Abstract
Background
Portal hypertension commonly accompanies advanced liver disease and often gives rise to life‐threatening complications, including haemorrhage from oesophageal and gastrointestinal varices. Variceal haemorrhage commonly occurs in children with chronic liver disease or portal vein obstruction. Prevention is therefore important. In adults, numerous randomised clinical trials have demonstrated benefits of non‐selective beta‐blockers and endoscopic variceal ligation as primary prevention in decreasing the risk of variceal haemorrhage. In children, band ligation, beta‐blockers, and sclerotherapy have been proposed as alternatives for primary prophylaxis of oesophageal variceal bleeding. However, primary prophylaxis is not the current standard of care in children because it is unknown whether those treatments are of benefit or cause harm when used for primary prophylaxis of oesophageal variceal bleeding in children and adolescents.
Objectives
To determine the benefits and harms of band ligation versus sclerotherapy for primary prophylaxis of oesophageal variceal bleeding in children and adolescents with chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis.
Search methods
We searched the Cochrane Hepato‐Biliary Group Controlled Trials Register, CENTRAL, PubMed, Embase, LILACS, and Science Citation Index Expanded (27 April 2020). We scrutinised the reference lists of retrieved publications, and performed a manual search from the main paediatric gastroenterology and hepatology conferences (NASPGHAN and ESPGHAN) abstract books from 2008 to 2019. We searched ClinicalTrials.gov, FDA, EMA, and WHO for ongoing clinical trials. There were no language or document type restrictions.
Selection criteria
We planned to include randomised clinical trials irrespective of blinding, language, or publication status for assessment of benefits and harms. If the search for randomised clinical trials retrieved quasi‐randomised and observational studies, then we read them through to extract information on harms.
Data collection and analysis
We planned to summarise data from randomised clinical trials by standard Cochrane methodologies. We planned to assess risk of bias and use GRADE to assess the certainty of evidence per outcome. Our primary outcomes were all‐cause mortality, serious adverse events and liver‐related morbidity, and quality of life. Our secondary outcomes were oesophageal variceal bleeding and adverse events not considered serious. We planned to analyse data with intention‐to‐treat. We planned to use Review Manager 5 to analyse the data.
Main results
We found no randomised clinical trials assessing band ligation versus sclerotherapy for primary prophylaxis of oesophageal variceal bleeding in children with chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis.
Authors' conclusions
Randomised clinical trials assessing the benefits or harms of band ligation versus sclerotherapy for primary prophylaxis of oesophageal variceal bleeding in children with chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis are lacking. Therefore, trials with adequate power and proper design, assessing the benefits and harms of band ligation versus sclerotherapy on patient‐relevant clinical outcomes such as mortality, quality of life, failure to control variceal bleeding, and adverse events are needed. Unless such trials are conducted and the results become published, we cannot make any conclusions regarding the benefits or harms of these two interventions.
Plain language summary
Band ligation versus sclerotherapy for primary prophylaxis of oesophageal varices in children
Background
Portal hypertension is defined as an increase in the blood pressure within a system of veins (a type of blood vessel) called the portal venous system, which drains blood from the gastrointestinal tract (gut) and spleen into the liver. Portal hypertension commonly accompanies advanced liver disease and often gives rise to life‐threatening complications, including haemorrhage (bleeding) from oesophageal (gullet) and gastrointestinal varices (enlarged or swollen veins).
In adults, numerous randomised clinical trials (studies where people are randomly allocated to one of two or more treatment groups) have demonstrated benefits of medicines called non‐selective beta‐blockers and endoscopic variceal ligation (where an enlarged vein is tied off or ligated by a rubber band) on the risk of first variceal haemorrhage. These treatments are used as primary prophylaxis (preventing or increasing resistance to disease that has not occurred) in adults, but it is unknown whether they are of benefit or cause harm when used in children and adolescents. Sclerotherapy (the endoscopic injection of tissue irritants that cause obliteration of blood vessels) is the only endoscopic prophylactic option currently available in infants weighing less than 10 kg of body weight (because of the size).
Aims
We aimed to conduct a systematic review of randomised clinical trials to assess the benefits and harms of band ligation versus sclerotherapy for prevention of oesophageal variceal bleeding in children with chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis (blockage or narrowing of the portal vein (the blood vessel that brings blood to the liver from the intestines) by a blood clot). We searched for trials to 27 April 2020.
Key results
We found no randomised clinical trials for inclusion in this systematic review. Accordingly, we lack results from randomised clinical trials to conclude if band ligation compared with sclerotherapy may be beneficial or not in children and adolescents with oesophageal varices. There is a need for well‐designed trials that should include important clinical outcomes such as death, quality of life, failure to control of variceal bleeding, and side effects.
Background
Description of the condition
There are scarce data on the prevalence and burden of liver disease in children and adolescents, and the natural history of portal hypertension in children is different than in adults. In adults, the cause of portal hypertension is mostly intrahepatic, whereas the cause of portal hypertension in children is mostly extrahepatic. The main underlying condition that results in the development of portal hypertension in children is extrahepatic portal vein obstruction (Di Giorgio 2019), followed by cirrhotic aetiologies, such as biliary atresia (Shneider 2016; Chapin 2018). In adults with portal hypertension, a hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG) of 10 mmHg or more, has been associated with the formation of oesophageal varices. Data on HVPG gradient values in children are limited. One study in children with portal hypertension found that HVPG was not associated with the presence of varices or history of variceal bleeding, suggesting the possibility of intrahepatic shunting in children with advanced liver disease (Ebel 2019).
Variceal haemorrhage also commonly occurs in children with chronic liver disease or portal vein obstruction (Lykavieris 2000; Miga 2001; van Heurn 2004; Duche 2013; Di Giorgio 2019). One study of 125 children, with biliary atresia with signs of portal hypertension or previous history of gastrointestinal bleeding, reported that 88 (70%) developed oesophageal varices (Duche 2010). In children with biliary atresia, the incidence of variceal haemorrhage ranged from 17% to 29% over a five‐ to 10‐year period (Miga 2001; van Heurn 2004; Duche 2013; Angelico 2019; Parolini 2019). One prospective study of 50 children, with oesophageal varices primarily due to cirrhosis, who did not receive active treatment for prevention of variceal bleeding, showed that 42% of the children had upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage during a median follow‐up of 4.5 years (Goncalves 2000). Available studies in children with portal hypertension due to portal vein thrombosis suggest that up to 50% of children experience a major variceal haemorrhage by 16 years of age (Lykavieris 2000). Variceal bleeding in children with portal hypertension has been associated with significant morbidity and variable mortality rates. In one study of children with portal hypertension due to chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis, postacute variceal bleeding morbidity occurred in 64% of children after their first episode of bleeding (Carneiro 2018). Mortality rates in children with variceal bleeding of cirrhotic aetiologies were between 2% and 19% (Eroglu 2004; van Heurn 2004; Carneiro 2018). In contrast, variceal bleeding in children with portal vein thrombosis and no parenchymal liver disease seemed to carry less than 3% risk of mortality (Lykavieris 2000; Di Giorgio 2019).
Description of the intervention
Randomised clinical trials have demonstrated benefits of band ligation and non‐selective beta‐blockers in decreasing the incidence of first variceal haemorrhage in adults, based on which these interventions have become primary prevention in adults (Garcia‐Tsao 2007; Garcia‐Tsao 2017). Results on the use of sclerotherapy, band ligation, and beta‐blockers for primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding in children have been reported in several other publications (Goncalves 2000; Samanta 2011; Lampela 2012; Duche 2013; Duche 2017; Galand 2018; Angelico 2019). However, none of these interventions have been assessed in randomised clinical trials. Various surveys regarding primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding in children, conducted by paediatric gastroenterologists, have shown different approaches to the management of children with portal hypertension (Gana 2011a; Verdaguer 2016; Jeanniard‐Malet 2017). This suggests that many paediatric specialists apply the guidelines for management of portal hypertension in adults to children and adolescents. However, there is an important variation of care provided by physicians, probably secondary to the lack of good‐quality studies.
There are several differences in the pathophysiology of portal hypertension between adults compared to children and adolescents. Therefore, precautions must be taken before extrapolating facts and data from adults to children or adolescents. Children are more dependent on chronotropy for maintenance of systemic blood pressure during hypovolaemia than adults who depend mainly on vasoconstriction. The main concern is that by limiting tachycardia in children, the use of a non‐selective beta‐blocker may impair tolerance to hypovolaemia and may lead to a more adverse outcome from variceal bleeding. Second, the efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and adverse event profiles of the drugs may differ significantly between children and adults (Ling 2005). Finally, the principal aetiologies of liver disease and portal hypertension are different in these populations, as described above. In contrast, although the use of band ligation is frequently used in children, there is a limitation in infants. The currently available equipment for band ligation is too large to be introduced into the oesophagus of infants weighing less than 10 kg of body weight, and sclerotherapy is the only endoscopic treatment option for this group of infants.
How the intervention might work
Band ligation is an endoscopic procedure in which an enlarged vein in the oesophagus is ligated by a rubber band to stop blood flow and create haemostasis. Sclerotherapy is an endoscopic procedure that involves the passage of an oesophagoscope, and it accomplishes vascular obliteration by injection of a sclerosing agent. Sclerosants are tissue irritants that cause vascular thrombosis and endothelial damage, leading to endofibrosis and vascular obliteration when injected into or adjacent to blood vessels. When a sclerosant is injected directly into the vein, blood clots are formed and the bleeding is stopped. When a sclerosant is injected into the area beside the distended vein, it prevents the bleeding by thickening and swelling the tissue around the veins (Al‐Khazraji 2019). This can be used to treat variceal bleeding and prevent variceal bleeding as well.
Why it is important to do this review
Variceal haemorrhage commonly occurs in children with oesophageal varices secondary to chronic liver disease or portal vein obstruction, and it has been associated with increased mortality (Mileti 2011; Chapin 2018). This has been mentioned as one of the most important areas that needs to be addressed in children with portal hypertension (Gana 2010; Gana 2011b; Ling 2011; Shneider 2012).
Band ligation leads to mechanical obliteration of the varices, reducing the intra‐varix blood flow. One 2001 meta‐analysis showed that endoscopic variceal ligation for primary prophylaxis of oesophageal varices in adults with cirrhosis reduced the incidence of variceal haemorrhage and mortality by 64% compared with no therapy (Imperiale 2001). There are no evidence‐based recommendations for the prophylactic management of children at risk of variceal haemorrhage because of the lack of appropriate good‐quality randomised clinical trials, as shown in the Summary of the Baveno VI Pediatric Satellite Symposium (Shneider 2016). Various surveys conducted by paediatric gastroenterologists have found a wide range of practices regarding primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding in children (Groszmann 2004; Gana 2011b; Shneider 2016; Verdaguer 2016; Jeanniard‐Malet 2017). In one survey of 30 paediatric gastroenterologists in the US, approaches to the management of children with portal hypertension, using screening endoscopy and primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding, varied considerably among the respondents. In this survey, 63% of gastroenterologists performed surveillance of oesophageal varices and 84% offered primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding in children (Groszmann 2004). In one survey in Canada, 70% of paediatric gastroenterologists reported that they would consider screening for oesophageal varices in children with liver disease and evidence of cirrhosis or portal hypertension (such as splenomegaly, thrombocytopenia, or portosystemic collaterals on sonography). However, only 58% of respondents who would screen for varices would provide primary prophylactic treatment (Gana 2011a). One survey of 35 Chilean paediatric gastroenterologists showed that 29 (83%) gastroenterologists had screened children for oesophageal varices because of clinical evidence of portal hypertension and 12 (34%) gastroenterologists had screened every child with chronic liver disease. Twenty‐eight (80%) respondents had used primary prophylaxis, mainly beta‐blockers, but also band ligation and sclerotherapy (Verdaguer 2016). One survey conducted in 38 hospital with French‐speaking staff showed that more than 75% of the centres had used endoscopy to screen children diagnosed with chronic liver diseases with suspected portal hypertension (Jeanniard‐Malet 2017). Among these 28 centres, 20 (71%) had performed primary prophylaxis for portal hypertension within their institution, one (4%) had done so only for children with cystic fibrosis because of its particular medical recruitment, and seven (25%) had referred the children to a tertiary centre. In cases of grade 2 varices with red marks and grade 3 varices, more than 90% of the centres had performed sclerotherapy or endoscopic variceal ligation. Approximately 20% of centres had used beta‐blockers (Jeanniard‐Malet 2017). This suggests that there is an important variation of care provided by physicians, probably due to the lack of good‐quality studies.
Different treatments have been proposed for the primary prophylaxis of oesophageal varices bleeding. This systematic review is one of six reviews that are being conducted to examine the utility of these treatments modalities (Gana 2019; Gattini 2020a; Gattini 2020b; Cifuentes 2021a; Cifuentes 2021b). In this context, we performed a systematic review on band ligation versus sclerotherapy for primary prevention of oesophageal varices bleeding in children (Gana 2015).
Objectives
To determine the benefits and harms of band ligation versus sclerotherapy for primary prophylaxis of oesophageal variceal bleeding in children and adolescents with chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis.
Methods
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Types of studies
Randomised clinical trials, regardless of publication status, language, or blinding. The trials were to compare band ligation versus sclerotherapy, administered as primary prophylaxis of oesophageal variceal bleeding in children with chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis.
We planned to examine the full texts of quasi‐randomised and observational studies for report of harm only, provided that these were retrieved with the searches for randomised clinical trials. We aimed to report the occurrence of adverse events using a narrative synthesis.
Types of participants
Children (up to 18 years old) with chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis, irrespective of the aetiology, severity of disease, and duration of illness, in whom the presence of oesophageal varices was confirmed by oesophagogastroduodenoscopy. The review planned to focus on children and adolescents who had not yet had gastrointestinal bleeding from oesophageal varices (primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding).
Children or adolescents with a previous surgical portal‐systemic shunt procedure or insertion of a transjugular intrahepatic portal‐systemic shunt, previous sclerotherapy of oesophageal varices, or previous history of upper gastrointestinal bleeding are a distinct group in whom the diagnosis or natural history of oesophageal varices had been modified. These children and adolescents constituted an exclusion criterion of this review, unless study data were subdivided following patient groups.
Types of interventions
Experimental:
endoscopic band ligation of oesophageal varices.
Control:
sclerotherapy of oesophageal varices with any type of sclerotherapy, dosage, and duration of treatment.
Co‐interventions were allowed as long as they were administered comparably to the two intervention groups.
Types of outcome measures
Primary outcomes
All‐cause mortality.
Serious adverse events and liver‐related morbidity (i.e. proportion of participants who developed ascites, hepatorenal syndrome, hepatocellular carcinoma, or hepatic encephalopathy). A serious adverse event, defined according to the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) Guidelines for Good Clinical Practice (ICH‐GCP 1997), was any untoward medical occurrence that resulted in death, was life‐threatening, required inpatient hospitalisation or prolongation of existing hospitalisation, resulted in persistent or significant disability or incapacity, or was a congenital anomaly or birth defect. All other adverse events were considered non‐serious adverse events.
Quality of life determined exclusively by means of validated scales, classifications and measurement systems such as the Paediatric Quality of Life Inventory (PedsQL), Child Health Questionnaire (CHQ), and DISABKIDS questionnaires.
Secondary outcomes
Oesophageal variceal bleeding.
Adverse events considered not serious (any adverse event that did not meet the above criteria for serious adverse events).
We planned to collect follow‐up data for the listed outcomes during the trial, and up to five years' follow‐up, the last of which was planned as the primary time point for analysis for conclusions.
Search methods for identification of studies
Electronic searches
We searched the Cochrane Hepato‐Biliary Group Controlled Trials Register (maintained and searched internally by the Cochrane Hepato‐Biliary Group Information Specialist via the Cochrane Register of Studies Web; 27 April 2020); Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL; 2020, Issue 4) in the Cochrane Library; PubMed (1809 to 27 April 2020), Embase (Elsevier; 1974 to 27 April 2020), LILACS (Latin American and Caribbean Health Science Information database, Bireme; 1982 to 27 April 2020), and Science Citation Index Expanded (Web of Science; 1900 to 27 April 2020) (Royle 2003). We scrutinised the reference lists of the retrieved publications. We also searched the trial registries ClinicalTrial.gov (clinicaltrials.gov/), European Medicines Agency (EMA) (www.ema.europa.eu/ema/), World Health Organization International Clinical Trial Registry Platform (www.who.int/ictrp), and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (www.fda.gov) for ongoing trials. Due to heavy traffic generated by the COVID‐19 outbreak, the ICTRP Search Portal was not accessible from outside WHO at the time of last searches. However, trials from both ClinicalTrials.gov and the WHO trials register are included in CENTRAL. We applied no language or document type restrictions. Appendix 1 displays search strategies with the time spans of the searches.
Searching other resources
We tried to identify additional references by manually searching the reference lists of articles from the computerised databases and relevant review articles. Furthermore, we performed a manual search from the main paediatric gastroenterology and hepatology conferences such as North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (NASPGHAN), and European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) abstract books from 2008 to 2018. We applied no language or document type restrictions.
Data collection and analysis
We followed the available guidelines provided in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2011; Higgins 2019). We planned to use Review Manager 5 for our analysis (Review Manager 2014).
Selection of studies
We planned to retrieve publications if they were potentially eligible for inclusion based on an abstract review, or if they were relevant, review articles for a manual reference search. Two review authors (LC and DG) independently assessed the publications for eligibility using the inclusion criteria. Abstracts were only to be included if there were sufficient data for analysis. Three review authors (LC, DG, and JCG) planned to resolve any disagreements by consensus. If non‐randomised clinical studies obtained with the searches for randomised clinical trials reported harms, we planned to report the occurrence of the adverse events in a narrative way.
Data extraction and management
Two review authors (LC and DG) planned to independently complete a pilot data extraction form on all included studies. We planned to retrieve the following data.
General information: title, journal, year, publication status, and trial design.
Sample size: number of participants meeting the criteria and total number screened.
Baseline characteristics: baseline diagnosis, age, sex, race, disease severity, and concurrent medications used. Severity of liver disease of the studied population may be considered using the Child Pugh score (Pugh 1973), the paediatric end‐stage liver disease (PELD) scores for children aged less than 12 years (McDiarmid 2002), and model for end‐stage liver disease (MELD) for children aged 12 years and older (Kamath 2001).
All‐cause mortality, non‐variceal bleeding of the upper gastrointestinal tract, oesophageal variceal bleeding, and quality of life determined exclusively using validated scales.
Adverse events: serious and non‐serious.
Follow‐up times for all outcomes, as defined in each trial.
Funding.
One review author (JCG) was to arbitrate in case of disagreements in data extraction.
Assessment of risk of bias in included studies
Two review authors (LC and DG) planned to independently assess the risk of bias of each included trial according to the recommendations in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2011) and methodological studies (Schulz 1995; Moher 1998; Kjaergard 2001; Wood 2008; Savović 2012a; Savović 2012b; Savović 2018). We planned to use the following definitions in the assessment of risk of bias.
Allocation sequence generation
Low risk of bias: sequence generation was achieved using computer random number generation or a random number table. Drawing lots, tossing a coin, shuffling cards, and throwing dice were adequate if performed by an independent person not otherwise involved in the trial.
Unclear risk of bias: the method of sequence generation was not specified.
High risk of bias: the sequence generation method was not random.
Allocation concealment
Low risk of bias: the participant allocations could not have been foreseen in advance of, or during, enrolment. Allocation was controlled by a central and independent randomisation unit. The allocation sequence was unknown to the investigators (e.g. if the allocation sequence was hidden in sequentially numbered, opaque, and sealed envelopes).
Unclear risk of bias: the method used to conceal the allocation was not described so that intervention allocations may have been foreseen in advance of, or during, enrolment.
High risk of bias: the allocation sequence was likely to have been known to the investigators who assigned the participants.
Blinding of participants and personnel
Low risk of bias: blinding of participants and personnel performed adequately using a placebo. We defined lack of blinding as unlikely to affect the evaluation of mortality (Savović 2012a; Savović 2012b; Savović 2018).
Unclear risk of bias: insufficient information to assess blinding.
High risk of bias: no blinding or incomplete blinding.
Blinding of outcome assessors
Low risk of bias: blinding of outcome assessors performed adequately using a placebo. We defined lack of blinding as unlikely to affect the evaluation of mortality (Savović 2012a; Savović 2012b; Savović 2018).
Unclear risk of bias: there was insufficient information to assess blinding.
High risk of bias: no blinding or incomplete blinding.
Incomplete outcome data
Low risk of bias: missing data were unlikely to make treatment effects depart from plausible values. Sufficient methods, such as multiple imputation, were employed to handle missing data.
Unclear risk of bias: there was insufficient information to assess whether missing data in combination with the method used to handle missing data were likely to induce bias on the results.
High risk of bias: the results were likely to be biased due to missing data.
Selective outcome reporting
Low risk of bias: the trial reported the following predefined primary outcomes: all‐cause mortality, gastrointestinal bleeding, and serious adverse events. If the original trial protocol was available, the outcomes were to be those called for in that protocol. If the trial protocol was obtained from a trial registry (e.g. www.clinicaltrials.gov), the outcomes sought were to be those enumerated in the original protocol if the trial protocol was registered before or at the time that the trial was begun. If the trial protocol was registered after the trial was begun, those outcomes were to be considered unreliable.
Unclear risk: not all predefined outcomes were reported fully, or it was unclear whether data on these outcomes were recorded or not.
High risk: one or more predefined outcomes were not reported.
Other bias
Low risk of bias: the trial appeared to be free of other bias domains including vested interests that could put it at risk of bias.
Unclear risk of bias: the trial may or may not have been free of other domains that could have put it at risk of bias.
High risk of bias: there were other factors in the trial that could have put it at risk of bias
Overall bias risk assessment
Low risk of bias: all domains in a trial were low risk of bias using the definitions described above.
High risk of bias: one or more of the bias domains in a trial were of unclear or high risk of bias.
We planned to generate a 'Risk of bias' graph and a 'Risk of bias' summary to show a summary of this assessment.
Measures of treatment effect
For dichotomous outcomes, we planned to calculate the risk ratio (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). For continuous outcomes such as health‐related quality of life, we planned to calculate the mean difference (MD) with 95% CI if all studies reported it using the same scale, and standardised mean difference (SMD) with 95% CI if the studies used different scales for its reporting.
Unit of analysis issues
The unit of analysis was to be the participant undergoing treatment (i.e. primary prophylaxis of oesophageal variceal bleeding in children with chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis) according to the intervention group to which the participant was randomly assigned. In the case of cross‐over trials, we planned to use the outcome data after the period of the first intervention because the assigned treatments could have residual effects (Higgins 2011; Higgins 2019). Due to the clinical situation, we did not expect to find cluster‐randomised trials. In trials with multiple intervention groups, we planned to collect data for all trial intervention groups that met our inclusion criteria. We planned to divide the control group into two to avoid double‐counting in case this was a common comparator.
Dealing with missing data
We planned to perform an intention‐to‐treat analysis whenever possible; otherwise, we planned to use the data available to us and contact the original investigators to request the missing data.
Regarding the dichotomous primary outcomes, whenever possible, we planned to conduct the following two sensitivity analyses.
Extreme case analysis favouring the experimental intervention ('best‐worse' case scenario): none of the dropouts or children lost from the experimental arm, but all of the dropouts or children lost from the control group experienced the outcome; including all randomised children in the denominator.
Extreme case analysis favouring the control ('worst‐best' case scenario): all dropouts or children lost from the experimental group, but none from the control group experienced the outcome; including all randomised children in the denominator.
For the continuous primary outcome, quality of life, we planned to impute the standard deviation from P values, according to guidance in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2011; Higgins 2019). If the data were likely to be normally distributed, we planned to use the median for meta‐analysis when the mean was not available; otherwise, we planned to provide a median and interquartile range of the difference in medians. If it was not possible to calculate the standard deviation from the P value or the CIs, we planned to impute the standard deviation using the largest standard deviation in other trials for that outcome. This form of imputation can decrease the weight of the study for calculation of MDs and may bias the effect estimate to no effect for calculation of SMDs (Higgins 2011; Higgins 2019).
Assessment of heterogeneity
We planned to identify heterogeneity by visual inspection of the forest plots, using a standard Chi² test and a significance level of α = 0.1, in view of the low power of such tests. We planned to use the Chi² test for heterogeneity to detect between‐trial heterogeneity. In addition, we planned to specifically examine the degree of heterogeneity observed in the results with the I² test according to the following classification: from 0% to 40%, heterogeneity may not be important; from 30% to 60%, heterogeneity may be moderate; from 50% to 90%, heterogeneity may be substantial; and from 75% to 100%, heterogeneity may be considerable (Higgins 2003). If there was heterogeneity, we planned to determine the potential reasons for it by examining the individual trial and subgroup characteristics.
Assessment of reporting biases
We planned to assess reporting biases with funnel plots of the relative risk estimates from the individual trials (plotted on a logarithmic scale) against trial size or precision (variance) or the estimators in case there were at least 10 trials.
Data synthesis
Meta‐analysis and assessment of significance
We planned to conduct this systematic review according to the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2011; Higgins 2019). We planned to use Review Manager 5 to analyse data and produce summary estimates of the treatment effect (Review Manager 2014). We planned to present results with a random‐effects meta‐analysis because we expected that the included trials would be heterogeneous. We planned to present results of continuous outcomes as MD or SMD, with 95% CI (Higgins 2011; Higgins 2019).
Subgroup analysis and investigation of heterogeneity
We planned to perform the following subgroup analyses because we expected that we would observe heterogeneity.
Trials at low risk of bias compared to trials at high risk of bias because trials at high risk of bias may overestimate or underestimate a treatment effect (Higgins 2011; Higgins 2019).
Primary prophylaxis of small varices compared to primary prophylaxis of only medium or large varices because of the different risk of bleeding according to the variceal size (Garcia‐Tsao 2017).
Children with chronic liver disease compared to children with extrahepatic portal vein obstruction because of the differences in the physiopathology of the cause of the portal hypertension in children with liver disease and alteration in the portal inflow (Chapin 2018).
Severity of liver disease (Child Pugh A, B, or C, and PELD or MELD) because of the different risk of bleeding according to the impaired liver function (Garcia‐Tsao 2017).
Children with cholestatic compared to children with non‐cholestatic liver disease because of the different risk of bleeding according to different aetiologies (Chapin 2018).
Sensitivity analysis
In addition to the sensitivity analyses specified under Dealing with missing data, and in order to assess the robustness of the eligibility criteria, our intention was to undertake sensitivity analyses in an attempt to explain our findings as well as any observed heterogeneity.
We planned to conduct Trial Sequential Analysis to assess imprecision in our primary and secondary outcome results (Thorlund 2017; TSA 2017), and compare the results of our assessment with the assessments of imprecision using GRADEpro GDT.
Trial Sequential Analysis
We planned to perform Trial Sequential Analysis (Thorlund 2017; TSA 2017) because cumulative meta‐analyses are at risk of producing random errors due to sparse data and repetitive testing of the accumulating data (Wetterslev 2008). To minimise random errors, we planned to calculate the required information size (i.e. the number of children needed in a meta‐analysis to detect or reject a certain intervention effect) (Wetterslev 2008).
The required information size calculation should also account for the heterogeneity or diversity present in the meta‐analysis (Wetterslev 2008; Wetterslev 2009; Wetterslev 2017). In our meta‐analyses, we planned to base the diversity‐adjusted required information size (DARIS) on the event proportion in the control group; assumption of a plausible relative risk reduction of 20% or the relative risk reduction observed in the included trials with low risk of bias; a risk of type I error of 2.5% because of three primary outcomes and 3.3% because of two secondary outcomes, a risk of type II error of 20%, and the observed diversity of the meta‐analysis (Wetterslev 2009; Jakobsen 2014; Wetterslev 2017).
The underlying assumption of Trial Sequential Analysis is that testing for significance may be performed each time a new trial is added to the meta‐analysis. We planned to add the trials according to the year of publication, and, if more than one trial was published in a year, we planned to add trials alphabetically according to the last name of the first author. Based on the DARIS, we planned to construct trial sequential monitoring boundaries (Wetterslev 2008; Thorlund 2017; Wetterslev 2017). These boundaries determine the statistical inference one may draw regarding the cumulative meta‐analysis that has not reached the required information size; if the trial sequential monitoring boundary for benefit or harm is crossed before the required information size is reached, firm evidence may be established and further trials may be superfluous. However, if the boundary is not surpassed, it is most probably necessary to continue conducting trials in order to detect or reject a certain intervention effect. This can be determined by assessing if the cumulative Z‐curve crosses the trial sequential monitoring boundaries for futility.
We planned to downgrade our assessment of imprecision in GRADE (see below) by two levels if the accrued number of participants was below 50% of the DARIS, and one level if between 50% and 100% of DARIS. We did not plan to downgrade if the cumulative Z‐curve reached futility or DARIS.
'Summary of findings' tables
We planned to create a 'Summary of findings' table to present information about the certainty of the evidence, magnitude of effects of the interventions, and summary data, using GRADEpro GDT, for all‐cause mortality, serious adverse events, quality of life, oesophageal variceal bleeding, and adverse events considered not serious. We also planned to provide the time and range of follow‐up. The GRADE approach appraises the certainty of a body of evidence based on the extent to which one can be confident that an estimate of effect or association reflects the item being assessed. The certainty of a body of evidence considers within‐study risk of bias, indirectness of the evidence (population, intervention, control, outcomes), unexplained inconsistency (heterogeneity) of results (including problems with subgroup analyses), imprecision of results, and risk of publication bias (Lundh 2017). We defined the certainty of the evidence as 'high', 'moderate', 'low', or 'very low' as follows.
High certainty: we are very confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect.
Moderate certainty: we are moderately confident in the effect estimate: the true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different.
Low certainty: our confidence in the effect estimate is limited: the true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect.
Very low certainty: we have very little confidence in the effect estimate: the true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimate of effect.
Results
Description of studies
We found no randomised clinical trials that qualified for inclusion in our systematic review.
Results of the search
We identified 1321 records in the initial electronic search for endoscopic interventions for primary prophylaxis of oesophageal variceal bleeding in children and adolescents and six additional records through searching other sources. After removing duplicates, 966 records remained. For this current systematic review, assessing band ligation versus sclerotherapy, we identified 124 records for abstract review. We excluded 110 because they did not meet the requirements for inclusion in this review (Figure 1). We retrieved the full‐text of the remaining 14 publications and assessed them for eligibility. None of them met the inclusion criteria of our review (see Characteristics of excluded studies table). However, five of the studies were of possible interest in terms of harm (Table 1). We did not find any ongoing studies relevant to our research question.
1.
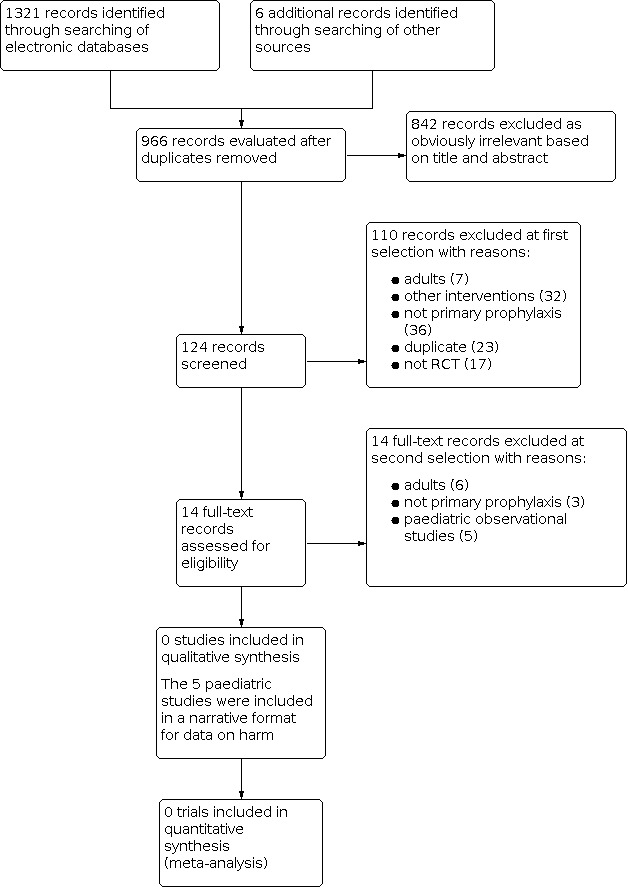
Study flow diagram.
1. Harms observed in observational studies.
| Study ID | Short summary | Report on harms |
| Duche 2013 | Single‐centre study of primary and secondary prophylaxis of bleeding in children with portal hypertension and high‐risk varices. 36 children (mean age 22 months) underwent primary prophylaxis for variceal bleeding with sclerotherapy or banding, or both, depending on age and weight of the child (15 (41%) banding; 16 (44%) sclerotherapy; 5 (14%) both). A mean number of 4.2 sessions was needed to eradicate varices; no bleeding from gastroesophageal varices was observed after eradication. |
In the primary prophylaxis group:
Mean follow‐up 2.3 years. |
| Duche 2017 | A single‐centre study (a later study of Duche 2013). 110 children with cirrhosis and 23 children with non‐cirrhotic causes of portal hypertension who underwent primary prophylaxis for variceal bleeding, from a cohort of 1300 children with portal hypertension were evaluated. | 110 children with cirrhosis:
Mean follow‐up 4.5 years. 23 children with non‐cirrhotic portal hypertension:
Mean follow‐up of 4.1 years. |
| Sutton 2015 | Single‐centre study assessing the efficacy and safety of primary prophylactic endoscopic band ligation and sclerotherapy for the prevention of variceal bleeding in children with portal hypertension of various aetiologies. Included 70 children with a mean age of 8.8 (standard deviation 4.7) years. Prophylactic endoscopic treatment (band ligation or sclerotherapy) was performed in 177 (65%) children, while 96 (35%) did not receive prophylactic endoscopic treatment. |
No severe or non‐severe adverse events in either group. |
| Sutton 2016 | Single‐centre observational study, presented in abstract form, assessing the efficacy and safety of primary prophylactic endoscopic band ligation and sclerotherapy for the prevention of variceal bleeding in children with portal hypertension. This abstract included 79 children with portal hypertension with a median age of 8 years. (This study followed the study of Sutton 2015 and was presented at a different conference.) |
No severe or non‐severe adverse events were reported in either group (prophylactic endoscopic treatment versus no prophylactic treatment). |
| Garcia Tirado 2019 | Single‐centre study presented in abstract form. It reported the outcomes of a small observational study of 9 children with portal hypertension due to a portal cavernoma, who received endoscopic treatment (variceal ligation/sclerotherapy) for primary (3 children) or secondary (6 children) prophylaxis of variceal bleeding. Of the 3 children who received endoscopic primary prophylaxis, the oesophageal varices were first degree in 2 and second degree in 1. None of these children bled during the follow‐up period of up to 9 months. No children presented complications during the procedures. |
No harms reported. |
Included studies
We found no trials that matched our inclusion criteria.
Excluded studies
We provided the reasons for exclusion of the 14 studies in the Characteristics of excluded studies table. Five of the 14 excluded studies were paediatric studies, and we read them to find reports on harm (Duche 2013; Sutton 2015; Sutton 2016; Duche 2017; Garcia Tirado 2019).
Risk of bias in included studies
Not assessed as no trials fulfilled the inclusion criteria.
Effects of interventions
No trial results due to lack of trials on the topic of this review.
Harms observed in observational studies, retrieved with the searches for randomised clinical trials
Five of the 14 excluded studies were considered for report of harms and are summarised in Table 1 (Duche 2013; Sutton 2015; Sutton 2016; Duche 2017; Garcia Tirado 2019).
Discussion
Summary of main results
We found no randomised clinical trials evaluating the use of band ligation versus sclerotherapy for primary prophylaxis of oesophageal variceal bleeding in children with chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis.
Overall completeness and applicability of evidence
Various observational studies reported experience with band ligation and sclerotherapy for primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding in children (Lampela 2012; Duche 2013; El‐Karaksy 2015; Sutton 2015; Sutton 2016; Duche 2017; Galand 2018; Angelico 2019). Studies on the use of endoscopic techniques for primary prophylaxis of portal hypertension in children suggested that these interventions have low rates of observed serious adverse effects (Duche 2013; Sutton 2015; Sutton 2016; Duche 2017; Garcia Tirado 2019; Table 1). Among the latter studies, only Duche 2017 reported one death, related to endoscopic sclerotherapy for primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding. However, these findings are limited by the design of the studies, small sample size, and short follow‐up period.
In summary, after performing a systematic review of the literature, we were unable to identify any randomised clinical trials evaluating the use of band ligation versus sclerotherapy for primary prophylaxis of oesophageal variceal bleeding in children with chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis.
One possible limitation for doing large randomised clinical trials in this area is the low prevalence of children with portal hypertension compared to adults. Also, the screening for varices in children with portal hypertension using endoscopy is not the current standard of care, and, therefore, several clinical practice, ethical, and financial challenges would need to be overcome if endoscopy and band ligation were to be included in a clinical trial protocol.
Quality of the evidence
We were unable to identify evidence from randomised clinical trials to support or refute the use of band ligation or sclerotherapy for primary prophylaxis of oesophageal variceal bleeding in children with chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis.
Potential biases in the review process
We identified no potential bias in the review process.
Agreements and disagreements with other studies or reviews
We identified no studies or systematic reviews to compare and discuss.
Authors' conclusions
Implications for practice.
Randomised clinical trials assessing the benefits or harms of band ligation versus sclerotherapy for primary prophylaxis of oesophageal variceal bleeding in children with chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis are lacking. Unless such trials are conducted and the results become published, we cannot make any conclusions regarding the benefits or harms of these two interventions.
Implications for research.
This systematic review has identified the need for well‐designed, adequately powered randomised clinical trials to assess the benefits and harms of band ligation versus sclerotherapy for primary prophylaxis of oesophageal variceal bleeding in children and adolescents with chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis. The randomised clinical trials should be multicentre and should include patient‐relevant clinical outcomes such as mortality, quality of life, failure to control variceal bleeding, and adverse events. The trials should follow the SPIRIT Statement (www.equator-network.org/reporting-guidelines/spirit-2013-statement-defining-standard-protocol-items-for-clinical-trials/; Chan 2013), The Foundation of Patient‐Centered Outcomes Research recommendations (PCORI 2012), and the CONSORT Statement (www.consort-statement.org/).
What's new
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 29 January 2021 | Amended | References within the review text updated |
History
Protocol first published: Issue 7, 2015 Review first published: Issue 11, 2020
Notes
This review will be updated once relevant randomised clinical trials for inclusion are identified.
Acknowledgements
Peer reviewers: Goran Bjelakovic, Serbia. Contact editors: Janus Christian Jakobsen, Denmark; Christian Gluud, Denmark. Sign‐off Editor: Christian Gluud, Denmark. Network Editor: Rachel Richardson, UK.
The authors wish express special gratitude to Dimitrinka Nikolova for all her help during the process.
We would also like to thank Jaime Cerda and Luis A Villarroel del Pino, for their work on the protocol.
Cochrane Review Group funding acknowledgement: the Danish State is the largest single funder of the Cochrane Hepato‐Biliary Group through its investment in the Copenhagen Trial Unit, Centre for Clinical Intervention Research, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital, Denmark. Disclaimer: the views and opinions expressed in this review are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the Danish State or the Copenhagen Trial Unit.
Appendices
Appendix 1. Search strategies
| Database | Time span | Search strategy |
| Cochrane Hepato‐Biliary Group Controlled Trials Register | April 2020 | (scleroth* OR scleros* OR alcoholic prolamine solution* OR ethanol* OR ethamolin* OR ethyl cellulos* OR phenol* OR polidocanol* OR (sodium AND (morrhuate OR tetradecyl)) OR hypertonic dextrose* OR scleromat* OR sotradecol*) AND ((endoscop* OR band* OR rubber) AND ligat*) OR (EBL OR EVL OR EBD) AND (child* OR pediat* OR paediat* OR infant* OR bab* OR newborn* OR pre‐school* OR preschool OR school* OR lactant* OR neonat* OR adolescent* OR youth OR young* OR toddler* OR teen* OR boy* OR girl* OR student* OR juvenil* OR minor* OR pubescen*) |
| Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) in the Cochrane Library | 2020, Issue 4 | #1 MeSH descriptor: [Sclerotherapy] explode all trees #2 MeSH descriptor: [Sclerosing Solutions] explode all trees #3 Scleroth* In Trials #4 Scleros* In Trials #5 alcoholic prolamine solution* In Trials #6 Ethanol* In Trials #7 Ethamolin In Trials #8 ethyl cellulose In Trials #9 MeSH descriptor: [Phenol] explode all trees #10 Phenol* In Trials #11 Polidocanol* In Trials #12 MeSH descriptor: [Sodium Morrhuate] explode all trees #13 Sodium morrhuate In Trials #14 MeSH descriptor: [Sodium Tetradecyl Sulfate] explode all trees #15 Sodium Tetradecyl In Trials #16 hypertonic dextrose In Trials #17 Scleromate In Trials #18 Sotradecol In Trials #19 #1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4 OR #5 OR #6 OR #7 OR #8 OR #9 OR #10 OR #11 OR #12 OR #13 OR #14 OR #15 OR #16 OR #17 OR #18 #20 MeSH descriptor: [Ligation] explode all trees #21 ((Endoscop* OR band* OR Rubber) ligat*) In Trials #22 (EBL or EVL or EBD) In Trials #23 #20 OR #21 OR #22 #24 MeSH descriptor: [Child, Preschool] explode all trees #25 MeSH descriptor: [Child] explode all trees #26 MeSH descriptor: [Adolescent] explode all trees #27 MeSH descriptor: [Infant, Newborn] explode all trees #28 MeSH descriptor: [Infant] explode all trees #29 (child* OR P*ediat* OR infant* OR baby OR pre‐school* OR lactant* OR neonate* OR adolescent* OR school‐child* OR youth OR toddler* OR teen* OR boy* OR girl* OR preschool* OR student* OR juvenile OR minor* OR pubescen* OR young* OR babies OR newborn*) In Trials #30 #24 OR #25 OR #26 OR #27 OR #28 OR #29 #31 #19 AND #23 AND #30 |
| PubMed | 1809 to April 2020 | #1 "Sclerotherapy"[Mesh] #2 "Sclerosing Solutions"[Mesh] #3 Scleroth* #4 Scleros* #5 "Sclerosing Solutions" [Pharmacological Action] #6 "alcoholic prolamine solution" [Supplementary Concept] #7 "ethanolamine oleate" [Supplementary Concept] #8 Ethanol* [tiab] #9 Ethamolin [tiab] #10 "ethyl cellulose" [Supplementary Concept] #11 "Phenol"[Mesh] #12 Phenol* [tiab] #13 "polidocanol" [Supplementary Concept] #14 Polidocanol* [tiab] #15 "Sodium Morrhuate"[Mesh] #16 Sodium morrhuate [tiab] #17 "Sodium Tetradecyl Sulfate"[Mesh] #18 Sodium Tetradecyl [tiab] #19 hypertonic dextrose [tiab] #20 Scleromate #21 Sotradecol [tiab] #22 #1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4 OR #5 OR #6 OR #7 OR #8 OR #9 OR #10 OR #11 OR #12 OR #13 OR #14 OR #15 OR #16 OR #17 OR #18 OR #19 OR #20 OR #21 #23 “Ligation”[Mesh] #24 ((Endoscop* OR band* OR Rubber) ligat* [tiab]) #25 (EBL OR EVL OR EBD [tiab]) #26 #23 OR #24 OR #25 #27 “Child, Preschool”[Mesh] #28 “Child”[Mesh] #29 “Adolescent”[Mesh] #30 “Infant, Newborn”[Mesh] #31 “Infant”[Mesh] #32 child* OR pediat* OR paediat* #33 infant* OR baby OR pre‐school* #34 lactant* OR neonate* OR adolescent* #35 school‐child* OR youth OR toddler* OR teen* #36 boy* OR girl* OR preschool* OR student* #37 juvenile OR minor* OR pubescen* #38 young* OR babies OR newborn* #39 #27 OR #28 OR #29 OR #30 OR #31 OR #32 OR #33 OR #34 OR #35 OR #36 OR #37 OR #38 #40 #22 AND #26 AND #39 |
| Embase (Elsevier) | 1966 to April 2020 | #1 'sclerotherapy'/exp AND [embase]/lim #2 'sclerosing agent'/exp AND [embase]/lim #3 scleroth*:ab,ti AND [embase]/lim #4 scleros*:ab,ti AND [embase]/lim #5 alcoholic prolamine solution:ab, ti OR alcoholic prolamine solutions:ab,ti AND [embase]/lim #6 'monoethanolamine oleate'/exp AND [embase]/lim #7 ethanol*:ab,ti AND [embase]/lim #8 ethamolin:ab,ti AND [embase]/lim #9 'ethyl cellulose'/exp AND [embase]/lim #10 'phenol'/exp AND [embase]/lim #11 phenol*:ab,ti AND [embase]/lim #12 'polidocanol'/exp AND [embase]/lim #13 polidocanol*:ab,ti AND [embase]/lim #14 'morrhuate sodium'/exp AND [embase]/lim #15 sodium morrhuate:ab,ti AND [embase]/lim #16 'tetradecyl sulfate sodium'/exp AND [embase]/lim #17 sodium tetradecyl:ab,ti AND [embase]/lim #18 hypertonic dextrose:ab,ti AND [embase]/lim #19 scleromate:ab,ti AND [embase]/lim #20 sotradecol:ab,ti AND [embase]/lim #21 #1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4 OR #5 OR #6 OR #7 OR #8 OR #9 OR #10 OR #11 OR #12 OR #13 OR #14 OR #15 OR #16 OR #17 OR #18 OR #19 OR #20 #22 'preschool child'/exp AND [embase]/lim #23 'child'/exp AND [embase]/lim #24 'adolescent'/exp AND [embase]/lim #25 'newborn'/exp AND [embase]/lim #26 'infant'/exp AND [embase]/lim #27 child* OR pediat* OR paediat* AND [embase]/lim #28 infant* OR 'baby'/exp OR baby OR 'pre‐school' AND [embase]/lim #29 lactant* OR neonate* OR adolescent* AND [embase]/lim #30 'school‐child' OR youth OR toddler* OR teen* AND [embase]/lim #31 boy* OR girl* OR preschool* OR student* AND [embase]/lim #32 juvenile OR minor* OR pubescen* AND [embase]/lim #33 young* OR babies OR newborn* AND [embase]/lim #34 #22 OR #23 OR #24 OR #25 OR #26 OR #27 OR #28 OR #29 OR #30 OR #31 OR #32 OR #33 #35 'ligation'/exp AND [embase]/lim #36 endoscop*:ab,ti OR band*:ab,ti OR 'rubber'/exp OR rubber:ab,ti AND ligat*:ab,ti AND [embase]/lim #37 ebl:ab,ti OR evl:ab,ti OR ebd:ab,ti AND [embase]/lim #38 #35 OR #36 OR #37 #39 #21 AND # 34 AND #38 |
| LILACS (Bireme) | 1982 to April 2020 | (Scleroth$ OR Scleros$ OR alcoholic prolamine solution$ OR ethyl cellulose OR polidocanol$ OR Sodium Morrhuate OR Sodium Tetradecyl OR Ethanol$ OR Ethamolin OR Phenol$ OR hypertonic dextrose OR Scleromate OR Sotradecol) [Words] and ( ligat$ AND (Endoscop$ OR band$ OR Rubber)) OR (EBL OR EVL OR EBD) [Words] and (child$ OR P$ediat$ OR infant$ OR baby OR pre‐school$ OR lactant$ OR neonate$ OR adolescent$ OR school‐child$ OR youth OR toddler$ OR teen$ OR boy$ OR girl$ OR preschool$ OR student$ OR juvenile OR minor$ OR pubescen$ OR young$ OR babies OR newborn$) [Words] |
| Science Citation Index Expanded (Web of Science) | 1900 to April 2020 | #1 TS=(Scleroth* OR Scleros* OR alcoholic prolamine solution* OR ethyl cellulose OR polidocanol* OR Sodium Morrhuate OR Sodium Tetradecyl OR Ethanol* OR Ethamolin OR Phenol* OR hypertonic dextrose OR Scleromate OR Sotradecol) #2 TS=( ligat* AND (Endoscop* OR band* OR Rubber)) #3 TS=(EBL OR EVL OR EBD) #4 #2 OR #3 #5 TS=(child* OR P*ediat* OR infant* OR baby OR pre‐school* OR lactant* OR neonate* OR adolescent* OR school‐child* OR youth OR toddler* OR teen* OR boy* OR girl* OR preschool* OR student* OR juvenile OR minor* OR pubescen* OR young* OR babies OR newborn*) #6 #1 AND #4 AND #5 |
s
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Avgerinos 2004 | Not a randomised clinical trial. This study investigated the early effects of endoscopic injection sclerotherapy and endoscopic band ligation in adults on hepatic venous pressure gradient during acute bleeding and the possible influence in outcome. |
| Berner 1994 | The trial was randomised but included adults (with previously documented high‐grade oesophageal varices to receive sclerotherapy or band ligation). |
| Bonilha 2011 | Not a randomised clinical trial. Prospective study in adults, assessing the rate of bacteraemia after elective band ligation and sclerotherapy with cyanoacrylate for oesophageal varices in adults with advanced liver disease. |
| Dobrucali 1998 | Not a randomised clinical trial. This was a single‐centre observational study comparing endoscopic ligation and sclerotherapy for secondary prophylaxis of oesophageal varices in adults. 79 adults admitted within 10 days of upper gastrointestinal bleeding episodes were included in this study. |
| Duche 2013 | An observational single‐centre study of primary and secondary prophylaxis of bleeding in children with portal hypertension and high‐risk varices. Considered for report of harm. |
| Duche 2017 | An observational study in which 110 children with cirrhosis and 23 children with non‐cirrhotic causes of portal hypertension underwent primary prophylaxis for variceal bleeding, from a cohort of 1300 children with portal hypertension. Considered for report of harm. |
| Garcia Tirado 2019 | An observational paediatric study of 9 children with portal hypertension due to a portal cavernoma. Children received endoscopic treatment (variceal ligation/sclerotherapy) for primary (3 children) or secondary (6 children) prophylaxis of variceal bleeding. Considered for report of harm. |
| Khatami 2011 | A randomised controlled trial of sclerotherapy versus band ligation but for a secondary prophylaxis of oesophageal varices in children with extrahepatic portal hypertension and oesophageal varices. This abstract was not subsequently published as a full text. |
| Lu 2013 | Not a randomised clinical trial. This observational study assessed the efficacy and safety of endoscopic ligation and sclerotherapy for secondary prophylaxis of oesophageal varices. The study included 10 children. All included children had active variceal bleeding, or had a high risk for bleeding varices, and recent clinical history of anaemia. Four children were repeatedly hospitalised because of recurrent bleeding. |
| Nakase 1994 | Not a randomised clinical trial. This observational study assessed the safety of band ligation therapy compared with sclerotherapy for the treatment of oesophageal varices in 19 adults. |
| Santos 2011 | The trial was a randomised controlled trial, but in adults. 38 adults with medium or large oesophageal varices and Child Pugh index ≥ 8 were randomised to receive band ligation versus cyanoacrylate injection. |
| Sutton 2015 | An observational study assessing the efficacy and safety of primary prophylactic endoscopic band ligation and sclerotherapy for the prevention of variceal bleeding in children with portal hypertension of various aetiologies. Considered for report of harms. |
| Sutton 2016 | An observational study assessing the efficacy and safety of primary prophylactic endoscopic band ligation and sclerotherapy for the prevention of variceal bleeding in 79 children with portal hypertension, with a median age of 8 years. Considered for report of harms. |
| Young 1993 | The trial was a randomised controlled trial, but in adults. The trial compared local complications of oesophageal variceal ligation and oesophageal variceal sclerotherapy for the treatment of oesophageal varices in 23 adults. |
Differences between protocol and review
During the review editorial process, following advice of peer reviewers and editors, we did the following modifications to the protocol part of the review (Gana 2015).
The title of our published protocol was 'Banding ligation versus sclerotherapy for primary prophylaxis of oesophageal variceal bleeding in children'. Following advice from peer reviewers and the contact editor, we modified the title and it now reads: 'Band ligation versus sclerotherapy for primary prophylaxis of oesophageal varices in children with chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis'.
We updated text in the background section.
We modified outcomes as follows.
We removed 'bleeding‐related mortality' (our secondary first outcome in the protocol) as it is covered by 'all‐cause mortality' and 'serious adverse events' in the review.
We defined the 'serious‐adverse events' outcome better, by also adding liver‐related morbidity (i.e. proportion of participants who developed ascites, hepatorenal syndrome, hepatocellular carcinoma, or hepatic encephalopathy).
We defined quality of life, that is, we planned to measure health‐related quality of life exclusively by means of validated scales, classification and measurement systems like the Paediatric Quality of Life Inventory (PedsQL), Child Health Questionnaire (CHQ), and DISABKIDS.
We modified the formulation of the 'non‐serious adverse events' in the protocol into 'Adverse events considered not serious (any adverse event that did not meet the above criteria for serious adverse events)' in this review in order to increase clarity.
We removed the secondary third outcome in the protocol 'Overall gastrointestinal bleeding' at contact editor’s request.
In addition, we added information about the timing of outcomes.
We formulated the text in Subgroup analysis and investigation of heterogeneity better.
We updated the methodological part of our protocol to reflect methodology developments at the time of the review preparation. This also included removal the 'for‐profit' bias risk domain as it is included in the GRADE factor: publication bias.
We expanded our search methods.
We detailed 'Unit of analysis issues'.
We moved the text on Trial Sequential Analysis in sensitivity analysis.
We defined the outcomes for presentation in 'Summary of findings' tables.
Two authors of the protocol, Jaime Cerda and Luis A Villarroel del Pino, did not continue work on the review.
Contributions of authors
JCG: formulated the research question; drafted and reviewed the final product. LC: provided methodological expert opinion; participated in the selection of titles, abstracts, and full texts; and reviewed the final product. DG: participated in the selection of titles, abstracts, and full texts; and reviewed the final product. RTR: provided the search strategies and reviewed the final product. All authors agreed on the publication of the review in its present form.
Sources of support
Internal sources
No source was provided, Other
External sources
No source was provided, Other
Declarations of interest
JCG: none LC: none DG: none RTR: none
Edited (no change to conclusions)
References
References to studies excluded from this review
Avgerinos 2004 {published data only}
- Avgerinos A, Armonis A, Stefanidis G, Mathou N, Vlachogiannakos J, Kougioumtzian A, et al. Sustained rise of portal pressure after sclerotherapy, but not band ligation, in acute variceal bleeding in cirrhosis. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2004;39(6):1623-30. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Berner 1994 {published data only}
- Berner JS, Gaing AA, Sharma R, Almenoff PL, Muhlfelder T, Korsten MA. Sequelae after esophageal variceal ligation and sclerotherapy: a prospective randomized study. American Journal of Gastroenterology 1994;89(6):852-8. [PMID: ] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bonilha 2011 {published data only}
- Bonilha DQ, Correia LM, Monaghan M, Lenz L, Santos M, Libera ED. Prospective study of bacteremia rate after elective band ligation and sclerotherapy with cyanoacrylate for esophageal varices in patients with advanced liver disease. Arquivos de Gastroenterologia 2011;48(4):248-51. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dobrucali 1998 {published data only}
- Dobrucali A, Bal K, Tuncer M, İlkova F, Çelik A, Uzunismail H, et al. Endoscopic banding ligation compared with sclerotherapy for the treatment of espohageal varices. Turkish Journal of Gastroenterology 1998;9:340-4. [Google Scholar]
Duche 2013 {published data only}
- Duche M, Ducot B, Ackermann O, Baujard C, Chevret L, Frank-Soltysiak M, et al. Experience with endoscopic management of high-risk gastroesophageal varices, with and without bleeding, in children with biliary atresia. Gastroenterology 2013;145(4):801-7. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Duche 2017 {published data only}
- Duche M, Ducot B, Ackermann O, Guerin F, Jacquemin E, Bernard O. Portal hypertension in children: high-risk varices, primary prophylaxis and consequences of bleeding. Journal of Hepatology 2017;66(2):320-7. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Garcia Tirado 2019 {published data only}
- Garcia Tirado D, Molera C, De La Calle E, Domínguez P, Larrarte M, Pujol G, et al. Endoscopic prophylaxis for upper digestive bleeding prevention in patients with portal cavernoma. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2019;68(Suppl 1):798. [Google Scholar]
Khatami 2011 {published data only}
- Khatami Ghazvini K, Khatami Ghazvini G, Farahmand F, Najafi Sani M. A prospective randomized clinical trial of sclerotherapy versus band ligation in the treatment of esophageal varices in children with extrahepatic portal hypertension. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2011;52:E71-2. [Google Scholar]
Lu 2013 {published data only}
- Lu JP, Huang Y, Chen SY, Wu J. Endoscopic treatment of gastroesophageal varices: efficacy and safety in children. Hong Kong Journal of Paediatrics 2013;18:139-46. [Google Scholar]
Nakase 1994 {published data only}
- Nakase H, Sakatani N, Nasuno K, Yamamoto Y, Ohno K, Sawai S. Effects of endoscopic esophageal varices ligation therapy on liver, kidney and lung function. Japanese Journal of Gastroenterological Endoscopy 1994;36(11):2147-55. [Google Scholar]
Santos 2011 {published data only}
- Santos MM, Tolentino LH, Rodrigues RA, Nakao FS, Rohr MR, Paulo GA, et al. Endoscopic treatment of esophageal varices in advanced liver disease patients: band ligation versus cyanoacrylate injection. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2011;23(1):60-5. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sutton 2015 {published data only}
- Sutton H, Davenport M, Baker AJ, Dhawan A, Grammatikopoulos T. Prophylactic endoscopic treatment of gastrointestinal varices in children with portal hypertension. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2015;62:277A-8A. [Google Scholar]
Sutton 2016 {published data only}
- Sutton H, Davenport M, Baker A, Dhawan A, Grammatikopoulos T. Prophylactic endoscopic therapy in children with portal hypertension. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2016;62:555-6. [Google Scholar]
Young 1993 {published data only}
- Young MF, Sanowski RA, Rasche R. Comparison and characterization of ulcerations induced by endoscopic ligation of esophageal varices versus endoscopic sclerotherapy. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy 1993;39(2):119-22. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Additional references
Al‐Khazraji 2019
- Al-Khazraji A, Curry MP. The current knowledge about the therapeutic use of endoscopic sclerotherapy and endoscopic tissue adhesives in variceal bleeding. Expert Review of Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2019;13(9):893-7. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Angelico 2019
- Angelico R, Pietrobattista A, Candusso M, Tomarchio S, Pellicciaro M, Liccardo D, et al. Primary prophylaxis for gastrointestinal bleeding in children with biliary atresia and portal hypertension candidates for liver transplant: a single-center experience. Transplantation Proceedings 2019;51(1):171-8. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Carneiro 2018
- Carneiro de Moura M, Chen S, Kamath BM, Ng VL, Ling SC. Acute variceal bleeding causes significant morbidity. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2018;67(3):371-6. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Chan 2013
- Chan AW, Tetzlaff JM, Gotzsche PC, Altman DG, Mann H, Berlin JA, et al. SPIRIT 2013 explanation and elaboration: guidance for protocols of clinical trials. BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.) 2013;346:e7586. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Chapin 2018
- Chapin CA, Bass LM. Cirrhosis and portal hypertension in the pediatric population. Clinics in Liver Disease 2018;22(4):735-52. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cifuentes 2021a
- Cifuentes LI, Gattini D, Torres-Robles R, Gana JC. Beta-blockers versus placebo or no intervention for primary prophylaxis of oesophageal variceal bleeding in children with chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2021, Issue 1. Art. No: CD011973. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011973.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cifuentes 2021b
- Cifuentes LI, Gattini D, Torres-Robles R, Gana JC. Band ligation versus sham or no intervention for primary prophylaxis of oesophageal variceal bleeding in children and adolescents with chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2021, Issue 1. Art. No: CD011561. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011561.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Di Giorgio 2019
- Di Giorgio A, De Angelis P, Cheli M, Vajro P, Iorio R, Cananzi M, et al. Etiology, presenting features and outcome of children with non-cirrhotic portal vein thrombosis: a multicentre national study. Digestive and Liver Disease 2019;51(8):1179-84. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Duche 2010
- Duche M, Ducot B, Tournay E, Fabre M, Cohen J, Jacquemin E, et al. Prognostic value of endoscopy in children with biliary atresia at risk for early development of varices and bleeding. Gastroenterology 2010;139(6):1952-60. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ebel 2019
- Ebel NH, Carlin K, Shaffer ML, Shivaram G, Hawkins M, Lane ER, et al. Hepatic venous pressure gradient measurements in children: correlation with hepatic histology and clinical indicators of portal hypertension. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2019;68(6):788-92. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
El‐Karaksy 2015
- El-Karaksy HM, El-Koofy N, Mohsen N, Helmy H, Nabil N, El-Shabrawi M. Extrahepatic portal vein obstruction in Egyptian children. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2015;60(1):105-9. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Eroglu 2004
- Eroglu Y, Emerick KM, Whitingon PF, Alonso EM. Octreotide therapy for control of acute gastrointestinal bleeding in children. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2004;38(1):41-7. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Galand 2018
Gana 2010
- Gana JC, Turner D, Roberts EA, Ling SC. Derivation of a clinical prediction rule for the noninvasive diagnosis of varices in children. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2010;50(2):188-93. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gana 2011a
- Gana JC, Valentino PL, Morinville V, O'Connor C, Ling SC. Variation in care for children with esophageal varices: a study of physicians', patients', and families' approaches and attitudes. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2011;52(6):751-5. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gana 2011b
- Gana JC, Turner D, Mieli-Vergani G, Davenport M, Miloh T, Avitzur Y, et al. A clinical prediction rule and platelet count predict esophageal varices in children. Gastroenterology 2011;141(6):2009-16. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gana 2019
- Gana JC, Cifuentes LI, Gattini D, Villarroel Del Pino LA, Pena A, Torres-Robles R. Band ligation versus beta-blockers for primary prophylaxis of oesophageal variceal bleeding in children with chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2019, Issue 9. Art. No: CD010546. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010546.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Garcia‐Tsao 2007
- Garcia-Tsao G, Sanyal AJ, Grace ND, Carey WD. Prevention and management of gastroesophageal varices and variceal hemorrhage in cirrhosis. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2007;102(9):2086-102. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Garcia‐Tsao 2017
- Garcia-Tsao G, Abraldes JG, Berzigotti A, Bosch J. Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: risk stratification, diagnosis, and management: 2016 practice guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2017;65(1):310-35. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gattini 2020a
- Gattini D, Cifuentes LI, Torres-Robles R, Gana JC. Sclerotherapy versus beta-blockers for primary prophylaxis of oesophageal variceal bleeding in children and adolescents with chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2020, Issue 1. Art. No: CD011659. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011659.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gattini 2020b
- Gattini D, Cifuentes LI, Torres-Robles R, Gana JC. Sclerotherapy versus sham or no intervention for primary prophylaxis of oesophageal variceal bleeding in children with chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2020, Issue 3. Art. No: CD011573. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011573.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Goncalves 2000
- Goncalves ME, Cardoso SR, Maksoud JG. Prophylactic sclerotherapy in children with esophageal varices: long-term results of a controlled prospective randomized trial. Journal of Pediatric Surgery 2000;35(3):401-5. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
GRADEpro GDT [Computer program]
- McMaster University (Developed by Evidence Prime) GRADEpro GDT. Version accessed 4 November 2019. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (Developed by Evidence Prime), 2015. Available at gradepro.org.
Groszmann 2004
- Groszmann RJ, Bosch J, editor(s). Portal Hypertension in the 21st Century. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2004. [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2003
- Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.) 2003;327(7414):557-60. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2011
- Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2019
- Higgins JP, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, et al, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.0 (updated August 2019). Cochrane, 2019. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
ICH‐GCP 1997
- International Conference on Harmonisation Expert Working Group. International conference on harmonisation of technical requirements for registration of pharmaceuticals for human use. ICH harmonised tripartite guideline. Guideline for good clinical practice CFR & ICH Guidelines. Vol. 1. Philadelphia (PA): Barnett International/PAREXEL, 1997. [Google Scholar]
Imperiale 2001
- Imperiale TF, Chalasani N. A meta-analysis of endoscopic variceal ligation for primary prophylaxis of esophageal variceal bleeding. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2001;33(4):802-7. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jakobsen 2014
- Jakobsen J, Wetterslev J, Winkel P, Lange T, Gluud C. Thresholds for statistical and clinical significance in systematic reviews with meta-analytic methods. BMC Medical Research Methodology 2014;14:120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jeanniard‐Malet 2017
- Jeanniard-Malet O, Duche M, Fabre A. Survey on clinical practice of primary prophylaxis in portal hypertension in children. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2017;64(4):524-7. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kamath 2001
- Kamath PS, Wiesner RH, Malinchoc M, Kremers W, Therneau TM, Kosberg CL, et al. A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2001;33(2):464-70. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kjaergard 2001
- Kjaergard LL, Villumsen J, Gluud C. Reported methodologic quality and discrepancies between large and small randomized trials in meta-analyses. Annals of Internal Medicine 2001;135(11):982-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lampela 2012
- Lampela H, Kosola S, Koivusalo A, Lauronen J, Jalanko H, Rintala R, et al. Endoscopic surveillance and primary prophylaxis sclerotherapy of esophageal varices in biliary atresia. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2012;55(5):574-9. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ling 2005
- Ling SC. Should children with esophageal varices receive beta-blockers for the primary prevention of variceal hemorrhage? Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology 2005;19(11):661-6. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ling 2011
- Ling SC, Walters T, McKiernan PJ, Schwarz KB, Garcia-Tsao G, Shneider BL. Primary prophylaxis of variceal hemorrhage in children with portal hypertension: a framework for future research. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2011;52(3):254-61. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lundh 2017
- Lundh A, Lexchin J, Mintzes B, Schroll JB, Bero L. Industry sponsorship and research outcome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2017, Issue 2. Art. No: MR000033. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.MR000033.pub3] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lykavieris 2000
- Lykavieris P, Gauthier F, Hadchouel P, Duche M, Bernard O. Risk of gastrointestinal bleeding during adolescence and early adulthood in children with portal vein obstruction. Journal of Pediatrics 2000;136(6):805-8. [PMID: ] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
McDiarmid 2002
- McDiarmid SV, Anand R, Lindblad AS. Development of a pediatric end-stage liver disease score to predict poor outcome in children awaiting liver transplantation. Transplantation 2002;74(2):173-81. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Miga 2001
- Miga D, Sokol RJ, Mackenzie T, Narkewicz MR, Smith D, Karrer FM. Survival after first esophageal variceal hemorrhage in patients with biliary atresia. Journal of Pediatrics 2001;139(2):291-6. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mileti 2011
- Mileti E, Rosenthal P. Management of portal hypertension in children. Current Gastroenterology Reports 2011;13(1):10-6. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Moher 1998
- Moher D, Pham B, Jones A, Cook DJ, Jadad AR, Moher M, et al. Does quality of reports of randomised trials affect estimates of intervention efficacy reported in meta-analyses? Lancet 1998;352(9128):609-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Parolini 2019
- Parolini F, Boroni G, Milianti S, Tonegatti L, Armellini A, Garcia Magne M, et al. Biliary atresia: 20–40-year follow-up with native liver in an Italian centre. Journal of Pediatric Surgery 2019;54(7):1440-4. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
PCORI 2012
- Basch E, Aronson N, Berg A, Flum D, Gabriel S, Goodman SN, et al. Methodological standards and patient-centeredness in comparative effectiveness research: the PCORI perspective. JAMA 2012;307(15):1636-40. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pugh 1973
- Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, Pietroni MC, Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. British Journal of Surgery 1973;60(8):646-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Review Manager 2014 [Computer program]
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Royle 2003
- Royle P, Milne R. Literature searching for randomized controlled trials used in Cochrane reviews: rapid versus exhaustive searches. International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care 2003;19(4):591-603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Samanta 2011
- Samanta T, Purkait R, Sarkar M, Misra A, Ganguly S. Effectiveness of beta blockers in primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding in children with portal hypertension. Tropical Gastroenterology 2011;32(4):299-303. [PMID: ] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Savović 2012a
- Savović J, Jones HE, Altman DG, Harris RJ, Jüni P, Pildal J, et al. Influence of reported study design characteristics on intervention effect estimates from randomized, controlled trials. Health Technology Assessment 2012;16(35):1-82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Savović 2012b
- Savović J, Jones HE, Altman DG, Harris RJ, Jüni P, Pildal J, et al. Influence of reported study design characteristics on intervention effect estimates from randomized, controlled trials. Annals of Internal Medicine 2012;157(6):429-38. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Savović 2018
- Savović J, Turner RM, Mawdsley D, Jones HE, Beynon R, Higgins JP, et al. Association between risk-of-bias assessments and results of randomized trials in Cochrane Reviews: the ROBES Meta-Epidemiologic Study. American Journal of Epidemiology 2018;187(5):1113-22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schulz 1995
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias. Dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273(5):408-12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Shneider 2012
- Shneider BL, Bosch J, Franchis R, Emre SH, Groszmann RJ, Ling SC, et al. Portal hypertension in children: expert pediatric opinion on the report of the Baveno v Consensus Workshop on Methodology of Diagnosis and Therapy in Portal Hypertension. Pediatric Transplantation 2012;16(5):426-37. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Shneider 2016
- Shneider BL, Ville de Goyet J, Leung DH, Srivastava A, Ling SC, Duche M, et al. Primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding in children and the role of MesoRex bypass: summary of the Baveno VI Pediatric Satellite Symposium. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2016;63(4):1368-80. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Thorlund 2017
- Thorlund K, Engstrøm J, Wetterslev J, Brok J, Imberger G, Gluud C. User manual for Trial Sequential Analysis (TSA). ctu.dk/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/tsa_manual_ENG.pdf 2017 (accessed 28 January 2021).
TSA 2017 [Computer program]
- Copenhagen Trial Unit TSA - Trial Sequential Analysis. Version 0.9.5.10 Beta. Copenhagen: Copenhagen Trial Unit, 2017. ctu.dk/tsa/downloads/.
van Heurn 2004
- Heurn LW, Saing H, Tam PK. Portoenterostomy for biliary atresia: long-term survival and prognosis after esophageal variceal bleeding. Journal of Pediatric Surgery 2004;39(1):6-9. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Verdaguer 2016
- Verdaguer DS, Gana AJ. Management of pediatric patients with esophageal varices [Enfrentamiento de pacientes pediatricos con varices esofagicas]. Revista Medica de Chile 2016;144(7):879-85. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wetterslev 2008
- Wetterslev J, Thorlund K, Brok J, Gluud C. Trial sequential analysis may establish when firm evidence is reached in cumulative meta-analysis. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2008;61(1):64-75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wetterslev 2009
- Wetterslev J, Thorlund K, Brok J, Gluud C. Estimating required information size by quantifying diversity in a random-effects meta-analysis. BMC Medical Research Methodology 2009;9:86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wetterslev 2017
- Wetterslev J, Jakobsen JC, Gluud C. Trial Sequential Analysis in systematic reviews with meta-analysis. BMC Medical Research Methodology 2017;17(1):39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wood 2008
- Wood L, Egger M, Gluud LL, Schulz KF, Jüni P, Altman GD, et al. Empirical evidence of bias in treatment effect estimates in controlled trials with different interventions and outcomes: meta-epidemiological study. BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.) 2008;336:601-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to other published versions of this review
Gana 2015
- Gana JC, Cifuentes LI, Cerda J, Villarroel del Pino LA, Peña A, Torres-Robles R. Banding ligation versus sclerotherapy for primary prophylaxis of oesophageal varices in children. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 7. Art. No: CD011803. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011803] [DOI] [Google Scholar]


