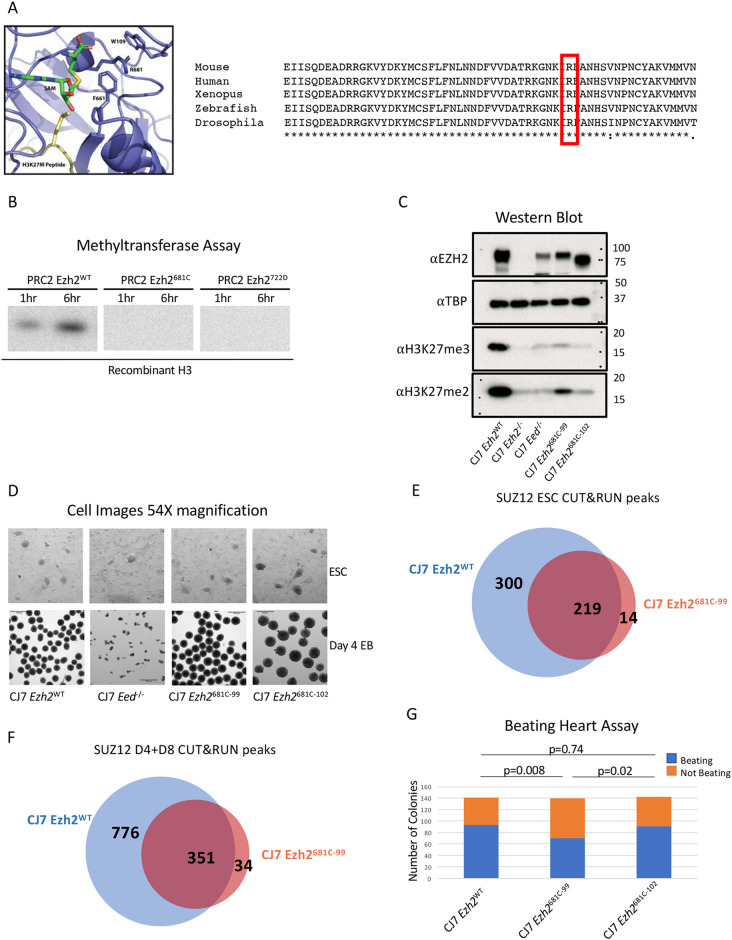
Fig. 2.
Point mutation of a conserved residue within the SET domain inhibits methyltransferase activity. (A) Diagram of Ezh2 SET domain structure with the 681 residue labeled. The SAM methyl donor is in green and the H3K27 M peptide is in yellow. An alignment of Ezh2 SET domains with the analogous residue is highlighted in red. It is highly conserved across species (right). (B) In vitro methyltransferase assay with PRC2 comprising WT or mutant EZH2, EED, SUZ12 and AEBP2. Recombinant H3 is the substrate and a radioactive SAM was the methyl donor. Reactions progressed for 1 or 6 h. (C) Western blot from WT, mutant and PRC2 knockout cells probed with H3K27me, EZH2 and control TBP antibodies. (D) Representative images showing 54× magnification of embryonic stem cells (ESCs) or of embryoid bodies (EBs) that have differentiated for 4 days from WT, 681C-99, 681C-102 and Eed−/− cells. (E) Venn diagram showing the overlap in CUT&RUN SUZ12 peaks between WT and 681C-99 mutant ESCs. (F) Venn diagram showing the overlap in CUT&RUN SUZ12 peaks between WT and 681C-99 mutant differentiated cells. (G) Quantification of beating heart assay from WT, 681C-99 and 681C-102 cells that were differentiated as EBs for 4 days and then individually plated in differentiation media. Blue shows the number of EBs that gave rise to beating cells and orange shows those that did not. For each cell type, 140 individual EBs were differentiated. P-values were calculated using a two proportion z-test.