To the editor:
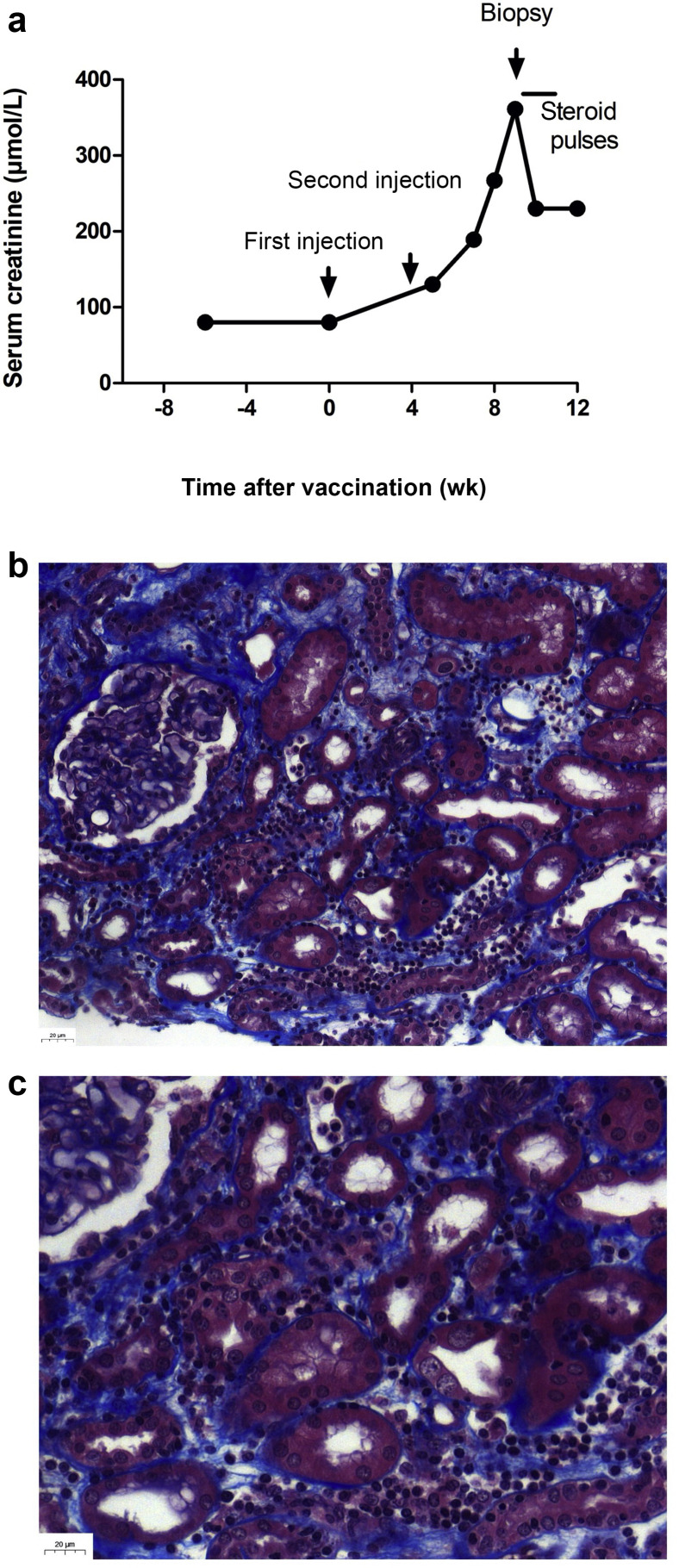
Anti–severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccination is recommended in patients who underwent a transplant because of an increased risk of developing severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), and mortality.1 Because of a weak immunogenicity of mRNA 2-dose vaccines in transplant patients, the French Health Authority recommended to offer a third dose to immunosuppressed patients to boost the immune response.2 , 3 However, no biological monitoring before and after vaccination is recommended. We report on the case of a 23-year-old non–human leukocyte antigen–sensitized patients who underwent a kidney transplant who presented an acute rejection after the second dose of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine (Pfizer-BioNTech). She had undergone a deceased donor kidney transplantation for nephronophthisis 18 months earlier. The post-transplant period was uneventful. Her maintenance therapy was based on tacrolimus (target trough level, 5 ng/ml and 7 ng/ml), mycophenolic acid, and low-dose steroid. Fifteen days before the first dose, her serum creatinine level was at 80 μmol/L and anti–SARS-CoV-2 serology was negative. Eight days after the second dose, systematic blood tests revealed impaired kidney function at 130 μmol/L, which then raised to 360 μmol/L (Figure 1 ). A kidney biopsy revealed a cellular acute rejection. Donor-specific anti–human leukocyte antigen antibodies became detectable with a weak intensity, targeting donor human leukocyte antigen class II antigens. Anti–SARS-CoV-2 spike protein antibodies became positive. Tacrolimus trough level was unchanged at 5 ng/ml. At 10 days, after steroid pulses (500 mg/d for 3 days), the patient’s serum creatinine level had decreased to 230 μmol/L. Another kidney biopsy is planned to discuss the use of polyclonal antibodies. Hence, this report suggests that kidney function should be carefully monitored in kidney transplantation undergoing anti–SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, especially if a third boost dose is performed.
Figure 1.
(a) Outcome of kidney function before and after transplantation and (b,c) kidney pathology. Trichrome Masson staining exhibited inflammatory infiltration, tubulitis, edema, and peritubular capillaritis (original magnification ×20 [b] and ×40 [c]). Kidney biopsy was scored as follows, according to the Banff 2019 classification4: i2, t2, v0, g0, ptc1, ti1, i-IFTA0, C4d0, cg0, mm0, ah1, cv0, ci0, ct0. To optimize viewing of this image, please see the online version of this article at www.kidney-international.org.
References
- 1.Caillard S., Anglicheau D., Matignon M., et al. An initial report from the French SOT COVID Registry suggests high mortality due to COVID-19 in recipients of kidney transplants. Kidney Int. 2020;98:1549–1558. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.08.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Boyarsky B.J., Werbel W.A., Avery R.K., et al. Immunogenicity of a single dose of SARS-CoV-2 messenger RNA vaccine in solid organ transplant recipients. JAMA. 2021;325:1784–1786. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.4385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.https://www.mesvaccins.net/textes/dgs_urgent_n43_vaccination_modalites_d_administration_des_rappels.pdf Centre opérationnel de régulation et de réponse aux urgences sanitaires et sociales. Vaccins contre la Covid-19: modalités d'administration des rappels. Available at: Accessed April 11, 2021.
- 4.Mengel M., Loupy A., Haas M., et al. Banff 2019 Meeting Report: molecular diagnostics in solid organ transplantation-consensus for the Banff Human Organ Transplant (B-HOT) gene panel and open source multicenter validation. Am J Transplant. 2020;20:2305–2317. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]