Abstract
Background
Traditional medicine is a major component in the primary healthcare system in the southeast of Iran, which has a rich floral diversity. However, there is no comprehensive report on the use of medicinal herbs in this specific region. This traditional usage of medicinal plants by local communities could serve as a source for pharmacological and phytochemical studies. The main objective of this study was to identify ethnopharmacological knowledge on medicinal plant species and their local healing applications by the folk communities of Kerman province in the southeast of Iran.
Methods
In this cross-sectional study, data were collected from 217 herbal healers using semi-structured questionnaires, open interviews, and field surveys. Factors including use reports (UR) for each species, frequency of citation (FC), and informant consensus factor (ICF) were used to analyze the data. Plant species were identified by botanists through standard taxonomic methods.
Results
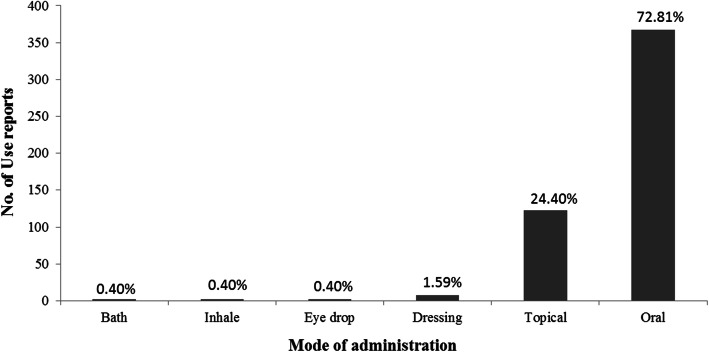
A total of 402 medicinal plants were used in healing practices by the local communities of Kerman province. These species belong to 273 genera of 73 families, among which 367 species are dicotyledons, 27 are monocotyledons, 7 species are cryptogam, and one species is gymnosperm. An important implication from the current study is the identification of the traditional medicinal use of 292 plant species in this region for the first time. Asteraceae, Apiaceae, Lamiaceae, and Fabaceae were the dominant medicinally utilized plant families, respectively. Leaf, flower, fruit, and seed were the most common plant parts used. Generally, crude drugs were used in the form of decoction, followed by poultice and infusion forms. Moreover, oral route is considered as the most common administration route followed by topical route. Endocrine (diabetes), dermatological, gastrointestinal, and respiratory problems were ranked as the most frequent ailment categories for which medicinal plants in this region were applied, respectively. Our findings suggested dominant use of Asteraceae and Apiaceae plants for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders, Lamiaceae plants for respiratory and gastrointestinal ailments, and Apocynaceae plants for dermatological problems.
Conclusion
Our findings suggested that Asteraceae and Apiaceae plants were used for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders, Lamiaceae plants for respiratory and gastrointestinal ailments, and Apocynaceae and Euphorbiaceae plants for dermatological problems. Among the medicinal plants with high UR and new ethnobotanical uses, Rhazya stricta was used for wound healing, Calotropis procera, Clematis ispahanica and Euphorbia spp. for eczema, Cionura erecta for the treatment of cough, Launaea acanthodes for the treatment of gastrointestinal parasites, Berberis integrrima as an antidiabetic medicinal herb, Dracocephalum polychaetum and Rydingia persica for various types of chronic diseases, Citrus limon and Citrus aurantium for the treatment of ocular diseases and making the traditional kohl, Calendula officinalis for the treatment of pterygium and Prosopis farcta for preventing nasal bleeding. The identified medicinal plants can be further evaluated for their pharmacological activity and underlying mechanisms of action.
Keywords: Ethnobotany, Medicinal plants, ICPC category, Kerman province, Iran
Introduction
According to the reports, medicinal use of plants dates back to at least 60,000 years. During this time, traditional systems of medicines have employed medicinal plants and their derivatives as valuable sources of new biologically active compounds and have been clinically practiced all over the world [1]. Until now, approximately 80% of the world’s population still use traditional herbal medicines [2]. In fact, herbal medicines can serve as complementary or alternative therapies for different types of diseases because of their low cost, availability, and generally fewer side effects [3]. Several FDA-approved drugs including artemisinin (from Artemisia annua), quinine (from Cinchona officinalis), vinblastine, vincristine, vinorelbine (from Vinca rosea), and etoposide (from Mayapple) primarily originate from traditional herbal medicines [4]. It has been estimated that nearly 400,000 flowering plant species exist on earth, among which only 6% have been evaluated for their biological properties, and still more than 90% remains unexplored [5]. Therefore, ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants provides valuable information for the synthesis of new drugs.
Around 8000 plant species have been listed in Iran, of which 2300 species have medicinal properties among which 75% (1728) are endemic species in Iran [6, 7].
Kerman province with 23 cities and 171,993 square kilometers area has covered about 11% of the land area of Iran [8], located in the southeast of this country, and bordered by 5 provinces of Yazd, South Khorasan, Hormozgan, Fars, and Sistan and Baluchestan. It has a unique biodiversity due to its diverse natural resources and climatic conditions including desert and semi-desert in the north, and dry, mountainous and Mediterranean in the south. Kerman province is a vast plain with the lowest altitude in Lut desert (300 m) and the highest altitude in the mountaintop of Hezar (4419 m) [8]. Based on the traditional pharmacopoeia and medicinal plant reports in some parts of this province, medicinal herbs mostly belong to the families of Labiatae, Rosaceae, Papilionacae, Compositae, and Umbelliferae, and the genera of Salvia, Nepeta, Artemisia, Astragalus, Ferula, Plantago, Ephedra, and Amygdalus [9, 10].
From the cultural point of view, Kerman province has around 89 tribal communities (including Baluch, Turkish, and Fars), most of them still being partially dependent on the medicinal plants. Therefore, this province is home to different cultures and beliefs resulting in rich traditional knowledge and traditional medicine practices. For example, the old city of Jiroft in the southeastern Kerman province dates to about 5000 years ago, which, according to the reports, is the beginning of human civilization [11]. In this respect, traditional medicine has played a key role in Iranian culture and civilization [12]. Therefore, this rich traditional knowledge is useful not only in the ancient medical systems but also in the present healthcare systems [10], especially for primary health care needs [13]. In fact, the dependence of the folk communities in Kerman on the medicinal herbs is not only due to the low availability to the health care system, but it is also rooted in the Iranian-rich culture of traditional medicine [14, 15]. For example, in the face of epidemiological diseases (e.g., cholera and colds), scientists of the Iranian traditional medicine (ITM) such as Avicenna, Rhazes, and Aghili Alavi Shirazi have suggested prescription of various herbal remedies. At present, the locals of Kerman, based on their ancient knowledge, utilize herbal medicines such as Thymus fedtschenkoi, Zataria multiflora, Dracocephalum polychaetum, and Glycyrrhiza glabra in the treatment of epidemics. Generally, Kerman province with a diverse climate and biodiversity is home to various cultures (from the prehistoric times to the present) and the center of agriculture in Iran [10, 16]. Accordingly, in some areas of this region, certain non-registered herbaceous species are used that can be obtained by the local people. There are many villages and nomadic districts that are largely dependent on the ethnomedicinal knowledge for primary health care, with many specific traditional herbal medicine practices in this region that have not been recorded anywhere else. Hence, the current study aimed to carefully investigate and record the ethnobotanical knowledge of the whole districts and cultures, particularly subcultures that had the maximum dependence on the traditional health care system of the Kerman province.
Materials and methods
Study area
The present study was carried out in Kerman province in the southeast of Iran with 23 cities and 3,164,716 inhabitants. Regarding population, the most populated city is Kerman with the following other cities as progressively less populated: Jiroft, Sirjan, Rafsanjan, Kahnuj, Rudbar, Anbarabad, Qale Ganj, Manojan, Faryab, Zarand, Bam, Fahraj, Narmashir, Rigan, ShahrBabak, Baft, Rabor, Orzueeyeh, Bardsir, Ravar, Anar, and Koohbanan. In the current study, in each city, skilled herbalists, nomadic districts, and key villages were selected for data sampling. Kerman province is located between the 55 min and 25° to 32° north latitude and 26 min and 53° to 29 min and 59° east of the Greenwich meridian, as the largest province in Iran with the total area of 183.285 km2, and the elevation of 400 to 4501 m above the sea level. About 6.3 million hectares of deserts of Iran (equivalent to 20%) are located in Kerman province. The area of the forests of Kerman province is 1.3 million hectares and belongs to the two vegetation regions of Irano-Turanian and Khaleej-Omani.
Species of the Irano-Turanian forest of Kerman are comprised of Pistacia atlantica, Pistacia khinjuk, Juniperus excels, Prunus scoparia, Crataegus azarolus, Celtis australis in the mountainous area, and Haloxylon spp. and Calligonum spp. in the desert area. Also, the species of Khaleej-Omani include Calotropis procera, Tamarix spp., Prosopis spp., and Ziziphus spp. and the endemic rare species of Tecomella undulate with the local names Golpar and Anar sheytan (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Study area, Kerman province, southeast Iran
Plant identification
Based on the maps, access roads, natural features, vegetation, and subcultures in the study area, each city was classified into districts. Then, the number of the informants was determined. The plant specimens were collected during the field surveys from nomadic, rural, and urban areas of Kerman province from 2017 to 2019. The herbarium specimens were prepared following standard methods [17–19] and identified with the help of Herbarium of the University of Jiroft and Kerman Agricultural and Natural Resources Research and Education Center. Nomenclature was corrected using an online database (the international plant names index and the plant lists). The voucher herbarium specimens were deposited in the herbarium of the Department of Plant Biology, University of Jiroft, Jiroft, Iran. The voucher specimens were identified by one of the authors (H.B) and reaffirmed by taxonomic experts from the Department of Plant Biology at the herbarium of the University of Jiroft.
Ethnobotanical data collection
After classification of each city into districts, ethnobotanical surveys were carried out from October 2017 to the end of May 2019. The ethnobotanical data was collected using field surveys, open interviews, and semi-structured questionnaires. A total of 217 local informants (91 females and 126 males) aged between 30 and 79 years old were interviewed. Demographic properties including educational level, gender, age group, and occupation are recorded in Table 1. Also, geographical location and altitude (the lowest being 409 m in Manojan and the highest being 2800 m in Lalehzar) of each district are recorded in Table 2. Furthermore, information on local name, medicinal use, part(s) of the plant used, preparation, and administration methods is recorded (Table 3).
Table 1.
Demographic profile of the local healers (n=217)
| Characteristics | Abundance | Relative abundance | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 126 | 57.60 |
| Female | 91 | 42.60 | |
| Education | Primary level | 103 | 47.47 |
| Secondary level | 86 | 39.63 | |
| Graduate | 28 | 12.90 | |
| Age group | 30-45 | 51 | 23.50 |
| 46-60 | 132 | 60.83 | |
| 61-79 | 34 | 15.67 | |
| Occupation | Nomadic tribe | 94 | 43.31 |
| Farmer | 78 | 35.94 | |
| Herbal healer | 45 | 20.74 | |
Table 2.
Studied districts in the Kerman province with in-detail demographic characteristics of the local informants
| Area | Village- nomadic district | Altitude | Location | Number of informants | Gender | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude | Longitude | Male | Female | ||||
| Jiroft | Esfandaghe | 1724 | 515518 | 3173088 | 6 | 5 | 1 |
| Boluk | 653 | 550080 | 3123049 | 4 | 3 | 1 | |
| Northen Jebal barez | 1973 | 586377 | 3198024 | 5 | 4 | 1 | |
| Sardooiyeh | 2622 | 532724 | 3234040 | 13 | 7 | 6 | |
| Central part | 682 | 573397 | 3172706 | 8 | 5 | 3 | |
| Anbarabad | Southern Jebal barez | 890 | 613586 | 3136457 | 9 | 7 | 2 |
| Central part | 597 | 581969 | 3150210 | 5 | 2 | 3 | |
| Kahnuj | Dehkehan | 810 | 556930 | 3066254 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Dehzard | 518 | 548076 | 3086568 | 2 | - | 2 | |
| Central part | 513 | 568775 | 3090872 | 5 | 4 | 1 | |
| Faryab | Sargorij | 692 | 555482 | 3111865 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Mehuiyeh | 649 | 539817 | 3107390 | 3 | 2 | 1 | |
| Moordan | 1118 | 508786 | 3125367 | 1 | 1 | - | |
| Central part | 659 | 522398 | 3107510 | 1 | 1 | - | |
| Rudbar-e Jonub | Zehkalut | 385 | 656761 | 3075068 | 2 | - | 2 |
| Mil-e Farhad | 816 | 674888 | 3113175 | 1 | 1 | - | |
| Central part | 488 | 597867 | 3100902 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Qaleh Ganj | Sorkhqleh | 439 | 595145 | 3071601 | 1 | 1 | - |
| Maarz | 937 | 591255 | 2998867 | 3 | 2 | 1 | |
| Central part | 407 | 586721 | 3045020 | 4 | 1 | 3 | |
| Manujan | Nodej | 464 | 544955 | 3044682 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Central part | 358 | 549652 | 3035783 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Baft | Bazenjan | 2346 | 470709 | 3235218 | 2 | - | 2 |
| Khabr | 2039 | 434312 | 3188268 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Central part | 2262 | 461018 | 3233719 | 5 | 3 | 2 | |
| Rabor | Sardmeshk | 2495 | 509371 | 3247951 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Qanat Malek | 2300 | 503669 | 3238948 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| Central part | 2332 | 491445 | 3240172 | 4 | 3 | 1 | |
| Sirjan | Balvard | 2035 | 407806 | 3254993 | 6 | 4 | 2 |
| Pariz | 2313 | 379188 | 3305535 | 4 | 2 | 2 | |
| Central part | 1744 | 372254 | 3258624 | 5 | 1 | 4 | |
| Rafsanjan | Bahreman | 1330 | 377582 | 3419214 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Kabutatkhan | 1662 | 438574 | 3352462 | 3 | 3 | - | |
| Central part | 1515 | 403788 | 3364209 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Anar | Central part | 1414 | 334675 | 3416022 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| Ravar | Central part | 1181 | 481234 | 3459578 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Zarand | Hotkan | 2325 | 479943 | 3412892 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| Mahmud abad | 1651 | 454636 | 3406622 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| Central part | 1656 | 458637 | 3408681 | 4 | 3 | 1 | |
| Shahr Babak | Estabraq | 1794 | 316665 | 3326121 | 2 | 2 | - |
| Mehrabad | 1817 | 319991 | 3327739 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Meymand | 2218 | 343549 | 3345546 | 5 | 2 | 3 | |
| Central part | 1840 | 318777 | 3332404 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| Koohbanan | Joz | 1989 | 431829 | 3470143 | 2 | 2 | - |
| Central part | 1991 | 431755 | 3475352 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Bam | Dehbakri | 2039 | 589237 | 3215060 | 5 | 4 | 1 |
| Central part | 1068 | 631396 | 3220002 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Fahraj | Central part | 678 | 683329 | 3204470 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Narmashir | Central part | 753 | 665948 | 3204479 | 2 | 2 | - |
| Rigan | Koosha | 1586 | 658487 | 3137050 | 2 | - | 2 |
| Central part | 756 | 666076 | 3203853 | 2 | - | 2 | |
| Orzueeyeh | Central part | 1044 | 436602 | 3148052 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| Bardsir | Lalehzar | 2800 | 481843 | 3266686 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| Negar | 2090 | 480752 | 3302559 | 3 | 3 | - | |
| Central part | 2042 | 459122 | 3311509 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Kerman | Mahan | 1854 | 524742 | 3327108 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Shahdad | 429 | 568791 | 3365494 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| Rayen | 2161 | 542947 | 3274724 | 4 | 2 | 2 | |
| Jopar | 1887 | 510333 | 3324762 | 5 | 4 | 1 | |
| Central part | 1757 | 508230 | 3351251 | 11 | 7 | 4 | |
| Total | 217 | 126 | 91 | ||||
Table 3.
Medicinal plants used by ethnic communities in the Kerman province
| Family | Scientific name | Local name (Persian); Voucher no. |
Plant part used |
Medicinal use (UR) | ICPC category |
Preparation | Mode of application | (UR) | A, B, C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acanthaceae | Blepharis edulis (Forssk.) Pers. | Anjereh 503 | Leaf, Seed | Wound healing (3), Ear ache (2), Eye ache (2), Sore throat (3) | DER-S | Poultice, Decoction | Topical | 10 | A |
| Amaranthaceae | Amaranthus retroflexus L. | Sorkhmaghz 598 | Leaf | Jaundice (18) | GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 18 | B, C |
| Amaranthaceae | Anabasis aphylla L. | Aldorak 596 | Aerial parts | Weight loss (3), Constipation (1) | OTH-A, GAS-D | Aromatic water | Oral | 4 | B, C |
| Amaranthaceae | Seidlitzia rosmarinus Bunge ex Boiss. | Shoor 594 | Aerial parts | Washing powder (5) | -, - | Powder | - | 5 | B, C |
| Amaranthaceae | Salsola incanescens C.A. Mey. | Jar 593 | Aerial parts | Washing powder (2) | -, - | Powder | - | 2 | B, C |
| Amaranthaceae | Dysphania botrys (L.) Mosyakin & Clemants | Dermeneh 595 | Young flowering branches | Beauty of skin and hair (4) | DER-S | Oil | Topical | 4 | B, C |
| Amaranthaceae | Suaeda aegyptiaca (Hasselq.) Zohary | Somsil 597 | Aerial parts | Blood purifier (4), Anemia (29), Vegetable (48) | OTH-A, Blood-B | Vegetable | Oral | 81 | B, C |
| Amaryllidaceae | Allium atroviolaceum Boiss. | Piaze vahshi 268 | Bulb | Reduce blood sugar (2) | MET-T | Vegetable | Oral | 2 | B, C |
| Amaryllidaceae | Allium iranicum (Wendelbo) Wendelbo. | Serit 245 | Leaf | Aromatic (4), Flavoring of food (33), Digestive (6) | NER-N, -, GAS-D | Spice | Oral | 43 | B, C |
| Amaryllidaceae | Ixiolirion tataricum (Pall.) Schult. & Schult.f. | Kheyaroo 269 | Leaf and flower | Pickle (6) | OTH-A | Vegetable | Oral | 6 | B, C |
| Amaryllidaceae | Narcissus tazetta L. | Narges 267 | Bulb, Leaf | Face rash treatment (3), Sterility treatment (2), Gastric discomfort (2), Blood coagulation (4), Anti-depressants (5) | DER-S, DER-S, GAS-D, Blood-B, NER-N | Mask, Decoction, infusion | Topical, Oral | 16 | A, C |
| Anacardiaceae | Pistacia atlantica Desf. | Baneh 623 | Seed | Bone and joint pains (5), Burn healing (68), Wound healing (26), Eczema (34) | SKE-L,DER-S, DER-S, DER-S | Oil | Topical | 208 | A |
| Olibanum | Scar (39) | DER-S | Poultice | Topical | |||||
| Olibanum | Lung infections (1) | RES-R | Fume | Inhale | |||||
| Leaf, Olibanum | Stomach ulcers (31), Toothache (2) | GAS-D, GAS-D | Extract, Gum | Oral | |||||
| Fruit, Olibanum | Disinfectant (2) | OTH-A | Edible | Oral | |||||
| Anacardiaceae | Pistacia khinjuk Stocks | Kasour 621 | Seed, Leaf | Hemorrhoid (1), Stomachache (9), Toothache (2), Memory Improvement (2), Jaundice (1) | CAR-K, GAS-D, GAS-D, NER-N, GAS-D | Nuts, Mixed with date, Gum | Oral | 15 | A |
| Anacardiaceae | Pistacia vera L. | Pesteh 620 | Fruit | Reinforcing sexual desire (2), Anti-nausea (1), Anti-diarrhea (1), Constipation (3) | OTH-A, GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D, | Nuts | Oral | 7 | A |
| Apiaceae | Ammi majus L. | Golsefid 220 | Fruit | Anti-nausea (5), diuretic (4) | GAS-D, URO-U | Decoction | Oral | 9 | A |
| Apiaceae | Anethum graveolens L. | Maitokhm 234 | Seed | Blood fat (3), Gastric discomfort (32), Energetic (2), Reduce blood sugar (2), Joint pain (5) | Blood-B, GAS-D, OTH-A, MET-T, SKE-L | Decoction | Oral | 44 | A |
| Apiaceae | Apium graveolens L. | Karafs 221 | Aerial parts | Relaxing (1), Disinfectant (2), Flavoring of food (40) | NER-N, OTH-A, - | Mixed with food, Vegetable | Oral | 43 | B, C |
| Apiaceae | Bunium persicum (Boiss.) B.Fedtsch. | Ziresiah 227 | Seed | Menstrual disorders (30), Flavoring of food (115), Digestive (2), Parasite repellent (3), Carminative (4), Antispasmodic (31), | GYN-X, OTH-A, GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D, NER-N | Decoction, Infusion, Mixed with food | Oral | 185 | A |
| Apiaceae | Carum carvi L. | Ziresiah 230 | Fruit | Carminative (6), Relaxing (1) | GAS-D, NER-N | Infusion | Oral | 7 | A, C |
| Apiaceae | Conium maculatum L. | Showkaran 233 | Whole plant | Cough (4), Respiratory ailments (6) | RES-R, RES-R | Decoction | Oral | 10 | A |
| Apiaceae | Coriandrum sativum L. | Geshniz 238 | Leaf, Seed, Aerial parts | Reduce blood sugar (3), Intestinal infections (2), Blood fat (4), lactiferous (5), Flavoring of food (18) Carminative (3) | MET-T, GAS-D, Blood-B, PRE-W, OTH-A, GAS-D | Decoction, Dried vegetable | Oral | 35 | A |
| Apiaceae | Cuminum cyminum L. | Ziresabz 225 | Seed | Menstrual disorders (10), Flavoring of food (14), Body tonic (5) | GYN-X, -, OTH-A | Decoction, Infusion, Mixed with food | Oral | 29 | A |
| Apiaceae | Daucus carota L. | Havij 235 | Bulb | Anemia (8), Sight enhancement (7), Appetizing (3) | Blood-B, EYE-F, OTH-A | Salad | oral | 18 | A, C |
| Apiaceae | Dorema ammoniacum D. Don | Oshtork 258 | Gum | Disinfectant (4), Edible (7), Infectious wound healing (11) | OTH-A, OTH-A, DER-S | Powder, Mask, Poultice, Vegetable | Oral | 22 | A |
| Apiaceae | Dorema aucheri Boiss. | Oshtork 249 | Gum | Disinfectant (4), Edible (7), Infectious wound (11) | OTH-A, OTH-A, DER-S | Powder, Mask, Poultice, Vegetable | Oral | 22 | A |
| Apiaceae | Ducrosia anethifolia (DC.) Boiss. | Reshkak 291 | Leaf, Seed | Abdominal pains (6), Body tonic (7), Child Carminative (9) | GAS-D, OTH-A, GAS-D | Infusion | Oral | 22 | A |
| Apiaceae | Ducrosia assadii Alava. | Reshkak 237 | Leaf and fruit | Wound and burns healing (8) | DER-S | Oil | Topical | 8 | A |
| Apiaceae | Eryngium billardieri Delile | Chichagh 240 | Aerial parts | Expectorant (4), Bronchitis (4), Antispasmodic (1), Carminative (2), Cough (4), Pain relief (3), Reduce rheumatic pain (1) | RES-R, RES-R, NER-N, GAS-D, RES-R, SKE-L | Decoction | Oral | 19 | B, C |
| Apiaceae |
Eryngium bungei Boiss. |
Shoochagh 242 | Aerial parts | Pain relief (4) | NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 4 | B |
| Apiaceae | Ferula assa-foetida L. | Anghouze 245 | Gum | Parasite intestine (16), Expectorant (2), Menstrual disorders (2), Gastritis (5) | GAS-D, RES-R, GYN-X, GAS-D | Fume, Infusion | Oral | 25 | A |
| Apiaceae | Ferula gummosa Boiss. | Anghouzeh 236 | Gum | Cough (6), Laxative (3) | RES-R, GAS-D | Infusion | Oral | 9 | A |
| Apiaceae | Ferula oopoda (Boiss. & Buhse) Boiss. | Anghouzeh 252 | Latex, Fruit | Toothache (35), Carminative (18), Intestinal parasite (30), Tooth infection (10), Expectorant (4) | GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D, RES-R | Poultice, Decoction | Oral | 97 | A |
| Apiaceae | Ferula ovina (Boiss.) Boiss. | Anghouze shirin 247 | Aerial parts | Carminative (15) | GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 15 | A |
| Apiaceae | Ferula persica Willd. | Anghouzeh 250 | Latex, Fruit | Cough (6), Laxative (3) | RES-R, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 9 | A |
| Apiaceae | Ferula szowitziana DC. | Anghouze 254 | Latex | Stomachache (6) | GAS-D | Cooked with meat and vegetables | Oral | 6 | A |
| Apiaceae | Ferulago angulata (Schltdl.) Boiss. | Garchi 257 | Aerial parts | Carminative (6), Flavoring of butter (1), Aromatherapy (1) | GAS-D, OTH-A | Decoction, Powder, Dressing | Oral | 8 | A |
| Apiaceae | Foeniculum vulgare Mill. | Badiuon 244 | Seed | Carminative (41), Gastric discomfort (27), Bone and joint pains (12), Asthma (1), Digestive (11) | GAS-D, GAS-D, SKE-L, RES-R, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 92 | A |
| Apiaceae | Pulicaria undulata (L.) C.A.Mey. | Sooteh 259 | Leaf | Dysentery (10), Wound healing (3) | GAS-D, DER-S | Decoction, Poultice | Oral, Topical | 14 | A, C |
| Apiaceae | Heracleum persicum Desf. ex Fisch., C.A.Mey. & Avé-Lall. | Golpar 258 | Fruit, Flower | Relaxing (8) | NER-N | Aromatic water | Oral | 8 | B, C |
| Apiaceae | Levisticum officinale W.D.J.Koch | Karasm 262 | Aerial part | Carminative (5), Gastric discomfort (10), Blood pressure (19) | GAS-D, GAS-D, CAR-K | Aromatic water | Oral | 34 | B, C |
| Apiaceae | Levisticum persicum Freyn & Bornm. | Karasm 260 | Aerial parts, Stem | Pickle (3), Aromatherapy (1), Flavoring of food (2) | OTH-A, OTH-A | Decoction, Dressing, Powder | Oral | 5 | A |
| Apiaceae | Petroselinum crispum (Mill.) Fuss | Jafari 229 | Young branches | Urinary stone (3), Digestive (12), Anemia (5) | URO-U, GAS-D, Blood-B | Decoction | Oral | 20 | A |
| Apiaceae | Pimpinella saxifraga L. | Jafari Kouhi 263 | Leaf | Stomachache (21) | GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 21 | A |
| Apiaceae | Platychaete aucheri (Boiss.) Boiss. | Zarbarook 255 | Leaf | Asthma (7) | RES-R | Decoction | Oral | 7 | A, C |
| Apiaceae | Prangos cheilanthifolia Boiss. | Sekbinch 280 | Young branches, Gum | Carminative (5) | GAS-D | Mixed with food | Oral | 5 | B, C |
| Apiaceae | Prangos ferulacea (L.) Lindl. | Garchi 253 | Foliage | Flavoring of dairy (8), Parasite repellent (6), Toothache (7), Carminative (3), Acne (2), Infectious wound (5) | -, GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D, DER-S, DER-S | Edible, Decoction, Poultice | Oral, Topical | 41 | B, C |
| Apiaceae | Prangos uloptera DC. | Jashir 270 | Young branches | Carminative (15), Body tonic (17) | GAS-D, OTH-A | Mixed with food | Oral | 32 | A, C |
| Apiaceae | Psammogeton stocksii (Boiss.) Nasir | Izbok 273 | Aerial parts | Febrifuge (4) | OTH-A | Decoction | Oral | 4 | B, C |
| Apiaceae | Scandix stellata Banks & Sol. | Badiyan koohi 275 | Whole plant | Body tonic (25), Stomach tonic (13) | OTH-A, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 38 | B, C |
| Apiaceae | Trachyspermum ammi (L.) Sprague | Kaserk 277 | Fruit | Stomachache (19), Carminative (7) | GAS-D, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 26 | A |
| Apiaceae | Pycnocycla spinosa Decne. | Sagdandan 279 | Root | Scorpion bite (1) | OTH-A | Decoction | Oral | 2 | B, C |
| Apiaceae | Pycnocycla bashgardiana Mozaff. | Pvander 288 | Flower | Stomachache (2) | GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 3 | B, C |
| Apocynaceae | Calotropis procera (Aiton) Dryand. | Kark 849 | Latex | Eczema (98), Scorpion bite (9), Earache (4), Toothache (6), Cancer (1) | DER-S, DER-S, Ear-H, GAS-D, CAN-C | Latex | Topical, Oral | 151 | B |
| Leaf | Reduce blood sugar (11), Bruise (10) | MET-T, SKE-L | Poultice | Topical | |||||
| Apocynaceae | Cionura erecta (L.) Griseb. | Jaze sabz 852 | Leaf | Sore throat (3), Expectorant (77), Cough (87) | OTH-A, RES-R, RES-R | Decoction | Oral | 167 | B, C |
| Apocynaceae | Nerium oleander L. | Gish 861 | Leaf | Stomachache (3), Skin diseases (1) | GAS-D | Decoction, Latex | Oral | 4 | A, C |
| Apocynaceae | Pergularia tomentosa L. | Keshtook 855 | Latex | Eczema (2), Constipation (1), Parasite repellent (2), Cancer (1) | DER-S, GAS-D, CAN-C | Poultice, Decoction | Topical, Oral | 15 | B, C |
| Whole parts | Hair removal of animal skin (9) | OTH-A | Decoction | Topical | |||||
| Apocynaceae | Periploca aphylla Decne. | Shirbadam 853 | Latex, Aerial parts | Burn healing (3), Skin inflammation (5) | DER-S, DER-S | Mask, Poultice | Topical | 8 | B, C |
| Apocynaceae | Rhazya stricta Decne. | Eshbarg 859 | Leaf | Scorpion and snake bite (5), Sore throat (2), Febrifuge (41), Ear ache (1), Eye ache (1) | DER-S | Decoction | Bath | 173 | B |
| Leaf | Wound healing (63), Joint pains (57), Reduce blood sugar (3) | DER-S, SKE-L, MET-T | Poultice | Topical | |||||
| Arecaceae | Phoenix dactylifera L. | Mogh 1123 | Pollen | Improvement of male fertility (11) | PRE-W | Mixed with honey | Oral | 17 | B, C |
| Pith parenchyma | Memory improvement (5) | NER-N | Edible | Oral | |||||
| Arecaceae | Nannorrhops ritchieana (Griff.) Aitch. | Daz1 125 | Fruit | Vegetable (8) | OTH-A | Edible | Oral | 8 | B, C |
| Asparagaceae | Leopoldia comosa (L.) Parl. | Sirmook 1235 | Bulb | Anti-diarrhea (2), Bronchitis (3), Cough (1) | GAS-D, RES-R, RES-R | Mixed with food | Oral | 6 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Achillea eriophora DC. | Gole bengerask 921 | Flowering branches | Relaxing (4), Gastric discomfort (7), Parasite repellent (3), Anti-diarrhea (10), Menstrual disorders (2), Cramps, Febrifuge (8), Stomachache (12) | NER-N, GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D, GYN-X, SKE-L, OTH-A, GAS-D | Infusion, Powder | Oral | 46 | A |
| Asteraceae | Achillea santolinoides Lag. | Gole bengerask 918 | Flowering branches | Relaxing (4), gastric discomfort (7), Parasite repellent (3), Anti-diarrhea (10), Menstrual disorders (2), Cramps, Febrifuge (8), Stomachache (12) | NER-N, GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D, GYN-X, SKE-L, OTH-A, GAS-D | Infusion, Powder | Oral | 46 | A, C |
| Asteraceae | Achillea wilhelmsii C. Koch | Gole bengerask 922 | Flowering branches | Stomach ache (12), Disinfectant (1), Blood purifier (2), Carminative (4), Diuretic (1), Antispasmodic (6) | GAS-D, OTH-A, Blood-B, GAS-D, URO-U,NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 26 | A |
| Asteraceae | Arctium lappa L. | Babaadam 950 | Leaf | Vertigo (3), Blood purifier (2), Antispasmodic (4), Detoxification (1), Food digestion (7), Parasite repellent (1), Kidney diseases (2) | NER-N, OTH-A, NER-N, OTH-A, GAS-D, GAS-D, URO-U | Poultice, Decoction | Oral | 20 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Artemisia absinthium L. | Afsantin 930 | Leaf, Flower | Intestinal parasites (5) | GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 5 | A |
| Asteraceae | Artemisia aucheri Boiss. | Jaz 934 | Flowering branches | Relaxing (6), Abdominal pains (27), Respiratory diseases (3), Body tonic (6), Febrifuge (25) | NER-N, GAS-D, RES-R, OTH-A, OTH-A | Decoction | Oral | 68 | A, C |
| Flowering branches | Beauty of skin and hair (1) | DER-S | Essential oil, Aromatic water | Topical | |||||
| Asteraceae | Artemisia persica Boiss. | Dermene torki 931 | Flowering branches | Febrifuge (44), Gastric infection (62), Stomachache (73) | OTH-A, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 179 | A, C |
| Asteraceae | Artemisia scoparia Waldst. & Kitam. | Dermeneh 932 | Aerial parts | Stomachache (13) | GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 13 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Artemisia sieberi Besser | Sorkhdermon 953 | Flowering branches | Anti-nausea (20), Antispasmodic, (8) Parasite repellent (18) | GAS-D, NER-N, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 61 | A |
| Flowering branches | Bruise (15) | SKE-L | Decoction | Topical | |||||
| Asteraceae | Atractylis cancellata L. | Kharcharkha 940 | Gum, Leaf | Vegetable (3) | OTH-A | Row, Powder | Oral | 3 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Calendula officinalis L. | Gole bahari 942 | Aerial parts | Carminative (2), Pancreatic cancer (1) | GAS- D, CAN-C | Infusion | Oral | 8 | B, C |
| Aerial parts | Acne (3), Pterygium (2) | DER-S, EYE-F | Oil, Aromatic water | Topical, Eye drop | |||||
| Asteraceae | Carthamus lanatus L. | Kharzard 971 | Flower | Bruise (2) | SKE-L | Poultice | Topical | 2 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Carthamus oxyacantha M.Bieb. | Golrangzard 972 | Leaf and flower | Purgative (1), Menstrual disorders (1), Blood purifier (1) | GAS-D, GYN-X, OTH-A | Decoction | Oral | 3 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Centaurea benedicta (L.) L. | Khar moghadas 980 | Flowering branches | Memory tonic (2) | NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 2 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Centaurea bruguierana (DC.) Hand.-Mazz. | Gole gandom 981 | Aerial parts | Anti-inflammatory (2) | SKE-L | Decoction | Oral | 2 | A |
| Asteraceae | Cichorium intybus L. | Kasni 925 | Leaf and Flower | Jaundice (15), Liver diseases (2), Diuretic (2), Febrifuge (13), Antihypertensive (2), Laxative (55) | GAS-D, GAS-D, URO-U, OTH-A,CAR-K, GAS-D | Aromatic water, Maceration | Oral | 89 | A, C |
| Asteraceae | Cichorium pumilum Jacg. | Kasni 913 | Leaf and Flower | Jaundice (14), Liver diseases (2), Febrifuge (14), Blood purifier, Antihypertensive (2), Laxative (50) | GAS-D, GAS-D, OTH-A, OTH-A, GAS-D | Aromatic water, Maceration | Oral | 96 | A |
| Root | Appetizing (5) | OTH-A | Decoction | Oral | |||||
| Asteraceae | Cirsium arvense (L.) Scop. | Kangar 925 | Root, Pith parenchyma | Gastric discomfort (8), Appetizing (2), Disinfectant (4), Febrifuge (7) | GAS-D, OTH-A, OTH-A, OTH-A | Decoction | Oral | 21 | A |
| Asteraceae | Cota tinctoria (L.) J.Gay | Babouneh 939 | Flowering branches | Throat pains (4), Nervous problems (13), Common cold (14), Anti-diarrhea (20), Prostate (5) | GAS-D, NER-N, RES-R, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 56 | A, C |
| Asteraceae | Cousinia congesta Bunge. | Poloosh 945 | Gum | Asthma (2) | RES-R | Decoction | Oral | 2 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Cyanus depressus (M.Bieb.) Soják | Gole gandom 977 | Flower | Digestive (11), Cough (1), Laxative (6) | GAS-D, RES-R, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 18 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Echinops ritrodes Bunge | Kaloor 983 | Fruit | Gastric discomfort (7) | GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 7 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Glebionis coronaria (L.) Cass. ex Spach. | Davoodi 986 | Aerial parts | Blood purifier (2), Eyesight enhancement (2) | OTH-A, EYE-F | Infusion | Oral | 4 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Gundelia tournefortii L. | Kangar 974 | Pith parenchyma | Gastric discomfort (8), Constipation (12), Reduce Blood fat (1), Blood purifier (15) | GAS-D, GAS-D, OTH-A, OTH-A | Edible, Salad | Oral | 36 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Hertia angustifolia (DC.) Kuntze | Karkich biabani 975 | Leaf, Flower | Pain relief (4) | NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 4 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Hertia intermedia (Boiss.) Kuntze | Karkich 973 | Flowering branches | Insect bite (5), Purgative (2), Parasite repellent (1) | DER-S, GAS-D, GAS-D | Poultice, Decoction | Topical, Oral | 8 | A |
| Asteraceae | Inula britannica L. | Mosafa 979 | Aerial parts | Reducing thirst (3) | OTH-A | Syrup | Oral | 3 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Lactuca orientalis (Boiss.) Boiss. | Jaroo 958 | Latex, Flower | Insomnia (3) | OTH-A | Decoction | Oral | 3 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Lactuca serriola L. | Kahokhardar 916 | Aerial parts, Latex | Bone and joint pains (1), Purgative (1) | SKE-L, GAS-D | Poultice, Decoction | Topical, Oral | 2 | A |
| Asteraceae | Launaea acanthodes (Boiss.) Kuntze | Goojar 918 | Aerial parts | Animal parasite repellent (122), Pain relief (4) | GAS-D, NER-N | Maceration | Oral | 126 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Matricaria chamomilla L. | Babounak 946 | Flowering branches | Anti-inflammation (2), Anti-nausea (3) | SKE-L, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 5 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Onopordum carmanicum (Bornm.) Bornm. | Kangar 919 | Young branches | Gastric discomfort (4) | GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 4 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Onopordum leptolepis DC. | Kangar 920 | Aerial parts | Urinary stone (6), Abdominal pains (9), Anti-diarrhea (8) | URO-U, GAS-D, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 23 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Rhaponticum repens (L.) Hidalgo | Talkhe sadi 927 | Aerial parts | Baby fever (2), Cancer (2) | OTH-A, CAN-C | Poultice, Decoction | Topical | 4 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Scorzonera mucida "Rech.f., Aellen & Esfand. | Kalaghoo 912 | Fresh leaf | Infectious wound (3) | DER-S | Poultice | Topical | 3 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Senecio glaucus L. | Bangdaneh 990 | Aerial parts | Chronic wound (6) | DER-S | Poultice | Topical | 6 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn. | Kharmaryam 995 | Leaf | Fatty liver (35), Reduce blood sugar (3) | GAS-D, MET-T | Decoction | Oral | 38 | A, C |
| Asteraceae | Sonchus asper (L.) Hill | Shirtighak 996 | Leaf | Skin rash (3) | DER-S | Poultice | Topical | 3 | A |
| Asteraceae | Sonchus oleraceus (L.) L. | Shirtighak 997 | Leaf | Skin rash (3) | DER-S | Poultice | Topical | 4 | A |
| Asteraceae | Tanacetum parthenium (L.) Sch.Bip. | Babouneh 960 | Aerial parts | Parasite repellent (4), Migraine (2), Anti-inflammation (10), Peptic ulcer (3), Gastritis (6) | OTH-A, NER-N, SKE-L, GAS-D, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 25 | A |
| Asteraceae | Taraxacum assemanii Boiss. | Shirdandan 998 | Leaf, Flower | Liver tonic (1), Diuretic (1) | GAS-D, URO-U | Decoction | Oral | 2 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Taraxacum pseudocalocephalum Soest. | Gasedak 906 | Seed | Blood fat (1) | Blood-B | Decoction | Oral | 1 | B, C |
| Asteraceae | Tragopogon graminifolius DC. | Sheng 999 | Leaf, Root | Diuretic (3), Gastrointestinal disorders (2) | URO-U, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 5 | B, C |
| Berberidaceae | Berberis integerrima Bunge | Zarch 681 | Root | Reduce blood sugar (61), Animal parasite repellent (2), Hepatitis (2), Joint pains (22), Breaking bone healing (15), Leaving addiction (27) | MET-T, GAS-D, CAR-K, GAS-D, SKE-L, SKE-L | Decoction | Oral | 182 | A |
| Leaf | Textile fiber color (9), Blood pressure (28) | OTH-A, CAR-K | Decoction | - | |||||
| Fruit | Blood purifier (30), Heat regulation (1), Hives (3), Laxative (4) | OTH-A, OTH-A, DER-S, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | |||||
| Biebersteiniaceae | Biebersteinia multifida DC. | Piche bahman 683 | Root | Reinforcing sexual desire (9), Pain relief (5), Colic (3) | OTH-A, NER-N, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 17 | B, C |
| Bignoniaceae | Tecomella undulata (Sm.) Seem. | Golparak 701 | Stem bark, Leaf | Skin ailments (79), Eczema (64), Reduce blood sugar (41), Urinary problems (10) | DER-S, DER-S, MET-T | Poultice, Decoction | Topical | 194 | A |
| Boraginaceae | Anchusa azurea Mill. | Gavzaban 710 | Flower | Relaxing (4) | NER-N | Decoction, Infusion | Oral | 4 | A, C |
| Boraginaceae | Buglossoides arvensis (L.) I.M.Johnst. | Sangdaneh 711 | Leaf, Root | Pain relief (6) | NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 6 | B, C |
| Boraginaceae | Caccinia macranthera (Banks & Sol.) Brand | Gavzaban 720 | Flower | Relaxing (3) | NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 3 | A, C |
| Boraginaceae | Cordia myxa L. | Pohil 724 | Fruit | Common cold (5), Appetizing (4),Throat pain (10), Eczema (2), Kidney stone (5) | RES-R, -, GAS-D, DER-S, URO-U | Poultice, Infusion | Oral, Topical | 26 | B, C |
| Boraginaceae | Echium amoenum Fisch. & C.A.Mey. | Golgavzaban 734 | Flower | Sleeplessness (27), Relaxing (76), Anorexia (1) | NER-N, NER-N, Psy-P | Decoction | Oral | 104 | A, C |
| Boraginaceae | Nonea caspica (Willd.) G.Don | Gavzabanak 715 | Leaf, Flower | Relaxing (2), Anorexia (1) | RES-R, NER-N, Psy-P | Decoction | Oral | 5 | A |
| Boraginaceae | Nonea persica Boiss. | Serkoee Cheskoee 712 | Flower and Leaf | Relaxing (3), Heart tonic (5), Expectorant (2), Disinfectant (4), | NER-N, CAR-K, RES-R, OTH-A | Decoction | Oral | 14 | B, C |
| Boraginaceae | Onosma stenosiphon Boiss. | Hoochoo 716 | Root | Women infection (7), Pain relief (6), Bruise (8), Wound sucker (13), Burn healing (9) | GYN-X, NER-N, DER-S, DER-S, DER-S | Poultice, Decoction | Oral, Topical | 43 | B, C |
| Boraginaceae | Solenanthus circinatus Ledeb. | Choobe Azar 725 | Stem bark | Bruise (95) | DER-S | Poultice | Topical | 95 | B, C |
| Boraginaceae | Trichodesma stocksii Boiss. | Gavzaban 727 | Flower | Nerve tonic (6), Respiratory ailments (1), Sore throat (1), Relaxing (1) | NER-N, RES-R, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 9 | A |
| Brassicaceae | Alyssum linifolium Stephan ex Willd. | Ghodoomeh 756 | Seed | Laxative (3), Cough (2) | GAS-D, RES-R | Decoction | Oral | 5 | A, C |
| Brassicaceae | Alyssum szovitsianum Fisch. & C.A.Mey. | Toodari karopoo 740 | Seed | Laxative (14) | GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 14 | B, C |
| Brassicaceae | Brassica nigra (L.) K.Koch | Khardal 750 | Root, Leaf, Seed | Memory improvement (1), Skin clarification (2) | NER-N, DER-S | Poultice, Decoction | Oral, Topical | 3 | B, C |
| Brassicaceae | Brassica rapa L. | Shalgham 749 | Root | Respiratory ailments (5) ,Common cold (69) | RES-R, RES-R | Edible | Oral | 74 | A |
| Brassicaceae | Capsella bursa-pastoris (L.) Medik. | Kisekeshish 745 | Aerial parts | Blood purifier (7) | Blood-B | Decoction | Oral | 7 | B, C |
| Brassicaceae | Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb. ex Prantl | Khakshir 762 | Seed | Laxative (42), Disinfectant (5), Reducing thirst (7), Constipation (46), Throat infection (10), Intestinal pain (7), Blood purifier (4), Heatstroke (7), Anti-diarrhea (5) | GAS-D, GAS-D, OTH-A, -, GAS-D , GAS-D, GAS-D, OTH-A, GAS-D |
Decoction, Syrup, Maceration |
Oral | 96 | A |
| Brassicaceae | Eruca vesicaria (L.) Cav. | Mandow 755 | Young stem and leaf | Body tonic (2) | OTH-A | Salad | Oral | 2 | B, C |
| Brassicaceae | Erysimum crassicaule (Boiss.) Boiss. | Khakshire talkh 760 | Seed | Respiratory ailments (4) | RES-R | Maceration | Oral | 4 | A, C |
| Brassicaceae | Fortuynia garcinii (Burm.f.) Shuttlew. | Shabboo 765 | Aerial parts, Laef and flower | Migraine (5), Relaxing (6), Menstrual disorders (2), Flavoring of food (4), Antispasmodic (3), Stomach tonic (6) | NER-N, NER-N, GYN-X, NER-N, GAS-D | Decoction, Infusion, Mixed with food | Oral | 26 | A, C |
| Brassicaceae | Goldbachia laevigata (M.Bieb.) DC. | Nakhonak 780 | Seed | Antimicrobial (1) | OTH-A | Decoction | Oral | 1 | B, C |
| Brassicaceae | Lepidium draba L. | Mookoo 759 | Leaf | Eczema (4), Reduce rheumatic pain (7), Diuretic (8), Gastritis (4), Stomach acidification (4), Cough (8), Flavoring of food (16), Anemia (3) | DER-S, SKE-L, URO-U, GAS-D, GAS-D, RES-R, OTH-A, Blood-B | Poultice, Decoction | Topical, Oral | 54 | B, C |
| Brassicaceae | Lepidium latifolium L. | Tarantizak 770 | Aerial parts | Pickle (9), Body tonic (3) | OTH-A , OTH-A | Edible | Oral | 12 | B, C |
| Brassicaceae | Lepidium sativum L. | Shahi 776 | Leaf | Muscle cramps (2), Reduce rheumatic pain (3) | SKE-L, SKE-L, SKE-L, SKE-L | Decoction | Oral | 5 | B, C |
| Brassicaceae | Raphanus caudatus L. | Torobcheh 784 | Root | Digestive (6), Urinary problems (2) | GAS-D, URO-U | Vegetable, Decoction | Oral | 8 | B, C |
| Brassicaceae | Sisymbrium irio L. | Khakshir 763 | Seed | Laxative, Constipation | GAS-D, GAS-D | Infusion | Oral | A | |
| Brassicaceae | Isatis tinctoria L. | Vasmeh 783 | Leaf | Hair tonic and hair color (24) | DER-S | Powder mixed with water | Topical | 24 | A, C |
| Brassicaceae | Thlaspi perfoliatum L. | Kisehchoochan 785 | Seed | Diuretic (5) | URO-U | Decoction | Oral | 5 | B, C |
| Cannabaceae | Cannabis sativa L. | Kanaf 1240 | Seed, Leaf, flowering branches | Urinary problems (3), Sleeplessness (2), Nervous system tonic (7), Relaxing (2) | URO-U, NER-N, NER-N, NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 14 | B, C |
| Campanulaceae | Campanula kermanica (Rech.f., Aellen & Esfand.) Rech.f. | Gole ghifoo 1325 | Flower and leaf | Cough (4) | RES-R | Decoction | Oral | 4 | B, C |
| Capparidaceae | Capparis spinosa L. | Dak 634 | Fruit, Leaf | Liver diseases (1), Anemia (1), Joint pains (3), Antimicrobial (12), Pickle (7), Eczema (16) | RES-R, OTH-A, SKE-L, OTH-A, OTH-A, DER-S | Decoction, Poultice | Oral , Topical | 40 | A |
| Caprifoliaceae | Lomelosia olivieri (Coult.) Greuter & Burdet | Sarbanafsheh talkh 1331 | Flower | Diarrhea (5), Joint pans (4) | GAS-D, SKE-L | Decoction, Poultice | Topical, Oral | 9 | B, C |
| Caprifoliaceae | Scabiosa candollei DC. | Talhkou 1332 | Flower | Anti-diarrhea (8), Abdominal pains (5), Bone and joint pains (2) | GAS-D, GAS-D, SKE-L | Decoction, Poultice | Topical | 16 | A |
| Caprifoliaceae | Scabiosa flavida Boiss. & Hausskn. | Sarbanafsheh talkh 1334 | Flower | Anti-diarrhea (4), Joint pans (3) | GAS-D, SKE-L | Decoction, Poultice | Topical, Oral | 7 | B, C |
| Caprifoliaceae | Valeriana ficariifolia Boiss. | Alafe gorbe 1337 | Root, Rhizome | Relaxing (5) | NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 5 | B, C |
| Caryophyllaceae | Dianthus crinitus Sm. | Ghernefel 612 | Seed | Toothache (17), Breath freshener (2) | OTH-A, RES-R | Decoction, Poultice | Oral, Topical | 19 | B, C |
| Caryophyllaceae | Dianthus orientalis Adams | Mikhak 611 | Leaf, Flower | Toothache (24), Breath freshener (2), Headache (18), Nerve pain (27) | OTH-A, RES-R, NER-N, NER-N | Poultice, Decoction | Oral, Topical | 71 | A |
| Caryophyllaceae | Herniaria hirsuta L. | Fetgh 613 | Aerial parts | Burn wound healing (5) | DER-S | Poultice | Topical | 5 | B, C |
| Cleomaceae | Cleome coluteoides Boiss. | Alafe maar 1350 | Leaf, Flower and Fruit | Diuretic (5), Laxative (2), Anti-nausea (2), psoriasis (2) | URO-U, GAS-D, GAS-D, DER-S | Decoction, Poultice | Oral | 11 | B, C |
| Colchicaceae | Colchicum schimperi Janka ex Stef. | Hasratoo 452 | Root | Wart treatment (5), Joint pains (6), Reduce the pain of gout disease (4) | DER-S, SKE-L, NER-N | Poultice | Topical | 15 | B, C |
| Convolvulaceae | Convolvulus arvensis L. | Pichak 791 | Leaf, Flower, Seed | Gastric discomfort (12), Wound healing (3), Asthma (2) | GAS-D, DER-S | Decoction, Poultice | Oral, Topical | 17 | A |
| Convolvulaceae | Cressa cretica L. | Alaf mourcheh 790 | Aerial parts | Antifungal (4), Antibacterial (14) | OTH-A, OTH-A | Poultice | Topical | 18 | A |
| Convolvulaceae | Cuscuta epithymum (L.) L. | Ses 792 | Aerial parts | Diuretic (2), Jaundice (2) | URO-U, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 4 | A, C |
| Cucurbitaceae | Citrullus colocynthis (L) Schrad. | Gelgenjak 890 | Fruit, Seed, Root | Reduce blood sugar (91), Reduce rheumatic pain (3), Scorpion bite (6), Chronic ulcers (5), Antihypertensive (4), Febrifuge (2), Bone and joint pains (8) | MET-T, DER-S, DER-S, OTH-A, CAR-K, DER-S, SKE-L | Poultice, powder | Topical, Oral | 119 | A |
| Cucurbitaceae | Cucumis sativus L. | Kheyar 889 | Aerial parts | Laxative (13) | GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 13 | A, C |
| Cucurbitaceae | Cucurbita moschata Duchesne | Kadoohalvaee 891 | Seed | Prostate (6) | URO-U | Decoction | Oral | 6 | A, C |
| Cucurbitaceae | Cucurbita pepo L. | Kadoo 885 | Fruit | Blood fat (8), Constipation (4) | Blood-B, GAS-D | Edible | Oral | 12 | A, C |
| Cupressaceae | Juniperus excelsa M.Bieb. | Avors 203 | Fruit | Common cold (14), Hair tonic and hair color (3), Freshener body (6), Skin rash (31), Wound healing (12) | RES-R, DER-S, OTH-A, DER-S, DER-S | Powder, Bath, Decoction, Poultice | Topical, Oral | 143 | B |
| Leaf | Pest Control (15), Algae Pool Control (3), Wood corrosion (10), Pain relief (4) | OTH-A, OTH-A, OTH-A, NER-N | Dressing, Powder, Decoction | Topical, Oral | |||||
| Leaf and fruit | Stomach tonic (7), Appetizing (5), Reduce rheumatic pain (11) | GAS-D, OTH-A, SKE-L | Decoction, Poultice | Oral, Topical | |||||
| Elaeagnaceae | Elaeagnus angustifolia L. | Senjed 544 | Seed | Joint pains (26), Anti-diarrhea (48), Peptic ulcer (10) | SKE-L, GAS-D, GAS-D | Poultice, Powder | Topical, Oral | 90 | A |
| seed | Health tonic (6) | OTH-A | Oil | Oral | |||||
| Ephedraceae | Ephedra distachya L. | Khimouk 182 | Young branches | Stomachache (12), Relaxing (8), Peptic ulcer (62), Stomach burning, (22) Traditional tannery (10), Relaxing (1) | GAS-D, NER-N, GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D, NER-N | Decoction, Infusion | Oral | 115 | B, C |
| Ephedraceae | Ephedra foliata Boiss. ex C.A.Mey. | Khimouk 180 | Young branches | Stomachache (2), Relaxing (3), Peptic ulcer (3), Relaxing (1) | GAS-D, NER-N, GAS-D, NER-N | Decoction, Infusion | Oral | 9 | B, C |
| Ephedraceae | Ephedra major Host | Alijoon 185 | Young branches, Fruit | Respiratory ailments (4), Cough (4), Common cold (5), Pain relief (24), Relaxing (1) | RES-R, RES-R, RES-R, NER-N, NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 53 | A |
| Young branches, Fruit | Traditional tannery (15) | OTH-A | Decoction | - | |||||
| Ephedraceae | Ephedra intermedia Schrenk & C.A.Mey. | Khimouk 179 | Young branches | Common cold (5), Stomachache (7), Weight loss (36), Peptic ulcer (50), Traditional tannery (15), Relaxing (1) | RES-R, GAS-D, OTH-A, GAS-D, OTH-A, NER-N | Decoction, Infusion | Oral | 114 | B, C |
| Ephedraceae | Ephedra pachyclada Boiss. | Hoome nar 186 | Young branches, Fruit | Cramp (9), Food coloring (10) | SKE-L, OTH-A | Decoction, Infusion | Oral | 19 | A, C |
| Ephedraceae | Ephedra strobilacea Bunge | Khimook 189 | Young branches, Fruit | Pain relief (37), Gastric discomfort (53), Relaxing (1) | NER-N, GAS-D, NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 91 | A |
| Euphorbiaceae | Euphorbia bussei Pax | Shirsag 470 | Young leaf | Treatment of Blister (5), Skin stimulant (3), Reduced vision (3), Anemia (2) | DER-S, DER-S, EYE-F, Blood-B | Decoction, Poultice | Oral, Topical | 13 | A, C |
| Euphorbiaceae | Euphorbia granulata Forssk. | Shirbeng 472 | Latex | Eczema (2) | DER-S | Latex | Topical | 2 | B, C |
| Euphorbiaceae | Euphorbia helioscopia L. | Shirbeng 484 | Leaf, Seed | Joint pains (3), Skin rash (3), Reduce rheumatic pain (2) | SKE-L, DER-S, SKE-L | Decoction, Poultice | Topical, Oral | 8 | A |
| Euphorbiaceae | Euphorbia peplus L. | Alafe zegi l475 | Latex | Eczema (2) | DER-S | Latex | Topical | 2 | B, C |
| Euphorbiaceae | Euphorbia serpens Kunth | Gazeroo 477 | Latex | Eczema (10) | DER-S | Latex | Topical | 10 | B, C |
| Euphorbiaceae | Euphorbia turcomanica Boiss. | Farfeyeon 478 | Latex | Eczema (3) | DER-S | Latex | Topical | 3 | B, C |
| Euphorbiaceae | Ricinus communis L. | Kenton 499 | Seed | Laxative (3), Skin patches (2), Hair tonic (5), Disinfectant (4) | GAS-D, DER-S, DER-S, OTH-A | Poultice, Oil | Topical | 13 | A |
| Fabaceae | Alhagi maurorum Medik. | Adoor 675 | Aerial parts |
Urinary stone (13), Hemorrhoid (2), Reduce rheumatic pain (1) |
URO-U, CAR-K, SKE-L | Decoction, Poultice | Topical, Oral | 15 | A, C |
| Fabaceae | Alhagi pseudalhagi (M. Bieb.) Desv. ex B. Keller & Shap. | Adoor 674 | Aerial parts | Urinary stone (13), Child jaundice (4) | URO-U, GAS-D | Aromatic water, Decoction | Oral | 17 | A |
| Fabaceae | Astracantha lateritia (Boiss. & Hausskn.) Podlech | Khar 640 | Stem | Hair tonic (22), Eczema (45) | DER-S, DER-S | Gel | Topical | 67 | B, C |
| Fabaceae | Astragalus eremophilus Boiss. | Gavan 643 | Seed | Reinforcing sexual desire (3), Asthma (5), Preventing of the Blood coagulation (2), Expectorant (5) | OTH-A, RES-R, Blood-B , RES- R | Decoction | Oral | 15 | A |
| Fabaceae | Astragalus fasciculifolius subsp.arbusculinus (Bornm. & Gauba) Tietz | Anzaroot 645 | Gum, Stem bark | Ear infection (3), Earache (2), Cough (3), Stomachache (5), Livestock parasite (6), Common cold (4), Detoxification (5), Foot-and-mouth disease of livestock (10), Wart (6), Eye ache (2) | Ear-H , Ear-H, RES-R, GAS-D, GAS-D, RES-R, OTH-A, GAS-D, DER-S, EYE-F | Poultice, Decoction | Oral, Topical | 46 | B, C |
| Fabaceae | Astragalus gossypinus Fisch. | Gavan 641 | Gum, Stem bark | Traditional kohl (67), Hair beauty (15), Hair tonic (15) | DER-S, DER-S, DER-S | Gel, Poultice | Topical | 97 | B, C |
| Fabaceae | Astragalus ovoideus Širj. & Rech.f. | Margin 685 | Gum | Anti-stress (4), Relaxing (4) | NER-N, NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 8 | B, C |
| Fabaceae | Cercis siliquastrum L. | Argavan 646 | Leaf, Stem bark | Gastric discomfort (3), Expectorant (2) | GAS-D, RES-R | Decoction, Infusion | Oral | 5 | B, C |
| Fabaceae | Cicer arietinum L. | Nokhod kermani 659 | Seed | Hair tonic (2), Diuretic (3) | DER-S, URO-U, CAN-C | Decoction, Poultice | Oral, Topical | 5 | A, C |
| Fabaceae | Cicer kermanense Bornm. | Nokhod-e kermani 660 | Fruit | Hair tonic (2), Diuretic (3), Menstrual regulation (2) | DER-S, URO-U, GYN-X | Decoction, Poultice | Topical, Oral | 7 | A |
| Fabaceae | Colutea persica Boiss. | Feh 652 | Stem bark | Wound healing (3) | DER-S | Poultice | Topical | 3 | B, C |
| Fabaceae | Dalbergia sissoo DC. | Jag 653 | Stem bark | Abortion (2), Expectorant (7), Anti-parasitic (2), Burn healing (2), Anti-nausea (2), Reducing thirst (1) | PRE-W, RES-R, GAS-D, DER-S, GAS-D, GAS-D | Decoction, Poultice | Oral, Topical | 16 | A |
| Fabaceae | Genista tinctoria L. | Rangineh 654 | Aerial parts | Anti-diarrhea (2), Gastric discomfort (4), Abdominal pains (3), Constipation (2) | GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 11 | A |
| Fabaceae | Glycyrrhiza glabra L. | Matki 650 | Root | Stomach ulcers (28), Aphthous ulcer (83), Expectorant (9), Breaking bone healing (14), Prostate (4) | GAS-D, GAS-D, RES-R, SKE-L, URO-U | Decoction, Poultice | Oral | 138 | A, C |
| Fabaceae | Lathyrus sativus L. | Karoo 661 | Arial part | Laxative (5), Common cold (2), Fatty liver (2), Jaundice (3), Eczema (2) | GAS-D, RES-R, GAS-D, GAS-D, DER-S | Edible, Poultice | Oral, Topical | 14 | B, C |
| Fabaceae | Lens culinaris Medik. | Adas 663 | Seed | Body tonic (10) | OTH-A | Edible | Oral | 10 | A, C |
| Fabaceae | Medicago sativa L. | Yonjeh 665 | Young Leaf | Intestinal parasites (1), Eyesight tonic (7), Appetizing (2), Anemia (8) | GAS-D, EYE-F, OTH-A, OTH-A | Edible | Oral | 28 | A |
| Root | Stomach tonic (3), Gastric discomfort (3), Leaving addiction (2), Reduce blood sugar (2) | GAS-D, GAS-D, NER-N, MET-T | Decoction | Oral | |||||
| Fabaceae | Melilotus officinalis (L.) Pall. | Kalilalmolk 697 | Leaf and young stem | Common cold (4), Diuretic (2), Relaxing (9), Antispasmodic (3) | RES-R, URO-U, NER-N, NER-N | Edible | Oral | 18 | B, C |
| Fabaceae | Onobrychis altissima Grossh. | Esperes 670 | Leaf, Flower | Jaundice (7), Appetizing (2) | GAS-D, OTH-A | Decoction | Oral | 9 | A |
| Fabaceae | Ononis spinosa L. | Kharkhar 668 | Root | Inflammation of the urinary tract (6), Diuretic (6) | URO-U, URO-U | Decoction | Oral | 12 | B, C |
| Fabaceae | Phaseolus vulgaris L. | Loobia sabz 669 | Fruit | Cardiovascular diseases (5), Diuretic (2), Cancer (1) | CAR-K, URO-U, CAN-C | Mixed with food | Oral | 8 | B, C |
| Fabaceae | Prosopis cineraria (L.) Druce | Kahoor 655 | Latex | Eczema (10) | DER-S | Latex of burning stem | Topical | 26 | B, C |
| Stem bark | Traditional tannery (16) | OTH-A | Decoction | - | |||||
| Fabaceae | Prosopis farcta (Banks & Sol.) J.F.Macbr. | Kahoorak 684 | Dried Fruit | Antihistamine (2), Preventing of nose bleeding (2) | RES-R, RES-R | Decoction | Oral | 4 | B, C |
| Fabaceae | Sophora alopecuroides L. | Talkheh 687 | Whole plant | Antihypertensive (1), Antibacterial (2), Constipation (2), Pain relief (1) | CAR-K, OTH-A, GAS-D, NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 6 | B, C |
| Fabaceae | Sophora mollis (Royle) Baker | Talkheh 688 | Seed | Antihypertensive (1), Antibacterial (2), Constipation (2), Pain relief (1) | CAR-K, OTH-A, GAS-D, NER-N | Mixed with food | Oral | 6 | B, C |
| Fabaceae | Sophora pachycarpa C.A.Mey. | Talkheh 690 | Seed | Antihypertensive (1), Antibacterial (2), Constipation (2), Pain relief (1) | CAR-K, OTH-A, GAS-D, NER-N | Mixed with food | Oral | 6 | B, C |
| Fabaceae | Taverniera cuneifolia (Roth) Ali | Lati 614 | Leaf | Wound healing (9) | DER-S | Poultice | Topical | 9 | B, C |
| Fabaceae | Taverniera nummularia DC. | Daf 615 | Leaf | Wound healing (9) | DER-S | Poultice | Topical | 9 | B, C |
| Fabaceae | Tragacantha fasciculifolia (boiss.) Kuntze | Khaar 680 | Stem and leaf | Hair tonic (3), Gingival inflammation (5) | DER-S, GAS-D | Gum, Powder | Topical, Oral | 8 | B, C |
| Fabaceae | Trifolium repens L. |
Shabdare sefid 693 |
Aerial parts | Blood purifier (3), Cough (2), Cardiovascular disorders (1), Anti-diarrhea (3), Digestive (4), Burn healing (6) | OTH-A, RES-R, CAR-K, GAS-D, GAS-D, DER-S | Decoction, vegetable | Oral | 9 | A, C |
| Fabaceae | Trigonella foenum-graecum L. | Shanbalileh 694 | Leaf and young stem | Antihypertensive (6), Reduce blood sugar (5) | CAR-K, MET-T | Decoction | Oral | 21 | A |
| Fabaceae | Vicia faba L. | Bagla 689 | Seed | Reduce the blood fat (3), Constipation (4) | Blood-B, GAS-D | Food | Oral | 7 | A |
| Fabaceae | Vicia sativa L. | Mash 617 | Seed | Anti-diarrhea (2), Diuretic (1), Gumboil (2) | GAS-D, URO-U, GAS-D | Eat as food | Oral | 5 | A |
| Fabaceae | Lens culinaris Medik. | Adas 630 | Seed | Anti-diarrhea (2), Diuretic (1), Gumboil (2) | GAS-D, URO-U, GAS-D | Eat as food | Oral | 5 | A |
| Geraniaceae | Erodium cicutarium (L.) L'Hér. | Soozan Kalaghoo 1411 | Aerial parts | Antibacterial (2), Wound healing (5), Anti-diarrhea (3), Intestinal infection (4) | OTH-A, DER-S, GAS-D, GAS-D | Decoction, Poultice | Oral | 14 | B, C |
| Geraniaceae | Geranium rotundifolium L. | Soozani 1412 | Bulb | Intestinal infection (3), Anti-diarrhea (1) | GAS-D, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 4 | A, C |
| Gentianaceae | Centaurium pulchellum (Sw.) Druce | Ghontorionasa 1413 | Aerial parts | Febrifuge (4), Body tonic (3), Carminative (3) | OTH-A, OTH-A, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 10 | B, C |
| Gisekiaceae | Gisekia pharnaceoides L. | Bargdyereii 1416 | Aerial parts | Remove skin bur (5) | DER-S | Dressing | Topical | 5 | A |
| Hypericaceae | Hypericum perforatum L. | Raee 859 | Leaf and flower | Burn wound (3) | DER-S | Poultice | Topical | 3 | A, C |
| Iridaceae | Iris germanica L. | Zanbagh 314 | Aerial parts | Antifungal (2), Reduce rheumatic pain (2) | OTH-A, SKE-L | Decoction | Oral | 4 | B, C |
| Iridaceae | Moraea sisyrinchium (L.) Ker Gawl. | Zanbagh 317 | Aerial parts | Cough (3), Common cold (5) | RES-R, RES-R | Decoction | Oral | 8 | A, C |
| Juglandaceae | Juglans regia L. | Gerdoo 1450 | Leaf | Beans pest (12), Arthritis (1), treatment of Secretions of the womb (2) | OTH-A, SKE-L, GYN-X | Powder, Decoction | Topical | 16 | A, C |
| Root bark | Tooth germ (2) | GAS-D | Tooth brush | Oral | |||||
| Lamiaceae | Ajuga chamaecistus Ging. ex Benth. | Sameesk 811 | Leaf and flowering branched | Febrifuge (5), Antihypertensive (4), Kidney disorders (2), Antifungal (1) | OTH-A, CAR-K, URO-U, OTH-A | Vegetable | Oral | 12 | B, C |
| Lamiaceae | Clinopodium graveolens (M.Bieb.) Kuntze. | Melangoo 813 | Fruit, Seed, Aerial parts | Detoxification (7), Peptic ulcer (6), Dry cough (8), Expectorant (8) | OTH-A, GAS-D, RES-R, RES-R | Vegetable, mixed with food, Decoction | Oral | 29 | B, C |
| Lamiaceae | Dracocephalum polychaetum Bornm. | Zarab 834 | Leaf, flowering branches | Reduce rheumatic pain (2), Stomachache (34), Toothache (15), Headache (12), Reduce blood sugar (8), Anti-diarrhea (26), Detoxification (33), Body tonic (37), Relaxing (9), Back pain (23), Blood purifier (17) | SKE-L, GAS-D, GAS-D, NER-N, MET-T, GAS-D, OTH-A, OTH-A, NER-N, SKE-L, CAR-K | Decoction, Infusion | Oral | 216 | B |
| Lamiaceae | Lallemantia royleana (Benth.) Benth. | Malangoo 821 | Fruit | Carminative (3), Cough (4), Constipation (4), Expectorant (3), Vermicide (5), Dysentery (3) | GAS-D, RES-R, GAS-D, RES-R, GAS-D, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 22 | A |
| Lamiaceae | Lamium album L. | Gazaneh 816 | Flowering branches, Root | Anti-diarrhea (2), Wound healing (2), Reduce rheumatic pain (3) | GAS-D, DER-S, SKE-L | Decoction, Poultice | Oral, Topical | 7 | A |
| Lamiaceae | Lavandula angustifolia Mill. | Ostokhodoos 823 | Leaf | Bone and joint pains (20), Reduce rheumatic pain (12), Relaxing (10) | SKE-L, SKE-L, NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 62 | A, C |
| Lamiaceae | Leonurus cardiaca L. | Dom shir 825 | Leaf | Cardiac distress (4) | CAR-K | Decoction | Oral | 4 | A |
| Lamiaceae | Marrubium vulgare L. | Boogandoo 820 | Leaf and flower | Bone and joint pains (4), Reduce blood sugar (7), Antibacterial (1), Reinforcing sexual desire (3), Prostate (4), Anti-diarrhea (6), Women diseases (3) | SKE-L, MET-T, OTH-A, OTH-A, URO-U, GAS-D, GYN-X | Decoction | Oral, Topical | 28 | B, C |
| Lamiaceae | Melissa officinalis L. | Badranjbooye 830 | Foliage | Bone and joint pains (12), Appetizing (10), Headache (5), Dizziness (6) | SKE-L, -, NER-N, NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 33 | A, C |
| Lamiaceae | Mentha longifolia (L.) L. | Poodeneh 827 | Leaf and Flower | Stomach ache (31), Edible (44), Common cold (6), Anti-diarrhea (30), Carminative (14), Cough (6), Gastrointestinal pains (27), Antispasmodic (3) | GAS-D, -, RES-R, GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D, NER-N, | Edible, Decoction | Oral | 161 | A |
| Lamiaceae | Mentha spicata L. | Pooneh sonbolehee 832 | Leaf and flower | Anti-diarrhea (10), Carminative (5), Antispasmodic (6), Pain relief (7) | GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D, NER-N | Infusion, Mixed with food, Aromatic water | Oral | 28 | A |
| Lamiaceae | Nepeta bornmuelleri Hausskn. ex Bornm. | Poodeneh 837 | Aerial parts | Relaxing (4), Anti-diarrhea (12), Carminative (2) | NER-N, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 18 | A |
| Lamiaceae | Nepeta bracteata Benth. | Zoofa 840 | Flowering branches | Disinfectant (9), Common cold (15) | OTH-A, RES-R | Decoction, Powder | Oral | 24 | A |
| Lamiaceae | Nepeta cataria L. | Nana 841 | Leaf | Cough (17), Febrifuge (22), Colic (18), Stomachache (42), Edible (62), Common cold (35), Anti-diarrhea (68), Carminative (19), Cough (9), Antispasmodic (7), Gastrointestinal pains (31) | RES-R, OTH-A, GAS-D, GAS-D, -, RES-R, GAS-D, GAS-D, RES-R, GAS-D, GAS-D | Infusion, Mixed with food, Aromatic water | Oral | 328 | A |
| Lamiaceae | Nepeta daenensis Boiss. | Pooodneh 842 | Leaf and flowering branched | Antimicrobial (2), Stomachache (5), Anti-diarrhea (14) | OTH-A, GAS-D, GAS-D | Aromatic water | Oral | 21 | A |
| Lamiaceae | Lophanthus dschuparensis (Bornm.) Levin | Pooodneh 843 | Leaf and flowering branched | Antimicrobial (2), Stomachache (5), Anti-diarrhea (14) | OTH-A, GAS-D, GAS-D | Aromatic water | Oral | 21 | B, C |
| Lamiaceae | Nepeta glomerulosa Boiss. | Badrange golmowroo 844 | Aerial parts | Disinfectant (6), Joints pain (2) | OTH-A, SKE-L | Decoction, Powder | Oral | 8 | A |
| Lamiaceae | Nepeta ispahanica Boiss. | Gole Zoofa 845 | Leaf, Flower | Anti-inflammatory (6), Antifungal (5), Antispasmodic (3) | SKE-L, OTH-A, NER-N | Aromatic water, Decoction | Oral | 14 | A |
| Lamiaceae | Nepeta rivularis Bomm. | Pooodneh 846 | Leaf and flowering branched | Antimicrobial (1), Stomachache (7), Anti-diarrhea (15) | OTH-A, GAS-D, GAS-D | Aromatic water | Oral | 23 | A |
| Lamiaceae | Nepeta saccharata Bunge. | Pooodneh 847 | Leaf and flowering branched | Antimicrobial (2), Stomachache (5), Anti-diarrhea (14) | OTH-A, GAS-D, GAS-D | Aromatic water | Oral | 21 | A |
| Lamiaceae | Nepeta supina Steven | Makhleseh 848 | Leaf and flowering branched | Anti-nausea (7) | GAS-D | Aromatic water | Oral | 7 | A, C |
| Lamiaceae | Nepeta teucriifolia Willd. | Poodeneh 837 | Leaf and flowering branched | Antimicrobial (2), Stomachache (5), Anti-diarrhea (14), Anti-nausea (8), Gastrointestinal pains (4), Carminative (3) | OTH-A, GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D | Aromatic water | Oral | 36 | A |
| Lamiaceae | Ocimum basilicum L. | Reyhan 835 | Aerial parts | Sore throat (2), Common cold (8), Flavoring of food (16), Digestive (5), Asthma (2) | OTH-A, RES-R, -, GAS-D, RES-R | Edible, decoction | Oral | 33 | A |
| Lamiaceae | Origanum vulgare L. | Mirzangoo 810 | Aerial parts | Carminative (2), Diuretic (3), Disinfectant (3), Flavoring of food (5) | GAS-D, URO-U, OTH-A, OTH-A | Decoction, Poultice, mixed with food | Oral, Topical | 13 | A, C |
| Lamiaceae | Rydingia persica (Burm.f.) Scheen &V.A.Albort | Golder 822 | Leaf, Flower | Reduce blood sugar (26), Liver diseases (10), Leaving addiction (28), Bone and joints pains (69), Bone tonic (68), Body tonic (52), Relaxing (1) | MET-T,GAS-D, NER-N, SKE-L, SKE-L, OTH-A, NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 254 | B, C |
| Lamiaceae | Salvia compressa Vent. | Morporzou 806 | Aerial parts | Stomachache (47), Anti-diarrhea (25), Gastric discomfort (20), Women infection (18) | GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D, GYN-X | Decoction | Oral | 110 | A |
| Lamiaceae | Salvia leriifolia Benth. | Nowroozak 807 | Foliage | Carminative (5), Stomach tonic (9) | GAS-D, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 14 | A, C |
| Lamiaceae | Salvia macrosiphon Boiss. | Mooreshk 812 | Seed | Menstrual disorders (13), Leaving addiction (16), Anti-diarrhea (5), Antibacterial (4), Carminative (2), Reduce blood sugar (4), Wound healing (7), Blood purifier (1), Respiratory infection (2), Expectorant (3) | GYN-X, NER-N, GAS-D, OTH-A, GAS-D, MET-T, DER-S, CAR-K, RES-R, RES-R | Decoction, Poultice | Oral, Topical | 56 | A |
| Lamiaceae | Salvia mirzayanii Rech.f. & Esfand. | Mourporzoo 814 | Leaf and young branches | Stomachache (54), Leaving addiction (11), Anti-diarrhea (46), Women infection (6) | GAS-D, NER-N, GAS-D, GYN-X | Decoction, Poultice | Oral | 117 | A |
| Lamiaceae | Stachys lavandulifolia Vahl | Gole moureshk 831 | Leaf | Antifungal (5) | OTH-A | Decoction | Oral | 5 | A, C |
| Lamiaceae | Stachys inflata Benth. | Gole moorshak 805 | Leaf and flower | Febrifuge (4), Body tonic (4), Anti-inflammatory (4), Respiratory ailments (2) | OTH-A, OTH-A, SKE-L, RES-R | Decoction | Oral | 14 | A |
| Lamiaceae | Teucrium polium L. | Kalpooreh 819 | Leaf and young branches | Menstrual disorders (17), Bone pain (21), Child diarrhea (58), Stomachache (70), Febrifuge (34), Carminative (15), Reduce rheumatic pain (2), Anti-nausea (4), Anti-diarrhea (16), Reduce blood sugar (3), Gastrointestinal infection (20) | GYN-X, SKE-L, GAS-D, GAS-D, OTH-A, GAS-D, SKE-L, GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 260 | A |
| Lamiaceae | Teucrium scordium L. | Maryamgoli 815 | Flowering branches | Stomachache (17) | GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 17 | A, |
| Lamiaceae | Thymus fedtschenkoi Ronneger. | Avishan 828 | Leaf and flower | Cough (102), Expectorant (31), Common cold (55), Antibacterial (20), Sore throat (32) | RES-R, RES-R, RES-R, RES-R, OTH-A | Decoction | Oral | 240 | A |
| Lamiaceae | Zataria multiflora Boiss. | Avishane-shirazi 807 | Leaf and young stem | Cough (104), Expectorant (36), Common cold (64), Sore throat (43), Antibacterial (32) | RES-R, RES-R, RES-R, RES-R, OTH-A | Decoction | Oral | 281 | A |
| Lamiaceae | Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam. | Aghalaleh 804 | Leaf and flower | Flavoring of food (30), Common cold (20), Nerve tonic (13), Relaxing (15) | OTH-A, RES-R, NER-N, NER-N | Edible, Decoction | Oral | 83 | A |
| Lamiaceae | Ziziphora tenuior L. | Kakooti 803 | Aerial parts | Gastrointestinal pains (18), Body tonic (9), Stomach tonic (5), Flavoring of food (30) | GAS-D, OTH-A, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 62 | A |
| Liliaceae | Tulipa biflora Pall. | Laleh 1010 | Bulb | Cough (6) | RES-R | Powder | Oral | 6 | A |
| Linaceae | Linum album Ky. ex Boiss. | Gole-sefidoo 604 | Seed | Prostate (3), Weight loss (2), Anorexia (4) | URO-U, OTH-A, Psy-P | Infusion | Oral | 14 | B, C |
| Linaceae | Linum usitatissimum L. | Ketan 606 | Seed | Prostate (3), Weight loss (2), Anorexia (4) | URO-U, OTH-A, Psy-P | Infusion | Oral | 9 | A, C |
| Lythraceae | Lawsonia inermis L. | Hana 1020 | Leaf | Jaundice (63), Fingernail and hair tonic (57), Eczema (18), Burn scar (21) | GAS-D, DER-S, DER-S, DER-S | Bath, Decoction, Poultice | Oral, Topical | 164 | A |
| Root | Diuretic (3), Bronchitis (2) | DER-S, RES-R | Decoction | Oral | |||||
| Lythraceae | Punica granatum L. | Anar 1021 | Peel skin | Stomach ulcers (35), Wound healing (32), Sore throat (10) | GAS-D, DER-S, OTH-A | Poultice, Decoction, Powder | Oral, Topical | 77 | A |
| Malvaceae | Althaea aucheri Boiss. | Khatmi 584 | Leaf | Laxative (30), Cough (3), Antihypertensive (7), Jaundice (15), Skin discomfort (8) | GAS-D, RES-R, CAR-K, GAS-D, DER-S | Maceration | Oral | 63 | A |
| Malvaceae | Grewia tenax (Forssk.) Fiori. | Pootoorak 570 | Stem | Cough (2) | RES-R | Decoction | Oral | 2 | B, C |
| Malvaceae | Hibiscus sabdariffa L. | Chay torsh 571 | Leaf | Antihypertensive (10) | CAR-K | Decoction | Oral | 10 | A, C |
| Malvaceae | Malva microcarpa Pers. | Khatmi 574 | Seed, Leaf | Pain relief (13), Anti-inflammatory (10), Disinfectant (3), Jaundice (19), Infectious wound (6) | NER-N, SKE-L, OTH-A, GAS-D, DER-S | Decoction, Maceration, Poultice | Oral, Topical | 51 | A |
| Malvaceae | Malva neglecta Wallr. | Khatmi sefid 575 | Seed, Leaf | Diuretic (5), Anti-inflammatory (3) | URO-U, SKE-L | Maceration | Oral | 8 | A, C |
| Malvaceae | Malva sylvestris L. | Khatmi 577 | Seed, Leaf | Heatstroke (4), Febrifuge (4), Mouth and throat protuberance (5), Cough (6), | OTH-A, OTH-A, GAS-D, RES-R, | Maceration | Oral | 19 | A |
| Menispermaceae | Cocculus pendulus (J.R.Forst. & G.Forst.) Diels | Pichakoo 1030 | Leaf | Febrifuge (9) | OTH-A | Decoction | Oral | 9 | B, C |
| Moraceae | Ficus carica L. | Anjir 1040 | Fruit, Leaf | Constipation (5), Memory improvement (3), Common cold (5), Sore throat (6) | GAS-D, NER-N, RES-R, OTH-A | Infusion | Oral | 19 | B, C |
| Moraceae | Ficus johannis Boiss. | Anjir-e dalmi 1042 | Leaf | Stomach tonic (15) | GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 15 | B, C |
| Moraceae | Morus alba L. | Toot-e sefid 1043 | Fruit | Reduce blood sugar (2), Relaxing (2), Diuretic (1) | MET-T, NER-N, URO-U | Edible | Oral | 11 | A |
| Leaf | Febrifuge (3) | OTH-A | Edible | Oral | |||||
| Stem bark | Constipation (3) | GAS-D | Edible | Oral | |||||
| Moraceae | Morus nigra L. | Shahtoot 1044 | Fruit | Common cold (8), Sore throat (7), Urinary infection (2) | RES-R, OTH-A, URO-U | Syrup | Oral | 17 | A |
| Myrtaceae | Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehnh. | Kalitus 1700 | Leaf | Common cold (28), Respiratory ailments (22), Disinfectant (3) | RES-R, RES-R, OTH-A | Decoction, Poultice | Oral, Topical | 54 | A |
| Myrtaceae | Myrtus communis L. | Moordaneh 1050 | Leaf, Seed | Common cold (14), Relaxing (3), Removing the armpit odor (5) | RES-R, NER-N, OTH-A | Decoction | Oral, Topical | 22 | A |
| Myrtaceae | Syzygium cumini (L.) Skeels | Jam1051 | Ash of Leaf and seed | Blood purifier (4), Gastric discomfort (4) | OTH-A, GAS-D | Burnt ash | Oral | 8 | B, C |
| Nitrariaceae | Peganum harmala L. | Esfand 1060 | Fruit, Seed | Disinfectant (52), Reduce rheumatic pain (2), Reduce blood sugar (9), bruise (18) | OTH-A, SKE-L, MET-T, SKE-L | Poultice, Decoction | Topical, Oral | 81 | A |
| Oleaceae | Jasminum officinale L. | Yas sefid 1065 | Flower | Antivirus (2), Relaxing (6) | OTH-A, NER-N | Infusion | Oral | 8 | B, C |
| Oleaceae | Olea europaea L. | Zeytoon 1066 | Leaf, Fruit | Antihypertensive (21), Bone and joint pains (5), Appetizing (2), Urinary, (5), Hair tonic (3) | CAR-K, DER-S, SKE-L, OTH-A, URO-U | Decoction, Oil, Pickle | Oral, Topical | 61 | A |
| Leaf, Fruit | Antibacterial (4) | OTH-A | Decoction, Poultice | Topical, Oral | |||||
| Oil | Reduce blood sugar (5), Remove bur from skin (16) | MET-T, DER-S | Oil, Poultice | Topical, Oral | |||||
| Oleaceae | Syringa persica L. | Yas 1069 | Stem bark, Fruit | Relaxing (3) | NER-N | Infusion | Oral | 3 | B, C |
| Onagraceae | Epilobium angustifolium L. | Bid alafi 1070 | Leaf and seed | Pesticide (4), Anti-inflammation of mucosa and mouth (6), Wound healing (9), Heart tonic (8), Febrifuge (7) | OTH-A, OTH-A, DER-S, CAR-K, OTH-A | Decoction | Oral | 34 | A |
| Onagraceae | Epilobium hirsutum L. | Bid alafi korkee 1072 | Leaf, Root | Relaxing (5) | NER-N | Infusion | Oral | 5 | B, C |
| Orobancheaceae | Orobanche ramosa L. | Poor 1080 | Stem | Stomachache (19) | GAS-D | Edible, Decoction | Oral | 19 | B, C |
| Papaveraceae | Fumaria indica (Hausskn.) Pugsley. | Shatereh 1090 | Leaf and young branches | Anti-diarrhea (5), Anti-nausea (4), Stomachache (5) | GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 14 | A |
| Papaveraceae | Fumaria officinalis L. | Shatreh 1091 | Foliage | Blood purifier (6) | OTH-A | Infusion | Oral | 6 | A, C |
| Papaveraceae | Fumaria parviflora Lam. | Shatereh 1093 | Leaf and young branches | Anti-diarrhea (3), Anti-nausea (4), Stomachache (4), Blood purifier (6), Diuretic (3), Cutaneous itching (5) | GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D, OTH-A, URO-U, DER-S | Decoction | Oral | 25 | A |
| Papaveraceae | Fumaria vaillantii Loisel. | Shatereh1095 | Leaf and young branches | Anti-diarrhea (3), Anti-nausea (4), Stomachache (4) | GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 11 | B, C |
| Papaveraceae | Hypecoum pendulum L. | Shatereh 1096 | Root, Leaf | Cough (3), Anti-diarrhea (2) | RES-R, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 5 | B, C |
| Papaveraceae | Papaver dubium L. | Taryakoo 1098 | Bulb, Leaf | Eczema (3), Acne (4), Anti-inflammatory (5), Bronchitis (6), Cough (5), Pain relief (3) | DER-S, DER-S, SKE-L, RES-R, RES-R, NER-N | Mixed with vinegar, Decoction | Topical, Oral | 32 | B, C |
| Papaveraceae | Roemeria hybrida (L.) DC. | Shagayeg 1099 | Flower | Pain relief (9) | NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 9 | B, C |
| Pedalicaceae | Sesamum indicum L. | Konjed 1140 | Seed |
Prevention of hair loss (24), Blood fat (5) |
DER-S, Blood-B | Decoction, Oil | Oral, Topical | 29 | A |
| Plantaginaceae | Plantago amplexicaulis Cav. | Tangbar 491 | Leaf, Seed | Wound healing (5), Allergy (3), Heatstroke (2), Infectious disease (3), Stomachache (2), Respiratory ailments (2) | DER-S, OTH-A, OTH-A, OTH-A, GAS-D, RES-R | Poultice, Decoction | Topical, Oral | 17 | B, C |
| Plantaginaceae | Plantago ciliata Desf. | Kowchak 493 | Leaf, Seed | Antibacterial (4), Burns (9), Anti-inflammatory (2), Constipation (3) | OTH-A, DER-S, SKE-L, GAS-D | Poultice, Decoction, Syrup | Topical, Oral | 13 | A |
| Plantaginaceae | Plantago gentianoides Sm. | Tangbar 494 | Leaf, Seed | Constipation (5), Anti-inflammatory (5), Cough (4) | GAS-D, SKE-L, RES-R | Decoction | Oral | 14 | B, C |
| Plantaginaceae | Plantago indica L. | Kowchak 495 | Seed | Anti-inflammatory (2), Constipation (3) | SKE-L, GAS-D |
Decoction, Poultice, Syrup |
Topical, Oral | 5 | B, C |
| Plantaginaceae | Plantago lanceolata L. | Kowchak 490 | Leaf, Root,Seed | Baby jaundice (22), Constipation (18), Blood coagulation (3), Asthma (4), Stomachache (6) | OTH-A, GAS-D, Blood-B, RES-R, GAS-D | Dressing, Decoction | Topical, Oral | 40 | A |
| Plantaginaceae | Plantago major L. | Barhang 492 | Aerial parts | Dry cough (6), Itchy throat (8), Alzheimer (5), Cancer (2), Anti-inflammatory (3), Baby jaundice (21), Cough (2), Expectorant (4), Burn healing (4) | RES-R, RES-R, NER-N, CAN-C, SKE-L, OTH-A, RES-R, RES-R, DER-S | Dressing, Decoction | Topical, Oral | 28 | A |
| Plantaginaceae | Plantago ovata Forssk. | Tokhm sefid 499 | Seed | Anti-inflammatory (2), Constipation (3) | SKE-L, GAS-D |
Decoction, Poultice, Syrup |
Topical, Oral | 5 | B, C |
| Plantaginaceae | Veronica anagallis L. | Sizab 489 | Aerial parts | Stomach tonic (10), Diuretic (7) | GAS-D, URO-U | Decoction | Oral | 17 | B |
| Platanaceae | Platanus orientalis L. | Chenar 487 | Fruit, Root, Leaf, Stem bark | Acne (3), Snakebite (3), Hoarseness (2) | DER-S, DER-S, OTH-A | Poultice, Decoction | Oral, Topical | 8 | B, C |
| Plumbaginaceae |
Acantholimon scorpius (Jaub.&Spach) Boiss |
Kharposhtoo 511 | Root | Livestock wound healing (6), Washing powder (10) | DER-S, OTH-A | Poultice, Powder | Topical | 16 | B, C |
| Poaceae | Avena sativa L. | Jow dosar 334 | Leaf, Seed | Disinfectant (3) | OTH-A | Decoction | Topical | 3 | B, C |
| Poaceae | Cymbopogon schoenanthus (L.) Spreng. | Kaboo 335 | Leaf and stem | Body tonic (4) | OTH-A | Decoction | Oral | 4 | B, C |
| Poaceae | Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers. | Marg 337 | Aerial parts | Anti-diarrhea (3), Asthma (2) | GAS-D, RES-R | Decoction | Oral | 8 | B, C |
| Poaceae | Desmostachya bipinnata (L.) Stapf | Kerteh 339 | Root | Body tonic (4) | OTH-A | Decoction | Oral | 4 | B, C |
| Poaceae | Hordeum distichon L. | Jow 329 | Fruit | Febrifuge (2), Reducing thirst (3) | OTH-A, OTH-A | Decoction | Oral | 7 | B, C |
| Poaceae | Hordeum vulgare L. | Jow 328 | Fruit | Reduce blood sugar (3) | MET-T | Decoction, | Oral | 7 | A |
| Buds | Acne (4) | DER-S | Mask | Topical | |||||
| Poaceae | Melica persica Kunth | Oshlom 325 | Aerial parts | Washing powder (7) | OTH-A | Powder | - | 7 | B, C |
| Poaceae | Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. ex Steud. | Ney 324 | Root and Rhizome | Breast milk reduction (5) | OTH-A | Pickle | Oral | 5 | A, C |
| Poaceae | Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv. | Garch 340 | Seed | Hair tonic (5), Carminative (2) | DER-S, GAS-D | Poultice, Decoction | Topical, Oral | 7 | A |
| Poaceae | Sorghum halepense (L.) Pers. | Garch 342 | Seed | Diuretic (6) | URO-U | decoction | Oral | 5 | A |
| Poaceae | Triticum aestivum L. | Gandom 345 | Oil of seed | Eczema (6) | DER-S | Poultice | Topical | 6 | B, C |
| Poaceae | Zea mays L. | Zorat 347 | Style | Kidney stone (27) | URO-U | Decoction | Oral | 37 | A, C |
| Polygonaceae | Polygonum persicaria L. | Bandvash 430 | Leaf and flower | Asthma (8), Constipation (5) | RES-R, GAS-D | Infusion, Oil, Aromatic water | Oral | 13 | B, C |
| Polygonaceae | Pteropyrum aucheri Jaub. and Spach | Perent 425 | Foliage | Acne (4), Infectious wounds (5) | DER-S, ER-S | Poultice | Topical | 9 | B, C |
| Polygonaceae | Rheum ribes L. | Rohoo 432 | Aerial parts | Reduce blood sugar (5), Stomach and liver tonic (3), Appetizing (2), Laxative (6), Blood purifier (3), Vermicide (2), Bone tonic (4), Sight Enhancement (6) | MET-T, GAS-D, OTH-A, GAS-D, OTH-A, GAS-D, SKE-L, EYE-F | Decoction | Oral | 31 | B, C |
| Polygonaceae | Rumex crispus L. | Torshak 437 | Aerial parts | Laxative (4), Acute pulmonary embolism (7), Detoxificant of body (5) | GAS-D, RES-R, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 16 | B, C |
| Polygonaceae | Rumex vesicarius L. | Torshak 438 | Laef and petiole | Reduce blood sugar (2) | GAS-D | Vegetable | Oral | 2 | A |
| Portulacaceae | Portulaca oleracea L. | Gholfeh 561 | Leaf, Seed | Stomach tonic (1), Reducing thirst (2), Febrifuge (1), Cough (6), Blood purifier (12) | GAS-D, -, OTH-A, RES-R, OTH-A | Vegetable | Oral | 21 | B, C |
| Primulaceae | Anagallis arvensis L. | Delpasand 1145 | Aerial parts | Liver cysts (4), Urinary stones (4) | GAS-D, URO-U | Infusion | Oral | 8 | A |
| Primulaceae | Lysimachia maritima (L.) Galasso, Banfi & Soldano. | Shabdari 1147 | Whole plant | Antispasmodic (5), Bronchitis (3) | NER-N, RES-R | Decoction | Oral | 8 | B, C |
| Primulaceae | Primula capitellata Boiss. | Pamchoo1149 | Root and flower | Vermicide (4), Antispasmodic (8) | GAS-D, NER-N | Aromatic water | Oral | 12 | B, C |
| Primulaceae | Samolus valerandi L. | Alaf 1150 | Aerial parts | Body tonic (4) | OTH-A | Decoction | Oral | 4 | A |
| Pteridaceae | Adiantum capillus-veneris L. | Siahlengoo 1170 | Leaf | Common cold (49), Expectorant (51), Relaxing (3), Menstrual disorders (2), Earache (3) | RES-R, RES-R, NER-N, GYN-X, Ear-H | Decoction | Oral | 110 | A, C |
| Ranunculaceae | Adonis aestivalis L. | Chashm gargavol 1180 | Whole plant | Anti-inflammatory (5) | SKE-L | Decoction | Oral | 5 | B, C |
| Ranunculaceae | Adonis microcarpa DC. | Chashm gargavo 1182 | Flower | Anti-inflammatory (3) | SKE-L | Decoction | Oral | 3 | B, C |
| Ranunculaceae | Anemone biflora DC. | Shagayeg neman1185 | Flower | Common cold (6) | RES-R | Decoction | Oral | 6 | B, C |
| Ranunculaceae | Clematis ispahanica Boiss. | Chaspakoo 1187 | Aerial parts | Diuretic (3), Joint pain (3), Headache (3), Eczema and psoriasis (3) | URO-U, SKE-L, NER-N, DER-S | Decoction | Oral | 12 | A |
| Ranunculaceae | Consolida rugulosa (Boiss.) Schrödinger | Zaban mooshoo 1189 | Aerial parts | Anti-inflammatory (4) | SKE-L | Decoction | Oral | 4 | B, C |
| Ranunculaceae | Nigella sativa L. | Siahdaneh 1190 | Seed | Blood pressure (7), Blood fat (7), Asthma (2) | CAR-K, Blood-B, RES-R | Infusion | Oral | 16 | B, C |
| Ranunculaceae | Ranunculus arvensis L. | Alaleh 1192 | Flower | Urinary disease (3) | URO-U | Aromatic water | Oral | 3 | B, C |
| Ranunculaceae | Ranunculus muricatus L. | Alaleh 1193 | Root, Leaf, Flower | Skin diseases (2) | DER-S | Poultice | Topical | 2 | B, C |
| Ranunculaceae | Thalictrum minus L. | Sadabi 1195 | Aerial parts | Gastric discomfort (4) | GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 4 | A |
| Resedaceae | Ochradenus aucheri Boiss. | Kolirim1200 | Leaf | Parasite repellent (2), Wound healing (3) | GAS-D | Decoction, Poultice | Oral | 5 | B, C |
| Resedaceae | Reseda aucheri Boiss. | Varas 1205 | Leaf | Laxative (1), Diuretic (3) Reducing thirst (3) | GAS-D, URO-U, OTH-A | Decoction, Row | Oral | 5 | B, C |
| Rhamnaceae | Rhamnus persica Boiss. & Hohen | Titoomari 1210 | Fruit | Anti-diarrhea (11) | GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 11 | B, C |
| Rhamnaceae | Rhamnus prostrata Jacq. | Titoomari 1211 | Fruit | Anti-diarrhea (5) | GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 5 | B, C |
| Rhamnaceae | Sageretia thea (Osbeck) M.C. Johnst. Ch | Bastel 215 | Fruit | Laxative (2), Blood purifier (2) | GAS-D, CAR-K | Decoction | Oral | 4 | A |
| Rhamnaceae | Ziziphus jujuba Mill. | Annab 1218 | Fruit | Bronchitis (3), Common cold (4), Laxative (20) | RES-R, RES-R, GAS-D | Infusion, Edible | Oral | 24 | B, C |
| Rhamnaceae | Ziziphus nummularia (Burn.f.)Wight & Am. | Konar 1220 | Leaf | Common cold (3), Antimicrobial (1) | RES-R, OTH-A | Decoction, Poultice | Oral, Topical | 4 | A |
| Rhamnaceae | Ziziphus spina-christi (L.) Desf. | Konar 1221 | Leaf, Fruit | Stomach tonic (5), Hair tonic (4), Infectious tuber (2), Skin rash (7) | GAS-D, DER-S, DER-S, DER-S | Eat as fruit, Poultice, Shampoo | Oral, Topical | 18 | A |
| Rosaceae | Agrimonia eupatoria L. | Ghafes 370 | Aerial parts | Wound healing (18), Fatty liver (8), Anti-diarrhea (7) | DER-S, GAS-D, GAS-D | Poultice, Decoction | Topical, Oral | 33 | A, C |
| Rosaceae |
Amygdalus elaeagnifolia Spach |
Arjan 372 | Stem, Fruit | Nuts (18), Eczema (7) | OTH-A, DER-S | burning of semi dried wood, Edible | Oral,Topdical | 25 | B, C |
| Rosaceae | Amygdalus wendelboi Freitag | Archen 373 | Latex | Eczema (4), Bone and joint pains (3) | DER-S | Latex of burning stem | Topical | 7 | B, C |
| Rosaceae | Cotoneaster kotschyi (C.K.Schneid.) G.Klotz | Siahchoo 375 | Latex, Leaf | Jaundice (5), Constipation (6), Dry cough(4) | GAS-D, GAS-D, RES-R | Infusion | Oral | 15 | A |
| Rosaceae | Crataegus ambigua C.A.Mey. ex A.K.Becker | Kalkouhi 365 |
Leaf, fruit, Flower |
Relaxing (5), Spasms (4), Cardiac distress (4), Hypertension (4), Anti-diarrhea (7) | NER-N, NER-N, CAR-K, CAR-K, GAS-D | Decoction, Salad | Oral | 24 | B, C |
| Rosaceae | Crataegus azarolus L. | KalKoohi 380 | Leaf and fruit | Antihypertensive (6), Relaxing (11), Antispasmodic (10), Cardiac distress (5) | CAR-K, NER-N, NER-N, CAR-K | Decoction | Oral | 32 | A |
| Rosaceae | Crataegus meyeri Pojark. | Kalkouhi 381 |
Leaf, fruit, Flower |
Relaxing (5), Spasms (4), Cardiac distress (4), Antihypertensive (4) | Decoction | Oral | 17 | B, C | |
| Rosaceae | Cydonia oblonga Mill. | Beh 351 | Seed | Sore throat (4) | OTH-A | Decoction | Oral | 4 | B, C |
| Rosaceae | Prunus dulcis (Mill.) D.A.Webb | Badam-e shirin 353 | Seed | Hair tonic (5), Preventing of hair loss (9) | DER-S, DER-S | Oil | Topical | 14 | B, C |
| Rosaceae | Prunus eburnea (Spach) Aitch. & Hemsl. | Archen 354 | Fruit, Gum | Bone and joint pains (6), Allergies (5), Hair tonic (3) | OTH-A, DER-S | Decoction, Poultice | Oral, Topical | 14 | B, C |
| Rosaceae | Prunus lycioides (Spach) C.K.Schneid. | Badame koohi 355 | Leaf and fruit | Preventing of hair loss (5) | DER-S | Poultice, Oil | Topical | 8 | B, C |
| Rosaceae | Prunus mahaleb L. | Mahlab 356 | Leaf bark | Relaxing (5), Liver cysts (4), Parasite repellent (4), Joint pain (4) | NER-N, GAS-D, GAS-D, SKE-L | Decoction, dressing | Oral, Topical | 17 | A |
| Rosaceae | Prunus orientalis (Mill.) Koehne | Archen 357 | Fruit | Bone and joint pains (6), Allergies (5), hair tonic (3) | OTH-A, DER-S | Decoction, Poultice | Oral, Topical | 14 | B, C |
| Rosaceae | Prunus persica (L.) Batsch | Holo 358 | Fruit | Laxative (6) | GAS-D | Nuts, Maceration | Oral | 6 | B, C |
| Rosaceae | Prunus scoparia (Spach) C.K.Schneid. | Badam-e koohi 376 | Seed | Anti-dandruff (29), Preventing of hair loss (27), Earache (3), Health and beauty of the skin (8), Cancer prevention (3), Burned wound healing (4) | DER-S, DER-S, Ear-H, DER-S, CAN-C, DER-S | Poultice, Nut, Oil | Topical, Oral | 74 | B |
| Stem bark | Stomach tonic (4) | GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | |||||
| Rosaceae | Prunus avium (L.) L. | Gilas 378 | Pedicel | Kidney stone (7) | URO-U | Decoction | Oral | 24 | A, C |
| Rosaceae | Prunus cerasus L. | Albaloo 359 | Pedicel | Kidney stone (5) | URO-U | Decoction | Oral | 5 | A, C |
| Rosaceae | Rosa beggeriana Schrenk ex Fisch. & C.A.Mey. | Roz sefid 360 | Flower | Stomach tonic (5), Relaxing (8) | GAS-D, NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 13 | B, C |
| Rosaceae | Rosa canina L. | Korrik 362 | Leaf, Flower, Fruit | Relaxing (5) | NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 5 | B, C |
| Rosaceae | Rosa damascena Herrm. | Gole mohammadi 374 | Flower | Flavoring of food (8), Laxative (25), Nervous tonic (43) | OTH-A, GAS-D, NER-N | Aromatic water | Oral | 76 | B, C |
| Rosaceae | Rosa moschata Herrm. | Korrik 377 | Flower | Nervous tonic (3) | NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 3 | B, C |
| Rosaceae | Rubus caesius L. | Saghder 371 | Leaf, Fruit | Laxative (14) | GAS-D | Decoction, Syrup | Oral | 14 | A |
| Rosaceae | Sanguisorba minor Scop. | Gheytaran 379 | Fruit | Common cold (3), Relaxing (4), Cough (4), Jaundice (5), Toothache (6) | RES-R, NER-N, NER-N, GAS-D, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 32 | A |
| Rubiaceae | Plocama aucheri (Guill.) M.Backlund & Thulin | Khargo l520 | Foliage | Bone and joint pain (3), Reduce rheumatic pain (2), Reduce blood sugar (3), Digestive (3) | SKE-L, SKE-L, MET-T, GAS-D | Decoction, Infusion, Poultice | Topical, Oral | 11 | B, C |
| Rubiaceae | Rubia albicaulis Boiss. | Roonask 523 | Fruit | Bone tonic (4), Constipation (3) | SKE-L, GAS-D | Decoction, Infusion | Oral | 7 | B, C |
| Rubiaceae | Rubia tinctorum L. | Roonask 524 | Root | Bone tonic (4), Constipation (3) | SKE-L, GAS-D | Decoction, Infusion | Oral | 7 | B, C |
| Rutaceae | Citrus aurantium L. | Nareng 527 | Flower | Anti-diarrhea (5), Relaxing (8), Eye diseases (8), Traditional kohl (3) | GAS-D, NER-N, EYE-F | Decoction, Kohl | Oral | 24 | B, C |
| Rutaceae | Citrus limon (L.) Osbeck | Limoo torsh 528 | Fruit, Seed | Eye diseases (15), Traditional kohl (3) | EYE-F | Juice, Kohl | Eye Drop | 18 | B, C |
| Rutaceae | Haplophyllum robustum Bunge | Sadoo 530 | Aerial parts | Gastric discomfort (1) | GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 1 | B, C |
| Rutaceae | Haplophyllum tuberculatum Juss. | Gahich 531 | Aerial parts | Febrifuge (2), Headache (2) | GAS-D, NER-N | Decoction, Poultice | Oral, Topical | 4 | A |
| Rutaceae | Ruta graveolens L. | Soddab 535 | Leaf | Urinary stone (6) | URO-U | Decoction | Oral | 6 | A |
| Salicaceae | Populus alba L. | Sepidar 600 | Stem bark and leaf | Blood purifier (4), Pain relief (3) | OTH-A, NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 7 | A |
| Salicaceae | Populus euphratica Oliv. | Senewbar 601 | Stem bark | Parasite repellent (7) | GAS-D | Decoction | 4 | A | |
| Salicaceae | Salix aegyptiaca L. | Beedmeshk 605 | Inflorescence | Laxative (3), Anti-diarrhea (2), Gastrointestinal pains (2), Menstruation pains (3) | GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D, GYN-X | Decoction, Aromatic water | Oral | 10 | A |
| Salicaceae | Salix alba L. | Beed 606 | Stem bark, Leaf | Febrifuge (21), Common cold (6) | OTH-A, RES-R | Decoction, Aromatic water | Oral | 27 | A |
| Salvadoraceae | Salvadora oleoides Decne. | Pir 1230 | Fruit | Appetizing (7), Laxative (4), Parasite repellent (10), Hemorrhoids (4), Bronchitis (3) | OTH-A, GAS-D, GAS-D, CAR-K, RES-R | Decoction, Edible | Oral | 28 | B, C |
| Salvadoraceae | Salvadora persica L. | Chooch1231 | Fruit | Appetizing (5), Expectorant (8) | OTH-A, RES-R | Decoction, Edible | Oral | 15 | B, C |
| Scrophulariaceae | Scrophularia scopolii Hoppe ex Pers. | Makhleseh 842 | Young stem, Fruit | Waist pain (3), Respiratory diseases (2) | OTH-A, SKE-L | Poultice, Decoction | Topical, Oral | 5 | A, C |
| Scrophulariaceae | Scrophularia striata Boiss. | Makhleseh 840 | Fruit | Gastric discomfort (2), Respiratory diseases (2), Waist pain (3), Wound healing (2) | GAS-D, RES-R, OTH-A, DER-S | Poultice, Decoction | Oral, Topical | 9 | A, C |
| Solanaceae | Datura stramonium L. | Tatooreh 1250 | Leaf, Seed | Sexual tonic (6), Bone and join pains (8), Reduce rheumatic pain (5), Asthma (5), Cough (4), Burn (5) | OTH-A, SKE-L, SKE-L, RES-R, RES-R, DER-S | Decoction, Poultice | Oral, Topical | 33 | B, C |
| Solanaceae | Hyoscyamus reticulatus L. | Bonji 1255 | Aerial parts | Pain relief (9), Leaving addiction (9), Narcotic (15) | NER-N, NER-N, RES-R | Infusion | Oral | 33 | A, C |
| Solanaceae | Hyoscyamus senecionis Willd. | Bangdaneh 1256 | Flower | Pain relief (8) | NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 8 | A, C |
| Solanaceae | Hyoscyamus squarrosus Griff. | Bangdaneh 1257 | Whole plant | Pain relief (8) | NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 8 | A, C |
| Solanaceae | Lycium barbarum L. | Zeel 1260 | Fruit | Sleeplessness (4) | NER-N | Eat as fruit | Oral | 8 | B, C |
| Solanaceae | Lycium depressum Stocks | Zeel 1261 | Fruit | Anticonvulsant (11) | OTH-A, NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 11 | B |
| Solanaceae | Lycium shawii Roem. & Schult. | Dahir1262 | Leaf | Vision enhancement (2) | EYE-F | Crashed Juice | Topical | 2 | B, C |
| Solanaceae | Physalis alkekengi L. | Aroosak-e posht-e pardeh 1265 | Fruit | Kidney diseases (3), Laxative (5), Expectorant (2) | OTH-A, GAS-D, RES-R | Edible | Oral | 10 | B, C |
| Solanaceae | Solanum nigrum var.villosum L. | Roopas 1268 | Fruit | Febrifuge (6), Blood coagulation (5), Pain relief (4) | OTH-A, Blood-B, NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 15 | A |
| Solanaceae | Solanum lycopersicum L. | Gewjeh 1251 | Fruit | Infectious wounds (5) | DER-S | Poultice | Topical | 5 | B, C |
| Solanaceae | Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal | Kahkenj 1270 | Aerial parts | Nerve tonic (5) | NER-N | Decoction | Oral | 5 | A |
| Tamaricaceae | Tamarix aphylla (L.) Karst. | Koor gaz 1350 | Latex of burning stem | Eczema (16), Skin disease (8) | DER-S, DER-S | Poultice | Topical | 24 | B, C |
| Tamaricaceae | Tamarix kotschyi Bunge | Gole kist 1351 | Latex of burning stem | Eczema (16), Skin disease (8) | DER-S, DER-S | Poultice | Topical | 24 | B, C |
| 1Thymelaeaceae | Daphne mucronata Royale | Terveet 704 | Leaf | Influenza (3), Arthritis (3), Blood cancer (1) | MET-T, RES-R, SKE-L, CAN-C | Decoction, Dressing | Oral, Topical | 7 | A |
| Thymelaeaceae | Daphne oleoides Schreb. | Terveet 705 | Foliage | Traditional dyeing (10), Natural color for textile (10) | OTH-A, OTH-A | Decoction, Fume | - | 24 | B, C |
| Foliage | Constipation (4) | GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | |||||
| Thymelaeaceae | Daphne stapfii Bornm.& Keisslere. | Terveet 706 | Fruit | Influenza (3), Arthritis (3) | MET-T, RES-R, SKE-L | Decoction, Fume, Poultice | Oral, Inhale, Topical | 6 | B, C |
| Thymelaeaceae | Diarthron lessertii (Wikstr.) Kit Tan | Gole bidi 708 | Leaf and flowering branches | Stomachache (2), Stomach and liver tonic (2), Arthritis (2) | GAS-D, GAS-D, SKE-L | Aromatic water, Poultice | Oral, Topical | 6 | B, C |
| Urticaceae | Parietaria judaica L. | Gooshe Moosh 323 | Leaf and flower | Diuretic (3), Acute pulmonary embolism (4) | URO-U, RES-R | Decoction | Oral | 7 | B, C |
| Urticaceae | Urtica dioica L. | Soosonakoo 320 | Leaf and flower | Urinary stone (7), Reduce blood sugar (4) | URO-U, MET-T | Infusion | Oral | 11 | A |
| Urticaceae | Urtica urens L. | Soosonakoo 321 | Aerial parts | Febrifuge (5), Gastrointestinal pains (4), Relaxing (2), Anti parasite (2), Toothache(3) | OTH-A, GAS-D, NER-N, GAS-D, GAS-D | Decoction, Aromatic water | Oral | 15 | B, C |
| Violaceae | Viola odorata L. | Gol-e banafsheh 1370 | Leaf and flower | Laxative (8), Chronic cough (5), Expectorant (3) | GAS-D, RES-R, RES-R | Decoction | Oral | 16 | B, C |
| Verbenaceae | Verbena officinalis L. | Shahpasand 1380 | Aerial parts | Febrifuge (3), Nerve tonic (7) | OTH-A, NER-N | Poultice, Decoction | Topical | 10 | A |
| Vitaceae | Vitis vinifera L. | Maviz 1390 | Dried Fruit | Memory improvement (5) | NER-N | Nuts | Oral | 5 | A |
| Xanthorrhoeaceae | Aloe vera (L.) Burm.f. | Alovera 1500 | glazed materials | Diabetic wound (7), Eczema (22) | DER-S, DER-S | Poultice | Topical | 29 | A |
| Xanthorrhoeaceae | Asphodelus tenuifolius Cav. | Peemazoo1505 | Seed | Diuretic (15) | URO-U | Decoction | Oral | 17 | A |
| Root | Herbal adhesive (2) | OTH-A | Crushed extract | - | |||||
| Xanthorrhoeaceae | Eremurus kopetdaghensis M.Pop.ex B.Fedtsch. | Horishoo 1510 | Root, Leaf and flower | Herbal adhesive (4), Vegetable (8), Jaundice (6), Liver Disease (5), Disinfectant (4) | OTH-A, OTH-A, GAS-D, GAS-D, OTH-A | Vegetable, Decoction. Poultice | Topical, Oral | 27 | B, C |
| Xanthorrhoeaceae | Eremurus persicus (Jaub. & Spach) Boiss. | Serishoo 1511 | Leaf and flower | Flavoring of food (15), Laxative (6), Herbal adhesive (4), Vegetable (7), Disinfectant (3), Jaundice (6), Liver and kidney Disease (2) | OTH-A, GAS-D, OTH-A, OTH-A, OTH-A, GAS-D, GAS-D | Powder, Vegetable, Decoction. Poultice | Topical, Oral | 52 | B, C |
| Root | Liver and stomach discomfort (31) | GAS-D | Powder | Oral | |||||
| Zygophyllaceae | Fagonia bruguieri DC. | Alaf kharoo 1550 | Aerial parts | Appetizing (2), Vermicide (2), Carminative (5) | OTH-A, GAS-D, GAS-D | Decoction, infusion | Oral | 9 | A |
| Zygophyllaceae | Tribulus terrestris L. | Kharkhesak 1555 | Aerial parts | Kidney stone (43) | URO-U | Decoction | Oral | 43 | A |
| Zygophyllaceae | Zygophyllum eurypterum Boiss. & Buhse. | Gich 1560 | Seed | Lactiferous (4), Anti-nausea (3), Stomach tonic (4), Laxative (4), Vermicide (3) | PRE-W, GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 18 | B, C |
| Zygophyllaceae | Zygophyllum fabago L. | Gich 1561 | Seed | Lactiferous (4), Anti-nausea (3), Stomach tonic (4), Laxative (4), Vermicide (3) | PRE-W, GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D, GAS-D | Decoction | Oral | 18 | B, C |
C: indicate the medicinal plants which reported in this region for the first. A: indicate the ethno-medicinal uses of the medicinal plants which quoted in the in the Persian ethnobotany, B: was not quoted in the in the Persian ethnobotany.
Ailment categories
All recorded ailments and medicinal plant uses were categorized based on the International Classification of Primary Care (ICPC-2) (http://www.who.int/classifications/icd/adaptations/icpc2/en/).
Some modifications were made for diseases such as low back pain, which were not matched with the broad classification of diseases. Therefore, low back pain, infections, and some nontherapeutic applications (pickle, flavoring of food, appetizing, vegetable, thirst, pest control, food coloring, herbal adhesive, and washing powder) were placed in the General and Unspecified category.
According to the results, 16 disease categories were set, namely: (1) General and Unspecified; (2) Gastrointestinal; (3) Ophthalmological; (4) Ear, Nose and Throat; (5) Cardiovascular; (6) Hematological and immune mechanism; (7) Musculoskeletal; (8) Neurological; (9) Psychological; (10) Respiratory; (11) Dermatological; (12) Endocrine/ Metabolic and Nutritional; (13) Urological; (14) Pregnancy, Childbearing, Family Planning; (15) Female Genitals; and (16) Cancer.
Data analysis
Data was analyzed using descriptive and quantitative statistical methods. In this regard, the ethnomedicinal data was analyzed using frequency, citation, and use reports. Use report was recorded whenever an informant cited a plant species or part(s) used for a particular ailment. Use reports were also quantified to define the highly used plant species for a particular ailment. Additionally, ICF was employed to determine the homogeneity of the information as follows:
ICF = Nur − Nt / Nur − 1
Nur is the number of use citations for each ailment category and Nt is the number of plant species used for the same ailment category by all the healers [20]. ICF ranged between 0 and 1. ICF value is higher (near to 1) when a few plant species are cited by a higher proportion of healers, indicating homogeneity of information about the usage of specific plants. A low value (close to 0) demonstrates the healers’ disagreement about the usage of the plant for a particular ailment category [21].
In order to find out the importance of a specific plant species by informants, the index of relative frequency of citation (RFC) was calculated by dividing the frequency of citation (FC) by the total frequency of informants (RFC = FC/N). In this formula, FC is the number of informants who mentioned plant species as useful and N is the total frequency of informants in the survey [22].
Moreover, in order to determine cultural significance of each plant species, cultural importance index (CI) [22] was calculated as follows:
Independent samples t-test was run to compare medicinal uses between men and women. One-way ANOVA and post hoc was used to compare medicinal uses among age groups, educational levels, and occupations.
Results and discussion
Botanical diversity
In this ethnobotanical survey which covered the whole Kerman province (23 cities and 3,164,716 population), a total of 217 local informant interviews revealed the application of 402 medicinal plants for the treatment of 95 diseases across 16 ICPC ailments categories. These results showed that herbal medicines are mainly used to treat ailments among the local communities and indicated the rich floral diversity of this region.
These species belong to 273 genera of 73 families where 367 species are Dicotyledons, 27 species Monocotyledons, 7 species Cryptogam, and one species Gymnosperm. An important implication of the current study is the identification of the traditional medicinal uses of 292 plant species in this region for the first time. Information about these recorded medicinal plants is summarized in Table 3 in terms of local names, voucher specimens, part(s) used, healing practices, drug preparation, ICPC classification, and use report (%).
Asteraceae, Apiaceae, and Lamiaceae with 43, 38, and 37 species were the dominant medicinally utilized plant families, respectively (Fig. 2). In the south of this province, Sadat-Hosseini et al. reported that Apiaceae, Asteraceae, and Lamiaceae are the dominant medicinal plant families [10]. Moreover, in several ethnobotanical studies in the neighboring provinces (in Sistan and Baluchesta [23], and in Isfahan [24]) and countries (like Turkey [25, 26], and Georgia [27]), similar results were reported on the dominance of two or three of these plant families. From the phytochemical point of view, the dominance of Apiaceae, Asteraceae, and Lamiaceae families might be due to phytochemical composition, which are clues to high content of essential oils and phenolic constituents responsible for antimicrobial and antioxidant properties [28, 29].
Fig. 2.
Top dominants medicinally utilized plant families
Nepeta, Prunus, Ferula, Plantago, Ephedra, Euphorbia, Artemisia, Salvia, Artemisia, and Astragalus were the dominant medicinally used plant genera. Moreover, the findings of Saber et al. revealed that Salvia, Nepeta, Artemisia, Astragalus, Ferula, Plantago, Ephedra, Amygdalus, and Crataegus are the most frequently and popularly used medicinal plant genera in this district [8]. In general, the therapeutic significance of some plant families in a specific district may be related to the common distribution of their species [30].
There were some species like Tecomella undulata that were classified under vulnerable and endangered category of the IUCN list due to low reproduction and overexploitation [31, 32] while Pergularia tomentosa is a rare and endangered plant species which grows in the south of Kerman. Our previous research revealed that a low percentage of Kerman rangelands is vegetated with this plant and inhabitants uprooted it to meet their pharmacological needs [33].
The finding showed that the majority of the medicinal plant species (95%) belong to the wild habitat and the rest to cultivated areas. Other reports in this district [16, 27] confirm our results. In this case, informants of this region believed that wild plants are more medicinally effective than cultivated ones. Moreover, similar results were reported by Hu et al. in China [2].
With respect to healthcare policies, despite the relative adequate health services in this study area, local people and herbalists preferred herbal medicine due to the synthetic drugs side effects compared to herbal medicine. Furthermore, the general health policies that have been approved by the fifth development plan, as well as the national document on medicinal plants and traditional medicine, which emphasizes the organization and development of natural and traditional products, could play an important role in shaping people’s inclination towards traditional medicine [34]. Moreover, the medicinal plants’ availability, low cost, positive experiences, and reliable Iranian references like Avicenna could be the other reasons to form positive attitudes. Kerman province is a pivotal state in the ancient Iran (Persia) and it is estimated that the human civilization emerged from Jiroft in the south of this province [11]. Therefore, with a rich history, it has developed a sound traditional health care system.
Plant parts used
To prepare crude drugs (Fig. 3) from 15 plant parts, the most common plant parts used were leaf, flower, fruit, and seeds with 26.03, 15.36, 13.85, and 12.73 percentages, respectively. According to many reports, the leaf is the most common medicinal plant part used in the ethnopharmacological applications [35, 36]. Field discussion and other similar reports [30] indicated that availability, abundance, efficiency of use, and attention to the conservation points are the main reasons for the maximum usage of the leaves by local healers. In fact, local informants believed that different parts of the medicinal plants could have different therapeutic effects. In other words, plant organs have received varying degrees of attention based on traditional herbal medicine experiences of the ethnic communities. For instance, the root of Berberis integerrima is decocted and taken orally to treat diabetes while its leaf is used to treat hypertension. In addition, latex of Calotropis procera was used to cure eczema but its leaf is taken in the form of poultice to treat bruise and diabetes.
Fig. 3.
Plant parts used in traditional herbal drug preparation and the number of use reports
Preparation and application modes
The medicinal herbs were prepared in 14 forms including decoction, poultice, infusion, aromatic water, powder, vegetable, maceration, syrup, mask, fume, brush, and shampoo by local communities. The most common form of the crude drug was decoction (52.99%), followed by poultice (18.32%) and infusion (7.56%) (Fig. 4). The local informants of Kerman province believed that by decocting the medicinal plants parts, their extract becomes more concentrated and obtains better taste and stronger efficacy. Based on various reports [9, 16, 37–40], decoction is the most common method to prepare herbal medicine.
Fig. 4.
Crude drug type and the number use reports
The medicinal drugs administrated in six categories included oral, topical, dressing, eye drop, inhale, and bath. Analyzing the ethnobotanical data showed that the most common administration route was oral, followed by topical (Fig. 5). Other ethnobotanical studies in Iran and other countries revealed that ethnic communities mostly prefer these two methods of preparation [5, 10, 41]. But some plant species such as Lawsonia inermis, Juniperus excels, Rhazya stricta, and Pistacia atlantica are utilized in both topical and oral administration routes. For example, bath with the aqueous extract of Lawsonia inermis leaves is known as an effective method for the treatment of jaundice. The poultice of this plant is used to cure skin disorders like eczema and wound scar while its root is decocted and used orally as a diuretic and for the treatment of bronchitis.
Fig. 5.
Mode of herbal drug administration and the number of use reports
Informant consensus factors (ICF)
The ICF values for different ailment categories treated by the local informants in this survey ranged from 0.25 to 0.92 (Table 4). Endocrine (diabetes), dermatology, gastrointestinal, and respiratory with 0.92, 0.91, 0.90, and 0.89 ICF, respectively, were ranked as the most popular ailment categories for medicinal plants in this region.
Table 4.
Informant consensus agreement for ailment categories in the Kerman province
| ICPC categories | Recorded ailments | Nt* | Nur** | ICF value*** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
General and Unspecified (OTH-A) |
Health and body tonic (88), Fever (279), Disinfectant (116), Detoxification (51), Sore throat (142), Allergy (13), Back pain (6), Undefined illness (59), No diseases (344) | 136 | 1052 | 0.87 |
| Digestive (GAS-D) | Constipation (146), Toothache (127), Gastritis (395), Intestinal worm (69), Diarrhea (492), Jaundice (191), Nausea (54), Stomachic (781), Tooth germ (2), Liver ailment (115), Carminative (229), Vomiting (16), Digestive (32) | 243 | 2609 | 0.90 |
| Ophthalmological (EYE-F) | Eye Sight enhancement (5), Pterygium (2), Eye diseases (8) | 6 | 15 | 0.64 |
| Ear (Ear-H) | Earache (9), Ear diseases (5) | 5 | 14 | 0.69 |
| Cardiovascular (CAR-K) | Blood pressure (105), Hemorrhoids (13), Heart tonic (13), Cardiovascular disease (6), Blood purifier (115) | 37 | 252 | 0.85 |
|
Blood, Blood Forming Organs and Immune Mechanism (Blood-B) |
Anemia (42), Blood coagulation (14), Blood fat (31) | 87 | 16 | 0.82 |
| Musculoskeletal (SKE-L) | Bone and Joint pains (215), Anti-inflammation (74), Muscular cramps (2), Rheumatism (58), Arthritis (9), Waist pain (6) | 60 | 364 | 0.83 |
| Neurological (NER-N) | Dizziness (9), Nervous problems (115), Migraine (7), Antispasmodic (93), Pain relief (161), Relaxing (246), Sleeplessness (33) Alzheimer (5), Memory Improvement (18), Depression (5), Headache (40), Leaving addiction (100), Anticonvulsant (7) | 112 | 852 | 0.86 |
| Psychological (Psy-P) | Anorexia (10) | 4 | 10 | 0.66 |
| Respiratory (RES-R) | Cough (445), Asthma (37), Respiratory diseases (112), Colds (454), Bronchitis (48), Itchy throat (8), Acute pulmonary embolism (18), Influenza (6) | 121 | 1128 | 0.89 |
| Skin (DER-S) | Bites (32), Bruise (138), Burn (144), Wound (317), Eczema (368), Skin ailments (105), Skin rash (50), Beauty of skin and hair (13), Acne (22), Scar (61), Blister (5), Skin patches (2), Skin bur, (22) Hair tonic (208), Dandruff (29), Hair leprosy (36), Warts (11) | 132 | 1563 | 0.91 |
| Endocrine/ Metabolic and Nutritional (MET-T) | Diabetes (310) | 25 | 310 | 0.92 |
| Urological (URO-U) | Urinary problems (75), Kidney stone (77), Kidney diseases (14) | 32 | 191 | 0.83 |
|
Pregnancy, Childbearing, Family Planning (PRE-W) |
Male infertility (11), Lactiferous (13) | 6 | 24 | 0.78 |
| Female Genital (GYN-X) | Menstrual irregular (79), Women infection (31), Ovarian augmentation (3) | 113 | 16 | 0.86 |
| Cancer (CAN-C) | Tumorous cancer (9), Blood cancer (1) | 7 | 9 | 0.25 |
Nt= number of plant species used in each ailment category; NUR= number of mentions in each used category; ICF= Informant Consensus actor.
Diabetes disorder scored the highest ICF (0.92). This unexpected result is due to the high use report of few medicinal plants for treating diabetes mellitus such as Citrullus colocynthis, Berberis integerrima, and Tecomella undulata with 91, 61, and 41 use reports, respectively. In this case, C. colocynthis, a reputed medicinal plant in Kerman province, is well known due to its antidiabetic properties [42]. Moreover, in this case, the locals extremely used the root of Berberis integerrima and stem bark of T. undulata in treating diabetes mellitus. Field surveys and discussion with herbalists revealed that stress caused by poor economic conditions and job pressures can be one of the reasons for the high prevalence of diabetes in this region, but it needs more investigation.
Second ICF was found in dermatological ailment category with 1563 use reports. These findings are due to high use reports for plant species such as Calotropis procera, Pergularia tomentosa, Rhazya srticta, and Tecomella undulata in the treatment of eczema, wound healing, and other skin disorders. High ICF of dermatological disorders in this region might be due to high and long-term sunlight exposure, which caused skin disorders [10]. In addition, based on the field surveys, some environmental problems such as dust and wind associated with the particles of sands especially in the cities of Shahdad, Roodbar, Bam, Baravat, Qale Ganj, and Fahraj can be considered critical risk factors. Heidari et al. reported that the main reason for the skin diseases in the desert areas of the Kerman province like city of Bam is the dusty winds [43].
The third highest ICF (0.90) was found in gastrointestinal ailment category for 243 medicinal plant species. Species like Artemisa spp. Glycyrrhiza glabra and Nepeta cataria were typical medicinal herbs for gastrointestinal disorders. Such findings indicated the rich and high level of informant consensus on the variety of medicinal herbs used to treat gastrointestinal ailments, and confirmed the prevalence of gastrointestinal ailments among people who lived in a specific region [30]. Moreover, ITM (e.g., Canon) has attracted considerable attention for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders [44, 45]. Several studies in Iran and other countries reported that the species Nepeta cataria [46, 47], Glycyrrhiza glabra [48, 49], and Artemisa spp. [50, 51] were traditionally used to treat gastrointestinal diseases.
The 4th disease category with ICF value of 0.89 was respiratory disorders. Zataria multiflora, Thymus fedtschenkoi, and Cionura erecta were major plant species for cough with 104, 102, and 87 use reports, respectively. The large number of use reports for respiratory disorder category might be attributed to undesirable working conditions of local populations, like agriculture and husbandry in the dry and dusty regions without quick access to the health care systems. In confirmation of the present findings, Khanjani et al. studied the relationship between air pollution and respiratory diseases in Kerman from 2006 to 2010 and reported that sandstorms and the dust content increase of the atmosphere exacerbate respiratory diseases in this region [52].
Use report
Medicinal plants of the families Lamiaceae (such as Nepeta cataria and Zataria multiflora), Asteraceae (like Artemisia persica and Launaea acanthodes), and Apiaceae (such as Bunium persicum) had the largest number of use report in this area. Bibak and Moghbeli, and Sadat-Hosseini et al. studied the medicinal plants of the Jiroft and Kanuj in the south of Kerman and, similar to the findings of the current study, confirmed the importance of traditional medication of these three families [10, 16]. In addition, plant species of the Apocynaceae family (like Cionura erecta, Rhazya stricta, and Calotropis procera) were ranked with a high use report. In this case, Cionura erecta is a well-known medicinal plant in the southern regions of Kerman for the treatment of sore throat and cough with no official records.
Cultural importance and relative frequency of citation index
The highest CI was found for Nepeta cataria, Zataria multiflora, Teucrium polium, Rydingia persica, and Thymus fedtschenkoi. The second highest CI was found for Dracocephalum polychaetum and Pistacia atlantica. These findings revealed that the first CI of the medicinal plants in Kerman province belonged to the Lamiaceae family. Additionally, Pistacia atlantica was ranked as an important medicinal plant with high CI index in this region. High CI values show that these medicinal plants are either highly utilized, or their uses are rising in traditional herbal medicine in a specific region [53].
However, for the RFC index, Lawsonia inermis, Artemisia persica, Zataria multiflora, and Nepeta cataria were classified as the first rank. In other words, the mentioned medicinal plants were referred by most of the informants. RFC value specifies the usefulness of medicinal plant species [5]. Table 5 shows the ranking based on each index (CI and RFC) for 20 dominant medicinal plant species with the highest CI and RFC indices.
Table 5.
Comparison of dominant plants by using indices and species ranking based on each index (RFC and CI)
| Family | Scientific name | RFC | CI | RFC ranking | CI ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cucurbitaceae | Citrullus colocynthis (L) Schrad. | 0.42 | 0.55 | 4 | 4 |
| Asteraceae | Launaea acanthodes (Boiss.) Kuntze | 0.37 | 0.58 | 4 | 4 |
| Fabaceae | Glycyrrhiza glabra L. | 0.56 | 0.64 | 3 | 4 |
| Cupressaceae | Juniperus excelsa M.Bieb. | 0.41 | 0.66 | 4 | 4 |
| Apocynaceae | Calotropis procera (Aiton) Dryand. | 0.63 | 0.70 | 2 | 4 |
| Lamiaceae | Mentha longifolia (L.) L. | 0.49 | 0.74 | 3 | 3 |
| Lythraceae | Lawsonia inermis L. | 0.77 | 0.76 | 1 | 3 |
| Apocynaceae | Cionura erecta (L.) Griseb. | 0.31 | 0.77 | 4 | 3 |
| Apocynaceae | Rhazya stricta Decne. | 0.63 | 0.80 | 2 | 3 |
| Asteraceae | Artemisia persica Boiss. | 0.79 | 0.82 | 1 | 3 |
| Berberidaceae | Berberis integerrima Bunge | 0.66 | 0.84 | 2 | 3 |
| Apiaceae | Bunium persicum (Boiss.) B.Fedtsch. | 0.73 | 0.85 | 2 | 3 |
| Bignoniaceae | Tecomella undulata (Sm.) Seem. | 0.51 | 0.89 | 3 | 3 |
| Anacardiaceae | Pistacia atlantica Desf. | 0.75 | 0.96 | 2 | 2 |
| Lamiaceae | Dracocephalum polychaetum Bornm. | 0.64 | 1.00 | 2 | 2 |
| Lamiaceae | Thymus fedtschenkoi Ronneger. | 0.86 | 1.11 | 1 | 1 |
| Lamiaceae | Rydingia persica (Burm.f.) Scheen &V.A.Albort | 0.67 | 1.17 | 2 | 1 |
| Lamiaceae | Teucrium polium L. | 0.72 | 1.20 | 2 | 1 |
| Lamiaceae | Zataria multiflora Boiss. | 0.87 | 1.29 | 1 | 1 |
| Lamiaceae | Nepeta cataria L. | 0.89 | 1.51 | 1 | 1 |
Based on the independent samples t-test, women had more knowledge about the medicinal plants (t = 1.87, p = 0.04). Based on the field surveys, women in Kerman province are the preparers of the plant species for the medicinal applications, and it can be concluded that women had more practical experience in traditional medicine in this region. The findings of Sadat-Hosseini et al. in the southern part of this region also confirmed our results [10].
The results of ANOVA showed that there were significant differences between the three age groups (F = 3.17, p = 0.02), and different levels of education (F = 2.56, p = 0.03). Also, based on Duncan’s test, the two older age groups (older than 45 years old) with low level of education had more traditional knowledge about the medicinal plants. Based on these results and other reports like that of Hu et al., despite the importance of the traditional medicine for the older inhabitants, the younger generation does not show interest, which means that the ethnobotanical knowledge does not further flourish [2].
Finally, based on the results of ANOVA and Duncan’s tests, occupation of the informants had a significant effect on their traditional medicinal knowledge (F = 4.19, p = 0.01), and genuine information belonged to the herbal healers, nomadic people, and villagers, respectively. Field surveys revealed that herbal healers, due to their job requirement, record and learn the relevant knowledge of the other ethnic groups like nomadic and villagers and usually have more comprehensive traditional knowledge.
Ethnopharmacological knowledge of tribes and different area
In the hot and dry regions of Kerman province like Kahnuj, Roodbar, Anbarabad, Qale Ganj, Manojan, Faryab, Bam, Fahraj, Narmashir, Rigan, and plain part of Jiroft, most inhabitants are from Baluch tribe and the natives of Jiroft and Kahnooj. Based on the results, medicinal plants such as Berberis integerrima, R. persica, Calotropis procera, and R. stricta are widely used to treat dermatological diseases. The rate of drug abuse in these regions is more than in mountainous areas because these cities are in the neighborhood of Afghanistan and the availability of drugs is thus higher. Hence, medicinal plants such as the plant from the genus Achillea (A. wilhelmsii, A. eriophora, A. santolinoides), Berberis integerrima, and R. persica are used individually or in combination by the locals for stopping drug abuse.
Tribal communities and folk people, who live in the mountainous areas such as Hezar, Sirch, and Jebal barez, mainly use the herbal medicine for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders. Based on the field surveys and discussion with the herbal healers, the main food of the nomadic people is milk and its derivatives especially curd and buttermilk, and they do not have a diverse diet. There is a significant relationship between the consumption of low-diversity diets and the risk of non-communicable diseases [54, 55].
New traditional medicinal uses
According to the in-depth comparison of the current ethnobotanical findings with previous national reports, a large volume of unrecorded traditional medicine knowledge was gathered. A major implication of the current study is identification of traditional medicinal use of 292 plants in the Kerman province and 201 plants species in the Persian ethnobotany for the first time. This unrecorded knowledge is summarized based on the plant families as follows:
Amaranthaceae (Amaranthus retroflexus for the treatment of jaundice; Anabasis aphylla and Seidlitzia rosmarinus as traditional washing powders), Apiaceae (Eryngium billardieri and Eryngium bungei in pain relief, Prangos ferulacea as parasite repellents); Apocynaceae (Cionura erecta for sore throat and cough, Rhazya stricta for joint pains and body ache, Calotropis procera in the healing of skin disorders like eczema); Asteraceae (Launaea acanthodes as intestinal parasite repellents, Artemisia spp. for the treatment of gastric infection and stomachache, Calendula officinalis for the treatment of pterygium); Boraginaceae (Cordia myxa for common cold, sore throat and kidney stone); Ephedraceae (Ephedra distachya and Ephedra foliata for peptic ulcer and as materials in traditional tannery), Euphorbiaceae (Euphorbia serpens for eczema); Fabaceae (Astracantha lateritia for hair tonic and eczema, Prosopis cineraria for eczema and in traditional tannery, Prosopis farcta in preventing nose bleeding) Lamiaceae (Dracocephalum polychaetum as potent and multipurpose medicinal plant); Plantaginaceae (Plantago amplexicaulis, Plantago gentianoides and Plantago indica for constipation and jaundice); Polygonaceae (Pteropyrum aucheri in healing of infectious wounds); Ranunculaceae (Clematis ispahanica in healing of eczema and psoriasis); Rosaceae (Rosa moschata as nerve tonic, Prunus scoparia in cancer prevention); Rubiaceae (Plocama aucheri in reducing rheumatic pain and blood sugar); Rutaceae (Citrus limon and Citrus aurantium for the treatment of eye diseases and making the traditional kohl); Salvadoraceae (Salvadora oleoides as parasite repellent). Tamaricaceae (Tamarix aphylla and Tamarix kotschyi in healing of eczema and skin disease); Thymelaeaceae (Daphne oleoides in traditional dyeing); Violaceae (Viola odorata for chronic cough and as expectorant); and Zygophyllaceae (Zygophyllum eurypterum and Zygophyllum fabago as lactiferous and vermicide). These findings highlight the importance of the documentation of such valuable ethnobotanical information. Also, some of these medicinal plants can be targeted for pharmacological and bioactive studies with the aim of identifying phytochemical content and therapeutic applications.
Conclusion
Our extensive study in Kerman as the vastest province in Iran with 23 cities, 171,993 square kilometers area, and 89 tribal communities revealed rich traditional medicinal knowledge of its local populations. Traditionally, they used 402 medicinal plant species in 73 families to meet their pharmacological needs. Besides the common oral and topical utilization of the crude herbal drugs, dressing and bath with the medicinal plants are the exceptional mode of application in Kerman province. The highest ICF values belonged to diabetes, digestive, skin, and respiratory disorders, respectively.
Our findings suggested that Asteraceae and Apiaceae plants were dominantly used for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders, Lamiaceae plants for respiratory and gastrointestinal ailments, and Apocynaceae plants for dermatological problems.
For several medicinal plants with high use reports such as Cionura erecta, Tecomella undulata, and Launaea acanthodes, scanty pharmacological and phytochemical data has been reported. On the other hand, the top list included Rhazya stricta: wound healing; Calotropis procera: eczema; Berberis integerrima: diabetes and addiction cessation; Dracocephalum polychaetum: stomachache, diarrhea, detoxification and strengthening body; Rydingia persica: leaving addiction; Launaea acanthodes: parasite repellent; Cionura erecta: expectorant; and Tecomella undulate: skin ailments, eczema, and diabetes. These results highlight the need for further bioactive and phytochemical studies on the mentioned medicinal plants. Finally, some frequently used medicinal plants like Cionura erecta, Dracocephalum polychaetum, and Tecomella undulate are endangered and restricted in small parts of their habitats. Therefore, urgent conservation measures are needed.
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank the ethnic communities and local herbal healers of Kerman province for their helps in data sampling and continuing support of this study. We would like to acknowledge the University of Jiroft for financial support.
Abbreviation
- ITM
Iranian traditional medicine
Authors’ contributions
SHH and HB designed the work. AS, ARQ, and ASh participated in the organization of the ethnobotanical and ethnopharmacological data. HB conducted the botanical analysis. SHH participated in all steps (designing, field work, data analysis, literature search, etc.). The authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ information
The authors have doctoral qualification in Medicinal plants, Plant systematic, Biology, Pharmacognosy, and Pharmaceutical Biotechnology. This work is based on the research project of SH, which is granted by the University of Jiroft.
Funding
This study was supported by research grants (No: 3818-97-6) from the University of Jiroft. We thank the University of Jiroft for technical and financial support.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this survey are included in this article.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was reviewed and approved by the Research Deputy at the University of Jiroft. The organization of the institute does not involve an Ethics Committee; therefore, there is no specific ethics code assigned to this study. However, each research proposal, like the one corresponding to the current study, is comprehensively reviewed by the university until an approval code is granted (No: 3818-97-6). We would like to clarify that this study did not involve any intervention and all questions from local informants were performed with prior verbal consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
All the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Seyed Hamzeh Hosseini, Email: Hamze@ujiroft.ac.ir.
Hossein Bibak, Email: hbibak@ujiroft.ac.ir.
Abdollah Ramzani Ghara, Email: a.ramzani@ujiroft.ac.ir.
Amirhossein Sahebkar, Email: amirhossein.sahebkar@uwa.edu.au.
Abolfaz Shakeri, Email: plantchem87@gmail.com.
References
- 1.Fabricant DS, Farnsworth NR. The value of plants used in traditional medicine for drug discovery. Environ Health Perspect. 2001;109(suppl 1):69–75. doi: 10.1289/ehp.01109s169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hu R, Lin C, Xu W, Liu Y, Long C. Ethnobotanical study on medicinal plants used by Mulam people in Guangxi, China. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2020;16(1):1–50. doi: 10.1186/s13002-020-00387-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Feng L, Zhai Y-Y, Xu J, Yao W-F, Cao Y-D, Cheng F-F, et al. A review on traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology of Eclipta prostrata (L.) L. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019;245:112109. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 4.Prasad S, Tyagi AK. Traditional medicine: the goldmine for modern drugs. Adv Tech Biol Med. 2015;3(1):1–2. doi: 10.4172/2379-1764.1000e108. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ojha SN, Tiwari D, Anand A, Sundriyal RC. Ethnomedicinal knowledge of a marginal hill community of Central Himalaya: diversity, usage pattern, and conservation concerns. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2020;16:1–21. doi: 10.1186/s13002-020-00381-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ghahraman A. Plant systematic: coromophytes of Iran. Tehran: Iran University press; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nasseri M. Development of traditional medicine based on WHO guidance. Med Daneshvar Biomanthly J Shahed Univ. 2004;11(52):53–66. [Google Scholar]
- 8.SABER AS, Naseri A, Rahmani GH, Kalirad A. Medicinal plants of Kerman province. 2005;
- 9.Nasab FK, Khosravi AR. Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants of Sirjan in Kerman Province, Iran. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;154(1):190–197. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sadat-Hosseini M, Farajpour M, Boroomand N, Solaimani-Sardou F. Ethnopharmacological studies of indigenous medicinal plants in the south of Kerman, Iran. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017;199:194–204. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nazari S, Rameshrad M, Hosseinzadeh H. Toxicological effects of Glycyrrhiza glabra (licorice): a review. Phyther Res. 2017;31(11):1635–1650. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sahranavard S, Ghafari S, Mosaddegh M. Medicinal plants used in Iranian traditional medicine to treat epilepsy. Seizure. 2014;23(5):328–332. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2014.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Organization WH. WHO traditional medicine strategy 2002–2005. 2002. Geneva World Heal Organ. 2002;
- 14.Pirbaloutl AG. Medicinal plants used in Chaharmahal and Bakhtyari districts of Iran. Herba Pol. 2009;55(2):69–77. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Moosavi J. The place of Avicenna in the history of medicine. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2009;1(1):3. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bibak H, Moghbeli F. Collection, identification and traditional usage of medicinal plants in Jiroft County. 2017;
- 17.Rechinger KH, Browicz K, Persson K, Wendelbo P. Flora Iranica, Akademische Druck-U. Verlagsanstalt, Graz. 1982;150(2):108–216. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Davis PH. Flora of Turkey Edinburgh University Press. Edinburgh; 1988.
- 19.Mozaffarian VA, Mozaffarian VA, Mozaffarian V. Dictionary of Iranian plant names. 1996;
- 20.Trotter R, Logan M, Trotter RT, Logan MH. Informant consensus: a new approach for identifying potentially effective medicinal plants. 1986;
- 21.Heinrich M, Ankli A, Frei B, Weimann C, Sticher O. Medicinal plants in Mexico: healers’ consensus and cultural importance. Soc Sci Med. 1998;47(11):1859–1871. doi: 10.1016/S0277-9536(98)00181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Tardío J, Pardo-de-Santayana M. Cultural importance indices: a comparative analysis based on the useful wild plants of Southern Cantabria (Northern Spain) Econ Bot. 2008;62(1):24–39. doi: 10.1007/s12231-007-9004-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sadeghi Z, Kuhestani K, Abdollahi V, Mahmood A. Ethnopharmacological studies of indigenous medicinal plants of Saravan region, Baluchistan, Iran. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;153(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Haerinasab M. Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants and introduction to some poisonous plant species of Ardestan (Isfahan Province) J Med Plants. 2019;2(70):122–143. doi: 10.29252/jmp.2.70.122. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Özdemir E, Alpınar K. An ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plants in western part of central Taurus Mountains: Aladaglar (Nigde–Turkey) J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;166:53–65. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.02.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Polat R. Ethnobotanical study on medicinal plants in Bingöl (City center)(Turkey) J Herb Med. 2019;16:100211. doi: 10.1016/j.hermed.2018.01.007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bussmann RW, Zambrana NYP, Sikharulidze S, Kikvidze Z, Kikodze D, Tchelidze D, et al. A comparative ethnobotany of Khevsureti, Samtskhe-Javakheti, Tusheti, Svaneti, and Racha-Lechkhumi, Republic of Georgia (Sakartvelo), Caucasus. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2016;12(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s13002-016-0110-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bakar F, Acikara OB, Ergene B, Nebioglu S, Citoglu GS. Antioxidant activity and phytochemical screening of some Asteraceae plants. Turk J Pharm Sci. 2015;12(2):123–132. doi: 10.5505/tjps.2015.18209. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sonmezdag AS, Kelebek H, Selli S. Identification of aroma compounds of Lamiaceae species in Turkey using the purge and trap technique. Foods. 2017;6(2):10. doi: 10.3390/foods6020010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Panmei R, Gajurel PR, Singh B. Ethnobotany of medicinal plants used by the Zeliangrong ethnic group of Manipur, northeast India. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019;235:164–182. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Goyal R, Sharma PL, Singh M. Pharmacological potential of Tecomella undulate in acute and chronic inflammation in rat. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res. 2010;1:108–114. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Baig MB, Shabbir A, Nowshad K, Muhammad K. Germplasm conservation of multipurpose trees and their role in agroforestry for sustainable agricultural production in Pakistan. Int J Agric Biol. 2008;10(2).
- 33.Hosseini SH, Azarnivand H, Ayyari M, Chahooki MAZ, Erfanzadeh R, Piacente S, et al. Modeling potential habitats for Pergularia tomentosa using maximum entropy model and effect of environmental variables on its quantitative characteristics in arid rangelands, southeastern Iran. J Ecol Environ. 2018;42(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s41610-018-0083-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sanoubar Tahaiee N, Rashidi K, Hazhir MS. Survey of Sanandaj medical society members attitudes and extent of their knowledge about herbal drugs and their prescription in 2001. Sci J Kurdistan Univ Med Sci. 2006;11(3):44–48. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Gumisiriza H, Birungi G, Olet EA, Sesaazi CD. Medicinal plant species used by local communities around Queen Elizabeth National Park, Maramagambo Central Forest Reserve and Ihimbo Central Forest Reserve, south western Uganda. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019;239:111926. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.111926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Al-Fatimi M. Ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plants in central Abyan governorate, Yemen. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019;241:111973. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.111973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Miara MD, Bendif H, Hammou MA, Teixidor-Toneu I. Ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plants used by nomadic peoples in the Algerian steppe. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018;219:248–256. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.03.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sarri M, Mouyet FZ, Benziane M, Cheriet A. Traditional use of medicinal plants in a city at steppic character (M’sila, Algeria) J Pharm Pharmacogn Res. 2014;2(2):31–35. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Nanagulyan S, Zakaryan N, Kartashyan N, Piwowarczyk R, Łuczaj Ł. Wild plants and fungi sold in the markets of Yerevan (Armenia) J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2020;16:1–27. doi: 10.1186/s13002-020-00375-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sargin SA, Selvi S, Büyükcengiz M. Ethnomedicinal plants of Aydıncık district of Mersin, Turkey. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;174:200–216. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Amiri MS, Joharchi MR, TaghavizadehYazdi ME. Ethno-medicinal plants used to cure jaundice by traditional healers of Mashhad, Iran. IJPR. 2014;13(1):157. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ostovan F, Olomi H, Gol A. The Citrullus Colocynthis pulp antioxidant activity on oxidative stress factors of liver in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Physiol Pharmacol. 2014;17(4).
- 43.Heidari F, Shirani K. Source of Eolian Facies using Geomorphological and Sedimen Tological Methods (Case Study: Ab-Barik Watershed of Bam in Kerman) JWSS-Isfahan Univ Technol. 2017;21(3):39–54. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Derakhshan AR, Yousefi M, Dehghan S, Zargaran A, Khodadoost M. Digestion process and causes of indigestion based on Avicenna’s view and modern medicine. Tradit Med Res. 2019;4(3):140–147. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Naseri M, Babaeian M, Ghaffari F, Kamalinejad M, Feizi A, Mazaheri M, et al. Bloating: Avicenna’s perspective and modern medicine. J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med. 2016;21(2):154–159. doi: 10.1177/2156587215622915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Baser KHC, Kirimer N, Kurkcuoglu M, Demirci B. Essential oils of nepeta species growing in Turkey. Chem Nat Compd. 2000;36(4):356–359. doi: 10.1023/A:1002832628159. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Formisano C, Rigano D, Senatore F. Chemical constituents and biological activities of Nepeta species. Chem Biodivers. 2011;8(10):1783–1818. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201000191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Farina C, Pinza M, Pifferi G. Synthesis and anti-ulcer activity of new derivatives of glycyrrhetic, oleanolic and ursolic acids. Farm. 1998;53(1):22–32. doi: 10.1016/S0014-827X(97)00013-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Jalilzadeh-Amin G, Najarnezhad V, Anassori E, Mostafavi M, Keshipour H. Antiulcer properties of Glycyrrhiza glabra L. extract on experimental models of gastric ulcer in mice. Iran J Pharm Res IJPR. 2015;14(4):1163. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 50.Nikbakht MR, Sharifi S, Emami SA, Khodaie L. Chemical composition and antiprolifrative activity of Artemisia persica Boiss. and Artemisia turcomanica Gand. essential oils. Res Pharm Sci. 2014;9(2):155. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 51.Rajaei P, Mohamadi N. Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants of Hezar mountain allocated in south east of Iran. IJPR. 2012;11(4):1153. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Khanjani N, Ranadeh Kalankesh L, Mansouri F. Air pollution and respiratory deaths in Kerman, Iran (from 2006 till 2010) Iran J Epidemiol. 2012;8(3):58–65. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Tuttolomondo T, Licata M, Leto C, Bonsangue G, Gargano ML, Venturella G, et al. Popular uses of wild plant species for medicinal purposes in the Nebrodi Regional Park (North-Eastern Sicily, Italy) J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;157:21–37. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.08.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Hann CS, Rock CL, King I, Drewnowski A. Validation of the Healthy Eating Index with use of plasma biomarkers in a clinical sample of women. Am J Clin Nutr. 2001;74(4):479–486. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/74.4.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Conklin AI, Monsivais P, Khaw K-T, Wareham NJ, Forouhi NG. Dietary diversity, diet cost, and incidence of type 2 diabetes in the United Kingdom: a prospective cohort study. PLoS Med. 2016;13(7). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this survey are included in this article.