Patients in the active phase of treatment for cancer are a population at risk of coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) with poor prognosis.1 While a majority of patients treated for cancer expressed their will to be vaccinated as early as December 2020 in a French survey,2 no data were available in terms of vaccine efficacy and tolerance, because they were excluded from initial registration trials.
From the beginning of French vaccination campaign, we set up a BNT162b2 (Pfizer/BioNtech) vaccine monitoring observatory (VMO) for vaccinated patients under active treatment in the Department of Oncology of the Saint Jean Polyclinic, Nice, France (∼9000 annual treatment sessions). All participants signed a written consent after receiving an information letter and the VMO was registered with the French authorities, according to ethical and legal policies. A control group of healthy volunteers (HVs), i.e. without known ongoing cancer, was also formed and vaccinated during the same period. Serological assays were realized at week (w) 0 during the first vaccination, during the booster (w3-w4) and 3-4 weeks after the booster (w6-w8). Immunogenicity was measured with Elecsys® Anti-SARS-CoV-2 immunoassay (Roche Diagnostics, Mélan, France) with detection of antibodies directed to total antibodies against the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike (S) protein receptor-binding domain (quantitative detection). Serum showing a result ≥ 0.8 UI/ml was declared positive.
We report the results of the first 122 assessable patients with solid tumors included since 18 January 2021 having carried out at least two serologies by 15 March 2021 out of 194 vaccinated patients during this period (64.4%). Three patients were excluded from the final analysis because they had pre-vaccine anti-SARS-CoV-2 immunity. The median age of the 122 patients was 69.5 years (44-90 years), with 64 men (52.5%) and 58 women (47.5%). We analyzed 31 HVs; 2 were excluded from the analysis because they had pre-vaccine immunity against SARS-CoV-2. Among the remaining 29 HVs with a median age of 53 years (range: 21-81 years), 13 carried out the intermediate assessment at w3-w4 and 24 carried out their final w6-w8 assessment.
Among the 122 patients, 105 (86.0%) were treated with chemotherapy (CT) ± targeted therapy. One patient developed COVID-19 with a positive PCR at day 12 from vaccine dose 1. The outcome was quickly favorable and the patient had his booster dose at w3. During the first serological analysis at w3-w4, 58 [47.5%, 95% confidence interval (CI) 38.4-56.8] patients had an anti-S seroconversion. After recall at w6-w8, 40 (95.2%, 95% CI 83.8-99.4) of the analyzable patients presented an anti-S seroconversion; 2 patients kept an anti-S level <0.8 IU/ml. In comparison with the control group, 13 (100.0%, 95% CI 75.3-100.0) patients had an anti-S seroconversion at w3-w4 and 24 (100.0%, 95% CI 85.7-99.4) at w6-w8. Fewer patients under CT had an anti-S seroconversion at w3-w4 than patients without CT, and with targeted therapy alone (42.9% versus 76.5%; P = 0.016).
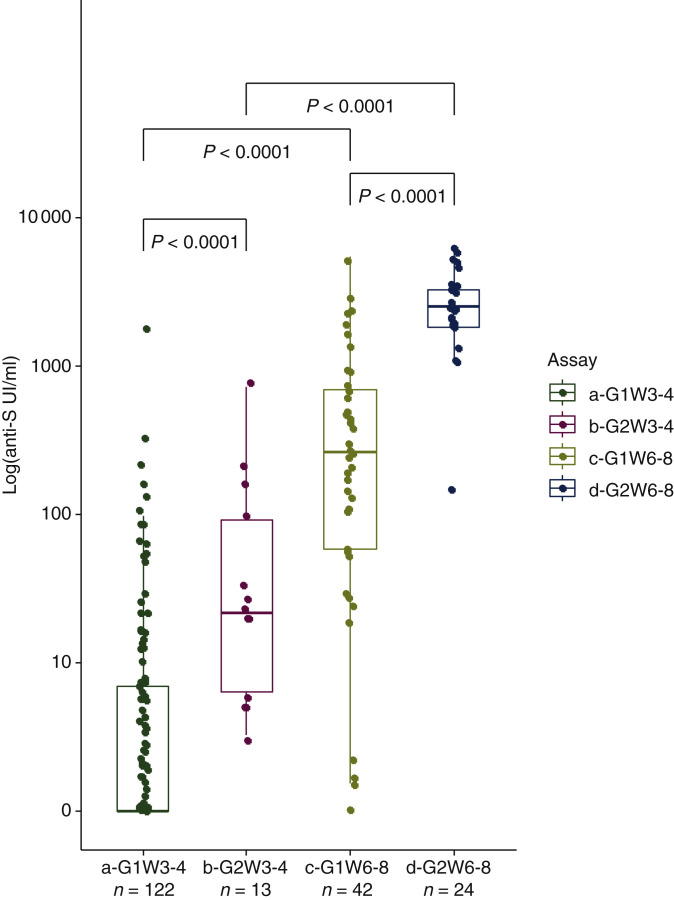
Median anti-S antibody levels were significantly lower than the levels observed in the HV group at w3-w4 (0.52 UI/ml, range: 0-1962 UI/ml, respectively, versus 21.6 UI/ml, range: 3.26-723.2 UI/ml, P < 0.001) and at w6-w8 (245.2 UI/ml, range: 0-5467 UI/ml, respectively, versus 2517 UI/ml, range: 157.6-6318.0 UI/ml, P < 0.001) (Figure 1 ). After the booster dose, the median anti-S antibody levels increased significantly for both patients and HVs (P < 0.001).
Figure 1.
Humoral quantitative anti-spike (S) antibody (logarithmic scale) response at week (w) 3-w4 and w6-w8 from dose 1 of BNT162b2 (Pfizer/BioNtech) messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccine in patients with active treatment for cancer (G1; n = 122) and in a healthy volunteer (HV) group (G2; n = 24).
a-G1W3-4: cohort of patients with active treatment for cancer at w3-w4/from dose 1 of BNT162b2 (Pfizer/BioNtech) mRNA vaccine (date of booster dose); b-G2W3-4: HV group at w3-w4; c-G1W6-8: cohort of patients at w6-w8 from dose 1 of vaccine; d-G2W6-8: HV group at w6-w8.
No serious adverse event was reported.
Impaired immunogenicity of BNT162b2 anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in immunocompromised patients was reported among solid organ transplant recipients.3 Among patients under cancer therapy, influenza vaccine was less efficient compared to the whole population.4 Considering the high proportion of weakly responsive or unresponsive patients in this setting after a single dose, patients should be informed of the need to maintain strict social protection measures for at least 6-8 weeks after the first dose of the vaccine and we strongly recommend not to shift the booster dose schedule in patients under CT. The duration of immunity acquired under CT as well as the level of protection against the different SARS-CoV-2 variants are unknown. As already shown for influenza vaccine,5 efficacy of a second booster dose (third dose) has to be studied.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We acknowledge the following individuals for their assistance with this study, none of whom was compensated for his or her contributions: Drs Steve-Dumont Marie and Leylavergne Sabine for vaccines order management; the whole team of the day hospital nurses of the Saint Jean Polyclinic (Fiancet Annabel, Nisi Bianca, Coli Cecilia, Sarkis Pauline, Rebuffel Jennifer, Getrey Charlotte, Feraud Linda) and the medical assistants (Barriere Stéphanie, Chopard Edith, Caron Muriel) for their daily management of vaccinations and the management of patient schedules; Schiappa Renaud for declaring the database to French authorities; Drs Cassuto Ophélie, Borchiellini Delphine, Peyrade Frédéric, Gastaud Lauris, Hoch Benjamin, Denis Eric, Moubarak Carl, Etienne Cédric, Marcq Laurent and Musini Elisa for their help in designing and the smooth running of the study; Cerballiance Côte d'Azur staff for the biological support and financial support; and above all the patients and healthy volunteers who participated in the study.
Funding
Cerballiance Côte d'Azur supported the additional cost for antibodies dosage (no grant number). No additional funding or support was reported.
Disclosure
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Wang Q., Berger N.A., Xu R. Analyses of risk, racial disparity, and outcomes among US patients with cancer and COVID-19 infection. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7(2):220–227. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.6178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Barrière J., Gal J., Hoch B. Acceptance of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination among French patients with cancer: a cross-sectional survey. Ann Oncol. 2021;32(5):673–674. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.01.066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Boyarsky B.J., Werbel W.A., Avery R.K. Immunogenicity of a single dose of SARS-CoV-2 messenger RNA vaccine in solid organ transplant recipients. JAMA. 2021;325(17):1784–1786. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.4385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Meerveld-Eggink A., de Weerdt O., van der Velden A.M.T. Response to influenza virus vaccination during chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2011;22(9):2031–2035. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdq728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rousseau B., Loulergue P., Mir O. Immunogenicity and safety of the influenza A H1N1v 2009 vaccine in cancer patients treated with cytotoxic chemotherapy and/or targeted therapy: the VACANCE study. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(2):450–457. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdr141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]