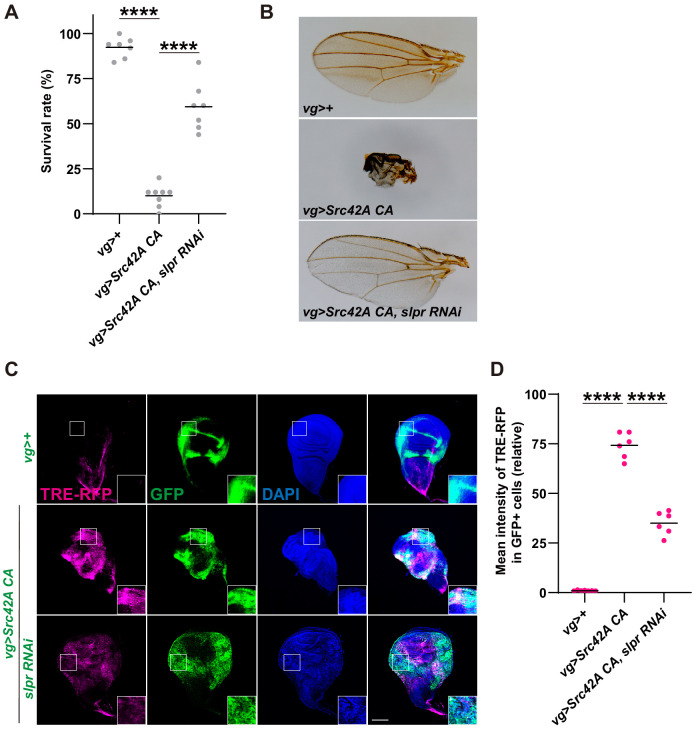
Figure 2. Inhibition of Slpr suppresses the phenotypes induced by Src activation.
(A) Src42A constitutively active (CA) expression in the wing disc induces organismal lethality, which is suppressed by knockdown of slpr. One-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post-test. (B) The small, disheveled wing phenotype of the rare escapers with Src42A CA is suppressed by knockdown of slpr. (C) Src42A CA-mediated JNK activation, which was detected by the TRE-RFP reporter, is suppressed by knockdown of slpr. (D) Quantification of TRE-RFP in C. One-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post-test. Scale bars, 100 µm.