Abstract
The Limnospira genus is a recently established clade that is economically important due to its worldwide use in biotechnology and agriculture. This genus includes organisms that were reclassified from Arthrospira, which are commercially marketed as “Spirulina.” Limnospira are photoautotrophic organisms that are widely used for research in nutrition, medicine, bioremediation, and biomanufacturing. Despite its widespread use, there is no closed genome for the Limnospira genus, and no reference genome for the type strain, Limnospira fusiformis. In this work, the L. fusiformis genome was sequenced using Oxford Nanopore Technologies MinION and assembled using only ultra-long reads (>35 kb). This assembly was polished with Illumina MiSeq reads sourced from an axenic L. fusiformis culture; axenicity was verified via microscopy and rDNA analysis. Ultra-long read sequencing resulted in a 6.42 Mb closed genome assembled as a single contig with no plasmid. Phylogenetic analysis placed L. fusiformis in the Limnospira clade; some Arthrospira were also placed in this clade, suggesting a misclassification of these strains. This work provides a fully closed and accurate reference genome for the economically important type strain, L. fusiformis. We also present a rapid axenicity method to isolate L. fusiformis. These contributions enable future biotechnological development of L. fusiformis by way of genetic engineering.
Keywords: Limnospira, Arthrospira, Spirulina, genome, nanopore, axenicity, cyanobacteria, long-read
Introduction
Limnospira is a recently established genus that contains three species reclassified from Arthrospira based on morphological, molecular, and ecological differences between the two genera (Nowicka-Krawczyk et al., 2019). Spirulina (Arthrospira) platensis SAG 85.79 (SAG 85.79 = CCALA 026 = UTEX 2340), Arthrospira maxima UTEX 2720, and Arthrospira platensis PCC 8005 were reclassified to Limnospira fusiformis, L. maxima, and L. indica, respectively (Voronichin, 1934; Nowicka-Krawczyk et al., 2019). Limnospira fusiformis is the type species of this new genus (Nowicka-Krawczyk et al., 2019). Although more strains possibly fall under the new Limnospira genus, there is insufficient evidence to reclassify them (Nowicka-Krawczyk et al., 2019). Both Arthrospira and Limnospira comprise photosynthetic filamentous cyanobacteria that form multicellular cylindrical trichomes (Belay and Gershwin, 2007; Nowicka-Krawczyk et al., 2019). Their cultivation is simple, inexpensive, and their alkaline growth preference makes commercial production less prone to living contaminants (Kebede and Ahlgren, 1996; Nowicka-Krawczyk et al., 2019). These aspects make Limnospira/Arthrospira attractive for use in many biotechnological and agricultural applications, including wastewater treatment, biofuels, biomanufacturing, medicine, and nutritional supplementation (Belay et al., 1993; Tokuşoglu and üUnal, 2003; Belay and Gershwin, 2007; Abed et al., 2016; Jiang et al., 2017; Aikawa et al., 2018; Czerwonka et al., 2018; Mehan et al., 2018; Zinicovscaia et al., 2018). Both L. fusiformis and L. maxima are mass-produced, economically important, and are approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for human consumption (Belay and Gershwin, 2007; Sili et al., 2012; Nowicka-Krawczyk et al., 2019). Both are, confusingly, known as “Spirulina” in commercial settings (Sili et al., 2012; Nowicka-Krawczyk et al., 2019).
Documented consumption of “Spirulina” dates to ancient Aztec civilization (Walker et al., 2014; Wan et al., 2016). Presently, “Spirulina” is globally consumed as a nutritional supplement because they are extremely nutrient dense (Campanella et al., 1999; Tokuşoglu and üUnal, 2003; Babadzhanov et al., 2004). A recent market research report predicted the global “Spirulina” market to reach $629.6 million and 68,025.2 tons by 2025 (Spirulina Market - Global Opportunity Analysis and Industry Forecast, 2019–2025).
In addition to being a massively utilized commercial “Spirulina” strain, L. fusiformis is one of two that have a publicly available genetic system (A. platensis C1 being the second) (Jeamton et al., 2017; Dehghani et al., 2018). Despite its economic importance and status as the type species for the Limnospira genus, a published reference genome for L. fusiformis does not yet exist.
There are many sequenced genomes in the “Spirulina” grouping; many of these were sequenced using short-read technologies resulting in multi-contig assemblages due to their repeat ridden character (Fujisawa et al., 2010; Carrieri et al., 2011; Cheevadhanarak et al., 2012; Sili et al., 2012; Lefort et al., 2014; Dong et al., 2015; Xu et al., 2016; Suzuki et al., 2019). A recent L. fusiformis KN assembly produced a non-final 5.78 Mb genome composed of 401 scaffolds with an N50 of 32,852 (GCA_014489865.1), demonstrating the limitations of a short-read approach. The nearest relative with an associated genome publication in the Limnospira clade is of L. indica PCC 8005 (formerly A. platensis PCC 8005, or A. nitrilum PCC 8005), and like other members of this group, Janssen et al. found its genome to be highly repetitive with components such as CRISPR arrays and transposable elements (Janssen et al., 2010). Repeat-rich genomes are difficult to close, and an unclosed genome can lead to missing genes and other assembly errors. Furthermore, an unclosed genome makes it difficult to identify contaminating sequences, which can confuse downstream genomics studies. Fully closed genomes provide a complete and accurate picture of an organism’s genetics, providing useful biological insights. Long-read sequencing can accurately span repetitive regions, making it a valuable approach for closing repeat rich genomes (Fraser et al., 2002; Amarasinghe et al., 2020). Indeed, long-read sequencing technology has produced the only closed genomes in the “Spirulina” grouping (Arthrospira sp. TJSD092 (GCA_003060805.1) and “Arthrospira sp.” PCC 9108 (GCA_016745315.1).
In this study we sequenced, assembled, and closed the 6.42 Mb genome in a single contig using Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT) MinION long-read technology, and polished the assembly with a high-accuracy, short-read Illumina MiSeq library sourced from an axenic culture. With this work we present a novel axenicity protocol and a fully closed genome for L. fusiformis, the type strain for the newly described Limnospira genus.
Materials and Methods
Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
A xenic culture of Limnospira fusiformis was purchased from the University of Texas Culture Collection of Algae (UTEX 2340). The cells were grown in modified SAG medium (162 mM NaHCO3, 38 mM Na2CO3, 2.9 mM K2HPO4, 29.4 mM NaNO3, 5.74 mM K2SO4, 17.1 mM NaCl, 0.81 mM MgSO4 ⋅ 7H2O, 0.27 mM CaCl2 ⋅ 2H2O, 12.13 μM Na2EDTA ⋅ 2H2O, 2.16 μM FeCl3 ⋅ 6H2O, 1.32 μM MnCl2 ⋅ 4H2O, 0.22 μM ZnCl2, 0.134 μM CoCl2 ⋅ 6H2O, 0.154 μM Na2MoO4 ⋅ 2H2O, 0.08 μM CuSO4 ⋅ 5H2O, 0.15 μM ZnSO4 ⋅ 7H2O, 10 μM H3BO3, 0.1 μM cyanocobalamin) shaking at 150 rpm in 30°C with 12 h 80 μmol photons per m2s light cycles using a 90 CRI light source with a color temperature of 3,000 K.
Optimum Centrifugal Force for Selective Gas Vesicle Collapse
L. fusiformis gas vesicle persistence was tested using various centrifugal forces. A L. fusiformis culture in log-phase settled overnight and buoyant cells were collected from the surface layer. The cells were centrifuged for 10 min at 2,000, 4,000, 8,000, or 16,000 g. As a control, one sample was not centrifuged. Both the pellet and surface cells from each sample were microscopically examined for changes in gas vesicles via phase-contrast microscopy at 600× magnification using a Nikon Eclipse E400.
Physical L. fusiformis Purification Treatments
Xenic L. fusiformis cultures were inoculated (OD750:0.2) in modified SAG medium. Culture growth was measured in 24 h intervals via OD750. Once the cultures reached the log phase of growth, they were incubated without shaking overnight to allow the formation of a layer of floating cells. Floating filaments were collected from the culture’s liquid surface and vortexed at medium speed for 15 s followed by 15 s on ice for 1 min. The vortexed culture was filtered using a 40 μm nylon cell strainer and washed with sterile SAG media to remove contaminants smaller than 40 μm. Filaments that remained on the strainer were suspended in 1 mL of sterile SAG, briefly vortexed, then centrifuged for 10 min at 8,000 g to separate the cellular mass into two phases: filaments pelleted with contaminants and buoyant filaments at the surface. The surface layer of filaments were collected, resuspended in sterile SAG, and centrifuged at 8,000 g a second time. The final surface layer was examined using dark-field microscopy using a Nikon Eclipse E400 at 200× magnification to assess contaminants. A portion of these cells had DNA extracted for Nanopore sequencing and genome assembly. The remaining cells were treated with further chemical purification to establish an axenic culture.
Chemical L. fusiformis Purification Treatments
Sterile SAG media was supplemented with 65 μg/mL ampicillin, 77 μg/mL cefoxitin, and 100 μg/mL meropenem (Choi et al., 2008; Sena et al., 2011). The pH of the media was adjusted to 12.15 using NaOH, then re-sterilized by 0.22 μm filtration. Cells that were physically treated were inoculated into this media and incubated in the dark for 4 days at 150 rpm and 30°C.
After 4 days, the entire culture was filtered through a 1 μm polycarbonate filter. Cells retained on the membrane were gathered and suspended in 1 mL sterile SAG medium. The cell suspension was centrifuged and the surface layer was collected. These surface layer cells were examined for contaminating species using dark-field and phase-contrast microscopy using a Nikon Eclipse E400 at 200× and 600× magnification. DNA was extracted from these cells and sequenced with Illumina sequencing to polish the genome assembly and to verify axenicity.
DNA Extraction
We adapted a CTAB-based A. platensis DNA extraction method to purify and preserve high molecular weight DNA (Morin et al., 2010). Throughout the method, to preserve high molecular weight DNA we used wide-bore tips, pipetted slowly, and only mixed with gentle inversion and finger-flicking to prevent mechanical DNA shearing. L. fusiformis cells were resuspended in 0.5 mL sterile extraction buffer (0.15 M NaCl, 0.1 M EDTA, pH 8.0) and subjected to three freeze-thaw cycles using dry ice and a 37°C bath to damage the cell walls and increase the efficiency of cell lysis. The cells were centrifuged for 10 min at 8,000 g, collected, and resuspended in CTAB buffer (75 mM Tris-HCl, 2% CTAB, 1.4 M NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, H2O, pH 8). These cells were enzymatically lysed with 50 mg of lysozyme at 37°C for 30 min. The lysed cells were incubated at 37°C for 1 h with 2% SDS, 5 mg/mL proteinase K, and 100 μg/mL RNase A. Following this incubation, the lysed cells were gently mixed by slow inversion and incubated at 65°C for 10 min to optimize the formation of CTAB -protein and -polysaccharide complexes.
The sample was incubated with 1 volume of 24:1 chloroform: isoamyl alcohol on ice for 30 min. The sample was centrifuged for 10 min at 3,500 g and the aqueous phase was transferred to a fresh tube. One volume of phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1) was added, mixed with gentle inversion, and centrifuged for 3 min at 3,500 g. The aqueous phase was transferred to a fresh tube and the phenol:chloroform:isoamyl wash was repeated until the interphase was cleared of flocculent material. The aqueous phase was gently washed with one volume of 24:1 chloroform:isoamyl alcohol, centrifuged for 3 min at 3,500 g, and transferred to a fresh tube. The chloroform:isoamyl alcohol wash was repeated 4 more times.
The final aqueous phase was gently mixed with 1/10 volume 3 M NaOAc (pH 5.4) and 2.5 volumes of 100% ethanol to precipitate DNA. The sample was incubated at −20°C overnight, then centrifuged at 3,500 g for 1 h at 4°C to pellet the DNA. The supernatant was removed, and the DNA was washed twice with 70% ethanol and mixed by inversion. Following the last wash, the DNA pellets were allowed to air dry. TE (1X) buffer was added to the DNA pellet and it was then incubated at 37°C until fully dissolved. The DNA purity was assessed with a Nanodrop UV/VIS spectrophotometer and the size was observed on a 0.5% agarose gel alongside a NEB 1 kb extended ladder (#N3239S). We consistently extracted pure high molecular weight DNA using this method (Supplementary Figures 1, 2). High molecular weight DNA was selected for Nanopore sequencing via gel extraction.
DNA Sequencing
L. fusiformis cells that had undergone only physical purification were sequenced using one Oxford Nanopore Technologies’ (ONT) MinION flowcell. The DNA was prepared for sequencing using the SQK-LSK109 protocol following the manufacturer’s instructions. DNA extracted from the axenic L. fusiformis culture—which had undergone both physical and chemical treatments—was shipped to the University of California Davis DNA Technologies and Expression Analysis Cores for Illumina library preparation and sequencing. The DNA was sheared and size selected for 500 bp fragments and sequenced using a single Illumina MiSeq 2 × 300 run using index AAGGTACA, which accounted for 17% of the 21.8 M reads with an overall Q30 > 80%.
Long-Read Genome Assembly
Default settings were used for all tools unless otherwise specified. The MinION reads were basecalled using ONT’s basecaller, Bonito v0.1.51. The basecalled MinION reads were filtered to include reads > 35 kb and these were assembled using Shasta v0.4.0 (Shafin et al., 2019). This assembly was polished using PEPPER v0.1.12, followed by three rounds of polishing with the Illumina data using Pilon v1.22 (Walker et al., 2014). NCBI’s Prokaryotic Genome Annotation Pipeline was used to annotate the genome3. BUSCO v4.1.4 was used to assess genome quality by tabulating the 773 single-copy core cyanobacterial orthologs represented in the cyanobacteria_odb10 model (Seppey et al., 2019). NCBI tblastn and blastp (Altschul et al., 1990) were used to identify missing orthologs reported by BUSCO. The genome was oriented using dnaA as a marker for the origin of replication; it was placed on the top strand and as the first gene using Geneious v11.0.5. Repeats were identified using the Repeat Finder v1.0.1 Geneious plugin. PlasmidSPAdes v3.12.0 and Bandage v0.8.1 were used to identify potential plasmids within the Illumina data (Wick et al., 2015; Antipov et al., 2016). PhyML v2.2.4 with 1,000 bootstrap steps and a Jukes-Cantor genetic distance model was used to build a maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree using published cpcAB gene sequences (Guindon et al., 2010). The phylogenetic tree was visualized with SeaView v5.0.4 (Gouy et al., 2010).
Short-Read Genome Assembly
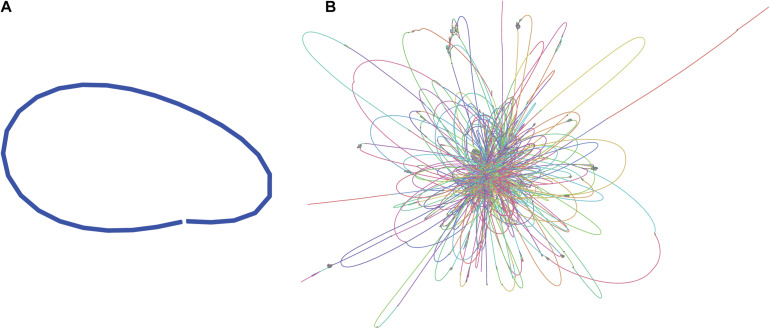
Illumina paired-end sequences were merged and adapters were trimmed using SeqPrep4, specifying a minimum overlap of 50 bases and enabling merging with the -s option. Of the 3.7 M original read-pairs, 2/3 were able to be merged, resulting in 2.36 M merged reads and 1.21 M unmerged read-pairs. The 1.2 M read-pairs and 2.36 M merged reads were assembled with the SPAdes-bwa mem v3.12.0 assembler using parameters -t 16 (16 threads) -v 1 (verbose level errors). This assembly was used only for visualization purposes (Figure 1B).
FIGURE 1.
Assembly graphs of L. fusiformis assemblies using (A) nanopore data (Shasta), (B) illumina data (SPAdes) (images generated using Bandage: Wick et al., 2015).
Axenicity Verification
Axenicity was verified using RNAmmer 1.2 to detect ribosomal RNA genes in axenic Illumina contigs (Lagesen et al., 2007). Organisms were identified by their ribosomal RNA genes using NCBI BLAST (Altschul et al., 1990).
Results
Genome
Sequencing Approach Produced a Closed Genome Assembly
The L. fusiformis (Table 1) genome is highly repetitive, which may cause misassembly with short-read data, such as that produced by Illumina sequencing. We used long-read nanopore sequencing to assemble the genome to circumvent issues posed by repeated sequences. We performed nanopore sequencing on DNA that was extracted from a physically treated culture that resulted in predominantly L. fusiformis DNA (Figure 2B and Supplementary Figure 13). Ultra-long read libraries maximize the overlaps between reads, minimize the opportunities for misassembles caused by common repeats, and thereby reduce the need for a completely axenic culture. We acquired 1.72 M reads from a single MinION flowcell and filtered for reads > 35 kb (17,345 reads). The filtered reads resulted in a fully closed genome assembly with 114× coverage, at a predicted base accuracy of ∼96.4% (Jain et al., 2018; Mulroney et al., 2020). To ensure the most reliable genome assembly, we isolated and sequenced an axenic culture using selective gas vesicle collapse, filtration, antibiotic treatments and alkaline pH selection. DNA extracted from this culture was sequenced using short-read Illumina (157× coverage). The nanopore genome assembly was polished using this short-read library, with a predicted > 99% average base accuracy (Jain et al., 2018) (see section “Materials and Methods”). This produced an NCBI-classified complete assembly level genome (Kitts et al., 2016) with an N50 of 6.42 Mb. In contrast, the short-read only assembly had an N50 of 51.6 kb, thus it was discarded and not used outside of Figure 1B. The advantage of the ultra-long read library is clearly apparent when comparing assemblies using the two techniques independently (Figure 1). When combined, we produced a closed 6.42 Mb circular genome assembled as a single chromosome (Table 2).
TABLE 1.
Classification and general features of L. fusiformis according to the MIGS standard (Field et al., 2008).
| Classification and general features of Limnospira fusiformis SAG 85.79 | ||
| Property | Term | References |
| Current classification | Domain Bacteria Phylum Cyanobacteria Class Cyanophyceae Order Oscillatoriales Genus Limnospira Species fusiformis SAG 85.79 | TASa TASb NAS TASa TASb |
| Cell shape | Spiral | NAS |
| Sporulation | None | NAS |
| Encoded traits | Antibiotic resistance beta-lactam and fluoroquinolones | IDA |
| Temperature range | 20–40°C | TASc |
| Optimum temperature | 30–45°C | TASc |
| pH | 8.0–10.0 | TASc |
| Carbon source | Phototroph, mixotroph | TASc |
| Energy source | Phototroph | TASc |
| Relationship to oxygen | Aerobic | TASc |
| Pathogenicity | None | NAS |
| Origin | Natron Lake, Chad | NAS |
| Habitat | Freshwater | NAS |
| Latitude | 14.306969 N | NAS |
| Longitude | 18.581542 E | NAS |
| Obtained from | University of Texas, Strain UTEX 2340 | NAS |
Evidence codes: IDA, Inferred from Direct Assay (first time in publication); TAS, Traceable Author Statement. TASa : (Muhling, 2000), TASb : (Furmaniak et al., 2017), TASc : (Vonshak, 1997); NAS, Non-traceable Author Statement. These evidence codes are from the Gene ontology Project (Ashburner et al., 2000).
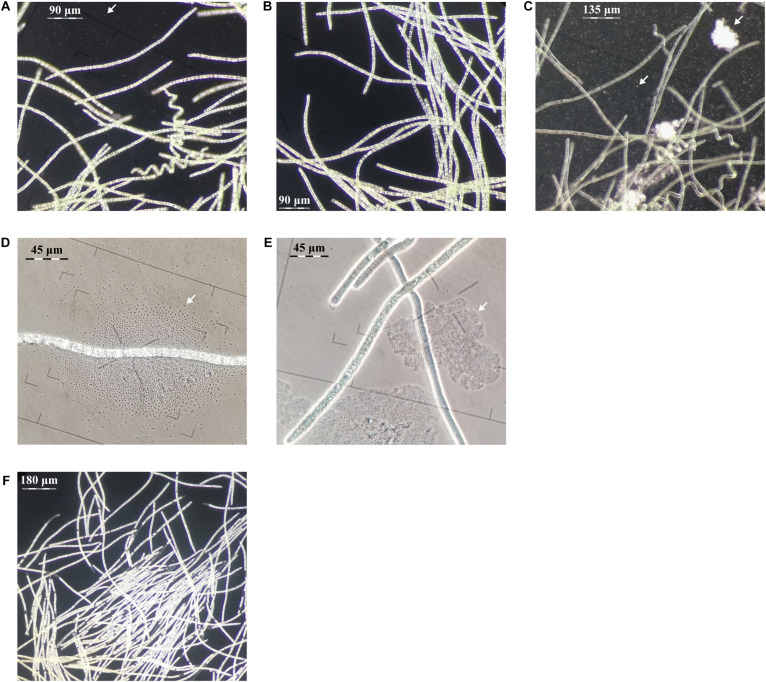
FIGURE 2.
Evaluation of centrifugation, elevated pH and antibiotic purification methods for L. fusiforms (contaminants shown with arrows). (A) Buoyant cells obtained from a culture of L. fusiformis before any treatment that contained contaminants. Applying only centrifugation resulted in (B) a surface layer of partially purified trichomes and (C) a pellet containing debris and contaminants. (D) Buoyant cells obtained from a culture of L. fusiformis before any treatment. (E) Applying only elevated pH (12.15 pH for 4 days) resulted in a culture with lysed contaminants (likely Microcystis sp. based on morphology; Sant’Anna et al., 2008). (F) The combination of filtration, centrifugation (B), pH treatments (E), and an antibiotic cocktail resulted in an axenic L. fusiformis culture.
TABLE 2.
Genome assembly details and summary statistics for Limnospira fusiformis SAG 85.79 (MIGS standard, Field et al., 2008).
| Project summary | ||
| Genome assembly details | ||
| Property | Term | |
| Finishing quality | Complete | |
| Libraries used | Nanopore 1D genomic DNA by Ligation SQK-LSK109 | |
| Sequencing platforms | Oxford Nanopore MinION, Illumina MiSeq | |
| Fold coverage | 114.0× | |
| Assemblers | Shasta v. 0.4.0 | |
| Gene calling method | Prokaryotic Genome Annotation Pipeline (https://github.com/ncbi/pgap) | |
| Genome database release | Genbank | |
| Genbank ID | NZ_CP051185.1 | |
| Project relevance | Biotechnology | |
| Genome statistics | ||
| Property | Term | % total |
| Genome size (bp) | 6,423,694 | 100.00% |
| DNA coding region (bp) | 5,317,886 | 82.8% |
| DNA G+C content (bp) | 2,882,690 | 44.9% |
| Total genes | 5,994 | 100% |
| Protein coding genes | 5,344 | 89.2% |
| RNA genes | 51 | 0.85% |
| rRNA operons | 2 | |
| tRNAs | 41 | |
| CRISPR arrays | 7 | |
Genome completeness is an important measure for assembly quality. One method to assess genome completeness is to identify core genes of the clade. We used BUSCO to assess genome completeness by tabulating the 773 single-copy core cyanobacterial orthologs (Seppey et al., 2019). The BUSCO score was 98.9% (765/773 complete). Of these complete genes, five were duplicated. Additionally, there were three genes that were fragmented and five that were reported missing. With further analysis of the five missing genes using NCBI tblastn and blastp (Altschul et al., 1990): two were present in alternate forms (inositol monophosphatase and n-acetyltransferase); recF and riboflavin synthase subunit alpha had 3′ truncations possibly derived from sequencing errors; and like all other Limnospira species, miniribonuclease 3 is also not present in L. fusiformis but ribonuclease 3 is present.
The genomes of L. fusiformis and its close relative Arthrospira sp. TJSD092 are within 10.7 kb in size and share the same 44.9% GC content (GCA_003060805.1). The DNA coding region (CDS) comprises 82.8% of the genome, with a total of 5,994 genes, 5,344 of which are protein-coding and 51 are RNA genes. The genome contains two rRNA operons and 41 tRNAs.
Selfish DNA elements tend to be repetitive, and we found that 29.6% of the genome is annotated as repetitive DNA (Geneious v11.0.5). Selfish DNA elements were abundant in the L. fusiformis genome and included 518 transposases, 12 recombinases, 89 toxin/antitoxin elements, and seven CRISPR arrays. We also found 37 reverse transcriptases and eight phage annotations, indicating possible viral associations with this genome. Furthermore, these sequences appeared to be widespread among Limnospira, where we found homologues of these genes using blastx (E < e-36, ≥ 98% coverage, data not shown), suggesting that these selfish elements are endemic to the clade.
L. fusiformis contains the HsdR, HsdM, and HsdS type I restriction modification system as well as a Res-Mod type III system. The seven CRISPR clusters are comparable to the three-to-nine clusters present in other “Spirulina” genomes (Table 3). The genome’s type I and III restriction modification systems and CRISPRs are the main defense mechanisms that inhibit the stable transformation of Arthrospira (Cheevadhanarak et al., 2012; Jeamton et al., 2017).
TABLE 3.
Summary of Limnospira and “Arthrospira” genome assemblies.
| Strain | Assembly level | Sequencing technology | Coverage | N50 (bp) | References |
| L. fusiformis SAG 85.79 | Complete | Nanopore; Illumina | 114× | 6,423,694 | This study GCA_012516315.1 |
| “Arthrospira sp.” TJSD092 | Complete | Illumina; PacBio | 190× | 6,434,389 | Genbank accession: GCA_003060805.1 |
| “Arthrospira sp.” PCC 9108 | Complete | PacBio | 191× | 6,763,964 | Genbank accession: GCA_016745315.1 |
| L. indica PCC 8005 | Chromosome | 454; Sanger | n/a | 1,412,831 | Janssen et al., 2010: GCA_000973065.1 |
| Limnospira sp. BM01 | Chromosome | Illumina | 6.43× | 61,454 | Genbank accession: GCA_014250495.1 |
| “A. platensis” NIES-39 | Chromosome | ABI 3730 | 11× | 619,347 | Fujisawa et al., 2010: GCA_000210375.1 |
| “A. platensis” C1 | Chromosome | 454; Sanger | 28× | 206,210 | Cheevadhanarak et al., 2012: GCA_000307915.1 |
| “A. platensis” YZ | Chromosome | ABI 3730; Illumina | 86× | 1,054,592 | Xu et al., 2016: GCA_001611905.1 |
| Limnospira fusiformis KN | Scaffold | Illumina | 350× | 32,852 | Genbank accession: GCA_014489865.1 |
| “A. maxima” CS-328 | Contig | n/a | n/a | 92,573 | Carrieri et al., 2011: GCA_000173555.1 |
| “A. platensis” NIES-46 | Contig | MiSeq | 42× | 40,752 | Suzuki et al., 2019: GCA_009176225.1 |
| A. platensis Paraca | Contig | Illumina | 36× | 72,660 | Lefort et al., 2014: GCA_000175415.3 |
| “Arthrospira sp.” TJSD091 | Contig | Illumina | 130× | 49,578 | Dong et al., 2015: GCA_000974245.1 |
| “A. platensis” O9.13F | Contig | Illumina | 20× | 6,514 | Genbank accession: GCA_003268325.1 |
| “A. platensis” FACHB-971 | Contig | Illumina | 50× | 39,263 | Genbank accession: GCA_014698385.1 |
| “A. platensis” FACHB-439 | Contig | Illumina | 50× | 44,370 | Genbank accession: GCA_014698675.1 |
| “A. platensis” FACHB-835 | Contig | Illumina | 50× | 34,814 | Genbank accession: GCA_014698815.1 |
| Arthrospira sp. PLM2.Bin9 | Contig | Illumina | 18× | 36,014 | Genbank accession: GCA_007732545.1 |
Assembly level as described previously (Kitts et al., 2016).
Phylogenetic Analysis Confirmed L. fusiformis Placement in the Limnospira Clade
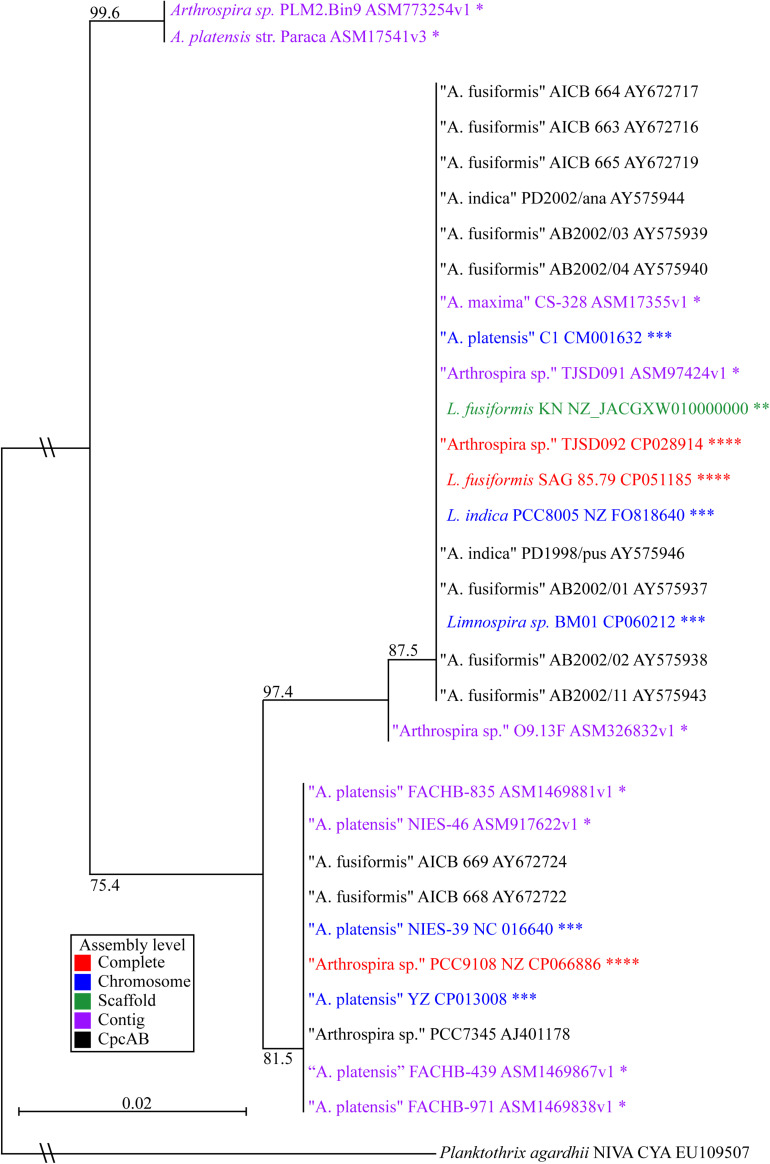
We built a phylogenetic tree based on the phycocyanin alpha and beta subunits, cpcAB (Figure 3; Manen and Falquet, 2002). The tree includes all Arthrospira and Limnospira genome assemblies, as well as additional strains that were previously placed in the Limnospira clade with publicly available cpcAB sequences (Nowicka-Krawczyk et al., 2019).
FIGURE 3.
Limnospira phylogenetic tree based on cpcAB loci. The sequence sources of the cpcAB loci are denoted: complete genome (red ****), chromosome assembly (blue ∗∗∗), scaffold assembly (green ∗∗), contig assembly (purple ∗), cpcAB sequence only (black). Bootstrap values of major branch points are shown. Quotation marks are used to indicate species proposed for Limnospira membership.
Figure 3 shows L. fusiformis and most of the “Arthrospira” strains placed in the Limnospira clade (Nowicka-Krawczyk et al., 2019). A. platensis Paraca and Arthrospira sp. PLM2.Bin9 are the only strains not clearly in the Limnospira clade. Consistent with previous results (Cheevadhanarak et al., 2012; Nowicka-Krawczyk et al., 2019), the Limnospira clade is split into two major groups (Figure 3). Of the sequenced genomes (Table 3), Arthrospira sp. PCC 9108 and A. platensis NIES-39, NIES-46, YZ, FACHB-971, FACHB-439, and FACHB-835 are grouped together in one branch while a second group contains L. fusiformis SAG 85.79, Arthrospira sp. TSJD092, Limnospira sp. BM01, L. fusiformis KN, Arthrospira sp. TSJD091, A. platensis C1, A. maxima CS-328, L. indica PCC 8005, and Arthrospira sp. O9.13F (Figure 3).
Extrachromosomal Elements Were Not Detected
A report from 1993 (Song et al., 1993) indicated the presence of a plasmid in Spirulina platensis, however, this finding has not been described elsewhere (Fujisawa et al., 2010; Cheevadhanarak et al., 2012; Lefort et al., 2014). Therefore, we conducted a search for circular extrachromosomal DNA elements within the L. fusiformis genome. We used PlasmidSPAdes and Bandage to identify circular contigs within the Illumina library and screened the elements that were present in both outputs (Wick et al., 2015; Antipov et al., 2016). Our search for extrachromosomal elements was conducted with the short-read axenic library in order to exclude contaminating elements present in the long-read xenic library. We did not identify any extrachromosomal elements belonging to L. fusiformis (the PhiX Control v3 circular spike-in Illumina control library was present, as expected).
Axenicity
Selective Gas Vesicle Collapse Is an Effective Physical Treatment
Gas vesicles allow A. platensis cells to float during log-phase (Kim et al., 2005). If these vesicles proved to be more robust than the vesicles of contaminating species, this property could be used as a separation method. Under phase-contrast microscopy, gas vesicles appear as bright irregular shapes within these ∼80 μm buoyant trichomes (Cohen-Bazire et al., 1969; Sili et al., 2012). Gas vesicles collapse under pressure, causing cells to lose their buoyancy and appear darker and more hollow (Cohen-Bazire et al., 1969; Walsby and Bleything, 1988). We cultured xenic L. fusiformis under standard growth conditions and observed buoyancy from day three to at least day eight. These xenic cultures were pressurized with centrifugal forces at 2,000, 4,000, 8,000, and 16,000 g, and selective separation was found at 8,000 g (Supplementary Figures 3–11).
We enriched for L. fusiformis using selective gas vesicle collapse to deplete contaminating microbes. L. fusiformis cells were briefly vortexed to remove contaminating bacteria attached to the trichomes (Figure 2A), filtered at 40 μm, centrifuged to pellet the contaminants (Figure 2C), then transferred from the surface layer to sterile media (Figure 2B). Dark-field microscopy images at each stage confirmed the purification (Figures 2A–C and Supplementary Figures 12–14). We implemented these findings as a novel axenicity technique—selective gas vesicle collapse.
An Axenic L. fusiformis Culture Was Established Under Antibiotic and Alkaline Conditions
L. fusiformis tolerates elevated alkaline conditions and specific antibiotics, unlike microcystin-producing species (i.e., Microcystis aeruginosa, Oscillatoria spp., and Nostoc spp.), which often contaminate “Spirulina” supplements (Moreno et al., 2004; Sena et al., 2011; Roy-Lachapelle et al., 2017; Borowitzka, 2018; Khong et al., 2019). We found the highest tolerable pH (12.15) also caused contaminating species (i.e., Microcystis spp.) to lyse (Figures 2D,E and Supplementary Figures 15, 16). This high pH combined with an antibiotic cocktail selected against any residual contaminating species while minimizing damage to L. fusiformis, resulting in an axenic culture (Figure 2F and Supplementary Figure 17; Choi et al., 2008; Sena et al., 2011).
Microscopy and rDNA Sequence Analysis Support Axenicity of Prepared Culture
The treated culture was analyzed under dark-field microscopy and no contaminating organisms were detected. We then compared sequencing data from samples that had only undergone physical treatments—represented by the nanopore data—with samples that were subjected to physical and chemical treatments—represented by the Illumina data. We conducted a computational search for 16s and 23s ribosomal RNA gene sequences within these respective data sets. Four contaminating ribosomal gene sequences were identified within the nanopore data, with best matches to: Coraliomargarita akajimensis, Lishizhenia caseinilytica, Halomonas desiderata, and a member of Xanthomonadacae. When physical and chemical treatments were combined (see section “Materials and Methods” for details), only ribosomal RNA gene sequences from L. fusiformis were detected. Based on these results we concluded that physical treatment alone was not sufficient to induce axenicity. However, axenicity was achieved when physical treatment was used in combination with chemical treatment.
Discussion
Long-read sequencing enabled closure of the Limnospira fusiformis genome in a single pass. The 6.42 Mb genome, assembled as a single circular chromosome, required the scaffolding power of long reads (>35 kb) and the accuracy afforded by the short-read library. Assemblies of this highly repetitive “Spirulina” family have been previously attempted without the guidance of long-reads; multi-contig drafts or incorrect genome structure can be the result (Alkan et al., 2011; Tørresen et al., 2019). Indeed, the only closed genomes in the group have been possible with long-read produced scaffolds (Table 3). We believe our approach allows for a simple assembly that is less error prone when compared to using short-read data alone.
Nowicka-Krawczyk proposed the Limnospira clade using rRNA nucleotide sequences of 64 “Arthrospira” strains and established L. fusiformis, L. indica, and L. maxima as the founding members of the genus (Nowicka-Krawczyk et al., 2019). Phylogenetic analysis using published cpcAB sequences (Manen and Falquet, 2002) from that clade combined with the currently available Arthrospira genomes (Table 3) shows that most of these are grouped with Limnospira, with the exception of A. platensis Paraca and Arthrospira sp. PLM2.Bin9 (Figure 3). Furthermore, the optimal pH conditions derived from publications, media recipes, or the isolate geography establishes the Limnospira clade with an alkaline preference (pH 8–10), as described by Nowicka-Krawczyk (ATCC medium 1679); (BioSample: SAMN10237416; Vonshak, 1997; Şeker et al., 2008; Carrieri et al., 2011; Cheevadhanarak et al., 2012; Miklaszewska et al., 2012; Lefort et al., 2014; Dong et al., 2015; Shiraishi, 2015; Dineshkumar et al., 2016; Xu et al., 2016; Suzuki et al., 2019; Yadav et al., 2020; Zhao et al., 2020). With A. platensis Paraca and Arthrospira sp. PLM2.Bin9 as an outgroup, we propose that the two subclades (Figure 3) should be reclassified as Limnospira, which is consistent with Nowicka-Krawczyk’s rRNA analysis.
In contrast with previous studies which provided time-intensive broad-spectrum or rapid, contaminant-specific approaches, we focused on rapid and broad-spectrum selection using sequencing to verify axenicity (Table 4). Broad-spectrum selection is important when contaminating species are unknown. The protocol we have developed can be completed in 7 days, and the use of antibiotics, elevated pH, and selective gas vesicle collapse provides the necessary selection.
TABLE 4.
“Arthrospira” and Limnospira axenicity methods.
| Method | Description | Time required | Verification | Strain |
| Shiraishi (2015) | Washing by vortexing and filtration Individual trichomes selected for axenic culture propagation | >1 month | Microscopy and agar plating | A. platensis UTEX 1926 |
| Sena et al. (2011) | Washing by filtration pH treatment Antibiotic treatment Propagation Serial dilutions | ∼3 weeks | Microscopy and agar plating | A. platensis Lefevre 1963/M-132-1 |
| Choi et al. (2008) | Washing by centrifugation Antibiotic treatment | 7 days | Microscopy and agar plating | A. platensis SAG 21.99 |
| Physical and chemical treatments (this work) | Surface layer collection from culture Washing by vortexing and filtration Washing by centrifugation and surface layer extraction Antibiotic and pH treatment | 7 days | Microscopy and 16s and 23s rDNA identification | L. fusiformis (formerly known as A. platensis SAG 85.79) |
We have provided an accurate reference genome and a rapid axenicity method for Limnospira fusiformis and now propose the optimization of genetic engineering methods as the next step in progressing L. fusiformis research. Two stable transformation methods are described for Limnospira species—Rhizobium radiobacter (syn. Agrobacterium tumefaciens)-based DNA transfer and Tn5 transposon-mediated genome manipulation (Jeamton et al., 2017; Dehghani et al., 2018). Both methods integrate DNA into non-specific genomic loci but targeted edits may be possible when used in conjunction with other molecular tools (Vergunst et al., 1998; Tzfira et al., 2003; Fan et al., 2015; Chen and Wang, 2019). Targeted mutations to the restriction modification system in L. fusiformis would be an ideal target for improving its transformation efficiency, as has been done in other organisms (Hoshino et al., 1980; Kretz et al., 1991; Hobson et al., 2008; Ferri et al., 2010). With the rapid proliferation of genetic engineering tools, new methods for customizing L. fusiformis will become applicable as it finds continued success in the global market.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, PRJNA623410.
Author Contributions
MH, LM, and DB devised the project and designed the experiments. DB and LM supervised the project. MH performed the genome experiments. MH and T-KT-D performed the axenicity experiments. All authors contributed to bioinformatic analysis, wrote, and approved the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
LM has received reimbursement for travel, accommodation and conference fees to speak at events organized by ONT. The authors declare that this study received materials from Zymo Research, Biomatters Inc., and Avantor Biosciences. These sponsors were not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article or the decision to submit it for publication.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Chris Vollmers and his lab for performing the DNA size selection, providing material for an ONT library preparation, and for their valuable advice. We also thank Mark Akeson’s lab, especially Miten Jain, for providing materials and advice for Nanopore sequencing. Much gratitude toward Marilou Sison-Mangus’ lab for providing CTAB and advice on cyanobacteria culturing and DNA purification. Sincere thanks to Elliot Roth of Spira Inc. for strain and culturing advice. We would also like to thank our teammates from the UCSC iGEM team of 2017, who we began this project with. We give a special acknowledgment to team members Mark Lund, Marissa Taub, Tyler Myers, Hailey Loehde-Woolard, Sarah Medor, and Jethro Marasigan who helped with culturing and brainstorming during the early stages of this research. We thank corporate sponsors Zymo Research, Biomatters Inc., and Avantor Biosciences for providing research materials.
Funding. Special thanks to the following for funding support: The UCSC 2016 iGEM team, UCSC colleges and administration, UCSC Giving Day and crowdfunding donors.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2021.657995/full#supplementary-material
References
- Abed E., Ihab N., Suliman E., Mahmoud A. (2016). Impact of Spirulina on nutritional status, haematological profile and anaemia status in malnourished children in the gaza strip: randomized clinical trial. Matern. Pediatr. Nutr. 2:2. 10.4172/2472-1182.1000110 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Aikawa S., Inokuma K., Wakai S., Sasaki K., Ogino C., Chang J.-S., et al. (2018). Direct and highly productive conversion of cyanobacteria Arthrospira platensis to ethanol with CaCl2 addition. Biotechnol. Biofuels 11:50. 10.1186/s13068-018-1050-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkan C., Sajjadian S., Eichler E. E. (2011). Limitations of next-generation genome sequence assembly. Nat. Methods 8 61–65. 10.1038/nmeth.1527 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. (1990). Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215 403–410. 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amarasinghe S. L., Su S., Dong X., Zappia L., Ritchie M. E., Gouil Q. (2020). Opportunities and challenges in long-read sequencing data analysis. Genome Biol. 21:30. 10.1186/s13059-020-1935-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antipov D., Hartwick N., Shen M., Raiko M., Lapidus A., Pevzner P. A. (2016). plasmidSPAdes: assembling plasmids from whole genome sequencing data. Bioinforma. Oxf. Engl. 32 3380–3387. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw493 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M., Ball C. A., Blake J. A., Botstein D., Butler H., Cherry J. M., et al. (2000). Gene Ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 25 25–29. 10.1038/75556 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babadzhanov A. S., Abdusamatova N., Yusupova F. M., Faizullaeva N., Mezhlumyan L. G., Malikova M. K. (2004). Chemical Composition of Spirulina platensis Cultivated in Uzbekistan. Chem. Nat. Compd. 40 276–279. 10.1023/B:CONC.0000039141.98247.e8 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Belay A., Gershwin M. E. (2007). Spirulina in Human Nutrition and Health. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. [Google Scholar]
- Belay A., Ota Y., Miyakawa K., Shimamatsu H. (1993). Current knowledge on potential health benefits of Spirulina. J. Appl. Phycol. 5 235–241. 10.1007/BF00004024 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Borowitzka M. A. (2018). “Chapter 3 - Biology of microalgae,” in Microalgae in Health and Disease Prevention, eds Levine I. A., Fleurence J. (Cambridge, MA: Academic Press; ), 23–72. 10.1016/B978-0-12-811405-6.00003-7 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Campanella L., Crescentini G., Avino P. (1999). Chemical composition and nutritional evaluation of some natural and commercial food products based on Spirulina. Analusis 27 533–540. 10.1051/analusis:1999130 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Carrieri D., Ananyev G., Lenz O., Bryant D. A., Dismukes G. C. (2011). Contribution of a Sodium Ion Gradient to Energy Conservation during Fermentation in the Cyanobacterium Arthrospira (Spirulina) maxima CS-328 ▽. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77 7185–7194. 10.1128/AEM.00612-11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheevadhanarak S., Paithoonrangsarid K., Prommeenate P., Kaewngam W., Musigkain A., Tragoonrung S., et al. (2012). Draft genome sequence of Arthrospira platensis C1 (PCC9438). Stand. Genomic Sci. 6:43. 10.4056/sigs.2525955 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. P., Wang H. H. (2019). An engineered cas-transposon system for programmable and precise DNA transpositions. bioRxiv [Preprint] 10.1101/654996 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi G.-G., Bae M.-S., Ahn C.-Y., Oh H.-M. (2008). Induction of axenic culture of Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis based on antibiotic sensitivity of contaminating bacteria. Biotechnol. Lett. 30 87–92. 10.1007/s10529-007-9523-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Bazire G., Kunisawa R., Pfennig N. (1969). Comparative study of the structure of gas vacuoles. J. Bacteriol. 100 1049–1061. 10.1128/JB.100.2.1049-1061.1969 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerwonka A., Kaławaj K., Sławińska-Brych A., Lemieszek M., Bartnik M., Kk W., et al. (2018). Anticancer effect of the water extract of a commercial Spirulina (Arthrospira platensis) product on the human lung cancer A549 cell line. Biomed. Pharmacother. 106 292–302. 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.116 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehghani J., Adibkia K., Movafeghi A., Barzegari A., Pourseif M., Maleki-Kakelar H., et al. (2018). Stable transformation of Spirulina (Arthrospira) platensis: a promising microalga for production of edible vaccines. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 102 9267–9278. 10.1007/s00253-018-9296-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dineshkumar R., Narendran R., Sampathkumar P. (2016). Cultivation of Spirulina platensis in different selective media. Indian J. Mar. Sci. 45 1749–1754. [Google Scholar]
- Dong S., Chen J., Wang S., Wu Y., Hou H., Li M., et al. (2015). Draft genome sequence of cyanobacteria Arthrospira sp. TJSD091 isolated from seaside wetland. Mar. Genomics 24 197–198. 10.1016/j.margen.2015.05.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan D., Liu T., Li C., Jiao B., Li S., Hou Y., et al. (2015). Efficient CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted mutagenesis in Populus in the first generation. Sci. Rep. 5:12217. 10.1038/srep12217 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferri L., Gori A., Biondi E. G., Mengoni A., Bazzicalupo M. (2010). Plasmid electroporation of Sinorhizobium strains: The role of the restriction gene hsdR in type strain Rm1021. Plasmid 63 128–135. 10.1016/j.plasmid.2010.01.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field D., Garrity G., Gray T., Morrison N., Selengut J., Sterk P., et al. (2008). The minimum information about a genome sequence (MIGS) specification. Nat. Biotechnol. 26 541–547. 10.1038/nbt1360 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser C. M., Eisen J. A., Nelson K. E., Paulsen I. T., Salzberg S. L. (2002). The value of complete microbial genome sequencing (you get what you pay for). J. Bacteriol. 184 6403–6405. 10.1128/JB.184.23.6403-6405.2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa T., Narikawa R., Okamoto S., Ehira S., Yoshimura H., Suzuki I., et al. (2010). Genomic structure of an economically important cyanobacterium, Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis NIES-39. DNA Res. Int. J. Rapid Publ. Rep. Genes Genomes 17 85–103. 10.1093/dnares/dsq004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furmaniak M. A., Misztak A. E., Franczuk M. D., Wilmotte A., Waleron M., Waleron K. F. (2017). Edible Cyanobacterial genus Arthrospira: actual state of the art in cultivation methods, genetics, and application in medicine. Front. Microbiol. 8:2541. 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02541 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouy M., Guindon S., Gascuel O. (2010). SeaView version 4: a multiplatform graphical user interface for sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree building. Mol. Biol. Evol. 27 221–224. 10.1093/molbev/msp259 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guindon S., Dufayard J.-F., Lefort V., Anisimova M., Hordijk W., Gascuel O. (2010). New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 59 307–321. 10.1093/sysbio/syq010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobson N., Price N. L., Ward J. D., Raivio T. L. (2008). Generation of a restriction minus enteropathogenic Escherichia coli E2348/69 strain that is efficiently transformed with large, low copy plasmids. BMC Microbiol. 8:134. 10.1186/1471-2180-8-134 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino T., Uozumi T., Beppu T., Arima K. (1980). High efficiency of heterologous transformation of a Restrictionless and Modificationless mutant of bacillus subtilis 168. Agric. Biol. Chem. 44 621–623. 10.1080/00021369.1980.10864001 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Jain M., Koren S., Miga K. H., Quick J., Rand A. C., Sasani T. A., et al. (2018). Nanopore sequencing and assembly of a human genome with ultra-long reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 36 338–345. 10.1038/nbt.4060 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen P. J., Morin N., Mergeay M., Leroy B., Wattiez R., Vallaeys T., et al. (2010). Genome sequence of the edible Cyanobacterium Arthrospira sp. PCC 8005. J. Bacteriol. 192 2465–2466. 10.1128/JB.00116-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeamton W., Dulsawat S., Tanticharoen M., Vonshak A., Cheevadhanarak S. (2017). Overcoming intrinsic restriction enzyme barriers enhances transformation efficiency in Arthrospira platensis C1. Plant Cell Physiol. 58 822–830. 10.1093/pcp/pcx016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang L., Wang Y., Yin Q., Liu G., Liu H., Huang Y., et al. (2017). Phycocyanin: a potential drug for cancer treatment. J. Cancer 8 3416–3429. 10.7150/jca.21058 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebede E., Ahlgren G. (1996). Optimum growth conditions and light utilization efficiency of Spirulina platensis (= Arthrospira fusiformis) (Cyanophyta) from Lake Chitu. Ethiopia. Hydrobiologia 332 99–109. 10.1007/BF00016689 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Khong N. M. H., Khaw Y. S., Nazarudin M. F., Yusoff F. M. (2019). Microcystis aeruginosa grown in different defined media leads to different cultivable heterotrophic bacteria composition that could influence cyanobacterial morphological characteristics and growth properties. bioRxiv [Preprint] 10.1101/721175 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S.-G., Choi A., Ahn C.-Y., Park C.-S., Park Y.-H., Oh H.-M. (2005). Harvesting of Spirulina platensis by cellular flotation and growth stage determination. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 40 190–194. 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2005.01654.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P. A., Church D. M., Thibaud-Nissen F., Choi J., Hem V., Sapojnikov V., et al. (2016). Assembly: a resource for assembled genomes at NCBI. Nucleic Acids Res. 44 D73–D80. 10.1093/nar/gkv1226 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretz P. L., Kohler S. W., Short J. M. (1991). Identification and characterization of a gene responsible for inhibiting propagation of methylated DNA sequences in mcrA mcrB1 Escherichia coli strains. J. Bacteriol. 173 4707–4716. 10.1128/jb.173.15.4707-4716.1991 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagesen K., Hallin P., Rødland E. A., Stærfeldt H.-H., Rognes T., Ussery D. W. (2007). RNAmmer: consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 35 3100–3108. 10.1093/nar/gkm160 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefort F., Calmin G., Crovadore J., Falquet J., Hurni J.-P., Osteras M., et al. (2014). Whole-genome shotgun sequence of Arthrospira platensis strain Paraca, a cultivated and edible Cyanobacterium. Genome Announc. 2:e00751–14. 10.1128/genomeA.00751-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manen J.-F., Falquet J. (2002). The cpcB-cpcA locus as a tool for the genetic characterization of the genus Arthrospira (Cyanobacteria): evidence for horizontal transfer. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 52 861–867. 10.1099/00207713-52-3-861 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehan L., Verma R., Kumar R., Srivastava A. (2018). Illumination wavelengths effect on Arthrospira platensis production and its process applications in River Yamuna water treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 23 91–96. 10.1016/j.jwpe.2018.03.010 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Miklaszewska M., Waleron M., Morin N., Calusinska M., Wilmotte A., Marsac N. T. D., et al. (2012). Elucidation of the gas vesicle gene clusters in cyanobacteria of the genus Arthrospira (Oscillatoriales, Cyanophyta) and correlation with ITS phylogeny. Eur. J. Phycol. 47 233–244. 10.1080/09670262.2012.692817 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno I. M., Maraver J., Aguete E. C., Leao M., Gago-Martínez A., Cameán A. M. (2004). Decomposition of microcystin-LR, microcystin-RR, and microcystin-YR in water samples submitted to in vitro dissolution tests. J. Agric. Food Chem. 52 5933–5938. 10.1021/jf0489668 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin N., Vallaeys T., Hendrickx L., Natalie L., Wilmotte A. (2010). An efficient DNA isolation protocol for filamentous cyanobacteria of the genus Arthrospira. J. Microbiol. Methods 80 148–154. 10.1016/j.mimet.2009.11.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhling M. (2000). Characterization of Arthrospira (Spirulina) strains. Available online at: http://etheses.dur.ac.uk/1198/ (accessed December 29, 2020) [Google Scholar]
- Mulroney L., Wulf M. G., Schildkraut I., Tzertzinis G., Buswell J., Jain M., et al. (2020). Identification of high confidence human poly(A) RNA isoform scaffolds using nanopore sequencing. boiRxiv [Preprint] 10.1101/2020.11.18.389049 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowicka-Krawczyk P., Mühlsteinová R., Hauer T. (2019). Detailed characterization of the Arthrospira type species separating commercially grown taxa into the new genus Limnospira (Cyanobacteria). Sci. Rep. 9:694. 10.1038/s41598-018-36831-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy-Lachapelle A., Solliec M., Bouchard M. F., Sauvé S. (2017). Detection of Cyanotoxins in algae dietary supplements. Toxins 9:76. 10.3390/toxins9030076 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sant’Anna C. L. A., Teresade P., Werner V. R., Dogo C. R., Rios F. R., de C. (2008). Review of toxic species of Cyanobacteria in Brazil. Algol. Stud. 126 251–265. 10.1127/1864-1318/2008/0126-0251 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Şeker A., Shahwan T., Eroğlu A. E., Yılmaz S., Demirel Z., Dalay M. C. (2008). Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic studies for the biosorption of aqueous lead(II), cadmium(II) and nickel(II) ions on Spirulina platensis. J. Hazard. Mater. 154 973–980. 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.11.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sena L., Rojas D., Montiel E., González H., Moret J., Naranjo L. (2011). A strategy to obtain axenic cultures of Arthrospira spp. cyanobacteria. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 27 1045–1053. 10.1007/s11274-010-0549-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seppey M., Manni M., Zdobnov E. M. (2019). “BUSCO: assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness,” in Gene Prediction: Methods and Protocols Methods in Molecular Biology, ed. Kollmar M. (New York, NY: Springer; ), 227–245. 10.1007/978-1-4939-9173-0_14 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafin K., Pesout T., Lorig-Roach R., Haukness M., Olsen H. E., Bosworth C., et al. (2019). Efficient de novo assembly of eleven human genomes using PromethION sequencing and a novel nanopore toolkit. bioRxiv [Preprint] 10.1101/715722 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiraishi H. (2015). Association of heterotrophic bacteria with aggregated Arthrospira platensis exopolysaccharides: implications in the induction of axenic cultures. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 79 331–341. 10.1080/09168451.2014.972333 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sili C., Torzillo G., Vonshak A. (2012). “Arthrospira (Spirulina),” in Ecology of Cyanobacteria II: Their Diversity in Space and Time, ed. Whitton B. A. (Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands; ), 677–705. 10.1007/978-94-007-3855-3_25 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Song Q., Shun T., Peijun Z., Tseng C. K. (1993). Isolation of plasmid from the blue-green algaSpirulina platensis. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 11 285–288. 10.1007/BF02850862 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Spirulina Market - Global Opportunity Analysis and Industry Forecast. (2019–2025). Meticulous Res. Available online at: https://www.meticulousresearch.com/product/spirulina-market-5070/?utm_source=Globnewswire.com&utm_medium=PressRelease&utm_campaign=Paid (accessed December 21, 2020) [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Yamaguchi H., Kawachi M. (2019). The draft genome of a hydrogen-producing Cyanobacterium, Arthrospira platensis NIES-46. J. Genomics 7 56–59. 10.7150/jgen.38149 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuşoglu Ö, üUnal M. K. (2003). Biomass nutrient profiles of three microalgae: Spirulina platensis, Chlorella vulgaris, and Isochrisis galbana. J. Food Sci. 68 1144–1148. 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2003.tb09615.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Tørresen O. K., Star B., Mier P., Andrade-Navarro M. A., Bateman A., Jarnot P., et al. (2019). Tandem repeats lead to sequence assembly errors and impose multi-level challenges for genome and protein databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 47 10994–11006. 10.1093/nar/gkz841 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzfira T., Frankman L. R., Vaidya M., Citovsky V. (2003). Site-specific integration of Agrobacterium tumefaciens T-DNA via double-stranded intermediates. Plant Physiol. 133 1011–1023. 10.1104/pp.103.032128 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergunst A. C., Jansen L. E. T., Hooykaas P. J. J. (1998). Site-specific integration of Agrobacterium T-DNA in Arabidopsis thaliana mediated by Cre recombinase. Nucleic Acids Res. 26 2729–2734. 10.1093/nar/26.11.2729 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonshak A. (1997). Spirulina Platensis Arthrospira: Physiology, Cell-Biology and Biotechnology. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. [Google Scholar]
- Voronichin N. N. (1934). Spirulina fusiformis Voronichin 1934: Algaebase. Available online at: https://www.algaebase.org/search/species/detail/?tc=accept&species_id=47838 (accessed December 21, 2020) [Google Scholar]
- Walker B. J., Abeel T., Shea T., Priest M., Abouelliel A., Sakthikumar S., et al. (2014). Pilon: an integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PLoS One 9:e112963. 10.1371/journal.pone.0112963 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsby A. E., Bleything A. (1988). The dimensions of Cyanobacterial gas vesicles in relation to their efficiency in providing buoyancy and withstanding pressure. Microbiology 134 2635–2645. 10.1099/00221287-134-10-2635 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Wan D., Wu Q., Kuča K. (2016). “Spirulina,” in Nutraceuticals, Chap. 42, ed. Gupta R. C. (Boston: Academic Press; ), 569–583. 10.1016/B978-0-12-802147-7.00042-5 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Wick R. R., Schultz M. B., Zobel J., Holt K. E. (2015). Bandage: interactive visualization of de novo genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 31 3350–3352. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv383 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu T., Qin S., Hl°u Y., Song Z., Ying J., Li P., et al. (2016). Whole genomic DNA sequencing and comparative genomic analysis of Arthrospira platensis: high genome plasticity and genetic diversity. DNA Res. 23 325–338. 10.1093/dnares/dsw023 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yadav A., Monsieurs P., Misztak A., Waleron K., Leys N., Cuypers A., et al. (2020). Helical and linear morphotypes of Arthrospira sp. PCC 8005 display genomic differences and respond differently to 60Co gamma irradiation. Eur. J. Phycol. 55 129–146. 10.1080/09670262.2019.1675763 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao W., Wang J., Xu S., Lei Y., Yang R., Shi L., et al. (2020). Bacterioplankton community variation in Bohai Bay (China) is explained by joint effects of environmental and spatial factors. MicrobiologyOpen 9:e997. 10.1002/mbo3.997 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinicovscaia I., Cepoi L., Povar I., Chiriac T., Rodlovskaya E., Culicov O. A. (2018). Metal uptake from complex industrial effluent by cyanobacteria Arthrospira platensis. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 229:220. 10.1007/s11270-018-3873-3 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, PRJNA623410.