterization reveals therapeutic vulnerabilities in lung adenocarcinoma. Cell. 2020;182(1):200–25. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.013. [Gillette MA, Satpathy S, Cao S, et al. Proteogenomic characterization reveals therapeutic vulnerabilities in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Cell, 2020, 182(1): 200-25. e35.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hellmann MD, Rizvi NA, Goldman JW, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab as first-line treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer(CheckMate 012): results of an open-label, phase 1, multicohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(1):31–41. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30624-6. [Hellmann MD, Rizvi NA, Goldman JW, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab as first-line treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer(CheckMate 012): results of an open-label, phase 1, multicohort study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2017, 18(1): 31-41.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zhang TF, Xie J, Arai S, et al. The efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/ PD-L1 antibodies for treatment of advanced or refractory cancers: a meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 2016;7(45):73068–79. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12230. [Zhang TF, Xie J, Arai S, et al. The efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/ PD-L1 antibodies for treatment of advanced or refractory cancers: a meta-analysis[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(45): 73068-79.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dawid IB, Breen JJ, Toyama R. LIM domains: multiple roles as adapters and functional modifiers in protein interactions. Trends Genet. 1998;14(4):156–62. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9525(98)01424-3. [Dawid IB, Breen JJ, Toyama R. LIM domains: multiple roles as adapters and functional modifiers in protein interactions[J]. Trends Genet, 1998, 14(4): 156-62.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Liu GY, Dean A. Enhancer long-range contacts: The multi-adaptor protein LDB1 is the Tie that binds. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2019;1862(6):625–33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2019.04.003. [Liu GY, Dean A. Enhancer long-range contacts: The multi-adaptor protein LDB1 is the Tie that binds[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech, 2019, 1862(6): 625-33.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wang DF, Lyu JL, Fang J, et al. Impact of LDB3 gene polymorphisms on clinical presentation and implantable cardioverter defibrillator(ICD) implantation in Chinese patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2019;20(9):766–75. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1900017. [Wang DF, Lyu JL, Fang J, et al. Impact of LDB3 gene polymorphisms on clinical presentation and implantable cardioverter defibrillator(ICD) implantation in Chinese patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy[J]. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B, 2019, 20(9): 766-75.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wei C, Hou D, Feng Y, et al. Molecular characterization and a duplicated 31-bp indel within the LDB2 gene and its associations with production performance in chickens. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378111920307150. Gene. 2020;761(2):145046. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.145046. [Wei C, Hou D, Feng Y, et al. Molecular characterization and a duplicated 31-bp indel within the LDB2 gene and its associations with production performance in chickens[J]. Gene, 2020, 761(2): 145046.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Choi HJ, Rho SS, Choi DH, et al. LDB2 regulates the expression of DLL4 through the formation of oligomeric complexes in endothelial cells. BMB Rep. 2018;51(1):21–6. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2018.51.1.140. [Choi HJ, Rho SS, Choi DH, et al. LDB2 regulates the expression of DLL4 through the formation of oligomeric complexes in endothelial cells[J]. BMB Rep, 2018, 51(1): 21-6.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Johnsen SA, Güngör C, Prenzel T, et al. Regulation of estrogendependent transcription by the LIM cofactors CLIM and RLIM in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2009;69(1):128–36. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1630. [Johnsen SA, Güngör C, Prenzel T, et al. Regulation of estrogendependent transcription by the LIM cofactors CLIM and RLIM in breast cancer[J]. Cancer Res, 2009, 69(1): 128-36.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yu HY, Jia RC, Zhao L, et al. LDB2 inhibits proliferation and migration in liver cancer cells by abrogating HEY1 expression. Oncotarget. 2017;8(55):94440–9. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21772. [Yu HY, Jia RC, Zhao L, et al. LDB2 inhibits proliferation and migration in liver cancer cells by abrogating HEY1 expression[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(55): 94440-9.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Han X, Wang L, Han QZ. Advances in the role of m6A RNA modification in cancer metabolic reprogramming. Cell Biosci. 2020;10:117. doi: 10.1186/s13578-020-00479-z. [Han X, Wang L, Han QZ. Advances in the role of m6A RNA modification in cancer metabolic reprogramming[J]. Cell Biosci, 2020, 10: 117.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Li ZH, Peng YX, Li JX, et al. N6-methyladenosine regulates glycolysis of cancer cells through PDK4. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):2578. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16306-5. [Li ZH, Peng YX, Li JX, et al. N6-methyladenosine regulates glycolysis of cancer cells through PDK4[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 2578.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bedi RK, Huang DZ, Eberle SA, et al. Small-molecule inhibitors of METTL3, the major human epitranscriptomic writer. ChemMedChem. 2020;15(9):744–8. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202000011. [Bedi RK, Huang DZ, Eberle SA, et al. Small-molecule inhibitors of METTL3, the major human epitranscriptomic writer[J]. ChemMedChem, 2020, 15(9): 744-8.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Niu Y, Lin ZY, Wan A, et al. RNA N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO promotes breast tumor progression through inhibiting BNIP3. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1004-4. [Niu Y, Lin ZY, Wan A, et al. RNA N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO promotes breast tumor progression through inhibiting BNIP3 [J]. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 46.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chen XY, Zhang J, Zhu JS. The role of m6A RNA methylation in human cancer. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1033-z. [Chen XY, Zhang J, Zhu JS. The role of m6A RNA methylation in human cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 103.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kretschmer J, Rao H, Hackert P, et al. The m6A reader protein YTHDC2 interacts with the small ribosomal subunit and the 5'-3' exoribonuclease XRN1. RNA. 2018;24(10):1339–50. doi: 10.1261/rna.064238.117. [Kretschmer J, Rao H, Hackert P, et al. The m6A reader protein YTHDC2 interacts with the small ribosomal subunit and the 5'-3' exoribonuclease XRN1[J]. RNA, 2018, 24(10): 1339-50.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ma L, Chen T, Zhang X, et al. The m6A reader YTHDC2 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma tumorigenesis by suppressing SLC7A11-dependent antioxidant function. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2213231720310065. Redox Biol. 2021;38(5):101801. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101801. [Ma L, Chen T, Zhang X, et al. The m6A reader YTHDC2 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma tumorigenesis by suppressing SLC7A11-dependent antioxidant function[J]. Redox Biol, 2021, 38(5): 101801.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.He JJ, Li Z, Rong ZX, et al. m6A reader YTHDC2 promotes radiotherapy resistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via activating IGF1R/AKT/S6 signaling axis. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/343344030_m6A_Reader_YTHDC2_Promotes_Radiotherapy_Resistance_of_Nasopharyngeal_Carcinoma_via_Activating_IGF1RAKTS6_Signaling_Axis. Front Oncol. 2020;10(1):1166. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01166. [He JJ, Li Z, Rong ZX, et al. m6A reader YTHDC2 promotes radiotherapy resistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via activating IGF1R/AKT/S6 signaling axis[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10(1): 1166.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zhou B, Liu C, Xu L, et al. N6-methyladenosine reader protein YT521-B homology domain-containing 2 suppresses liver steatosis by regulation of mRNA stability of lipogenic genes. Hepatology. 2021;73(1):91–103. doi: 10.1002/hep.31220. [Zhou B, Liu C, Xu L, et al. N6-methyladenosine reader protein YT521-B homology domain-containing 2 suppresses liver steatosis by regulation of mRNA stability of lipogenic genes[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 73(1): 91-103.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


