Abstract
Background
Randomised trials (also referred to as ‘randomised controlled trials’ or ‘trials’) are the optimal way to minimise bias in evaluating the effects of competing treatments, therapies and innovations in health care. It is important to achieve the required sample size for a trial, otherwise trialists may not be able to draw conclusive results leading to research waste and raising ethical questions about trial participation. The reasons why potential participants may accept or decline participation are multifaceted. Yet, the evidence of effectiveness of interventions to improve recruitment to trials is not substantial and fails to recognise these individual decision‐making processes. It is important to synthesise the experiences and perceptions of those invited to participate in randomised trials to better inform recruitment strategies.
Objectives
To explore potential trial participants’ views and experiences of the recruitment process for participation. The specific objectives are to describe potential participants’ perceptions and experiences of accepting or declining to participate in trials, to explore barriers and facilitators to trial participation, and to explore to what extent barriers and facilitators identified are addressed by strategies to improve recruitment evaluated in previous reviews of the effects of interventions including a Cochrane Methodology Review.
Search methods
We searched the Cochrane Library, Medline, Embase, CINAHL, Epistemonikos, LILACS, PsycINFO, ORRCA, and grey literature sources. We ran the most recent set of searches for which the results were incorporated into the review in July 2017.
Selection criteria
We included qualitative and mixed‐methods studies (with an identifiable qualitative component) that explored potential trial participants’ experiences and perceptions of being invited to participate in a trial. We excluded studies that focused only on recruiters’ perspectives, and trials solely involving children under 18 years, or adults who were assessed as having impaired mental capacity.
Data collection and analysis
Five review authors independently assessed the titles, abstracts and full texts identified by the search. We used the CART (completeness, accuracy, relevance, timeliness) criteria to exclude studies that had limited focus on the phenomenon of interest. We used QSR NVivo to extract and manage the data. We assessed methodological limitations using the Critical Skills Appraisal Programme (CASP) tool. We used thematic synthesis to analyse and synthesise the evidence. This provided analytical themes and a conceptual model. We used the GRADE‐CERQual (Confidence in the Evidence from Reviews of Qualitative research) approach to assess our confidence in each finding. Our findings were integrated with two previous intervention effectiveness reviews by juxtaposing the quantitative and qualitative findings in a matrix.
Main results
We included 29 studies (published in 30 papers) in our synthesis. Twenty‐two key findings were produced under three broad themes (with six subthemes) to capture the experience of being invited to participate in a trial and making the decision whether to participate. Most of these findings had moderate to high confidence. We identified factors from the trial itself that influenced participation. These included how trial information was communicated, and elements of the trial such as the time commitment that might be considered burdensome. The second theme related to personal factors such as how other people can influence the individual’s decision; and how a personal understanding of potential harms and benefits could impact on the decision. Finally, the potential benefits of participation were found to be key to the decision to participate, namely personal benefits such as access to new treatments, but also the chance to make a difference and help others. The conceptual model we developed presents the decision‐making process as a gauge and the factors that influence whether the person will, or will not, take part.
Authors' conclusions
This qualitative evidence synthesis has provided comprehensive insight into the complexity of factors that influence a person's decision whether to participate in a trial. We developed key questions that trialists can ask when developing their recruitment strategy. In addition, our conceptual model emphasises the need for participant‐centred approaches to recruitment. We demonstrated moderate to high level confidence in our findings, which in some way can be attributed to the large volume of highly relevant studies in this field. We recommend that these insights be used to direct or influence or underpin future recruitment strategies that are developed in a participant‐driven way that ultimately improves trial conduct and reduces research waste.
Plain language summary
What factors influence a person's decision whether or not to take part in a randomised trial?
What is the aim of this review?
Randomised trials are needed for understanding if and how different healthcare interventions (such as medicines, types of surgeries, health promotion activities, etc.) work or not. Getting people to take part in trials can be difficult and if not enough people participate, then the trial will not provide the information that it set out to. By learning more about what influences a person’s decision to take part in a trial, we can provide advice on how best to include people in trials.
To answer this question, we brought together the findings of 29 studies reporting the views and experiences of people who had been invited to take part in a randomised trial.
Key messages
Several factors influence a person’s decision to take part in a trial including: how the trial is set up and communicated; people’s own personal circumstances; and the potential benefits of participation. It is important that those working in trials take these into account when inviting people to participate. It is important that this is done in a manner that recognises that all people are different and may consider the trial in a different way.
What was studied in the review?
We searched for studies that examined the views of those who had been invited to take part in a randomised trial. We included studies with people who had agreed to take part as well as those who had decided not to take part. We included studies published since the start of the year 2000.
Our searches identified 29 studies (published in 30 papers) to include in this review. Sixteen studies were conducted in the UK, six in other European countries, three in the USA, one each in Canada, Australia, New Zealand and Tanzania. The trials that people had been invited to take part in were for cancer (n = 7); pregnancy and childbirth (n = 5); medicine and surgery (n = 11); mental health (n = 2); and health promotion (n = 4).
Our review pointed to three main factors that influenced whether potential participants agreed to take part in a trial or not. We judged the following findings to have moderate to high confidence.
What are the main findings?
People preferred to be invited in a face‐to‐face setting, with information communicated clearly. Written information was also useful. The timing of the invitation is important because potential participants could find it difficult to recognise the care they usually receive and care that would be provided as part of the trial.
Commitment to the trial can make people worried about participating. Some believed that extra appointments and the time involved would be a burden. Sometimes people are offered money as a way to recompense them for their commitment. Payment was welcomed by some, but was not seen as a very important factor that influences their decision.
If someone feels healthy, they may not wish to risk their health by taking part in a trial. However, if someone feels unwell, they may not want to risk making their health worse. On the other hand, someone who is healthy or very ill may feel they have “nothing to lose” by taking part in a trial, so it is not just about how healthy someone is but rather how they feel about their own health.
Also, the person’s doctor or nurse may say something that influences their decision, as can something said by family, friends or in the media. It is important for the people recruiting someone to know who has influence when that person is making their decisions.
People are influenced by the chance of improvement, the chance to feel better if the therapy or treatment works, or the opportunity to make a difference by helping others in the future.
Inviting people to take part in a trial should be done in a way that considers each person individually, because there is no “one size fits all” when it comes to making this decision.
How up‐to‐date is this review?
This review includes studies published up to 1 June 2017.
Background
Description of the topic
Randomised trials (also referred to as ‘randomised controlled trials’ or, simply, ‘trials’) are the optimal way to minimise bias in evaluating the effects of competing treatments, therapies and innovations in health care. By design, randomised trials minimise bias by offering a method that reduces the risk of systematic errors compared to other types of studies used in healthcare research (Burns 2011). They provide evidence to inform decision‐making by healthcare users, policy‐makers, clinicians and other healthcare professionals. In 2010, an estimated 75 trials evaluating healthcare interventions involving medicinal products, devices and other interventions were published globally each day (Bastian 2010).
The recruitment of potential participants is a process that trialists need to accomplish, and it is known to be a challenging part of any trial (Campbell 2007; Treweek 2018). Challenges in participant recruitment are widespread. Estimates suggest that approximately half of trials fail to recruit the target without an extension to time or budget, or both (Charlson 1984; Haidich 2001; McDonald 2006; Bower 2007; Sully 2013; Walters 2017).
If participant recruitment does not meet the target estimated sample size, a trial runs an increased risk of finding no statistically significant difference between intervention groups, even if one truly exists (Thoma 2010). This threatens the utility of trial results and raises important ethical questions about trial participation. If trials recruit to target but suffer delays and timeline extensions, this can result in increased costs, may delay the availability of beneficial interventions to the public, or could allow harmful or ineffective interventions to be used for longer periods than is ethically necessary (Watson 2006). In the very worst cases of poor recruitment, a trial can stall entirely, potentially leading to the premature stopping of the trial before the research question has been answered. A study of 125 randomised trials, funded by the National Institute for Health Research Health Technology Assessment (NIHR HTA) program in the UK, reported that five of these trials were ‘abandoned, stopped or closed down’. Recruitment issues were a common theme across all five trials, with participant recruitment ranging between just 0.25% and 20.8% of target (Raftery 2015). A study of one US medical centre identified 260 trials ended prematurely due to poor recruitment (0 or 1 participant) over five years at a cost of almost $1 million (Kitterman 2011). The size of the abandonment problem is significant and another study, of more than 1000 trials (two‐thirds sponsored by industry), found that 25% were abandoned, chiefly because of recruitment problems, administrative issues and running out of money (Kasenda 2014).
The reasons behind poor participant recruitment are diverse and likely multi‐layered, but it is clear that exploring factors that contribute to the decision‐making of potential participants is an important part of the process to improve the situation. Identification and understanding of determinants of decision‐making will provide trialists with the knowledge required to implement methods and potentially remove barriers and introduce facilitators that had not been used previously. Examples of potential determinants may include perceived subtleties such as methods of communication, or more fundamental aspects of the process such as randomisation and use of a placebo. This information could have implications on all aspects of the trial timeline, including on retention (Daykin 2018). Understanding both positive and negative influences on participants’ decision‐making has the potential to improve trial recruitment in regard to both the experience of recruitment and the number of people enrolled.
Why it is important to do this review
Previous reviews of the literature exploring patients’ perspectives of trial participation have focused largely on barriers to recruitment and how to remove those barriers (Prescott 1999; Ross 1999; Hall 2010; Kanarek 2012). Whilst this body of work offers valuable insight into potential reasons for poor recruitment, it focuses its scope to factors that act to impede or hinder trial participation only. This provides a partial picture of reasons that contribute to the decisions that potential participants make. However, knowing why potential participants do not participate in trials does not provide constructive information on why they do participate in trials. We are aware of reviews incorporating both barriers and facilitators to recruitment, but these have focused specifically on participation in trials for particular therapeutic indications such as oncology (Mattel 2004; Fayter 2007; Kanarek 2010), or trials within underrepresented populations such as indigenous people (Glover 2015), women and minorities (Schmotzer 2012), and African Americans, Latinos, Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders (George 2014).
An up‐to‐date comprehensive review of studies that explores factors that create both barriers and facilitators which contribute to the decisions made by potential trial participants, and covers various clinical specialities across a range of healthcare settings, provides a single point of access for information on participants’ views and experiences of the recruitment process for participation in trials.
This Qualitative Evidence Synthesis (QES) builds on a published Cochrane Review ‘Strategies to recruit participants to randomised trials’ (Treweek 2018), and a second systematic review of non‐randomised evaluations of strategies to improve participant recruitment to randomised trials (Gardner 2020), which provide evidence on the quantitative effects of interventions to improve recruitment to trials. QES is a robust approach to synthesising primary qualitative research to capture experiences, perceptions, and factors that impact on specific phenomena, in this case, certain components of the trial process (Hennessy 2018). QES can inform our understanding of intervention effectiveness by enabling a deeper understanding of individual characteristics and attitudes towards interventions (Noyes 2017a). This QES will provide trialists and researchers with evidence that can be used to plan, design and conduct recruitment strategies with participants’ experiences in mind; thus, improving the experience of recruitment as well as increasing the numbers of people enrolled in a trial. It is based on the published protocol for this Cochrane Methodology Review (Houghton 2017).
Objectives
To explore potential participants’ views and experiences of the recruitment process for participation in trials. The specific objectives were to:
describe potential participants’ perceptions and experiences of accepting or declining to participate in trials;
explore the barriers and facilitators to participating in trials;
explore to what extent the barriers and facilitators identified were addressed by strategies to improve recruitment evaluated in a previously published Cochrane Methodology Review (Treweek 2018) and a systematic review (Gardner 2020).
Methods
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Types of studies
In this review, we explored qualitative primary research. Studies that used and reported on widely accepted qualitative data collection and analysis methods were eligible for inclusion. Examples of data collection methods included individual and focus group interviews, with findings that were reported explicitly and illustrated by raw data (Finfgeld‐Connett 2013). Mixed‐method studies that included a qualitative component of data collection and analysis were eligible if the qualitative component was clearly identifiable and suitable for extraction (Sandelowski 2007). In addition, feasibility studies involving a qualitative component utilising qualitative methods of data collection and analysis were eligible.
Topic of interest
We included studies that examined the perceptions and experiences of the recruitment process or specific recruitment strategies to healthcare trials, or both. We excluded studies that focused on retention or the experience of taking part in a trial rather than the experience of being invited to participate.
The review explored the perceptions and experiences of potential participants in randomised trials. The term “potential participants” was defined as individuals, for example, patients or service users, with direct experience of accepting or declining invitations to participate in one or more randomised trial. To limit the size and scope of the review, studies that focused on recruiting adults with impaired cognition, or which focused on recruiting children were excluded because the process of information giving and consent would be rather different for these studies.
Studies exploring recruitment in randomised trials in health care were eligible for inclusion. A randomised trial is defined as a study in which participants are allocated at random to receive a specific intervention (this could involve medicinal products, medical devices, lifestyle interventions, or surgery) or a comparator (this could be a placebo, no intervention at all (i.e. standard practice), or another intervention) (Treweek 2018). Feasibility studies help to determine whether the study can be done on a larger scale (Bowen 2009). They were included as potentially informative about recruitment to trials. We excluded non‐healthcare trials and non‐human, laboratory‐based trials. Hypothetical studies were excluded as potential participants do not have the experience of being invited to participate in a trial. Studies that focused on the recruitment of sites rather than individuals were also excluded. We did not impose any geographical limitations.
Search methods for identification of studies
Searching for qualitative research is challenging due to unfocused titles, inadequate indexing and other factors (Booth 2011). Consensus has not been reached on whether systematic searching is optimal for qualitative synthesis (Tong 2012). A “berry picking model” of information retrieval (Bates 1989), has been supported by other authors (Barroso 2003; Booth 2011; Finfgeld‐Connett 2013), whereby searching for qualitative research is an iterative approach rather than a report of linear search strategies. The comprehensive approach that is necessary for a high‐quality, quantitative systematic review of clinical trials is not appropriate for qualitative evidence syntheses (Booth 2016).
We conducted a scoping search to help formulate our research question and identify key search terms. Three subsequent search strategies were developed with input from two Information Specialists and the author team. The first of these searches was run in October and November 2016, and update strategies were conducted in July 2017 and September 2019. Of these, only results from the 2016 and 2017 searches have been incorporated into this paper, and those from 2019 will be used in a future update.
Some resources used in the initial 2016 search were not included in subsequent strategies. Due to resource constraints, the author team chose to concentrate update searches on sources empirically demonstrated to have a higher prevalence of included studies. We did not search grey literature sources in the 2016 and 2017 update strategies. We developed our strategies to be expansive rather than exhaustive. Sensitivity was a lesser priority than the specificity of the search and gauging this was an iterative process.
In Appendix 1, we present the search strategy used for the Embase database in our 2017 search including field limiters. See Table 1 for additional information and the full list of electronic databases and their platforms, grey literature sources, relevant websites and professional body websites included in the 2016 searches and the update searches in 2017. See Appendix 2 for the search terms and limiters used in the update strategy conducted In September 2019.
1. Sources searched.
| Database/Other source/Type of source | Searched in 2016 |
Searched in 2017 |
| Ovid MEDLINE In‐Process & Other Non‐Indexed Citations and Ovid MEDLINE and Ovid MEDLINE Epub Ahead of Print | ✓ | x |
| Ovid MEDLINE® 1946 to present with daily update | x | ✓ |
| CINAHL Complete via EBSCOhost | ✓ | x |
| CINAHL | x | ✓ |
| Cochrane Library | ✓ | x |
| Embase (Elsevier) | ✓ | x |
| Embase (Ovid) | x | ✓ |
| Epistemonikos | ✓ | x |
| LILACS | ✓ | x |
| PsycINFO | ✓ | x |
| Google Books | ✓ | x |
| Google Scholar | ✓ | x |
| Conference abstracts and Scopus for conference proceedings only | ✓ | x |
| EThOS | ✓ | x |
| ProQuest A & I | ✓ | x |
| ProQuest UK & Ireland | ✓ | X |
| ORRCA (Online Resource for Recruitment research in Clinical triAls) | x | ✓ |
| Professional bodies* | ✓ | x |
| Key organisations** | ✓ | x |
We did not apply language or date restrictions in our 2016 or 2017 searches. However, some records were excluded on these grounds at the screening phase and our update strategy in 2019 included both restrictions. We did not apply geographic limits in any search.
The PRISMA and ENTREQ statements and MECIR manual were used to guide the conduct and reporting of searches (Moher 2009; Tong 2012; Higgins 2016).
Search Results
See the 'Characteristics of included studies', 'Characteristics of excluded studies' and 'Characteristics of studies awaiting classification' tables.
In the 2016 search, we identified 3150 records from electronic databases, 742 records through grey literature sources and one record was found via Twitter. After deduplication and screening, we identified 19 eligible records for inclusion in the review. The most recent search for which results were incorporated into this synthesis took place in July 2017. In this search, we identified 5090 records found through our electronic database searches and after deduplication, screening and assessment of eligibility we identified 11 eligible records for inclusion in the review. Therefore, the total number of records for which data were extracted was 30, which reported 29 studies. See Figure 1 for our adapted PRISMA flow diagram of the flow of information through the phases of this qualitative evidence synthesis.
1.
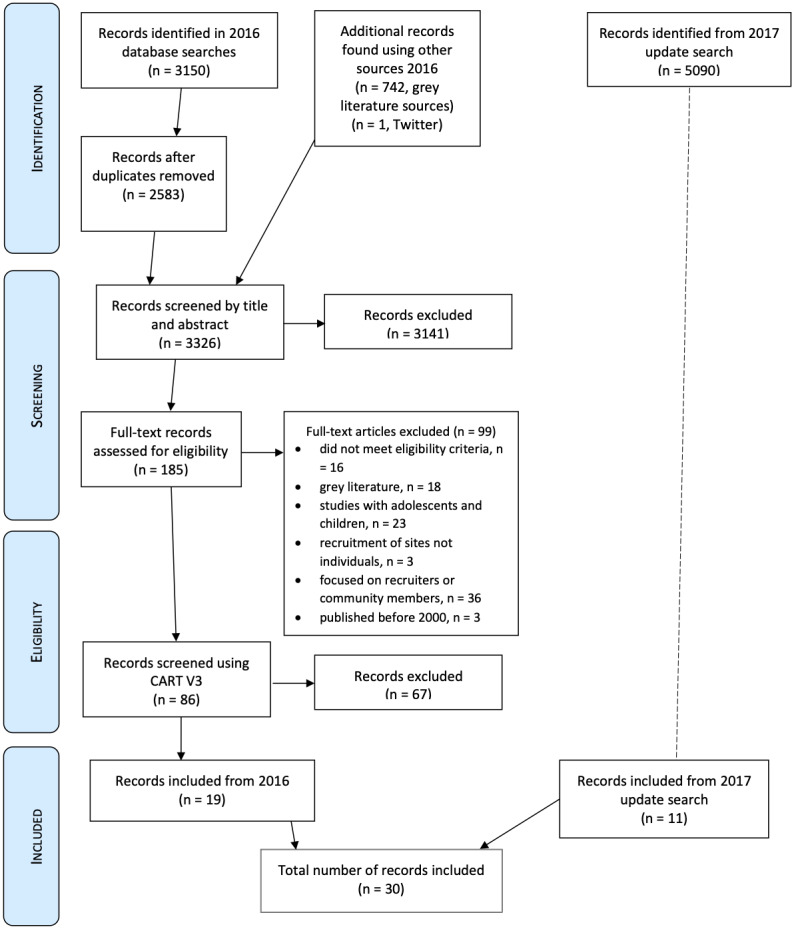
Adapted PRISMA 2016/2017
In the 2019 update search, we found 10,391 records which have not been incorporated into this review. See Figure 2 for an adapted PRISMA flow diagram from this update strategy, which shows how we dealt with the records (the process and total number of records at the identification, screening, assessment of eligibility and inclusion stages).
2.
Adapted PRISMA 2019
Data collection and analysis
Selection of studies
Five review authors (CH, MD, PM, AH, HG, LB) worked in pairs to independently screen the title and abstract of each citation against the original inclusion and exclusion criteria. If there was uncertainty or disagreement regarding whether a citation should be included, two review authors discussed decisions in order to moderate and resolve disagreements. Where necessary, another team member was consulted to confirm and agree on decisions. The same process was adopted for full‐text screening.
We have included a table listing studies that we excluded from our review at the full‐text stage and the main reasons for exclusion (Characteristics of excluded studies). Where the same study, using the same sample and methods, was presented in different reports, we collated these reports so that each study (rather than each report) was the unit of interest in our review.
Sampling of studies
We identified 86 studies that met our inclusion criteria. As large amounts of data can impair the quality of the analysis we applied the CART criteria to decrease the number of studies to a more manageable amount. This approach has been successfully used in a previous systematic review referring to the INTERUPT trial (Whitaker 2016; Aslam 2017). The CART criteria are used to focus the included studies using four broad criteria: Completeness, Accuracy, Relevance and Timeliness (Table 2). The development of these criteria was guided and supported by review author KS and her colleagues in EPPI‐Centre UCL, due to their experience in using similar sampling techniques.
2. Completeness, Accuracy, Relevance and Timeliness (CART) criteria.
| C: Completeness | We will not include studies that are incomplete and do not fully describe the methods used within the qualitative component of the study (partial records such as abstracts and short reports have already been excluded). |
| A: Accuracy | Accuracy will be measured based on the clear inclusion of qualitative research question/objectives using the CASP screening questions:=.
|
| R: Relevance |
|
| T: Timeliness | We will only include studies from 2000 onwards as they are likely to be more relevant than older studies. |
Data extraction and synthesis
Data extraction was managed using QSR NVIVO, which had been successfully used by members of the team in the past (Houghton 2016a; Houghton 2016b). All PDF versions of the reports were imported and coded in NVIVO using “Nodes”. Nodes are an NVIVO term for what would be more commonly referred to in research as codes signifying themes and subthemes (Houghton 2016b). The attributes function facilitated the identification of pertinent information about the trials and the studies that could be linked to data to check the characteristics of synthesis findings (Bazeley 2007). Review authors CH, MD and AH extracted the data from each of the included studies. NVIVO was a useful management system because it facilitated synthesis from the studies in a comprehensive and auditable way. It also facilitated the running of “queries” to determine the adequacy of the data, as outlined in the assessment of confidence in the review findings.
We synthesised qualitative data to determine the views and experiences of being recruited to trials and the factors that act as barriers and facilitators to potential participants’ willingness to participate. We used the RETREAT framework developed by Booth 2018 and deemed thematic synthesis as advocated by Thomas 2008 as the most suitable based on the domains of the framework, which are: Review question, Epistemology, Timeframe, Resources, Expertise, Audience and purpose, and Type of data. Thematic synthesis moves beyond description to create analytical, and therefore more interpretive, themes (Thomas 2008). Thematic synthesis identifies three key stages: line‐by‐line coding; developing descriptive themes and generating analytical themes. The findings generated from thematic synthesis are particularly useful to policymakers and practitioners (Booth 2016). This approach is suitable for synthesis when larger numberS of studies are included.
CH conducted line by line coding of each of the included studies. This generated a high number of codes that were subsequently developed into descriptive themes by the review team. NVIVO provided the necessary auditability and information on coding density needed for these discussions. The third stage involved generating the analytical themes. This stage of the process involves interpretation where the review authors will generate new constructs and explanations. The review team (CH, MD, PM, AH, LB) re‐read the findings and discussed these at length to cross check the general context against the subthemes and themes. The memo function of NVivo was used to explore whether their interpretation is a true representation of the combined attitudes and beliefs of study participants. Review authors independently ‘went beyond’ the content of the original studies by considering the themes against the original review questions. Once initial interpretations were obtained, review authors discussed these interpretations as a group and developed analytical themes (Thomas 2008). The analytical level was further refined and represented as a new model. We created a model to depict the core analytical findings. Furthermore, the integration of the Qualitative Evidence Synthesis (QES) with the prior intervention reviews facilitated new insights.
Assessment of methodological limitations in primary studies
We undertook an assessment of methodological limitations of the included studies using the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) quality assessment tool for qualitative studies (CASP 2013). This tool has been used in other reviews and protocols of QES published by Cochrane (e.g. Glenton 2013; Ames 2017; Munabi‐Babigumira 2017; Karimi‐Shahanjarini 2019).
Two members of the review team (LB, CH) independently applied the CASP tool to each study to assess the methodological limitations. Once both had completed their assessments, comparisons of the two appraisals were made. Both review authors discussed their ratings (as suggested by Noyes 2017b). We conducted a pilot on five included studies. The pilot aimed to ensure the feasibility of the tool and the integrity of the assessment (Table 3).
3. Assessment of methodological limitations.
| Study ID | Was there a clear statement of the aims of the research? | Is a qualitative methodology appropriate? | Was the research design appropriate to address the aims of the research? | Was the recruitment strategy appropriate to the aims of the research? | Were the data collected in a way that addressed the research issue? | Has the relationship between researcher and participants been adequately considered? | Have ethical issues been taken into consideration? | Was the data analysis sufficiently rigorous? | Is there a clear statement of findings? | How valuable is the research? | Overall assessment |
| Abhyankar 2016 | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | no concerns |
| Attwood 2016 | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | no concerns |
| Ballantyne 2017 | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | yes | Yes | yes | yes | yes | no concerns |
| Barnes 2012 | yes | yes | unclear | yes | unclear | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes | minor concerns |
| Bidad 2016 | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | Yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | no concerns |
| Bleidorn 2015 | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | Yes | unclear | yes | yes | yes | minor concerns |
| Blödt 2016 | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | Yes | Yes | yes | yes | yes | no concerns |
| Canvin 2006 | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | Yes | unclear | yes | yes | yes | moderate concerns |
| Chang 2004 | yes | yes | unclear | unclear | unclear | Yes | unclear | yes | yes | yes | moderate concerns |
| Chin 2016 | yes | yes | unclear | unclear | unclear | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes | minor concerns |
| Costenbader 2007 | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | no concerns |
| deLacey 2017 | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | no concerns |
| Dellson 2018 | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | no concerns |
| Gopinath 2013 | yes | yes | unclear | unclear | yes | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes | no concerns |
| Habersack 2013 | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | minor concerns |
| Harrop 2016a | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | no concerns |
| Hughes‐Morley 2016 | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | no concerns |
| Jackson 2010 | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | yes | no concerns |
| Madsen 2007a Madsen 2007b |
yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes | no concerns |
| McCann 2010 | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes | no concerns |
| Moynihan 2012 | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | no concerns |
| Normansell 2016 | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes | no concerns |
| Oude Rengerink 2015 | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes | no concerns |
| Sanders 2012 | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes | no concerns |
| Sawyer 2017 | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | no concerns |
| Smyth 2012 | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes | minor concerns |
| Tarimo 2010 | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes | no concerns |
| Taylor 2007 | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes | minor concerns |
| Wasan 2009 | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes | no concerns |
The appraisal of methodological limitations was not used to exclude studies. It is recognised that studies deemed to be of low quality may still provide new insights (Dixon‐Woods 2005; Noyes 2008). We did however use the appraisal as one of four components in assessing our confidence in the findings from the reviews (Lewin 2018). We considered the methodological assessment when judging the relative contribution of each study to the development of key findings.
Assessment of confidence in the review findings
Five review authors (CH, MD, PM, AH, LB) independently used the GRADE‐CERQual (Confidence in the Evidence from Reviews of Qualitative research) approach to assess our confidence in each finding (Lewin 2018). GRADE‐CERQual assesses confidence in the evidence, based on four key components.
Methodological limitations of included studies: the extent to which there are concerns about the design or conduct of the studies that contributed evidence to an individual review finding.
Coherence of the review finding: an assessment of how clear and cogent the fit is between the data from the studies and review finding that synthesises those data. By cogent, we mean well‐supported or compelling.
Adequacy of the data contributing to a review finding: an overall determination of the degree of richness and quantity of data supporting a review finding.
Relevance of the included studies to the review question: the extent to which the body of evidence from the studies supporting a review finding is applicable to the context (perspective or population, phenomenon of interest, setting) specified in the review question.
After assessing each of the four components, we made a judgement about the overall confidence in the evidence supporting each review finding. Of the findings, only one was deemed of low confidence. The overall moderate to high confidence could be attributed to the fact that the CART criteria had been applied for sampling purposes and so the included studies were highly relevant.
‘Summary of qualitative findings’ table
We have presented our summaries of the findings and our assessments of confidence in these findings in Table 4. We present detailed descriptions of our confidence assessment in Appendix 3.
4. 'Summary of qualitative findings' table.
| Summary of review finding | Studies contributing to the review finding | CERQual assessment of confidence in the evidence | Explanation of CERQual assessment | |
|
Trial influences on decision to participate Communication of trial information | ||||
| Finding 1: Trial information delivered verbally during face‐to‐face communication can be less confusing than written trial information | Barnes 2012, Moynihan 2012, Bleidorn 2015, Oud‐Rengerink 2015, Attwood 2016, Dellson 2018 | High confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding relevance and methodological limitations, and minor concerns regarding adequacy | |
| Finding 2: written trial information may be beneficial as an adjunct to verbal information and facilitates time and space for reflection without the added influence of recruiters’ presence |
Hughes‐Morley 2016, Jackson 2010, Sawyer 2017, Smyth 2011, Bleidorn 2015, Blodt 2016, de Lacey 2017 |
High confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding relevance and methodological limitations, and minor concerns regarding adequacy | |
| Finding 3: The person delivering trial information should have good communication skills, be approachable, trustworthy, person‐centred and knowledgeable with a good ability to address potential participants’ queries. Consideration needs to be given to whether a clinician or a researcher is the most appropriate person to provide the trial information |
Abhyankar 2016Chang 2004, Costenbader 2007, Harrop 2016a, Madsen 2007a, Madsen 2007b, Jackson 2010, Moynihan 2012, Smyth 2011, Habersack 2013, Oud‐Rengerink 2015, Tarimo 2010Bleidorn 2015, Ballantyne 2017, Sawyer 2017 |
High confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding coherence, moderate concerns regarding relevance and methodological limitations, and minor concerns regarding adequacy | |
| Finding 4: Potential participants value trial information that is robust yet concise, free of medical jargon, clearly identifies options, time commitment, randomisation process, treatment equivalence, intervention details, potential benefits and side effects. This could be made available in hard or soft copy, or both before a decision on participation is expected |
Jackson 2010, Hughes‐Morley 2016, Sawyer 2017, Taylor 2007, Habersack 2013, Oud‐Rengerink 2015, Canvin 2006, Costenbader 2007, Madsen 2007b, McCann 2010, Smyth 2011, Abhyankar 2016, Bidad 2016, Harrop 2016a, Ballantyne 2017, Dellson 2018, Attwood 2016, Blodt 2016, Moynihan 2012. |
High confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding relevance and methodological limitations, and minor concerns regarding adequacy | |
| Finding 5: The timing of trial information is important as the potential participant needs to be able to consider the trial information without confusing it with their diagnosis and standard treatment |
Abhyankar 2016Madsen 2007b, Moynihan 2012, Smyth 2011, Habersack 2013, Hughes‐Morley 2016, Sawyer 2017, Dellson 2018 |
High confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding coherence, moderate concerns regarding relevance and methodological limitations, and minor concerns regarding adequacy | |
| Significant trial components | ||||
| Finding 6: Potential participants consider participation disruptive and a burden when additional appointments or travel, or both are needed. Perceived time commitment as a result of trial participation was also identified as a concern for potential participants | Canvin 2006, Harrop 2016a, Costenbader 2007, Habersack 2013, Bleidorn 2015, Attwood 2016, Hughes‐Morley 2016, Normansell 2016, Ballantyne 2017 | High confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding adequacy and coherence, minor concerns regarding relevance and methodological limitations | |
| Finding 7: A financial benefit in terms of an incentive or reimbursement may not be an overly influencing factor for potential participants. However, it is viewed as a welcome acknowledgement of participants’ time and effort. Other incentives that may be welcome include additional health checks or medications that potential participants may otherwise not be able to afford | Chang 2004, Costenbader 2007, Wasan 2009, Tarimo 2010, Bleidorn 2015, Blodt 2016, Chin 2016, de Lacey 2017 | Moderate confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding adequacy, minor concerns regarding coherence and methodological limitations, and moderate concerns regarding relevance | |
| Finding 8: Potential participants’ perceptions of randomisation and freedom to withdraw from the trial were important factors in their decision whether to participate in a trial. This was particularly important if they did not fully understand the concept of randomisation or if they had a treatment preference |
Canvin 2006, Madsen 2007a, Madsen 2007b, Taylor 2007, Jackson 2010, Moynihan 2012, Smyth 2011, Gopinath 2013, Bleidorn 2015, Oud‐Rengerink 2015, Abhyankar 2016, Bidad 2016, Harrop 2016a, Hughes‐Morley 2016, Normansell 2016, Ballantyne 2017, Sawyer 2017, Dellson 2018 |
High confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding adequacy and coherence, minor concerns regarding relevance and methodological limitations | |
|
Personal influences on decision to participate Influence of other people | ||||
| Finding 9: The decision to participate is discussed with a range of other people; family, friends, HCPs, previous trial participants |
Smyth 2011, Abhyankar 2016, Madsen 2007b, Gopinath 2013, Habersack 2013, Oud‐Rengerink 2015, Chin 2016, Harrop 2016a, Hughes‐Morley 2016, Ballantyne 2017, de Lacey 2017, Dellson 2018, |
High confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding adequacy, minor concerns regarding coherence, relevance and methodological limitations | |
| Finding 10: HCPs in particular may influence decision‐making as potential participants place huge trust in them. This results in great potential for HCP influence being a key impact on decision‐making |
Chang 2004, Canvin 2006, Harrop 2016a, Costenbader 2007, Madsen 2007b, Jackson 2010, Moynihan 2012, Smyth 2011, Habersack 2013, Gopinath 2013, Bleidorn 2015, Oud‐Rengerink 2015, Abhyankar 2016, Hughes‐Morley 2016, Bidad 2016, Ballantyne 2017, Dellson 2018 |
High confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding adequacy and coherence, minor concerns regarding relevance and methodological limitations | |
| Finding 11: Internet searching and exposure to media sources with information on trial interventions may act as either a barrier or a facilitator for trial participation |
Madsen 2007a, Gopinath 2013, Habersack 2013, Bleidorn 2015, Harrop 2016a, Ballantyne 2017, de Lacey 2017, |
Low Confidence | Minor concerns regarding and methodological limitations, moderate concerns regarding coherence, adequacy and relevance | |
| Weighing up the risks and benefits | ||||
| Finding 12: potential participants may view trial participation as feeling like a guinea pig (i.e. being used for the experiment), which they considered as too risky |
Chang 2004, Canvin 2006, Costenbader 2007, Madsen 2007a, Madsen 2007bTaylor 2007, Tarimo 2010, Moynihan 2012, Habersack 2013, Gopinath 2013, Bleidorn 2015, Oud‐Rengerink 2015, Dellson 2018 |
Moderate confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding relevance and methodological limitations, and moderate concerns regarding adequacy | |
| Finding 13: The risk of participation may concern potential participants who view their health as good or they are healthy and worried that the trial would identify a health problem. Potential participants may deem themselves ineligible and decline if they have too many health problems | Canvin 2006, Costenbader 2007, Madsen 2007a, Madsen 2007b, Tarimo 2010, Barnes 2012, Sanders 2012, Habersack 2013, Bleidorn 2015, Oud‐Rengerink 2015, Attwood 2016, Harrop 2016a, Normansell 2016 | High confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding adequacy, minor concerns regarding coherence, relevance and methodological limitations | |
| Finding 14: if Potential participants sense a trial was safe, low risk, and would not impact on existing treatments they may feel they have nothing to lose if they participate | Canvin 2006, Madsen 2007a, Jackson 2010, Bleidorn 2015, Oud‐Rengerink 2015, Bidad 2016, Blodt 2016, Ballantyne 2017, de Lacey 2017, Sawyer 2017 | Moderate confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding adequacy and methodological limitations and moderate concerns regarding relevance. | |
| Finding 15: if Potential participants consider themselves desperate, they may feel they have nothing to lose if they participate | Madsen 2007b, Smyth 2011, Habersack 2013, Abhyankar 2016, Blodt 2016, de Lacey 2017, Dellson 2018 | Moderate confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding adequacy and methodological limitations and moderate concerns regarding relevance. | |
|
The Impact of potential outcomes on decision to participate Personal benefits of trial participation | ||||
| Finding 16: Potential participants recognise the benefit of access to new or existing treatments through trial participation | Attwood 2016: Barnes 2012; Blodt 2016; Bidad 2016: Canvin 2006: de Lacey 2017: Dellson 2018; Gopinath 2013; Habersack 2013; Jackson 2010; Madsen 2007a; Madsen 2007b; McCann 2010; Oud‐Rengerink 2015; Smyth 2011; Wasan 2009 | High confidence | Due to no concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding relevance, adequacy and minor concerns regarding methodological limitations | |
| Finding 17: Potential participants recognise that being in a trial may mean quicker access to services, better follow‐up care, increased contact time with physicians and a chance to learn more about their condition, as potential benefits to trial participation | Attwood 2016: Bidad 2016; Chang 2004; Costenbader 2007; Dellson 2018; Habersack 2013; Jackson 2010; McCann 2010; Oud‐Rengerink 2015; Sawyer 2017; Tarimo 2010; Wasan 2009 | High confidence | Due to no concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding relevance, adequacy and minor concerns regarding methodological limitations | |
| Finding 18: Potential participants may be managing symptoms for some time with feelings of desperation and trial participation brings hope of relief | Bleidorn 2015; Blodt 2016; de Lacey 2017; Dellson 2018; Madsen 2007b; McCann 2010; Wasan 2009 | Moderate confidence | Due to no or very minor concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding adequacy and methodological limitations and moderate concerns regarding relevance. | |
| Making a difference: benefits for others | ||||
| Finding 19: Altruism can be an important factor influencing potential participants’ decision to participate in a trial | Ballantyne 2017; Bidad 2016; Bleidorn 2015 ; Canvin 2006 ; Chang 2004; Costenbader 2007; de Lacey 2017; Dellson 2018; Habersack 2013; Harrop 2016a; Hughes‐Morley 2016; Madsen 2007a; McCann 2010; Moynihan 2012; Oud‐Rengerink 2015; Smyth 2011; Wasan 2009 | High confidence | Due to no concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding relevance, adequacy and minor/moderate concerns regarding methodological limitations | |
| Finding 20: Altruism can be conditional whereby potential participants’ desire to help others is dependent on the trial being low risk and with clear benefits | Abhyankar 2016; Attwood 2016; Bidad 2016; Canvin 2006; Chang 2004; Jackson 2010; McCann 2010; Oud‐Rengerink 2015 | Moderate confidence | Due to no concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding adequacy and Minor/moderate concerns regarding methodological limitations and moderate concerns regarding relevance | |
| Finding 21: Potential participants may feel an obligation or a moral duty to participate in a trial as a way of “giving back” | Ballantyne 2017; Bidad 2016; Bleidorn 2015; Canvin 2006; Chin 2016; Madsen 2007a; Tarimo 2010 | Moderate confidence | Due to no concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding relevance, moderate concerns regarding adequacy and minor/moderate concerns regarding methodological limitations. | |
| Finding 22: Potential participants may have a genuine interest in contributing to scientific knowledge and improved care | Ballantyne 2017; Bidad 2016; Bleidorn 2015; Blodt 2016; Canvin 2006; Chang 2004; Chin 2016; de Lacey 2017; Dellson 2018; Habersack 2013; Harrop 2016a; Hughes‐Morley 2016; Madsen 2007a; Moynihan 2012; Normansell 2016.; Oud‐Rengerink 2015; Sawyer 2017; Smyth 2011; Wasan 2009 | High confidence | Due to no or very minor concerns regarding coherence, relevance and adequacy and minor concerns regarding methodological limitations | |
CERQual: Confidence in the Evidence from Reviews of Qualitative research;HCP: healthcare professionals.
Integrating the qualitative findings with the linked Cochrane intervention review
On review of the different approaches to integration, we agreed that juxtaposing our findings in a matrix was the most suitable method for this specific context. This method is visually quite explicit and helps to identify gaps in research (Harden 2018). This allowed a clear presentation of implications from the experiences and perceptions of potential participants invited to be involved in trials and any strategies identified in intervention reviews that would address these implications for trial recruitment.
Four members of the review team (CH, HG, ST, LB) compared the findings from our QES with two intervention reviews (Treweek 2018; Gardner 2020). From our summary of findings, we created a table outlining the potential implications for trial recruitment from those findings. We then juxtaposed these into a matrix with the results from these two reviews (Table 5). It is evident from the matrix that most recruitment interventions that have been designed and evaluated by researchers do not directly target factors that participants themselves consider important when deciding on trial participation. It must be noted that the Treweek review was able to identify some strategies that might help recruitment, albeit with little certainty (Treweek 2018). In the Gardner review of non‐randomised studies of recruitment strategies, the level of certainty in the findings themselves was so low (Gardner 2020) that these are not presented and only the aims of the included trials are presented in the table. This stark disparity emphasises the need to use qualitative insights to understand what is meaningful to potential participants and design recruitment interventions and strategies that directly address these.
5. Juxtaposing the findings in matrix.
| Summary of qualitative findings | Implications for trialists | Treweek Review | Gardner Review |
| TRIAL INFLUENCES ON THE DECISION TO PARTICIPATE | |||
| Communication of trial information | |||
| Finding 1: Trial information delivered verbally during face‐to‐face contact can be less confusing than written trial information. | Will trial information be delivered verbally with face‐to‐face contact? | [D2] Researcher reading out the consent details (GRADE: very low). | |
| Finding 2: written trial information may be beneficial as an adjunct to verbal information and facilitates time and space for reflection without the added influence of recruiters’ presence | Will written information be offered as a supplement to / in addition to verbal information? | [C3] Giving quotes from previous participants in SMS messages (GRADE: moderate). [D3] Easy to read consent form (no GRADE). |
|
| Finding 3: The person delivering trial information should have good communication skills, be approachable, trustworthy, person‐centred and knowledgeable with a good ability to address potential participants’ queries. Consideration needs to be given to whether a clinician or a researcher is the most appropriate person to provide the trial information. |
Is the person delivering the trial information approachable, trustworthy, participant‐centred and knowledgeable with a good ability to address queries? Has the recruitment strategy identified whether a clinician or a researcher is the most appropriate person to provide the trial information? |
[E18] Trained recruiters from a similar ethnic background to study population already taking part in a trial as lay advocates (no GRADE). | |
|
Finding 4: Potential participants value trial information that is robust yet concise, free of medical jargon, clearly identify options, time commitment, randomisation process, treatment equivalence, intervention details, potential benefits and side effects. This could be made available in hard and/or soft copy before a decision on participation is expected. |
Has time been provided to ensure that the potential participant can consider the trial information at their own individual pace? Is information clear and concise free of medical jargon, clearly identifying options, time commitment, randomisation process, treatment equivalence, intervention details, potential benefits and side effects? |
[E1] Optimising the participant information leaflet (PIL) through a particular, bespoke process involving formal user‐ testing (GRADE: high) [E2] Using a brief patient information leaflet (PIL) (GRADE: moderate) [E4] Optimising the PIL through using user feedback (GRADE: moderate). [E15] providing a clinical trial booklet together with standard information (GRADE: very low). [E17] Educational material to provide additional information about a trial (no GRADE). |
|
| Finding 5: The timing of trial information is important as the potential participant needs to be able to consider the trial information without confusing it with their diagnosis and standard treatment. | Has the timing of the delivery of trial information been considered in order to ensure potential participants have the opportunity to consider the trial information as distinct from their diagnosis and standard treatment? | [E5] Sending a recruitment primer letter (GRADE: low). | [S16] Sawhney 2014 investigated the effect of telephone contact with participants that had been mailed information about the trial prior to their clinic appointment |
| Significant trial components | |||
| Finding 6: potential participants consider participation disruptive and a burden when additional appointments and/or travel are needed. Perceived time commitment as a result of trial participation was also identified as a concern for potential participants | Will trialists aim to minimise additional time commitment to the trial (beyond routine care)? | ||
|
Finding 7: A financial benefit in terms of an incentive or reimbursement may not be an overly influencing factor for potential participants. However, it is viewed as a welcome acknowledgement of participants’ time and effort. Other incentives that may be welcome include additional health checks or medications that potential participants may otherwise not be able to afford. |
Will trialists consider using incentives or reimbursements to acknowledge participants’ time and effort? Will trialists, where appropriate, consider including health assessments and monitoring as incentives for participation? |
[G1] Financial incentives offered to potential participants (GRADE: moderate). [E8] An enhanced recruitment package including more contact (GRADE: low) [E9] An enhanced recruitment package including more contact by telephone (GRADE: low). |
|
| Finding 8: Potential participants perceptions of randomisation and freedom to withdraw from the trial were important factors in their decision whether to participate in a trial. This was particularly important if they did not fully understand the concept of randomisation or if they had a treatment preference | Will trialists consider how best to explain randomisation and freedom to withdraw from the study? | ||
| PERSONAL INFLUENCES ON THE DECISION TO PARTICIPATE | |||
| Influence of other people | |||
| Finding 9: The decision to participate is discussed with a range of other people; family, friends, HCPs, previous trial participants | Will recruiters identify other people, such as family and friends, who influence potential participants’ decision and, where appropriate, include them in information giving sessions? | ||
| Finding 10: HCPs in particular may influence decision‐making as potential participants place huge trust in them. This results in great potential for HCP influence being a key impact on decision‐making | Will recruiters ensure HCPs who are involved in care, are knowledgeable about the study and able to answer questions in a non‐biased way? | ||
| Finding 11: Internet searching and exposure to media sources with information on trial interventions may act as either a barrier or a facilitator for trial participation | Will recruiters consider sourcing useful internet links and media sources with information on the intervention, to recommend to potential participants? | ||
| Weighing up the risks and benefits | |||
|
Finding 12: Potential participants may view trial participation as feeling like a guinea pig (i.e. being used for the experiment), which they considered as too risky Finding 13: The risk of participation may concern potential participants who view their health as good or they are healthy and worried that the trial would identify a health problem. Potential participants may deem themselves ineligible and decline if they have too many health problems. Finding 14: If potential participants sense a trial was safe, low risk, and would not impact on existing treatments they may feel they have nothing to lose if they participate Finding 15: If potential participants consider themselves desperate, they may feel they have nothing to lose if they participate |
Will recruiters be very clear when communicating risks to potential participants? Are the recruiters effective in communicating information, particularly when recruiting potential participants who are concerned about risks or feel that they have “nothing to gain” from trial participation? |
[E10] Emphasising risk in information (GRADE: low). [E11] Writing treatment effect as ’twice as fast’ rather than ’half as fast’ (GRADE: low). [E12] Emphasising pain in information (GRADE: low). [E16] Providing total information disclosure rather than leaving it to recruiters as to what to reveal (GRADE: very low). |
|
| The Impact of Potential Outcomes on Decision to Participate | |||
| Personal benefits of trial participation | |||
|
Finding 16: Potential participants recognise the benefit of access to new or existing treatments through trial participation Finding 17: Potential participants recognise that being in a trial may mean quicker access to services, better follow‐up care, increased contact time with physicians and a chance to learn more about their condition, as potential benefits to trial participation |
Will recruiters, where appropriate, highlight quicker access to services, better follow‐up care, increased contact time with physicians and an opportunity to learn more about their condition as potential benefits to trial participation? | ||
| Finding 18: Potential participants may be managing symptoms for some time with feelings of desperation and trial participation brings hope of relief | Will recruiters,demonstrate empathy to potential participants who may be managing symptoms and feelings of desperation or isolation for some time? | ||
| Making a difference: benefits for others | |||
|
Finding 19: Altruism can be an important factor influencing potential participants’ decision to participate in a trial Finding 20: Altruism can be conditional whereby potential participants’ desire to help others is dependent on the trial being low risk and with clear benefits Finding 21: Potential participants may feel an obligation or moral duty to participate in a trial as a way of “giving back” Finding 22: Potential participants may have a genuine interest in contributing to scientific knowledge and improved care |
Will recruiters highlight possible benefits of altruism and contribution to science as key potential benefits of trial participation? Will recruiters demonstrate their gratitude to potential participants for their contribution to the trial? |
||
Review author reflexivity
We exercised reflexivity throughout this review both as individual and group endeavours. Reflexivity, as used in primary qualitative research enhances rigour by acknowledging personal responses and contributions and can be used by each review team member (Thorne 2004; Jasper 2005; Walsh 2005). As a group, moderation meetings were held to discuss review findings and negotiate decisions and we continually reflected on any potential biases or preconceptions we held.
As with all qualitative endeavours, members of the team needed to acknowledge their professional backgrounds, research areas of interest and the impact these positions may have on all stages of this QES. Several members of the group are healthcare clinicians (CH, MD, PM, AH, JN, DD, LB). All review authors are researchers within health care, some with a focus on trials, trial methodology (HG, ST, DD, LB) and qualitative research in trials (CH, MD, PM, AH, LB). Trial recruitment methodology is a topic area of interest to HG, ST and DD, and these review authors are active researchers in this area. CH, MD, PM, AH, KS, JN, LB have training and expertise in qualitative research and the synthesis of qualitative studies.
Different team members needed to have topic and methodological expertise. These meant constructive discussions could take place about individuals’ varying perspectives. Team members were asked to identify their views about recruitment to trials, thus ensuring we had a declarative statement that positioned our thinking outside the experiences and perceptions of the participants that inform the findings of this review. The view across the team holds that trials of effects of healthcare interventions can improve healthcare decisions. The team noted that trials are dependent on recruiting and retaining participants; the voices of recruiters and participants are necessary to better inform how this is done.
Results
Findings
Results of the search
We found 86 studies that met our inclusion criteria. We selected 29 of these studies (published in 30 papers) for inclusion in the analysis (Figure 1). The sampled studies were published between 2004 and 2018.
Description of the studies
Study participants
The 29 studies in this review included the perspectives of 847 adult potential participants invited to participate in a randomised trial. Seven studies explored the decliners’ perspective, 10 studies explored the participants’ perspectives, and 12 studies included both participants and decliners. Following the CART exercise for purposeful sampling, very few studies included the perspectives of recruiters, and if they did, their perspectives were not extracted for this review.
Types of trials
Sixteen studies were conducted in the UK, six in other European countries (Austria n = 1, Denmark n = 1, Germany n = 2, Sweden n = 1, the Netherlands n = 1); three in the USA; and one each in Australia, Canada, New Zealand and Tanzania. The trials into which potential participants were invited were categorised by broad area of health care: oncology (n = 7); pregnancy and childbirth (n = 5); medicine and surgery (n = 11); mental health (n = 2); and health promotion (n = 4). None of the papers included reported on recruitment interventions as included in the two intervention reviews (Gardner 2020; Treweek 2018).
A variety of interventions (n = 25) were tested across the included trials, with some studies including potential participants across several trials. Interventions included, but were not exclusive to: types of surgery, cognitive behavioural therapy and other psychological therapies, pedometer use, HIV vaccines, pharmaceutical treatments (anti‐epileptic drugs, antibiotics, intravenous (IV) morphine), umbilical cord clamping, acupuncture, telehealth, pulmonary rehabilitation. These interventions were also broadly categorised as: surgical (n = 4), psychosocial (n = 3), pharmaceutical (n = 10), physical activity (n = 2), Complementary Alternative Medicine (CAM) (n = 2), mixed trials (e.g. comparison between surgical and pharmaceutical intervention) (n = 5), and other (n = 3).
Approaches to recruitment
Study participants provided views about several different recruitment procedures employed in the trials. These included: face‐to‐face invitation to participate during consultation with healthcare professionals; face‐to‐face invitation by research staff outside of a consultation; letter of invitation after being deemed eligible by healthcare professional referral/medical records/database; posters and flyers; telephone recruitment. Additional strategies identified included using follow‐up reminder letters and reminder phone calls or using an “opt‐out” strategy of recruitment.
Methodological limitations of the studies
We assessed 21 included studies as having no methodological limitations, with six studies having minor and two having moderate methodological limitations. Most studies clearly stated the aims, described the recruitment strategy, appropriately collected data and reported rigorous analysis. In all studies, we assessed the findings as sufficiently supported by the underlying data. Across most studies, there was poor reporting of the research design, so it was difficult to assess its appropriateness to the aims of the research. In 12 of the studies it was difficult to assess whether the relationship between researcher and participants had been adequately considered. In half of the studies it was not clear whether ethical issues had been taken into consideration. See Table 3 for full details of the assessment of methodological limitations for each study.
Confidence in the review findings
Out of 22 findings, we graded 14 findings as high confidence, seven findings as moderate confidence, and one finding as low confidence using the GRADE‐CERQual approach (See summary of qualitative findings in Table 4). Our explanation of the GRADE‐CERQual assessment for each review finding is shown in the full evidence profiles in Appendix 3.
Review findings
We developed three broad themes (and six subthemes) outlining the factors influencing potential participants’ decisions about whether to participate in a randomised trial (Table 6). Our 22 key findings are presented within these themes.
6. Overview of themes.
| Theme | Subtheme | Synopsis |
| Trial influences on decision to participate | Communication of trial information Significant trial components |
The how, when and who of trial information delivery Factors of participation such as burden, randomisation, financial incentives. |
| Personal influences on the decision to participate | Influence of other people Weighing up the risks and benefits |
Positive and negative influence of family, friends, healthcare professionals, media and online sources. Balancing the risks and benefits with the questions: “what I have got to lose?” and “what have I got to gain?” |
| The impact of potential outcomes on the decision to participate | Personal benefits of trial participation Making a difference: benefits for others |
Benefits of trial participation such as: accessing new treatments, improved quality of care, hope and options. Acting on altruism, helping others, curiosity and contribution to science |
Theme 1: Trial influences on decision to participate
This theme examines the factors relating to the trial itself on potential participants’ decision to enrol in a randomised trial. These factors focus on two subthemes: communication of trial information and significant trial components.
Communication of trial information
Finding 1: Trial information delivered verbally during face‐to‐face communication can be less confusing than written trial information (we have high confidence in this finding)
Potential participants believed that written information about the trial may have less influence than verbal information on their decision to participate in a trial (Attwood 2016; Dellson 2018). Written information could also be considered more confusing, with less opportunity to ask questions (Barnes 2012; Moynihan 2012; Oud‐Rengerink 2015). Some participants from cancer and medical trials were more reassured by face‐to‐face contact with a healthcare professional than a letter (Moynihan 2012; Bleidorn 2015; Dellson 2018). As identified in the study by Bleidorn 2015, “The communication with the [family physician] reassured some patients more than the information sheet – they highly valued the personal information and discussion of the trial which made them feel safe” (p.6).
Finding 2: Written trial information may be beneficial as an adjunct to verbal information and facilitates time and space for reflection without the added influence of recruiters’ presence (we have high confidence in this finding)
Some participants (primarily in pregnancy and gynaecological trials, with one psychotherapy trial) found letters appealing because they allowed for potential participants to decide whether or not to participate in their own time (Hughes‐Morley 2016; Sawyer 2017), acting as an adjunct to verbal information provided by a healthcare professional (Jackson 2010; Smyth 2011; Sawyer 2017). For others (again primarily women invited to trials for urinary tract infection, dysmenorrhoea and infertility), written information, in the form of posters or letters, was sufficient for them to take a decision to participate and they did not feel the need to consult with anyone else (Bleidorn 2015; Blodt 2016; de Lacey 2017).
One individual who declined participation in a therapy trial for treatment resistant depression believed, “The letter is a good idea…I mean if they sign you up you have to decide very quickly and you don’t have time to chew over the information, so having a letter makes sense, you can sit and think about it and decide what to do” (Hughes‐Morley 2016, p4).
Finding 3: The person delivering trial information should have good communication skills, be approachable, trustworthy, person‐centred and knowledgeable with a good ability to address potential participants’ queries. Consideration needs to be given to whether a clinician or a researcher is the most appropriate person to provide the trial information (we have high confidence in this finding)
Across all intervention types, when trial information was delivered in person, potential participants valued the demeanour and approachability of the individual delivering the information (Chang 2004; Costenbader 2007; Moynihan 2012; Ballantyne 2017; Sawyer 2017), and a human, person‐centred approach to the research was viewed favourably (Madsen 2007b; Bleidorn 2015). Irrespective of the intervention, several study authors concluded that delivery of trial information should come from someone knowledgeable who has good communication skills and can take the time to answer potential participants’ queries (Costenbader 2007; Jackson 2010; Tarimo 2010; Oud‐Rengerink 2015).
Potential participants invited to join cancer trials had concerns as to whether the recruiting clinician was trying to steer them towards a decision to participate based on their knowledge of the intervention (Abhyankar 2016). Additionally, potential participants did not like the feeling of being under pressure to consent (Moynihan 2012; Sawyer 2017). Participants from cancer trials (surgical and pharmaceutical) were, at times, suspicious about the motivation, regulation and the role of pharmaceutical companies in influencing physicians who provided trials information (Madsen 2007a; Moynihan 2012). Two studies identified mixed views as to whether the clinician or a member of the research team should provide the trial information (Smyth 2011; Sawyer 2017).
One woman who agreed to participate in a pregnancy and childbirth trial, asserted that “He [recruiting doctor] was very calm throughout the whole process … It was very much he talked to me directly, very clearly, concisely, didn’t mince his words, didn’t beat around the bush. Just very professional and very clear on what he was wanting and what was being said to me” (Sawyer 2017, p.4).
Finding 4: Potential participants value trial information that is robust yet concise, free of medical jargon, clearly identifies options, time commitment, randomisation process, treatment equivalence, intervention details, potential benefits and side effects. This could be made available in hard or soft copy, or both before a decision on participation is expected (we have high confidence in this finding)
Potential participants appreciated good quality information on the features of the trial (Jackson 2010; Hughes‐Morley 2016) and in some studies, those who decided to participate reported receiving adequate information (Jackson 2010; Harrop 2016a; Sawyer 2017). Potential participants in some studies sought “comprehensive" and "extensive" information about trial participation that was free of medical jargon (Taylor 2007; Habersack 2013, Oud‐Rengerink 2015). Participants, primarily in pharmaceutical and some surgical trials, wished for the detail about options, drug doses, risks and side effects at the recruitment stage rather than post consent and indicated that the decision to participate could be hindered by lack of information (Canvin 2006; Costenbader 2007; Madsen 2007b, McCann 2010; Smyth 2011; Abhyankar 2016).
In contrast, however, some potential participants could be deterred by information overload (Smyth 2011; Oud‐Rengerink 2015; Bidad 2016; Harrop 2016a), and some indicated that simple straightforward information was preferable (Ballantyne 2017). Participants in cancer trials, some of whom felt they had “nothing to lose” through participation, did not wish for the same level of detail to inform their decision (Dellson 2018). Participants also wanted to know about the exact time commitment expected from them if they participated in the trial (Attwood 2016; Blodt 2016). Potential participants required a clear explanation of randomisation and treatment equivalence (Canvin 2006; Madsen 2007b; Moynihan 2012; Bidad 2016), but at a time when they are not trying to receive information around treatment and diagnosis (Madsen 2007b). Habersack 2013 identified that “when responding to the question related to how they remember their physician’s briefing regarding the study, more than half of the interview partners referred to the extent and the manner of sharing information. The participants described the briefing predominantly with the words ‘‘extensive’’, ‘‘comprehensive’’ and ‘‘comprehensible’’. In contrast, the non‐participants indicated more short briefings (Habersack 2013, p.5).
Finding 5: The timing of trial information is important as the potential participant needs to be able to consider the trial information without confusing it with their diagnosis and standard treatment (we have high confidence in this finding)
Regarding the timing of presenting trial information, it was important to consider when the potential participant had received their diagnosis, if relevant, and their reaction to it (Madsen 2007b;Smyth 2011; Moynihan 2012; Habersack 2013; Abhyankar 2016; Hughes‐Morley 2016; Sawyer 2017; Dellson 2018). In some cases, recruitment to a trial began when they were still in shock over their diagnosis. In an oncology trial for instance, potential participants were trying to differentiate between information regarding their diagnosis and standard treatments, from information about the trial (Abhyankar 2016). In this study (Abhyankar 2016), trial information was delivered during clinics, either while in consultation or outside of consultation by research staff.
For example, one woman invited to an oncology trial for breast cancer, found it difficult to distinguish between standard treatment options and the trial, ‘When I was diagnosed with my lung secondaries, I was … I don’t know what the alternative was, …any way … various chemos were run past me, like “we could do this or we could do the other” …… and by the way, there is a trial on Taxol. Mm and that was broadly what I was told […]’ (Abhyankar 2016, p.88).
Significant trial components
Finding 6: Potential participants consider participation disruptive and a burden when additional appointments or travel, or both are needed. Perceived time commitment as a result of trial participation was also identified as a concern for potential participants (we have high confidence in this finding)
Certain aspects of the trial itself could impact on potential participants’ decision to enrol in a trial. For instance, some potential participants, across a variety of trials, viewed trial participation as disruptive, burdensome, and some wanted to "avoid the hassle" of additional appointments (Canvin 2006; Costenbader 2007; Habersack 2013; Attwood 2016; Hughes‐Morley 2016; Ballantyne 2017). As illustrated by one participant who declined participation in a therapy trial for depression, “the long‐term commitment was a nightmare for me as I was looking for work, going for interviews and not really knowing what I would be doing or where I would be over the next 18 months” (Hughes‐Morley 2016, p.8). This was not the perception of those in the study by Gopinath 2013 but follow‐up appointments in this trial were conducted over the telephone rather than in person.
Potential burden of trial participation was a particularly important factor when the individual’s health was perceived as stable or "good" (Costenbader 2007), or if individuals wanted immediate treatment without any trial "nonsense" (Harrop 2016a). It was common to cite the potential time commitment as another barrier to participation (Costenbader 2007; Bleidorn 2015; Attwood 2016; Hughes‐Morley 2016; Normansell 2016; Ballantyne 2017). The prospect of participating in a trial could also seem daunting (Attwood 2016).
Finding 7: A financial benefit in terms of an incentive or reimbursement may not be an overly influencing factor for potential participants. However, it is viewed as a welcome acknowledgement of participants’ time and effort. Other incentives that may be welcome include additional health checks or medications that potential participants may otherwise not be able to afford (we have moderate confidence in this finding)
Sometimes, trial participation could include financial reimbursement and this influential factor was explored in some of the included studies. Only one study identified financial reimbursement as an important factor impacting on the decision to participate (Wasan 2009). More so, financial reimbursement was seen as a nice "bonus" that participants were grateful for (Blodt 2016; Chin 2016). It was perceived as a good acknowledgement of time and effort (Blodt 2016; Chin 2016). However, Blodt 2016, in relation to recruiting to an acupressure trial for dysmenorrhoea, concluded that reimbursement would not impair potential participants’ judgement of risks and benefit when making decisions about trial participation. Compensation was often not the sole reason for participation (Chang 2004; Costenbader 2007; Blodt 2016; Chin 2016). As Chang 2004, concludes, “while some patients said that the monetary compensation was a nice feature and they were happy to get it, they stressed that they would have joined the study even without the money” (Chang 2004; p.8). In addition to direct financial incentive, participants felt that they could benefit from interventions (Chang 2004, de Lacey 2017), health checks (Tarimo 2010), or medications (Bleidorn 2015) that they could not otherwise afford. These studies were conducted in Australia, USA, Tanzania and Germany, where access to health care varies from public to private systems.
Finding 8: Potential participants’ perceptions of randomisation and freedom to withdraw from the trial were important factors in their decision whether to participate in a trial. This was particularly important if they did not fully understand the concept of randomisation or if they had a treatment preference (we have high confidence in this finding)
Potential participants’ perceptions and understanding of randomisation, equipoise and treatment preferences were significant in influencing their decision to participate. It was important to participants that they understood the concept of randomisation (Madsen 2007a; Madsen 2007b; Taylor 2007; Bidad 2016). For many potential participants, the uncertainty of being randomised was a barrier to participation (Canvin 2006; Madsen 2007a; Madsen 2007b; Moynihan 2012; Bleidorn 2015; Oud‐Rengerink 2015; Harrop 2016a). In particular, potential participants felt that being randomised to the placebo group would be an unnecessary burden because they would not have the chance of a new treatment (Habersack 2013; Bidad 2016; Ballantyne 2017). This was particularly evident where potential participants wanted the intervention (in these studies, chemotherapy, psychological therapies and probiotics) and not receiving it was perceived as "cruel" (Madsen 2007b; Hughes‐Morley 2016; Ballantyne 2017). There was also the perception among potential participants that one treatment was preferable over the other (Madsen 2007a; Jackson 2010; Gopinath 2013; Oud‐Rengerink 2015; Bidad 2016; Harrop 2016a; Normansell 2016). Treatment preference, primarily in surgical and pharmaceutical trials, was a key factor in decision‐making and could determine agreement to participate or not (Canvin 2006; Madsen 2007b; Jackson 2010; McCann 2010; Moynihan 2012; Gopinath 2013; Bleidorn 2015; Oud‐Rengerink 2015; Bidad 2016; Harrop 2016a; Normansell 2016). In other words, potential participants were less likely to accept randomisation if they had a clear preference for a particular treatment. As one pregnant woman outlined, “I would happily have taken part if I could have opted for iron tablets, but that choice wasn’t available. You have to participate blind, and then I don’t know who decides. I don’t know how that works, but someone else decides for you which of the two you are going to do.” (Oud‐Rengerink 2015).
Randomisation by computer or "drawing of lots", or both was a particular issue; potential participants had a feeling of treatment allocation being "pot luck" and "throwing a dice", rather than a more informed clinical decision (Canvin 2006; Madsen 2007b; Jackson 2010; Bidad 2016; Harrop 2016a). While equipoise was often purported, potential participants felt the healthcare professionals themselves implied that one treatment was preferential (Jackson 2010). Randomisation was more acceptable to those wishing to contribute to knowledge and science and trusted recruiting physicians (Jackson 2010; Blodt 2016). It was also more acceptable to those who perceived equivalence between treatments being randomised (Canvin 2006; Jackson 2010). In some studies, potential participants valued knowing that they could withdraw at any time, particularly after randomisation (Canvin 2006; Madsen 2007a; Jackson 2010). Knowing the decision to participate was voluntary acted as a facilitator (Canvin 2006; Madsen 2007b; Smyth 2011; Abhyankar 2016; Sawyer 2017; Dellson 2018). It was also important to know that they could withdraw from the study at any time (Sawyer 2017). Alternatively, some participants felt they had to participate and that they had no choice (Moynihan 2012). In these two studies, it was the clinician, who provided the trial information, but in the Sawyer 2017 study, potential participants emphasised the caring, supportive and non‐pressurised way in which the trial information was delivered. Recruiters must be cognisant of how they portray information and avoid therapeutic misconception: ensuring potential participants can differentiate between the randomised trial and routine care (Abhyankar 2016).
Theme 2: Personal influences on decision to participate
In this theme, we present personal and external influences on the decision to participate in a trial. These were developed into two subthemes: the influence of others on the person’s perceptions of trial participation and weighing up the risks and benefits.
Influence of other people
Finding 9: The decision to participate is discussed with a range of other people; family, friends, healthcare professionals, previous trial participants (we have high confidence in this finding)
Potential participants often sought advice from family and friends, particularly those with a healthcare background or previous experiences of the trial/intervention (Madsen 2007b; Gopinath 2013, Habersack 2013, Chin 2016, Harrop 2016a, Hughes‐Morley 2016, Ballantyne 2017). In the case of trials in pregnancy and childbirth, in most cases, both the woman and her partner needed to agree before decision‐making (Oud‐Rengerink 2015; Ballantyne 2017; de Lacey 2017). However, in some instances, the woman made the decision alone or with minimal partner influence (Smyth 2011; Ballantyne 2017). Similarly, in cancer trials, participants felt there was no option but to take part and so did not consult with their families in their decision‐making (Dellson 2018). When potential participants had contact with previous trial participants, they could also provide insight into treatment options (Harrop 2016a), their benefits (de Lacey 2017) or their possible side effects (Gopinath 2013; Abhyankar 2016). One potential participant who declined enrolment in a surgical trial for bladder cancer stated, “My sister lives in America and she, her in‐laws work in hospitals, micro‐biologists, technicians sort of thing. So I got them to um tell me what they thought, they’d all worked in where the robot had been um and came back with you know way to go you know, if you get a choice don’t do anything else sort of thing” (Harrop 2016a, p6).
Finding 10: Healthcare professionals in particular may influence decision‐making as potential participants place huge trust in them. This results in great potential for influence by healthcare professionals being a key impact on decision‐making(we have high confidence in this finding)
Some sought advice from a healthcare professional (nurse, midwife, obstetrician, family physician) unrelated to the trial to gain their expertise on the condition and related intervention (Costenbader 2007; Madsen 2007b; Gopinath 2013; Habersack 2013; Oud‐Rengerink 2015; Abhyankar 2016; Ballantyne 2017). Across a broad range of trials, potential participants often placed great trust in healthcare professionals, particularly those known to them, involved in recruiting to the trial, and believed they would only support trial participation if they believed that it was in the best interest of the potential participant (Chang 2004; Canvin 2006; Madsen 2007b; Jackson 2010; Smyth 2011; Moynihan 2012; Habersack 2013; Bleidorn 2015; Bidad 2016; Harrop 2016a; Hughes‐Morley 2016;Dellson 2018). Their perceived trust in the recruiting physician meant nothing "bad" could happen to them (Madsen 2007b; Bleidorn 2015). Some participants from pharmaceutical and surgical trials felt their healthcare professionals had an implicit preference and would only suggest they enrol into a trial if there was a potential benefit or therapeutic effect. (Canvin 2006; Jackson 2010; Moynihan 2012; Harrop 2016a). To explain, why he had agreed to join a bladder cancer trial, one participant said “..he/she’s a (doctor) who instils confidence in you .....and that is one of the things that was a consideration when push came to shove and I had to decide which way it (participation) was going....” (Moynihan 2012, p.4).
In contrast, some potential participants distrusted recruiting clinicians and believed external control of trials (through ethics and regulation) was important (Madsen 2007a; Ballantyne 2017). Potential participants' decision could be impacted if the recruiting healthcare professional indicated a lack of knowledge or inability to articulate the trial properly (Smyth 2011).
Finding 11: Internet searching and exposure to media sources with information on trial interventions may act as either a barrier or a facilitator for trial participation (we have low confidence in this finding)
Potential participants also sought information from the Internet on the trial/intervention and the associated risks (Gopinath 2013; Habersack 2013; Harrop 2016a; Ballantyne 2017; de Lacey 2017. This information could act as a facilitator (de Lacey 2017) or barrier (Gopinath 2013) to trial participation. Doing their investigations on the Internet could supplement the trial information or, in some cases, lead to preferences for certain treatments (Harrop 2016a). Those who did not access the Internet avoided it for fear of "bad news" (Habersack 2013). As one woman invited on to a breast cancer trial said, “…also can research a little, perhaps also on the internet, though I don’t like to do that so much. Of course, I did it before, but. … I talked with my doctor today anyhow. He also says that, most of the time, those who write are those who have had negative experiences; where the surgery failed” (Habersack 2013, p3).The media and television could also influence decision‐making (Madsen 2007a; Gopinath 2013; Bleidorn 2015), either negatively (Madsen 2007a; Bleidorn 2015) or positively (Gopinath 2013).
Weighing up the risks and benefits
Finding 12: Potential participants may view trial participation as feeling like a guinea pig (i.e. being used for the experiment), which they considered as too risky (we have moderate confidence in this finding)
The perceptions of personal harm and benefit were critical considerations for trial participation. Potential participants commonly equated trial participation to being a "guinea pig" (Chang 2004; Canvin 2006; Taylor 2007; Moynihan 2012; Gopinath 2013; Habersack 2013; Bleidorn 2015; Dellson 2018), and for some that was too risky to agree to take part in the trial (Costenbader 2007; Bleidorn 2015; Oud‐Rengerink 2015). One man who declined participation stated, “all I knew is ( ) you are going as a human guinea pig and they can do what they like..” (Moynihan 2012, p 8). There could be a perceived risk from taking tested drugs, either through a belief in non‐effect or side effects (Canvin 2006; Costenbader 2007; Madsen 2007a; Madsen 2007b; Tarimo 2010; Habersack 2013; Bleidorn 2015; Oud‐Rengerink 2015). A woman who declined participation in a trial for urinary tract infections asserted, “and fundamentally I was not opposed, however (...) but when he told me that I will get a drug as part of this study (...) then I kept my distance. (...) because I was thinking: Well, you do not need drugs actually. Maybe just a homeopathic remedy or something like that to solve the whole problem.” (Bleidorn 2015, p.7).
Finding 13: The risk of participation may concern potential participants who view their health as good or they are healthy and worried that the trial would identify a health problem. Potential participants may deem themselves ineligible and decline if they have too many health problems (we have high confidence in this finding).
People did not want to risk their health further, either when they were sick and did not want to get worse; or feeling well and did not want to "rock the boat" (Costenbader 2007; Bleidorn 2015; Normansell 2016), as identified by one decliner, “It’s like I’m feeling good right now. Don’t bother me with all that now. I am living my life” (Costenbader 2007, p.52).
Perception of risk could vary for individuals based on personality and previous positive or negative experience of healthcare systems (Gopinath 2013; Harrop 2016a; Ballantyne 2017). Some just did not like the intervention, for example, a walking programme or telehealth (Sanders 2012; Oud‐Rengerink 2015; Normansell 2016). Some participants declined, deeming themselves ineligible because they were too healthy and just wanted to get on "with everyday life" (Canvin 2006; Costenbader 2007; Barnes 2012; Bleidorn 2015; Attwood 2016; Hughes‐Morley 2016), or felt they had too many co‐morbidities and that participating in a trial would be an additional burden (Barnes 2012; Attwood 2016; Harrop 2016a;, Hughes‐Morley 2016). As one decliner outlined, “well at the moment I’ve got other health problems... and I didn’t want to be bothered with any more things to have to sort of connect me with hospitals ... I’m diabetic, got asthma, and chronic kidney disease’ (Barnes 2012, e375).
Finding 14: If potential participants sense a trial was safe, low risk, and would not impact on existing treatments they may feel they have nothing to lose if they participate (we have moderate confidence in this finding)
In some cases, agreement to participate was less about potential benefit but rather lack of identification of "active harm" (Canvin 2006; Oud‐Rengerink 2015). If the trial intervention (for example probiotics, acupressure) was considered to have very low risk or not jeopardise existing treatments, or both, there was little proposed risk to themselves (or baby in pregnancy trials) thus facilitating participation (Madsen 2007a; Bleidorn 2015; Oud‐Rengerink 2015; Bidad 2016; Blodt 2016; Ballantyne 2017; de Lacey 2017; Sawyer 2017). This resulted in a sense of safety that nothing "bad" could happen and there was "nothing to lose" (Jackson 2010; Bleidorn 2015; de Lacey 2017). As one woman who accepted participation in a cord clamping policy trial, it was a “very easy decision, to be honest, because I knew there would be no danger to the baby to be left on the cord. I would have never if there was a risk, but I felt that there was no risk so there wasn’t any query of it really. It was easy as that” (Sawyer 2017, p.6).
Finding 15: If potential participants consider themselves desperate, they may feel they have nothing to lose if they participate (we have moderate confidence in this finding)
“Nothing to lose” could also capture the feeling of desperation of the situation prior to the trial invitation (living with chronic pain or having a cancer diagnosis) and the need to regain control (Madsen 2007b; Blodt 2016; de Lacey 2017; Dellson 2018). The perception of having nothing to lose was important for those with a diagnosis of cancer as participation was seen to be preferable over "doing nothing" [standard care] (Abhyankar 2016; Dellson 2018). This could also mean keeping optimistic in the face of their diagnosis (Habersack 2013). In the case of cancer diagnosis, there was no perceived risk as trial participation was "life or death" (Abhyankar 2016; Dellson 2018). Likewise, in pre‐eclampsia, there was a similar feeling of life or death for both mother and baby (Smyth 2011). The deliberation between what potential participants had to lose or gain was prominent regardless of the type of trial or intervention. As one woman suggested, “so it’s as I said. I’m sick once a month and I find that quite a limitation given the fact that it’s [menstrual pain] not a disease. … And I just hoped that something could help. That I could just … cope with my everyday life. … Because up to now there has been no solution (Blodt 2016, p.5).
Theme 3: The impact of potential outcomes on decision to participate
Within this theme, we explore the potential outcomes of trial participation. The potential benefits of trial participation could be personal or for the benefit of others, therefore two subthemes were identified: 'Personal benefits of trial participation' and, 'Making a difference: benefits for others'.
Personal benefits of trial participation
Finding 16: Potential participants recognise the benefit of access to new or existing treatments through trial participation (we have high confidence in this finding)
Potential participants were more likely to agree to participate when they could anticipate a positive impact on their care (Madsen 2007a; Madsen 2007b; McCann 2010; Oud‐Rengerink 2015). Overall, potential benefits included receiving treatments, often new or alternative to standard care (Canvin 2006; Wasan 2009; Jackson 2010; Smyth 2011; Habersack 2013; Oud‐Rengerink 2015; Blodt 2016; de Lacey 2017; Dellson 2018). As one participant said, “because I have chronic back pain and I’m not happy with the medication I’ve got, and I’m interested in either finding something better, or at least helping with the process of researching it” (Wasan 2009, p.115).
Conversely, in the case of decliners, it was the perceived lack of personal benefit from the intervention that impacted on their decision (Bidad 2016). Some potential participants felt there was no benefit from trial participation due to a lack of personal relevance (Attwood 2016; Bidad 2016). For some, in the case of two similar treatments for stress incontinence, it was that they did not see one intervention as having greater potential value over another (Gopinath 2013). Some decliners had experienced an intervention (e.g. counselling) before, disliked it, and so did not want to receive it again (Barnes 2012).
Finding 17: Potential participants recognise that being in a trial may mean quicker access to services, better follow‐up care, increased contact time with physicians and a chance to learn more about their condition, as potential benefits to trial participation (we have high confidence in this finding)
Potential impact on care could also be perceived as the opportunity to have a health check secondary to trial participation (Tarimo 2010; Attwood 2016; Dellson 2018), quicker access to services (McCann 2010); better follow‐up care, and increased contact time with physicians (Wasan 2009; Jackson 2010; McCann 2010; Habersack 2013; Bidad 2016); or learn more about their condition and ways to manage it (Chang 2004; Costenbader 2007; McCann 2010). In pregnant women, this benefit could be for the unborn child and seemed like the "natural thing to do” (Oud‐Rengerink 2015; Sawyer 2017). As one woman in a breast cancer trial suggested, “and I believe, if I weren’t participating in the study, I don’t know if it would be as precise and personal with the follow‐up care ..Of course I am examined regarding my spine every six months; so that is automatically better. Otherwise I would not receive that” (Habersack 2013, p.3).
Finding 18: Potential participants may be managing symptoms for some time with feelings of desperation and trial participation brings hope of relief (we have moderate confidence in this finding)
Trial participation brought with it the "hope" for relief of symptoms such as chronic back pain, reflux, dysmenorrhoea or urinary tract infections; which in some instances potential participants had been self‐managing for some time (Wasan 2009; McCann 2010; Bleidorn 2015; Blodt 2016). This often manifested as a feeling of desperation of the situation before the trial invitation, where potential participants felt out of options other than to participate (Madsen 2007b; Blodt 2016; de Lacey 2017; Dellson 2018). As one participant in an oncology trial said, “And you can’t ask to have this treatment any other way. The only chance to get it is if you participate in the study” (Dellson 2018, p.5).
Making a difference: benefits for others
Finding 19: Altruism can be an important factor influencing potential participants’ decision to participate in a trial (we have high confidence in this finding)
Altruism was often cited by potential participants as an important motivating factor, contributing to improved care for others in the future (Chang 2004; Canvin 2006; Costenbader 2007; Madsen 2007a; Wasan 2009; McCann 2010; Smyth 2011; Moynihan 2012; Habersack 2013; Bleidorn 2015; Oud‐Rengerink 2015; Bidad 2016; Harrop 2016a; Hughes‐Morley 2016; Ballantyne 2017; de Lacey 2017; Dellson 2018). As outlined by one participant, “I can remember reading things, something that said look, it might not necessarily benefit you and I can remember thinking that of the people that have tried out drugs and techniques before I was trying to get pregnant [and how] that’s helped me. If I can be part of something that maybe I will get some benefit from [and if I don’t] maybe somebody else in 10 years’ time will get benefit out of it” (de Lacey 2017, p5).
Even those who declined participation acknowledged the value of research in helping other people (Bidad 2016). Some believed that altruism and a desire to help others was down to personality type (Bleidorn 2015; Bidad 2016; Ballantyne 2017). Chin 2016 identified different typologies of altruism: cultural, community, familial, professional, religious, political, experiential, moral, existential and psychological. A combination of these influenced potential participants’ altruistic motives.
Finding 20: Altruism can be conditional whereby potential participants’ desire to help others is dependent on the trial being low risk and with clear benefits (we have moderate confidence in this finding)
There was a certain amount of conflict between the desire to help other people and personal risk (Abhyankar 2016; Attwood 2016). As outlined by one woman invited on to a breast cancer trial, “’cos you do sometimes think you know you are helping other people by doing this, but then sometimes you think I don’t want to help anybody else, I want to look after myself” (Abhyankar 2016, p.87). The decision was more straightforward in cases where the perceived personal risk was low (Chang 2004; Canvin 2006; Oud‐Rengerink 2015). Conversely, it was more significant in more life‐changing diagnoses such as cancer (Bidad 2016). Sometimes altruism and personal benefit went hand in hand, whereby if the "community" would benefit, then the individual would also (Canvin 2006). Altruism was sometimes secondary to personal benefit (Jackson 2010), implying conditional altruism, whereby there must also be personal benefits from participation (McCann 2010; Bidad 2016).
Pure altruism was recognised as acceptance of randomisation even when it was not the preferred treatment/intervention (Bidad 2016). Alternatively, hypothetical altruism is seen where participants were allocated to their preferred treatment but said they would have participated regardless of allocation (Jackson 2010; Bidad 2016). There was evidence that this may have been due to a misunderstanding of randomisation (Bidad 2016). Bidad 2016 also identified weak altruism where participants had no real treatment preference going into the trial.
Finding 21: Potential participants may feel an obligation or a moral duty to participate in a trial as a way of “giving back” (we have moderate confidence in this finding)
Rather than altruism per se, some potential participants felt more of a duty to participate (Bidad 2016). It was considered a way to "give back", "pay back" and "do your part" (Canvin 2006; Bleidorn 2015; Bidad 2016; Ballantyne 2017), and sometimes seen as a moral obligation (Madsen 2007a; Tarimo 2010; Chin 2016; Ballantyne 2017), for religious reasons (Tarimo 2010), and in the case of one HIV vaccine trial, as atonement for previous wrong doings (Chin 2016). This brought a sense of pride in their contribution (Tarimo 2010; Chin 2016). One male invited on to a HIV vaccine trial outlined, “I’ve been part of negative stuff all my life. I ran the streets for a long time. I did drugs so many years. I tore down my community. I sold and did a lot of drugs. I hurt a lot of people. So eventually, I mean: I don’t do nothing negative no more, so I’m going to be part of something positive. Now I want to help” (Chin 2016, p.9).
Finding 22: Potential participants may have a genuine interest in contributing to scientific knowledge and improved care (we have high confidence in this finding)
For some potential participants, there was genuine curiosity and interest in contributing to the trial and scientific knowledge. Participants recognised the value of trials adding to new knowledge and improved care (Chang 2004; Canvin 2006; Madsen 2007a; Wasan 2009; Smyth 2011; Moynihan 2012; Habersack 2013; Bleidorn 2015; Oud‐Rengerink 2015; Bidad 2016; Hughes‐Morley 2016; Ballantyne 2017; de Lacey 2017; Sawyer 2017; Dellson 2018). This included being part of a larger endeavour, contributing to the bigger picture (Chin 2016; de Lacey 2017) and "doing something about it" (Hughes‐Morley 2016). As one woman invited on to a cord clamping trial suggested, “Basically, I think it’s like anything, isn’t it. Without research you don’t find out about things, so I totally support research. That was our feeling behind it, that, you know, if you don’t research these things, you don’t find out about it, do you? We’re completely open to research, and we think it’s a good thing, so it was important to take part” (Sawyer 2017, p.6).
Contribution to science and knowledge was recognised particularly with those who were familiar with research professionally (Bleidorn 2015; Oud‐Rengerink 2015), from participating in previous studies (Oud‐Rengerink 2015), or benefiting from previous research (Bleidorn 2015; Oud‐Rengerink 2015). This contribution helped to seek solutions to existing unsatisfactory or ineffective treatments (Bleidorn 2015; Blodt 2016), and pioneer new interventions (Harrop 2016a). Decliners also noted the need to contribute to science (Harrop 2016a; Hughes‐Morley 2016; Normansell 2016).
Conceptual model
From these themes, we concluded that for potential participants, the ultimate question was, “will I take part?”. To illustrate this, we developed a conceptual model (Figure 3) based on the concept of a gauge, whereby a potential participant decides ultimately whether to take part in the trial. The factors that impact on whether they participate can tip the gauge towards accepting participation or declining participation. The factors that tip the gauge towards declining include trial burden, feeling they have something to lose, or nothing to gain. How trial information is communicated may also tip the person towards declining as may the discouragement of other people. The factors that could tip the gauge towards accepting participation include the belief there is something to gain, the chance to make a difference and the sense that there is nothing to lose by participating. Again, how trial information is communicated, and the encouragement of others may incline some towards accepting participation.
3.
Conceptual model
As an example, a potential participant, who perceives themselves as healthy, may feel they have nothing to gain by participating in a trial. If the trial is deemed risky, inconvenient or burdensome, they may also feel that they have something to lose and so the gauge tips towards declining. Another example may be an individual with a life‐limiting condition. They may not benefit personally by participating, but they may feel they have something to gain by helping others, thus tipping the gauge towards accepting. Alternatively, they may not feel they have anything to gain, but by the nature of their diagnosis, they may feel they have nothing to lose, and therefore accept to participation in the trial. This decision‐making gauge analogy highlights that “gain” can move beyond personal benefit and “what’s in it for me?” encompasses the knowledge that participation in a trial is altruistic and contributes to science.
Limitations of the review
This review began with a very broad question. To make the review manageable, we needed to make decisions during the process to refocus on potential participants’ perspectives only. Even then, we retrieved a large number of relevant studies. By using the CART criteria as our sampling technique, we analysed highly relevant studies with rich data. We do acknowledge, however, that by using this technique, all perspectives may not have been captured. If we had used an approach that incorporated geographical spread and maximum representation from different participant groups, including ethnic minority groups and lower socioeconomic groups, we may have captured a wider breath of perspective.
Another limitation of our review team is that we did not have public and patient involvement (PPI) contributors on the team. PPI contributors would have provided valuable insights into the review process and we will invite PPI contributors in to the review team for future updates to this review.
Discussion
Summary of the main findings
We identified several key factors that impact on an individual’s decision whether to take part in a trial. These are presented under three main areas. Firstly, the trial itself and how the recruiters communicate about the trial can impact on decision‐making. Potential participants preferred to be invited in a face‐to‐face setting and provided with all the information needed in a clear way. Written information was useful for them to refer back to. The timing of invitation was very important as potential participants could find it difficult to distinguish between the care they would usually receive and care that would be provided as part of the trial. They may also be coming to terms with a diagnosis, which can impact on their decision. Commitment to the trial can make people worried about participating. Some believed that extra appointments and the time involved would be a burden. Sometimes people are offered money as a way to recompense them for their commitment. Payment was welcomed by some but was not seen as a very important factor that influences their decision.
Secondly, the individual’s view of their own health can influence their decision to take part in a trial. If someone feels healthy, they may not wish to risk their health by taking part. However, if someone feels unwell, they may not want to risk making their health worse. On the other hand, someone who is healthy or very ill may feel they have “nothing to lose” by taking part, so it is not just about how healthy someone is but rather how secure they feel about their own health. This perception of risk can be influenced by other people. The person’s doctor or nurse may say something that influences their decision, as can something said by family, friends or in the media. It is important for the people recruiting to know who has influence when the person is making their decisions
Finally, the possible benefits of taking part are key to the decision. Individuals are influenced by the chance of improvement to their health; the chance to feel better if the therapy or treatment works. Many welcome the opportunity to participate for reasons of altruism or the opportunity to make a difference by contributing to science.
Overall completeness and applicability of evidence
Due to the high number of relevant studies for our original question, we decided to refine the review to the perspective of adult potential participants only; with direct experience of being recruited to a randomised trial. We subsequently purposefully selected studies of high relevance, with the phenomenon of interest being the sole or major focus of the primary studies. The included studies cover a broad sample of trials from different areas of health care with a variety of interventions being tested. There was adequate representation from both acceptors and decliners, which ensures comprehensiveness of perspective. Particularly, individuals who had declined to participate in the trial itself may have been less likely to participate in the qualitative studies. The aim of qualitative studies is to provide insights through thick description to enhance the transferability of the findings, rather than aiming for generalisability.
Other potential shortcomings to the overall completeness may be due to omission of hypothetical trials whereby the perspectives of the general population are not represented fully. However, since our aim was to integrate the synthesis findings with the findings of the relevant Intervention reviews, it was argued that the perspectives around the acceptability of hypothetical trials would not have insight into specific experiences of recruitment and the strategies employed. We believe that experience‐based views were particularly valuable for illuminating unanticipated perspectives that hypothetical trials might not have uncovered. The included studies were primarily from Europe and the USA with only one study from Africa, two from Australasia and none from Asia. This is reflective of the geographical spread of the original (n = 85) studies for inclusion, with the other studies from Africa focusing more on hypothetical trials.
Overall, through application of GRADE CERQual, we have demonstrated the level of confidence in findings that are pertinent across a broad range of trials, incorporating a number of interventions (types of surgery, cognitive behavioural therapy and other psychological therapies, pedometer use, HIV vaccines, pharmaceutical treatments, umbilical cord clamping, acupuncture, telehealth, pulmonary rehabilitation) across many contexts of health care (oncology, pregnancy and childbirth, medical and surgical, mental health, and health promotion). The conclusions we drew from this synthesis were that regardless of the type of trial or nature of the proposed intervention, the strongest motivational factors to trial participation were the potential participants’ perceptions of their own health status and the subsequent level of risk involved in taking part in the trial. This comprehensive insight will be meaningful for recruiters and trialists across all types of trials.
Comparisons with other studies or reviews
Challenges to recruitment are well‐documented and several previous reviews have explored this issue. Previous reviews have examined the barriers to recruitment and reasons for poor recruitment to healthcare trials (Prescott 1999; Fletcher 2012). Primary research studies have also focused on the reasons for non‐participation. However, important lessons can also be learned from trials that recruited successfully (Fletcher 2012).
Previous systematic reviews and qualitative syntheses have focused on strategies that have helped or hindered recruitment specific to cancer trials (Townsley 2005; Fayter 2007; Boland 2015), or factors that impact on participant types, such as indigenous populations (Glover 2015). Previous qualitative syntheses have focused specifically on communicating equipoise during recruitment (Rooshenas 2016) and exploring pre‐trial preferences (Corbett 2016). There are commonalities in the findings across these reviews.
Our review examines these issues in a broader context, specifically from the perspective of potential participants across all trial types. The individual factors such as explanation of equipoise and potential participants’ treatments preferences, all feed into the broader questions of “what is in it for me?” and "will I take part?" It is this question that recruiters need to consider when designing trials and developing recruitment strategies; being cognisant of characteristics of the trial and intervention, but also the characteristics of the people being invited; in a person‐centred and individualised way.
Authors' conclusions
Implications for practice
On integrating our findings with previous intervention reviews by Treweek 2018 and Gardner 2020, we developed the following key questions that can be asked by trialists to guide their recruitment strategy.
Communication of trial information
Will trial information be delivered verbally with face‐to‐face contact?
Will written information be offered as a supplement to or in addition to verbal information?
Is the person delivering the trial information approachable, trustworthy, participant‐centred and knowledgeable with a good ability to address queries?
Has the recruitment strategy identified whether a clinician or a researcher is the most appropriate person to provide the trial information?
Has time been provided to ensure that the potential participant can consider the trial information at their own individual pace?
Is information clear and concise, free of medical jargon, clearly identifying options, time commitment, randomisation process, treatment equivalence, intervention details, potential benefits and side effects?
Has the timing of the delivery of trial information been considered in order to ensure potential participants have the opportunity to consider the trial information as distinct from their diagnosis and standard treatment?
Significant components of the trial itself
Will trialists aim to minimise additional time commitment to the trial (beyond routine care)?
Will trialists consider using incentives or reimbursements to acknowledge participants’ time and effort?
Will trialists, where appropriate, consider including health assessments and monitoring as incentives for participation?
Will trialists consider how best to explain randomisation and freedom to withdraw from the study?
Influence of other people
Will recruiters identify other people, such as family and friends, who influence potential participants’ decision and, where appropriate, include them in information‐giving sessions?
Will recruiters ensure healthcare professionals who are involved in care, are knowledgeable about the study and able to answer questions in a non‐biased way?
Will recruiters consider sourcing useful internet links and media sources with information on the intervention, to recommend to potential participants?
Weighing up the risks and benefits
Will recruiters be very clear when communicating risks to potential participants?
Are the recruiters effective in communicating information, particularly when recruiting potential participants who are concerned about risks or feel that they have “nothing to gain” from trial participation?
Personal benefits of trial participation
Will recruiters, where appropriate, highlight quicker access to services, better follow‐up care, increased contact time with physicians and an opportunity to learn more about their condition as potential benefits to trial participation?
Will recruiters, demonstrate empathy to potential participants who may be managing symptoms and feelings of desperation or isolation for some time?
Making a difference: benefits for others
Will recruiters highlight possible benefits of altruism and contribution to science as key potential benefits of trial participation?
Will recruiters demonstrate their gratitude to potential participants for their contribution to the trial?
These questions can guide recruitment in a practical manner. It is also important to use the conceptual model to enhance understanding of the complex factors that influence potential participants decision on whether to take part. Future development of recruitment strategies need to adopt this individualised participant‐centred approach to maximise recruitment, reduce research waste and ensure the ethical recruitment of participants to randomised trials.
Implications for research
The overarching confidence in our qualitative synthesised findings are moderate to high. This can be partly attributed to the high volume of good quality relevant studies pertinent to this review question. Our preliminary assessments of the results from our 2019 search further substantiate this. We conclude that ample evidence on why people agree or decline participation in trials exists and so there needs to be a strong justification for further general research in this field of recruitment from the potential participants’ perspective. There are, however, exceptions. Work in lower‐income countries is needed, particularly in Africa and Asia, which were not adequately represented in this Qualitative Evidence Synthesis (QES). In addition, factors that affect black, Asian and minority ethnic involvement in trials held in middle‐ and higher‐income countries, as well as that of other under‐represented groups, such as the socially disadvantaged, is needed.
In addition, further evidence synthesis of the experiences of recruitment in the context of trials with children, and adults who lack mental capacity to consent is needed. An up‐to‐date qualitative evidence synthesis of the recruiter perspective would also be useful in completing insight into trial recruitment.
However, what the trial community needs most now is the development and testing of robust recruitment strategies that are individualised and participant‐centred and draw directly from the experiences of those reported in this review. While this review focuses on recruitment, it is important to acknowledge the potentially complex impact that recruitment can have on retention (Daykin 2018), so this must be considered in developing future interventions. It is interesting to note that there was little to no mention of Public and Patient Involvement (PPI) groups in terms of recruitment strategies. There is now an increased awareness and value of PPI, and further exploration of PPI contributors in recruitment processes needs to be considered.
History
Protocol first published: Issue 5, 2017 Review first published: Issue 10, 2020
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Lynn Hampson for performing the update search in 2017. We are very grateful to Andrew Booth for answering multiple questions on the reporting and conduct of our search strategy. We also thank staff at Clarivate Analytics for answering our questions regarding deduplication in EndNote.
The Health Services Research Unit, University of Aberdeen, receives core funding from the Chief Scientist Office of the Scottish Government Health Directorates.
The Health Research Board‐Trials Methodology Research Network (HRB‐TMRN) receives core funding from the Health Research Board (HRB, Ireland).
Qualitative Research in Trials Centre (QUESTS), is embedded in the HRB‐TMRN.
We thank peer reviewers Claire Glenton and Bridget Young and the Cochrane Methodology Review Group (Mike Clarke) for their helpful feedback.
Appendices
Appendix 1. Strategy used to search Embase (Ovid) in 2017
| # | Search strings |
| 1 | (participat* OR recruit* OR enrol* OR non‐participat* OR nonparticipat* OR selection).ti ADJ8 (trial*).ti |
| 2 | (participat* OR recruit* OR non‐participat* OR nonparticipat*).ab ADJ8 (trial*).ab |
| 3 | (participat* OR recruit* OR non‐participat* OR nonparticipat*).if ADJ8 (trial*).if |
| 4 | (1 OR 2 OR 3) |
| 5 | (qualitative OR ethnograph* OR phenomenol* OR "grounded theory" OR hermeneutic* OR observation* OR "focus group" OR "focus groups" OR interview* OR "mixed method" OR "mixed methods" OR multimethod OR "multi‐method").ti,ab |
| 6 | (experience* OR perceive* OR perception* OR attitude* OR barrier* OR facilitat* OR challenge* OR opportunit* OR opinion* OR agree* OR accept* OR refuse* OR refusal OR decline* OR decision* OR decide*).ti,ab |
| 7 | (control*).ti,ab AND (trial OR trials).ti,ab |
| 8 | (random*).ti,ab |
| 9 | (7 OR 8) |
| 10 | (4 AND 5 AND 6 AND 9) |
Appendix 2. Update strategy used to search Embase (Ovid) in 2019 search
| # | Query |
| 1 | ((participat* or recruit* or enrol* or non‐participat* or nonparticipat* or selection) adj8 trial*).ab,kw,ti. |
| 2 | (qualitative or ethnograph* or phenomenol* or "grounded theory" or hermeneutic* or observation* or "focus group*" or interview* or "mixed method*" or multimethod or "multi‐method").ab,ti. |
| 3 | exp qualitative research/ |
| 4 | ethnography/ |
| 5 | exp phenomenology/ |
| 6 | exp grounded theory/ |
| 7 | exp hermeneutics/ |
| 8 | exp interview/ |
| 9 | exp multimethod study/ |
| 10 | 2 or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6 or 7 or 8 or 9 |
| 11 | (experience* or perceive* or perception* or attitude* or barrier* or facilitat* or challenge* or opportunit* or opinion* or agree* or accept* or refuse* or refusal or decline* or decision* or decide*).ab,ti. |
| 12 | (control* and (trial or trials)).ab,ti. |
| 13 | "random*".ab,ti. |
| 14 | exp "randomized controlled trial (topic)"/ |
| 15 | exp "controlled clinical trial (topic)"/ |
| 16 | 12 or 13 or 14 or 15 |
| 17 | 1 and 10 and 11 and 16 |
| 18 | limit 17 to english language |
| 19 | limit 18 to exclude medline journals |
Appendix 3. Full Evidence Profiles
Trial influences on Decision to Participate
Communication of trial information
| Summary of review finding | Studies contributing to the review finding | Methodological limitations | Coherence | Relevance | Adequacy | CERQual assessment of confidence in the evidence | Explanation of CERQual assessment | |
| Finding 1: Trial information delivered verbally during face‐to‐face communication can be less confusing than written trial information | Barnes 2012, Moynihan 2012, Bleidorn 2015, Oud‐Rengerink 2015, Attwood 2016, Dellson 2018 |
Minor concerns based on the assessment of four studies with no, and two studies with minor methodological limitations |
No or very minor concerns |
Minor concerns regarding relevance as studies had moderate geographical spread Included a range of medical/surgical, oncology, mental health, pregnancy and childbirth, and health promotion trials. Participants included both acceptors and decliners. |
No or very minor concerns | High Confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding relevance and methodological limitations, and minor concerns regarding adequacy | |
| Finding 2: Written trial information may be beneficial as an adjunct to verbal information and facilitates time and space for reflection without the added influence of recruiters’ presence | Hughes‐Morley 2016, Jackson 2010, Sawyer 2017, Smyth 2011, Bleidorn 2015, Blodt 2016, de Lacey 2017 |
Minor concerns based on the assessment of five studies with no, and two studies with minor methodological limitations |
No or very minor concerns |
Minor concerns regarding relevance as studies had moderate geographical spread Included a range of medical/surgical, oncology, mental health and pregnancy and childbirth. Participants included both acceptors and decliners. |
No or very minor concerns | High Confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding relevance and methodological limitations, and minor concerns regarding adequacy | |
| Finding 3: The person delivering trial information should have good communication skills, be approachable, trustworthy, person‐centred and knowledgeable with a good ability to address potential participants’ queries. Consideration needs to be given to whether a clinician or a researcher is the most appropriate person to provide the trial information | Abhyankar 2016, Chang 2004, Costenbader 2007, Harrop 2016a, Madsen 2007a, Madsen 2007b, Jackson 2010, Moynihan 2012, Smyth 2011, Habersack 2013, Oud‐Rengerink 2015, Tarimo 2010Bleidorn 2015, Ballantyne 2017, Sawyer 2017 |
Minor concerns based on the assessment of eleven studies with no, and three studies with minor and one study with moderate methodological limitations |
No or very minor concerns |
Moderate concerns regarding relevance as studies had moderate geographical spread Included a range of medical/surgical, oncology and pregnancy and childbirth. Participants included both acceptors and decliners. |
No or very minor concerns | High Confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding coherence, moderate concerns regarding relevance and methodological limitations, and minor concerns regarding adequacy | |
| Finding 4: Potential participants value trial information that is robust yet concise, free of medical jargon, clearly identifies options, time commitment, randomisation process, treatment equivalence, intervention details, potential benefits and side effects. This could be made available in hard or soft copy, or both before a decision on participation is expected | Jackson 2010, Hughes‐Morley 2016, Sawyer 2017, Taylor 2007, Habersack 2013, Oud‐Rengerink 2015, Canvin 2006, Costenbader 2007, Madsen 2007b, McCann 2010, Smyth 2011, Abhyankar 2016, Bidad 2016, Harrop 2016a, Ballantyne 2017, Dellson 2018, Attwood 2016, Blodt 2016, Moynihan 2012. |
Minor concerns based on the assessment of fifteen studies with no, and three studies with minor and one study with moderate methodological limitations |
No or very minor concerns |
Minor concerns regarding relevance as studies had moderate geographical spread Included a range of medical/surgical, oncology, mental health, pregnancy and childbirth, and health promotion trials. Participants included both acceptors and decliners. |
No or very minor concerns | High Confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding relevance and methodological limitations, and minor concerns regarding adequacy | |
| Finding 5: The timing of trial information is important as the potential participant needs to be able to consider the trial information without confusing it with their diagnosis and standard treatment | Abhyankar 2016Madsen 2007b, Moynihan 2012, Smyth 2011, Habersack 2013, Hughes‐Morley 2016, Sawyer 2017, Dellson 2018 |
Minor concerns based on the assessment of six studies with no, and two studies with minor methodological limitations |
No or very minor concerns |
Moderate concerns regarding relevance as studies had moderate geographical spread Included a range of, oncology, mental health and pregnancy and childbirth trials. Participants included both acceptors and decliners. |
No or very minor concerns | High Confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding coherence, moderate concerns regarding relevance and methodological limitations, and minor concerns regarding adequacy | |
Significant trial components
| Summary of review finding | Studies contributing to the review finding | Methodological limitations | Coherence | Relevance | Adequacy | CERQual assessment of confidence in the evidence | Explanation of CERQual assessment | |
| Finding 6: Potential participants consider participation disruptive and a burden when additional appointments or travel, or both are needed. Perceived time commitment as a result of trial participation was also identified as a concern for potential participants | Canvin 2006, Harrop 2016a, Costenbader 2007, Habersack 2013, Bleidorn 2015, Attwood 2016, Hughes‐Morley 2016, Normansell 2016, Ballantyne 2017 |
Minor concerns based on the assessment of six studies with no, two studies with minor and one study with moderate methodological limitations |
No or very minor concerns |
Minor concerns regarding relevance as studies had limited geographical spread Included a range of medical/surgical, oncology, mental health, pregnancy and childbirth, and health promotion trials. Participants included both acceptors and decliners. |
No or very minor concerns | High confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding adequacy and coherence, minor concerns regarding relevance and methodological limitations | |
| Finding 7: A financial benefit in terms of an incentive or reimbursement may not be an overly influencing factor for potential participants. However, it is viewed as a welcome acknowledgement of participants’ time and effort. Other incentives that may be welcome include additional health checks or medications that potential participants may otherwise not be able to afford | Chang 2004, Costenbader 2007, Wasan 2009, Tarimo 2010, Bleidorn 2015, Blodt 2016, Chin 2016, de Lacey 2017 |
Minor concerns based on the assessment of five studies with no, two studies with minor and one study with moderate methodological limitations |
Minor concerns |
Moderate concerns regarding relevance as studies had limited geographical spread Included mainly medical/surgical, with one pregnancy and childbirth, and one health promotion trial. Participants included mainly acceptors with only one study including decliners. |
No or very minor concerns | Moderate confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding adequacy, minor concerns regarding coherence and methodological limitations, and moderate concerns regarding relevance | |
| Finding 8: Potential participants’ perceptions of randomisation and freedom to withdraw from the trial were important factors in their decision whether to participate in a trial. This was particularly important if they did not fully understand the concept of randomisation or if they had a treatment preference | Canvin 2006, Madsen 2007a, Madsen 2007b, Taylor 2007, Jackson 2010, Moynihan 2012, Smyth 2011, Gopinath 2013, Bleidorn 2015, Oud‐Rengerink 2015, Abhyankar 2016, Bidad 2016, Harrop 2016a, Hughes‐Morley 2016, Normansell 2016, Ballantyne 2017, Sawyer 2017, Dellson 2018 |
Minor concerns based on the assessment of thirteen studies with no, three studies with minor and one study with moderate methodological limitations |
No or very minor concerns |
Minor concerns regarding relevance as studies had moderate geographical spread Included a range of medical/surgical, oncology, mental health, pregnancy and childbirth, and health promotion trials. Participants included both acceptors and decliners. |
No or very minor concerns | High confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding adequacy and coherence, minor concerns regarding relevance and methodological limitations | |
Personal Influences on Decision to Participate
Influence of other people
| Summary of review finding | Studies contributing to the review finding | Methodological limitations | Coherence | Relevance | Adequacy | CERQual assessment of confidence in the evidence | Explanation of CERQual assessment | |
| Finding 9: The decision to participate is discussed with a range of other people; family, friends, HCPs, previous trial participants | Smyth 2011, Abhyankar 2016, Madsen 2007b, Gopinath 2013, Habersack 2013, Oud‐Rengerink 2015, Chin 2016, Harrop 2016a, Hughes‐Morley 2016, Ballantyne 2017, de Lacey 2017, Dellson 2018, |
Minor concerns based on the assessment of nine studies with no, and three studies with minor methodological limitations |
Minor concerns |
Minor concerns regarding relevance as studies had moderate geographical spread Included a range of medical/surgical, oncology, mental health, pregnancy and childbirth, and health promotion trials. Participants included both acceptors and decliners. |
No or very minor concerns | High confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding adequacy, minor concerns regarding coherence, relevance and methodological limitations | |
| Finding 10: HCPs in particular may influence decision making as potential participants place huge trust in them. This results in great potential for HCP influence being a key impact on decision making | Chang 2004, Canvin 2006, Harrop 2016a, Costenbader 2007, Madsen 2007b, Jackson 2010, Moynihan 2012, Smyth 2011, Habersack 2013, Gopinath 2013, Bleidorn 2015, Oud‐Rengerink 2015, Abhyankar 2016, Hughes‐Morley 2016, Bidad 2016, Ballantyne 2017, Dellson 2018 |
Minor concerns based on the assessment of twelve studies with no, three studies with minor and two studies with moderate methodological limitations |
No or very minor concerns |
Minor concerns regarding relevance as studies had moderate geographical spread Included a range of medical/surgical, oncology, mental health, and pregnancy and childbirth trials. Participants included both acceptors and decliners. |
No or very minor concerns | High confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding adequacy and coherence, minor concerns regarding relevance and methodological limitations | |
| Finding 11: Internet searching and exposure to media sources with information on trial interventions may act as either a barrier or a facilitator for trial participation | Madsen 2007a, Gopinath 2013, Habersack 2013, Bleidorn 2015, Harrop 2016a, Ballantyne 2017, de Lacey 2017, |
Minor concerns based on the assessment of five studies with no, and two studies with minor methodological limitations |
Moderate concerns |
Moderate concerns regarding relevance as studies had limited geographical spread Included a range of medical/surgical, oncology, and pregnancy and childbirth trials. Participants included both acceptors and decliners. |
Moderate concerns | Low Confidence | Minor concerns regarding and methodological limitations, moderate concerns regarding coherence, adequacy and relevance | |
Weighing up the risks and benefits
| Summary of review finding | Studies contributing to the review finding | Methodological limitations | Coherence | Relevance | Adequacy | CERQual assessment of confidence in the evidence | Explanation of CERQual assessment | |
| Finding 12: Potential participants may view trial participation as feeling like a guinea pig (i.e. being used for the experiment), which they considered as too risky |
Chang 2004, Canvin 2006, Costenbader 2007, Madsen 2007a, Madsen 2007bTaylor 2007, Tarimo 2010, Moynihan 2012, Habersack 2013, Gopinath 2013, Bleidorn 2015, Oud‐Rengerink 2015, Dellson 2018 |
Minor concerns based on the assessment of seven studies with no, three studies with minor and two studies with moderate methodological limitations |
No or very minor concerns |
Minor concerns regarding relevance as studies had moderate geographical spread Included a range of medical/surgical, oncology, pregnancy and childbirth and health promotion trials. Participants included both acceptors and decliners. |
Moderate concerns | Moderate confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding relevance and methodological limitations, and moderate concerns regarding adequacy | |
| Finding 13: The risk of participation may concern potential participants who view their health as good or they are healthy and worried that the trial would identify a health problem. Potential participants may deem themselves ineligible and decline if they have too many health problems | Canvin 2006, Costenbader 2007, Madsen 2007a, Madsen 2007b, Tarimo 2010, Barnes 2012, Sanders 2012, Habersack 2013, Bleidorn 2015, Oud‐Rengerink 2015, Attwood 2016, Harrop 2016a, Normansell 2016 |
Minor concerns based on the assessment of eight studies with no, three studies with minor and one study with moderate methodological limitations |
Minor concerns |
Minor concerns regarding relevance as studies had moderate geographical spread Included a range of medical/surgical, oncology, mental health, pregnancy and childbirth, and health promotion trials. Participants included both acceptors and decliners. |
No or very minor concerns | High confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding adequacy, minor concerns regarding coherence, relevance and methodological limitations | |
| Finding 14: If potential participants sense a trial was safe, low risk, and wouldn’t impact on existing treatments they may feel they have nothing to lose if they participate | Canvin 2006, Madsen 2007a, Jackson 2010, Bleidorn 2015, Oud‐Rengerink 2015, Bidad 2016, Blodt 2016, Ballantyne 2017, de Lacey 2017, Sawyer 2017 |
Minor concerns based on the assessment of nine studies with no, one study with minor and one study with moderate methodological limitations |
No or very minor concerns |
Moderate concerns regarding relevance as studies had limited geographical spread Included a range of medical/surgical, oncology, and pregnancy and childbirth trials. Participants included both acceptors and decliners. |
Minor concerns | Moderate confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding adequacy and methodological limitations and moderate concerns regarding relevance. | |
| Finding 15: If potential participants consider themselves desperate, they may feel they have nothing to lose if they participate | Madsen 2007b, Smyth 2011, Habersack 2013, Abhyankar 2016, Blodt 2016, de Lacey 2017, Dellson 2018 |
Minor concerns based on the assessment of five studies with no and two studies with minor methodological limitations |
No or very minor concerns |
Moderate concerns regarding relevance as studies had limited geographical spread Included a range of medical/surgical, oncology, and pregnancy and childbirth trials. Participants included both acceptors and decliners |
Minor concerns | Moderate confidence | No or very minor concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding adequacy and methodological limitations and moderate concerns regarding relevance. | |
The Impact of Potential Outcomes on Decision to Participate
Personal benefits of trial participation
| Summary of review finding | Studies contributing to the review finding | Methodological limitations | Coherence | Relevance | Adequacy | CERQual assessment of confidence in the evidence | Explanation of CERQual assessment | |
| Finding 16: Potential participants recognise the benefit of access to new or existing treatments through trial participation | Attwood 2016: Barnes 2012; Blodt 2016; Bidad 2016: Canvin 2006: de Lacey 2017: Dellson 2018; Gopinath 2013; Habersack 2013; Jackson 2010; Madsen 2007a; Madsen 2007b; McCann 2010; Oud‐Rengerink 2015; Smyth 2011; Wasan 2009 | Minor concerns based on the assessment of eleven studies with no, three studies with minor and one study with moderate methodological limitations |
No or very minor concerns |
Minor concerns regarding relevance as studies had moderate geographical spread however almost half from England. Included a range of health promotion, medical/surgical, oncology, pregnancy & childbirth trials Participants included both acceptors and decliners |
Minor concerns regarding adequacy due to 16 studies contributing with reasonably thick data | High confidence | Due to no concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding relevance, adequacy and minor concerns regarding methodological limitations | |
| Finding 17: Potential participants recognise that being in a trial may mean quicker access to services, better follow‐up care, increased contact time with physicians and a chance to learn more about their condition, as potential benefits to trial participation | Attwood 2016: Bidad 2016; Chang 2004; Costenbader 2007; Dellson 2018; Habersack 2013; Jackson 2010; McCann 2010; Oud‐Rengerink 2015; Sawyer 2017; Tarimo 2010; Wasan 2009 | Minor concerns based on the assessment of ten studies with no, one study with minor and one study with moderate methodological limitations |
No or very minor concerns |
Minor concerns regarding relevance as studies had moderate geographical spread. Included a range of health promotion, medical/surgical, oncology, pregnancy & childbirth trials Participants included both acceptors and decliners |
Minor concerns regarding adequacy due to 12 studies contributing with reasonably thick data | High confidence | Due to no concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding relevance, adequacy and minor concerns regarding methodological limitations | |
| Finding 18: Potential participants may be managing symptoms for some time with feelings of desperation and trial participation brings hope of relief | Bleidorn 2015; Blodt 2016; de Lacey 2017; Dellson 2018; Madsen 2007b; McCann 2010; Wasan 2009 |
Minor concerns based on the assessment of six studies with no and one study with minor methodological limitations |
No or very minor concerns |
Minor concerns regarding relevance as studies had moderate geographical spread. Included a range of health promotion, medical/surgical, oncology, pregnancy & childbirth trials Participants included both acceptors and decliners |
Moderate concerns regarding adequacy due to only 7 studies contributing with reasonably thick data | Moderate confidence | Due to no or very minor concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding adequacy and methodological limitations and moderate concerns regarding relevance. | |
Making a difference: benefits for others
| Summary of review finding | Studies contributing to the review finding | Methodological limitations | Coherence | Relevance | Adequacy | CERQual assessment of confidence in the evidence | Explanation of CERQual assessment | |
| Finding 19: Altruism can be an important factor influencing potential participants’ decision to participate in a trial | Ballantyne 2017; Bidad 2016; Bleidorn 2015 ; Canvin 2006 ; Chang 2004; Costenbader 2007; de Lacey 2017; Dellson 2018; Habersack 2013; Harrop 2016a; Hughes‐Morley 2016; Madsen 2007a; McCann 2010; Moynihan 2012; Oud‐Rengerink 2015; Smyth 2011; Wasan 2009 |
Minor concerns based on the assessment of 12 studies with no, three studies with minor and two studies with moderate methodological limitations |
No or very minor concerns |
Minor concerns regarding relevance as studies had moderate geographical spread. Included a range of health promotion, medical/surgical, oncology, pregnancy & childbirth trials Participants included both acceptors and decliners |
Minor concerns regarding adequacy due to 17 studies contributing with reasonably thick data | High confidence | Due to no concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding relevance, adequacy and minor/moderate concerns regarding methodological limitations | |
| Finding 20: Altruism can be conditional whereby potential participants’ desire to help others is dependent on the trial being low risk and with clear benefits | Abhyankar 2016; Attwood 2016; Bidad 2016; Canvin 2006; Chang 2004; Jackson 2010; McCann 2010; Oud‐Rengerink 2015 |
Moderate concerns based on the assessment of 6 studies with no, and two studies with moderate methodological limitations |
No or very minor concerns | Minor concerns regarding relevance as studies had moderate geographical spread. Included a range of health promotion, medical/surgical, oncology, pregnancy & childbirth trials Participants included both acceptors and decliners |
Moderate concerns regarding adequacy due to only 8 studies contributing with reasonably thick data | Moderate confidence | Due to no concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding adequacy and Minor/moderate concerns regarding methodological limitations and moderate concerns regarding relevance | |
| Finding 21: Potential participants may feel an obligation or a moral duty to participate in a trial as a way of “giving back” | Ballantyne 2017; Bidad 2016; Bleidorn 2015; Canvin 2006; Chin 2016; Madsen 2007a; Tarimo 2010 |
Minor concerns based on the assessment of 12 studies with no, three studies with minor and two studies with moderate methodological limitations |
No or very minor concerns |
Minor concerns regarding relevance as studies had moderate geographical spread. Included a range of health promotion, medical/surgical, oncology, pregnancy & childbirth trials Participants included both acceptors and decliners |
Moderate concerns regarding adequacy due to only 7 studies contributing with reasonably thick data | Moderate confidence | Due to no concerns regarding coherence, minor concerns regarding relevance, moderate concerns regarding adequacy and Minor/moderate concerns regarding methodological limitations. | |
| Finding 22: Potential participants may have a genuine interest in contributing to scientific knowledge and improved care | Ballantyne 2017; Bidad 2016; Bleidorn 2015; Blodt 2016; Canvin 2006; Chang 2004; Chin 2016; de Lacey 2017; Dellson 2018; Habersack 2013; Harrop 2016a; Hughes‐Morley 2016; Madsen 2007a; Moynihan 2012; Normansell 2016.; Oud‐Rengerink 2015; Sawyer 2017; Smyth 2011; Wasan 2009 |
Minor concerns based on the assessment of 13 studies with no, four studies with minor and two studies with moderate methodological limitations |
No or very minor concerns |
No or very minor concerns regarding relevance as studies had good geographical spread. Included a range of health promotion, medical/surgical, oncology, pregnancy & childbirth trials Participants included both acceptors and decliners |
No or very minor concerns regarding adequacy due to 19 studies contributing with reasonably thick data | High confidence | Due to no or very minor concerns regarding coherence, relevance and adequacy and minor concerns regarding methodological limitations | |
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [author‐defined order]
Abhyankar 2016.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Oncology | |
| Country of Origin | England | |
| Participants or Decliners | Participants | |
| Notes | ||
Attwood 2016.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Health Promotion | |
| Country of Origin | England | |
| Participants or Decliners | Decliners | |
| Notes | ||
Ballantyne 2017.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Pregnancy and Childbirth | |
| Country of Origin | New Zealand | |
| Participants or Decliners | Participants | |
| Notes | ||
Barnes 2012.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Mental Health | |
| Country of Origin | England and Scotland | |
| Participants or Decliners | Decliners | |
| Notes | ||
Bidad 2016.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Oncology | |
| Country of Origin | England | |
| Participants or Decliners | Participants and Decliners | |
| Notes | ||
Bleidorn 2015.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Medical Surgical | |
| Country of Origin | Germany | |
| Participants or Decliners | Participants and Decliners | |
| Notes | ||
Blodt 2016.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Medical Surgical | |
| Country of Origin | Germany | |
| Participants or Decliners | Participants | |
| Notes | ||
Canvin 2006.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Medical Surgical | |
| Country of Origin | England | |
| Participants or Decliners | Participants and Decliners | |
| Notes | ||
Chang 2004.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Medical Surgical | |
| Country of Origin | USA | |
| Participants or Decliners | Participants | |
| Notes | ||
Chin 2016.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Health Promotion | |
| Country of Origin | USA | |
| Participants or Decliners | Participants | |
| Notes | ||
Costenbader 2007.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Medical Surgical | |
| Country of Origin | USA | |
| Participants or Decliners | Participants and Decliners | |
| Notes | ||
de Lacey 2017.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Pregnancy and Childbirth | |
| Country of Origin | Australia and New Zealand | |
| Participants or Decliners | Participants | |
| Notes | ||
Dellson 2018.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Oncology | |
| Country of Origin | Sweden | |
| Participants or Decliners | Participants | |
| Notes | ||
Gopinath 2013.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Medical Surgical | |
| Country of Origin | England | |
| Participants or Decliners | Decliners | |
| Notes | ||
Habersack 2013.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Oncology | |
| Country of Origin | Austria | |
| Participants or Decliners | Participants and Decliners | |
| Notes | ||
Harrop 2016a.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Oncology | |
| Country of Origin | Wales | |
| Participants or Decliners | Decliners (plus research nurses n = 2) | |
| Notes | ||
Hughes‐Morley 2016.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Mental Health | |
| Country of Origin | England | |
| Participants or Decliners | Decliners | |
| Notes | ||
Jackson 2010.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Medical Surgical | |
| Country of Origin | England | |
| Participants or Decliners | Participants | |
| Notes | ||
Madsen 2007a.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Oncology | |
| Country of Origin | Denmark | |
| Participants or Decliners | Participants and Decliners | |
| Notes | ||
Madsen 2007b.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Oncology | |
| Country of Origin | Denmark | |
| Participants or Decliners | Particpants and Decliners | |
| Notes | ||
McCann 2010.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Medical Surgical | |
| Country of Origin | Scotland | |
| Participants or Decliners | Participants and Decliners | |
| Notes | ||
Moynihan 2012.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Oncology | |
| Country of Origin | England | |
| Participants or Decliners | Participants and Decliners | |
| Notes | ||
Normansell 2016.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Health Promotion | |
| Country of Origin | England | |
| Participants or Decliners | Decliners | |
| Notes | ||
Oud‐Rengerink 2015.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Pregnancy and Childbirth | |
| Country of Origin | The Netherlands | |
| Participants or Decliners | Participants and Decliners | |
| Notes | ||
Sanders 2012.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Medical Surgical | |
| Country of Origin | England | |
| Participants or Decliners | Participants and Decliners | |
| Notes | ||
Sawyer 2017.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Pregnancy and Childbirth | |
| Country of Origin | England | |
| Participants or Decliners | Participants | |
| Notes | ||
Smyth 2011.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Pregnancy and Childbirth | |
| Country of Origin | England | |
| Participants or Decliners | Participants | |
| Notes | ||
Tarimo 2010.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Medical Surgical | |
| Country of Origin | Tanzania | |
| Participants or Decliners | Participants | |
| Notes | ||
Taylor 2007.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Medical Surgical | |
| Country of Origin | England | |
| Participants or Decliners | Decliners | |
| Notes | ||
Wasan 2009.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Discipline | Medical Surgical | |
| Country of Origin | Canada | |
| Participants or Decliners | Participants | |
| Notes | ||
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Audrey 2011 | Limited completeness and relevance |
| Barnett 2012 | Limited completeness and relevance |
| Bill‐Axelson 2008 | Limited relevance |
| Breitkopf 2011 | Limited relevance |
| Burke 2014 | Limited accuracy |
| Close 2016 | Limited completeness and relevance |
| Corsino 2013 | Limited relevance |
| Cox 2000 | Timeliness |
| Cox 2002 | Timeliness |
| das Nair 2014 | Limited relevance |
| Dellson 2011 | Limited relevance |
| Donovan 2002 | Limited Completeness and accuracy |
| Eborall 2011 | Partial relevance |
| Eng 2005 | Timeliness |
| Featherstone 2002 | Timeliness |
| Ford 2013 | Limited accuracy and relevance |
| Friedman 2015 | Limited accuracy and relevance |
| Fu 2014 | Limited accuracy and relevance |
| Haring 2016 | Limited accuracy |
| Harrop 2016b | Limited relevance |
| Hennink‐Kaminiski 2014 | Limited accuracy |
| Hepworth 2002 | Limited accuracy and relevance |
| Horwood 2016 | Limited accuracy and relevance |
| Hughes 2013 | Limited relevance |
| Hui 2016 | Limited relevance |
| Hussain‐Gambles 2004 | Limited relevance |
| Jones 2009 | Limited relevance |
| Joseph 2009 | Limited relevance |
| Kenealy 2015 | Limited relevance |
| Kenyon 2006 | Timeliness |
| Khalil 2007 | Limited accuracy and relevance |
| Kozica 2015 | Limited relevance |
| Lawton 2003 | Timeliness and limited relevance |
| Lawton 2016 | Limited relevance |
| Leach 2016 | Limited relevance |
| Lee 2016 | Limited relevance |
| Leighton 2012 | Limited relevance |
| Lie 2012 | Limited relevance |
| Linden 2007 | Limited relevance |
| Littlewood 2013 | Limited relevance |
| Locock 2011 | Limited relevance |
| Lowton 2005 | Limited relevance |
| Maher 2010 | Limited relevance |
| Medeossi 2014 | Limited relevance |
| Middlemiss 2015 | Limited relevance |
| Mills 2003 | Limited accuracy and relevance |
| Mills 2011 | Limited relevance |
| Nappo 2013 | Limited relevance |
| Newman 2006 | Limited relevance |
| Nguyen‐Xuan 2016 | Limited accuracy and completeness |
| Notley 2015 | Limited accuracy and completeness |
| Nyamathi 2004 | Limited accuracy and completeness |
| Reed 2013 | Limited completeness |
| Reynolds 2013 | Limited relevance |
| Ritchie 2015 | Limited relevance |
| Rivera‐Goba 2011 | Limited relevance |
| Rogers 2014 | Limited relevance |
| Rooney 2011 | Limited accuracy and relevance |
| Schapira 2014 | Limited accuracy and relevance |
| Scott 2011 | Limited relevance |
| Sheikh 2009 | Limited relevance |
| Sims‐Gould 2012 | Limited relevance |
| Snowdon 2012 | Limited relevance |
| Stevens 2004 | Limited accuracy |
| Thornton 2016 | Limited accuracy and relevance |
| Todkill 2013 | Limited relevance |
| Townsend 2013 | Limited relevance |
| Ulrich 2012 | Limited relevance |
| Unson 2001 | Timeliness |
| Whybrow 2017 | Limited relevance |
| Woods 2002 | Limited completeness |
Characteristics of studies awaiting classification [ordered by study ID]
Asiedu 2018.
| Notes | This article was identified in our 2019 search and will be assessed in the update of this review. |
Cooper 2017.
| Notes | This article was identified in our 2019 search and will be assessed in the update of this review. |
Craig 2018.
| Notes | This article was identified in our 2019 search and will be assessed in the update of this review. |
Denny 2018.
| Notes | This article was identified in our 2019 search and will be assessed in the update of this review. |
Duncan 2018.
| Notes | This article was identified in our 2019 search and will be assessed in the update of this review. |
Escarnot 2020.
| Notes | This article was identified in our 2019 search and will be assessed in the update of this review. |
Manton 2019.
| Notes | This article was identified in our 2019 search and will be assessed in the update of this review. |
Monteiro 2019.
| Notes | This article was identified in our 2019 search and will be assessed in the update of this review. |
Nadimpally 2017.
| Notes | This article was identified in our 2019 search and will be assessed in the update of this review. |
Norris 2019.
| Notes | This article was identified in our 2019 search and will be assessed in the update of this review. |
Perry 2016.
| Notes | This article was identified in our 2019 search and will be assessed in the update of this review. |
Phelps 2019.
| Notes | This article was identified in our 2019 search and will be assessed in the update of this review. |
Prout 2018.
| Notes | This article was identified in our 2019 search and will be assessed in the update of this review. |
Ridgeway 2017.
| Notes | This article was identified in our 2019 search and will be assessed in the update of this review. |
Thong 2019.
| Notes | This article was identified in our 2019 search and will be assessed in the update of this review. |
Tompkins 2019.
| Notes | This article was identified in our 2019 search and will be assessed in the update of this review. |
van den Berg 2017.
| Notes | This article was identified in our 2019 search and will be assessed in the update of this review. |
Zhao 2018.
| Notes | This article was identified in our 2019 search and will be assessed in the update of this review. |
Differences between protocol and review
Review Question
In our protocol, we stated that we would look at recruitment from the perspectives of recruiters and potential participants. When we conducted our search, we realised that this was too broad and refined our review to the perspectives of potential participants (acceptors and decliners) invited in to clinical trials that did not involve children or people with impaired consent.
Search Strategy
In our protocol, we stated that we would use Scopus, Web of Science and Google Scholar to perform citation searching. In this review, we did not perform citation or reference searching.
In our protocol, we stated our intention to design a search strategy which could include non‐English language results and use translation services if any such studies were found. At a later stage, we made the decision to exclude records published in a language other than English.
Assessment of methodological limitations
In our protocol, we stated that we would use an adapted version of Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP). On discussion within the team, the modified tool focused too much on the quality of reporting and so we reverted to the original version of CASP.
Integrating the qualitative findings with the linked Cochrane intervention review
In our protocol, we stated that would integrate with the previous version of the Cochrane Review by Treweek (Treweek 2010) examining randomised trials of interventions to improve recruitment to trials. We integrated with the updated version of this review (Treweek 2018) and a review by Gardner 2020 focusing on non‐randomised interventions to improve recruitment to trials.
Contributions of authors
CH, MD, PM, AH and LB designed the protocol with input from all authors. AC co‐designed (with members of the author team) and performed the original electronic searches in 2016 and the update searches in 2019. CH, MD, PM, AH and LB conducted study selection and data extraction, with input from JN, JT, KS, ST, DD, HG. CH, PM and LB conducted the CASP assessment. CH, MD, PM and AH conducted the GRADE CERQual assessment. CH, MD, PM, AH and LB assessed and synthesised the studies. AH designed the model. CH drafted the manuscript. All authors were involved in the data interpretation. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Declarations of interest
JN: Convenor of the QIMG and Co‐Chair of the Methods Executive
DD: Editor with the Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group
New
References
References to studies included in this review
Abhyankar 2016 {published data only}
- Abhyanker P, Velikova G, Summers B, Bekker HL. Identifying components in consent information needed to support informed decision making about trial participation: an interview study with women managing cancer. Social Science and Medicine 2016;161:83-91. [DOI: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2016.05.040] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Attwood 2016 {published data only}
- Attwood S, Morton KL, Mitchell J, Van Emmenis M, Sutton S. Reasons for non-participation in a primary care-based physical activity trial: a qualitative study. BMJ Open 2016;6:e011577. [DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-011577] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ballantyne 2017 {published data only}
- Ballantyne A, Pullon S, MacDonald L, Barthow C, Wickens K, Crane J. The experiences of pregnant women in an interventional clinical trial: Research In Pregnancy Ethics (RIPE) study. Bioethics 2017;31(6):476-83. [DOI: 10.1111/bioe.12361] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Barnes 2012 {published data only}
- Barnes M, Wiles N, Morrison J, Kessler D, Williams C, Kuyken W, et al. Exploring patients’ reasons for declining contact in a cognitive behavioural therapy randomised controlled trial in primary care. British Journal of General Practice 2012;62(598):e371-7. [DOI: 10.3399/bjgp12X641492] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bidad 2016 {published data only}
- Bidad N, MacDonald L, Winters ZE, Edwards SJL, Emson M, Grffin CL, . How informed is declared altruism in clinical trials? A qualitative interview study of patient decision-making about the QUEST trials (Quality of Life after Mastectomy and Breast Reconstruction). Trials 2016;17:431. [DOI: 10.1186/s13063-016-1550-7] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bleidorn 2015 {published data only}
- Bleidorn J, Bucak S, Gagyor I, Hummers-Pradier E, Dierks M-L. Why do – or don’t – patients with urinary tract infection participate in a clinical trial? A qualitative study in German family medicine. GMS German Medical Science 2015;13:17. [DOI: 10.3205/000221] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Blodt 2016 {published data only}
- Blödt S, Witt CM, Holmberg C. Women’s reasons for participation in a clinical trial for menstrual pain: a qualitative study. BMJ Open 2016;6:e012592. [DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-012592] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Canvin 2006 {published data only}
- Canvin K, Jacoby A. Duty, desire or indifference? A qualitative study of patient decisions about recruitment to an epilepsy treatment trial. Trials 2006;7:32. [DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-7-32] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Chang 2004 {published data only}
- Chang B-H, Hendricks AM, Slawsky MT, Locastro JS. Patient recruitment to a randomized clinical trial of behavioral therapy for chronic heart failure. BMC medical Research Methodology 2004;4:8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Chin 2016 {published data only}
- Chin LJ, Berenson JA, Klitzman RL. Typologies of altruistic and financial motivations for research participation: A qualitative study of MSM in HIV vaccine trials. Journal of Empirical Research on Human Research Ethics 2016;11(4):299-310. [DOI: 10.1177/1556264616679537] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Costenbader 2007 {published data only}
- Costenbader KH, Brome, D, Blanch D, Gall, V, Karlson E, Liang MH. Factors determining participation in prevention trials among systemic lupus erythematosus patients: a qualitative study. Arthritis & Rheumatism (Arthritis Care & Research) 2007;57(1):49-55. [DOI: 10.1002/art.22480] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
de Lacey 2017 {published data only}
- Lacey SL, Sanderman E, Smith CA. Acupuncture in reproductive medicine: the motivations of infertile women to participate in a randomised controlled trial. Journal of Psychosomatic Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2017;39(2):112-20. [DOI: 10.1080/0167482X.2017.1308349] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dellson 2018 {published data only}
- Dellson P, Nilsson K, Jernström H, Carlsson C. Patients’ reasoning regarding the decision to participate in clinical cancer trials: an interview study. Trials 2018;19:528. [DOI: 10.1186/s13063-018-2916-9] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gopinath 2013 {published data only}
- Gopinath D, Smith AR, Holland C, Reid FM. Why don’t women participate? A qualitative study on non-participation in a surgical randomised controlled trial. International Urogynecology Journal 2013;24:969-75. [DOI: 10.1007/s00192-012-1967-9] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Habersack 2013 {published data only}
- Habersack M, Luschin G. Insecurities of women regarding breast cancer research: a qualitative study. PLOS One 2013;8(12):e81770. [DOI: 10.1371/ journal.pone.0081770] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Harrop 2016a {published data only}
- Harrop E, Kelly J, Griffiths G, Casbard A, Nelson A. Why do patients decline surgical trials? Findings from a qualitative interview study embedded in the Cancer Research UK BOLERO trial (Bladder cancer: Open versus Lapararoscopic or RObotic cystectomy). Trials 2016;17:35. [DOI: 10.1186/s13063-016-1173-z] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hughes‐Morley 2016 {published data only}
- Hughes-Morley A, Young B, Hempel RJ, Russell IT, Waheed W, Bower P. What can we learn from trial decliners about improving recruitment? Qualitative study. Trials 2016;17:494. [DOI: 10.1186/s13063-016-1626-4] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jackson 2010 {published data only}
- Jackson CJ, Dixon-Woods M, Eborall H, Kenyon S, Toozs-Hobson P, Tincello DG. Women’s views and experiences of a patient preference trial in surgery: a qualitative study of the CARPET1 trial. Clinical Trials 2010;7:696-704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Madsen 2007a {published data only}
- Madsen SM, Holm S, Riis P. Attitudes towards clinical research among cancer trial participants and non-participants: an interview study using a grounded theory approach. Journal of Medical Ethics 2007;33:234-40. [DOI: 10.1136/jme.2005.015255] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Madsen 2007b {published data only}
- Madsen SM, Holm S, Riis P. Participating in a cancer clinical trial? The balancing of options in the loneliness of autonomy: a grounded theory interview study. Acta Oncologica 2007;46:49-59. [DOI: 10.1080/02841860600911164] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
McCann 2010 {published data only}
- McCann SK, Campbell MK, Entwistle VA. Reasons for participating in randomised controlled trials: conditional altruism and considerations for self. Trials 2010;11:31. [DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-11-31] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Moynihan 2012 {published data only}
- Moynihan C, Lewis R, Hall E, Jones E, Birtle A, Huddart R. The Patient Deficit Model Overturned: a qualitative study of patients' perceptions of invitation to participate in a randomized controlled trial comparing selective bladder preservation against surgery in muscle invasive bladder cancer (SPARE, CRUK/07/011). Trials 2012;13:228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Normansell 2016 {published data only}
- Normansell R, Holmes R, Victor C, Cook DG, Kerry S, Iliffe S, et al. Exploring non-participation in primary care physical activity interventions: PACE-UP trial interview findings. Trials 2016;17:178. [DOI: 10.1186/s13063-016-1299-z] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Oud‐Rengerink 2015 {published data only}
- Oude Rengerink K, Logtenberg S, Hooft L, Bossuyt PM, Mol BW. Pregnant womens’ concerns when invited to a randomized trial: a qualitative case control study. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth 2015;15:207. [DOI: 10.1186/s12884-015-0641-x] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sanders 2012 {published data only}
- Sanders C, Rogers A, Bowen R, Bower P, Hirani S, Cartwright M, et al. Exploring barriers to participation and adoption of telehealth and telecare within the Whole System Demonstrator trial: a qualitative study. BMC Health Services Research 2012;12:220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sawyer 2017 {published data only}
- Sawyer A, Chhoa C, Ayers S, Pushpa-Rakah A, Duley L. Women’s views and experiences of two alternative consent pathways for participation in a preterm intrapartum trial: a qualitative study. Trials 2017;18:422. [DOI: 10.1186/s13063-017-2149-3] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Smyth 2011 {published data only}
- Smyth RM, Jacoby A, Elbourne D. Deciding to join a perinatal randomised controlled trial: Experiences and views of pregnant women enroled in the Magpie Trial. Midwifery 2012;28:e538-45. [DOI: 10.1016/j.midw.2011.08.006] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Tarimo 2010 {published data only}
- Tarimo EA, Thorson A, Kohi TW, Mwami J, Bakari M, Sandström E, et al. Balancing collective responsibility, individual opportunities and risks: a qualitative study on how police officers reason around volunteering in an HIV vaccine trial in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. BMC Public Health 2010;10:292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Taylor 2007 {published data only}
- Taylor R, Dawson S, Roberts N, Sridhar M, Partridge MR. Why do patients decline to take part in a research project involving pulmonary rehabilitation? Respiratory Medicine 2007;101:1942-6. [DOI: 10.1016/j.rmed.2007.04.012] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wasan 2009 {published data only}
- Wasan AD, Taubenberger SP, Robinson WM. Reasons for participation in pain research: can they indicate a lack of informed consent? Pain Medicine 2009;10(1):111-9. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1526-4637.2008.00481.x] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to studies excluded from this review
Audrey 2011 {published data only}
- Audrey S. Qualitative research in evidence-based medicine: Improving decision-making and participation in randomized controlled trials of cancer treatments. Palliative Medicine 2011;25(8):758-65. [DOI: 10.1177/0269216311419548] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Barnett 2012 {published data only}
- Barnett J, Aguilar S, Brittner M, Bonuck K. Recruiting and retaining low-income, multi-ethnic women into randomized controlled trials: Successful strategies and staffing. Contemporary Clinical Trials 2012;33:925-32. [DOI: 10.1016/j.cct.2012.06.005] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bill‐Axelson 2008 {published data only}
- Bill-Axelson A, Christensson A, Carlsson M, Johan Norlén B, Holmberg L. Experiences of randomization: Interviews with patients and clinicians in the SPCG-IV trial. Scandinavian Journal of Urology and Nephrology 2008;42(4):358-63. [DOI: 10.1080/00365590801950253] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Breitkopf 2011 {published data only}
- Brietkopf CR, Loza M, Vincent K, Moench T, Stanberry LR, Rosenthal SL. Perceptions of reimbursement for clinical trial participation. Journal of Empirical Research in Human Research Ethics 2011;6(3):31-8. [DOI: 10.1525/jer.2011.6.3.31] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Burke 2014 {published data only}
- Burke NJ. Rethinking the therapeutic misconception: social justice, patient advocacy, and cancer clinical trial recruitment in the US safety net. BMC Medical Ethics 2014;15:68. [DOI: 10.1186/1472-6939-15-68] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Close 2016 {published data only}
- Close C, Sinclair M, McCullough JE, Liddle SD, Hughes CM. Factors affecting recruitment and attrition in randomised controlled trials of complementary and alternative medicine for pregnancy-related issues. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2016;Epub:6495410. [DOI: 10.1155/2016/6495410] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Corsino 2013 {published data only}
- Corsino L, Lin P-H, Batch BC, Intille S, Grambow SC, Bosworth HB, et al. Recruiting young adults into a weight loss trial: Report of protocol development and recruitment results. Contemporary Clinical Trials 2013;35(2):1-7. [DOI: 10.1016/j.cct.2013.04.002] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cox 2000 {published data only}
- Cox K. Enhancing cancer clinical trial management: recommendations from a qualitative study of trial participants’ experiences. Psycho-Oncology 2000;9:314-22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cox 2002 {published data only}
- Cox K. Informed consent and decision-making: patients' experiences of the process of recruitment to phases I and II anti-cancer drug trials. Patient Education and Counselling 2002;46:31-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
das Nair 2014 {published data only}
- das Nair R, Skellington Orr K, Vedhara K, Kendrick D. Exploring recruitment barriers and facilitators in early cancer detection trials: the use of pre-trial focus groups. Trials 2014;15:98. [DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-15-98] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dellson 2011 {published data only}
- Dellson P, Nilbert M, Bendhal P-O, Malstrom P, Carlsson C. Towards optimised information about clinical trials; identification and validation of key issues in collaboration with cancer patient advocates. European Journal of Cancer Care 2011;20:445–54. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2354.2010.01207.x] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Donovan 2002 {published data only}
- Donovan J, Mills N, Smith M, Brindle L, Jacoby A, Peters T, et al. Improving design and conduct of randomised trials by embedding them in qualitative research: ProtecT (prostate testing for cancer and treatment) study. BMJ 2002;325:766-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Eborall 2011 {published data only}
- Eborall HC, Stewart MC, Cunningham-Burley S, Price JF, Fowkes FG. Accrual and drop out in a primary prevention randomised controlled trial: qualitative study. Trials 2011;12:7. [DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-12-7] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Eng 2005 {published data only}
- Eng M, Taylor L, Verhoef M, Ernst S, Donnelly B. Understanding participation in a trial comparing cryotherapy and radiation treatment. Canadian Journal of Urology 2005;12(2):2607-13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Featherstone 2002 {published data only}
- Featherstone K, Donovan JL. ‘‘Why don’t they just tell me straight, why allocate it?’’ The struggle to make sense of participating in a randomised controlled trial. Social Science and Medicine 2002;55:709-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ford 2013 {published data only}
- Ford ME, Siminoff LA, Pickelsimer E, Mainous AG, Smith DW, Diaz VA, et al. Unequal burden of disease, unequal participation in clinical trials: solutions from African American and Latino community members. Health and Social Work 2013;38(1):29-38. [DOI: 10.1093/hsw/hlt001] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Friedman 2015 {published data only}
- Friedman DB, Foster C, Bergeron CD, Tanner A, Kim S-H. A qualitative study of recruitment barriers, motivators, and community-based strategies for increasing clinical trials participation among rural and urban populations. American Journal of Health Promotion 2015;29(5):332-8. [DOI: 10.4278/ajhp.130514-QUAL-247] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Fu 2014 {published data only}
- Fu SS, Rhodes KL, Robery C, Widome R, Forster JL, Joseph AM. Designing and evaluating culturally specific smoking cessation interventions for American Iindian communities. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2014;16(1):42-9. [DOI: 10.1093/ntr/ntt111] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Haring 2016 {published data only}
- Haring RC, Henry WA, Hudson M, Rodreguez EM, Taualii M. Views on clinical trial recruitment, biospecimen collection, and cancer research: population science from landscapes of the Haudenosaunee (People of the Longhouse). Journal of Cancer Education 2016;33(1):44-51. [DOI: 10.1007/s13187-016-1067-5] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Harrop 2016b {published data only}
- Harrop E, Noble S, Edwards M, Sivel S, Moore B, Nelson A, and on behalf of the FRAGMATIC Trial Management Group (TMG). “I didn’t really understand it, I just thought it’d help”: exploring the motivations, understandings and experiences of patients with advanced lung cancer participating in a non-placebo clinical IMP trial. Trials 2016;17:329. [DOI: 10.1186/s13063-016-1460-8] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hennink‐Kaminiski 2014 {published data only}
- Hennink-Kaminski HJ, Willoughby JF, McMahan D. Join the conquest: developing a campaign to increase participation in clinical research in North Carolina. Science Communication 2014;36(1):30-55. [DOI: 10.1177/1075547013492434 ] [Google Scholar]
Hepworth 2002 {published data only}
- Hepworth J, Paine B, Miles H, Marley J, MacLennan A. The willingness of women to participate in a long-term trial of hormone replacement therapy: a qualitative study using focus group. Psychology, Health & Medicine 2002;7(4):469-76. [DOI: 10.1080/1354850021000015285] [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Horwood 2016 {published data only}
- Horwood J, Johnson E, Goobrtmanhill R. Understanding involvement in surgical orthopaedic randomized controlled trials: a qualitative study of patient and health professional views and experiences. International Journal of Orthopaedic and Trauma Nursing 2016;20:3-12. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ijotn.2015.05.002] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hughes 2013 {published data only}
- Hughes JG, Russell W, Breckons M, Richardson J, Lloyd-Williams M, Molassiotis A. "Until the trial is complete you can't really say whether it helped you or not, can you?": exploring cancer patients' perceptions of taking part in a trial of acupressure wristbands. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2013;13:260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hui 2016 {published data only}
- Hui S-KA, Miller SM, Hazuda L, Engelman K, Ellerback EF. Novel method for recruiting representative at-risk individuals into cancer prevention trials: online health risk assessment in employee wellness programs. Journal of Cancer Education 2016;31:421-9. [DOI: 10.1007/s13187-015-0927-8] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hussain‐Gambles 2004 {published data only}
- Hussain-Gambles M, Leese B, Atkin K, Brown J, Mason S, Tovey P. Involving South Asian patients in clinical trials. Health Technology Assessment 2004;8(42):iii, 1-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jones 2009 {published data only}
- Jones RA, Steeves R, Williams I. Strategies for recruiting African American men Into prostate cancer screening studies. Nursing Research 2009;58(6):452-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Joseph 2009 {published data only}
- Joseph G, Dohan D. Recruiting minorities where they receive care: Insititutional barriers to cancer clinical trials recruitment in a safety-net hospital. Contemporary Clinical Trials 2009;30:552-9. [DOI: 10.1016/j.cct.2009.06.009] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kenealy 2015 {published data only}
- Kenealy TW, Hao'uli S, Arroll B. A qualitative study of recruiting for investigations in primary care: plan, pay, minimise intermediaries and keep it simple. SAGE Open Medicine 2015;3:2050312115596649. [DOI: 10.1177/2050312115596649] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kenyon 2006 {published data only}
- Kenyon S, Dixon-Woods M, Jackson CJ, Pitchforth E. Participating in a trial in a critical situation: a qualitative study in pregnancy. BMJ Quality and Safety 2006;15:98-101. [DOI: 10.1136/qshc.2005.015636] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Khalil 2007 {published data only}
- Khalil SS, Silverman HJ, Raafat M, El-Kamary S, El-Setouhy M. Attitutdes, understanding, and concerns regarding medical research amongst Egyptians: a qualitative pilot study. BMC Medical Ethics 2007;8:9. [DOI: 10.1186/1472-6939-8-9] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kozica 2015 {published data only}
- Kozica SL, Harrison CL, Teede HJ, Ng S, Moran LJ, Lombard CB. Engaging rural women in health lifestyle programs: insights from a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2015;16:413. [DOI: 10.1186/s13063-015-0860-5] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lawton 2003 {published data only}
- Lawton J, Fox A, Fox C, Kinmonth L. Participating in the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS): a qualitative study of patients’ experiences. British Journal of General Practice 2003;53:394-8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lawton 2016 {published data only}
- Lawton J, Snowdon C, Morrow S, Norman JE, Denison FC, Hallowell N. Recruiting and consenting into a peripartum trial in an emergency setting: a qualitative study of the experiences and views of women and healthcare professionals. Trials 2016;17:195. [DOI: 10.1186/s13063-016-1323-3] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Leach 2016 {published data only}
- Leach MJ, Ziaian T, Francis A, Agnew T. Recruiting dementia caregivers into clinical trials. Lessons learned from the Australian TRANSCENDENT Trial. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders 2016;30(4):338-44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lee 2016 {published data only}
- Lee GE, Ow M, Lie D, Dent R. Barriers and facilitators for clinical trial participation among diverse Asian patients with breast cancer: a qualitative study. BMC Women's Health 2016;16:43. [DOI: 10.1186/s12905-016-0319-1] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Leighton 2012 {published data only}
- Leighton P, Lonsdale AJ, Tildsley J, King AJ. The willingness of patients presenting with advanced glaucoma to participate in a trial comparing primary medical vs primary surgical treatment. Eye 2012;26:300-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lie 2012 {published data only}
- Lie M, May C, Kelly T, Robson S. ‘Let the computer choose?’: the experience of participants in a randomised preference trial of medical versus surgical termination of pregnancy. Sociology of Health & Illness 2012;34(5):746-60. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1467-9566.2011.01412.x] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Linden 2007 {published data only}
- Linden HM, Reisch LM, Hart A, Harrngton A, Nakano C, Jackson JC, et al. Attitudes toward participation in breast cancer randomized clinical trials in the African American community. a focus group study. Cancer Nursing 2007;30(4):261-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Littlewood 2013 {published data only}
- Littelwood C, Ashton J, Scott E, Mawson S, May S, Walters S. Developing the SELF study: a focus group with patients and the public. International Journal of Therapy and Rehabilitation 2013;20(4):200-6. [Google Scholar]
Locock 2011 {published data only}
- Locock L, Smith L. Personal experiences of taking part in clinical trials – a qualitative study. Patient Education and Counseling 2011;84:303-9. [DOI: 10.1016/j.pec.2011.06.002] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lowton 2005 {published data only}
- Lowton K. Trials and tribulations: Understanding motivations for clinical research participation amongst adults with cystic fibrosis. Social Science & Medicine 2005;61:1854–65. [DOI: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2005.03.039] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Maher 2010 {published data only}
- Maher L, White B, Donald A, Bates A, Enriques J, Pham S, et al. Using ethnographic fieldwork to inform hepatitis C vaccine preparedness studies with people who inject drugs. International Journal of Drug Policy 2010;21:194-201. [DOI: 10.1016/j.drugpo.2009.04.004] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Medeossi 2014 {published data only}
- Medeossi B-J, Stader J, Delany-Mretlwe S. ‘I heard about this study on the radio’: using community radio to strengthen Good Participatory Practice in HIV prevention trials. BMC Public Health 2014;14:876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Middlemiss 2015 {published data only}
- Middlemiss T, Lloyd-Williams M, Laird BJ, Fallon MT. Symptom control trials in patients with advanced cancer: a qualitativesStudy. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management 2015;50(5):642-9. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2015.05.009] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mills 2003 {published data only}
- Mills N, Donovan JL, Smith M, Jacoby A, Neal DE, Hamdy FC. Perceptions of equipoise are crucial to trial participation:a qualitative study of men in the ProtecT study. Controlled Clinical Trials 2003;24:272-82. [DOI: 10.1016/S0197-2456(03)00020-5] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mills 2011 {published data only}
- Mills N, Donovan JL, Wade J, Hamdy FC, Neal DE, Lane JA. Exploring treatment preferences facilitated recruitment to randomized controlled trials. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64:1127-36. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.12.017] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Nappo 2013 {published data only}
- Nappo SA Lafrate GB, Sanchez ZM. Motives for participating in a clinical research trial: a pilot study in Brazil. BMC Public Health 2013;13:19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Newman 2006 {published data only}
- Newman PA, Duan N, Roberts KJ, Seiden D, Rudy ET, Swendeman D, Popova S. HIV Vaccine trial participation among ethnic minority communities. Barriers, motivators, and implications for recruitment. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome 2006;41(2):210-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Nguyen‐Xuan 2016 {published data only}
- Nguyen-Xuan H-T, Thiollier G, Ruault O, Fauconnier A, Lucot J-P, Bader G. Study of factors motivating refusal of women to participate to a randomized clinical trial in gynecological surgery. Retrospective observational bicentric study [Étude des facteurs motivant le refus des femmes de participer à un essai clinique randomisé en chirurgie gynécologique. Étude observationnelle rétrospective bicentrique]. Journal de Gynecologie Obstetrique et Biologie de la Reproduction 2016;45(9):1054-9. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jgyn.2016.03.001] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Notley 2015 {published data only}
- Notley C, Christopher R, Hodgekins J, Byrne R, French P, Fowler D. Participant views on involvement in a trial of social recovery cognitive–behavioural therapy. British Journal of Psychiatry 2015;206:122-7. [DOI: 10.1192/bjp.bp.114.146472] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Nyamathi 2004 {published data only}
- Nyamathi A, Koniak-Griffin D, Tallen L, González-Figueroa E, Levson L, Mosley Y, et al. Use of community-based participatory research in preparing low income and homeless minority populations for future HIV vaccines. Journal of Interprofessional Care 2004;18(4):369-80. [DOI: 10.1080/13561820400011735] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Reed 2013 {published data only}
- Reed RL, Barton CA, Isherwood LM, Oliver Baxter JM, Roeger L. Recruitment for a clinical trial of chronic disease self-management for older adults with multimorbidity: a successful approach within general practice. BMC Family Practice 2013;14:125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Reynolds 2013 {published data only}
- Reynolds J, Mangesho P, Lemnge MM, Vestergaard LS, Chandler CIR. ‘. . . in the project they really care for us’: Meaning and experiences of participating in a clinical study of first-line treatment for malaria and HIV in Tanzanian adults. Global Public Health 2013;8(6):670-84. [DOI: 10.1080/17441692.2013.810297] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ritchie 2015 {published data only}
- Ritchie M, Kelly L, Moss J, Paul J, Shaw R (2015) Exploring attitudes towards a randomised controlled trial of venous access devices – a nested pre-trial qualitative study. Exploring attitudes towards a randomised controlled trial of venous access devices – a nested pre-trial qualitative study. Journal of Vascular Access 2015;16(5):407-12. [DOI: 10.5301/jva.5000447] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rivera‐Goba 2011 {published data only}
- Rivera-Goba MV, Dominguez DC, Stoll P, Grady C, Ramos C, Mican JM. Exploring decision-making of HIV-infected Hispanics and African Americans participating in clinical trials.. Journal of the Association of Nurses in AIDS care 2011;22(4):295-306. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jana.2010.10.007] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rogers 2014 {published data only}
- Rogers A, Harris T, Victor C, Woodcock A, Limb E, Kerry S, et al. Which older people decline participation in a primary care trial of physical activity and why: insights from a mixed methods approach. BMC Geriatrics 2014;14:46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rooney 2011 {published data only}
- Rooney LK, Bhopal R, Halani L, Levy ML, Partridge MR, Netuveli G, et al. Promoting recruitment of minority ethnic groups into research: qualitative study exploring the views of South Asian people with asthma. Journal of Public Health Advance Access 2011;33(4):604-15. [DOI: 10.1093/pubmed/fdq100] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schapira 2014 {published data only}
- Schapira MM, Mackenzie ER, Lam R, Casarett D, Seluzicki CM, Barg FK, e al. Breast cancer survivors willingness to participate in an acupuncture clinical trial: a qualitative study. Supportive Care in Cancer 2014;22(5):1207-15. [DOI: 10.1007/s00520-013-2073-3] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Scott 2011 {published data only}
- Scott C, Walker J, White P, Lewith G. Forging convictions: the effects of active participation in a clinical trial. Scoial Science and Medicine 2011;72:2041-8. [DOI: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2011.04.021] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sheikh 2009 {published data only}
- Sheikh A, Halani L, Bhopal R, Netuveli G, Partridge MR, Car J, et al. Facilitating the recruitment of minority ethnic people into research: qualitative case study of South Asians and asthma. PLOS Medicine 2009;6(10):e1000148. [DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000148] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sims‐Gould 2012 {published data only}
- Sims-Gould J, Miran-Khan K, Haggis C, Liu-Ambrose T. Timing, experience, benefits, and barriers: older women's uptake and adherence to an exercise program. Activities, Adaptation & Aging 2012;36(4):280-96. [DOI: 10.1080/01924788.2012.729188] [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Snowdon 2012 {published data only}
- Snowdon C, Elbourne D, Forsey M, Alfrevic Z. Views of emergency research (VERA):A qualitative study of women and their partners’ views of recruitment to trials in severe postpartum haemorrhage. Midwifery 2012;28:800-8. [DOI: 10.1016/j.midw.2011.11.009] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Stevens 2004 {published data only}
- Stevens T, Ahmedzai SH. Why do breast cancer patients decline entry into randomised trials and how do they feel about their decision later: a prospective,longitudinal, in-depth interview study. Patient Education and Counseling 2004;52:341-8. [DOI: 10.1016/S0738-3991(03)00041-7] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Thornton 2016 {published data only}
- Thornton LR, Amorrortu RP, Smith DW, Mainous III AG, Vernon SW, Tilley BC. Exploring willingness of elder Chinese in Houston to participate in clinical research. Contemporary Clinical Trials Communications 2016;4:33-8. [DOI: 10.1016/j.conctc.2016.06.006] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Todkill 2013 {published data only}
- Todkill D, Powell J. Participant experiences of an internet-based intervention and randomised control trial: interview study. BMC Public Health 2013;13:1017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Townsend 2013 {published data only}
- Townsend A, Cox SM. Accessing health services through the back door:a qualitative interview study investigating reasons why people participate in health research inCanada. BMC Medical Ethics 2013;14:40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ulrich 2012 {published data only}
- Ulrich CM, Knafl KA, Ratcliffe SJ, Richmond TS, Grady C, Miller-Davis C, et al. Developing a model of the benefits and burdens of research participation in cancer clinical trials. AJOB Primary Research 2012;3(2):10-23. [DOI: 10.1080/21507716.2011.653472] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Unson 2001 {published data only}
- Unson CG, Dunbar N, Curry L, Kenyon L, Prestwood L. The effects of knowledge, attitudes, and significant others on decisions to enroll in a clinical trial on osteoporosis implications for recruitment of older African American women. Journal of The National Medical Association 2001;93(10):392-401. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Whybrow 2017 {published data only}
- Whybrow P, Pickard R, Hrisos S, Rapley T. Equipoise across the patient population:optimising recruitment to a randomised controlled trial. Trials 2017;18:140. [DOI: 10.1186/s13063-016-1711-8] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Woods 2002 {published data only}
- Woods MN, Harris KJ, Mayo MS, Corley D, Schiebmeir M, Ahluwalia JS. Participation of African Americans in a smoking cessation trial: a quantitative and qualitative study. Journal of The National Medical Association 2002;94(7):609-18. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to studies awaiting assessment
Asiedu 2018 {published data only}
- Asiedu GB, Ridgeway JL, Carroll K, Jatoi A, Radecki Breitkopf C. “Ultimately, mom has the call”: Viewing clinical trial decision making among patients with ovarian cancer through the lens of relational autonomy. Health Expectations 2018;21:981-9. [DOI: 10.1111/hex.12691] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cooper 2017 {published data only}
- Cooper J Blake I, Lindsay JO, Hawkey CJ. Living with Crohn’s disease: an exploratory cross-sectional qualitative study into decision-making and expectations in relation to autologous haematopoietic stem cell treatment (theDECIDES study). BMJ Open 2017;7:e015201. [DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-015201] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Craig 2018 {published data only}
- Craig SR, Lahey T, Dixit A, Fordham von Reyn C. Altruism, scepticism, and collective decision-making in foreign-born U.S.residents in a tuberculosis vaccine trial. BMC Public Health 2018;18:535. [DOI: 10.1186/s12889-018-5460-3] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Denny 2018 {published data only}
- Denny E, Weckesser A, Jones G, Bibila S, Daniels J, Bhattacharya S: PRE-EMPT team. Women’s experiences of medical treatment for endometriosis and its impact on PREEMPTtrial participation: a qualitative study. Pilot and Feasibility Studies 2018;4:168. [DOI: 10.1186/s40814-018-0358-5] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Duncan 2018 {published data only}
- Duncan M, Korszun A, White P, Eva G, Bhui K, Rourke L, et al: SURECAN investigators. Qualitative analysis of feasibility of recruitment and retention in a planned randomised controlled trial of a psychosocial cancer intervention within the NHS. Trials 2018;19(1):327. [DOI: 10.1186/s13063-018-2728-y] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Escarnot 2020 {published data only}
- Ecarnot F, Meunier‑Beillard N, Quenot JP, Meneveau N. Factors associated with refusal or acceptance of older patients(≥ 65 years) to provide consent to participate in clinical research in cardiology: a qualitative study. Aging Clinical and Experimental Research 2020;32(1):133-40. [DOI: 10.1007/s40520-019-01172-z] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Manton 2019 {published data only}
- Manton KJ, Gauld CS, White KM, Griffin PM, Elliott SL. Qualitative study investigating the underlying motivations of healthy participants in phase I clinical trials. BMJ Open 2019;9:e024224. [DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-024224] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Monteiro 2019 {published data only}
- Monteiro TM, Katz L, Bento SF, Amorim MM, Moriel PC, Pacagnella, RC. Reasons given by pregnant women for participating in a clinical trial aimed at preventing premature delivery: a qualitative analysis. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth 2019;19:97. [DOI: 10.1186/s12884-019-2240-8] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Nadimpally 2017 {published data only}
- Nadimpally S, Bhagianadh D. "The invisible": Participant's experiences in clinical trials. Perspectives in Clinical Research 2017;8:5-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Norris 2019 {published data only}
- Norris M, Poltawski L, Calitri R, Shepherd AI, Dean SG, the ReTrainTeam. Hope and despair: a qualitative exploration of the experiences and impact of trial processes in a rehabilitation trial. Trials 2019;20(1):525. [DOI: 10.1186/s13063-019-3633-8] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Perry 2016 {published data only}
- Perry J, Wöhlke S, Heßling AC, Schicktanz S. Why take part in personalised cancer research? Patients’genetic misconception, genetic responsibility and in comprehension of stratification—an empirical-ethical examination. European Journal of Cancer Care 2016;26(5):e12563. [DOI: 10.1111/ecc.12563] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Phelps 2019 {published data only}
- Phelps EE, Tutton E, Griffin X, Baird J and on behalf of the TrAFFix study co-applicants. Facilitating trial recruitment: A qualitative study of patient and staff experiences of an orthopaedic trauma trial. Trials 2019;20(1):492. [DOI: 10.1186/s13063-019-3597-8] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Prout 2018 {published data only}
- Prout HC, Barham A, Bongard E, Tudor-Edwards R, Griffiths G, Hamilton W, et al. Patient understanding and acceptability of an early lung cancer diagnosis trial: a qualitative study. Trials 2018;19:419. [DOI: 10.1186/s13063-018-2803-4] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ridgeway 2017 {published data only}
- Ridgeway JL, Asiedu GB, Carroll K, Tenney M, Jatoi A, Radecki Breitkopf C. Patient and family member perspectives on searching for cancer clinical trials: a qualitative interview study. Patient Education and Counseling 2017;100:349-54. [DOI: 10.1016/j.pec.2016.08.020] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Thong 2019 {published data only}
- Thong ISK, Ulph F, Barrowclough C, Gregg L. Facilitators and barriers to participating in a randomized controlled trial of a psychological therapy for substance use. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 2019;207(6):487-96. [DOI: 10.1097/NMD.0000000000001000] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Tompkins 2019 {published data only}
- Tompkins CN, Neale J, Marsden J, Strang J. Factors influencing recruitment to a randomised placebo-controlled trial of oral naltrexone and extended release implant naltrexone: qualitative study. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 2019;99:52-60. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jsat.2019.01.012] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
van den Berg 2017 {published data only}
- den Berg P, Kendal S, Alderson HV, Body R. An exploration of patients’ experiences of participation in a randomised controlled trial of the Manchester Acute Coronary Syndromes (MACS) decision rule. BMJ Emergency Medicine Journal 2017;34:593-8. [DOI: 10.1136/emermed-2016-206073] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Zhao 2018 {published data only}
- Zhao Y, Ding A, Arya R, Patel JP. Factors influencing the recruitment of lactating women in a clinical trial involving direct oral anticoagulants: a qualitative study. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy 2018;40:1511-8. [DOI: 10.1007/s11096-018-0734-5] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Additional references
Ames 2017
- Ames HM, Glenton C, Lewin S. Parents' and informal caregivers' views and experiences of communication about routine childhood vaccination: a synthesis of qualitative evidence. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2017, Issue 2. Art. No: CD011787. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011787.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Aslam 2017
- Aslam RW, Hendry M, Booth A, Carter B, Charles JM, Craine N, et al. Intervention Now to Eliminate Repeat Unintended Pregnancy in Teenagers (INTERUPT): a systematic review of intervention effectiveness and cost-effectiveness, and qualitative and realist synthesis of implementation factors and user engagement. BMC Medicine 2017;15:155. [DOI: 10.1186/s12916-017-0904-7] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Barroso 2003
- Barroso J, Gollop CJ, Sandelowski M, Meynell J, Pearce PF, Collins LJ. The challenges of searching for and retrieving qualitative studies. Western Journal of Nursing Research 2003;25(2):153-78. [DOI: 10.1177/0193945902250034] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bastian 2010
- Bastian H, Glasziou P, Chalmers I. Seventy-five trials and eleven systematic reviews a day: How will we ever keep up? PLoS Medicine 2010;7(9):e1000326. [DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000326] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bates 1989
- Bates MJ. The design of browsing and berrypicking techniques for the online search interface. Online Review 1989;13(5):407-24. [DOI: 10.1108/eb024320] [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Bazeley 2007
- Bazeley P. Qualitative Data Analysis with NVivo. Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2007. [Google Scholar]
Boland 2015
- Boland J, Currow DC, Wilcock A, Tieman J, Hussain JA, Pitsillides C, et al. A systematic review of strategies used to increase recruitment of people with cancer or organ failure into clinical trials: implications for palliative care research. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management 49;4:762-72. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2014.09.018] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Booth 2011
- Booth A. Chapter 3: Searching for studies. In: Supplementary Guidance for Inclusion of Qualitative Research in Cochrane Collaborative Qualitative Methods Group. Version 1. Cochrane, 2011. [Google Scholar]
Booth 2016
- Booth A. Searching for qualitative research for inclusion in systematic reviews: a structured methodological review. Systematic Reviews 2016;5(1):74. [DOI: 10.1186/s13643-016-0249-x] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Booth 2018
- Booth A, Noyes J, Flemming K, Gerhardus A, Wahlster P, Wilt GJ, et al. Structured methodology review identified seven (RETREAT) criteria for selecting qualitative evidence synthesis approaches. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2018;99:41-52. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2018.03.003] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bowen 2009
- Bowen D, Kreuter M, Spring B, Cofta-Woerpel L, Linnan L, Weiner D, et al. How we design feasibility studies. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 2009;36:451-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bower 2007
- Bower P, Wilson S, Mathers N. Short report: How often do UK primary care trials face recruitment delays? Family Practice 2007;24(6):601-3. [DOI: 10.1093/fampra/cmm05110.1186/1471-2288-6-34] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Burns 2011
- Burns PB, Rohrich RJ, Chung KC. The levels of evidence and their role in evidence-based medicine. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 2011;128(1):305-10. [DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e318219c171] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Campbell 2007
- Campbell MK, Snowdon C, Francis D, Elbourne D, McDonald AM, Knights R, et al. Recruitment to randomised trials: Strategies for trial enrolment and participation study. The STEPS study. Health Technology Assessment 2007;11(48):iii-72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
CASP 2013
- CASP Critical Appraisal Skills Programme. 10 questions to help you make sense of qualitative research. CASP 2013.
Charlson 1984
- Charlson ME, Horwitz RI. Applying results of randomised trials to clinical practice: impact of losses before randomisation. British Medical Journal 1984;289(6454):1281-4. [DOI: 10.1136/bmj.289.6454.1281] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Corbett 2016
- Corbett MS, Watson J, Eastwood A. Randomised trials comparing different healthcare settings: an exploratory review of the impact of pre-trial preferences on participation, and discussion of other methodological challenges. BMC Health Services Research 2016;16:589. [DOI: 10.1186/s12913-016-1823-6] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Daykin 2018
- Daykin A, Clement C, Gamble C, Kearney A, Blazeby J, Clarke M, et al. ‘Recruitment, recruitment, recruitment’ – the need for more focus on retention: a qualitative study of five trials. Trials 2018;19:76. [DOI: 10.1186/s13063-018-2467-0] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dixon‐Woods 2005
- Dixon-Woods M, Agarwal S, Jones D, Young B, Sutton A. Synthesising qualitative and quantitative evidence: a review of possible methods. Journal of Health Service Research Policy 2005;10(1):45-53. [DOI: 10.1258/1355819052801804] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Fayter 2007
- Fayter D, McDaid C, Eastwood A. A systematic review highlights threats to validity in studies of barriers to cancer trial participation. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2007;60(10):e1-990.e33. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2006.12.013] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Finfgeld‐Connett 2013
- Finfgeld-Connett D, Johnson ED. Literature search strategies for conducting knowledge-building and theory-generating qualitative systematic reviews. Journal of Advanced Nursing 2013;69(1):194-204. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2012.06037.x] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Fletcher 2012
- Fletcher B, Gheorghe A, Moore D, Wilson S, Damery S. Improving the recruitment activity of clinicians in randomised controlled trials: a systematic review. BMJ Open 2012;2(1):e000496. [DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2011-000496] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gardner 2020
- Gardner HR, Albarquoni L, El Feky A, Gillies K, Treweek S. A systematic review of non-randomised evaluations of strategies to improve participant recruitment to randomised controlled trials. F1000Research 2020;9:86. [DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.22182.1] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
George 2014
- George S, Duran N, Norris K. A systematic review of barriers and facilitators to minority research participation among African Americans, Latinos, Asian Americans, and Pacific Islanders. American Journal of Public Health 2014;104(2):e16-e31. [DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2013.301706] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Glenton 2013
- Glenton C, Colvin CJ, Carlsen B, Swartz A, Lewin S, Noyes J, et al. Barriers and facilitators to the implementation of lay health worker programmes to improve access to maternal and child health: qualitative evidence synthesis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013, Issue 10. Art. No: CD010414. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010414.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Glover 2015
- Glover M, Kira A, Johnston V, Walker N, Thomas D, Chang AB, et al. A systematic review of barriers and facilitators to participation in randomized controlled trials by Indigenous people from New Zealand, Australia, Canada and the United States. Global Health Promotion 2015;22(1):21-31. [DOI: 10.1177/1757975914528961] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Haidich 2001
- Haidich A-B, Ionnidis JP. Determinants of patient recruitment in a multicenter clinical trials group: trends, seasonality and the effect of large studies. BMC Medical Research Methodology 2001;1:4. [DOI: 10.1186/1471-2288-1-4] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hall 2010
- Hall MJ, Egkeston B, Miller SM, Buzaglo JS, Millard J, Ridgway C, et al. Barriers to participation in cancer prevention clinical trials. Acta Oncologia 2010;49(6):757-66. [DOI: 10.3109/0284186X.2010.485209] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Harden 2018
- Harden A, Thomas J, Cargo M, Harris J, Pantoja T, Flemming K, et al. Cochrane Qualitative and Implementation Methods Group guidance series—paper 5: methods for integrating qualitative and implementation evidence within intervention effectiveness reviews. Journal of Cinical Epidemiology 2018;97:70-8. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.11.029] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hennessy 2018
- Hennessy M, Hunter A, Healy P, Galvin S, Houghton C. Improving trial recruitment processes: how qualitative methodologies can be used to address the top 10 research priorities identified within the PRioRiTy study. Trials 2018;19:584. [DOI: 10.1186/s13063-018-2964-1] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2016
- Higgins JP, Lasserson T, Chandler J, Tovey D, Churchill R. Methodological Expectations of Cochrane Intervention Reviews. London: Cochrane, 2016. [Google Scholar]
Houghton 2016a
- Houghton C, Murphy K, Meehan B, Thomas J, Brooker D, Casey D. From screening to synthesis: using NVivo to enhance transparency in qualitative evidence synthesis. Journal of Clinical Nursing 2016;26(5-6):873-81. [DOI: 10.1111/jocn.13443] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Houghton 2016b
- Houghton C, Murphy K, Brooker D, Casey D. Health care staffs' experiences and perceptions of caring for people with dementia in the acute setting: qualitative research synthesis. International Journal of Nursing Studies 2016;61:104-16. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2016.06.001] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jasper 2005
- Jasper MA. Using reflective writing within research. Journal of Research in Nursing 2005;10(3):247-60. [DOI: 10.1177/174498710501000303] [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Kanarek 2010
- Kanarek NF, Tsai HL, Metzger-Gaud S, Damron D, Guseynova A, Klamerus JF, et al. Geographic proximity and racial disparities in cancer clinical trial participation. Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network 2010;8(12):1343-51. [DOI: 10.6004/jnccn.2010.0102 ] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kanarek 2012
- Kanarek NF, Kanarel MS, Olatoye D, Carducci MA. Removing barriers to participation in clinical trials, a conceptual framework and retrospective chart review study. Trials 2012;13:237. [DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-13-237] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Karimi‐Shahanjarini 2019
- Karimi‐Shahanjarini A, Shakibazadeh E, Rashidian A, Hajimiri K, Glenton C, Noyes J, et al. Barriers and facilitators to the implementation of doctor‐nurse substitution strategies in primary care: a qualitative evidence synthesis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2019, Issue 4. Art. No: CD010412. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010412.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kasenda 2014
- Kasenda B, Elm E, You J, Blümle A, Tomonaga Y, Saccilotto R, et al. Prevalence, characteristics, and publication of discontinued randomized trials. JAMA 2014;311(10):1045-52. [DOI: 10.1001/jama.2014.1361] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kitterman 2011
- Kitterman D, Cheng S, Dilts D, Orwell E. The prevalence and economic impact of low-enrolling clinical studies at an academic medical center. Journal of the Association of American Medical Colleges 2011;86(11):1360-6. [DOI: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e3182306440] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lewin 2018
- Lewin S, Booth A, Glenton C, Munthe-Kaas H, Rashidian A, Wainwright M, et al. Applying GRADE-CERQual to qualitative evidence synthesis findings: introduction to the series. Implementation Science 2018;13:2. [DOI: 10.1186/s13012-017-0688-3] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mattel 2004
- Mattel C, Li Y, Beckett L, Chew H, Christensen S, Davies A, et al. An evaluation of barriers to accrual in the era of legislation requiring insurance coverage of cancer clinical trial costs in California. Cancer Journal 2004;10(5):294-300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
McDonald 2006
- McDonald AM, Knight RC, Campbell MK, Entwistle VA, Grant AM, Cook JA, et al. What influences recruitment to randomised controlled trials? A review of trials funded by two UK funding agencies. Trials 2006;7:9. [DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-7-9] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Moher 2009
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group. The PRISMA Group. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Medicine 2009;6(7):e000097. [DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Munabi‐Babigumira 2017
- Munabi-Babigumira S, Glenton C, Lewin S, Fretheim A, Nabudere H. Factors that influence the provision of intrapartum and postnatal care by skilled birth attendants in low- and middle-income countries: a qualitative evidence synthesis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2017, Issue 11. Art. No: CD011558. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011558.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Noyes 2008
- Noyes J, Popay J, Pearson A, Hannes K, Booth A. Chapter 20. Qualitative Research and Cochrane Reviews. In: Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2008:571-91. [DOI: 10.1002/9780470712184] [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Noyes 2017a
- Noyes J, Booth A, Cargo M, Flemming K, Garside R, Hannes K, et al. Cochrane Qualitative and Implementation Methods Group Guidance Series - paper 1: Introduction. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2017;97:35-8. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.09.025] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Noyes 2017b
- Noyes J, Booth A, Flemming K, Garside R, Harden A, Lewin S, et al. Cochrane Qualitative and Implementation Methods Group guidance series-paper 3: methods for assessing methodological limitations, data extraction and synthesis, and confidence in synthesized qualitative findings. Journal of clinical Epidemiology 2017;97:49-58. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.06.020] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Prescott 1999
- Prescott RJ, Counsell CE, Gillespie WJ, Grant AM, Russell IT, Kiauka S, et al. Factors that limit the quality, number and progress of randomised controlled trials. Health Technology Assessment 1999;3(20):iii-139. [DOI: 10.1016/s0895-4356(99)00141-9] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Raftery 2015
- Raftery J, Young A, Stanton L, Milne R, Cook A, Turner D, et al. Clinical trial metadata: defining and extracting metadata on the design, conduct, results and costs of 125 randomised clinical trials funded by the National Institute for Health Research Health Technology Assessment Programme. Health Technology Assessment 2015;19(11):1-166. [DOI: 10.3310/hta19110] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rooshenas 2016
- Rooshenas L, Elliott, D, Wade J, Jepson M, Paramasivan S, Strong S, et al. Conveying equipoise during recruitment for clinical trials: qualitative synthesis of clinicians' practices across six randomised controlled trials. PLOS Medicine 2016;13(10):e1002147. [DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002147] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ross 1999
- Ross S, Grant A, Counsell C, Gillespie W, Russell I, Prescott R. Barriers to participation in randomised controlled trials: a systematic review. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 1999;52(12):1143-56. [DOI: 10.1016/s0895-4356(99)00141-9 ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sandelowski 2007
- Sandelowski M, Barroso J, Voils CI. Using qualitative metasummary to synthesize qualitative and quantitative descriptive findings. Research Nurse Health 2007;30(1):99-111. [DOI: 10.1002/nur.20176] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sawhney 2014
- Sawhney V, Graham A, Campbell N, Schilling R. Does modification to the approach to contacting potential participants improve recruitment to clinical trials? Journal of Clinical Medicine Research 2014;6(5):384-7. [DOI: 10.14740/jocmr1879w] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schmotzer 2012
- Schmotzer G. Barriers and facilitators to participation of minorities in clinical trials. Ethnicity and Disease 2012;22:226-30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sully 2013
- Sully BG, Julious SA, Nicholl J. A reinvestigation of recruitment to randomised, controlled, multicenter trials: a review of trials funded by two UK funding agencies. Trials 2013;14(166):1-8. [DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-14-166] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Thoma 2010
- Thoma A, Farrokhyar F, McKnight, Bhandari M. How to optimize patient recruitment. Canadian Journal of Surgery 2010;53(3):205-10. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Thomas 2008
- Thomas J, Harden J. Methods for the thematic synthesis of qualitative research in systematic reviews. BMC Medical Research Methodology 2008;8:45. [DOI: 10.1186/1471-2288-8-45] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Thorne 2004
- Thorne S, Jensen L, Kearney MH, Noblit G, Sandelowski M. qualitative metasynthesis: reflections on methodological orientation and ideological agenda. Qualitative Health Research 2004;14(10):1342-65. [DOI: 10.1177/1049732304269888] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Tong 2012
- Tong A, Flemming K, McInnes E, Oliver S, Craig J. Enhancing transparency in reporting the synthesis of qualitative research: ENTREQ. BMC Medical Research Methodology 2012;12:181. [DOI: 10.1186/1471-2288-12-181] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Townsley 2005
- Townsley CA, Selby R, Siu LL. Systematic review of barriers to the recruitment of older patients with cancer onto clinical trials. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2005;23(13):3112-24. [DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2005.00.141] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Treweek 2010
- Treweek S, Mitchell E, Pitkethly M, Cook J, Kjeldstrøm M, Johansen M, et al. Strategies to improve recruitment to randomised controlled trials. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2010, Issue 4. Art. No: MR000013. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.MR000013.pub5] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Treweek 2018
- Treweek S, Pitkethly M, Cook J, Fraser C, Mitchell E, Sullivan F, et al. Strategies to improve recruitment to randomised trials. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2018, Issue 2. Art. No: MR000013. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.MR000013.pub6] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Walsh 2005
- Walsh D, Downe S. Meta-synthesis method for qualitative research: a literature review. Journal of Advanced Nursing 2005;50(2):204-11. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2005.03380.x] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Walters 2017
- Walters SJ, Bonacho dos Anjos Henriques-Cadby I, Bortolami O, Flight L, Hind D, Jacques RM, et al. Recruitment and retention of participants in randomised controlled trials: a review of trials funded and published by the United Kingdom Health Technology Assessment Programme. BMJ Open 2017;7:e015276. [DOI: :10.1136/bmjopen-2016015276] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Watson 2006
- Watson JM, Torgerson DJ. Increasing recruitment to randomised trials: a review of randomised controlled trials. BMC Medical Research Methodology 2006;6:34. [DOI: 10.1186/1471-2288-6-34] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Whitaker 2016
- Whitaker R, Hendry M, Aslam R, Booth A, Carter B, Charles JM, et al. Intervention Now to Eliminate Repeat Unintended Pregnancy in Teenagers (INTERUPT): a systematic review of intervention effectiveness and cost-effectiveness, and qualitative and realist synthesis of implementation factors and user engagement. Health Technology Assessment 2016;20(6):1-214. [DOI: 10.3310/hta20160] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to other published versions of this review
Houghton 2017
- Houghton C, Dowling M, Meskell P, Hunter A, Gardner H, Conway A, et al. Factors that impact on recruitment to randomised trials in health care: a qualitative evidence synthesis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2017, Issue 5. Art. No: MR000045. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.MR000045] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



